AP Stats Chapter 5
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
systematically favoring certain outcomes
bias
2 types of studies
observational, experiments
observational studies: observe individuals and measure varialbes to infer up to ______
population
experiments: _______ on individuals and obsoerve their responses to infer _____
impose some treatment, causation
Biased sampling methods
people who choose to respond (biased bc opinionated ppl tend to respond)
sample ppl easy to reach (biased bc doesn’t reprsent pop)
voluntary response, convenience sampling
How do you use a Random Digit Table to create a sample?

Every group of size n has equal chance of being selected
SRS - simple random sample
Take an SRS from diff strata of population & combine into 1 sample *minimizes variability between samples
Stratified Random Sampling
divide cluster into grps that are representative of population. take an SRS of clusters and sample ALL individuals in those clusters
cluster random sample
randomly select starting # then select every nth individual
systematic random sample
types of bias
subjects voluntarily choose to be in the sample, and people usually volunteer only if they have strong opinions.
leaving parts of pop out of sample
individuals are chosen but don’t respond
respondents lie (illegal or unpopular question)
wording question in a leading way
Voluntary response bias
Undercoverage
Non-response
Response Bias
Question Wording Bias
individuals from pop we are choosing from
Sampling Frame
What can we conclude from an Observational Study?
When can use our sample to make inferences about the population?
Association or correlation, not cause and effect
When our sample is representative of population
a phenomenon where a person experiences improvement in their condition after taking an inert substance or receiving a fake treatment
placebo effect
What is the defining feature of an Experiment? Why is it important?
Impose treatments
We can finally infer cause and effect
4 principles of experimental design
also draw the outline of an experiment
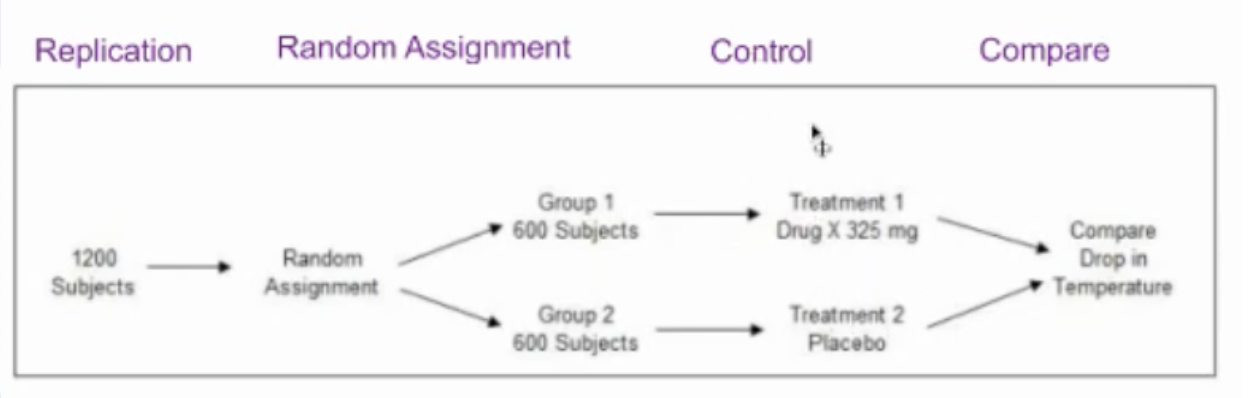
What is required for replication?
Larger samples
Separate similar subjects into blocks, then randomly assign from each block
block design
What is the goal of Random Assignment?
What is the goal of Random selection?
in experiments, All variables split approx 50/50 → similar treatment grps
in observational studies, sample is representative of population so we can infer up to pop
If difference in response variables is larger than we’d expect based on random chance
Statistically Significant
Match similar subjects ahead of time randomly assign one to each treatment (eg. twins, left/right body part). It maximizes the similarity between treatment groups: more precise results.
Matched Pairs design
To be blind in a study means the _____ don't know which treatment they are receiving, while the researchers do. (or particpants know but researchers don’t) To be double-blind means that neither the ______ nor the _____ know who is getting which treatment
participants, participants and researchers
Vocabulary for experiments
What you are experimenting on
the explanatory variables
the choices you have for each factor
the combinations you will test
Experimental units:
factors
levels
treatments
Random sampling _____ involves selecting an item from a population, recording it, and returning it before the next selection, allowing for the possibility of selecting the same item multiple times.
In contrast, Random sampling ______ means an item is not returned to the population after selection, so each item can only be selected once.
with replacement, without replacement
Lurking vs confounding variables
______: Could BOTH the explanatory and response variables be caused by the SAME third factor?
______: Are there TWO variables whose effects are so mixed that I can’t tell which one caused the response?
lurking
confounding