Gluteal, Hip and Thigh
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What are some anatomical landmarks of the pelvis
ASIS, Iliac crest, pubic tubercle, ischiopubic ramus
What landmark is used for pudendal nerve block
Ischial spine
What is fovea
The hole at the head of the femur → Where the artery of the ligament of the head of the femur is
What is the strongest ligament in the body
iliofemoral ligament (Y ligament); attached from the ASIS to the intertrochanteric crest of femur
What nerves innervate the anterior compartment
Femoral nerve
What nerves innervate the medial compartment
Obturator nerve
What nerves innervate the posterior compartment
Sciatic nerve
What is Trendelenburg sign
Pelvis of the patient drops to opposite side when standing on the affected limb
What causes the Trendelenburg sign
Weak paralyzed abductor muscle (gluteus medius and minimus) caused by superior gluteal nerve injury
What is the gait (walk) like for patients with positive Trendelenburg sign
Trunk of the body leans to the affected side to balance the center of gravity of the patient
Piriformis action
Lateral rotation of extended femur at hip joint; abduction of flexed femur at hip joint
What muscle is innervated by the superior gluteal nerve and abduct the femur at the hip joint
Gluteus medius, gluteus minimus and tensor fasciae latae
Function of gluteus medius and minimus
Abduct femus at hip joint, stabilization of pelvis, medial rotation
Gluteus maximus action and innervation
Extensor of flexed femur at hip joint; lateral rotation and abduction of thigh; inferior gluteal nerve
What is the shared action of obturator internus, gemellus superior and inferior and quadratus femoris
Lateral rotation of extended femur at hip joint; abduction of flexed femur at hip joint
Which muscles are innervated by the nerve to obturator internus
Obturator internus, gemellus superior
Which muscles are innervated by the nerve to quadratus femoris
Gemellus inferior, quadratus femoris
Muscles in the anterior compartment
Iliopsoas, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, rectus femoris, sartorius
Quadricep muscles
Vastus intermedialis/medialis/lateralis, rectus femoris
Which muscle in the anterior compartment is NOT innervated by the femoral nerve and what nerve is it innervated by
Psoas major → Innervate by the anterior rami
Anterior muscles that extend leg at knee joint
Vastus intermedius, lateralis, medialis
Anterior muscles that flex thigh at hip joint
Psoas major, iliacus, rectus femoris, sartorius
Rectus femoris action
Flex thigh at hip joint + extend leg at knee joint
Sartorius action
Flex thigh at hip joint + flex leg at knee joint
Muscles in the medial compartment
Gracillis, pectineus, Adductor brevis, adductor longus, adductor magnus, obturator externus
Which muscles of the medial compartment are NOT innervated by the obturator nerve
Hamstring part of adductor magnus → Sciatic nerve; Pectineus → Femoral nerve
Which medial compartment muscle adduct and medially rotate thigh at hip joint
Pectineus, adductor brevis, adductor longus, adductor magnus
Gracilis action
Adduct thigh at hip joint and flex leg at knee joint
Obturator externus action
Lateral rotation of thigh at hip joint
Posterior/hamstring muscles
Bicep femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus
Muscles that flex leg at hip join, extend thigh at hip joint, medially rotate thigh at hip joint and leg at knee joint
Semitendinosus, semimembranosus
Bicep femoralis action
Flex leg at knee joint; extend and lateral rotation of thigh at hip joint, leg at knee joint
Common origin of posterior compartment muscle + Hamstring part of adductor magnus
Ischial tuberosity
What is pes anserinus
Group of 3 muscle attached at the superior tubercle (pes anserinus) from all 3 compartment that are all 2 joint muscles that flex the knee
What muscles are part of the pes anserinus
Sartorius, gracilis, semitendinosus
What nerve passes through the piriformis muscle
Sciatic nerve, superior and inferior gluteal nerves
What does the sciatic nerve branch into
Common fibular nerve and tibial nerve
Sensory nerves of the hip and thigh
Anterior cutaneous and saphenous nerve
Which is the safest area of the gluteus to do an injection
Upper lateral quadrant; lower medial has the sciatic nerve, upper medial has the superior gluteal
What are the branches of the aorta in the hip and thigh
Aorta → Common iliac artery → Internal and external iliac artery → External iliac becomes the femoral artery at inguinal ligament → Popliteal artery at adductor hiatus
What are the arteries that supply the head of the femur
Lateral and medial circumflex + artery of ligament of head of femur
What is the origin of the gluteal artery
Internal iliac artery
What structures are in the femoral triangle
Femoral nerve artery and vein
What structures are in the popliteal fossa
Popliteal artery and vein, tibial nerve, common fibular nerve
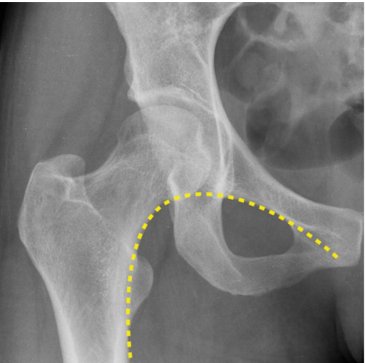
What is Shenton line used for
Find dislocation of the of hip
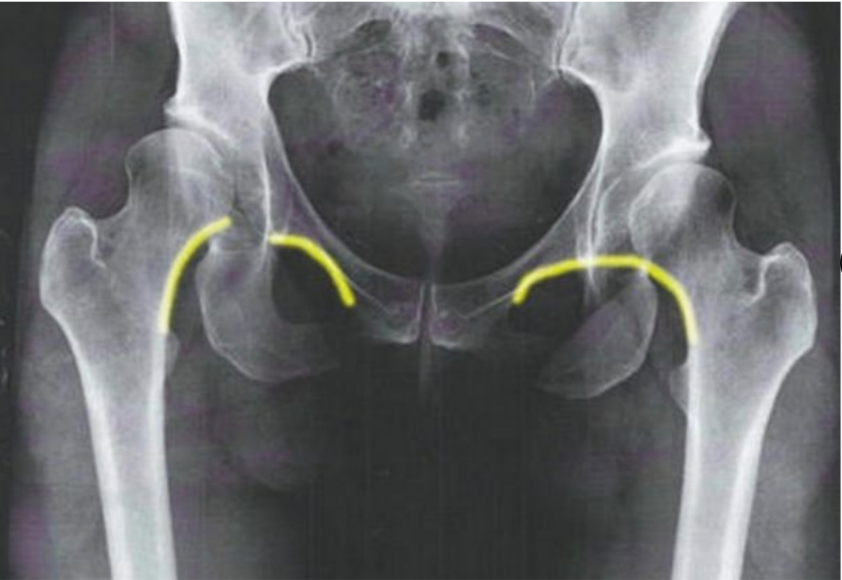
What does this image indicate
Hip dislocation
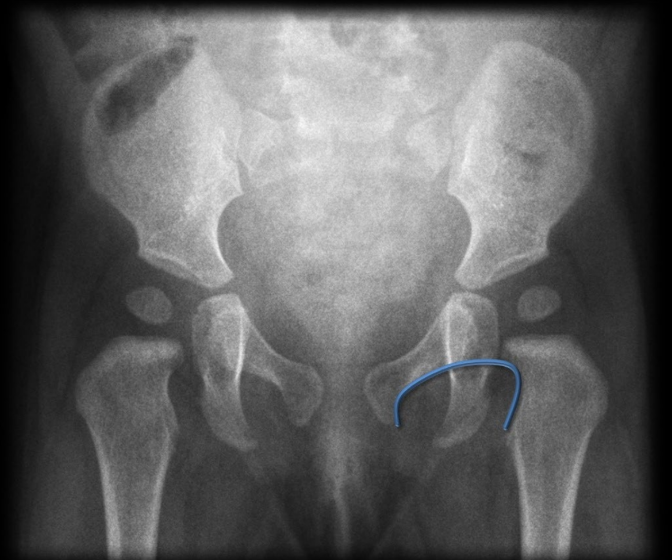
What does this image indicate
Normal hip and femur of a child
Lateral view femur
AP view femur
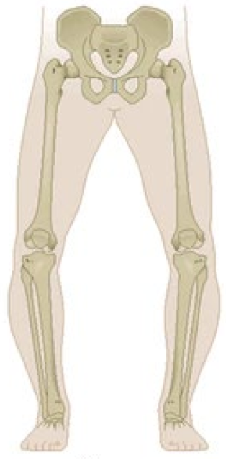
Genu varus
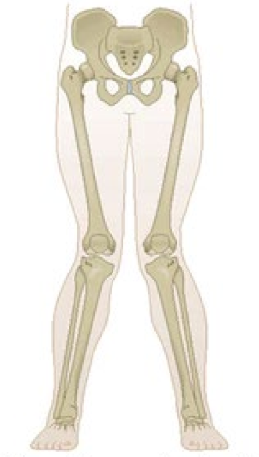
Genu valgus (knock knee)
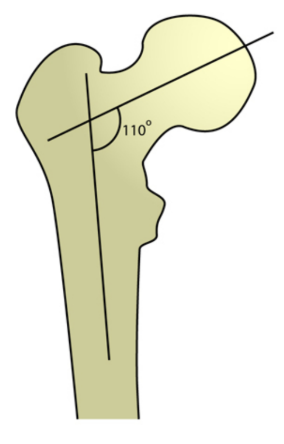
<120 degree
Coxa vara
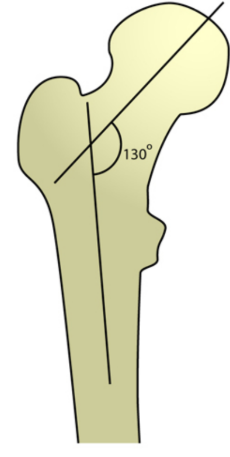
120-135 degree
Normal head of femur
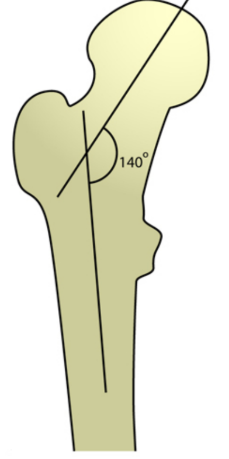
>135 degree
Coxa valga
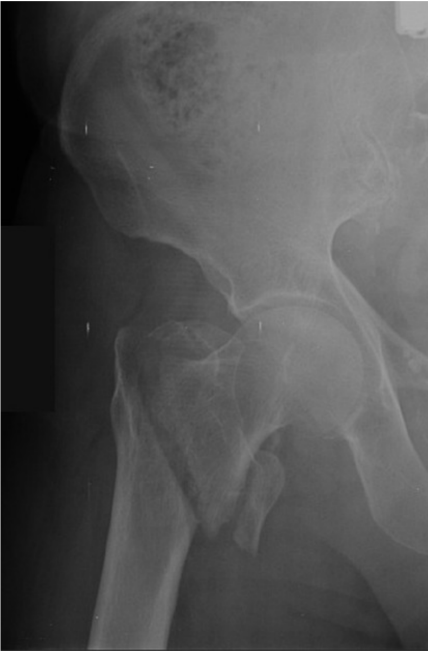
What is this image indicate
Intertrochanteric fracture
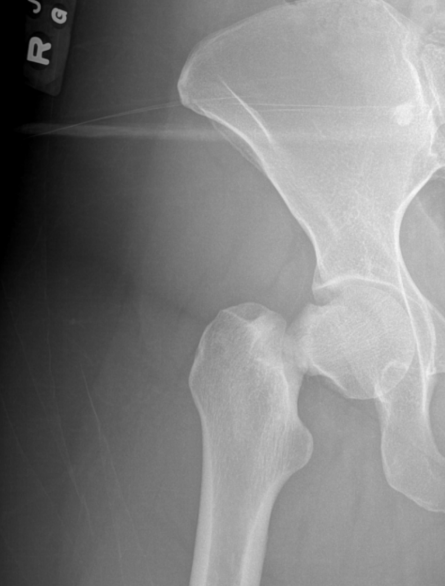
What does this image indicate
Femoral neck fracture
What artery would be affected in femoral neck fracture
Lateral and medial circumflex artery → High risk of avascular necrosis
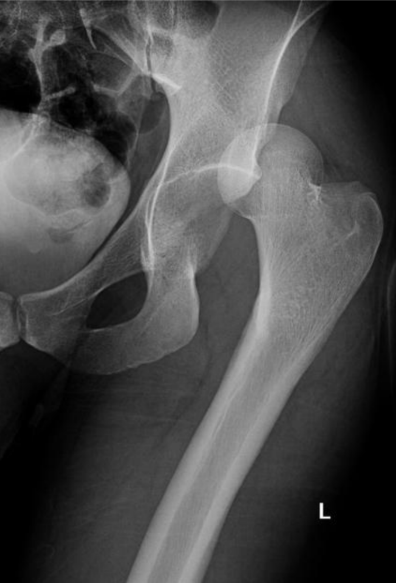
Dislocation of femur
Which type of hip dislocation is more common and what is the most vulnerable position
Posterior; found in car accidents where the leg is shortened, adducted and internally rotated (sitting); posterior part of the acetabulum also breaks with it