AQA A Level Biology Carbohydrates Flashcards
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what are the monomers of carbohydrates called?
monosaccharides
what are polymers of carbohydrates called?
polysaccharides
what is a common property of all monosaccharides?
soluble in water
name the 3 core monosaccharides
alpha glucose
beta glucose
galactose
fructose
these are all isomers
what is the structure of alpha glucose?
note carbon 1
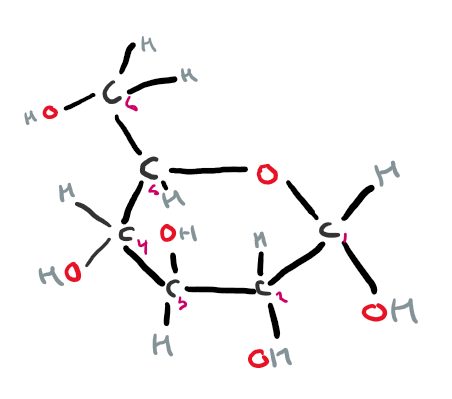
what is the structure of beta glucose?
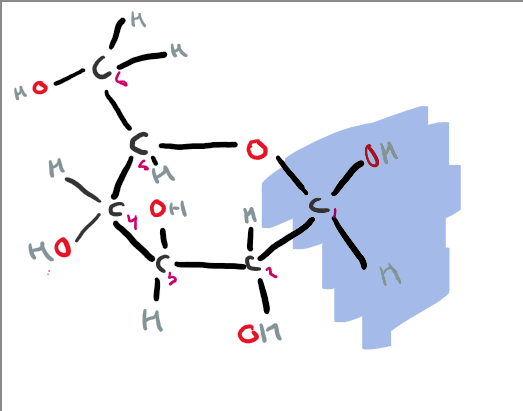
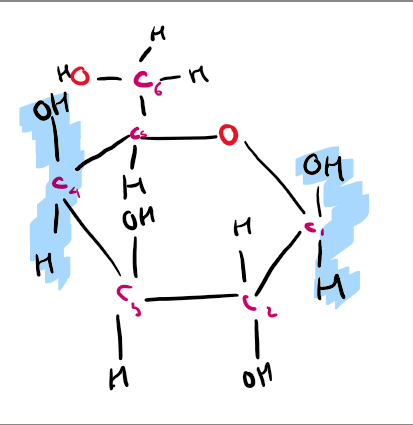
what is the structure of galactose?
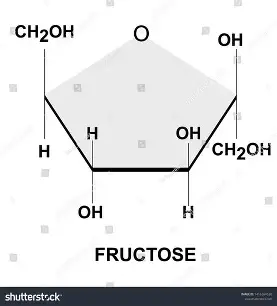
what is the structure of fructose?
what is two monosaccharides joined together called?
disaccharide
what type of reaction forms a disaccharide?
condensation (water is produced also)
in a disaccharide, what type of bond occurs between the two monosaccharides?
glycosidic
which are the core disaccharides?
maltose (C12H22O11)
sucrose
lactose
which monosaccharides form maltose?
alpha glucose
alpha glucose
which monosaccharides form sucrose?
alpha glucose
fructose
which monosaccharides form lactose?
alpha glucose
galactose
which reaction forms two monosaccharides from a disaccharide?
hydrolysis
requires water molecule
which carbon atoms does a glycosidic bond form between in maltose?
1,4
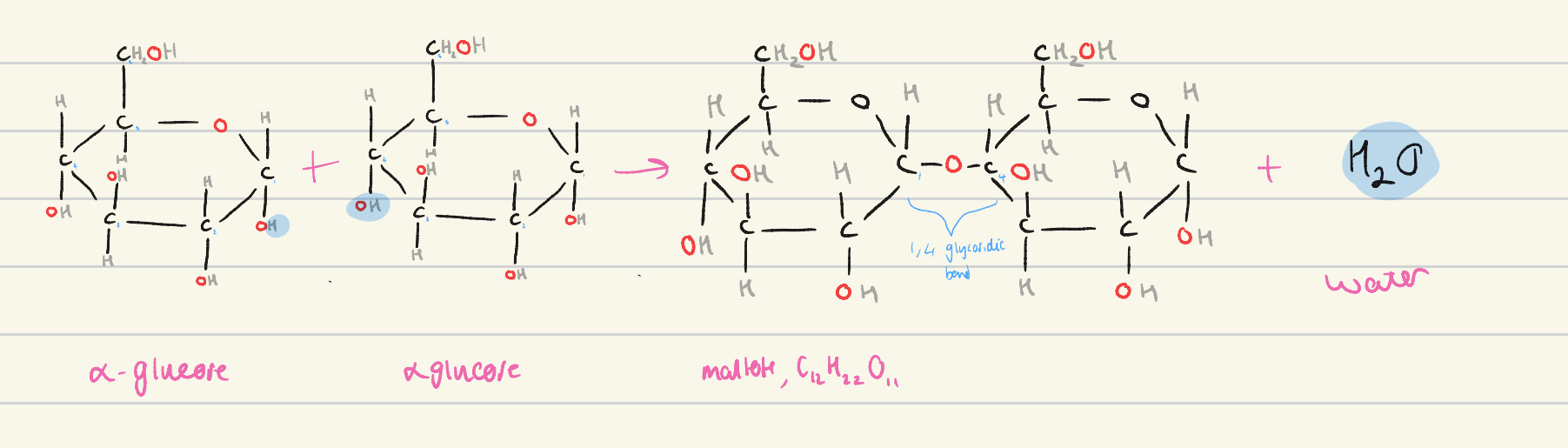
write an equation for the condensation of alpha glucose
alpha glucose + alpha glucose → maltose + water
which atoms are removed from the alpha glucose molecules in a condensation reaction?
one OH molecule, and one H molecule from an OH
draw an equation for the condensation of alpha glucose
what are reducing sugars?
sugars that readily lose electrons to another substances
what are non reducing sugars?
sugars that do not readily lose electrons to another substance
which substances are reducing sugars?
all monosaccharides
most disaccharides, except for sucrose
which substances are non reducing sugars?
sucrose
describe how you would test for the presence of reducing sugars
add benedicts reagant to food sample to boiling tube (it contains Cu2+ ions that are reduced)
heat in a water bath at 80C for 5 minutes
if a green/yellow/orange/brick red precipitate (increasing conc.) forms, the test is positive
if the solution remains blue the test is negative
qualitative test
describe how you would test for non reducing sugars
can only test after have been negatively tested for reducing sugars
add food sample to HCl in a boiling tube
heat in a boiling water bath for 5 mins, to hydrolyse the disaccharide to form monosaccharides
add an excess of sodium hydrogen carbonate (until litmus tests blue) to neutralise the acid, as benedicts requires an alkaline environment
carry out the benedict’s test
the same results apply
describe how you would make the benedict’s test quantitative
use a colorimeter, calibrated it with a standard sample of Benedict’s solution, compare percentage light absorbency (higher %, less reducing sugars)
filter out and dry the precipitate, then record its mass
describe how lactose intolerance arises and how it presents
all humans produce lactase in their small intestine when they are babies, to digest lactose in formula/breast milk
most humans stop producing lactase as the age - the exceptions produce it due to evolution by natural selection (mostly europeans)
lactase hydrolyses lactose to alpha glucose and galactose, which is absorbed into bloodstream
no lactase = no digestion, so lactose passes into the colon where bacteria ferment it, producing fatty acids and gases like CO2, CH4 and hydrogen - these cause symptoms like pain/bloating
what are the 3 core polysaccharides?
glycogen (a glucose)
starch (a glucose)
cellulose (B glucose)
what are the core properties of polysaccharides?
formed by condensation reaction
can be broken down into constituent monomers by hydrolysis reactions
insoluble in water
which monosaccharide makes up starch?
alpha glucose
which two polysaccharides is starch a mixture of?
amylose
amylopectin
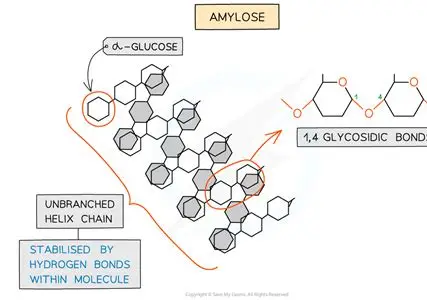
describe amylose
long unbranched chain of alpha glucose
angles of glycosidic (all 1-4) give it a coiled structure
the coil makes it compact so its good for storage
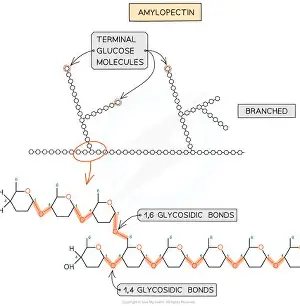
describe amylopectin
long branched chain of alpha glucose
it is branched due to having both 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
it has lots of side branches meaning it has more ends/terminal glucose molecules
this means the enzymes that break it down can get to the glycosidic bonds easily, so glucose can be released quickly
also coiled
describe the properties and functions of starch
energy store in plants
large molecules → insoluble → doesn’t affect water potential of cells → doesn’t make water enter cells by osmosis → cells do not burst → good for storage
hydrolysis forms alpha glucose which is easy to transport and used for respiration
describe the structure of glycogen
very similar to amylopectin (coiled with branches) but with a lot more branches
as it has more 1-6 linkages
these branches are shorter
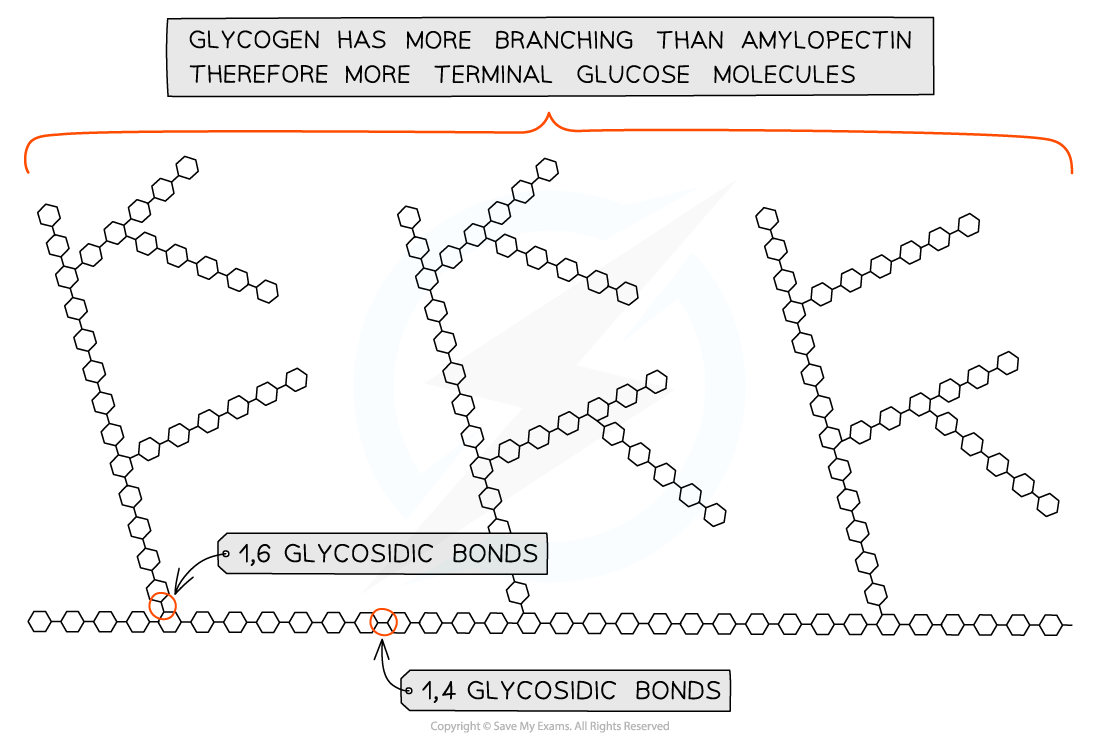
describe the properties and functions of glycogen
energy store in animals
shorter chains, more branches mean more terminal glucose molecules
this means that it is more readily hydrolysed than starch so stored glucose can be released faster, which is important for energy release in animals as they have higher respiratory needs
very compact molecule so is good for storage
describe the structure of cellulose
made of long, unbranched chains of B glucose (1-4 linkage)
each molecule is inverted 180 from the previous one, allowing this
the cellulose chains lie parallel to each other, and are linked together by collectively strong hydrogen bonds
this forms strong fibres called microfibriles
many microfibrils come together to form macrofibrils
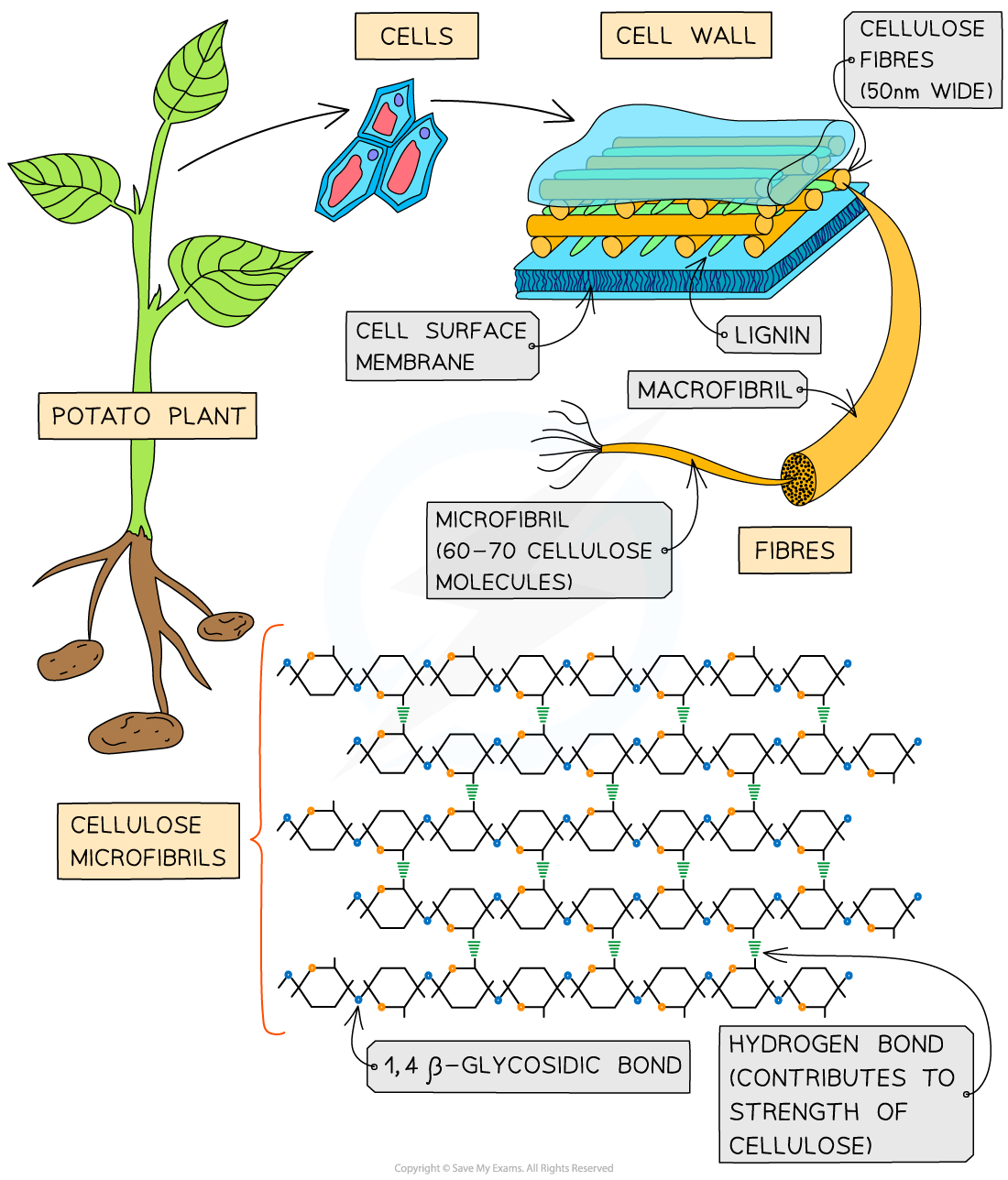
describe the properties and function of cellulose
structural molecule found in plants (cell walls)
fibres make it very strong, preventing cell walls from bursting when too much water enters (help to maintain turgidity)
difficult to digest as few organisms have cellulase
what is the iodine test for starch?
add iodine to food
blue black = positive
orange = negative