muscle tissue
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
the pinkest part
in a sample, how can you identify which part is muscle?
their complex cytoskeleton structure
what allows muscle cells to contract?
mesoderm
what is the embryonic origin of muscle tissue?
muscle fibers or myocytes
what is another word for muscle cells?
plasma membrane of a muscle cell
what is the sarcolemma?
sarcoplasm
what is the name for the cytoplasm specifically in a muscle cell?
endoplasmic reticulum of a muscle cell
what is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
sarcosomes
the mitrochondria of a muscle cell is called ...
cardiac, smooth, skeletal
what are the three types of muscle tissue?
cardiac and skeletal
which types of muscle tissue are striated?
smooth muscle
which type of muscle tissue is not striated?
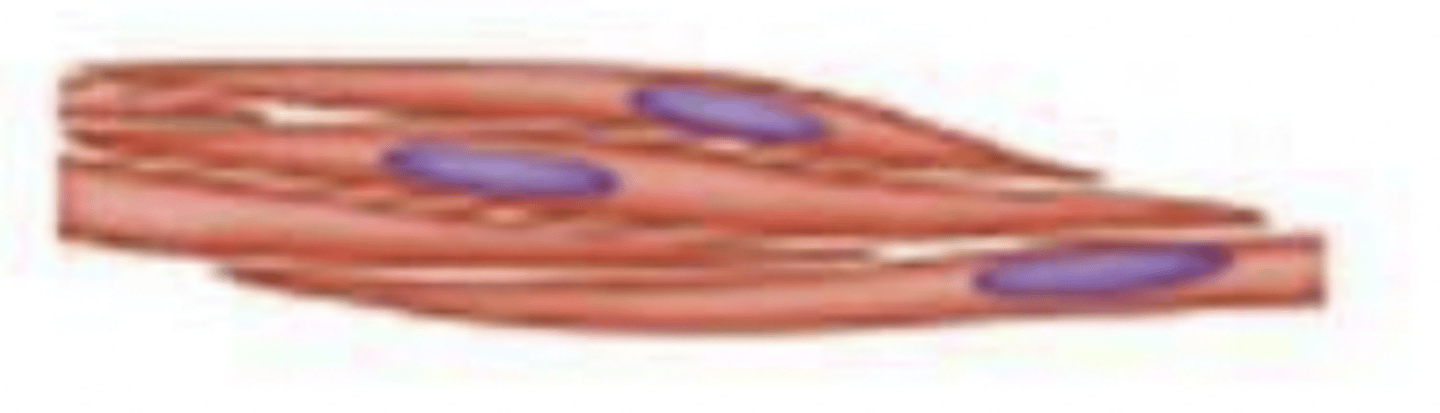
smooth
what type of muscle tissue?
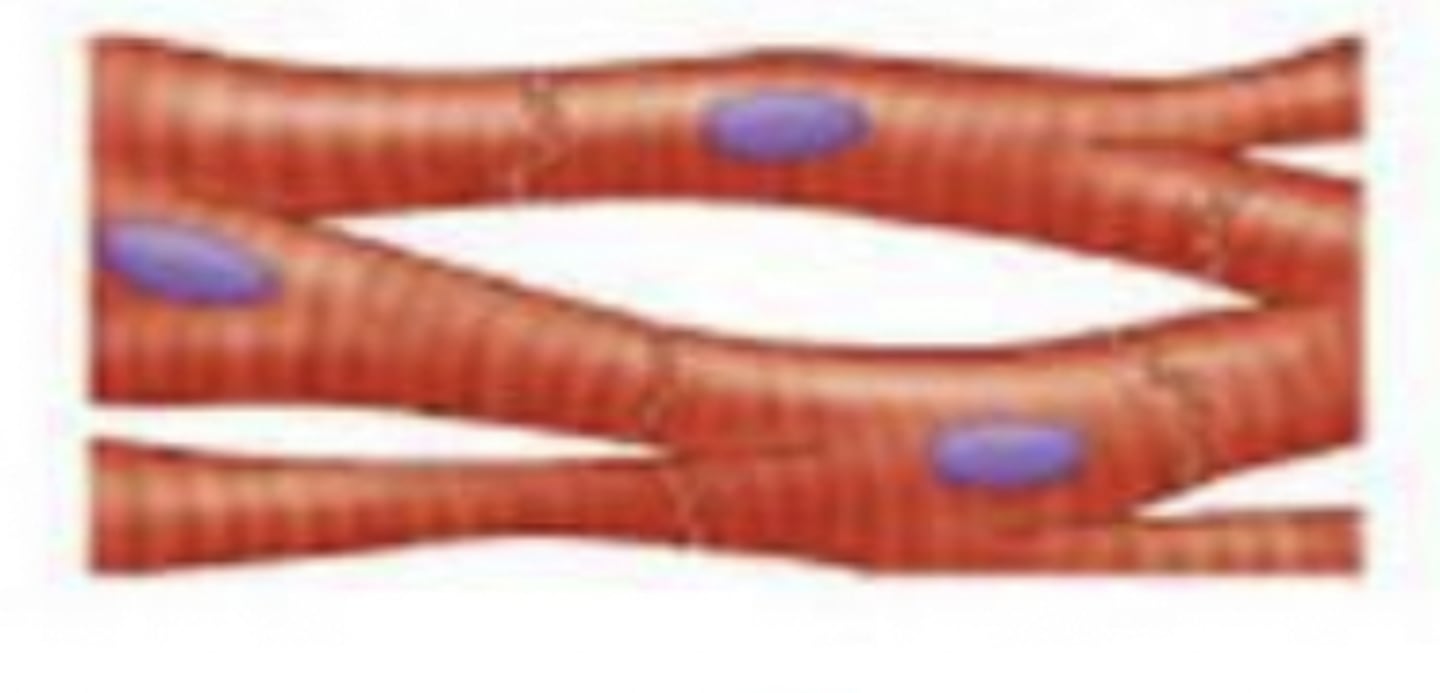
cardiac
what type of muscle tissue?
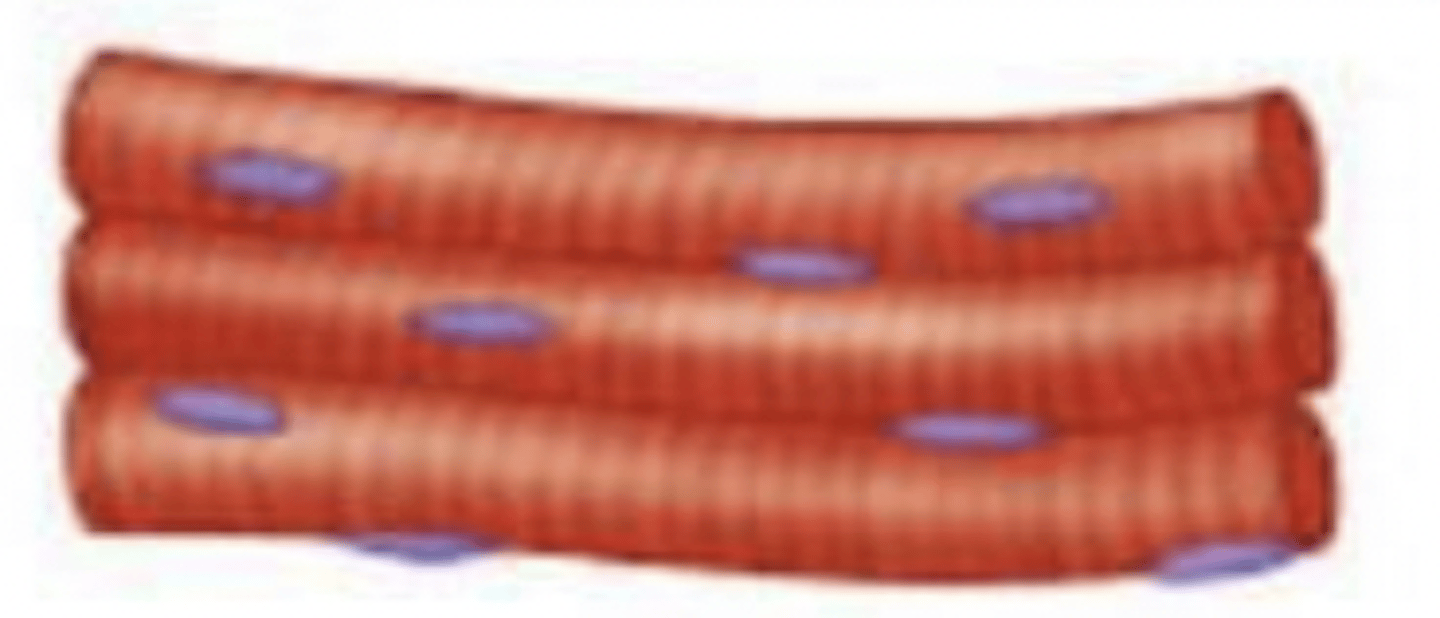
skeletal
what type of muscle tissue?
internal organs
where in the body would you find smooth muscle?
in the heart
where is cardiac muscle tissue found?
skeletal muscles
where in the body is there skeletal muscle?
yes
is skeletal muscle striated?
many
how many nuclei per skeletal muscle cell?
long, multinucleated, transverse striations, subsarcolemmic nuclei
describe the appearance of cells of skeletal muscle
skeletal
which type of muscle tissue produces voluntary contractions?
subsarcolemmic- in contact with plasma membrane
in a skeletal muscle fiber, where is the nuclei located?
a bundle of muscle fibers
what is a fascicle?
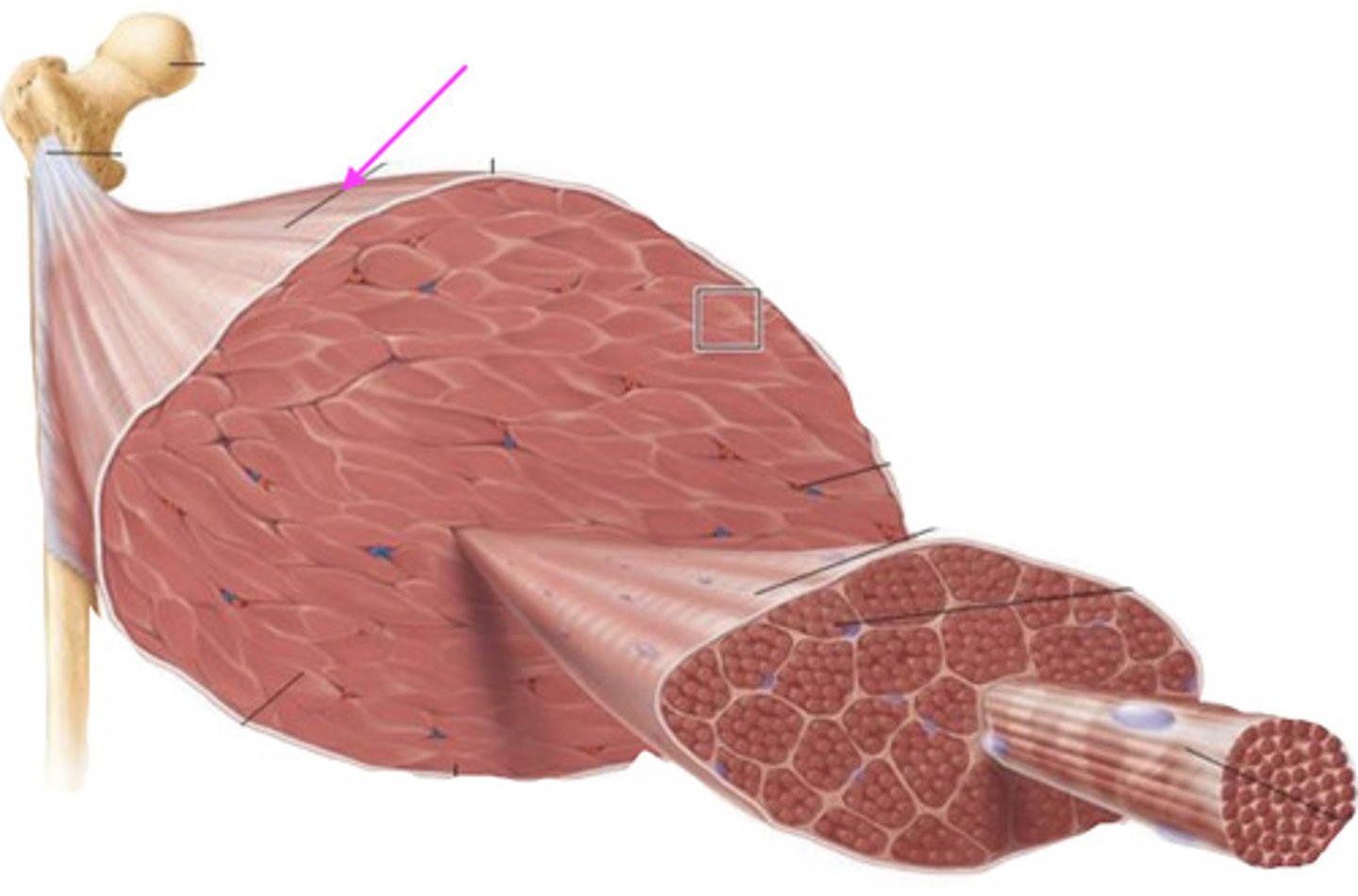
epimysium
what is the connective tissue called that surrounds the entire muscle?
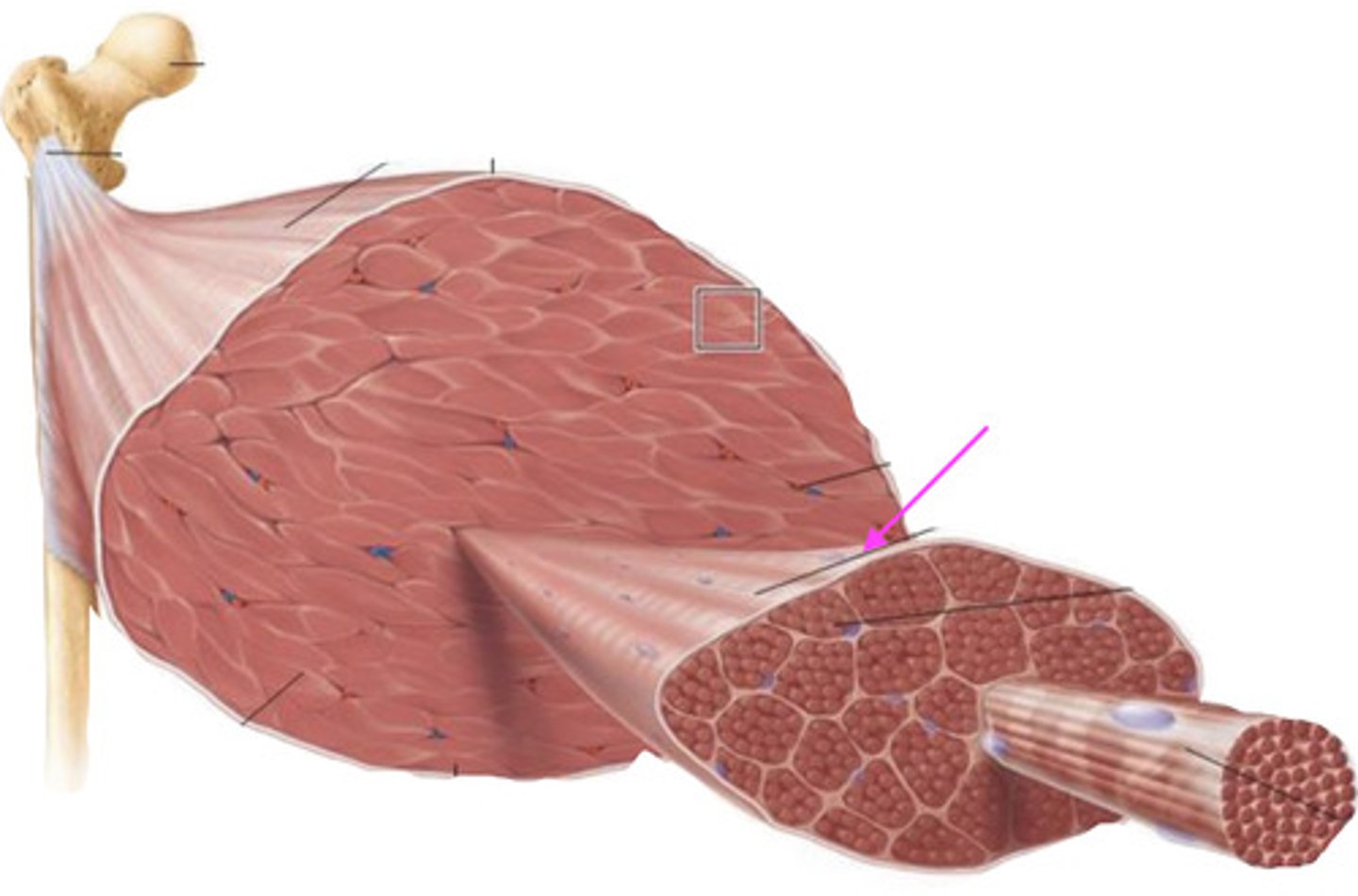
a fascicle
what does perimysium surround?
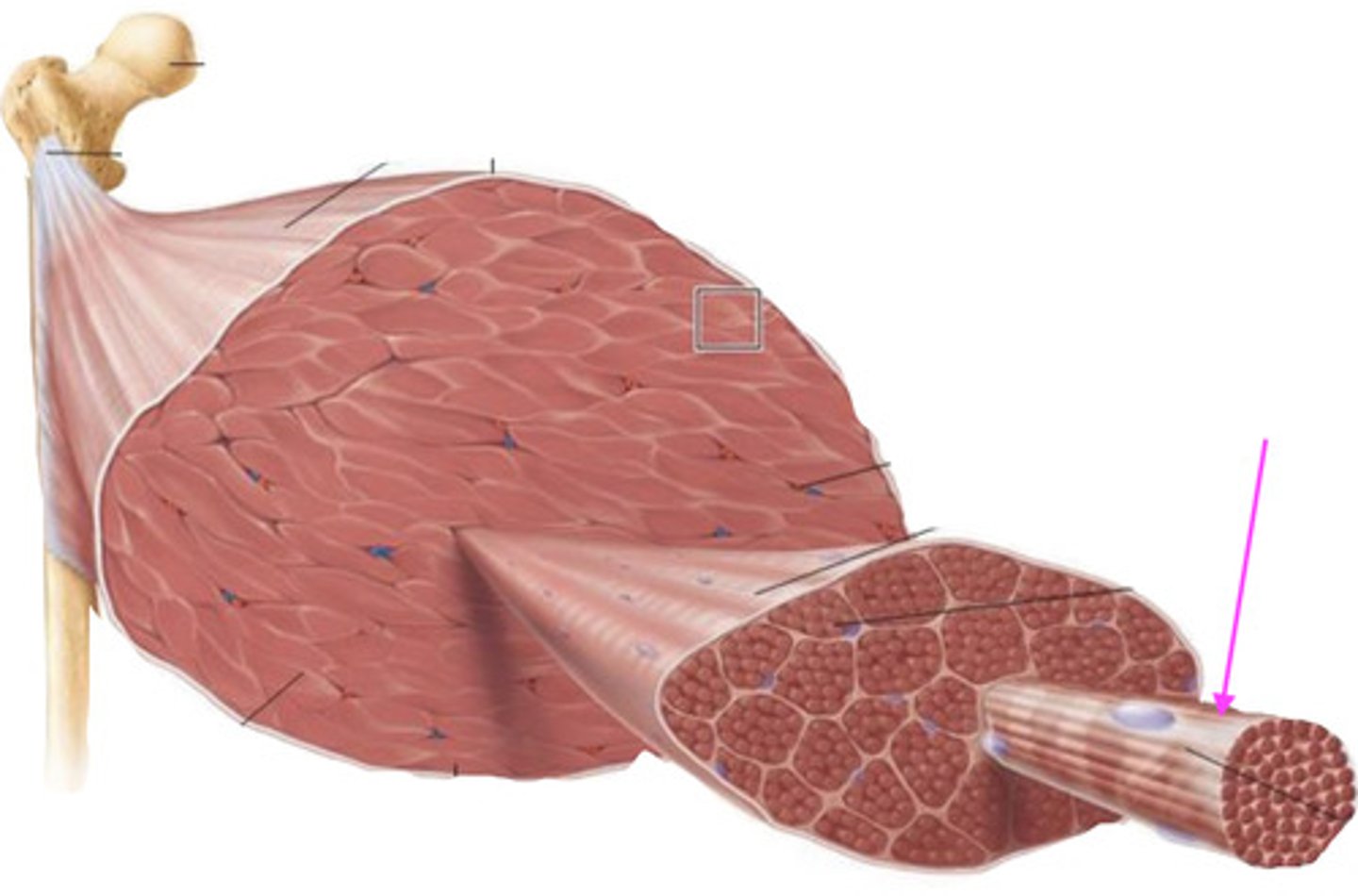
endomysium
what connective tissue surrounds a singular muscle fiber?
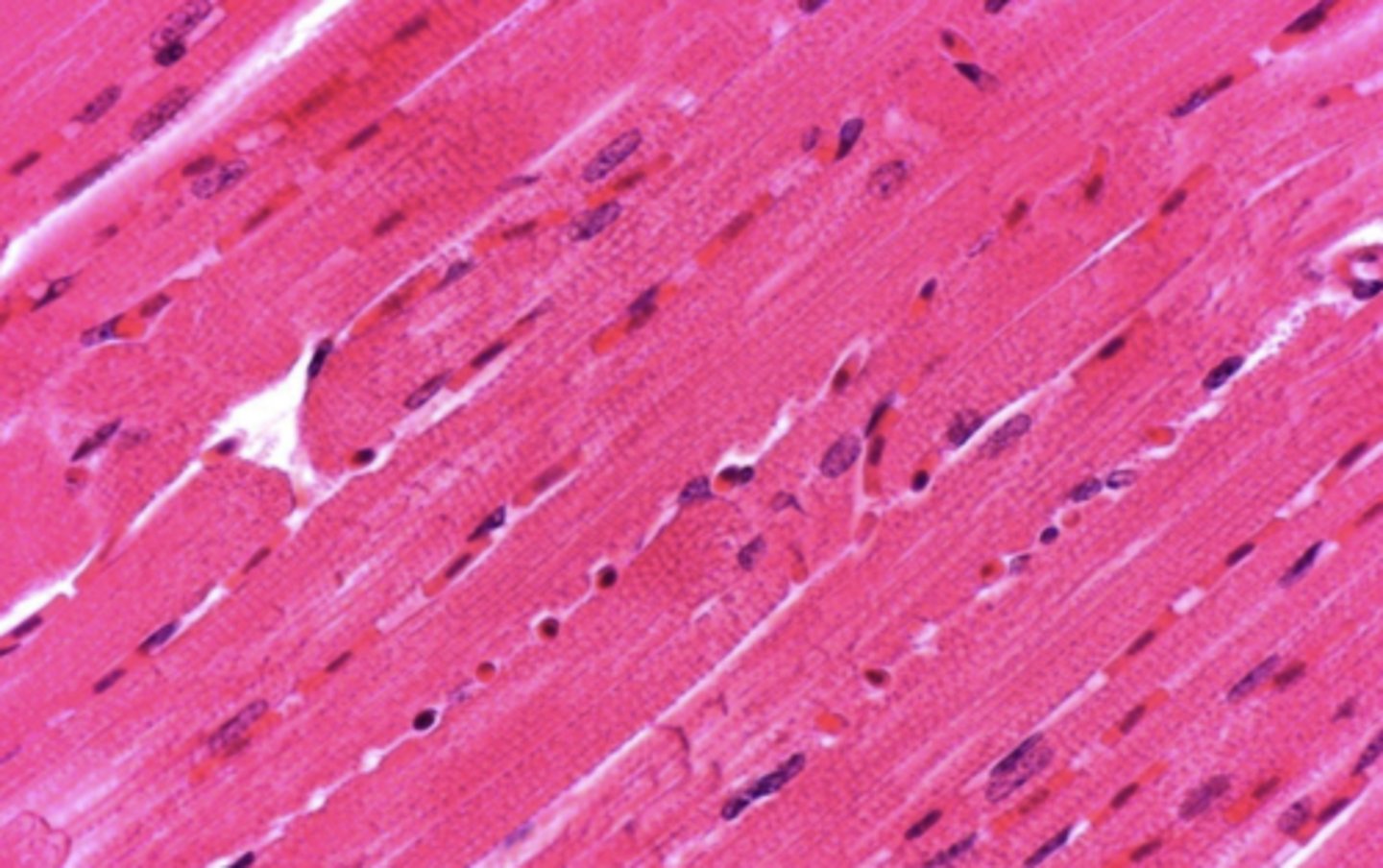
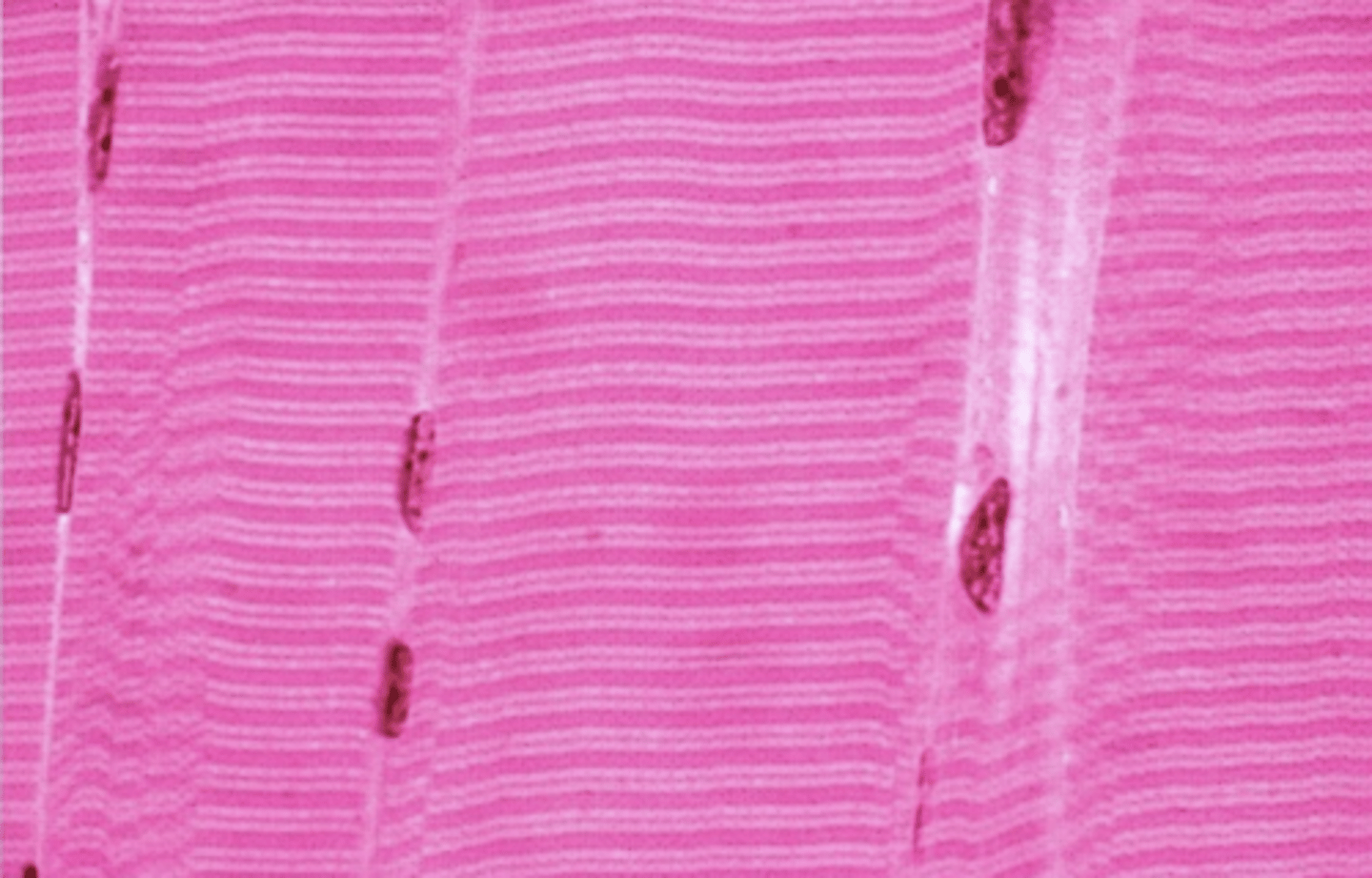
skeletal muscle
long fibers with many nuclei all at the edge of the cell in a line
what type of muscle tissue is this? how can you tell?
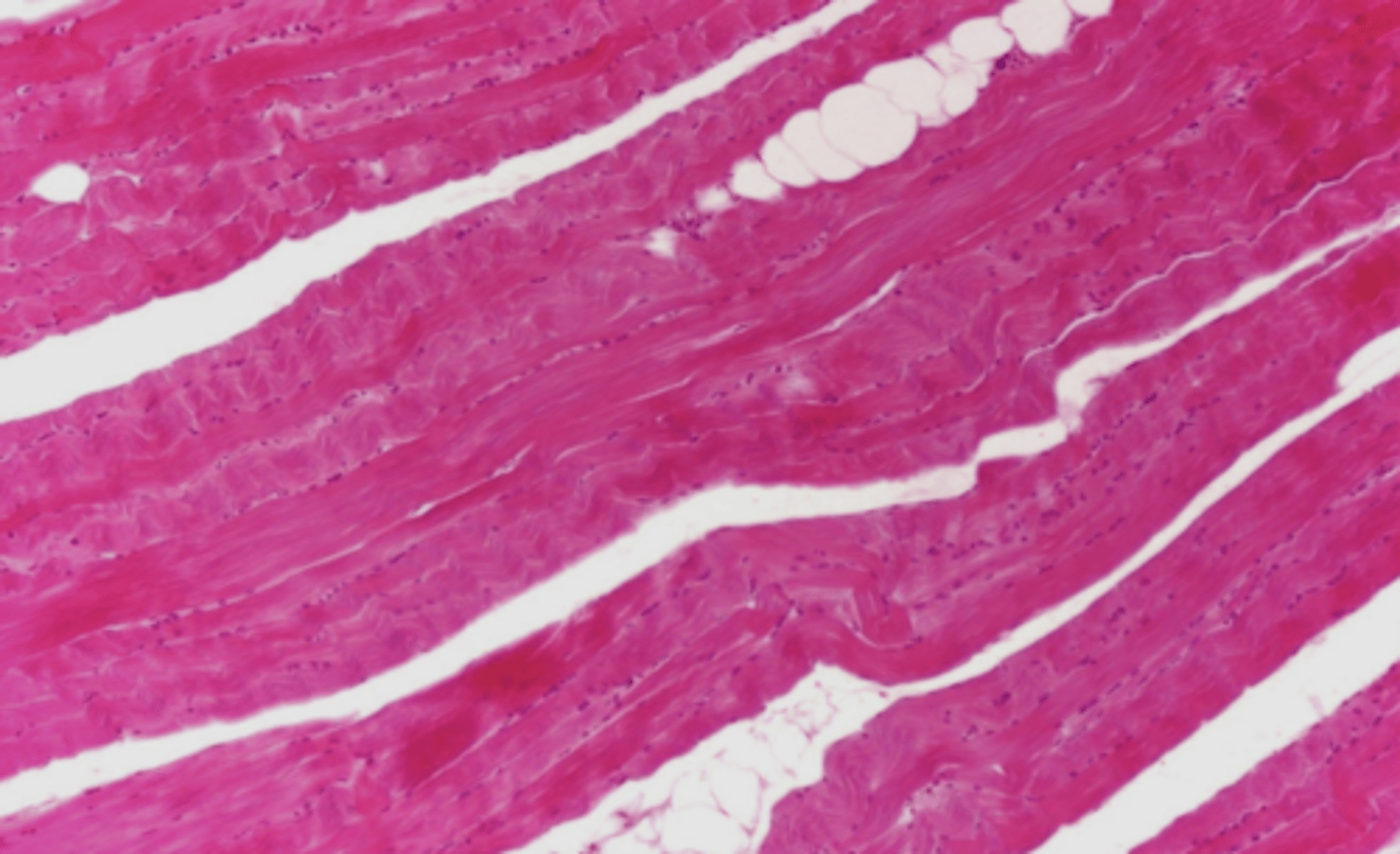
skeletal muscle
what type of muscle tissue is this?
epimysium
what is this connective tissue called?
perimysium
what is this connective tissue called?
endomysium
what is this connective tissue called?
perimysium
what is in blue?
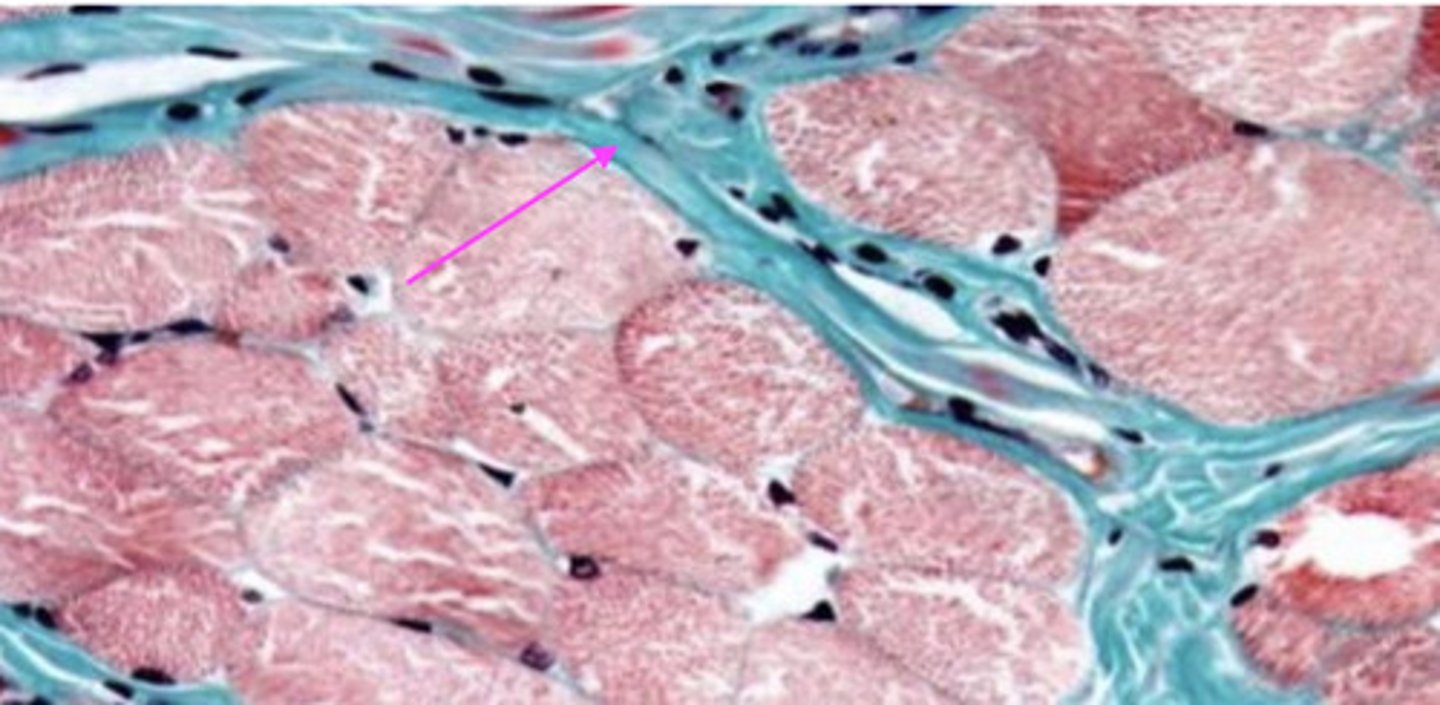
endomysium
what type of tissue is surrounding this structure?
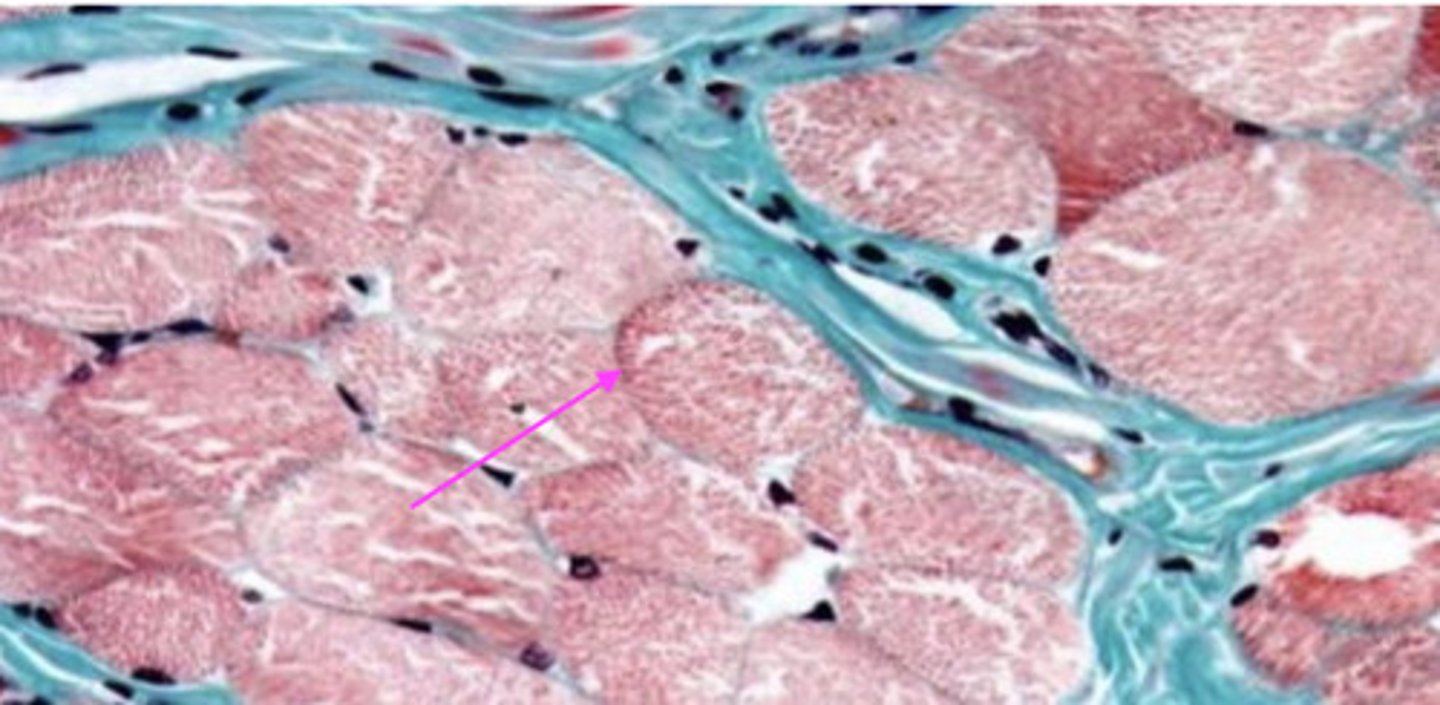
reticular connective tissue
what type of connective tissue makes up endomysium?
loose
perimysium is made up of ____ connective tissue
dense and irregular connective tissue
what type of CT makes up epimysium?
perimysium
which, epimysium, perimysium, or endomysium, has lots of capillaries and nerves?
oval
what shape is the nucleus of a skeletal muscle fiber?
transverse
are the striations transverse or longitudinal?
pink
the sarcoplasm is eosinophilic, which makes it appear ____
the A band
what part of the sarcomere retracts light/is anisotropic?
no, it is isotropic
does the I band of the sarcomere retract light?
the A band because it retracts light (anisotropic)
which band, A or I, is responsible for the visible striations?
H band and M line
the A band also consists of 2 other parts, what are they?
the H band
what is at 1?

2
where is the M line?
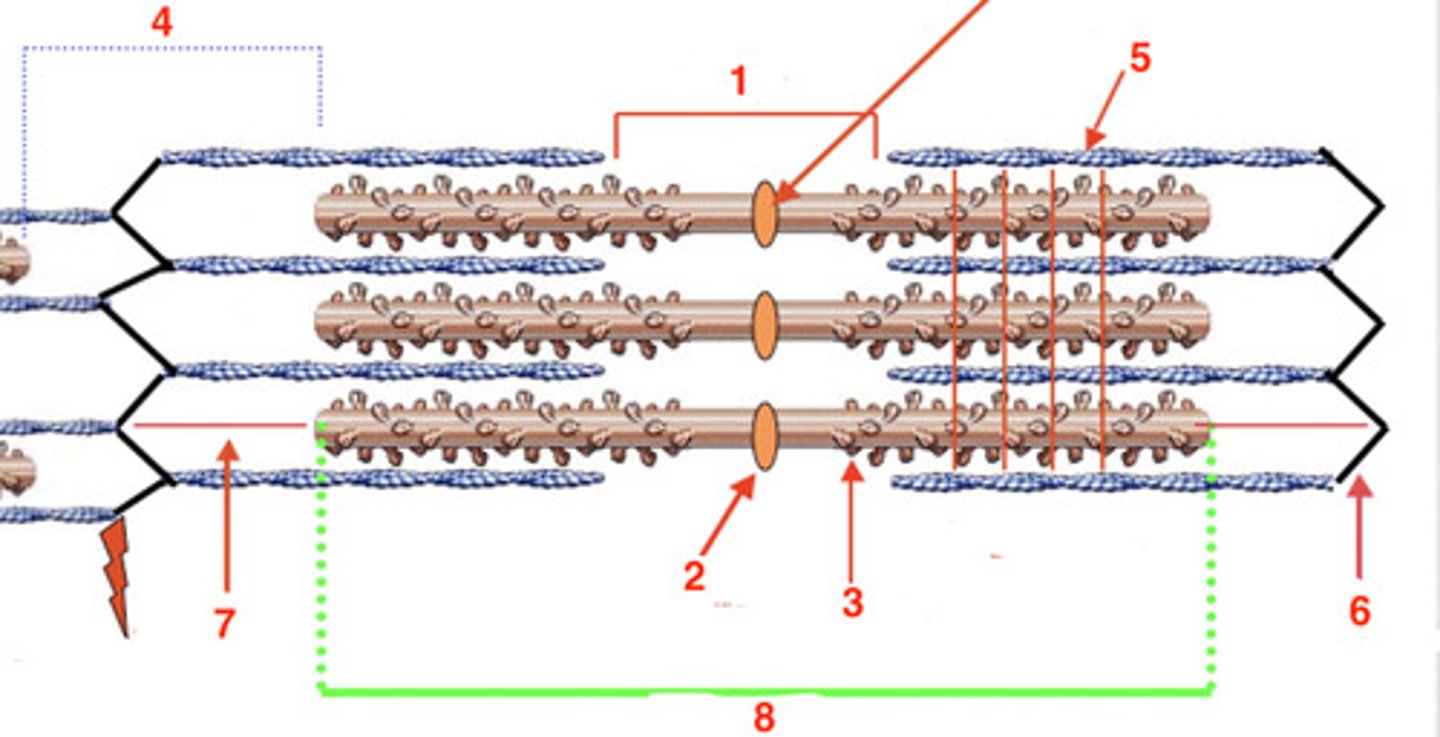
myosin
what is the protein at 3?
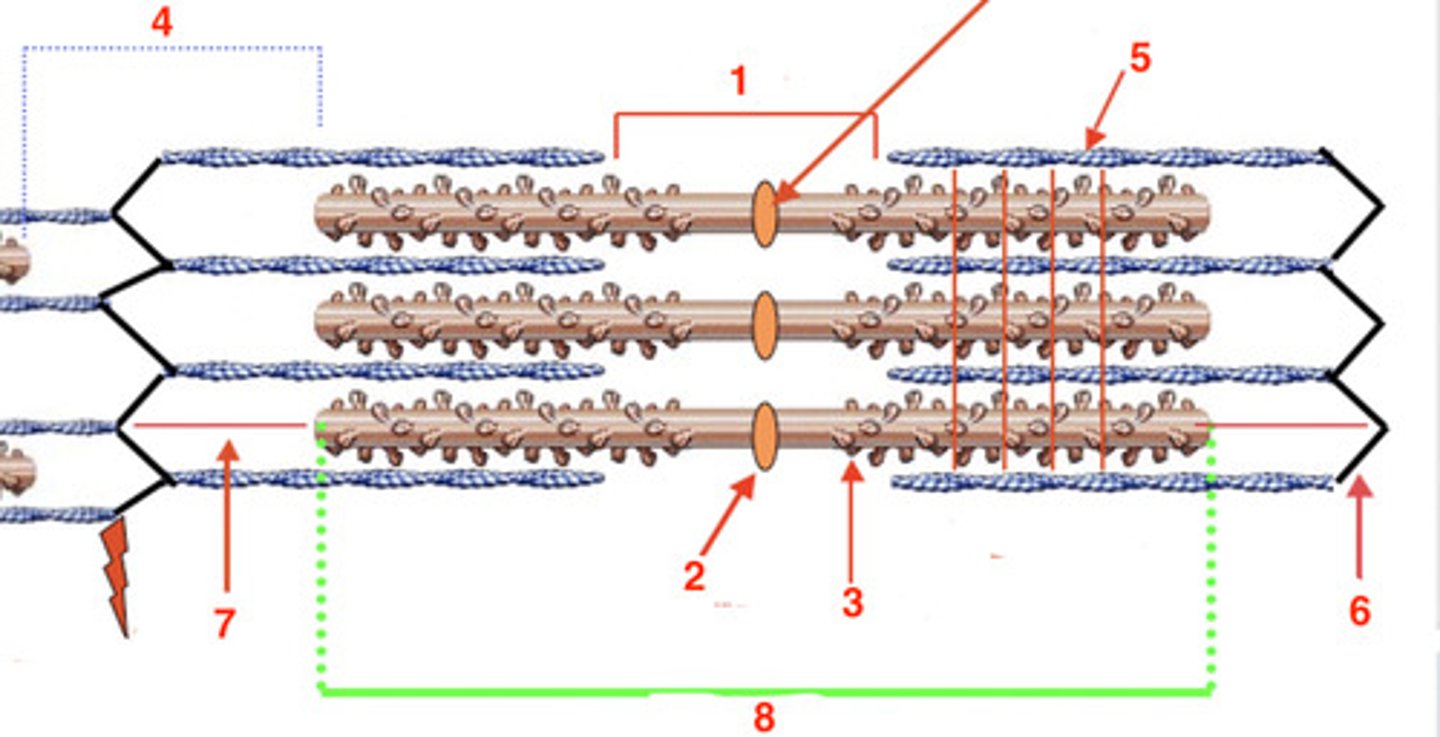
4
where is the I band?
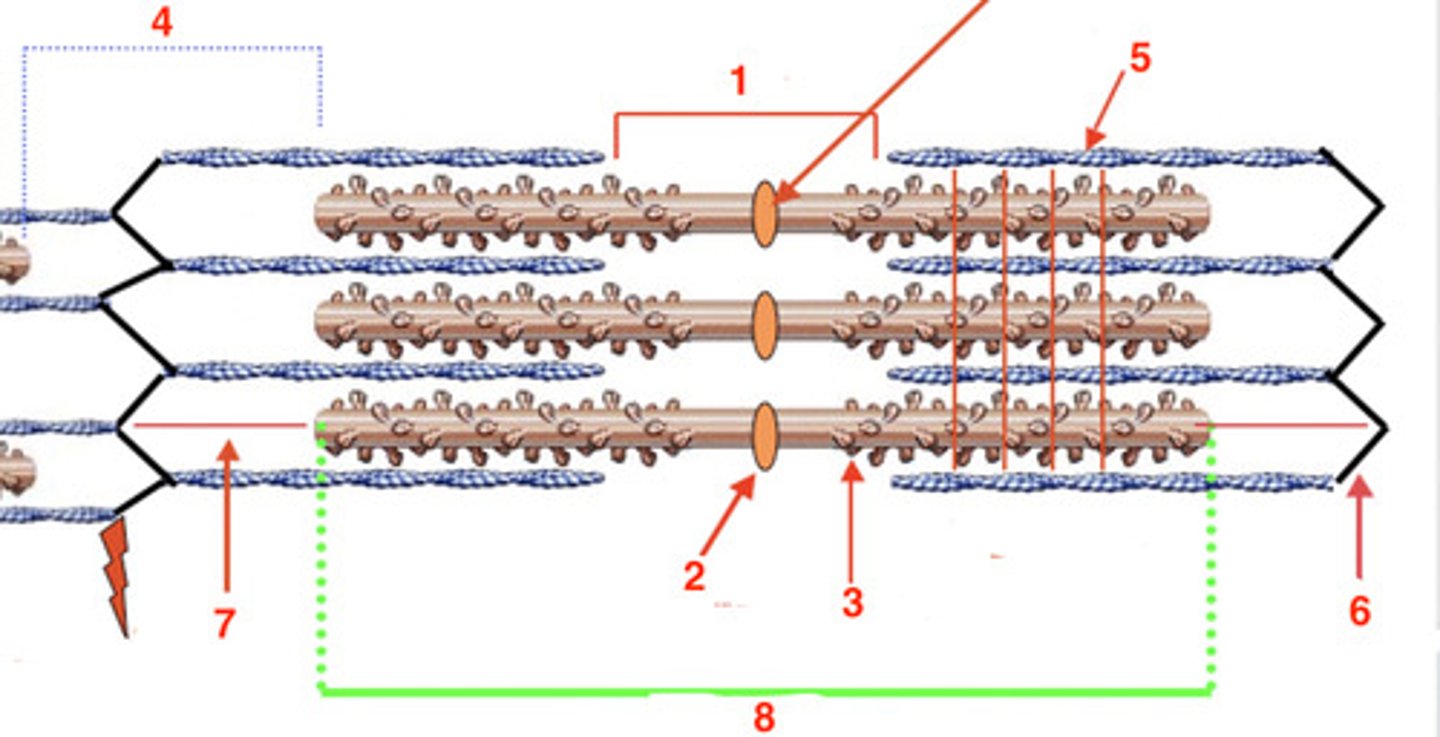
actin
what protein is at 5?
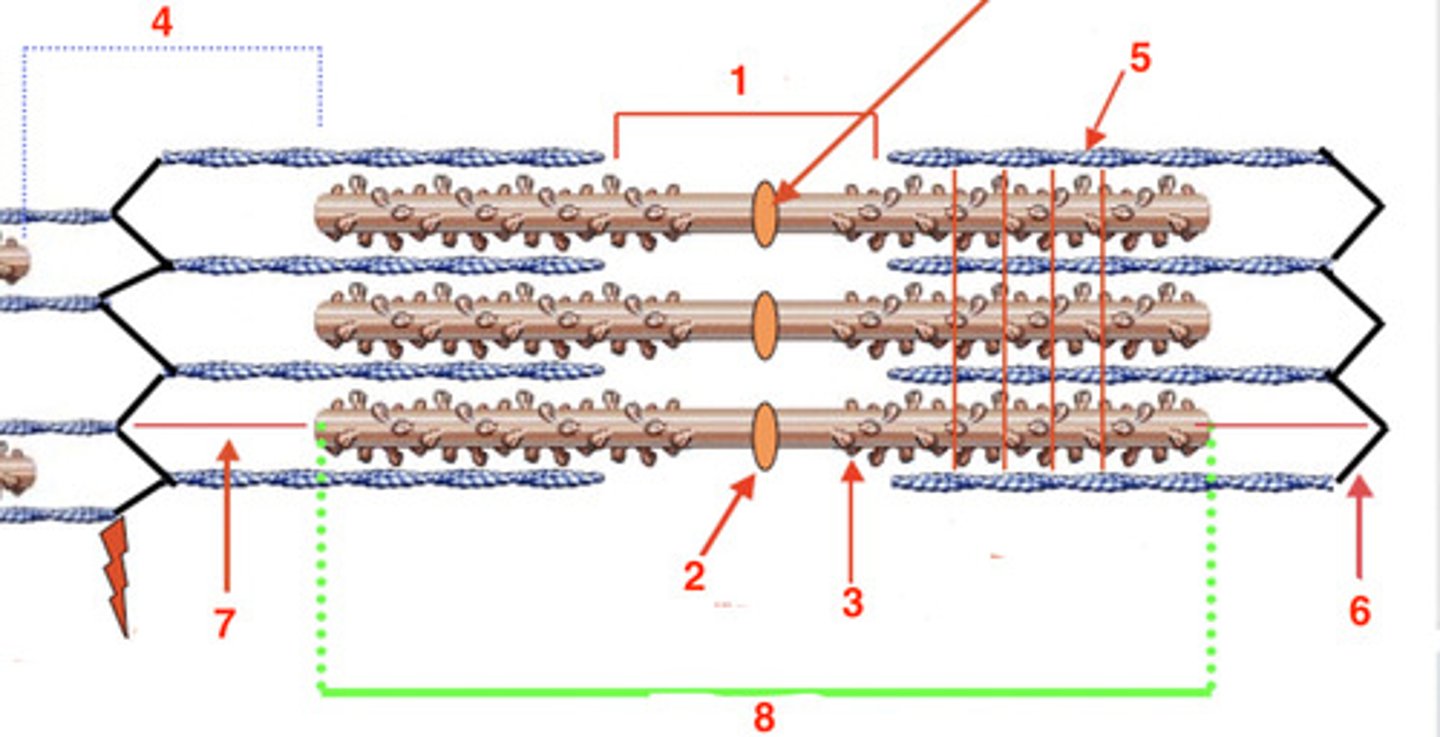
6
where is the Z-line?
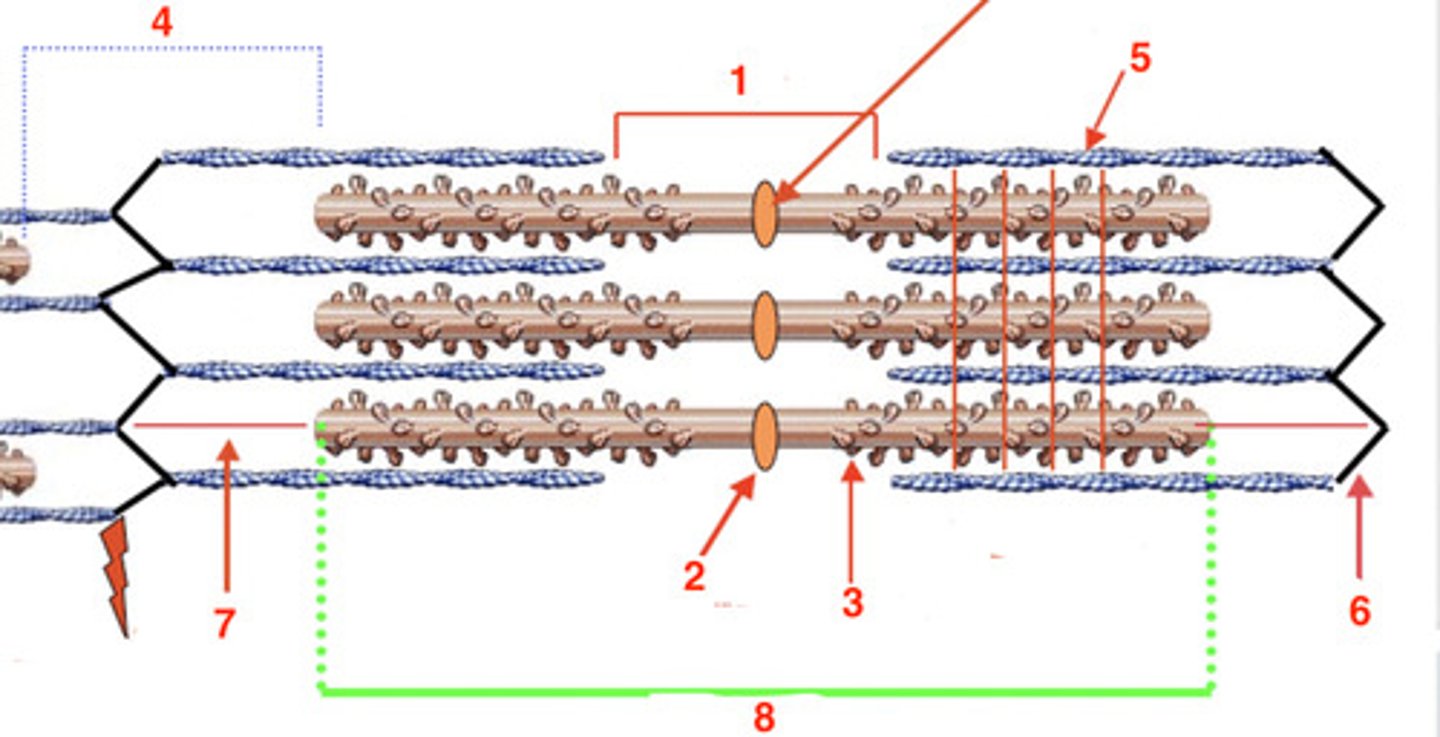
titin
what protein is at 7?
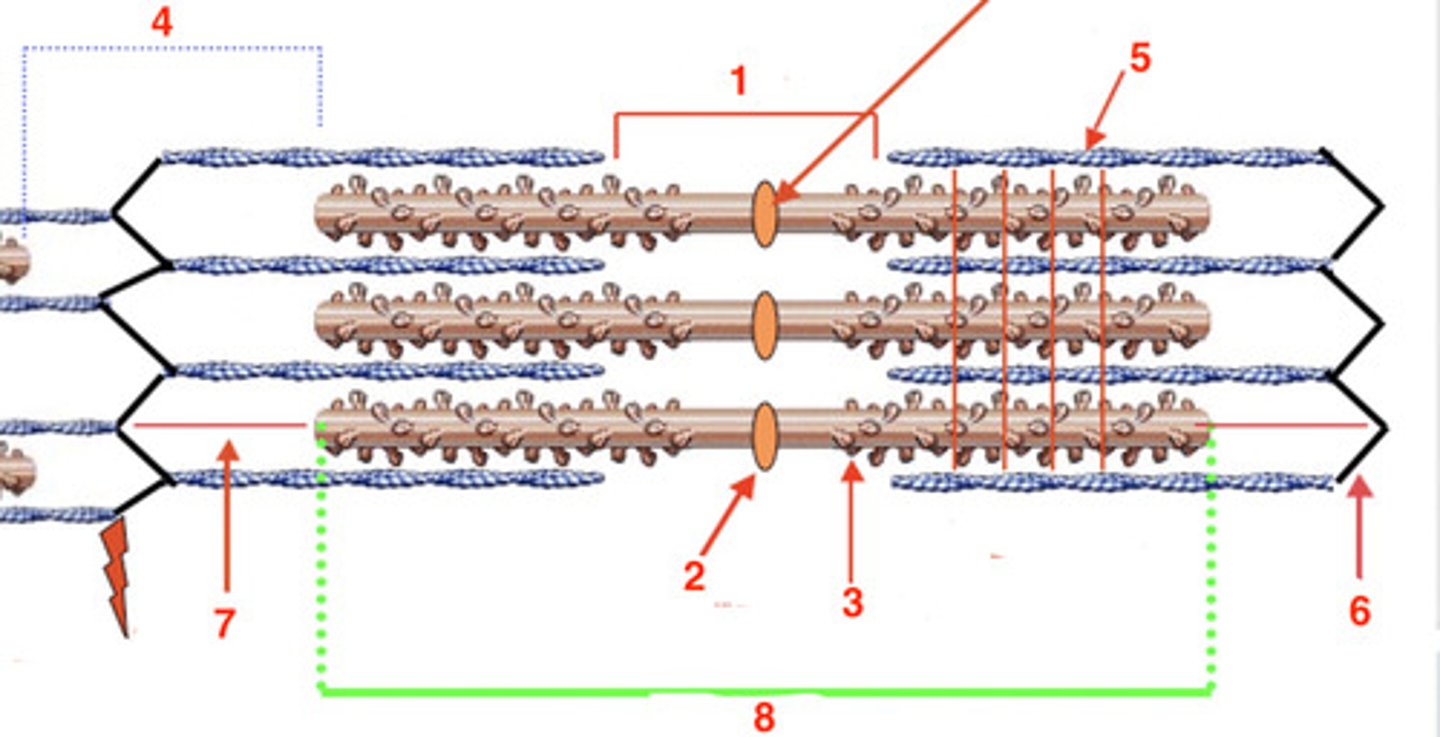
8
where is the A-band?
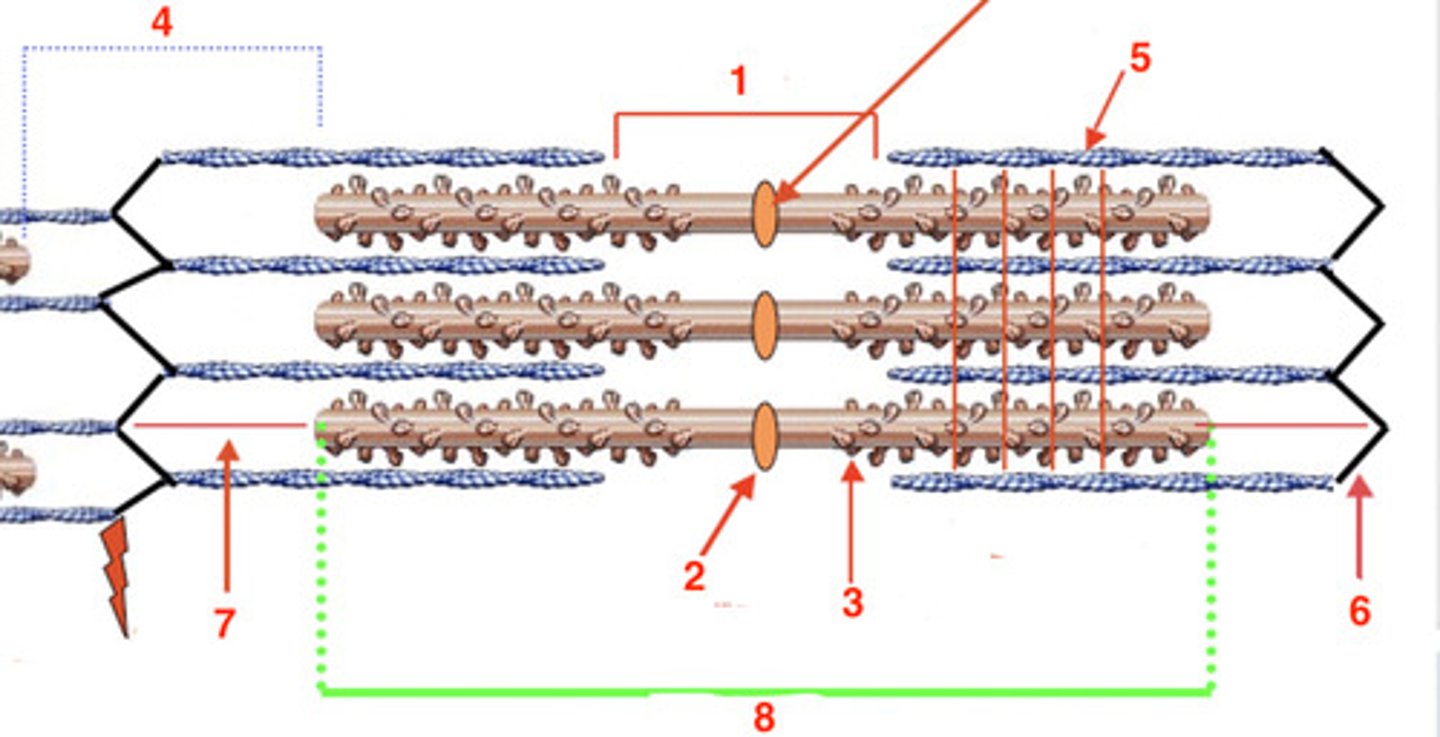
A
the visible striations are the ____ band

dystrophin
what is the protein on the inner surface of the
sarcolemma that confers membrane mechanical
reinforcement?
invaginations of the sarcolemma that allows the travel of Ca2+
what are T-tubules?
Ca2+ storage
what is the function of the smooth sarcoplasmic reticulum?
2 terminal cisternae and a T-tubule
triads are made up of..
sarcoplasmic reticulum
what is at 1?
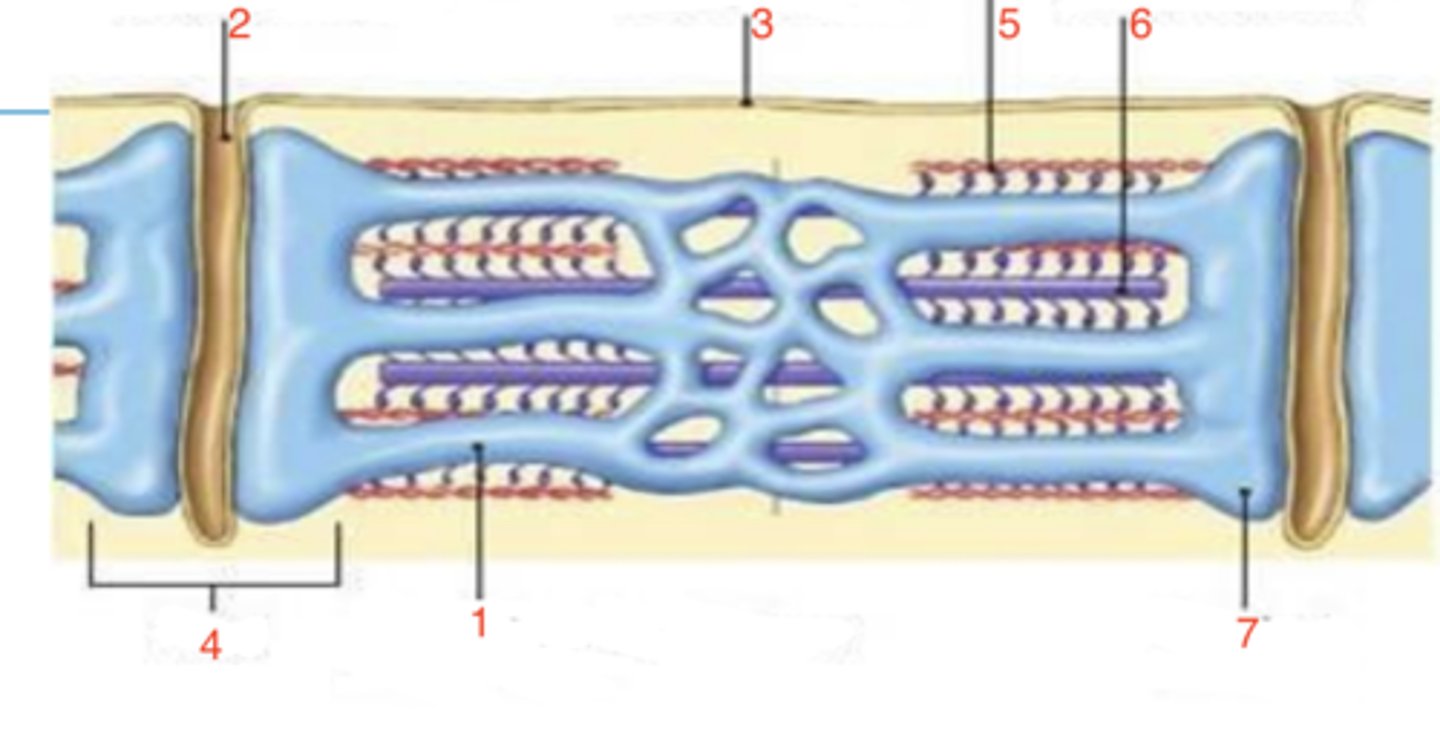
2
where is the T-tubule?
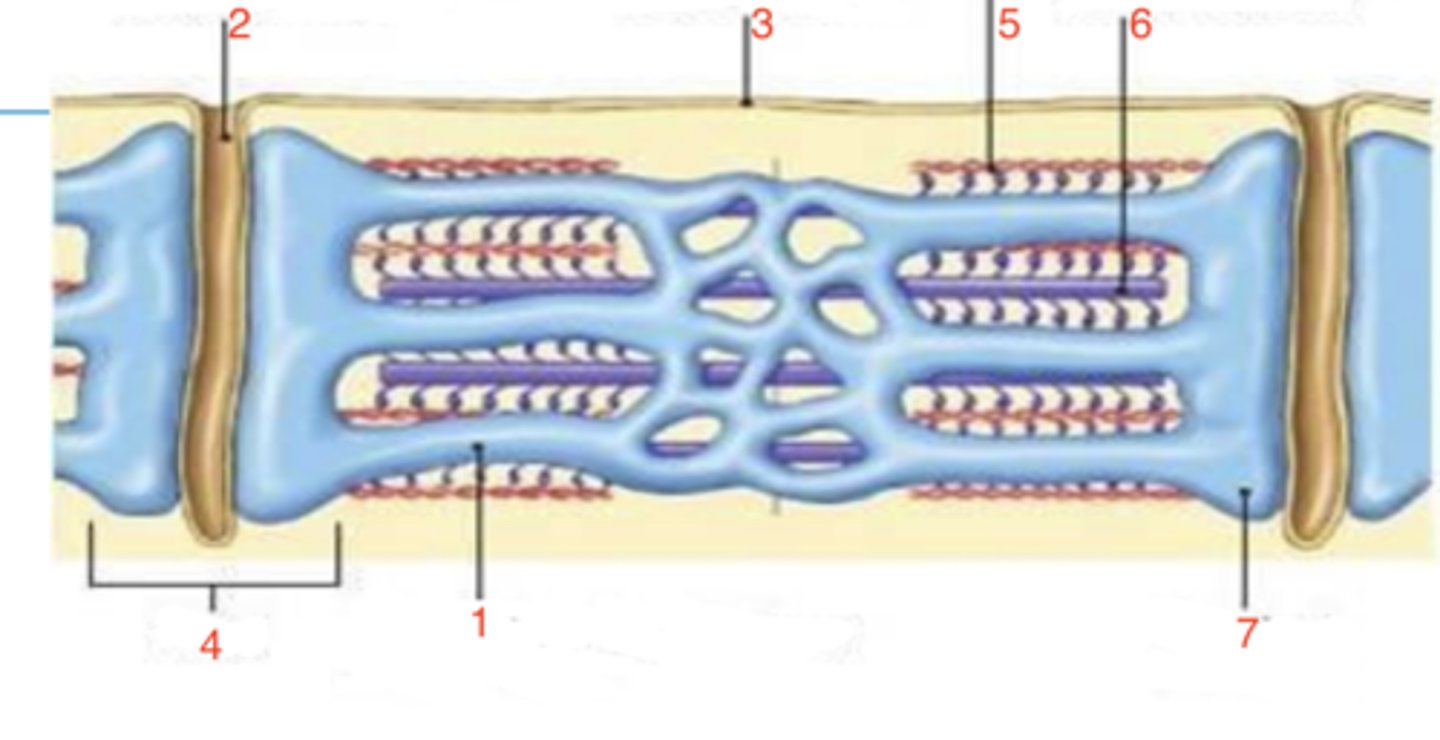
sarcolemma
what is 3?
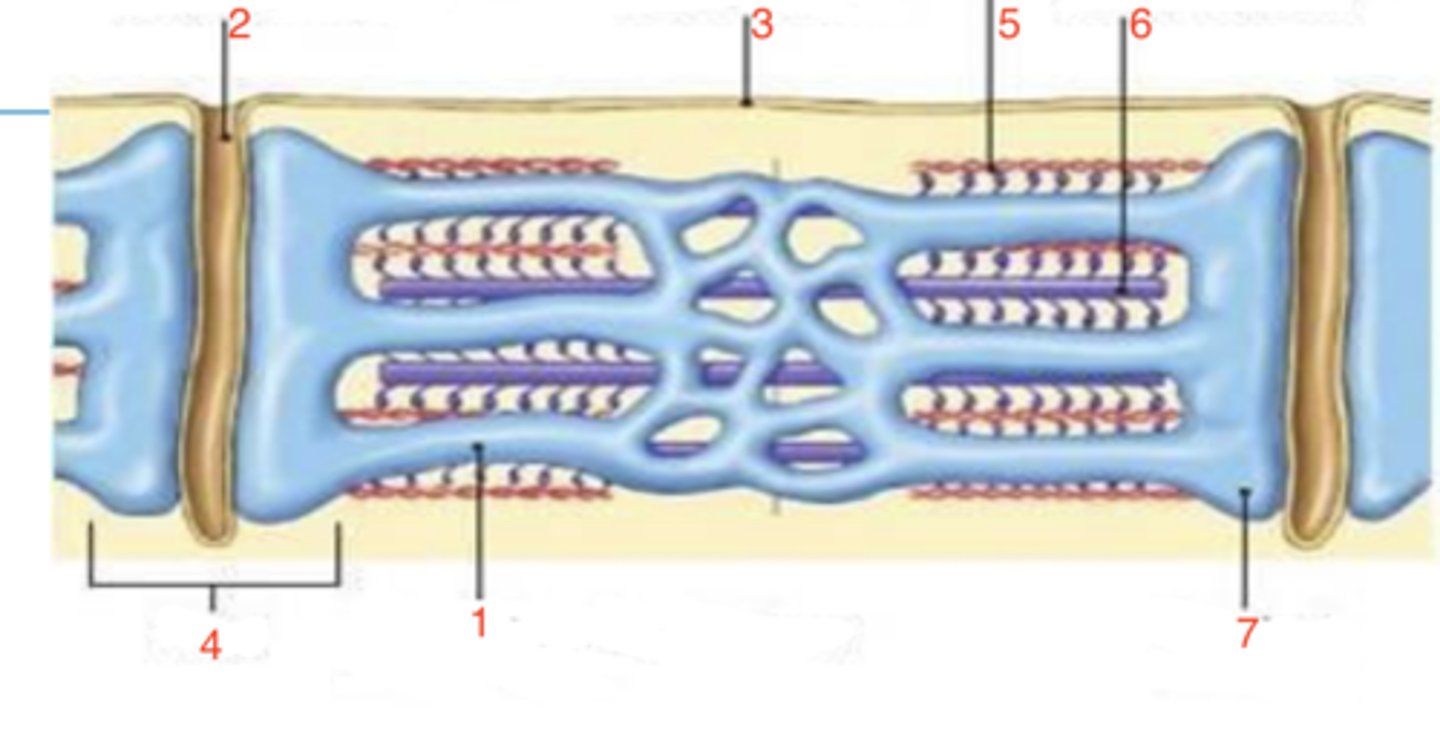
triad
what is 4?
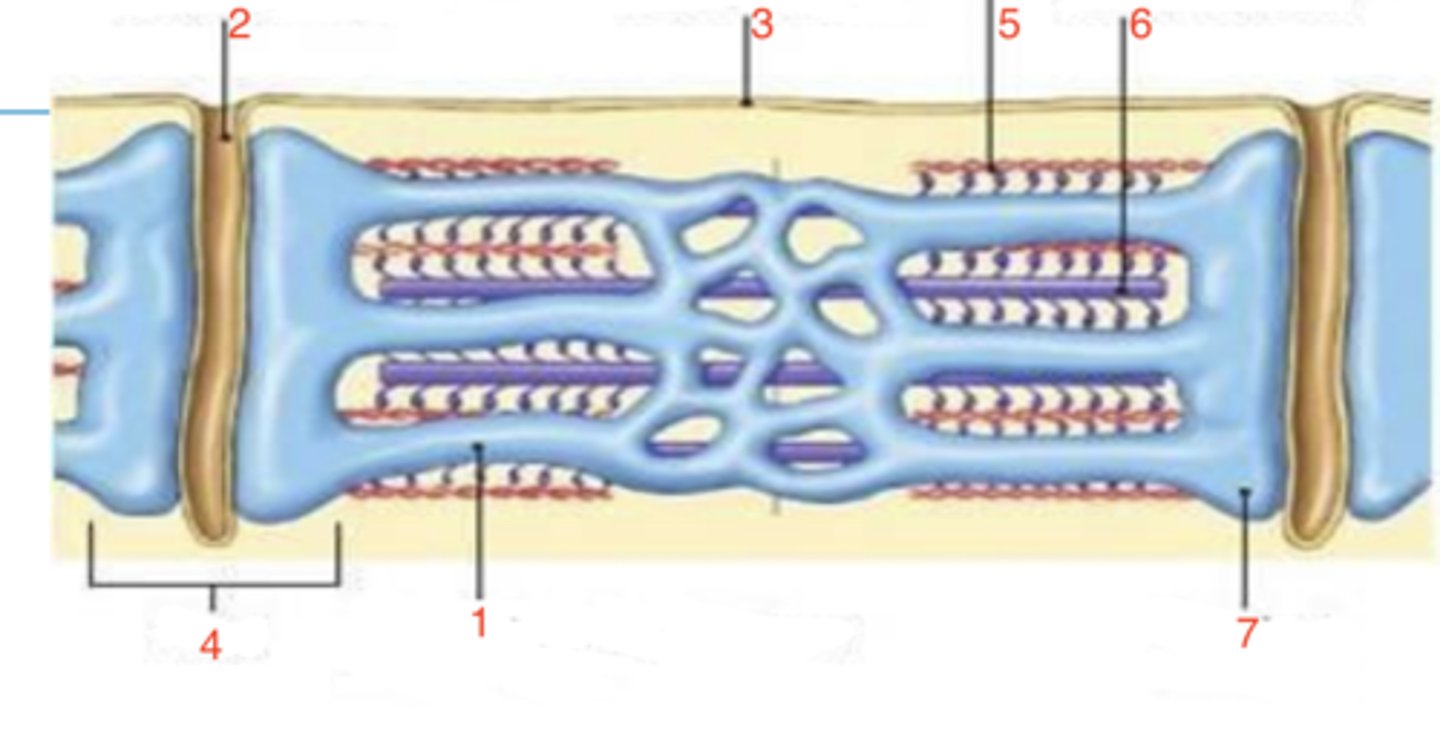
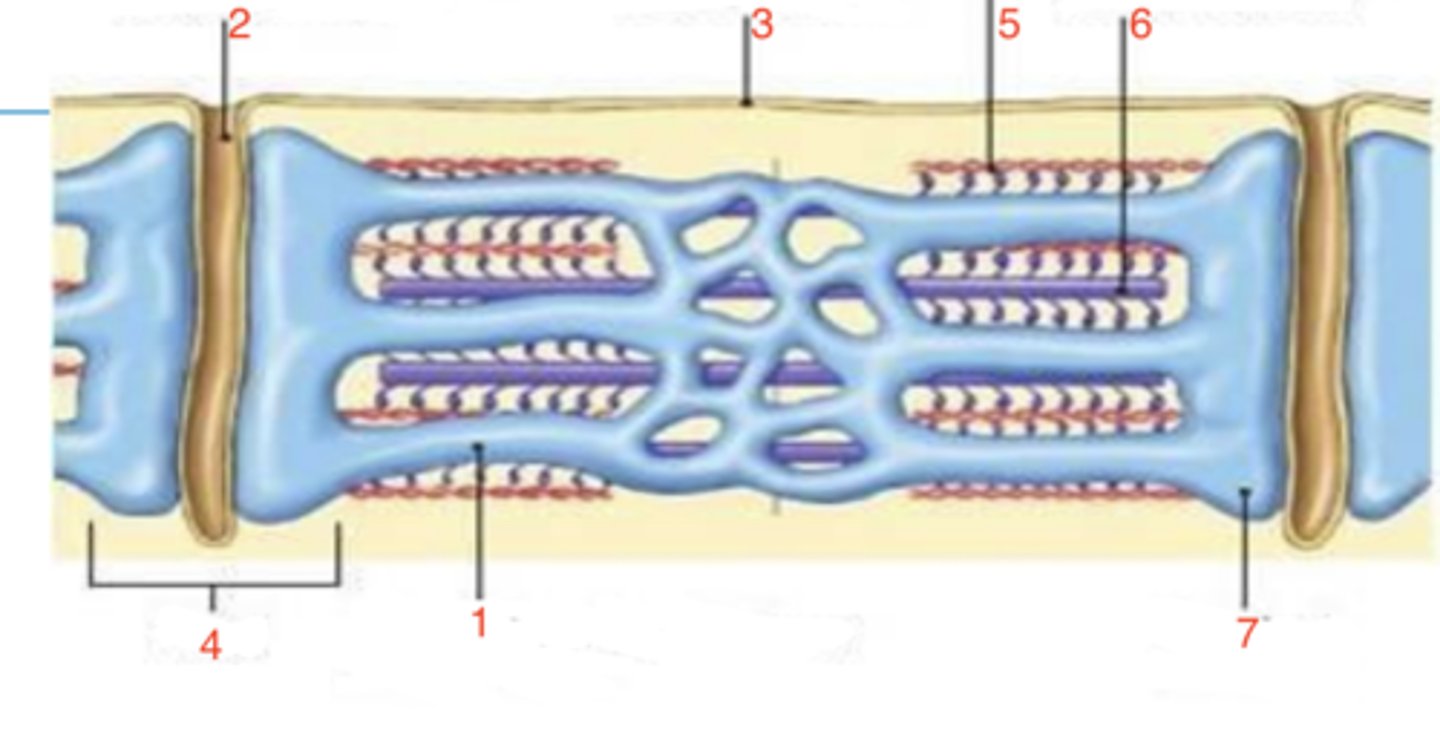
5
which is the thin filament?
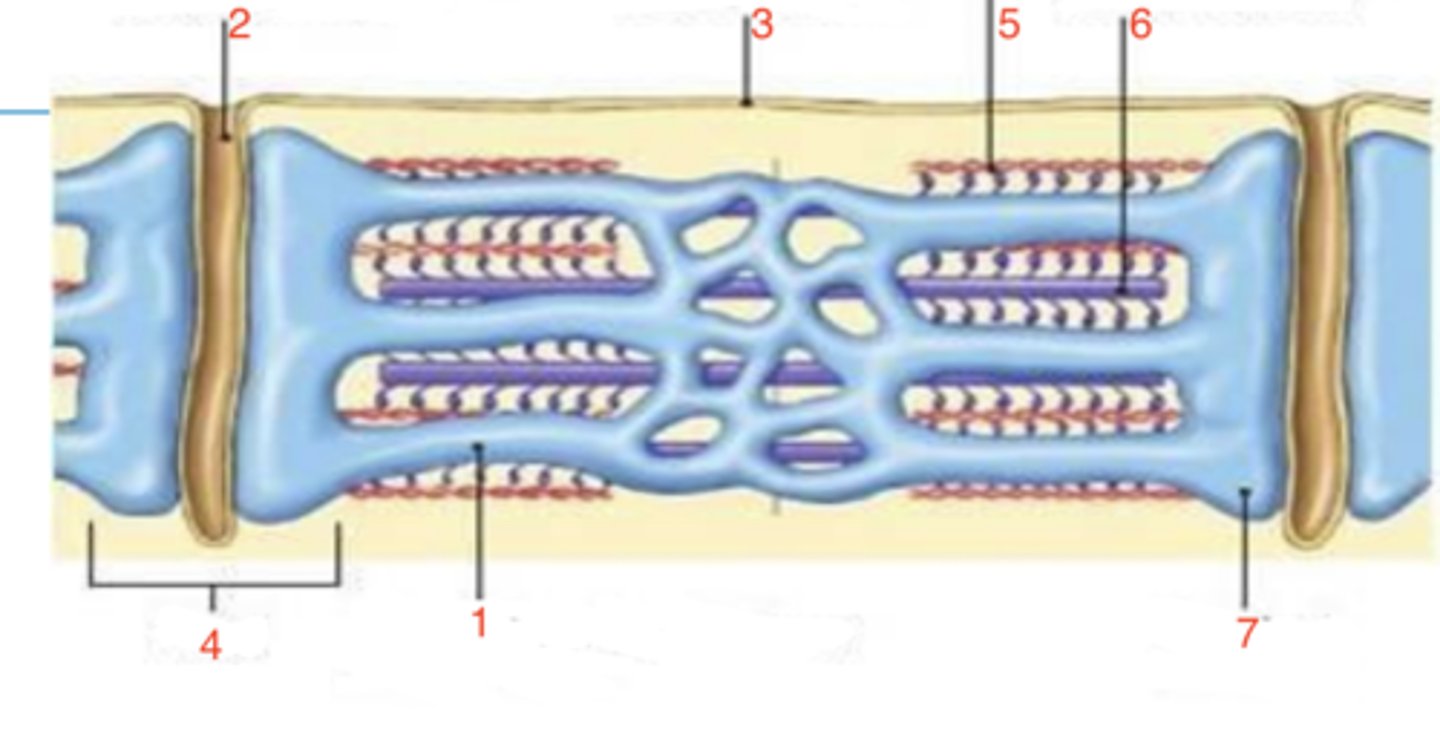
6
where is the thick filament?
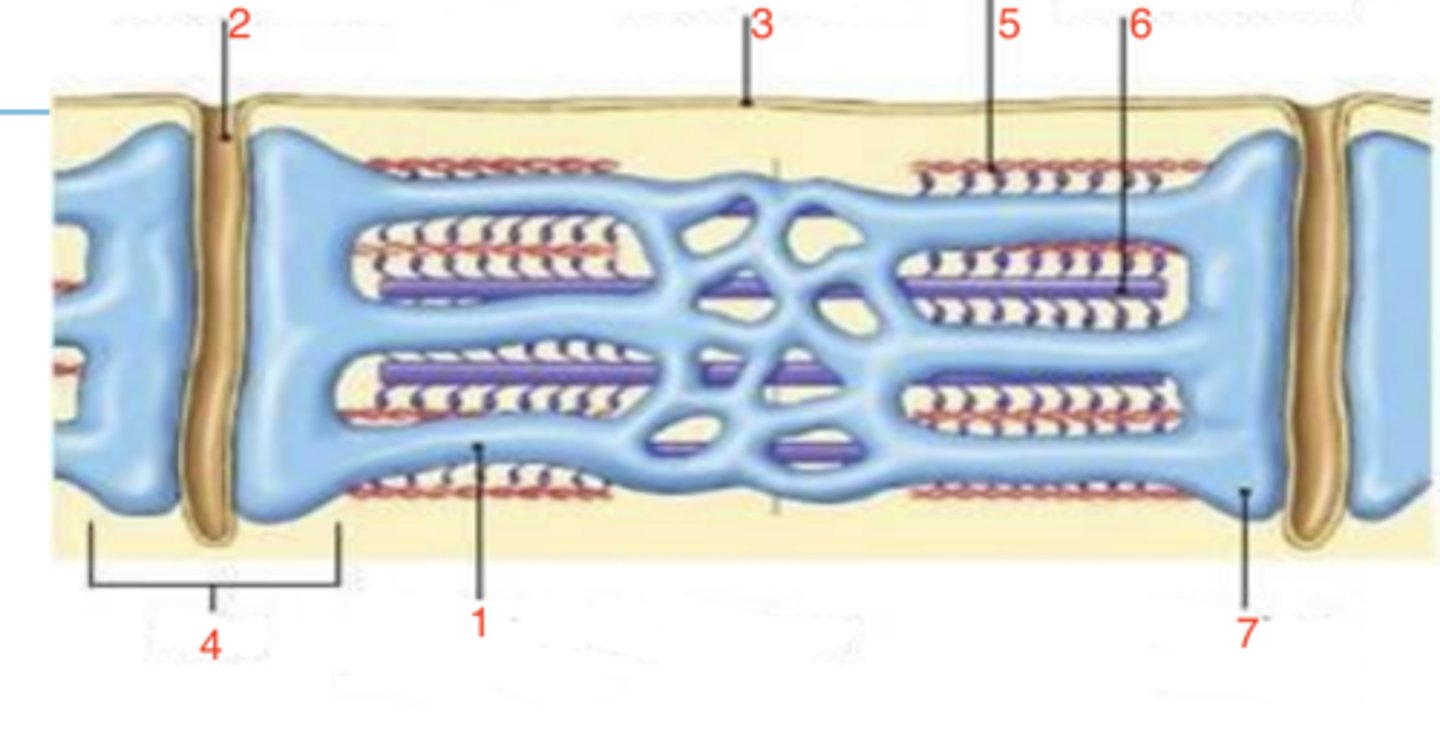
terminal cisternae
what is 7?
red
which fibers, white or red, are aerobic?
anaerobic
are white fibers aerobic or anaerobic?
red (type I), white (type II), intermediate
what are the three types of skeletal muscle fibers?
red
which type of skeletal muscle fiber has the most mitochondria/sarcosomes?
white
do red, white, or intermediate fibers have the least amount of mitochondria/sarcosomes?
red/type I
which type of skeletal muscle fiber produces long, slow contractions?
fast contractions
what type of contractions are produced by white fibers?
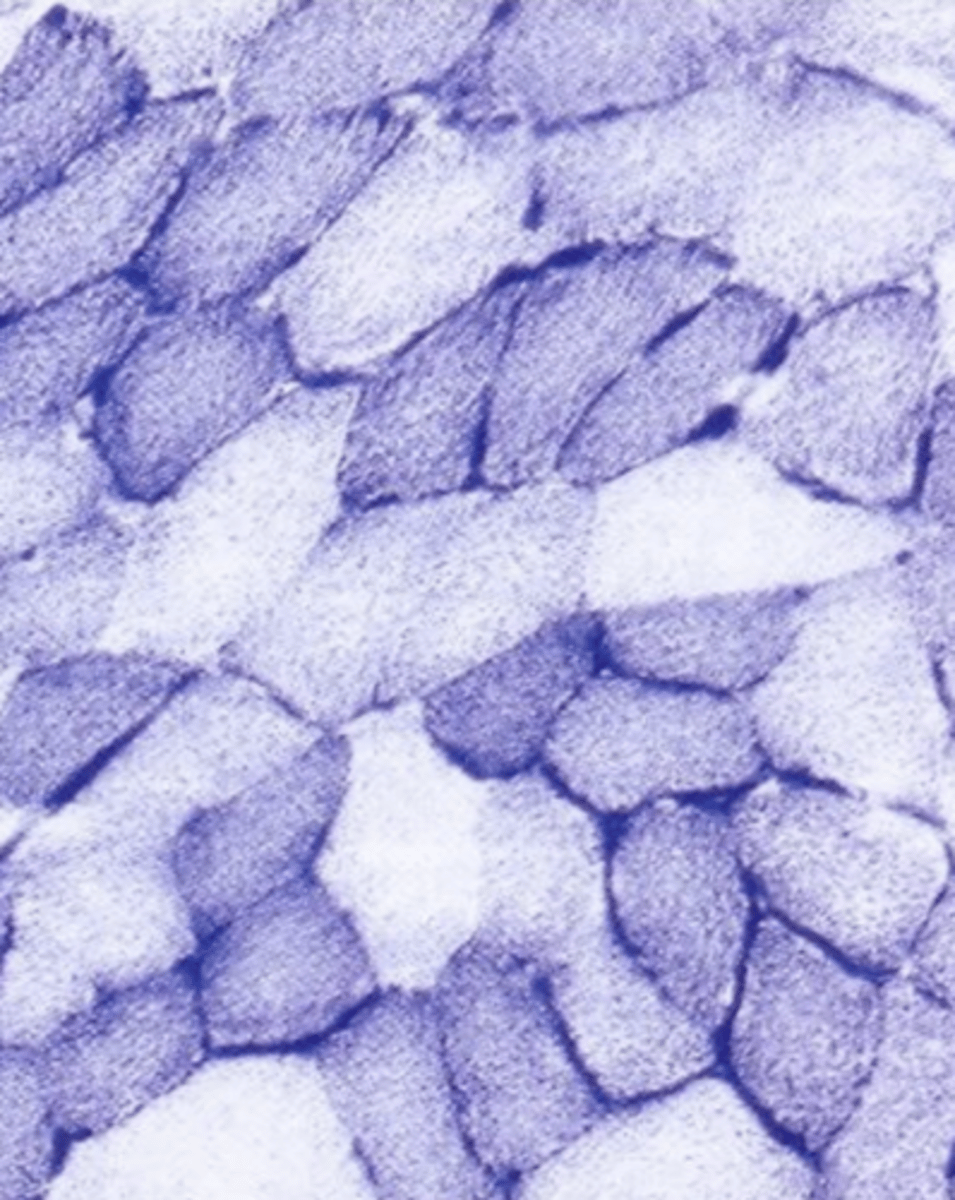
lighter
which are the white fibers?
darker
which are aerobic fibers?
actin
thin filaments are made of which protein?
thick
myosin makes up the ____ filaments
desmin, vimentin
what proteins make up the intermediate filaments?
covers myosin binding sites on actin
what is the function of tropomyosin?
actin
what is the orange part?
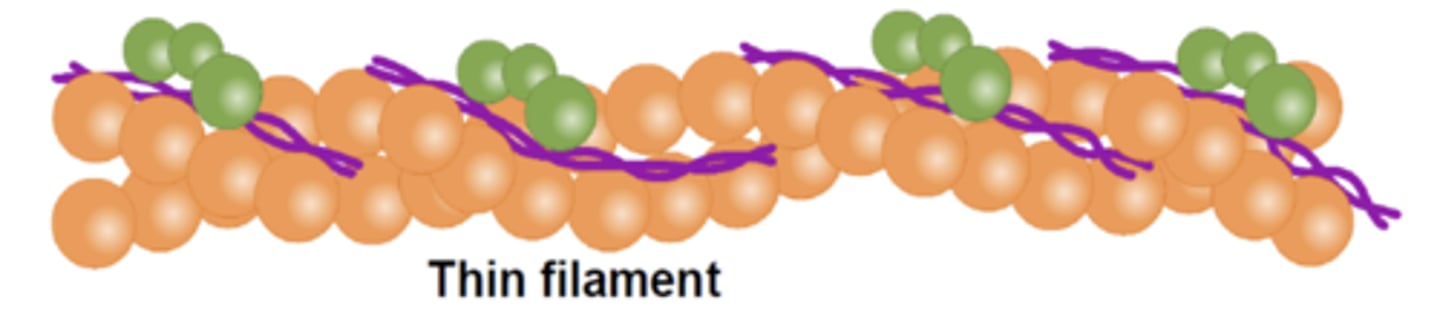
troponin
what protein is green?
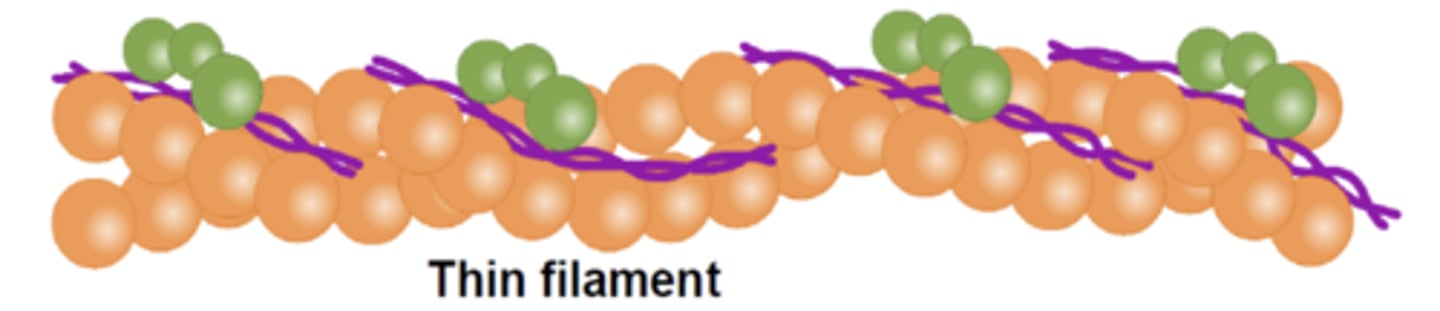
tropomyosin
which is the purple part?
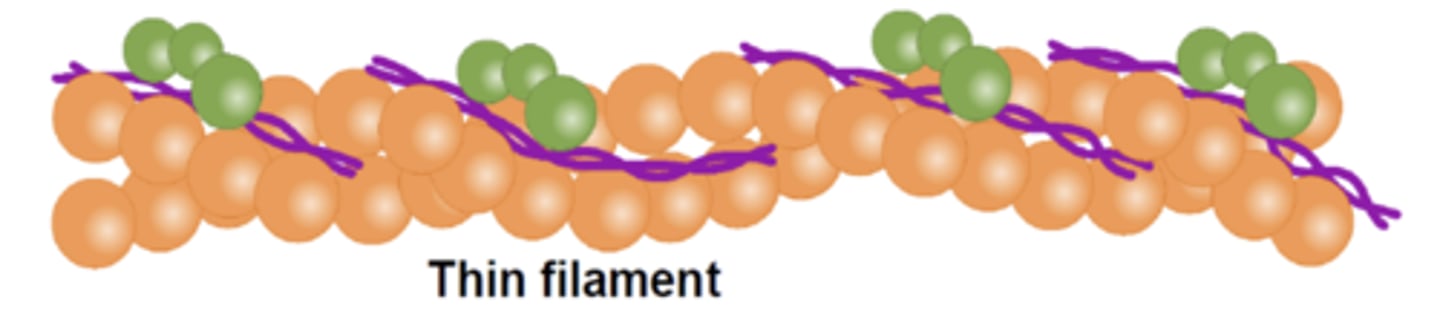
thin filament
which filament also consists of troponin and tropomyosin?
thick
titin helps form the ___ filament
yes
is cardiac muscle tissue striated?
1-2
how many nuclei per cardiac muscle cell?
cardiac
intercalated discs are present in what type of muscle tissue?
join cardiac muscle fibers together
what is the function of intercalated discs?
longitudinal
intercalated discs are only visible in a ____ cut
transverse
longitudinal or transverse cut?
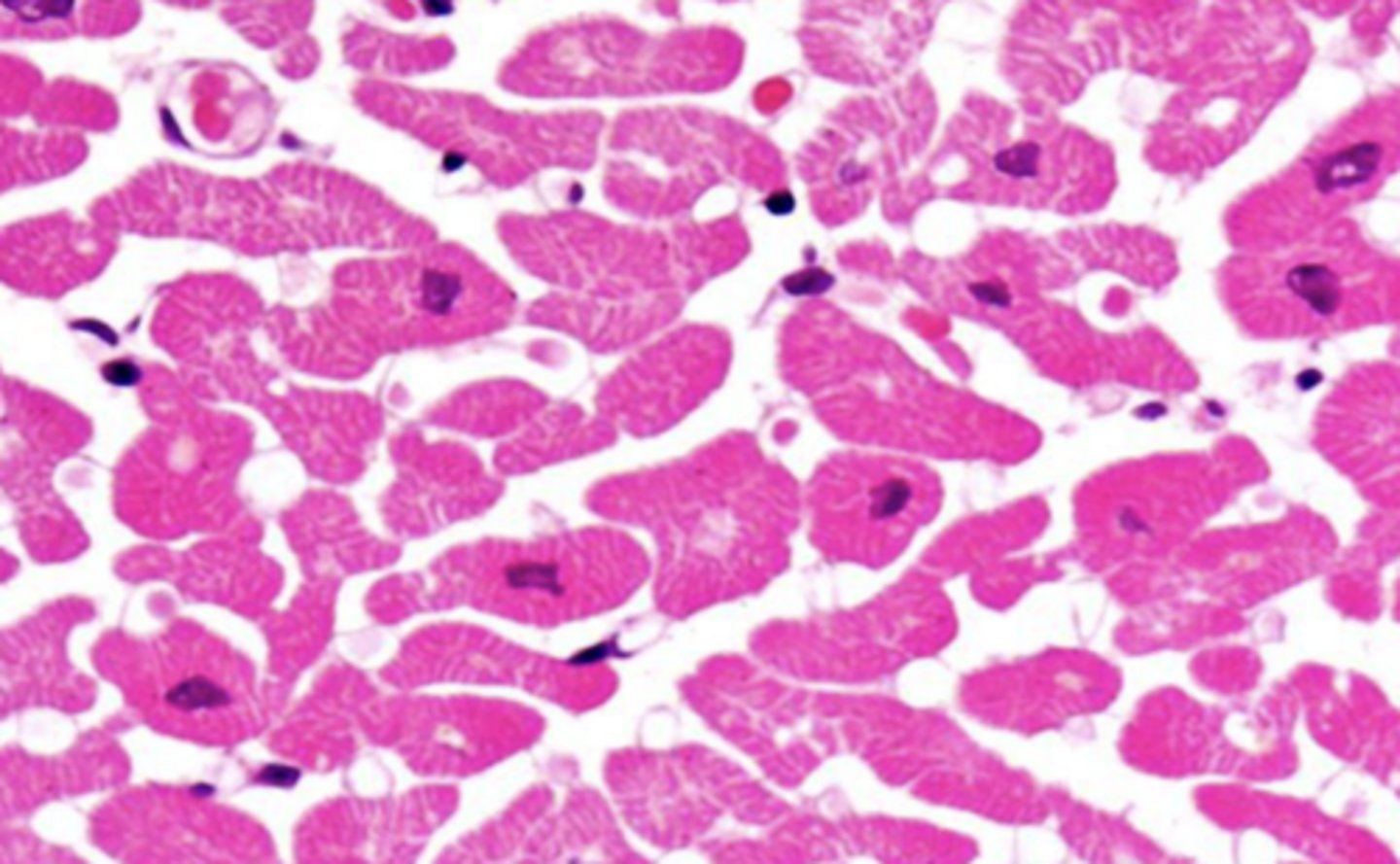
cardiac
intercalated discs, striated, 1-2 nuclei per cell
which type of muscle tissue? how can you tell?
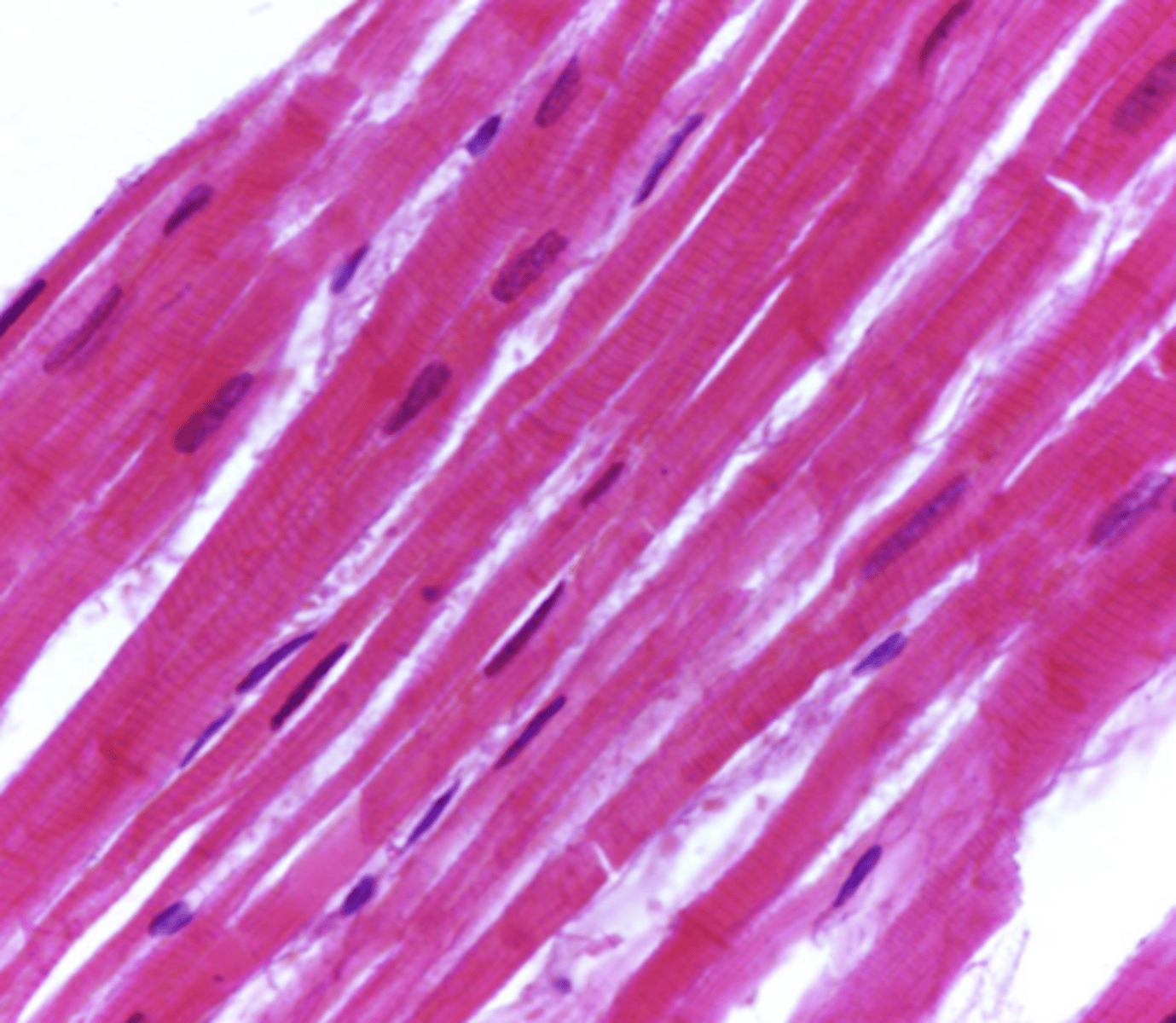
endomysium
cardiac muscle tissue only has which layer of connective tissue?
fusiform cells, unstriated, one nucleus
what is the appearance of smooth muscle tissue?
endomysium
what CT layer does smooth muscle have?
smooth muscle
one nucleus per cell, no striations, fusiform
what type of muscle tissue? why?
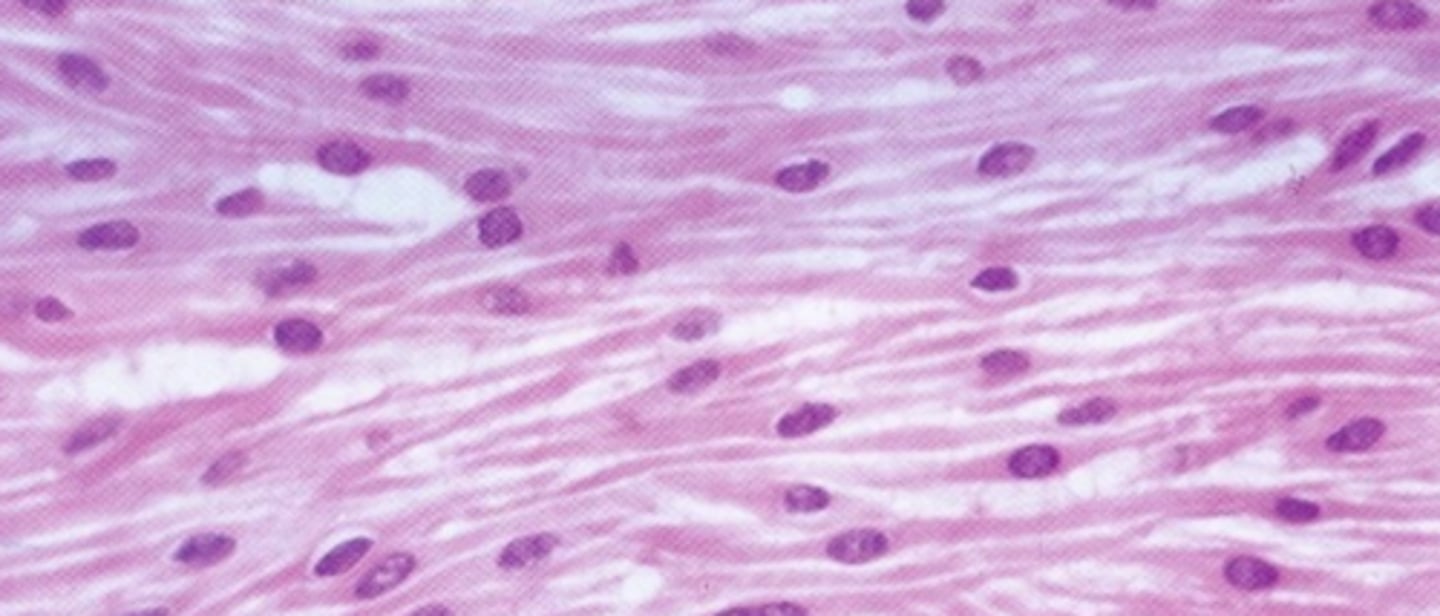
caveolaes
the T-tubules in smooth muscle tissue are called?
gap junctions
smooth muscle fibers are connected by...
uterus
smooth muscle is most regenerable in what organ?
satellite cells
in skeletal muscle, which cells are responsible for regeneration?
increase in number of cells
what does hyperplasia mean?
increase in size of cells
what does hypertrophy mean?
because regeneration is done by satellite cells, which only make up 5% of muscle cells
why does skeletal muscle tissue take so much longer to regenerate?