ischaemia, oedema, heart failure
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Haemorrhage def
Escape of blood from vascular system
Haemorrhage features
Overt/ internal
Acute/ chronic
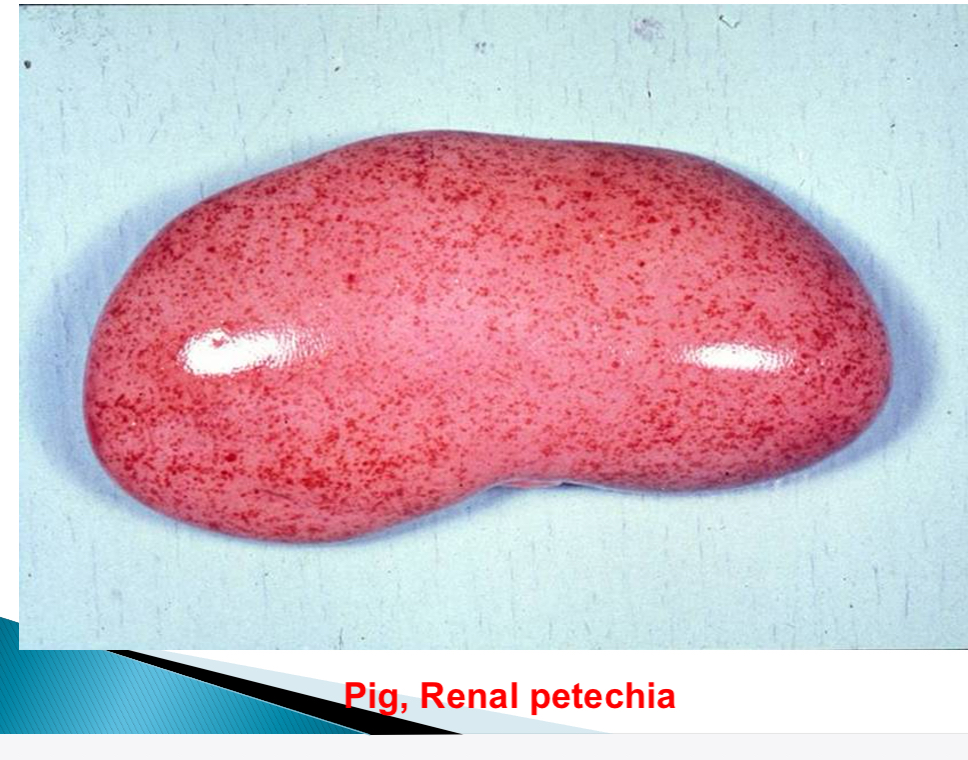
Haemorrhage size nomenclature - petechia size
1-2mm
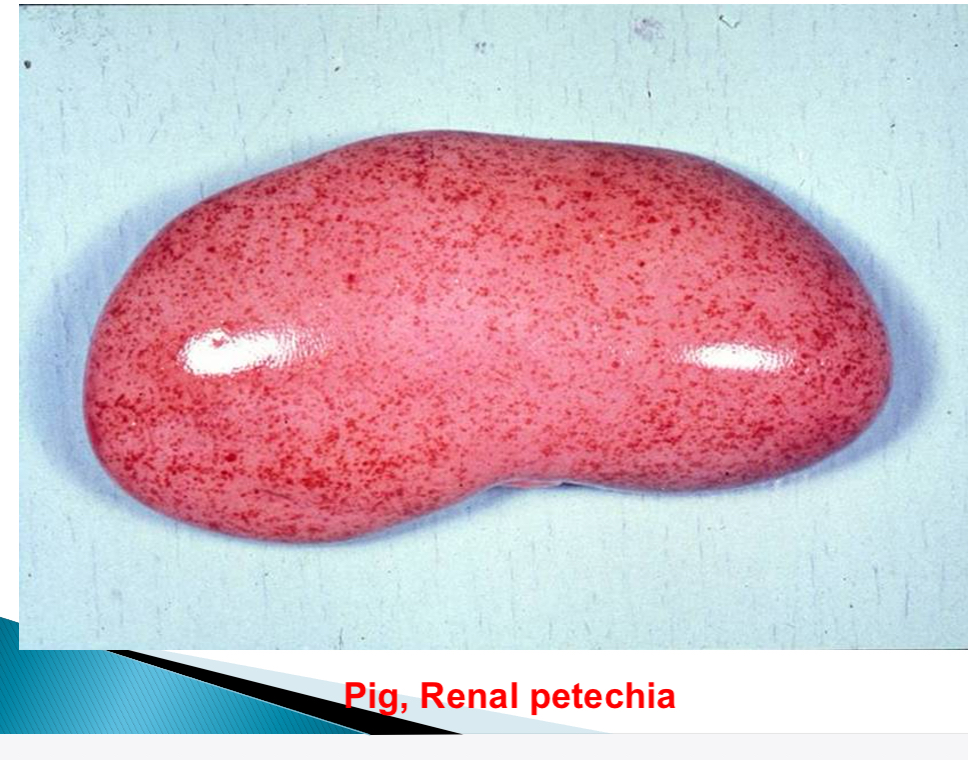
Haemorrhage size nomenclature - purpura size
>3mm
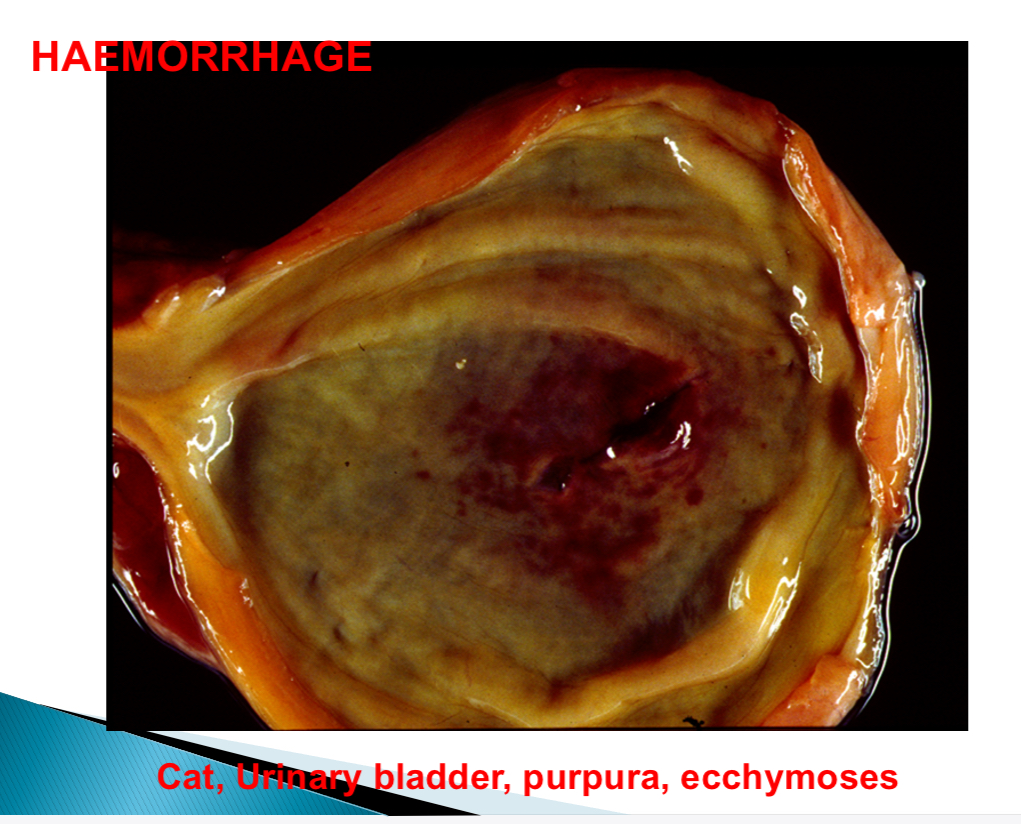
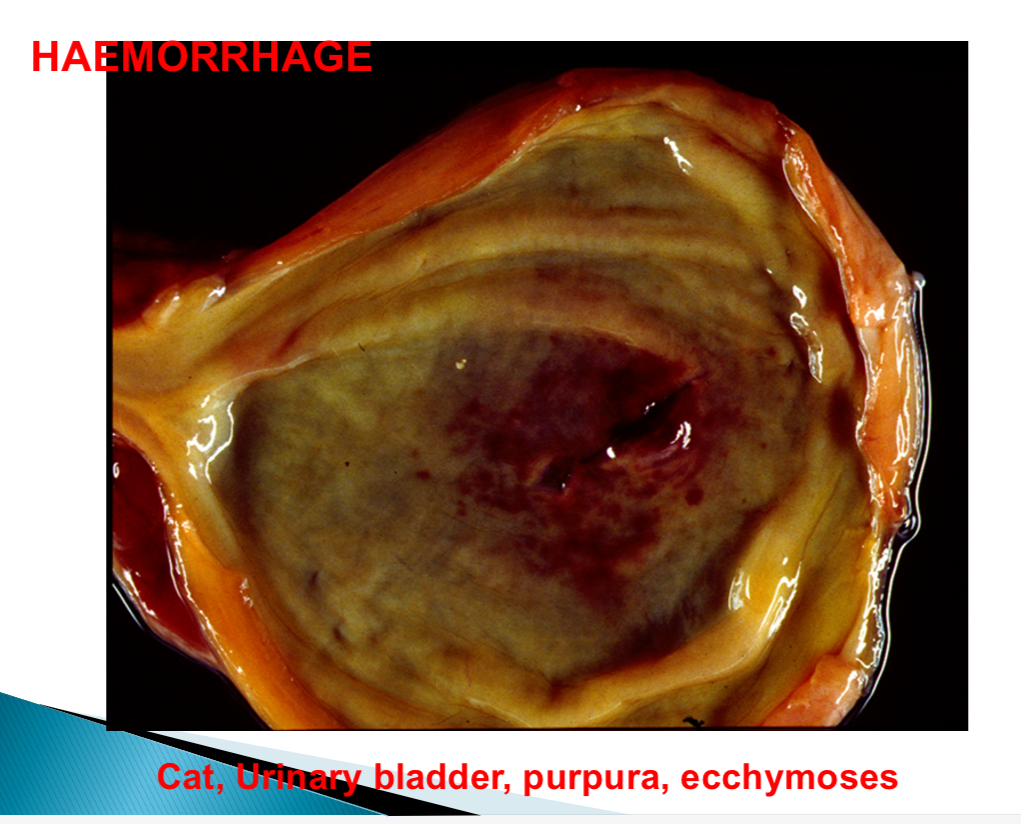
Haemorrhage size nomenclature - ecchymoses size
>1-2cm
Haemorrhage nomenclature - diapedesis
RBC traverse BV wall
Haemorrhage nomenclature - extravasation
Movement of WBC from capillaries to tissues
Haemorrhage nomenclature - haematoma
Solid swelling of clotted blood within tissue
Haemorrhage nomenclature - rhexis
Rupture of BV
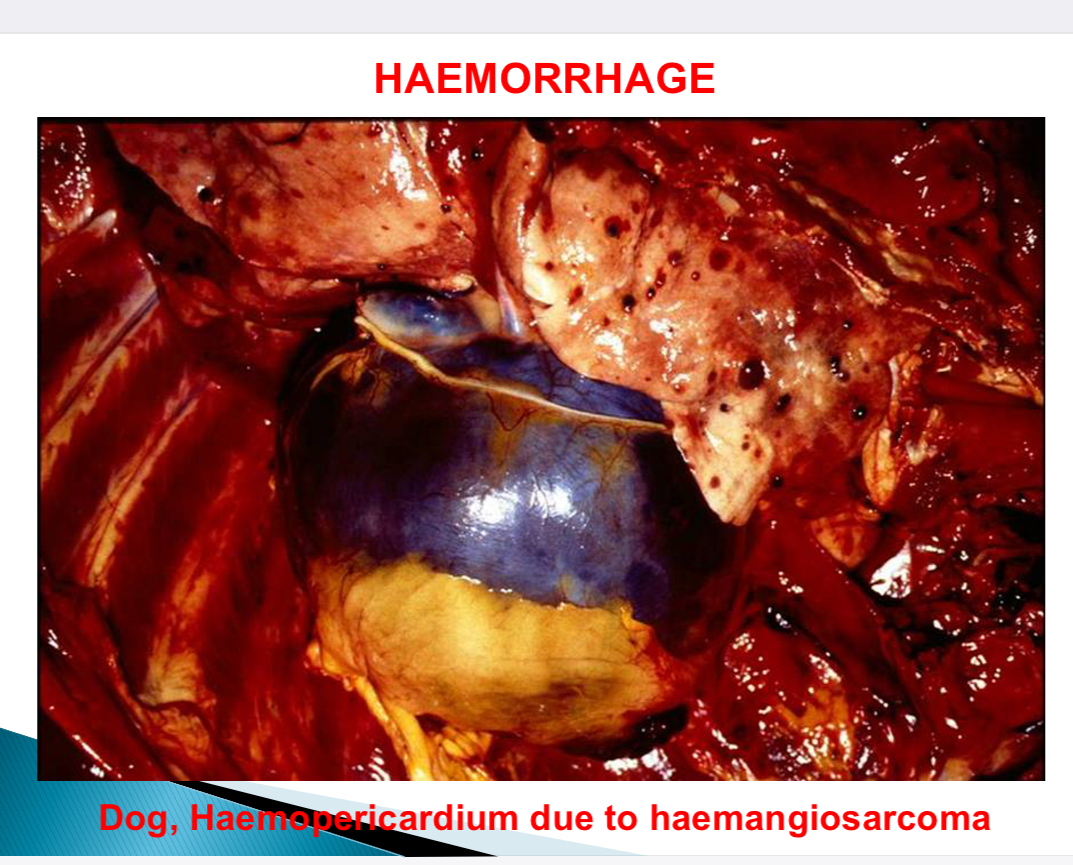
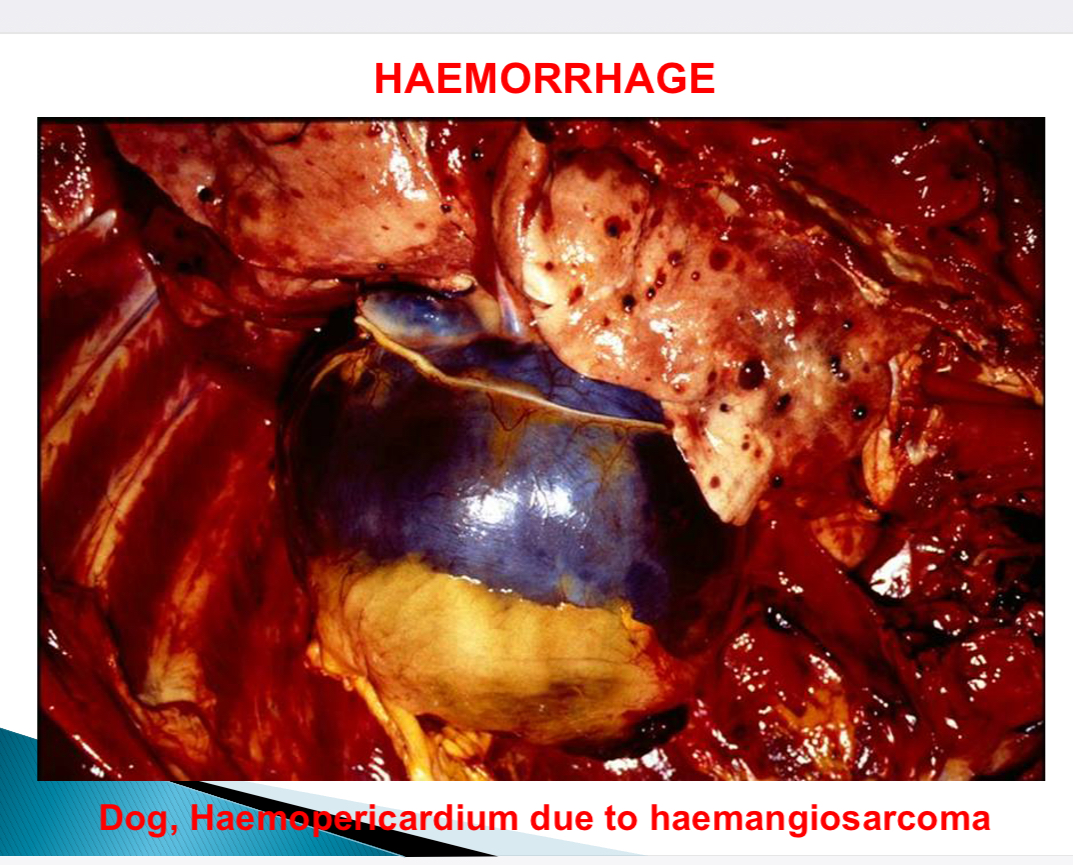
Haemorrhage nomenclature - based on body cavities
Haemothorax, haemopericardium/cardiac tamponade, haemoperitoneum/ascites, haemarthrosis
Causes of haemorrhage 9
Physiological, trauma, parasites, bacteria, virus, toxic agents, clotting deficiencies, neoplasm (angiogenesis), agonal (death)
Outcomes of haemorrhage
Haemorrhagic shock, complete recovery, loss of function, iron deficient anaemia
Stages of degradation of haemoglobin by macrophages
Haem → biliverdin → bilirubin → haemosiderin
Oedema def
Accumulation of extravascular fluid (in intercellular tissue space, body cavities)
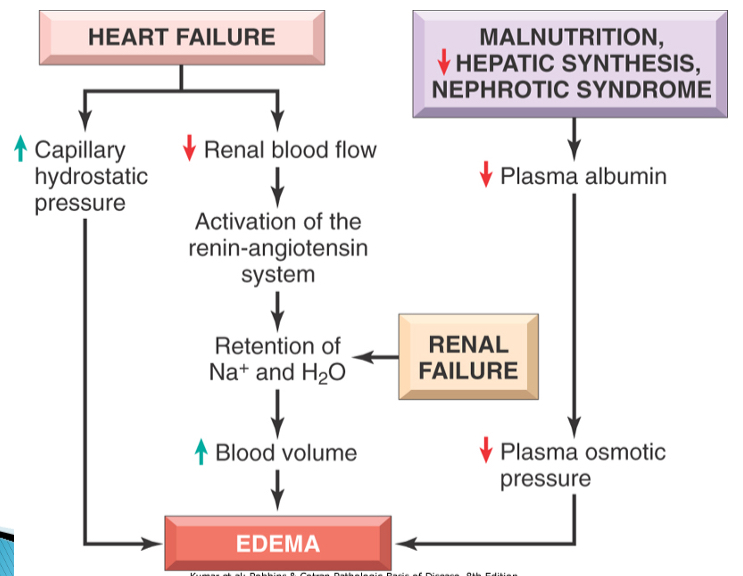
2 main Causes of oedema + appearance of fluid in each
Imbalance of forces responsible for transudation with normal capillary permeability → colourless fluid, low protein
Increased vascular permeability in inflammation → fibrinous/ purulent exudate
BV pressure changes that can cause oedema
Increased hydrostatic pressure - venous obstruction
Reduced plasma oncotic pressure - hypoproteinaemia
Lymphatic obstruction
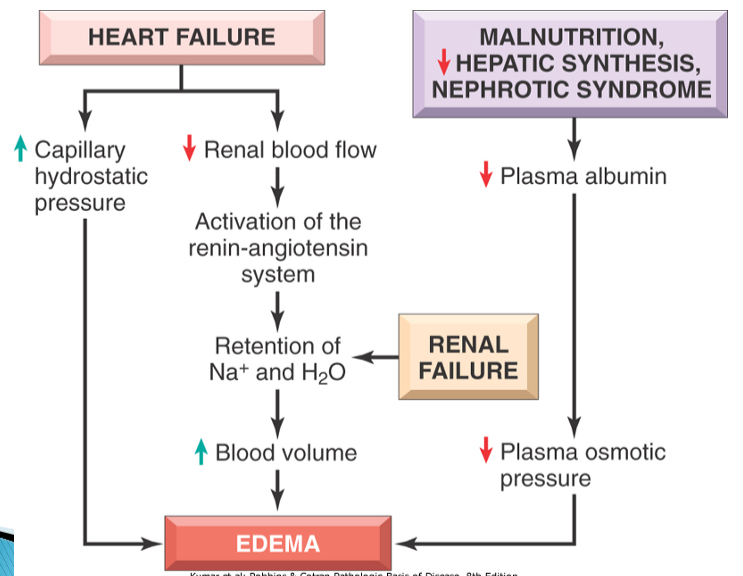
Causes of oedema 5
Increased hydrostatic pressure, reduced plasma oncotic pressure, lymphatic obstruction, sodium retention, inflammation
How can sodium retention occur
Excessive uptake with renal insufficiency
Increased tubular reabsorption
How can inflammation lesd to oedema
Increased capillary permeability
Diseases characterised by oedema + how
Cardiac disease - heart failure
Chronic liver disease - decreased protein
Renal disease - protein loss
Chronic parasitism - protein loss
Protein losing enteropathy
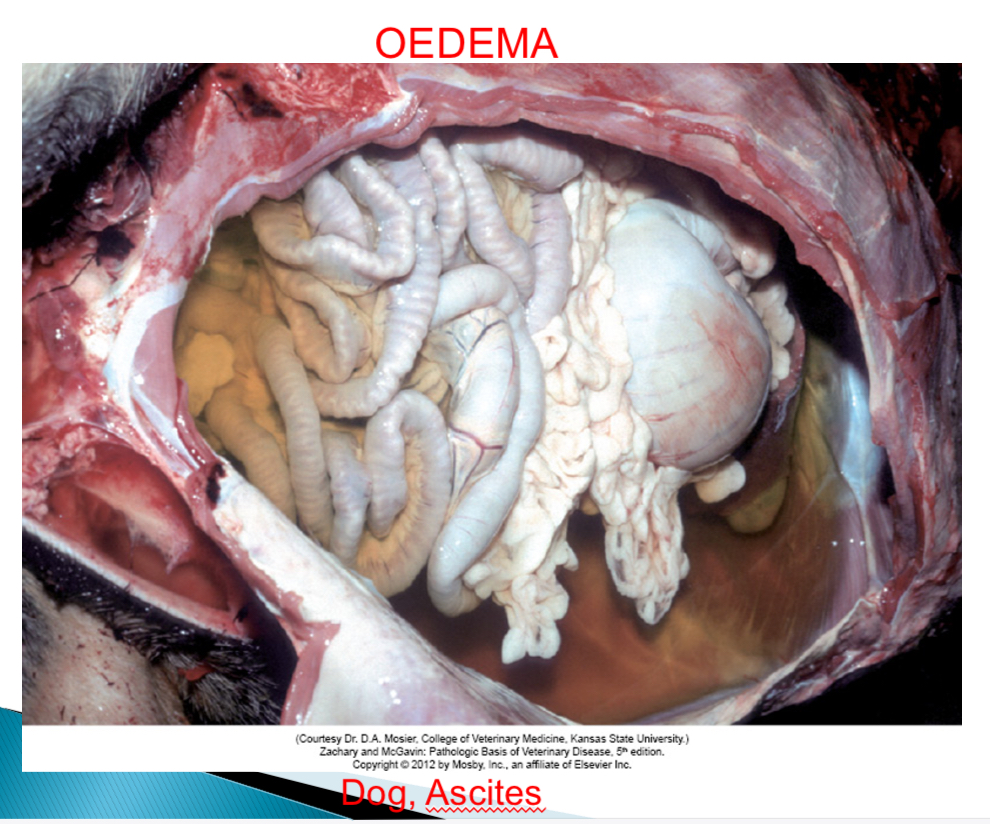
Ascites def
Oedema in peritoneum
Anasarca def
Generalised oedema
Oedema from inflammation features
Exudate fluid - high protein, inflammatory cells

Most common site of oedema in dog
Peritoneal cavity
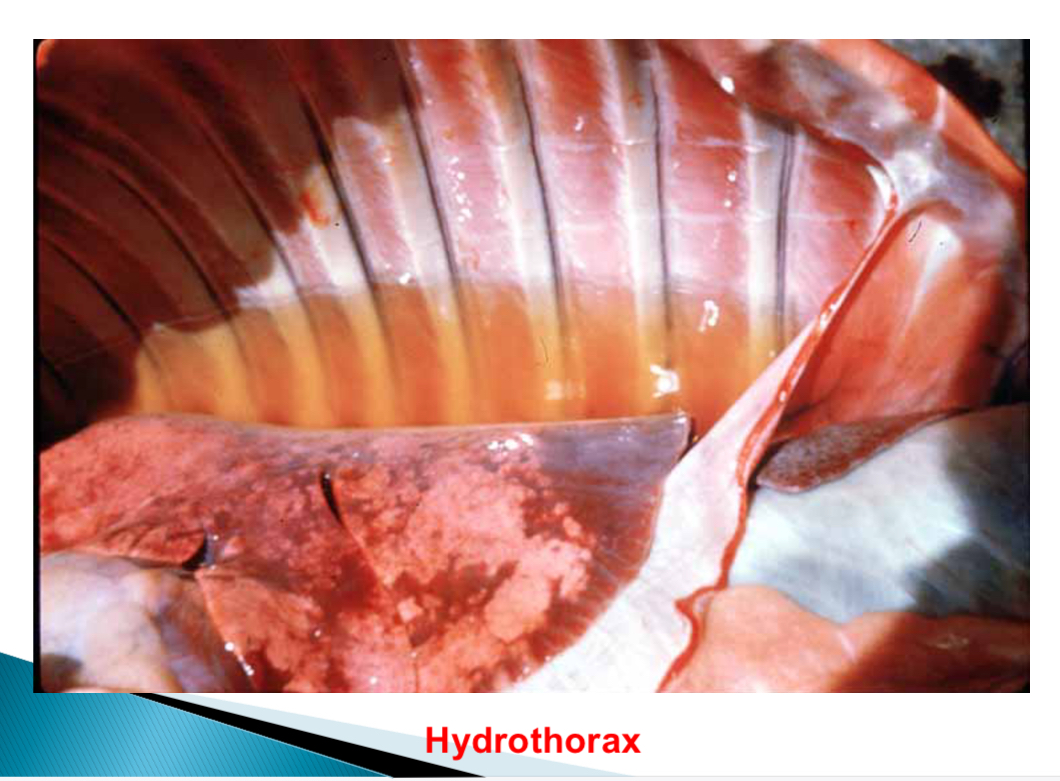
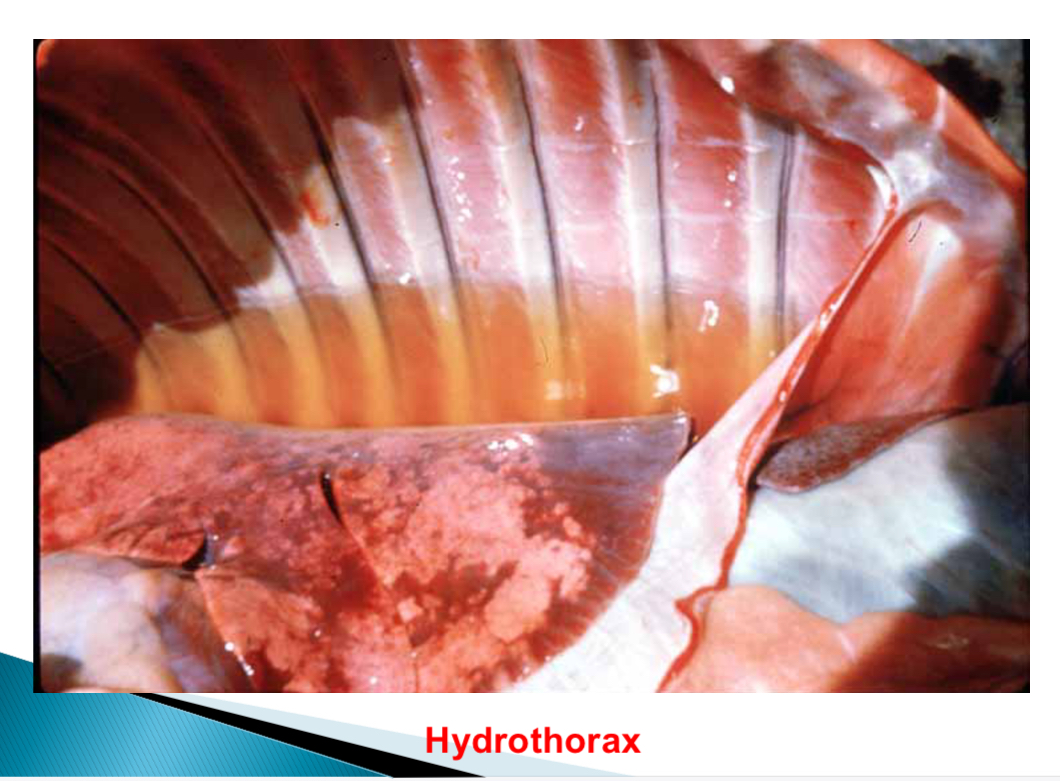
Most common site of oedema in cat
Thorax

Most common site of oedema in sheep (bottle jaw due to hypoproteinaemia)
Submandibular space, peritoneum

Most common site of oedema in horse
Limbs

Most common site of oedema in cattle
Brisket oedema (sc)

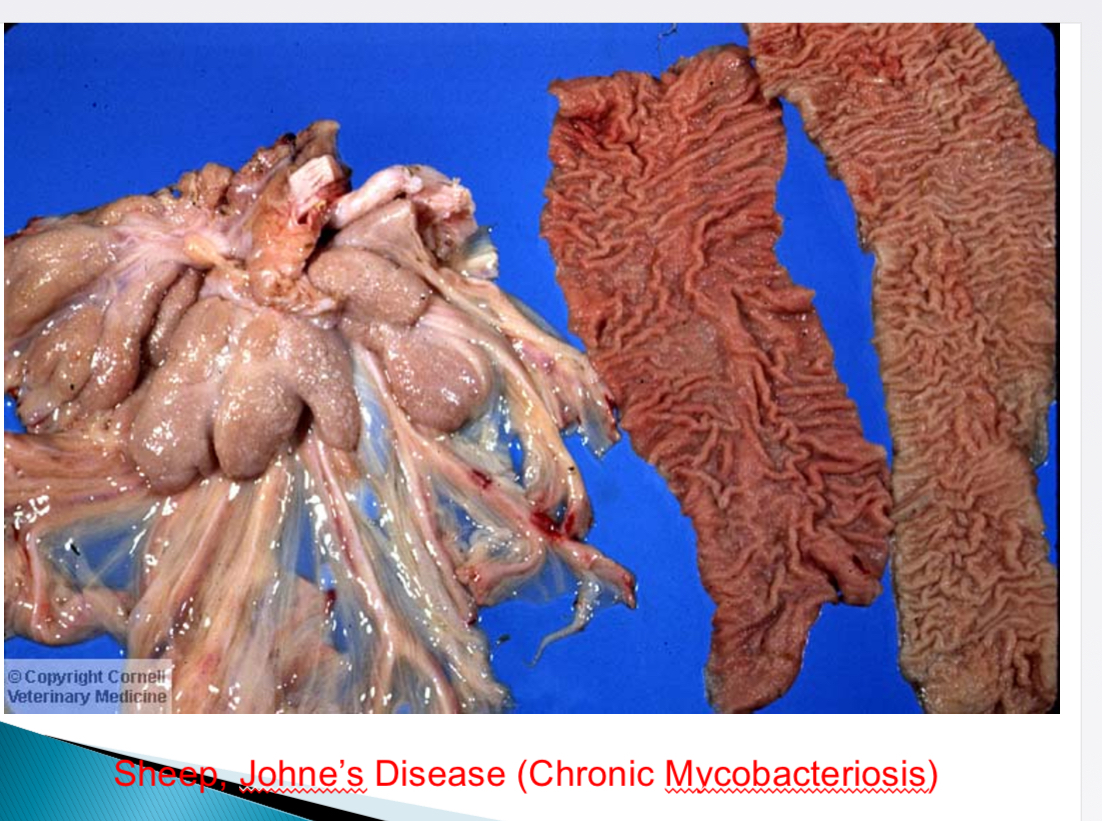
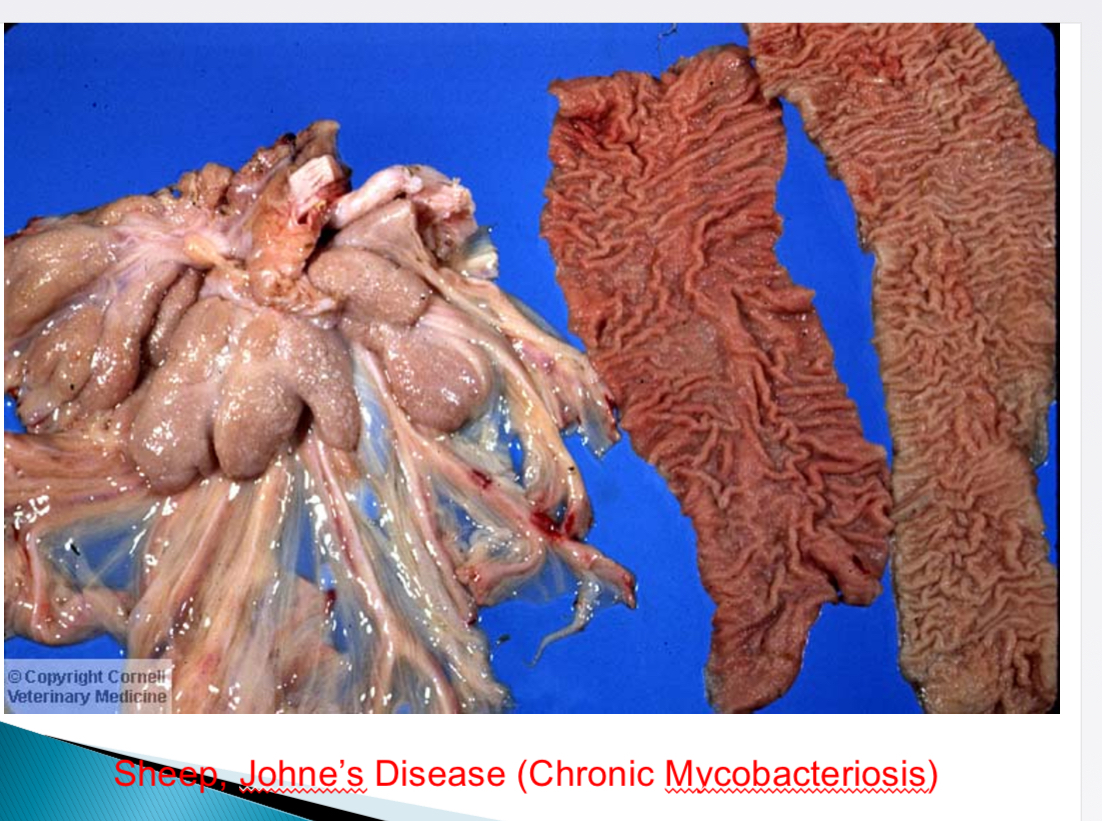
How can bottle jaw in sheep, goats, cattle occur
Johne’s disease (mycobacterium), intestinal parasites (haemonchus contortus), hepatic parasites (fasciola hepatica)→ hypoproteinaemia
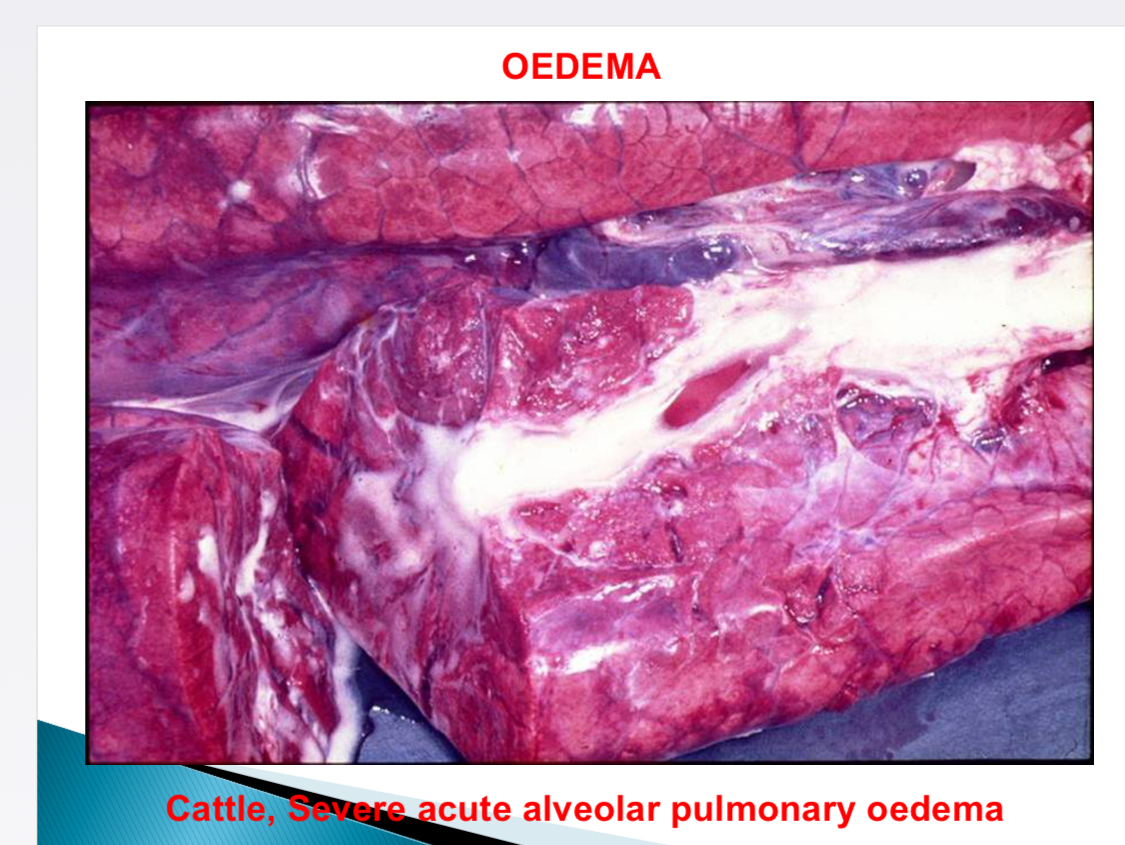
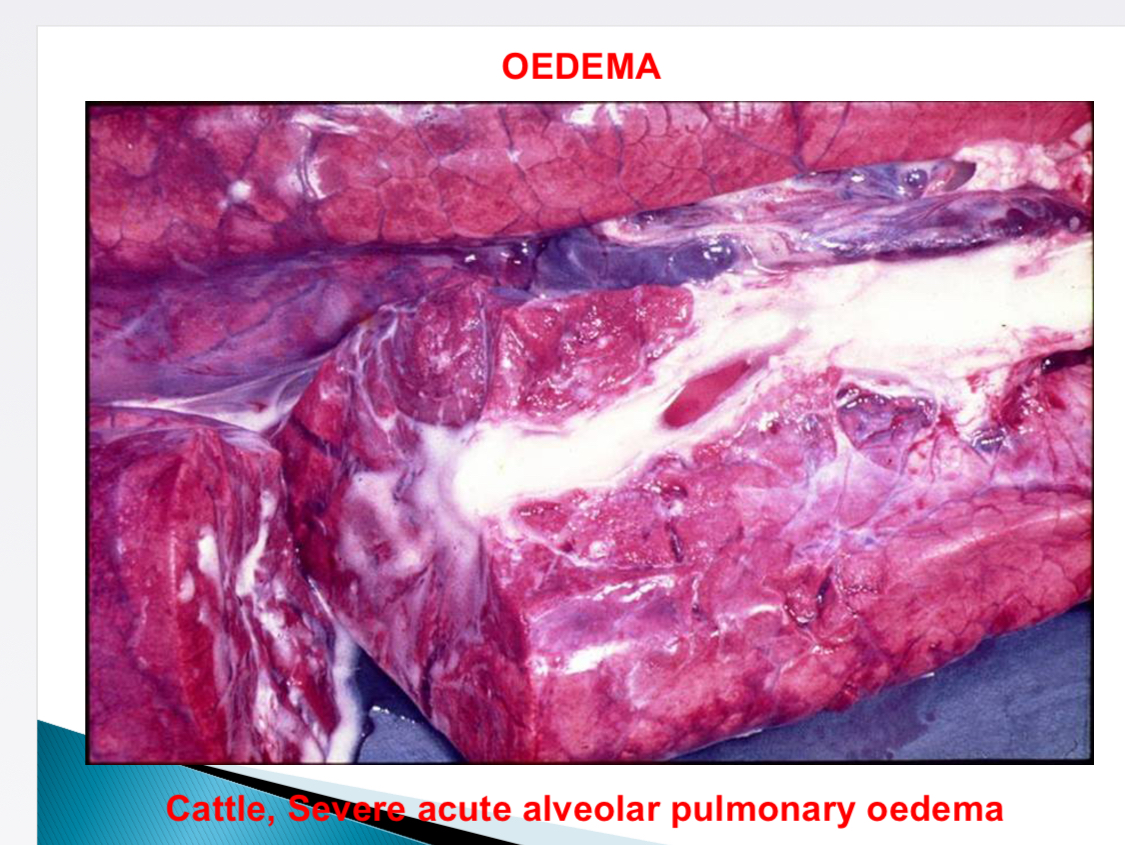
Causes of pulmonary oedema (frothy)
Irritant gases, inflammation, toxic, agonal change, left sided CHF, passive hyperaemia
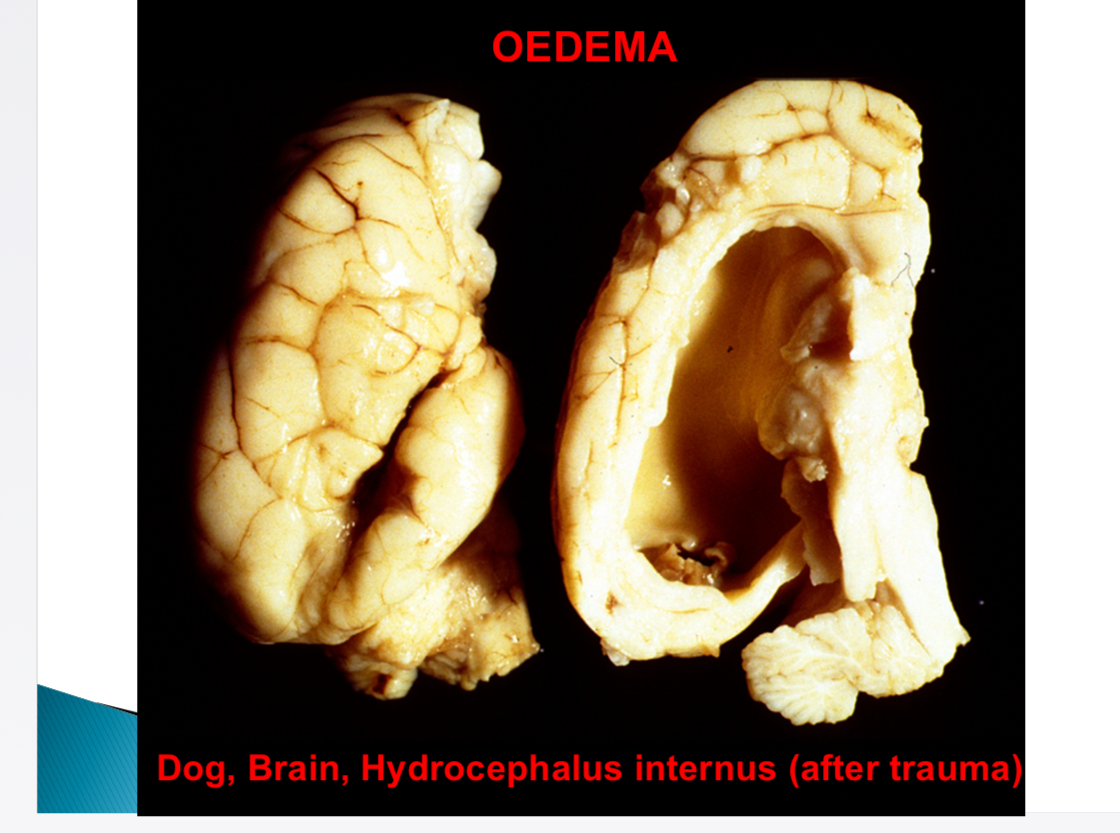
Why is CNS susceptible to oedema (hydrocephalus in ventricles, glaucoma)
No lymphatics
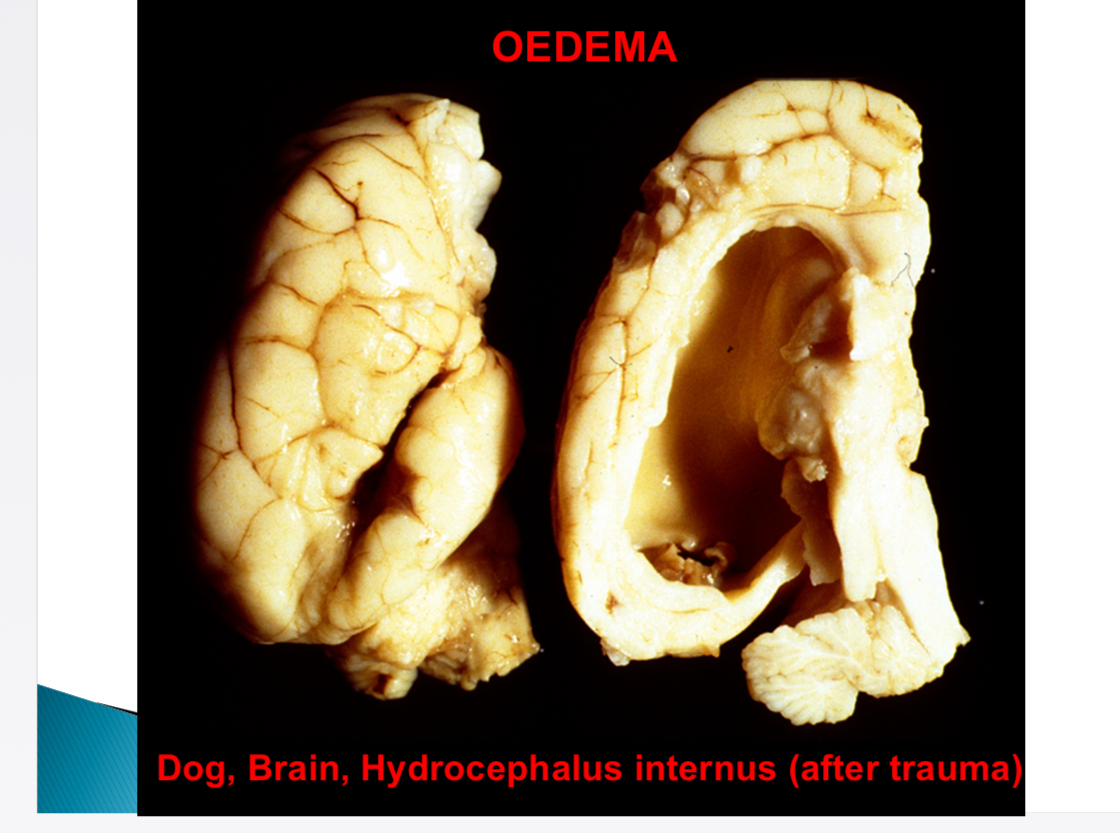
Causes of generalised passive hyperaemia
Heart failure, impeded venous return, increased pulmonary resistance
Heart failure def
Heart can’t pump blood at rate needed by tissues
How is arterial pressure + vital organ perfusion maintained (lead to heart failure)
Increased preload of dilation (contractility), myocardial hypertrophy, neurohormonal system (noradrenaline, RAAS, atrial natriuretic peptide)
CHF def
Build up of venous blood in systemic + pulmonary circulation
Consequences of CHF
Oedema, hypoxia, RAAS, chronic lung + liver congestion, fluid in peritoneum + thorax
Types of heart failure
Forward - from reduced CO + underperfusion
Backward/ CHF - from increased venous pressure
Consequences of left heart failure
Pulmonary congestion, pulmonary oedema, renal hypo perfusion → renin
Consequences of right heart failure (pressure overload of RV)
Increased pulmonary resistance, cardiac hypertrophy (concentric- pressure overload→ walls grow inward, eccentric- vol overload→lumen larger)
Effects of angiotensin 2
Arterioconstriction, increase cont, increase PCT na reabsorption, aldosterone release, ADH release (CD water reabsorption)
Noradrenaline - released from
Adrenergic cardiac nerves
Noradrenaline - Effect
Increase HR, increase cont
Atrial natriuretic peptide - release
Increased V load (CHF, chronic renal failure)
Atrial natriuretic peptide - Effects
Counteract RAAS - vasodilation, inhibit Na reabsorption, increase GFR, inhibit aldosterone secretion
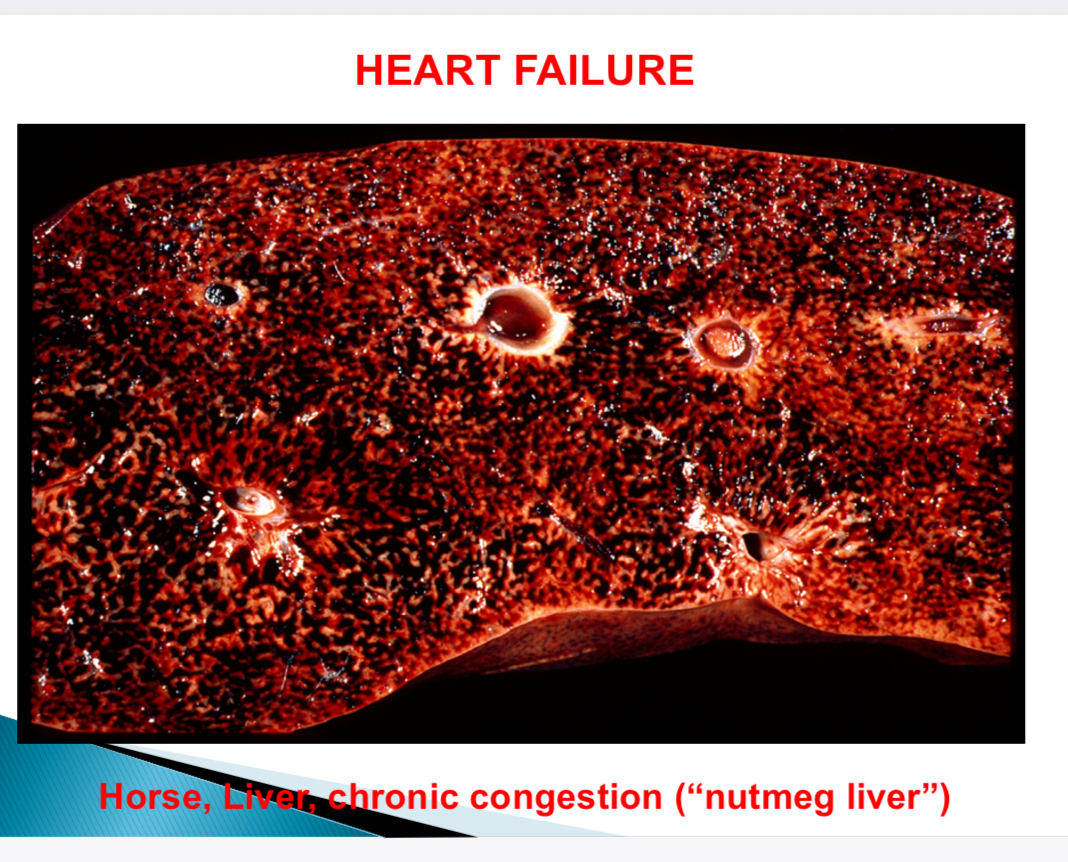
What is nutmeg liver
Liver appearance in chronic congestion of central vein dilation due to right sided CHF
Pale hepatocytes
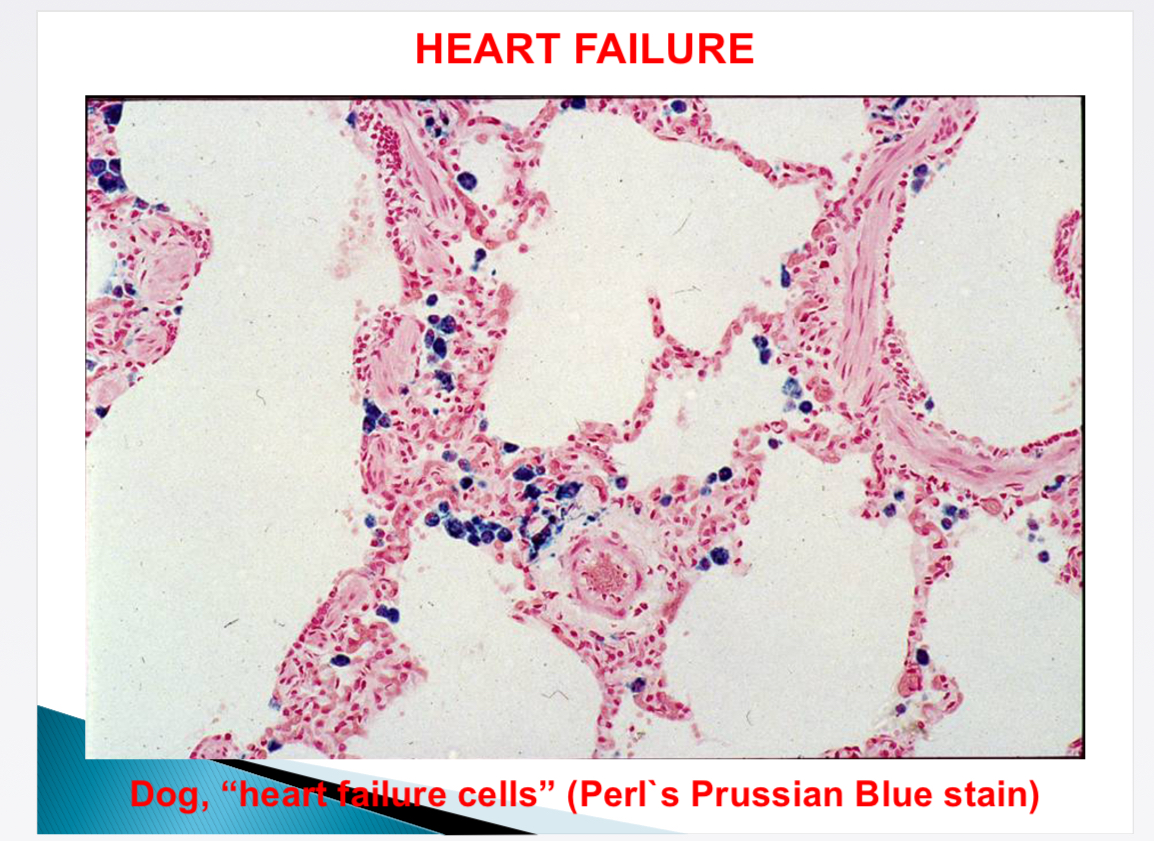
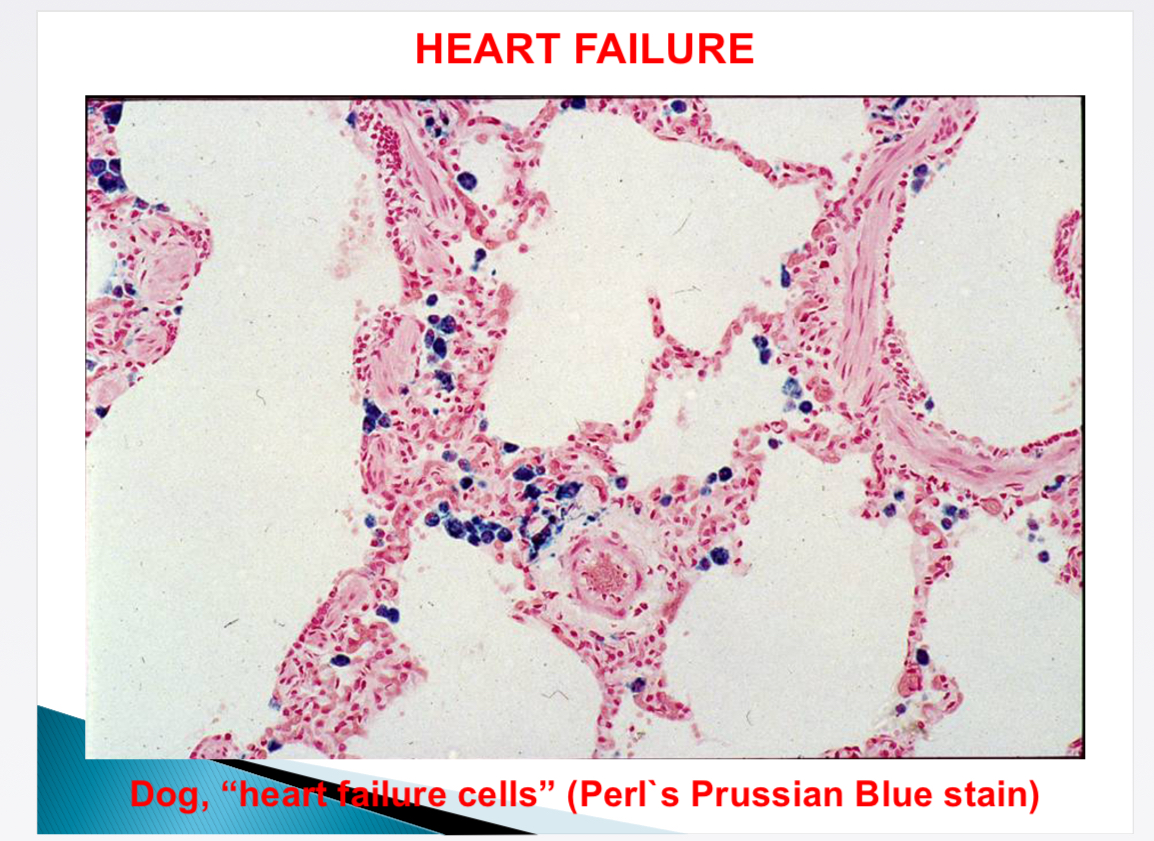
What is shown
Heart failure cells - alveolar capillaries leak → macrophages → haemosiderin (Perl’s Prussian blue stain)