Bone: Axial Functions
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
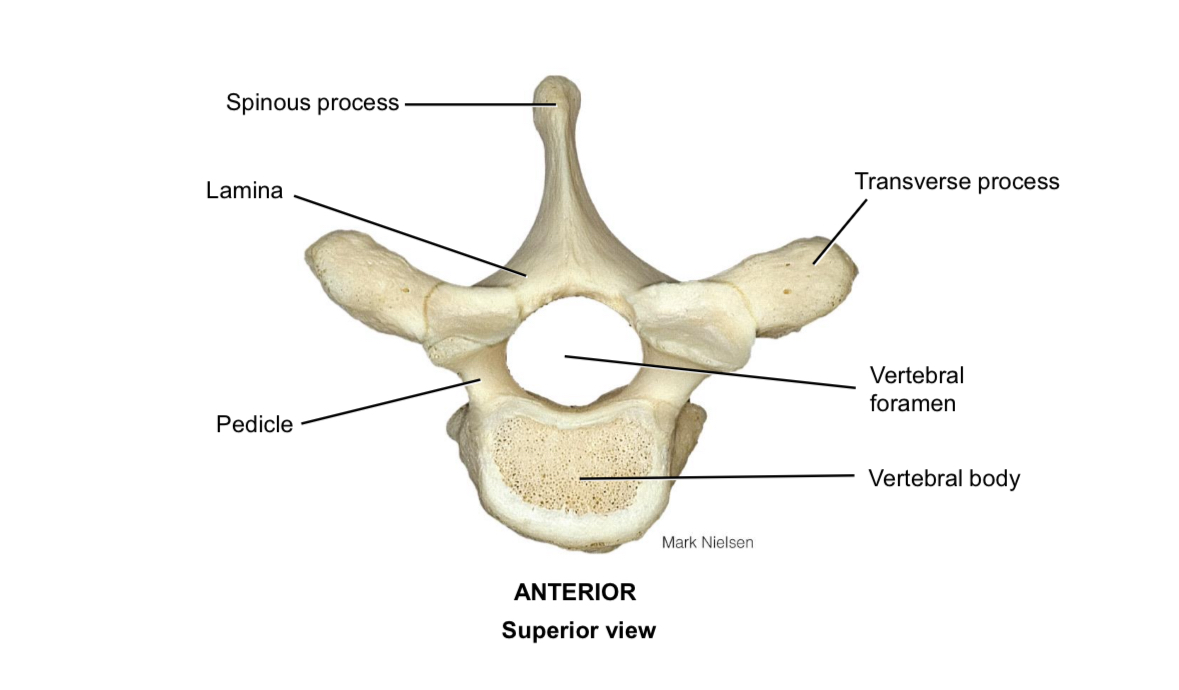
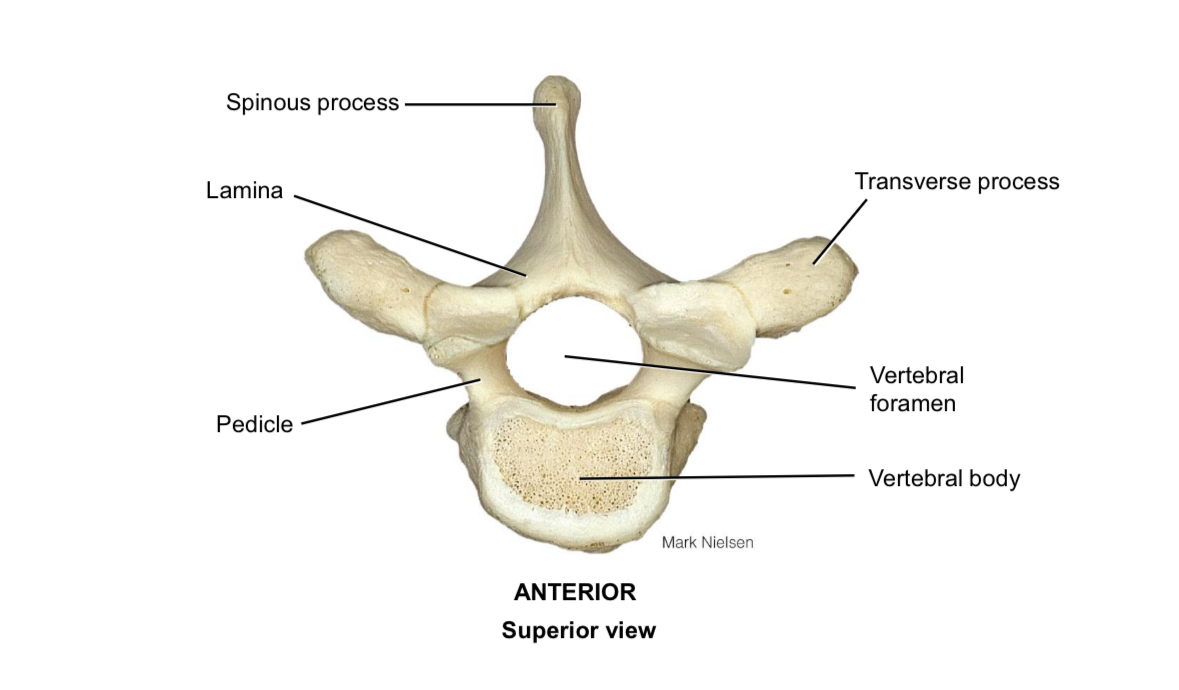
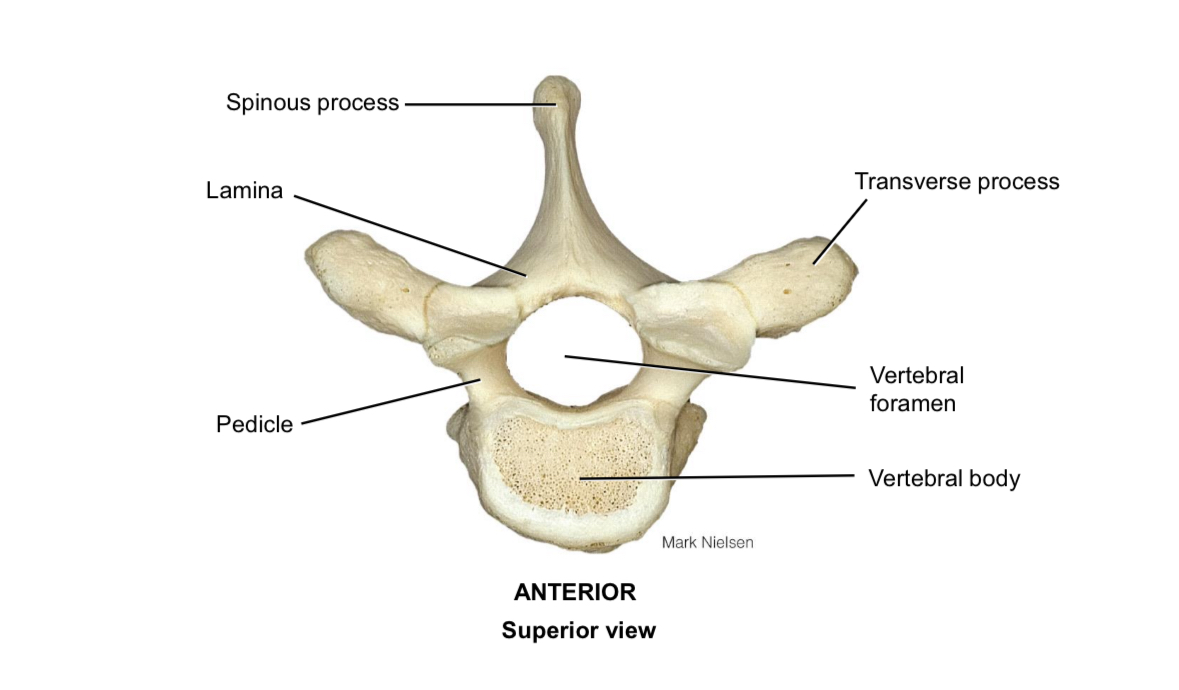
Body of vertebra
Supports the body weight
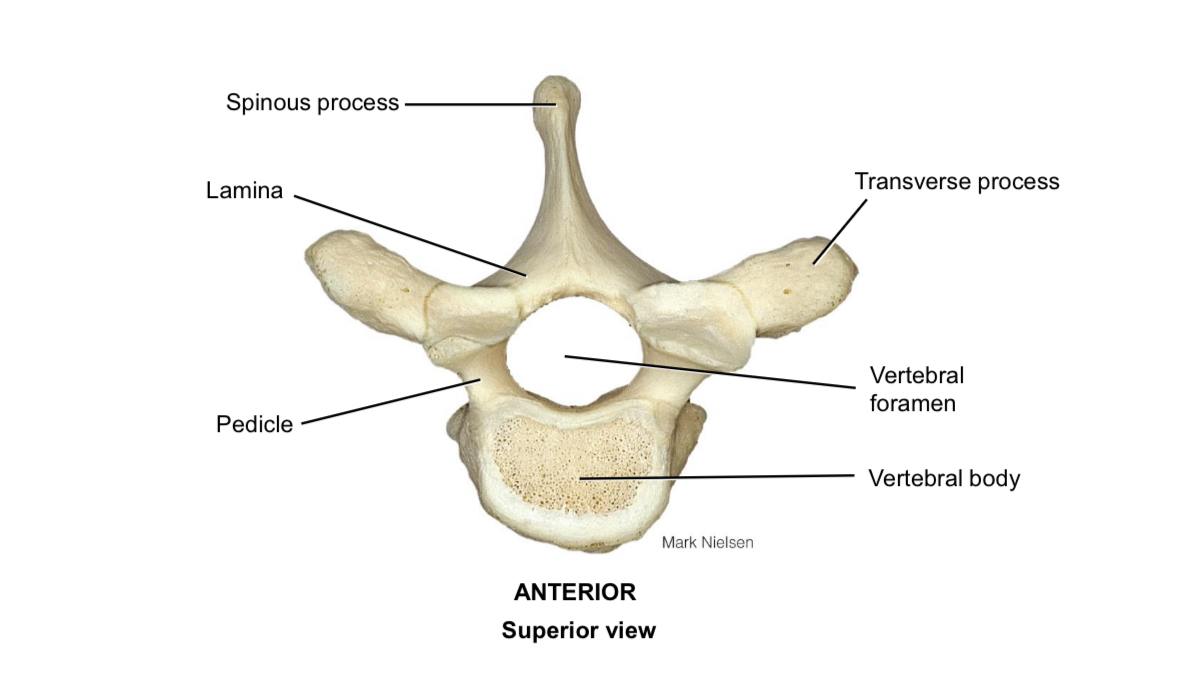
Pedicle
Connects the vertebral body to the vertebral arch
Lamina
Connects the spinous process to the transverse process
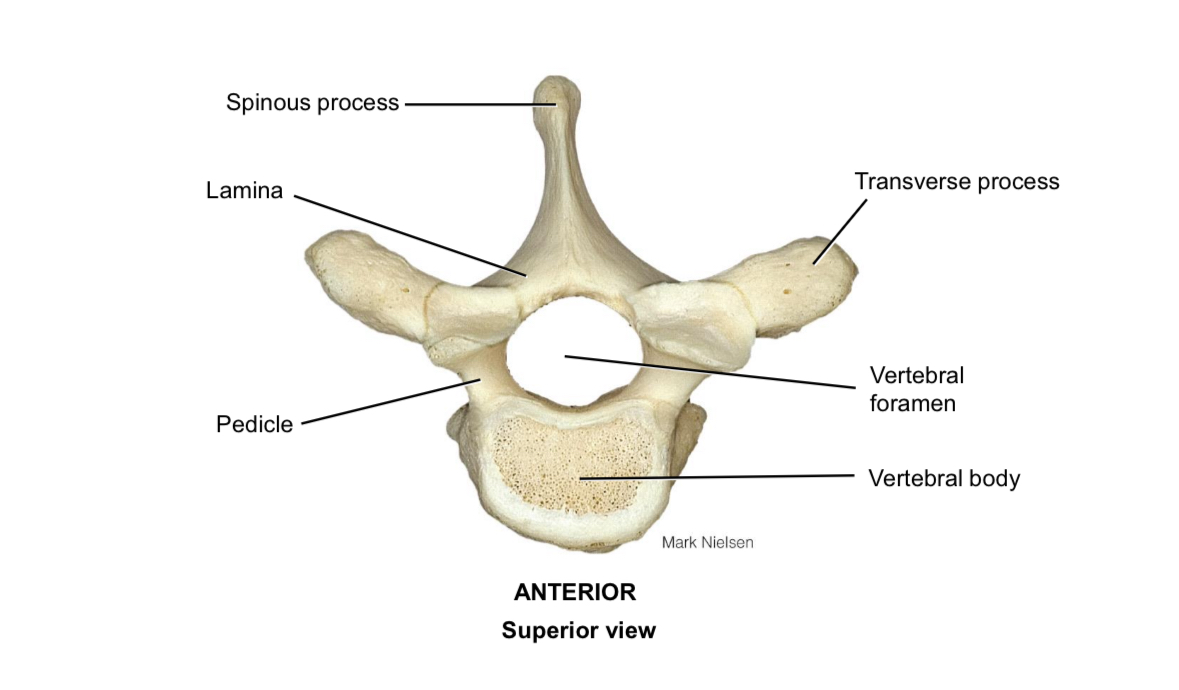
Spinous process
Muscle attachment
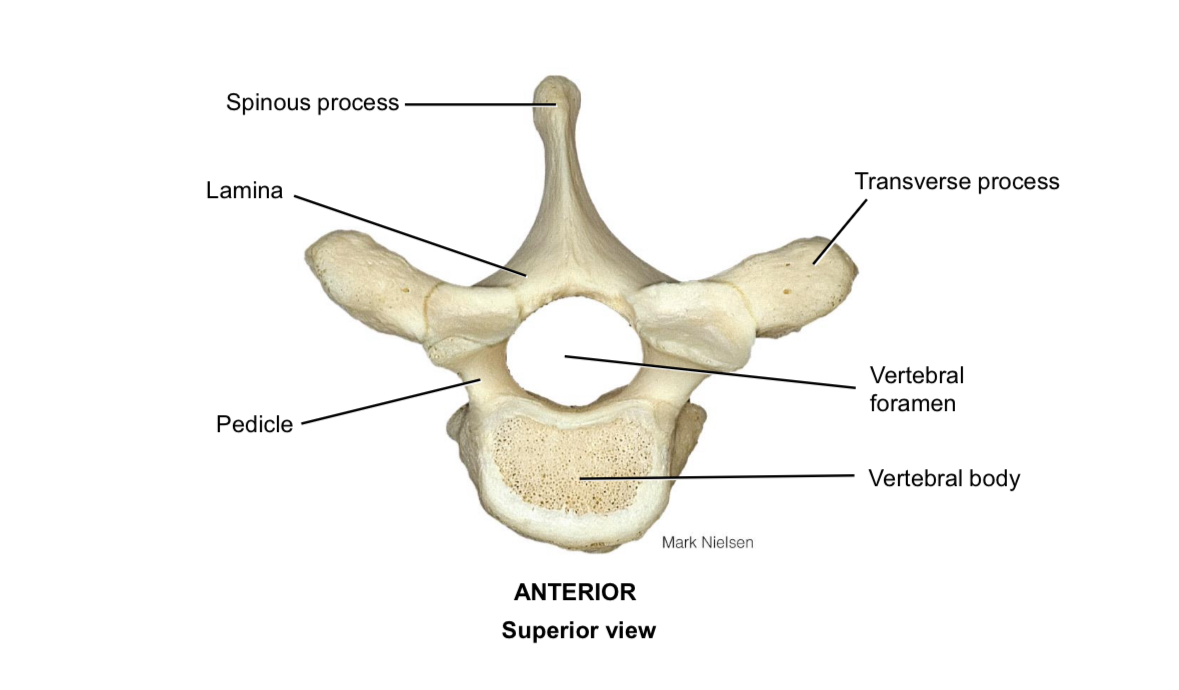
Transverse process
Muscle attachment
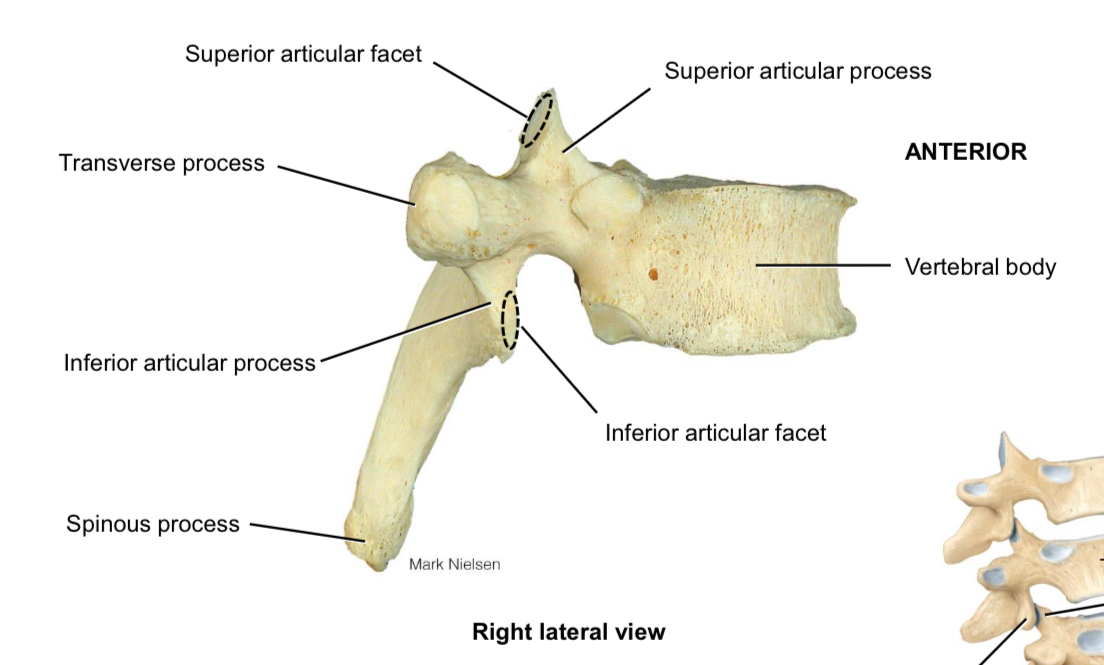
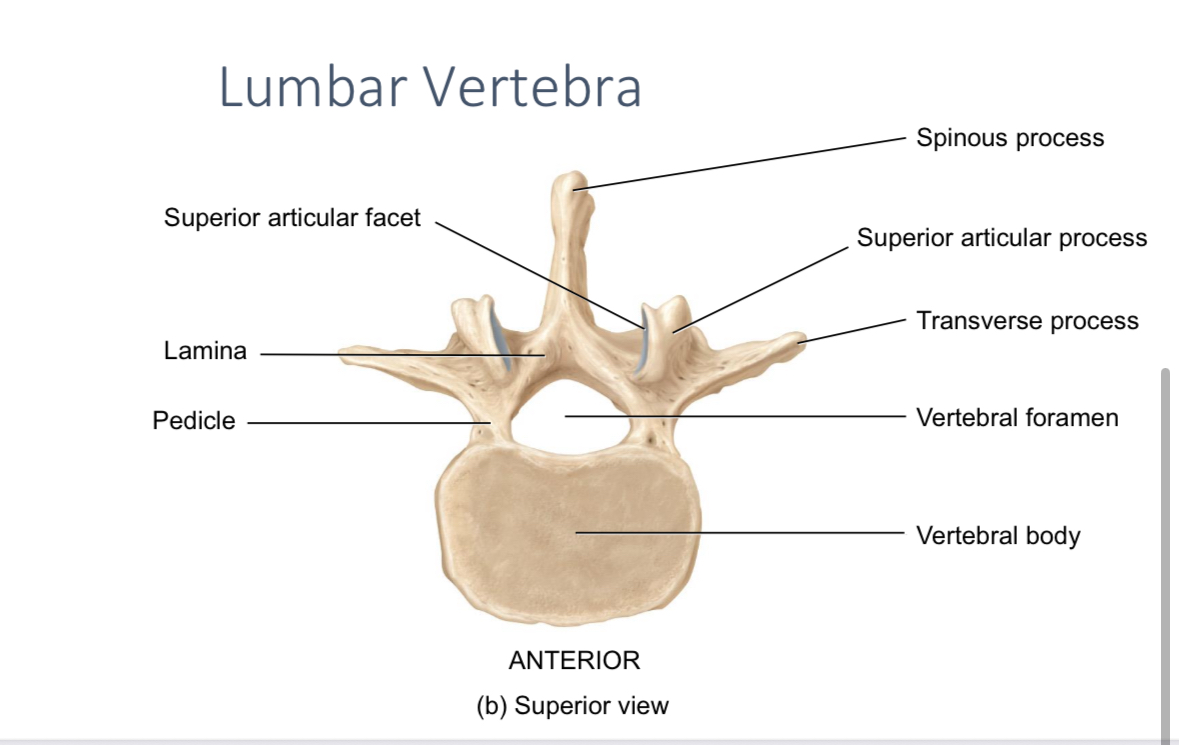
Superior articulation processes and facets
Articulate with the inferior articulation processes and facets of the vertebra above
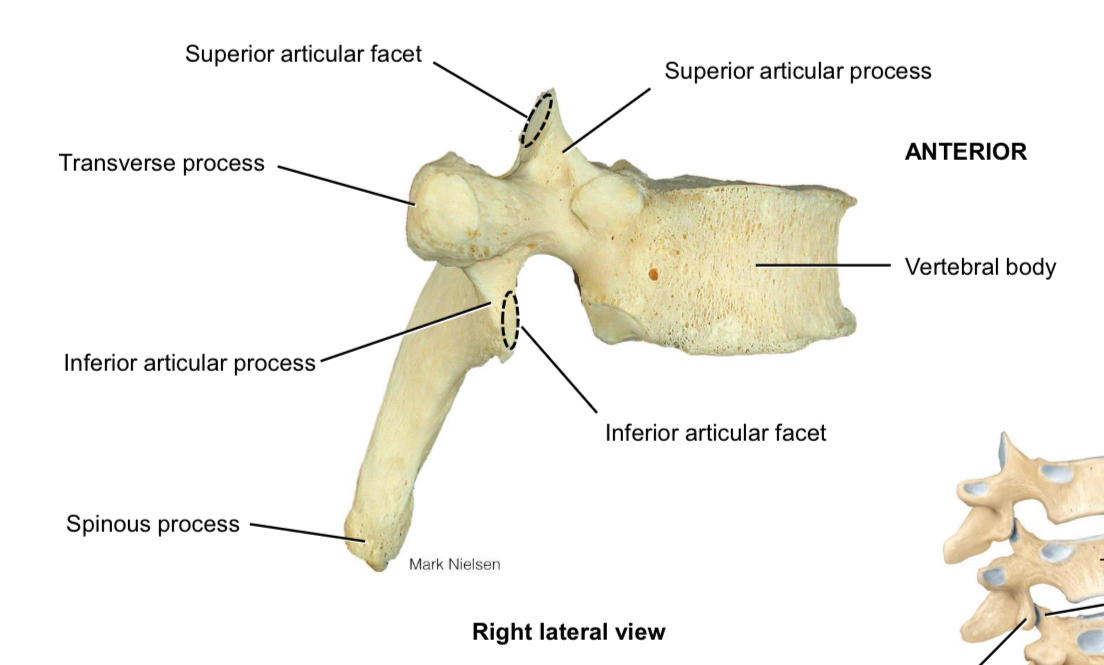
Inferior articular processes and facets
Articulate with the superior articular processes and facets of the vertebra below
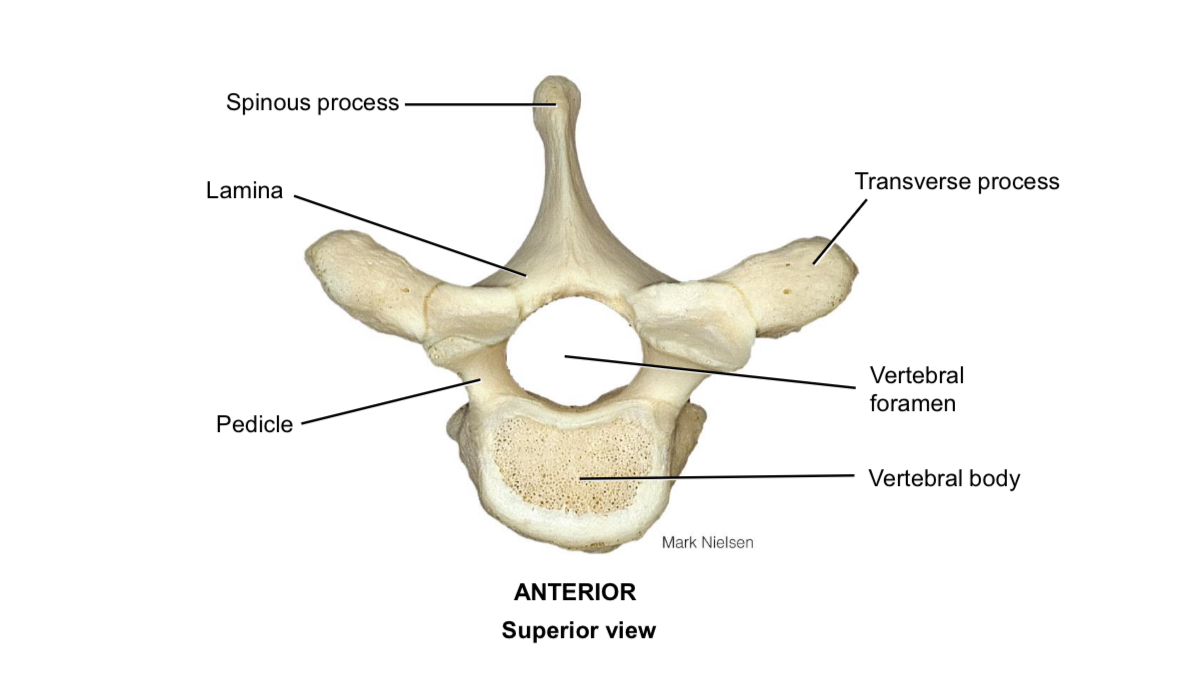
Vertebral foramen
Houses the spinal cord
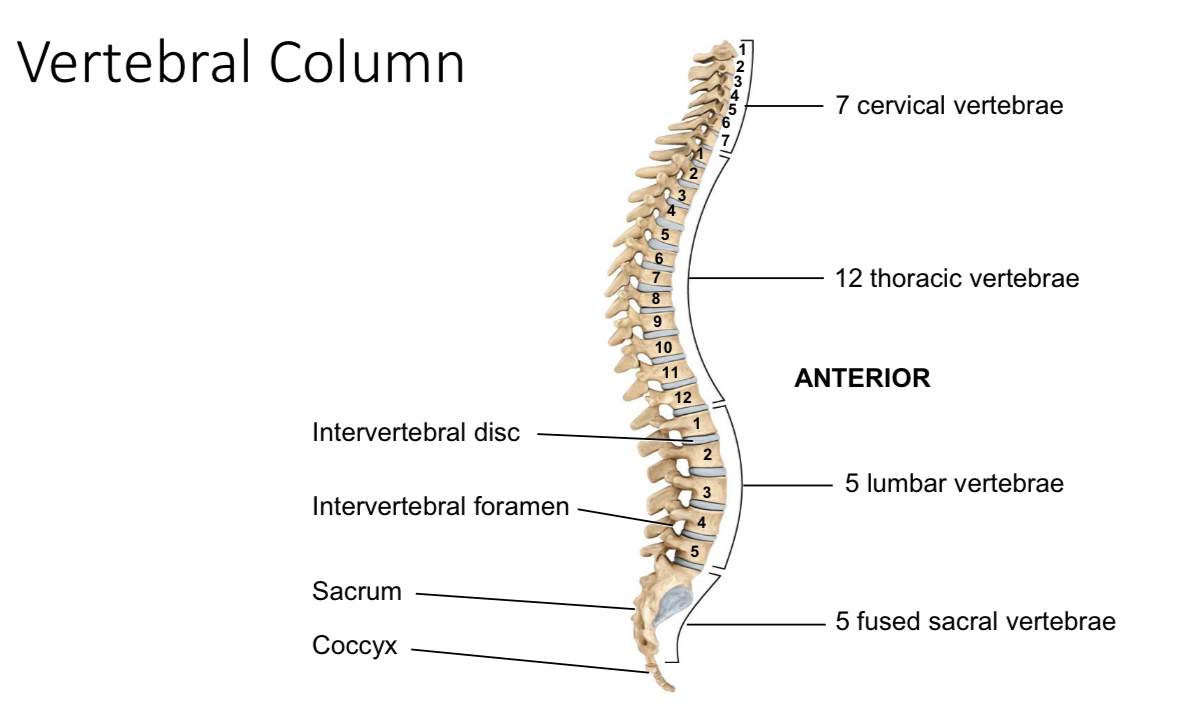
Intervetebral foramen
Passageway for spinal nerves and blood vessels
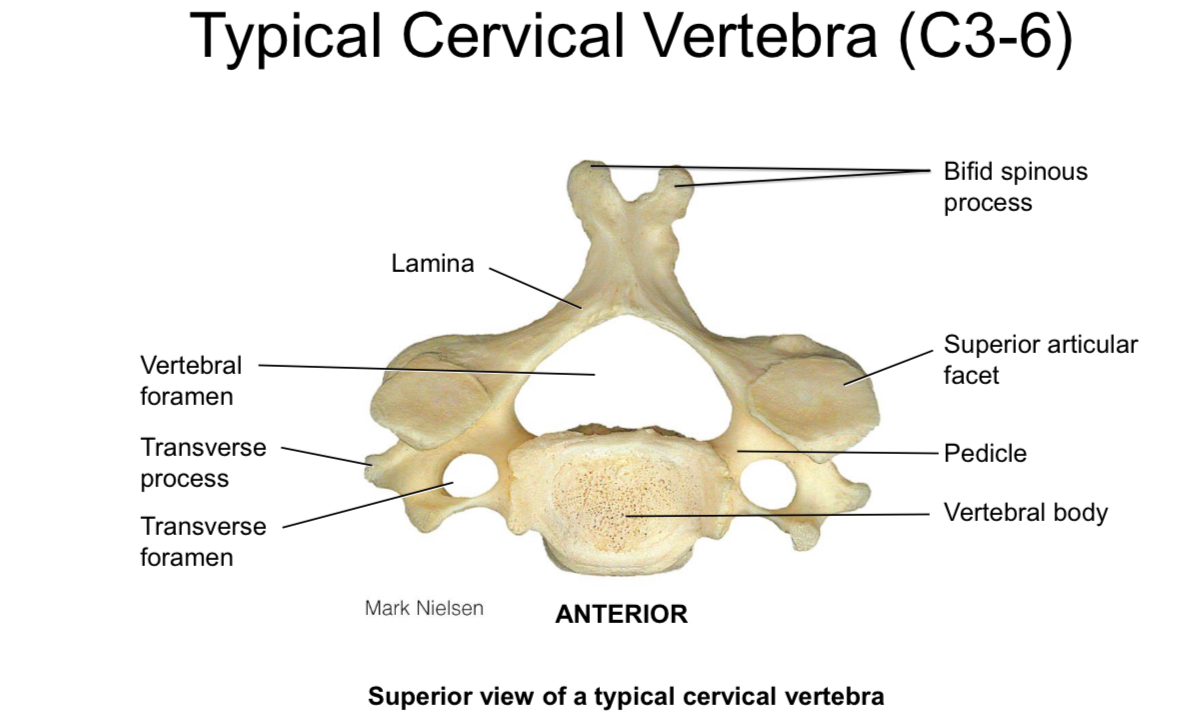
Transverse foramen
Allows the passage of the vertebral artery
Spinous process
Muscle attachment
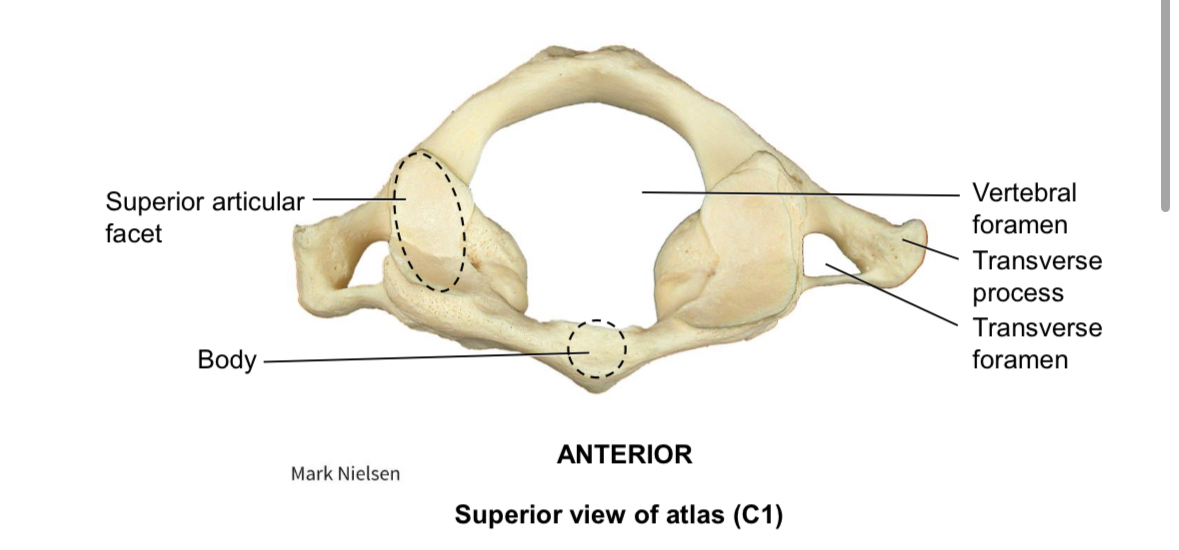
Atlas C1
Articulates with the occipital condoles allowing for nodding motion
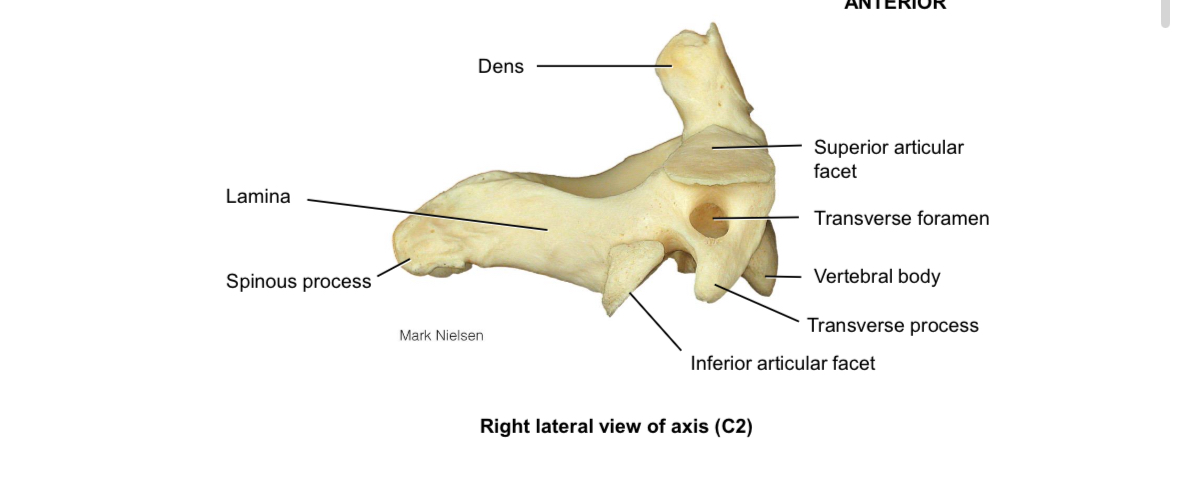
Axis C2 Dens
Articulates with the anterior arch of the atlas and allows for rotational movement
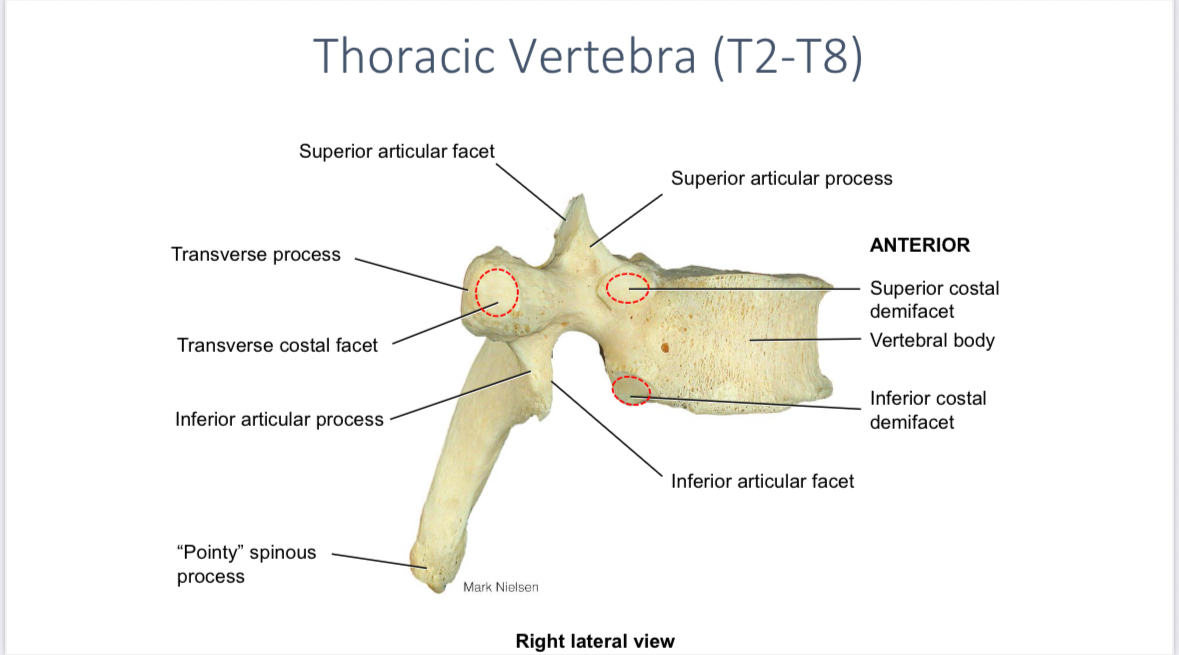
Transverse costal facets of the thoracic vertebrae
Articulate with the tubercle of ribs
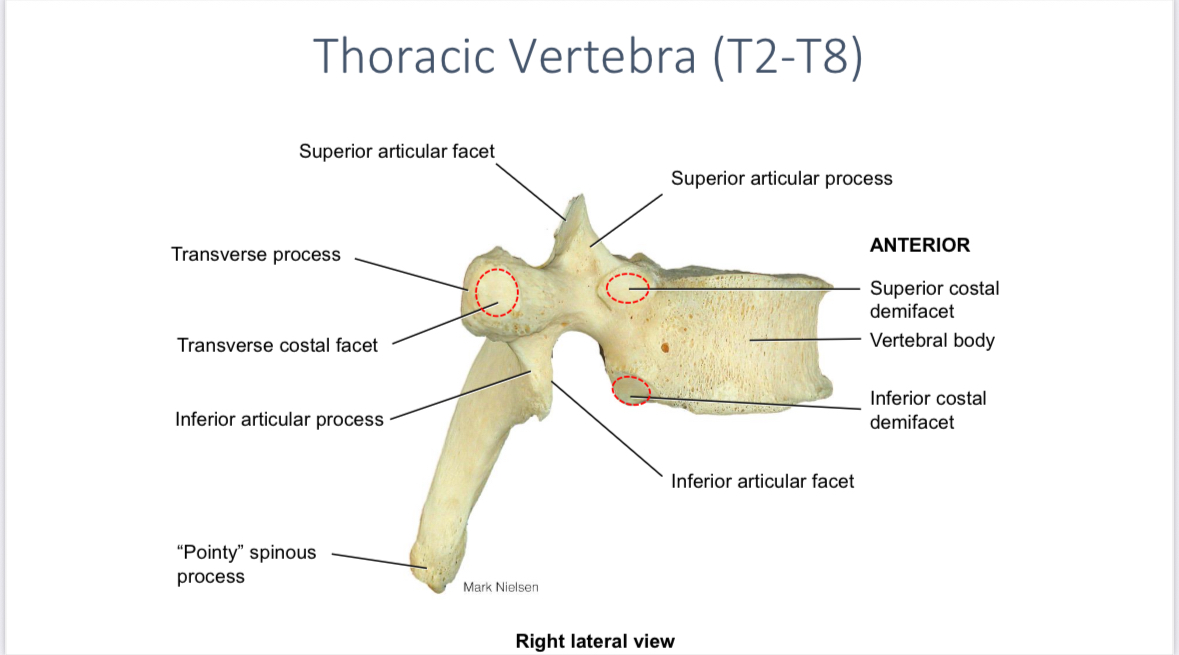
Superior and inferior demifacets of the thoracic vertebrae
Articulate with the head of the ribs
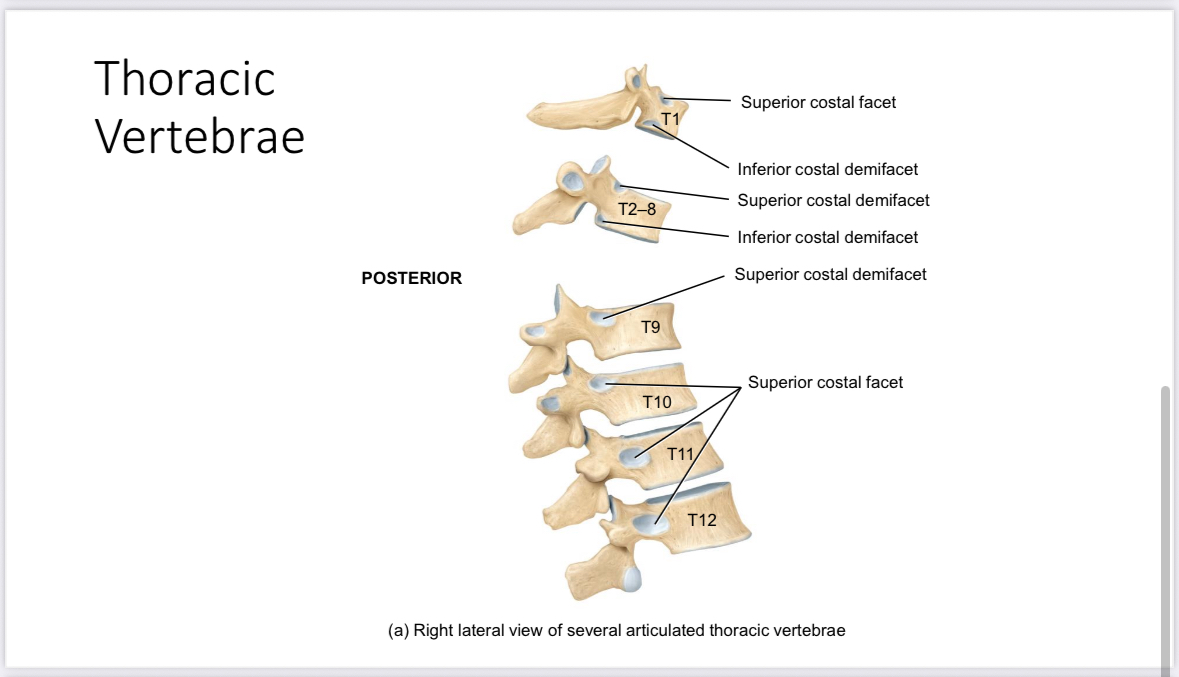
Costal facets of the thoracic vertebrae
Articulate with the head of ribs
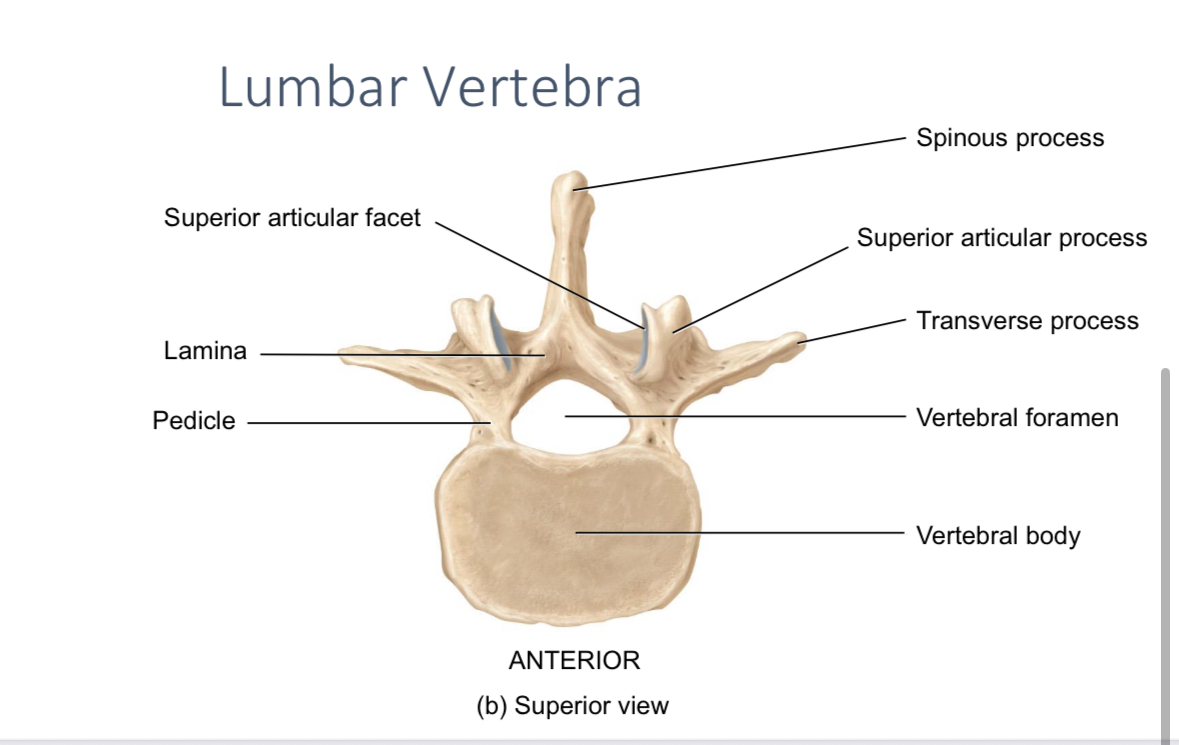
Lumbar vertebrae
Support the body weight and allow flexibility and rotation
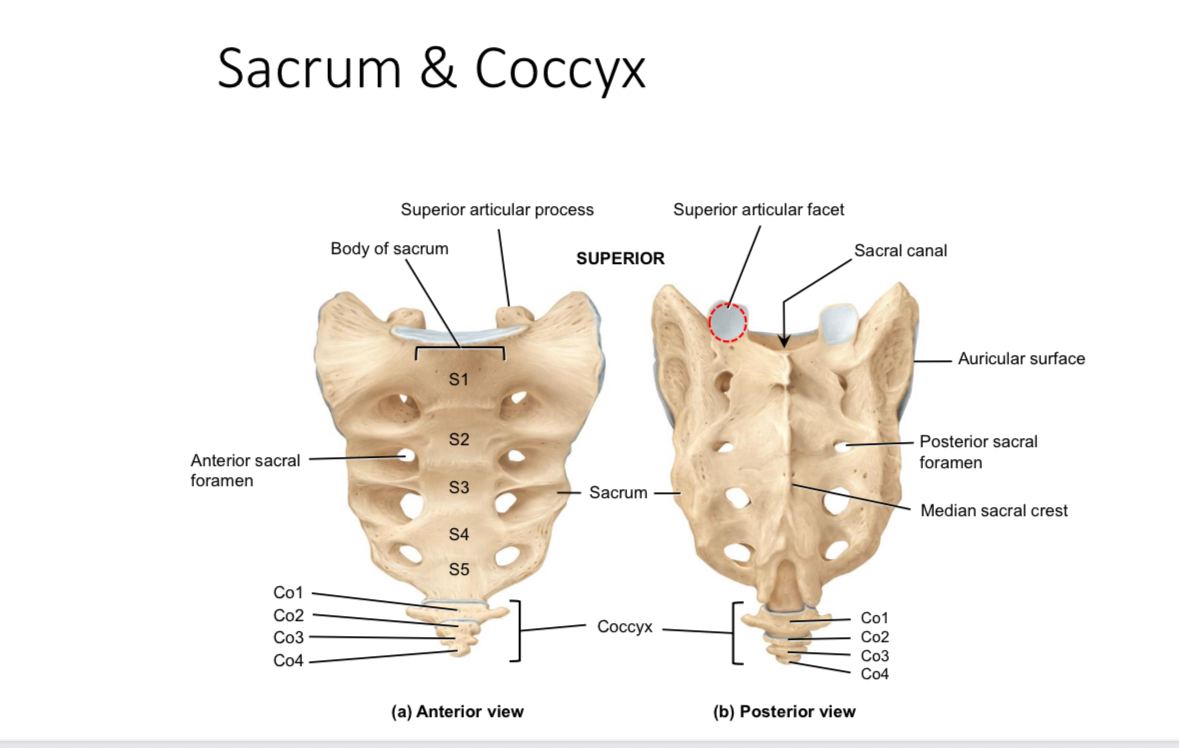
Sacrum: superior articular processes and facets
Articulate with the inferior articular processes and facets of last lumbar vertebrae
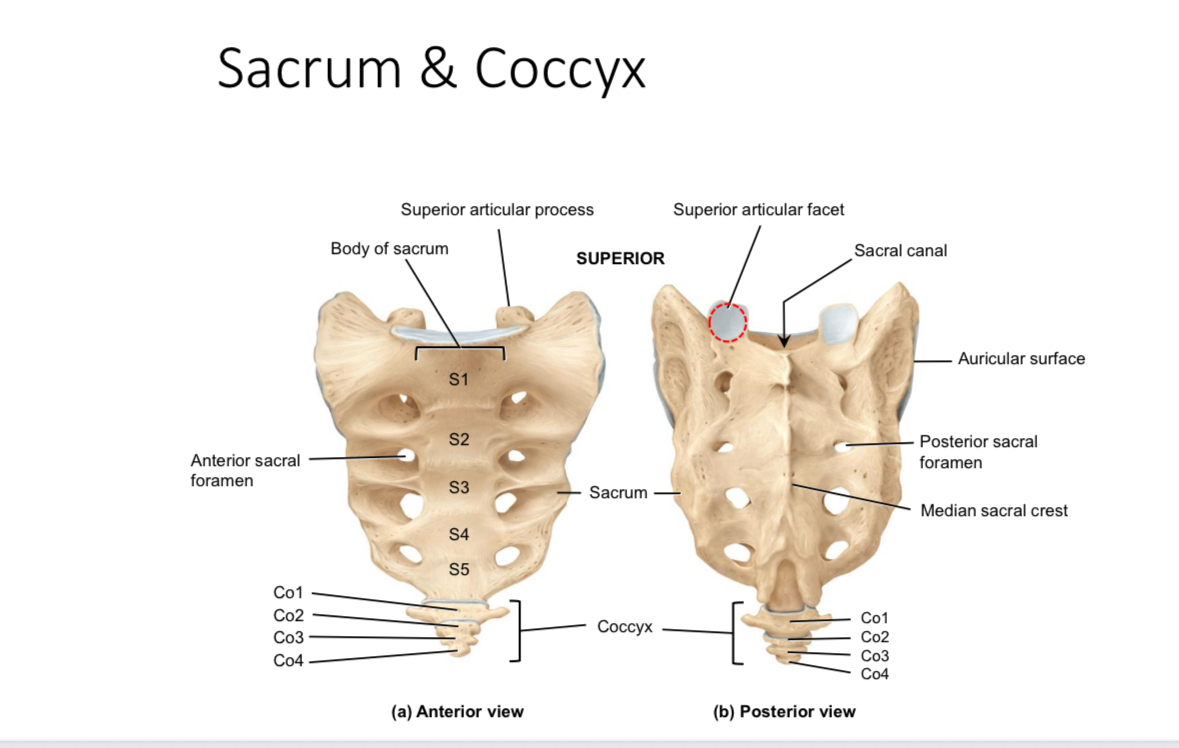
Sacrum: auricular surface
Articulates with the auricular surface of the ilium
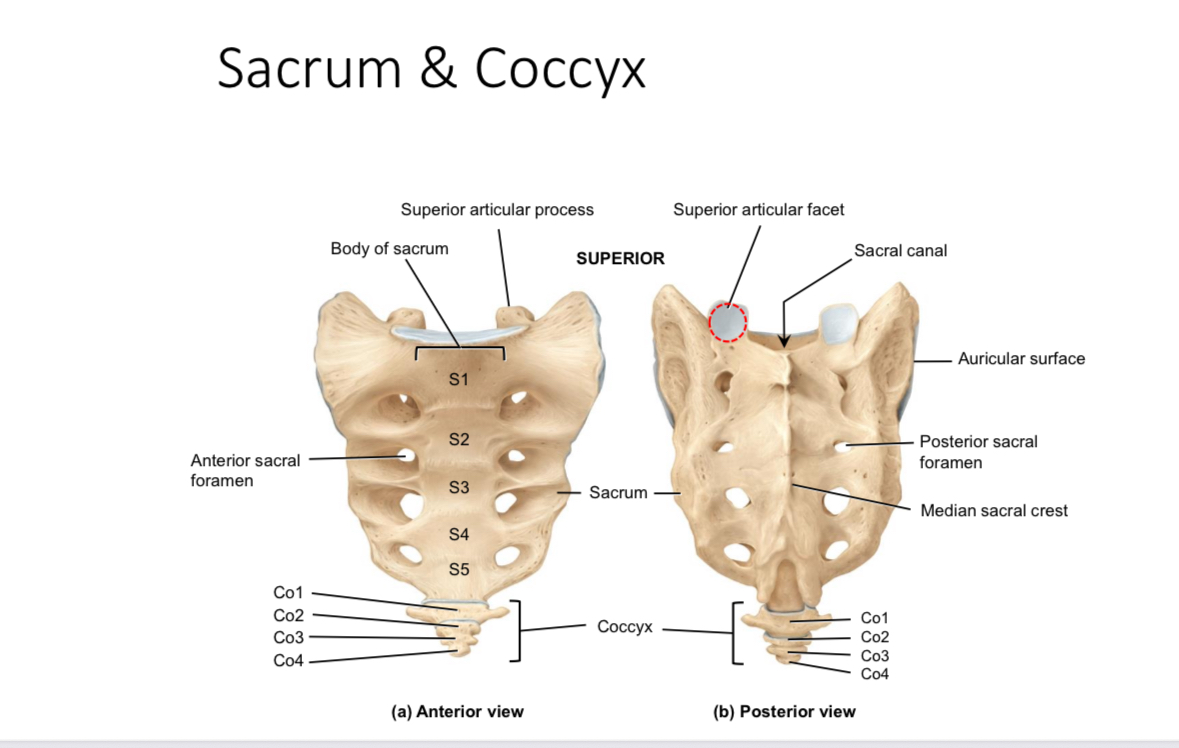
Sacrum: body
Supports body weight
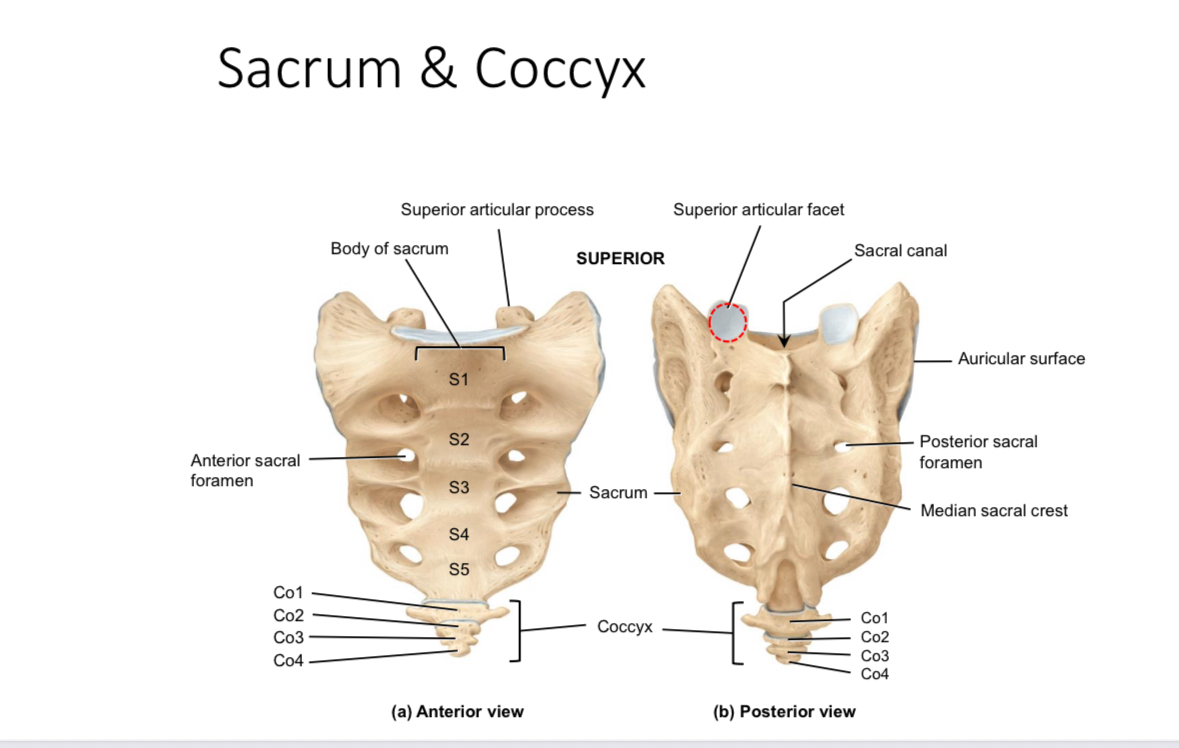
Sacrum: median sacral crest
Muscle attachment
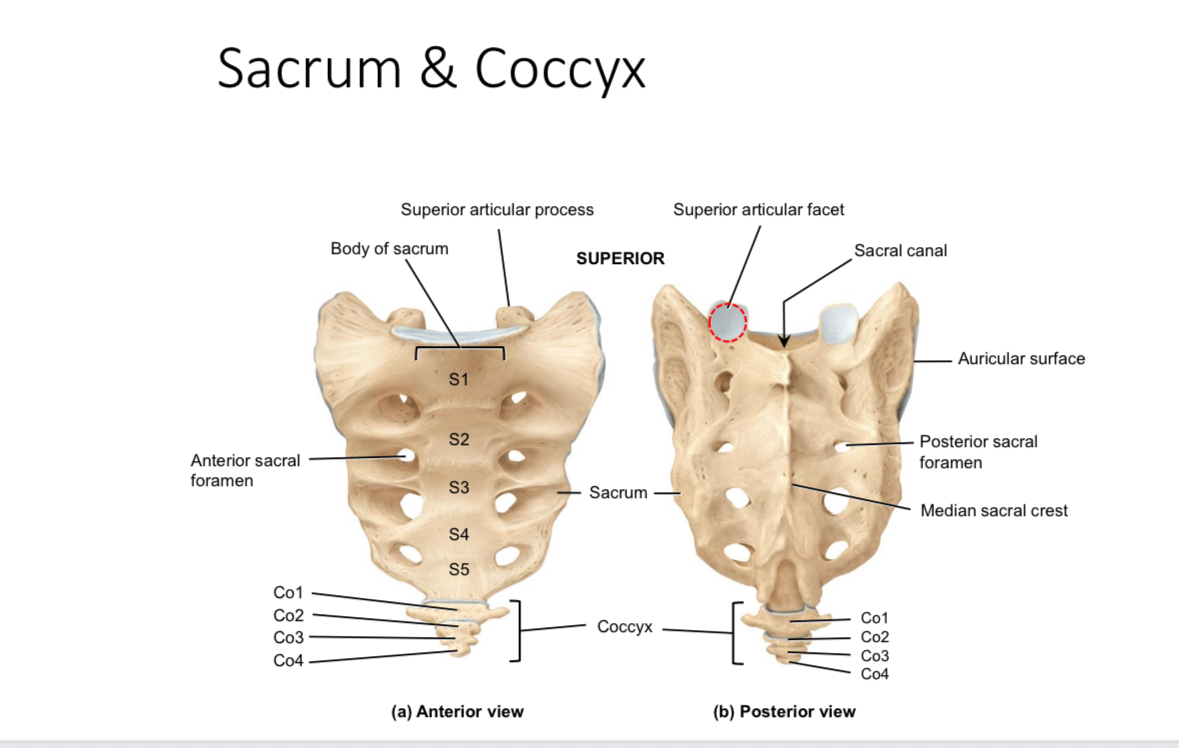
Sacrum: anterior and posterior sacral foramina
Passageways of nerves and blood vessels
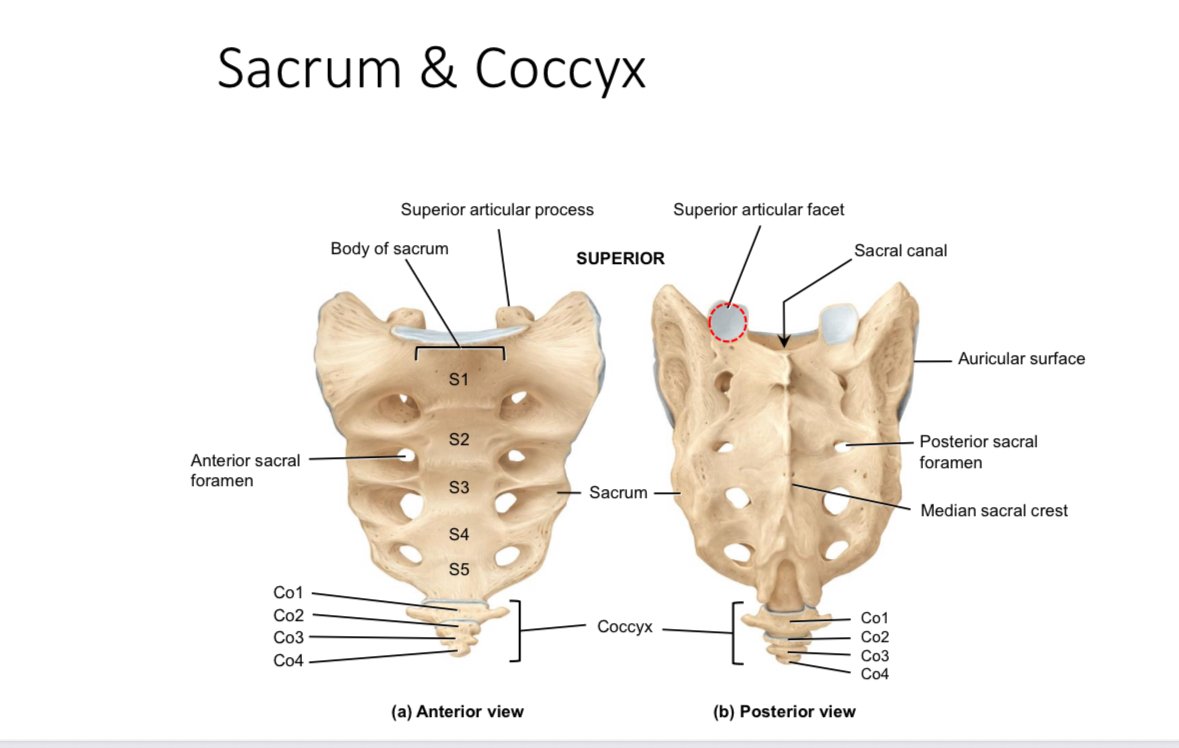
Sacrum: sacral canal
Houses the continuation of the spinal cord
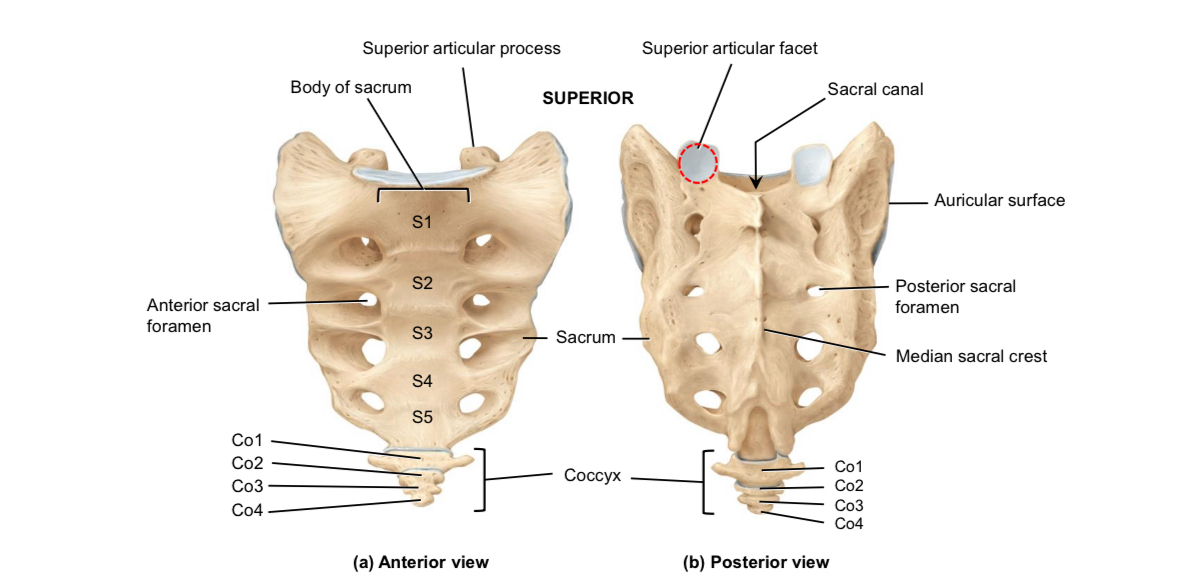
Coccyx
Provides attachment for ligaments and muscles and serves as an insertion point for some muscles of the pelvic floor
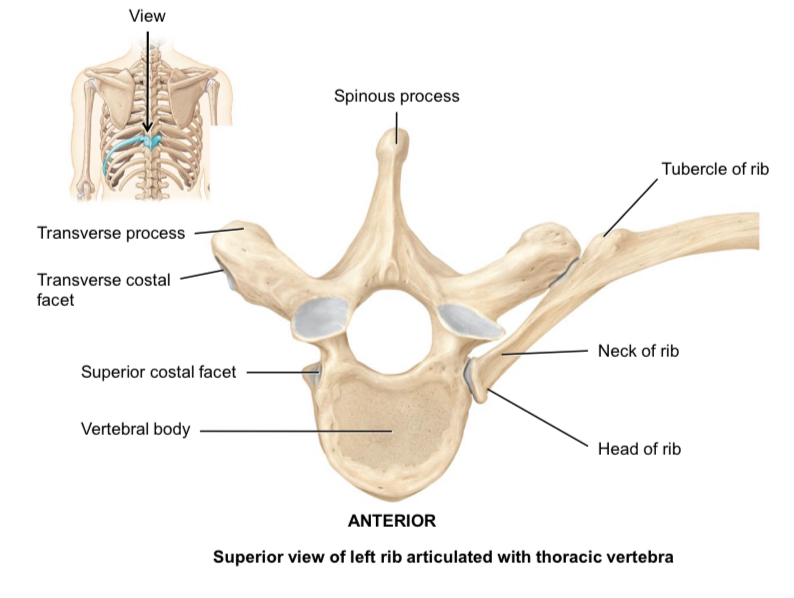
Head of rib
Articulates with the body of thoracic vertebrae
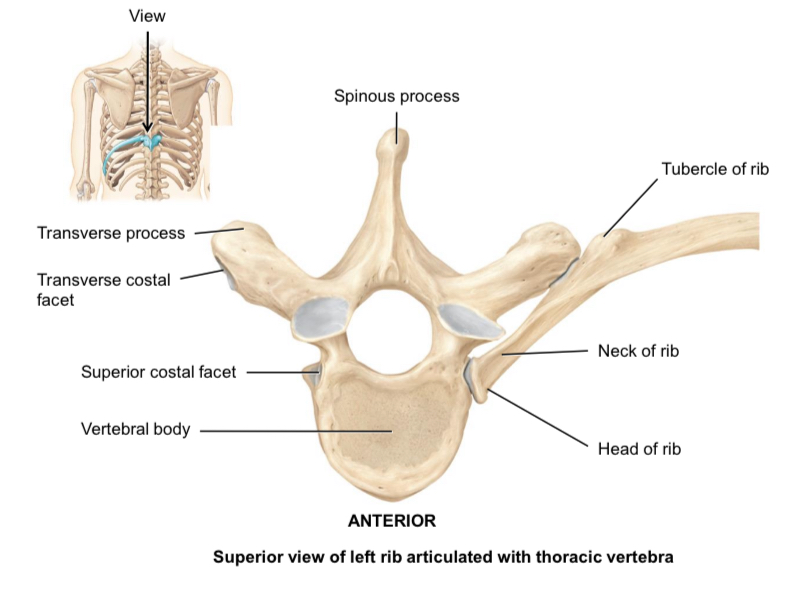
Tubercle of rib
Articulated with the transverse process of thoracic vertebrae
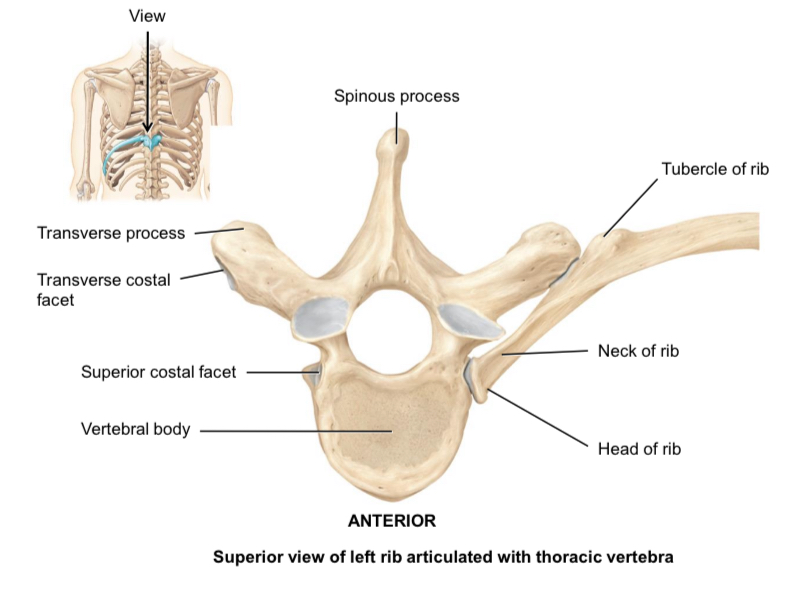
Neck of rib
Connects the head and the tubercle of the rib
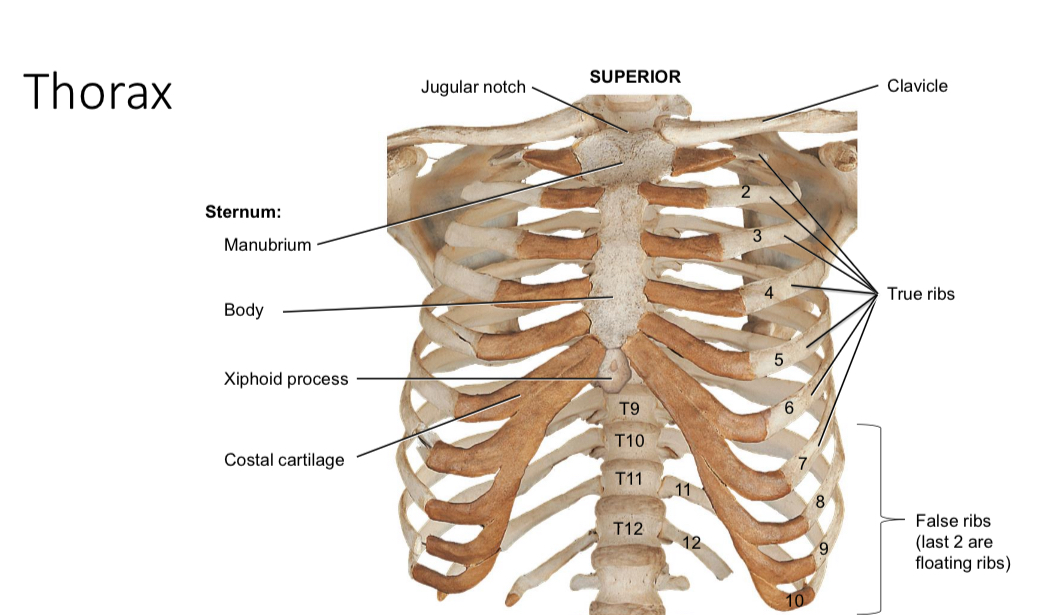
True ribs
Directly attached to the sternum via the costal cartilages and protect thoracic organs
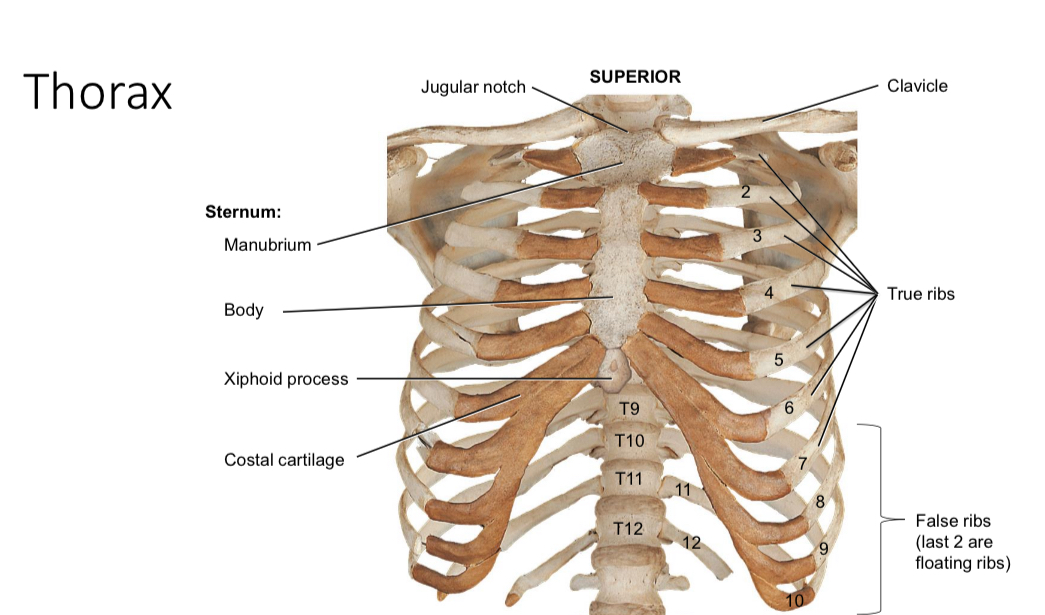
False ribs
Ribs 8-10: indirectly attach to sternum via the costal cartilages of rib 7; provide flexibility during breathing
Ribs 11-12: floating ribs with out any costal cartilage attachment; protect kidneys
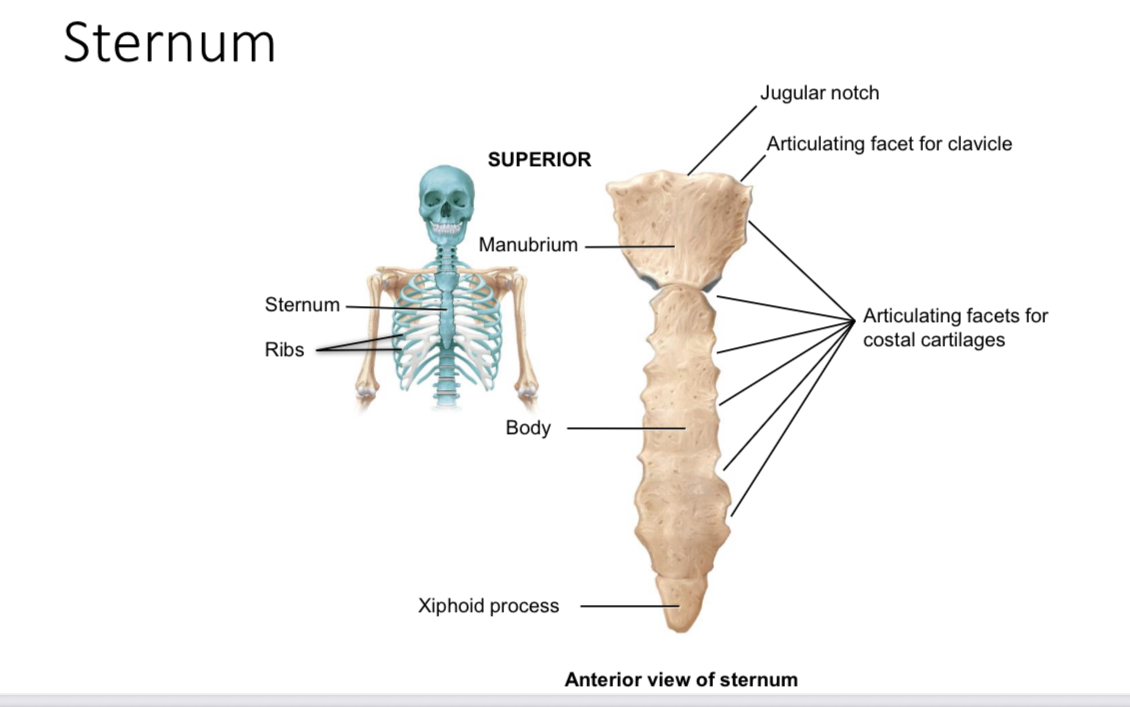
Sternum: articulating facets for clavicle of the manubrium
Articulate with the sternal end of each clavicle
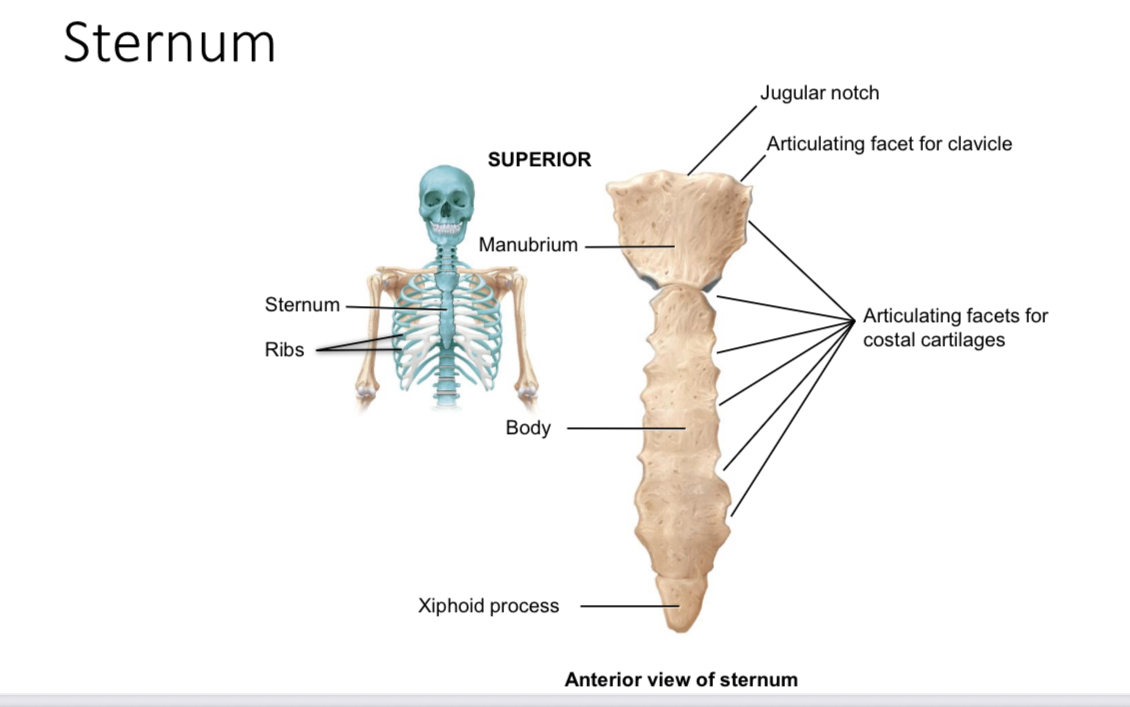
Sternum: articulating facets for costal cartilages of the manubrium
Articulate with the cartilages of the first rib
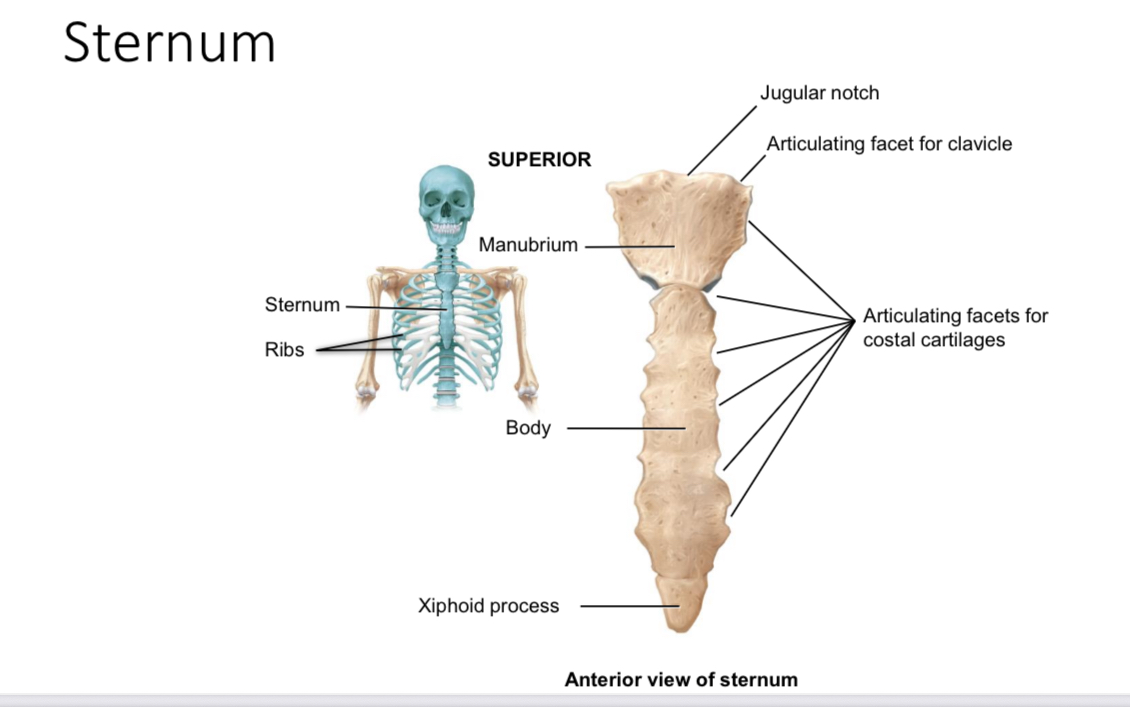
Suprasternal jugular notch
Ligament attachment
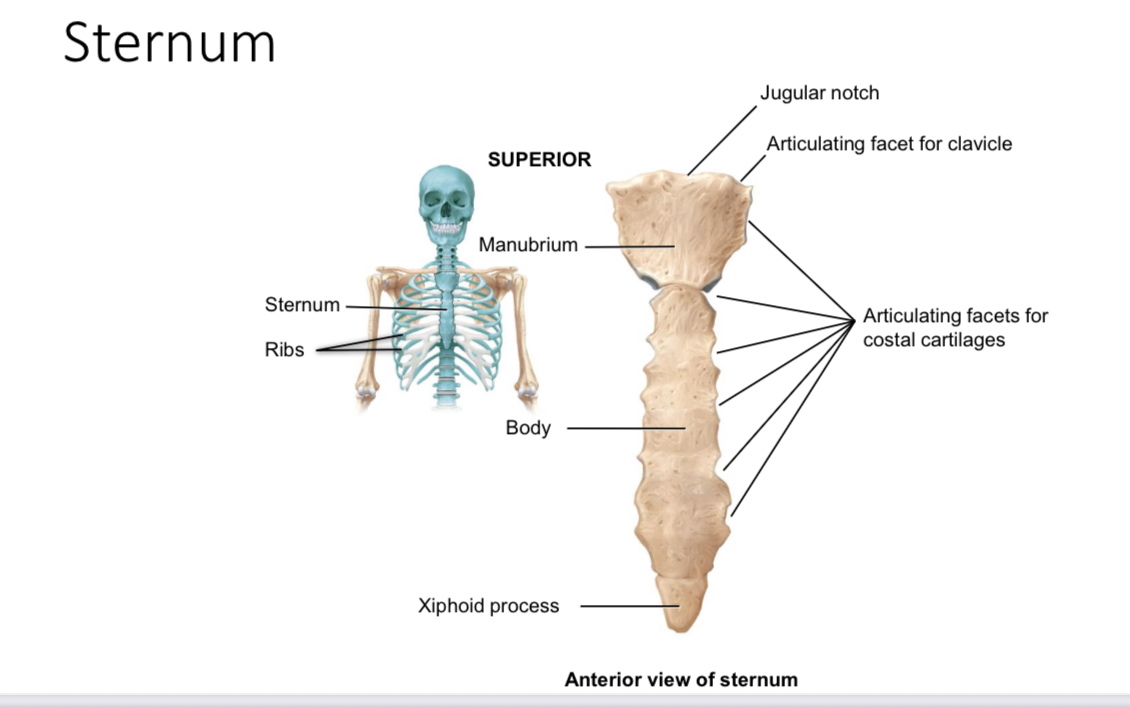
Body of sternum: articulating facets for costal cartilages
Articulate with the coastal cartilages of ribs 2-7
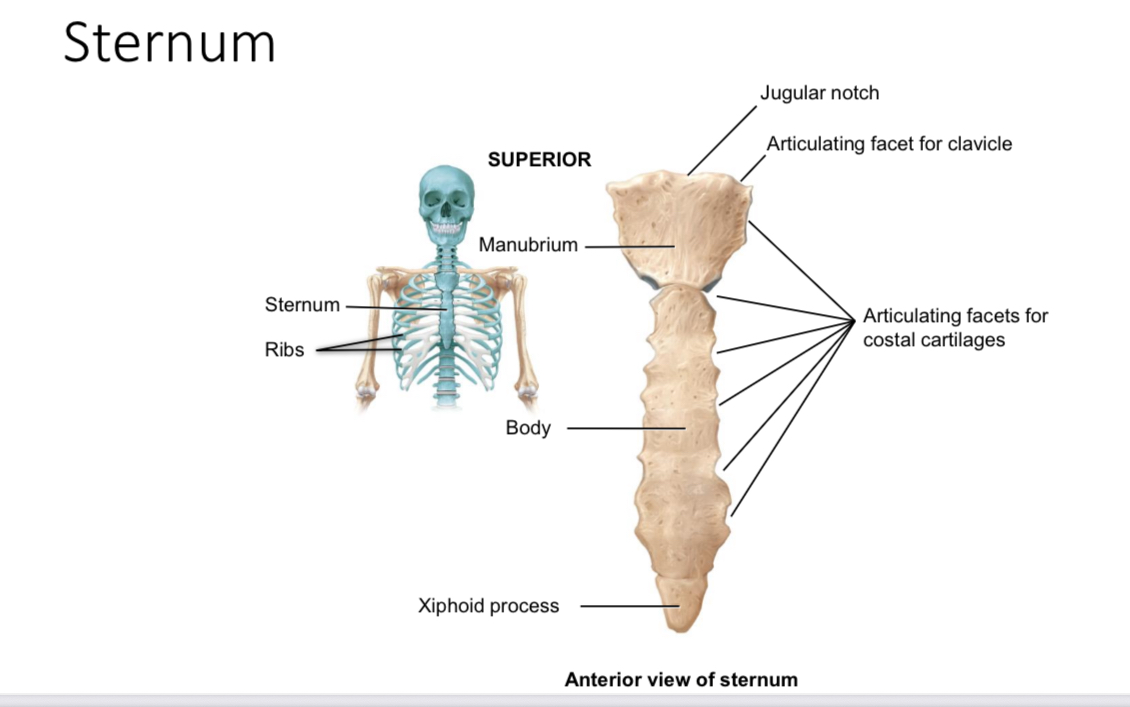
Xiphoid process of the sternum
Provides an attachment point for some abdominal muscles