Biliary and Pancreatic Conditions in Nursing
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Cholecystitis
-Inflammation of the gallbladder, often due to gallstones.
Cholesterol stones
-80% or more cholesterol
-appear yellow with a dark spot in the center
-oval
Pigment stones
-less than 20% cholesterol
-they are either black or brown
-form when bile has a high bilirubin concentration
cholelithiasis
stones
choledocholithiasis
stones in the common bile duct
Acalculous cholecystitis
the inflammation of the gallbladder without associated gallstones
-caused from surgery and trauma
Risk factors for Cholelithiasis
-Age >40
-female
-obesity
-multiple pregnancies
-Family history
-rapid weight loss diets
-oral contraceptives/estrogen therapy
-ileal resection or disease
-older adults due to decrease in gallbladder contractility
-native americans and mexicans
-cystic fibrosis
-low cal and low protein diet
-DM2
Diagnostic studies for Cholelithiasis
-abdominal x-ray
-ultrasound
-ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography)
-Percutaneous Transheptic Cholangiography (PTC) high risk patients more costly
-Labs
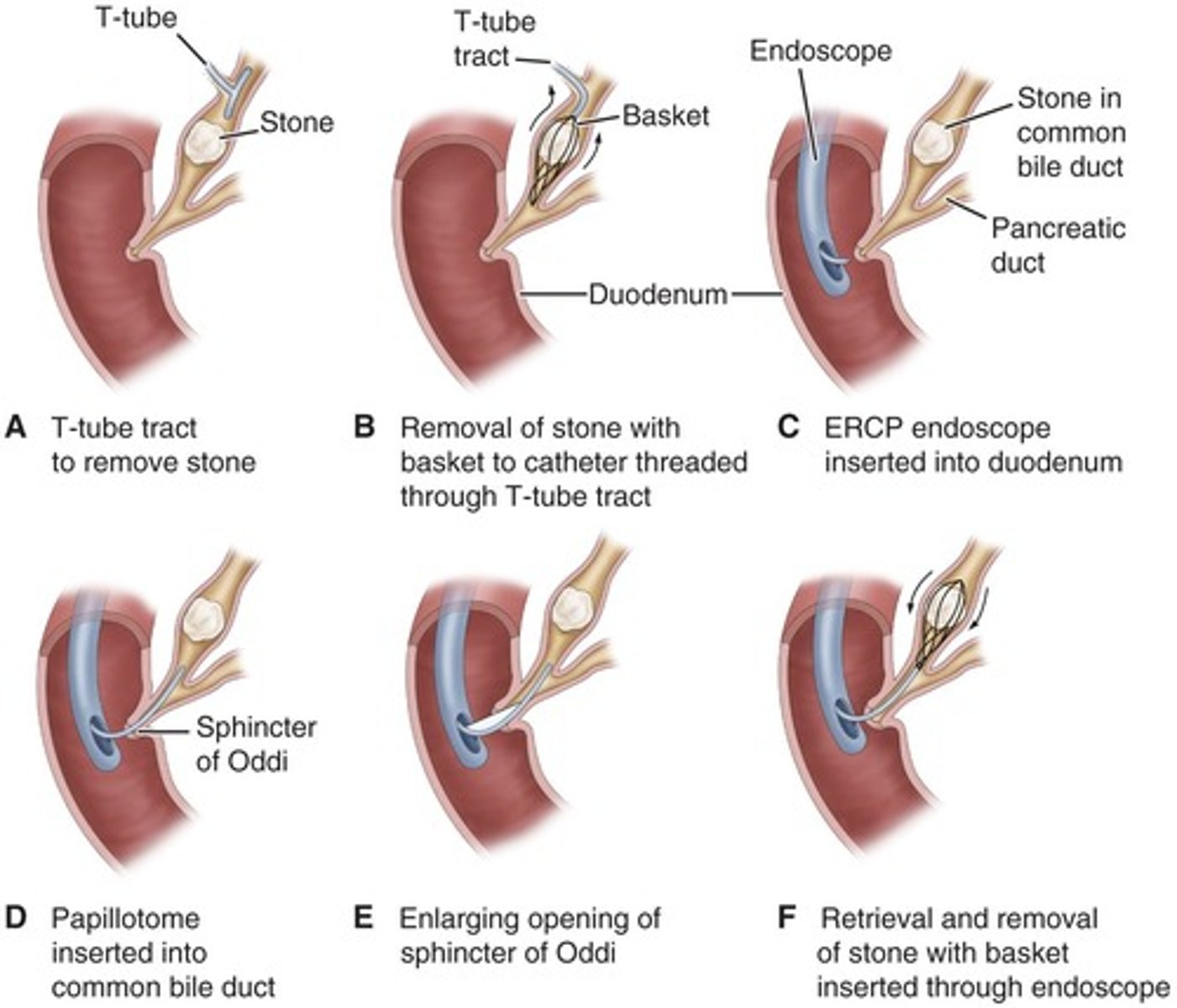
gold standard test for cholelithiasis
ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography)
ERCP PROCEDURE
-npo
-moderate sedation
-anticholinergic agents can make it easier for them to see
-during procedure observe for respiratory and CNS depression
-give IVF and position the patient
-After: observe vitals and check for perforation and other complications
-make sure gag reflex return
ULTRASOUND ACCURACY PERCENTAGE
Ultrasonography can detect calculi in the gallbladder or a dilated common bile duct with 90% accuracy
chole CM
-Epigastric distress
-biliary colic
-infection
-jaundice
-changes in urine and stool color
-vitamin deficiency
epigastric distress
◦Fullness, abdominal distention, vague upper right quadrant pain after eating a fatty meal
Vitamin deficiency in Chole
Deficiencies in vitamins A, D, E, K due to malabsorption.
chole infection signs
◦Fever, palpable abdominal mass
jaundice
◦Blockage of the common bile duct
-In black would be in eyes
Biliary colic
◦Severe right abdominal pain that radiates to the back or right shoulder, nausea and vomiting
◦Severe pain usually associated with nausea and vomiting usually several hours after a heavy meal
chole med management
-Nutritional (low fat diet)
-meds
-Nonsurgical removal
-Dissolving gallstones with infusion of solvent
-By instrumentation
-Intracorporeal or extracorporeal lithotripsy
Surgical
-laparoscopic cholecystectomy
-Open Cholecystectomy
laparoscopic cholecystectomy post surgery
-minimally invasive
-3-4 small incision
-carbon dioxide so they need to ambulate
-no heavy lifting
-narcotics will not best manage pain and can cause parylitc ileus
-gag reflex, clear to full to regular liquid diet
chole patients should avoid these foods
-eggs
-cream
-pork
-fried foods
-cheese
-rich dressings
-gas forming veggies
-alcohol
T tube
-non-surgical
-able to drain the fluids and remove the stone
-older adults
Lithotripsy
lasers that pulsate to get rid of the stone
post op chole nursing care
-Manage acute pain
◦Carbon dioxide (4-6L) ingested during surgery
-Improve, monitor respiratory status
-Maintain skin integrity
-Promotion of biliary drainage/monitor for infection, peritonitis
-Improve nutritional status
-Monitor for complications
◦Bleeding
◦GI symptoms r/t biliary leak
how to take care of laparoscopic cholecystectomy wound site
-4-6 weeks no lifting more than 5 lbs
-no baths and swimming
-dont rub just pat dry
-no scented soaps just let water run down
-monitor for infection
Acute pancreatitis
Inflammation of the pancreas, can be life-threatening.
How does the client need to sit post Chloecystectomy
low fowlers
If they are NPO with a nonlaproscopic (open) procedure they may have a
NGT
What else do you need to do postoperative chole
-ambulation
-progressive diet
-care of biliary drainage system
-coughing/deep breathing exercises
-splinting to reduce pain
chole patient and family teaching
-Medications & Activity (anti-inflammatory)
-Diet: at discharge, maintain a nutritious diet
◦Avoid excess fat
Fat restriction is usually lifted in 4–6 weeks.
-Instruct in wound care, dressing changes, care of T-tube
you cant take tylenol and what at the same time
percoset bc you can overdose
-Instruct chole patient and family
◦Report signs of gastrointestinal complications
◦Changes in color of stool
◦Report anorexia, vomiting, pain, abdominal distension, fever
◦Signs of inflammation and infections, such as pain and fever
open cholcystectomy
-JP drain
-fluid should get lighter
-empty drains
-take pain meds short term
-encourage cough and deep breath
-progress diet
-will be in hospital longer
acute pancreatitis
-Ranges from mild to severe & rapidly fatal
Two types: 1.interstitial
2.necrotizing- pancreas autodigests
At risk for:
-hypovolemic shock
-F & E imbalances
-sepsis
Pathophysiology
◦Self-digestion of pancreas by it’s own enzymes (trypsin)
◦Activation of enzymes leads to vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, necrosis, erosion and hemorrhage
risk factors for acute pancreatitis
-Biliary tract disease
-Gallstones-bile backs up into pancreas causing it to digest
-History of long-term alcohol abuse
-Bacterial or viral infection
-Blunt abdominal trauma
-ischemia vascular disease
-Hyperlipidemia
-Medications (BCP, diuretics, corticosteroids)
-more common in elderly but can affect all ages
acute pancreatitis CM
-Severe abdominal pain
-Abdominal guarding
-N/V
-Fever, jaundice, confusion
-Ecchymosis in the flank or umbilical area may occur
-Respiratory distress, hypoxia, tachypnea, renal failure, hypovolemia, shock
if they come in with pancreatitis but develop rigid board like abdomen what do you do
tell HCP
-could have developed into peritonitis
ACUTE pancreatitis diagnostics
-History/Physical
-Serum amylase/lipase elevated for 24 hrs after the onset of symptoms, amylase goes down after 48-72 hrs, lypase stays elevated
-Hypocalcemia
-Hyperglycemia, glycosuria, elevated serum bilirubin
-CT/MRI/US
-CBC:high WBC
After 24 hours what changes in labs
amylase goes down
what stays elevated 48-72 hrs
Serum lipase
hypocalcemia happens in
very severe cases
pancreatitis need the following
-IVF
-NPO
-NGT
-BED REST
-TPN so they can have nutrition without triggering digestion
-monitor I/O
-pain management
Ranson Criteria
Scoring system to assess severity of acute pancreatitis.
-6 or more of these is not good
-these criteria say how likely the patient is to die from pancreatitis
on admission to hospital criteria
Age >55 years
White blood cells (WBCs) >16,000 mm3
Serum glucose >200 mg/dL (>11.1 mmol/L)
AST >250 IU/L
acute pancreatitis care
-Oral fluid with-held
-Parenteral/enteral nutrition
-NGT
-Medications: pain meds IV narcotics
-ICU for fluid and blood loss
no eating or ambulation bc it will cause digestion
main problems for pancreatitis
-acute pain
-ineffective breathing
-imbalanced nutrition
-impaired skin integrity
complications for acute pancreatitis
-Fluid /Electrolyte disturbances (I/O)
-Necrosis of the pancreas (rigid abdomen)(sepsis)
-Shock (tachypnea) (low bp)
-Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
Chronic pancreatitis
-Long-term inflammation leading to pancreatic tissue destruction.
-cells replaced by fibrous tissue
-after recurring acute pancreatitis
-atrophy of pancreatic ducts
chronic pancreatitis etiology
-smoking
-alcohol abuse
-50x more likely in alcoholic patients
CM of chronic pancreatitis
-Severe upper abdominal pain, back pain
-N/V
-Opioids do not provide relief
-Weight loss- anorexia and fear of feeling bad after food
-Malabsorption
-Stools: frothy, fouls smelling (high fat content: steatorrhea)
diagnostic for chronic pancreatitis
-ERCP- looks at ducts to check for blockage
-MRI
-CT
-US
-Elevated serum amylase
-Abnormal glucose tolerance test: unable to make insulin
Steatorrhea
Fatty stools due to malabsorption in chronic pancreatitis.
chronic pancreatitis collaborative care
-Preventing and managing attacks
-Relieving pain
-Managing exocrine and endocrine pancreatic deficiency
-Pancreatic duct stone retrieval via ERCP
-Adjuvant pain management- ibuprophen
-Dietary management
-Manage diabetes
Surgery (Roux-en-Y)
◦Anastomosis of pancreatic duct to jejunum
◦Whipple
when patient is on TPN what do we monior
glucose 4-6 hrs
Whipple procedure
used for tumor on the ampulla bypass the pancreas so they make an anastamosis from stomach to the jejunum and connect it to the pancreas and bile duct
risks
-leak
-delayed gastric emptying
-blood clots
-should be NPO
-NG tube for suction
-irrigation
-drainage
-liquid to solid progression
-pain control IV narcotics then oral b4 patients discharge
Pancreatic cancer risk factors
-tobacco use
-diabetes
-chronic pancreatitis
-hereditary
-70% occurs in head of the pancreas
-rare before the age of 45
Clinical manifestations of pancreatic cancer
◦Pain
◦Weight loss
◦Anorexia, N/V
◦Ascites
◦Abdominal pain
◦Jaundice
◦Diabetes
◦Clay-colored stools
diagnostic tests for pancreatic cancer
◦CT
-ERCP
◦Percutaneous, fine-needle biopsy
medical management for cancer
-resection
-chemo in late stages
-whipple
-may need to do chemo first to reduce tumor size to do during whipple
-biologic agents: antibodies specifc to person to attack cancer
-total pancreatectomy: remove pancreas
Total pancreatectomy
Surgical removal of the entire pancreas.
Pain management in pancreatitis
Includes opioids and adjunctive medications for relief.
Nutritional management post-surgery
Focus on low-fat diet and gradual reintroduction of foods.