test 5 review
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is the type of anomalies these fall under - select from these (malformations, Deformation, Disruption, Dysplasia)
Clefting of the lip or palate is a type of _______
amputation of an extremity caused by amniotic bands ________
Clubbing of the extremities caused by oligohydramnios ______
1) Malformation
2) Disruption
3) Deformation
_____ pairs of autosomes and _____ sex chromosomes
a. 26, 7
b. 22, 2
c. 34,3
d. 46,4
22, 2
Which inheritance pattern requires only one parent to carry the affected gene for a child to have a 50% chance of inheriting the condition?
a) Autosomal recessive
b) Autosomal dominant
c) X-linked recessive
d) Multifactorial
Autosomal dominant
A child has a 25% chance of expressing a specific trait, a 50% chance of being a carrier, and a 25% chance of neither expressing the trait nor being a carrier. What is the most likely inheritance pattern?
a) Autosomal dominant
b) Autosomal recessive
c) X-linked dominant
d) Multifactorial
Autosomal recessive
Which of the following is NOT a typical reason for performing CVS?
a) Diagnosing chromosomal abnormalities
b) Determining fetal blood type
c) Assessing for genetic disorders
d) Confirming pregnancy
Confirming pregnancy
CVS is typically performed between which gestational weeks?
a) 6-8 weeks
b) 10-13 weeks
c) 16-18 weeks
d) 20-22 week
10-13 weeks
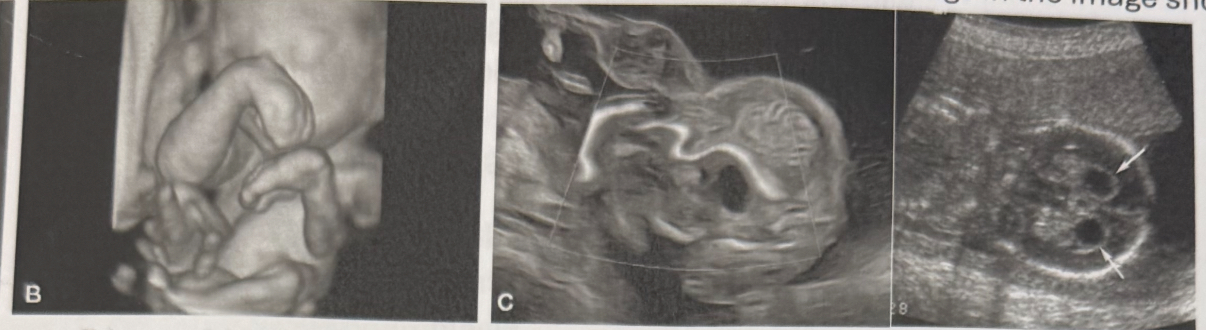
What is the most likely diagnosis based on the sonographic findings in the image shown?
Trisomy 21
Trisomy 18
Trisomy 13
Turner syndrome
Trisomy 18
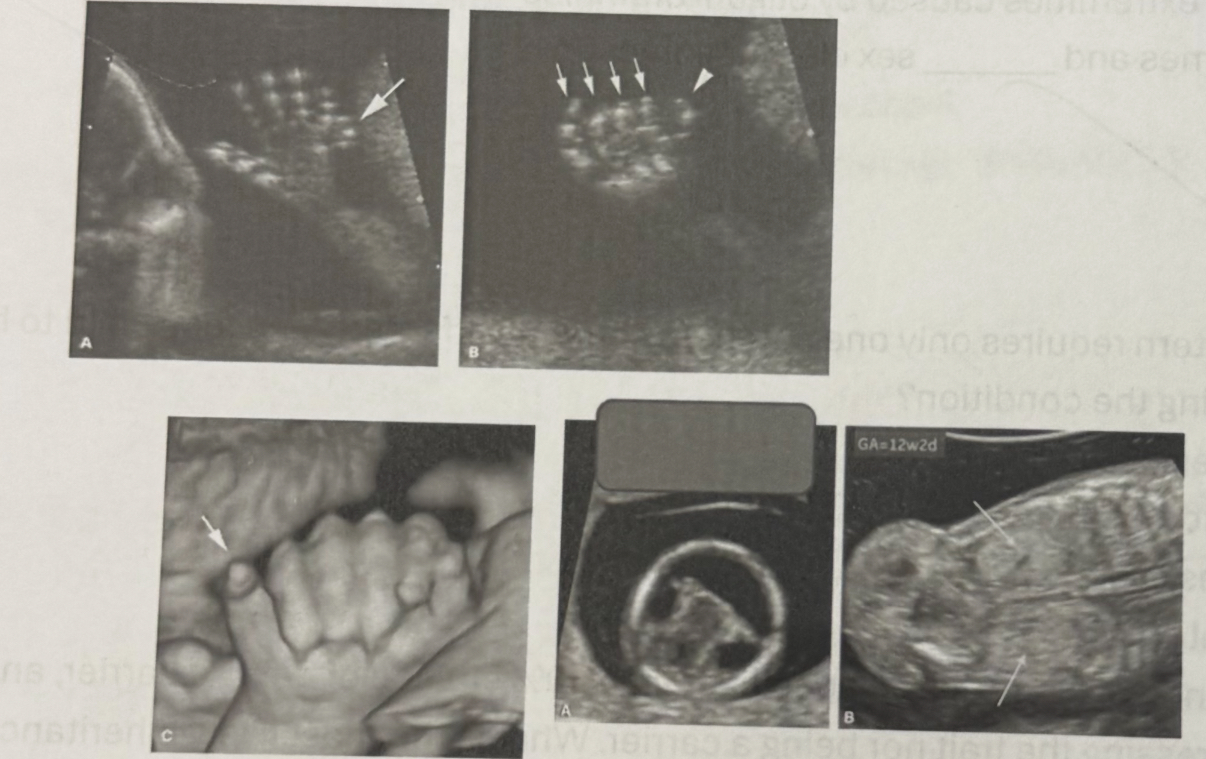
What is the most likely diagnosis based on the sonographic findings in the image shown?
a. Trisomy 21
b. Trisomy 18
c. Trisomy 13
d. Turner syndrome
Trisomy 13
A fetus with a karyotype revealing it has 69 chromosomes and sonographic findings of webbed fingers and intrauterine growth restriction most likely has:
a. trisomy 21.
b. trisomy 18
c. triploidy.
d. Turner syndrome
triploidy
Shortening of proximal segment of extremity (humerus or femur)- is called
a. Rhizomelia
b. Amelia
c. Mesomelia
d. Acromelia
Rhizomelia
A large space between the first and second toes is termed:
polydactyly.
clubfoot.
ulnaration.
sandal gap
sandal gap
Most common genetic skeletal dysplasia
Heterozygous achondroplasia
Homozygous achondroplasia
Short-rib polydactyly syndrome
Campomelic dysplasia
Heterozygous achondroplasia
Features are for Thanatophoric dysplasia except
a. Oligoamnios
b. Cloverleaf skull (Kleeblattschadel)
c. Severely shortened limbs
d. Hypoplastic thorax: because of narrow chest
Oligoamnios
What condition is associated with bilateral renal agenesis, oligohydramnios, and fusion of the lower extremities?
a. Sirenomelia
b. Acrenomelia
c. Syringomyelia
d. Schizomelia
Sirenomelia
A protein produced by the yolk sac and fetal liver that is found in excess in the maternal circulation in the presence of a neural tube defect is:
a. Calcium
b. Alpha feto protein
c. Prolactin
Alpha feto protein
The most common nonlethal skeletal dysplasia is:
achondrogenesis.
achondroplasia.
thanatophoric dysplasia.
osteogenesis imperfecta
achondroplasia
What is the maternal dietary supplement that has been shown to significantly reduce the likelihood of the fetus suffering from a neural tube defect?
AFP
Estriol
Folate
Pregnancy protein A
Folate
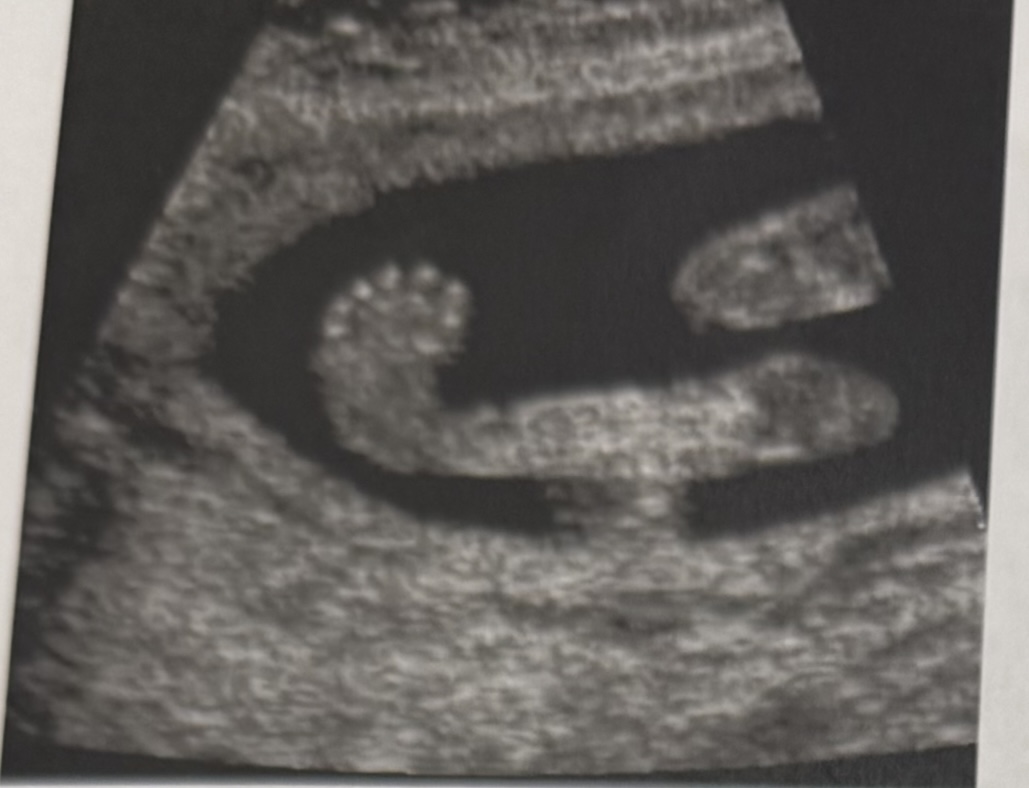
What is the image showing?
a. Tallies equino varus
b. Rocker bottom foot
c. Normal fetal foot
Tallies equino varus
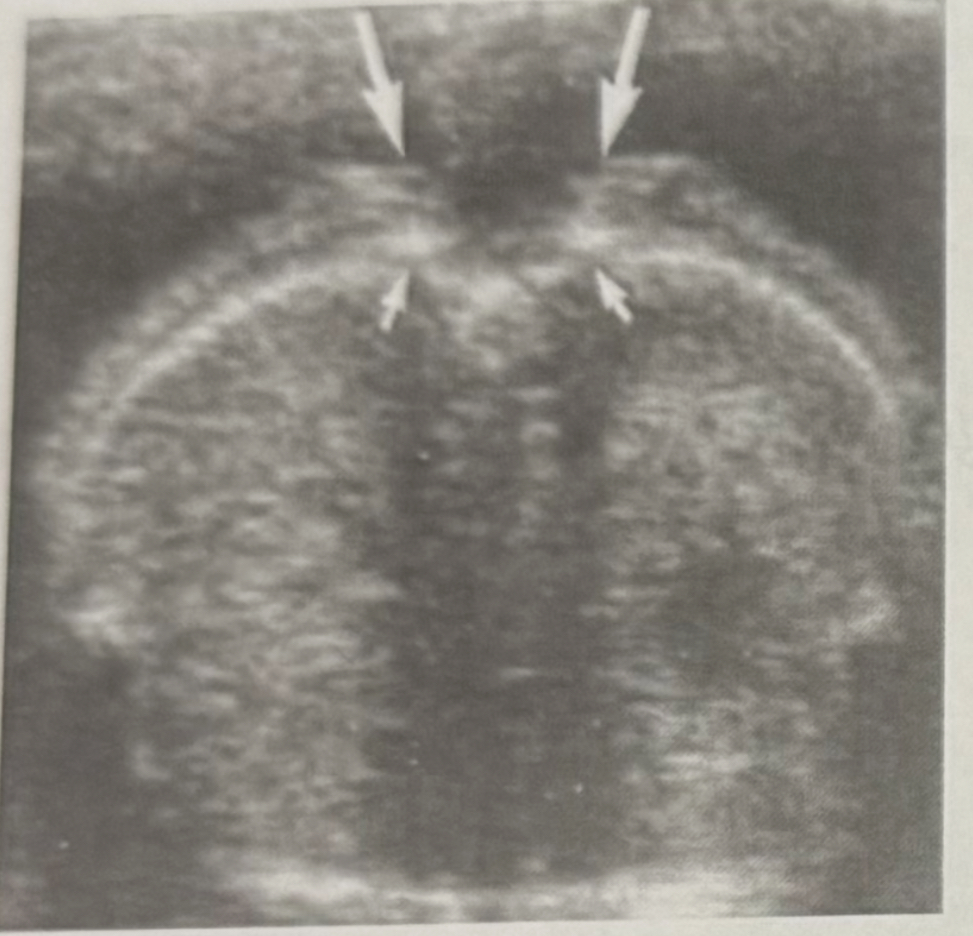
What is the section and what is shown?
a. Sagittal spine
b. Transverse spine
c. Coronal spine
Transverse spine
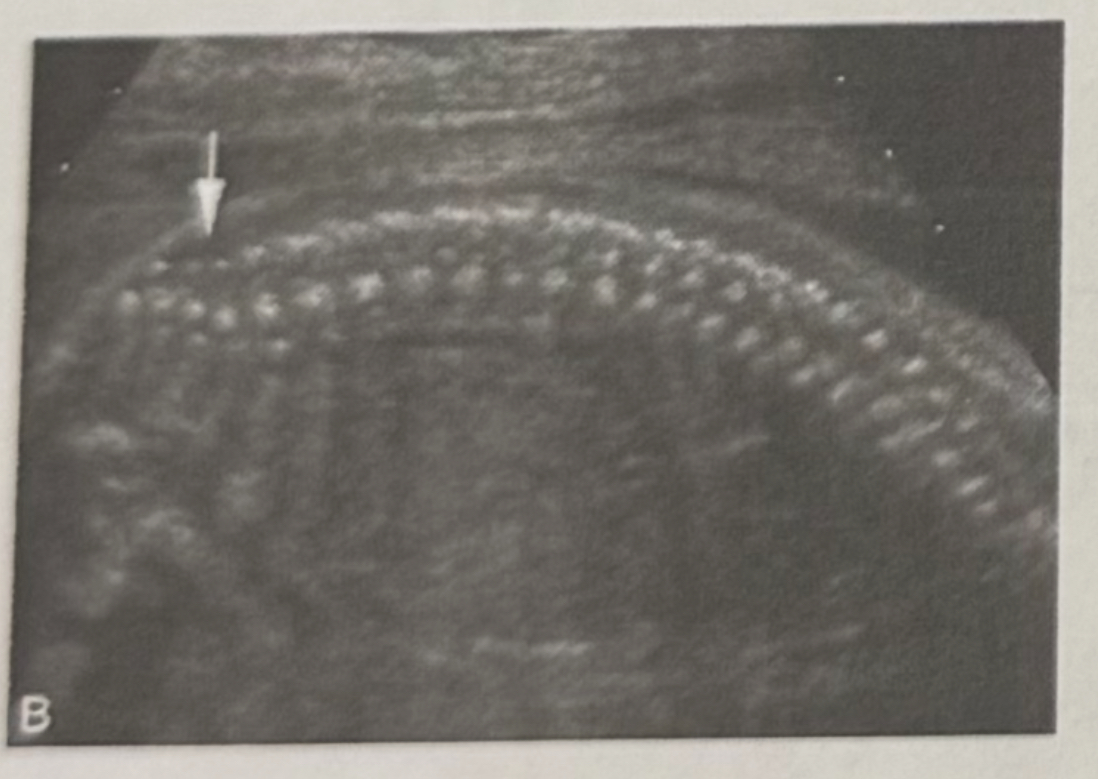
What is the plane of this spine?
Sagittal spine
Transverse spine
Coronal spine
Sagittal spine
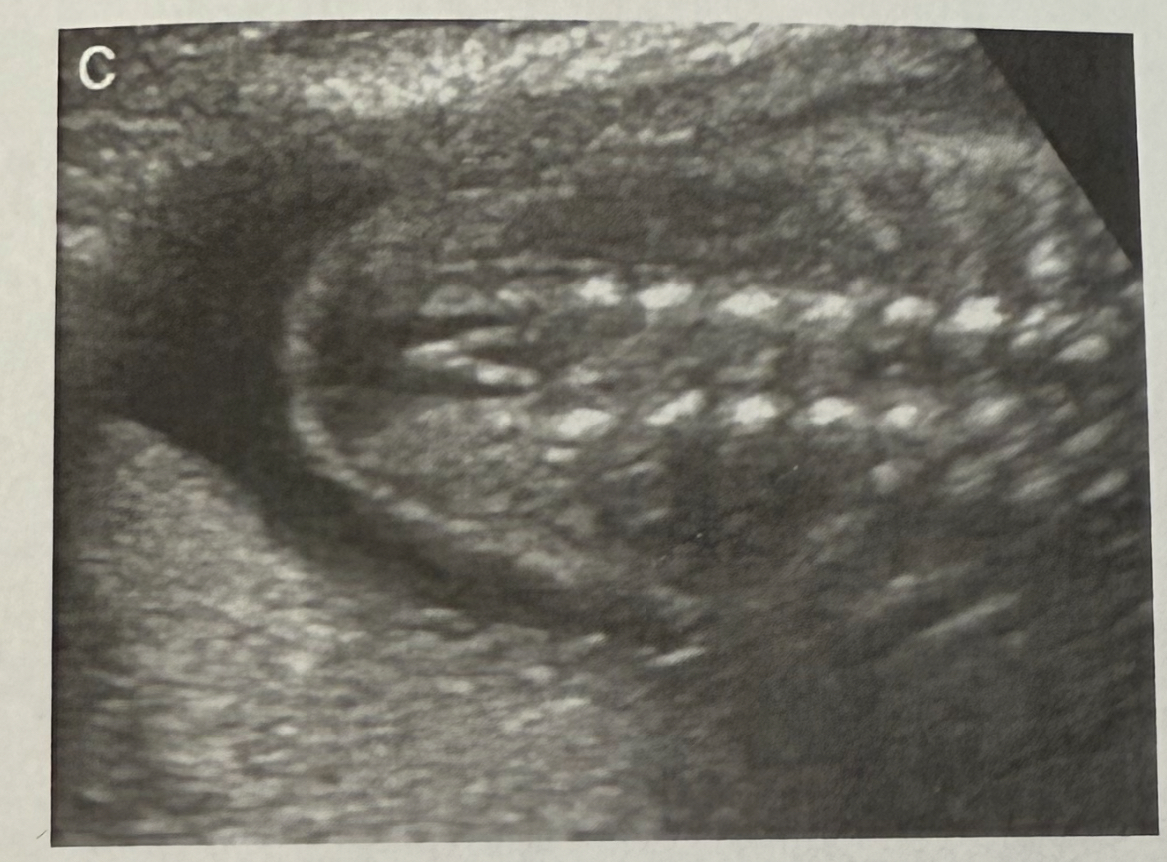
What is the plane of this spine?
Sagittal spine
Transverse spine
Coronal spine
Coronal spine
The condition associated with the absence of the sacrum and coccyx:
limb-body wall complex.
caudal regression syndrome.
thanatophoric dwarfism.
heterozygous achondroplasia
caudal regression syndrome.