Muscular System: Gross Anatomy of Skeletal Muscles
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
connective tissue sheaths
endomysium, perimysium, epimysium
-all come together to form attachment to bone
-tendons are dense regular CT
endomysium
loose connective tissue wrapping each muscle fiber
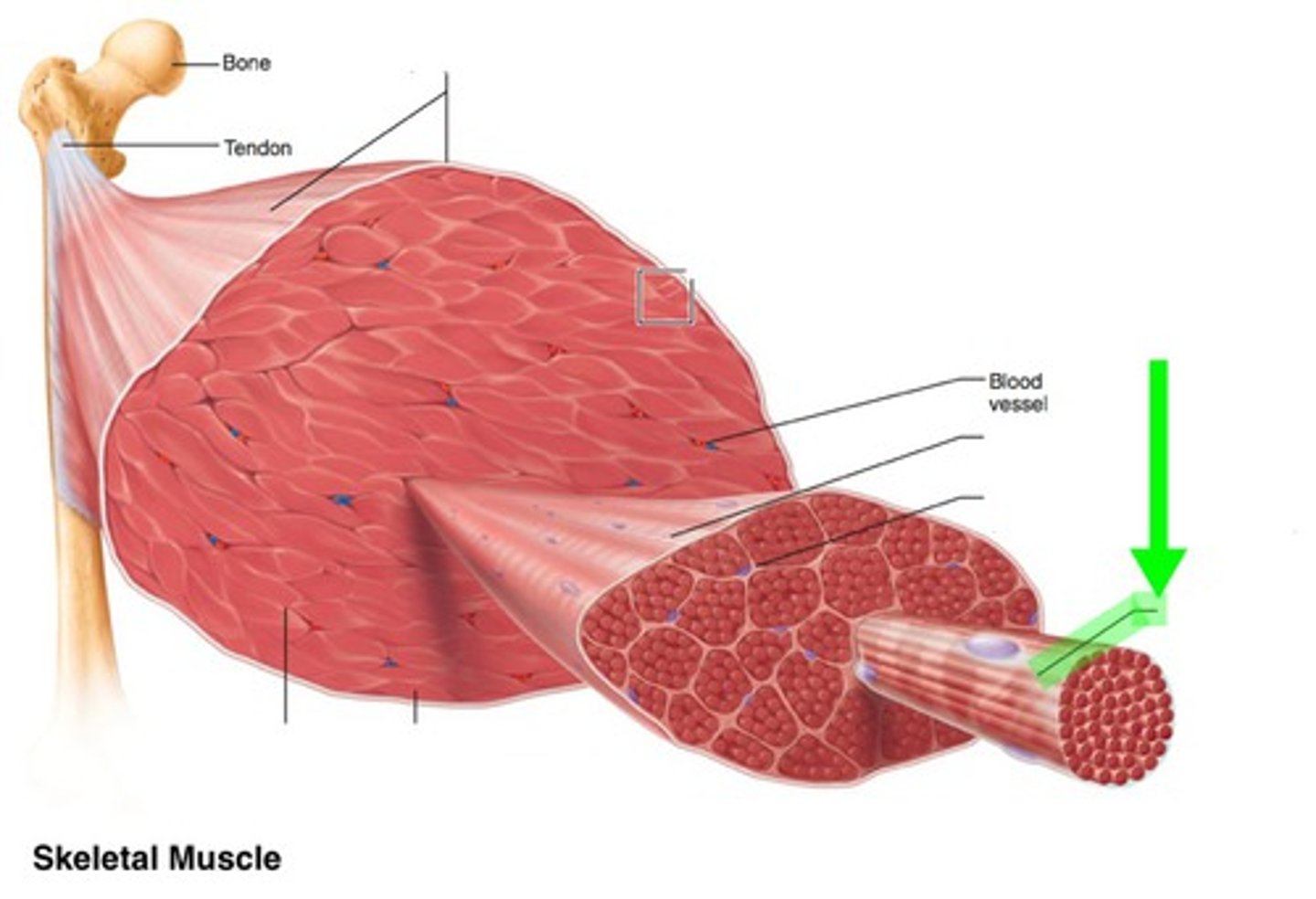
perimysium
dense regular connective tissue that surrounds each fascicle (group of muscle fibers)
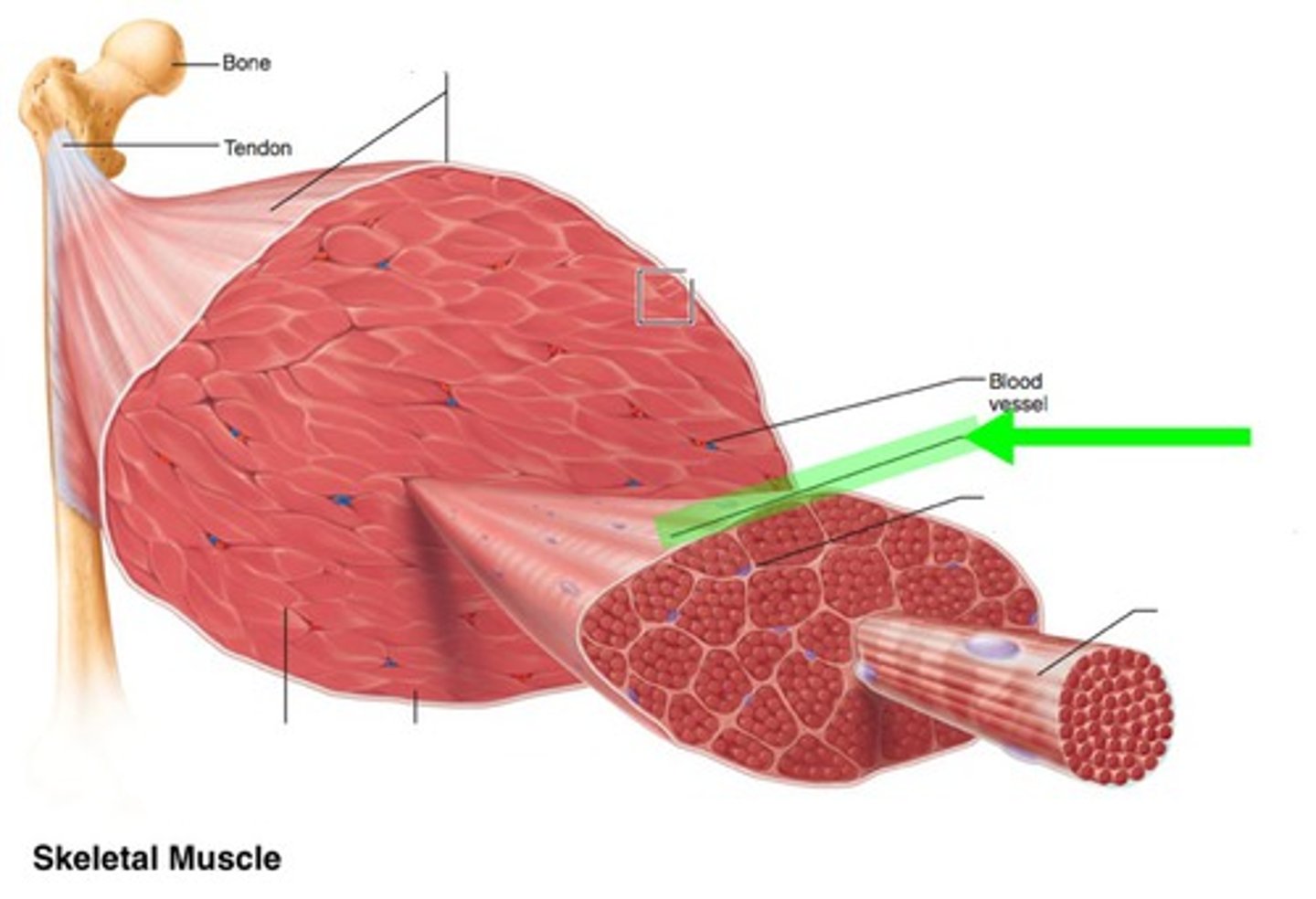
epimysium
dense irregular connective tissue surrounding entire muscle
nerves and blood vessels of a skeletal muscle
-each skeletal muscle is supplied by branches of one primary nerve, one primary artery, and one or more veins
-smallest nerve branches serve individual muscle fibers to form the neuromuscular junction
muscle attachments
-most skeletal muscles run from one bone to another
-one bone will move (insertion) the other remains fixed (origin)
-attach to origin and insertion by connective tissue (direct or indirect)
origin
less movable attachment
insertion
more moveable attachment
movement/action of muscle
insertion bone pulled into origin bone
direct (fleshy) attachments
epimysium directly attached to periosteum
indirect attachments
-tendon
-aponeurosis (sheet-like tendon, ie. thoracolumbar fascia)
-raphe (seam-like tendon, ie. linea alba)
fascicle arrangements
-bundles of muscle fibers
-arrangement tells about the action of a muscle: amount of movement, amount of force
-includes: circular, convergent, parallel (strap-like or fusiform), pennate (uni, bi, multi)
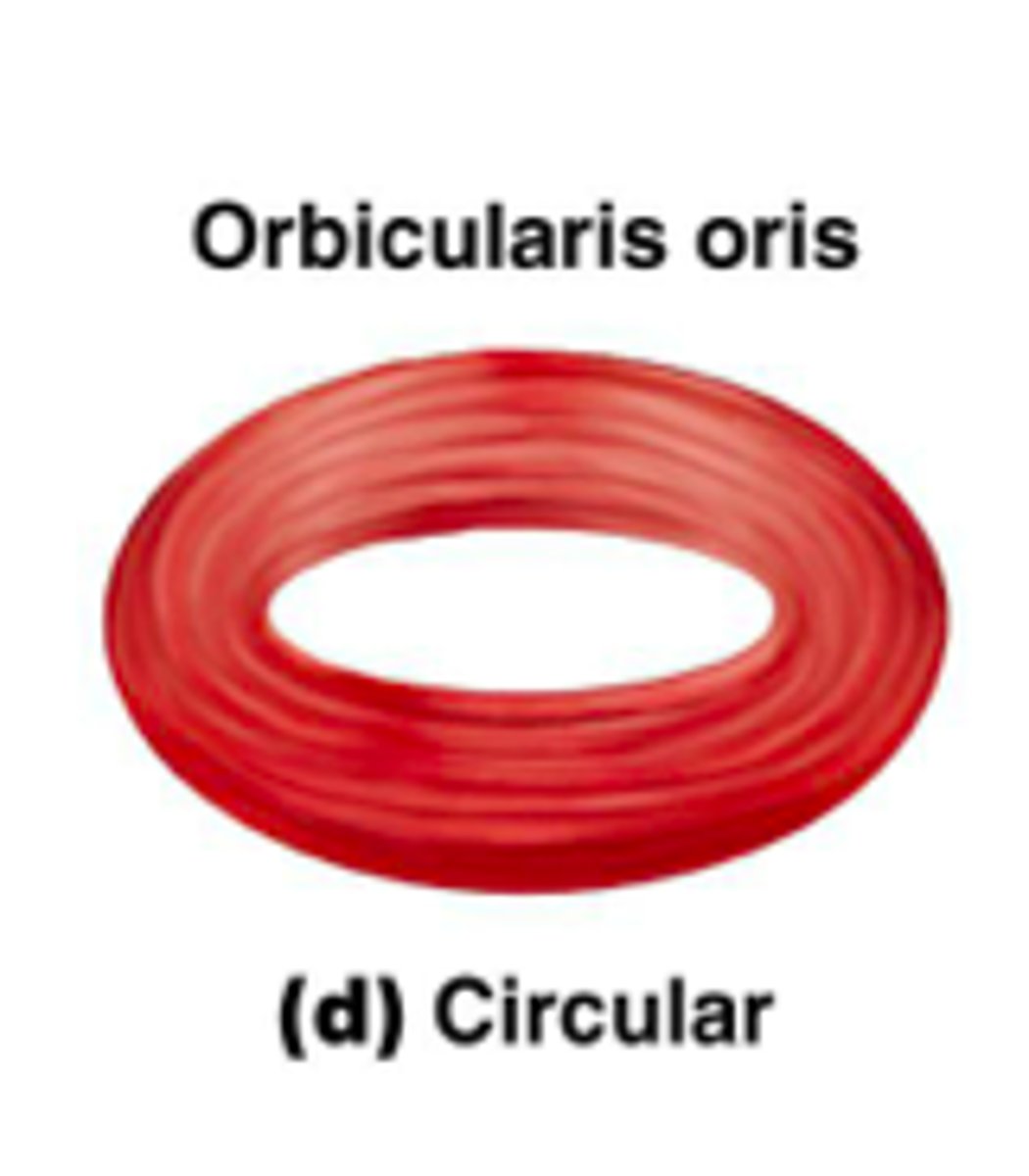
circular fascicle arrangement
-surround external body openings
-sphincter = general name for circular muscle
-ex: orbicularis oris and oculi
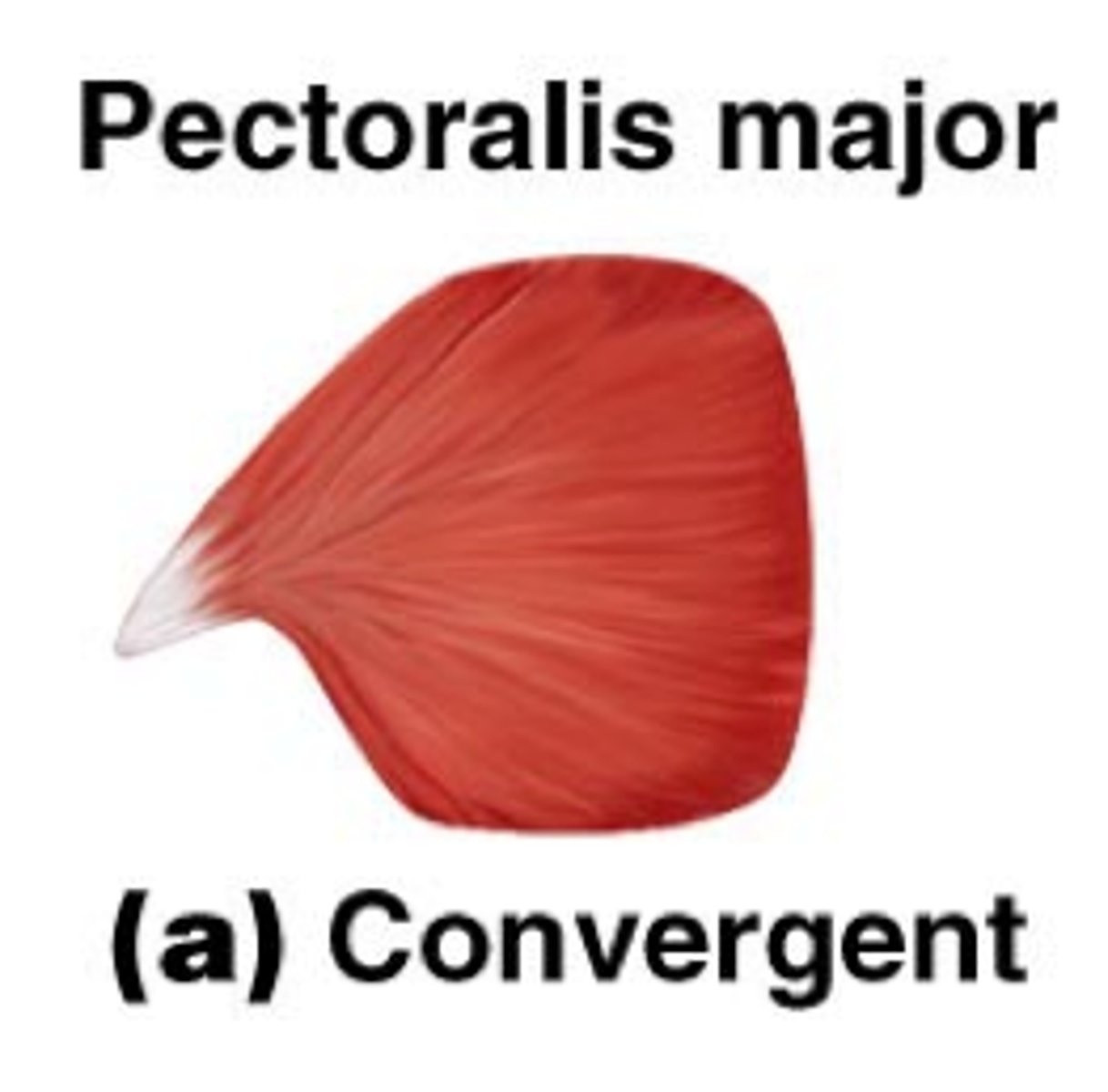
convergent fascicle arrangement
-origin of muscle is broad, fibers taper as approach insertion
-both force and range of motion benefit
-ex: pectoralis major
parallel fascicle arrangement: strap-like
-every fiber parallel and about the same length
-range of motion benefit
-ex: SCM, gracilis, sartorius

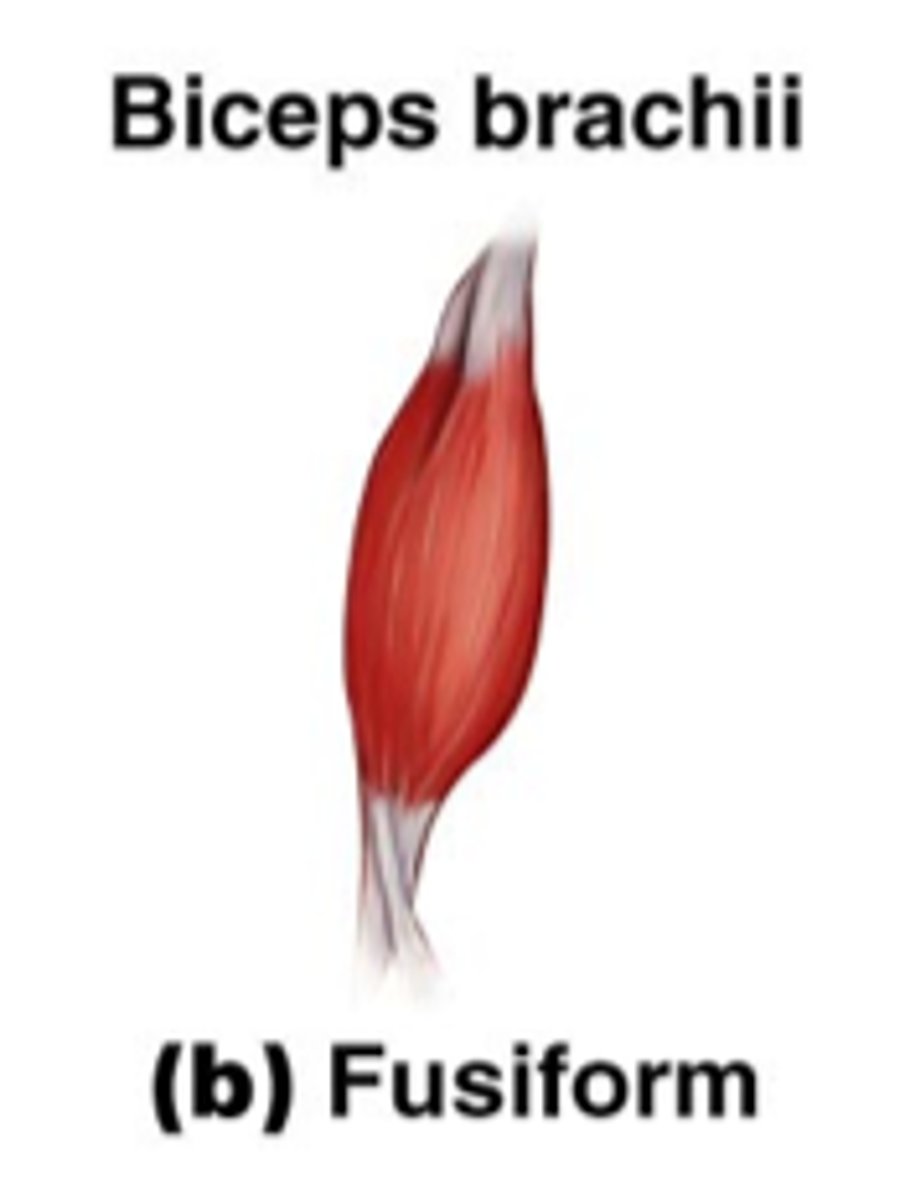
parallel fascicle arrangement: fusiform
-with expanded central belly
-range of motion and force production benefit
-ex: biceps brachii
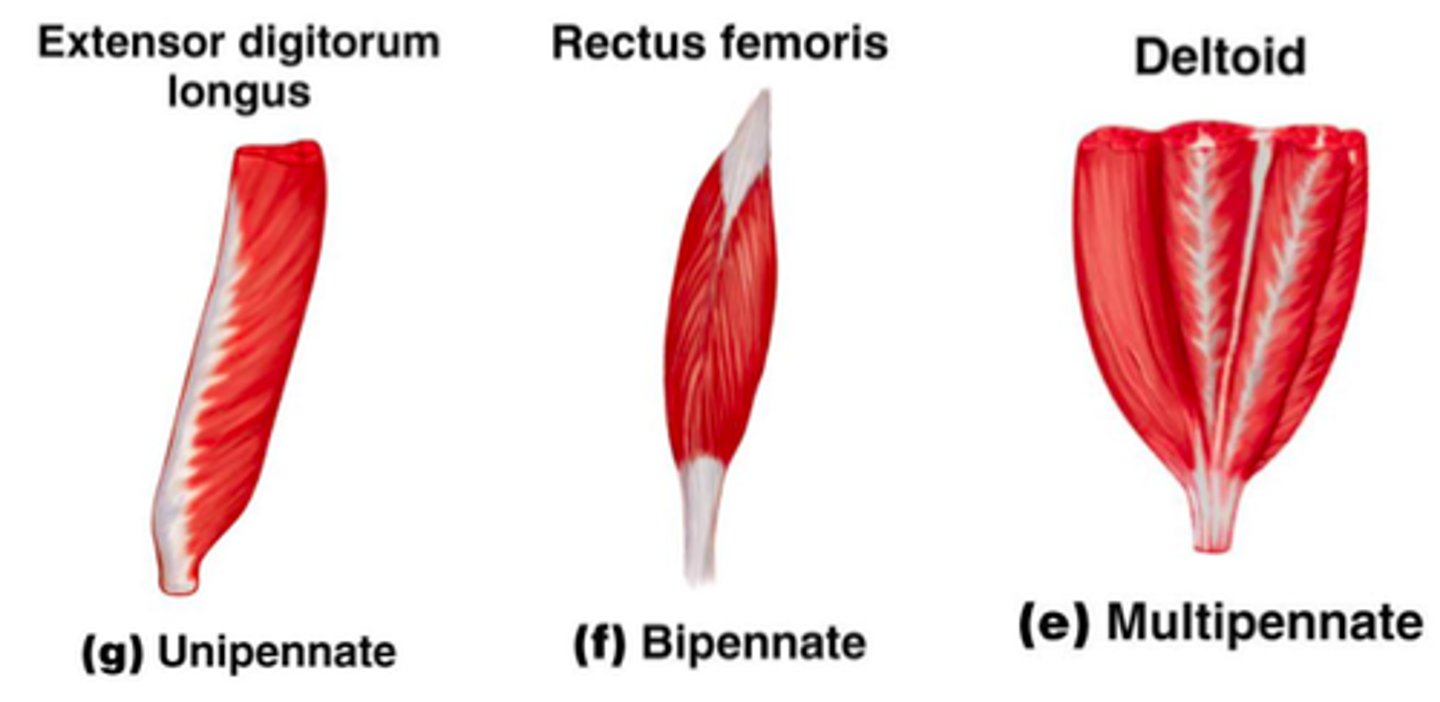
pennate fascicle arrangement
-feather-like, short fascicles attach obliquely to tendon
-unipennate, bipennate, multipennate
pennate fascicle arrangement: unipennate
-fibers come from one side
-ex: flexor pollicis longus
-range of motion and force benefit
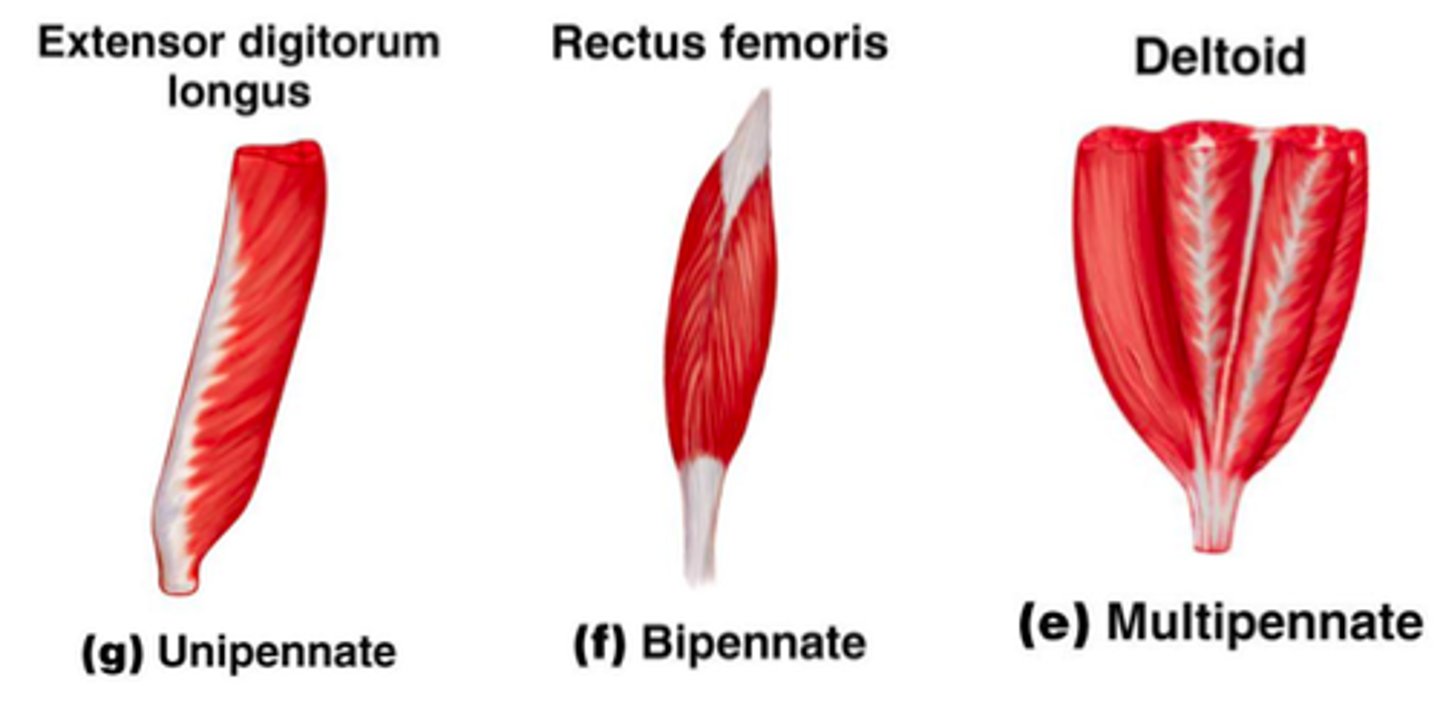
pennate fascicle arrangement: bipennate
-fibers anchor to both sides
-ex: rectus femoris
-range of motion and force benefit
pennate fascicle arrangement: multipennate
-multiple bipennate arrangements
-ex: deltoid
-force benefit
functional groups of skeletal muscles
prime mover, antagonist, synergist
prime mover (agonist)
major responsibility for certain movement
antagonist
opposes or reverses a movement
synergist
helps prime mover
-adds extra force
-reduces undesirable movements
-fixator (holds bone firmly in place)
a muscle that crosses on the anterior side of a joint produces...
flexion
-exception: knee
a muscle that crosses on the posterior side of a joint produces...
extension
a muscle that crosses on the lateral side of a joint produces...
abduction
a muscle that crosses on the medial side of a joint produces....
adduction
skeletal muscles can be named according to....
location, shape, relative size, direction of fascicles and muscle fibers, location of attachments, number of origins, actions
naming: location
ex: brachialis on the arm, intercostals between ribs
naming: shape
ex: quadratus femoris is 4-sided, deltoid triangular
naming: relative size
ex: maximus, minimus,
ex: longus, brevis
naming: direction of fascicles and muscle fibers
-oblique: lie at oblique angle to midline (ex: external oblique)
-transversus: lie at right angle to midline (ex: transversus abdominis)
-rectus (straight): parallel to the body midline (ex: rectus abdominis)
naming: location of attachments
-name reveals point of origin and insertion
-ex: coracobrachialis
naming: number of origins
-ex: biceps- two origins
naming: actions
-indicates type of muscle movement
-flexor, extensor, adductor, abductor