Bacteria Structural
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Prokaryotes
obsolete as it’s a catch-all for small organisms that lack an internal membrane system
Cocci Shape and Arrangement
provides morphology for identification; big part of naming but not always
Cocci
spherical-like shape; can be strepto-, staphylo-, and tetrads

Streptococci
cells are in a line
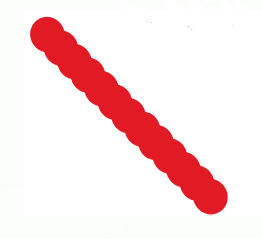
Diplococci
pairs

Staphylococci
cluster/clumped shape

Tetrad
groups of 4

Bacilli
rods; length-to-width ratio differ; ex. coccobacilli are short and wide
Vibrios
comma shaped
Spirilla
rigid spiral-shaped; ex. food poisoning
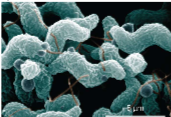
Spirochetes
flexible spiral-shaped; ex. lyme disease (can burrow through tissues)
Mycelium
network of long filaments (hyphae)
Pleomorphic
organisms that are variable in shape

Legionella
identified as chains of rods (streptobacilli)
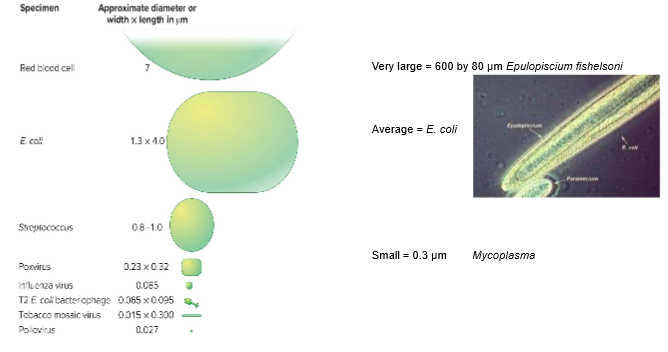
Bacterial Cell Size
can range from larger than a RBC to smaller than the largest virus; can’t say that bacteria is smaller than euks
What SA to Vol ratio do you want?
a high ratio because it increases efficiency of nutrient uptake and diffusion of molecules within a cell; essentially want where anywhere you are near the outside, you are near the core (want a high SA and low vol for more exchange w/ the exchange
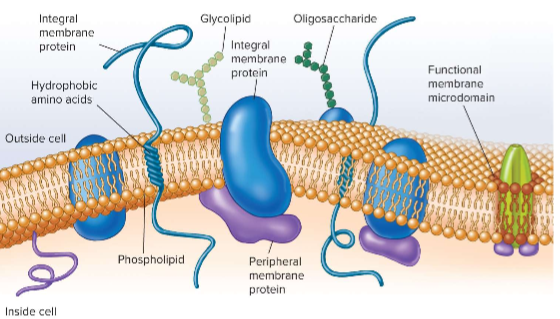
Common Bacterial Structures
provides a structural separation, open cytoplasmic environment and motility; want direct access to nucleus-like region and other stuff; has a cell envelope and flagella for motility; everything is exposed to everything else (can transcribe and translate at same time)
Plasma Membrane Structure
similiar in composition to other types of cells; has diff. lipids to make it move sturdy; selectively-permeable for nutrients
Selectively Permeable Barrier
acquires nutrients using transport systems; eliminates waste; they don’t have homeostatic things around them so they have to deal w/ the random enivironments; detects and responds to surrounding chemicals (more sensitive to tinier level changes - move from danger and towards food);
Aquiring Nutrients using Transport Systems
have to deal w/ diff. conc. of things so may have to rely more or active transport than passive
Metabolic Processes
respiration and photosynthesis
Bacterial Lipids
properties to adapt to the environment; ex. cholesterol in mems. of euks. and bacteriohopanetetrol in bacterial membranes which creates rigid differences in the phospholipid
What do common nutrients do in bacteria?
form structures; complete cofactors for enzymatic fcn; all of the stuff we need, they need (makes us good food) and need these to replicate?
Uptake of Nutrients Methods
microbes can only take in dissolved particles across a selectively permeable membrane; microorganisms use transport mechanisms
Microorganisms Transport Mechanisms
passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, primary/secondary active transport, and group translocation; transport dependent on environment
Transport is dependent on what?
the external environment; higher conc. → lower conc.
Passive Diffusion
depends on a gradient and lack of selective permeability w/ membrane like CO2
Facilitated Diffusion
depends on a gradient and lack of selective permeabability w/ membrane (can be a channel or carrier)
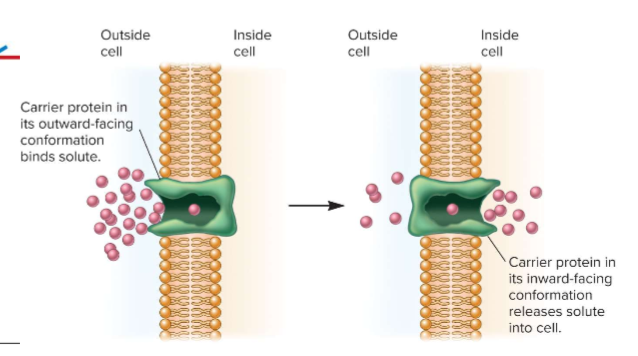
Active Transport
can be utilized to obtain nutrients against the gradient; lower conc. → higher conc.; requires ATP or protom motive force (PMF) and carrier protein
Secondary Active Transport
can use PE of ion gradients to cotransport substances w/o modifying them; ex. uniporter, symporter, or antiporter
Uniporter
type of secondary active transport; just one thing going in/out
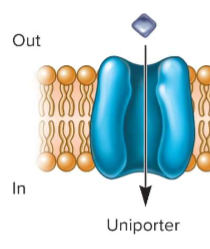
Symporter
type of secodary active transport; cotransporter; 2 things going in the same direction
Antiporter
type of secondary active transport; cotransporter; 2 things going in opposite directions
Group Translocation
chemically modifies the molcule as it is brought into the cell; important in salmonella
Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
sugar phosphotransferase system (PTS); donates phosphate group
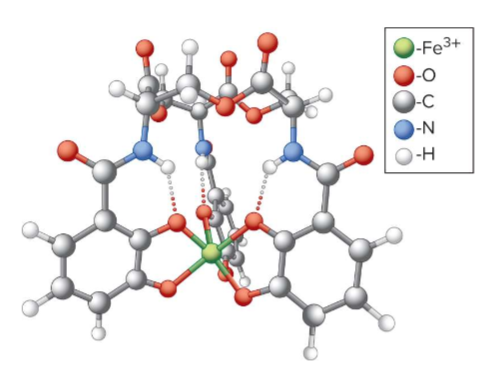
Siderophores
secreted by bacteria; complex w/ ferric ion for transport into cell; important transfer molecule; used bc microorgnisms need iron too and these iron close to membrane so cell can take it in
Bacterial Cell Walls
maintain shape of the bacterium and protects cell from osmotic lysis and toxic materials
Peptidoglycan
made up of amino acids and NEG/NAM; good for identification (ex. gram staining)
NEG and NAM
connects things together by either a direct connection (more rigid) or a peptide interbridge (more flexible)
Gram-Positive Cell Walls
composed primarily of peptidoglycan; features teichoic acid; has a plasma membrane inside the cell wall
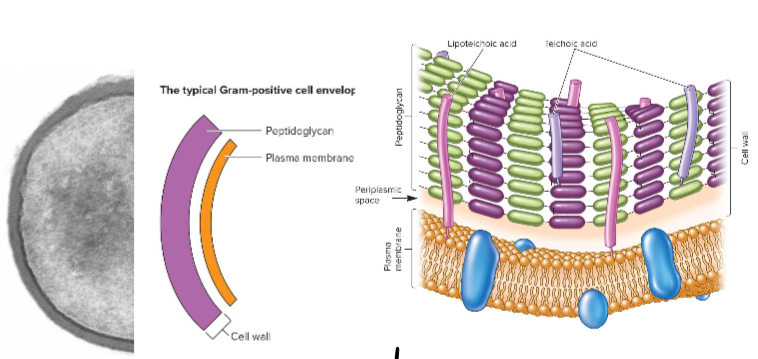
Lipoteichoic Acid
allows cells to interact on outiside of the cell
Gram-Negative Cell Wall Structure
2 phospholipid bilayers with peptidoglycan in between; highly active periplasmic space including metabolic and transport traffic
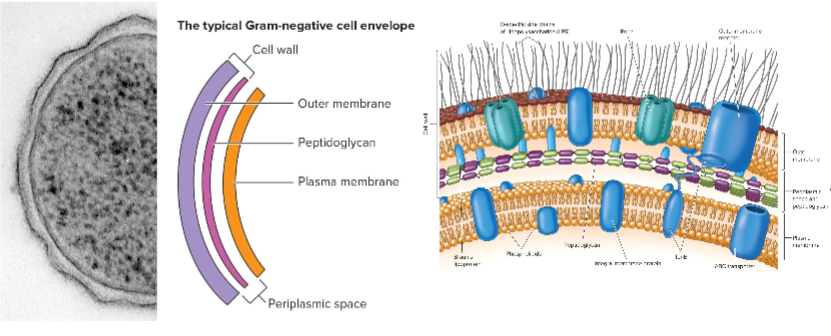
Periplasmic Space and Peptidoglycan
very active metabolically
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
common glycolipid found in gram negative outer membrane; vital to cell stability; can be a pathogenic feature of the cell; one of the most imflammatory thing we can have in our immune system; has 3 parts - lipid A, core polysaccharide, and O side chain (O antigen)
Lipid A
buried in outer membrane
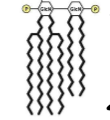
Core Polysaccharide
10 sugar structure joined to lipid A
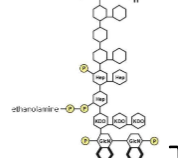
O Side Chain (O antigen)
polysaccharide that extends outward from the core (can change)
LPS
contributes to negative charge on cell structure; helps stabilize outer membrane structure bc outer membrane is looser compared to peptidoglycan; creates a permeability barrier; host defense protection; acts as an endotoxin
Gram-Negative Membrane Transport
2 stage process; first solute crosses outer membrane into periplasm and then crosses plasma membrane; porins are essential to this
Lysozyme
breaks beta (1-4) bond between NAG and NAM; destabilizes wall on outside
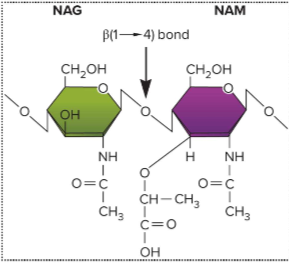
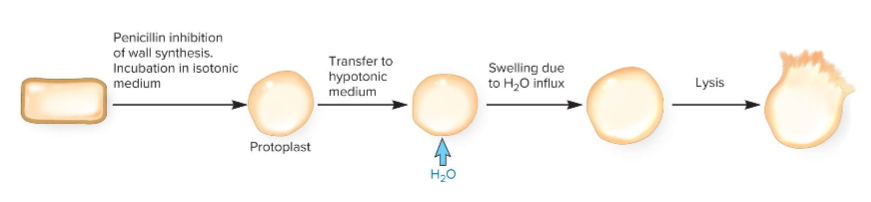
What happens when a cell loses its cell wall?
in may survive in isotonic environments; for gram negative, the peptidoglycan helps cells resist in hypertonic environments
Extracellular Vesicles
not cells; can transfer genetic info between cells and transfer toxin molecules; can’t survive on their own (like bacteria satellites)
Glycocalyx
on outside of cell wall and important for protection, attachment, and interaction with other cells; ex. capsules, S-layer, and slime layer
Capsules
tightly wound phospholipid layer
Slime Layer
disorganized glycoproteins (cause of cavities)
S-layer
crystal/tile-like layer around a cell
Cell
a boundary between an enxtracellular environment and an internal environment
Protoplast
includes the plasma membrane and everything inside of it; essentially what is left after the cell wall is gone
Cytoplasm
contains ribosomes, inclusions, chromosome, and plasmids
Bacterial Cytoskeleton
made up of protein filaments that polymerize to form functional filaments that extend to full inner dimensions of the cell; made up of monomers (actin, microtubules, and intermediate filaments)
Actin Example
MreB
Microtubules Example
FtsZ
Intermediate Filament Example
CreS which plays a big part in the shape of a structure
How do some bacteria maintain their shape?
some type of tight rod-like things to pull it into the shape (CreS); can use KO experiments to show that w/o it it was filamentus/bacillus instead of vibrio
What can even be found in bacteria?
membrane structures for specialized purposes
Inclusions
segregate cellular components so they don’t diffuse freely in the cytoplasm
Microcompartments
not bound by membranes but compartments for specific functions; ex. carboxysomes
Carboxysomes
CO2 fixing bacteria
Gas Vacoules
provide bouyancy to aquatic bacteria; allows it to change position; ex. CO2
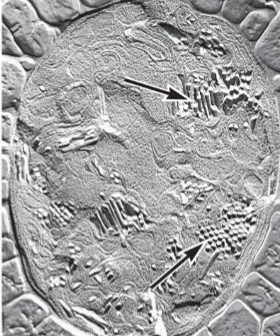
Magnetosomes
magnetite particles for orientation in Earth’s magnetic field; act like a compass
Bacterial Ribosomes
diff. size components and diff. structure than euk. ones
Nucleoid
location of chromosome and associated proteins; the chromosome bunches and and as it starts to collaspe, get interacting domains
Plasmids
extrachromosomal DNA; usually small, closed circular DNA molecules; genetic info passed through horizontal gene transfer; this is outside of larger chromosomal material
Pili and Fimbriae Functions
protection, attachment to surfaces, horizontal gene transfer, and cell movement
Fimbriae
stickiness to things/attachment; short and usually a lot of them
Pili
horizontal gene transfer using plasmids and other methods; long flagella-looking things
Flagellar Arrangement
helpful for identification; ex. monotrichous, lophotrichous, and pertrichous
Monotrichous
one singular flagella
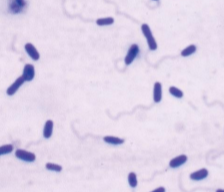
Lophotrichous
tufts of multiple flagella at 1 or both sides
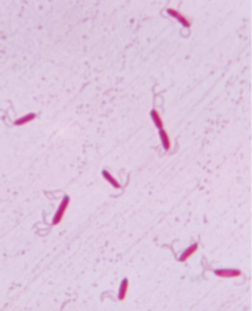
Peritrichous
swarming-like motion; a lot of them
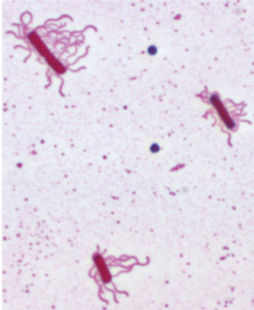
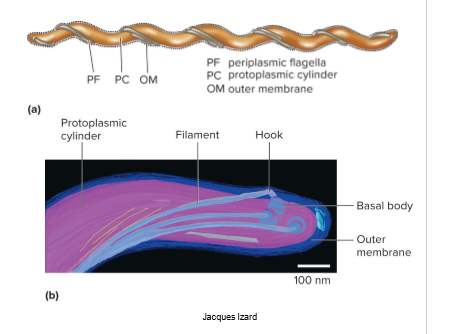
Bacterial Flagella Parts
filament, basal body, and a hook; diff. in gram + vs gram -; motor-like part uses PMF which causes conformational changes of the ring so controlable, metabolic process
Flagella Filament
self-assemble w/ help of filament cap at tip, not the base; makes cap and pushes it out
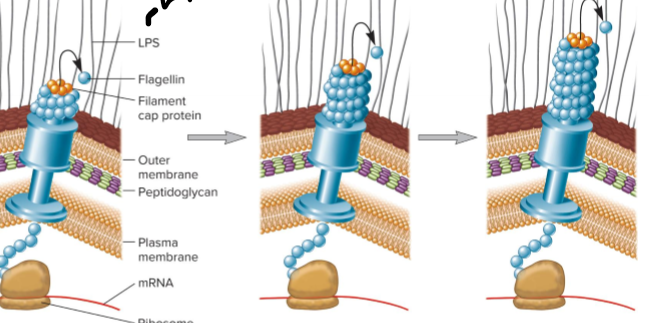
Flagellar-based Bacterial Motility
swimming, swarming, and gliding; also chemotaxis and twitching
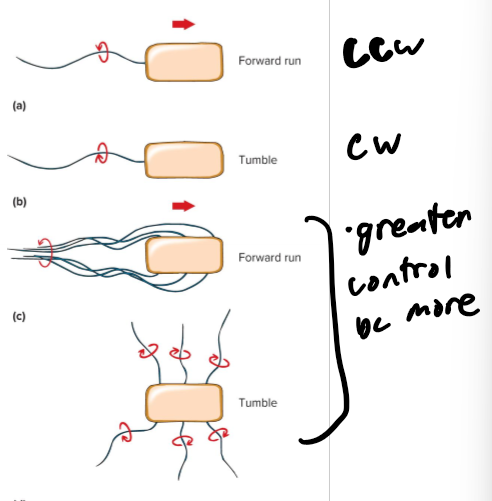
Swimming Motility
flagellum rotates like a propeller
ccw - forward run
cw - tumble
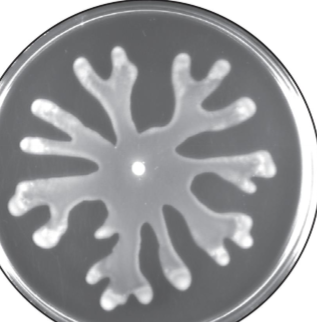
Swarming Motility
occurs when cells move in unison across a moist surface; usually uses peritchous flagella (highly controlled); ex. moving away from toxin
Spirochete Motility
axial fibril winds around the cell which allows it to burrow through tissues like a corkscrew
Twitching and Glidling Motility
short, intermittent, jerky motions; moves together by opening/closing the pili together
Chemotaxis
chemical attractants/repellents bind chemoreceptors that transmit signals throughout the chemosensing system; ex. tumbles (turns) more frequent when less food but slowly runs become longer and longer
Bacterial Endospore
complex, dormant structure; formed in response to lack of nutrients; not for reproduction but out of the need for survival; awaits detection of good nutrients
Endospore Structure
layered for a protective structure against adverse conditions
Sporulation
normally starts when growth slows due to lack of nutrients
Why are endospores bad for food safety?
since they are so resistant, they can survive through heat and other cooking porcesses that would kill other bacteria and then eventually they can come back
Endospore Formation
growth slows bc of lack of nutrients and continues through multiple stages
Endospore Formation Steps
activation → germination → outgrowth; cell divides → creates a septum → engulfs forespore (smaller “cell”) → cortex forms → coat and endospore maturation → original cell (big one) lysis
What happens to an endospore when conditions are favorable?
formation of vegetative cell the spore will activate, germinate, and complete outgrowth phase
From reading:
certain antibodies target cytoskeleton or inhibits protein synthesis (important bc bacteria’s ribosomes are different than euks.); murein ex of how to describes peptidoglycan (like glucose is a sugar)
MreB
bacterial actin; loops in bacteria
CreS
protein filament inside membrane