BIOL2200: Final Lab Practical, Office Hours Q&A
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
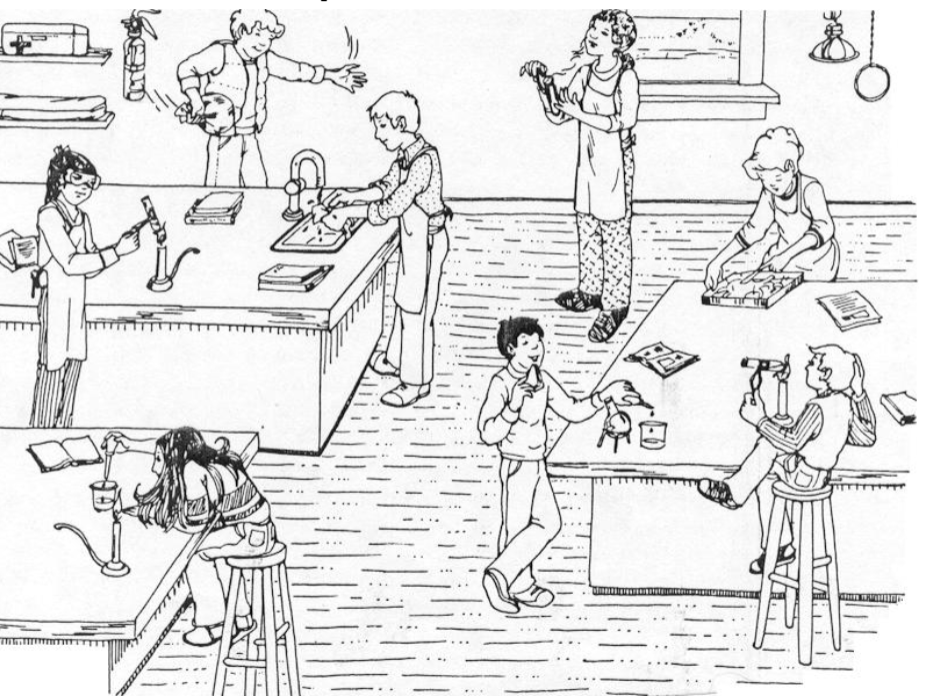
What violations of lab safety might appear in an image?
No goggles, no lab coat, loose hair, eating/drinking, open flame, playing sports, etc
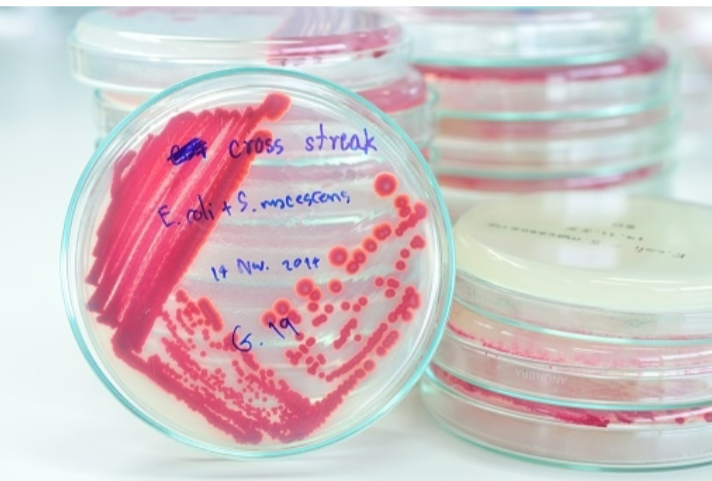
Where do used agar plates and test tubes go after incubation?
Biohazard bucket and biohazard rack
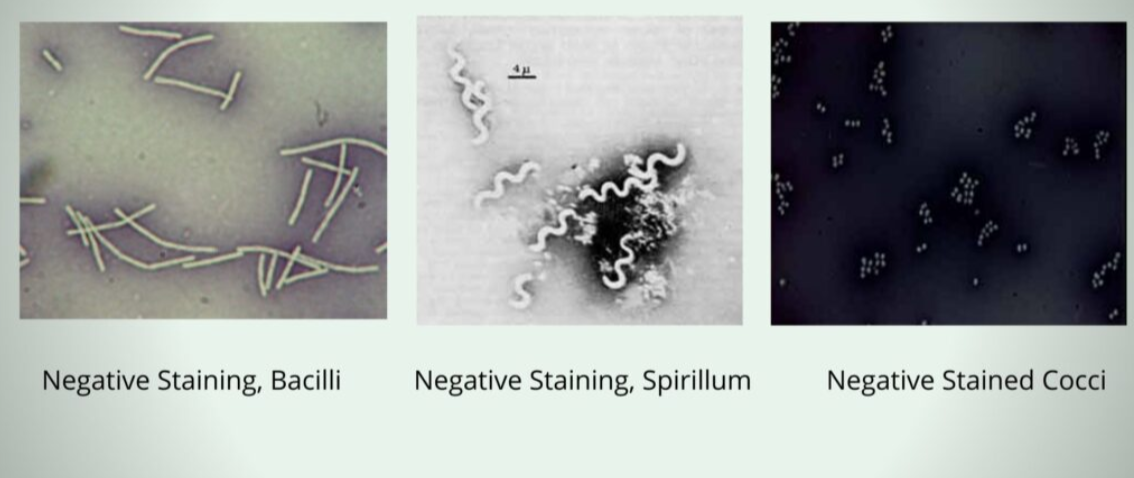
Where are negative stain slides disposed of?
Bleach bath (since microbes are still alive; not heat-fixed).
What kind of stain does not require heat fixing?
Negative stain.
What kind of stain does require heat fixing?
Positive stain.
What are stains used in negative staining — acidic or basic?
Acidic stains
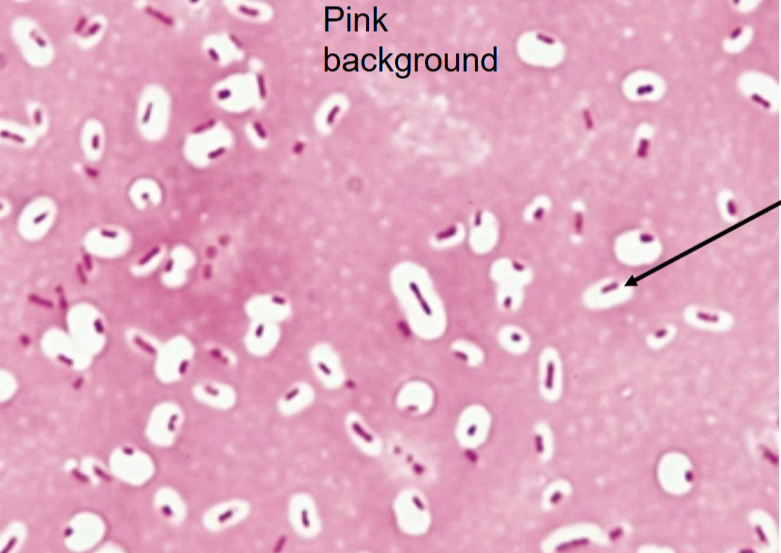
What structure is highlighted in a capsule stain?
Capsule — clear halo around the cell.

What structure is shown in the endospore stain?
Green endospore; red vegetative cell.

Possible genera that form endospores?
Bacillus and Clostridium (e.g., B. subtilis, C. diff).
Identify: Broth, slant, deep — what are they used for?
Broth = growth/turbidity; Slant = transport/storage; Deep = motility or O₂ requirements.
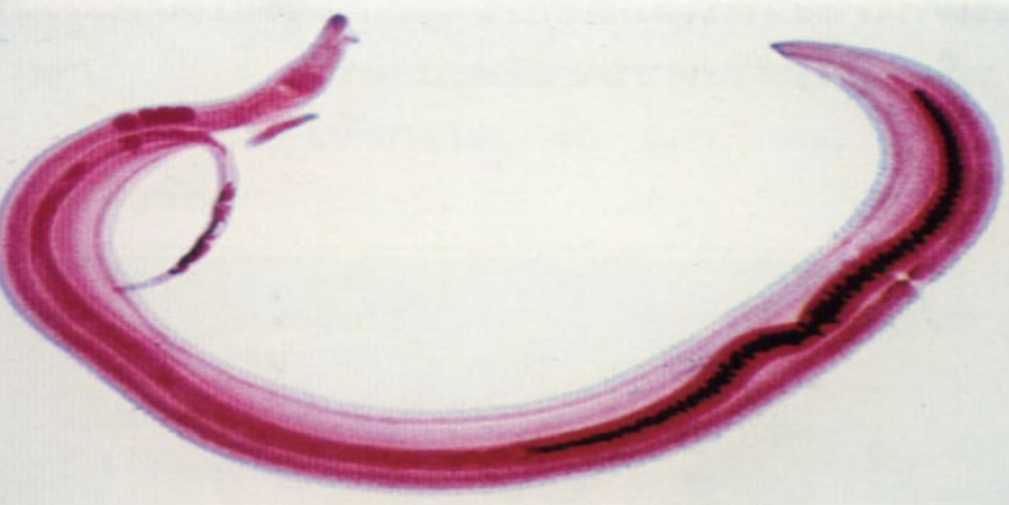
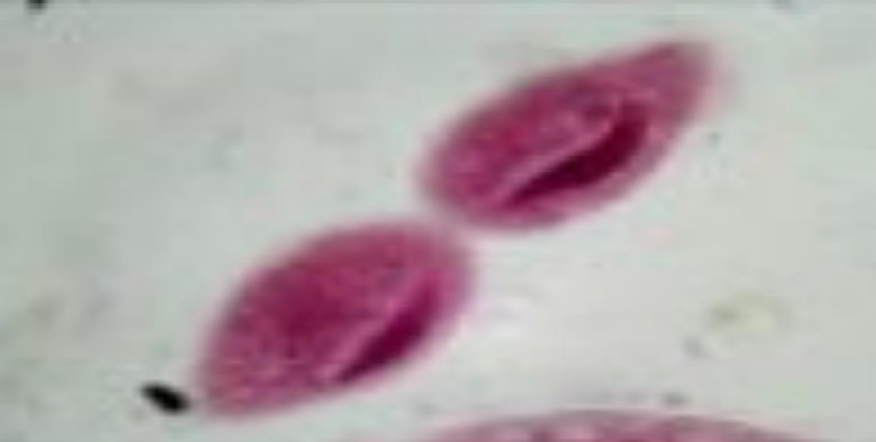
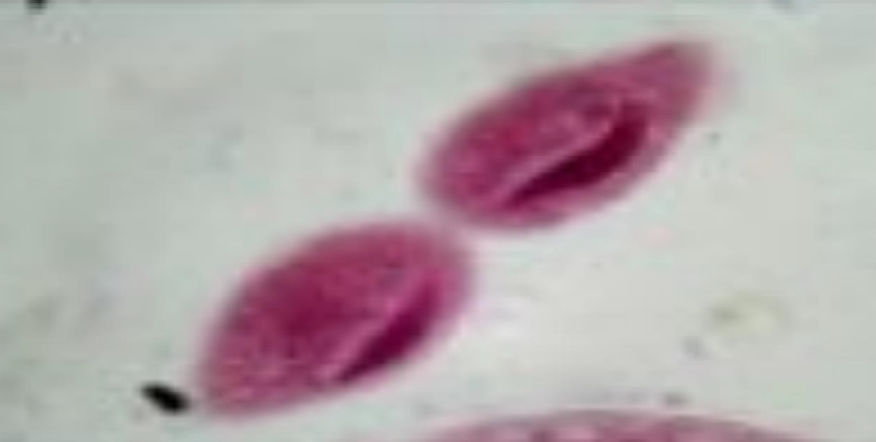
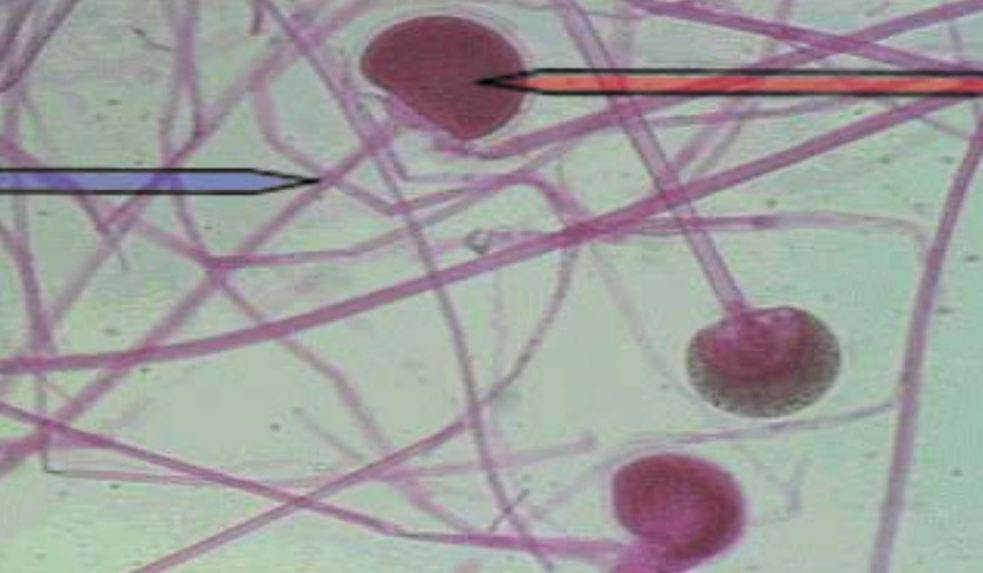
What is the name of this organism?
Schistosoma mansoni
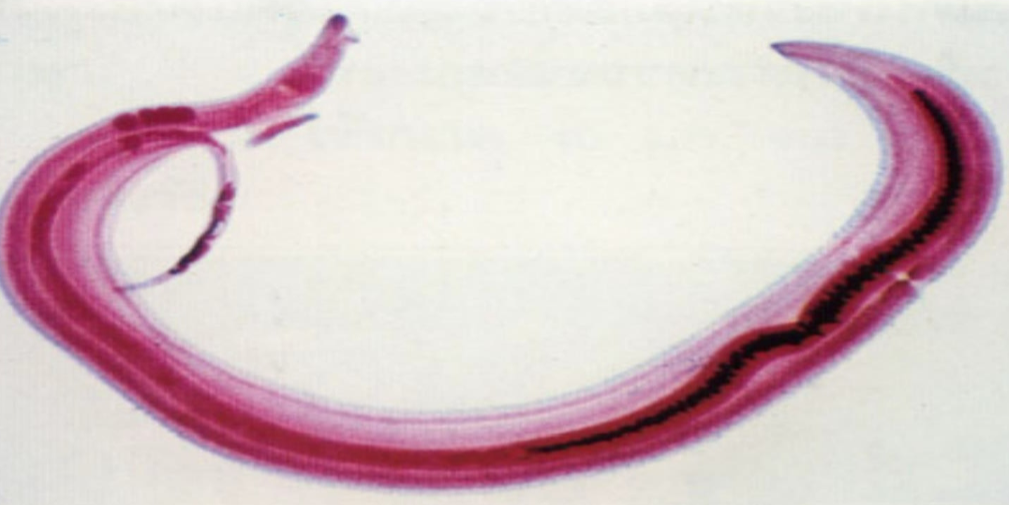
Schistosoma mansoni —
What is it?
What category does it belong to?
What is it’s sexual status?
Blood fluke; trematode; dioecious (male/female separate live in same body).
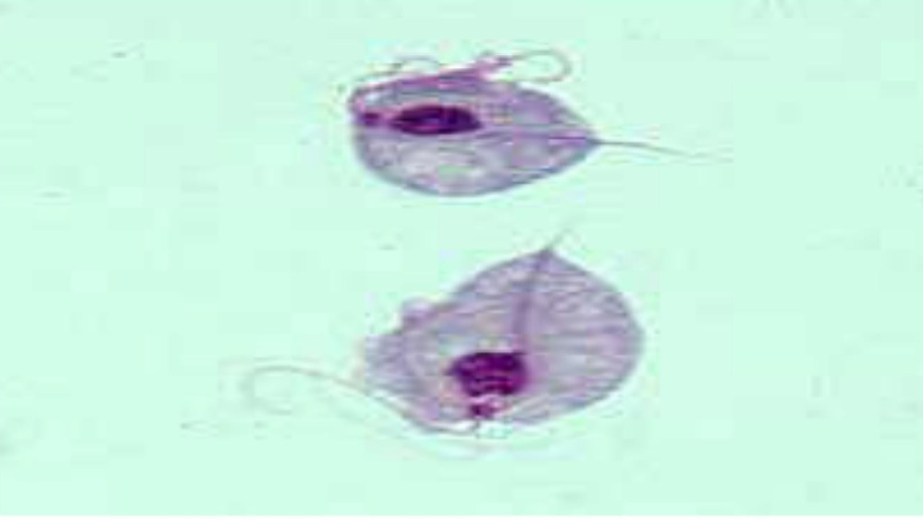
What is the name of this organism?
Trichomonas vaginalis

Trichomonas vaginalis —
What disease does it cause?
What is it’s method of motility?
What phylum does it belong to?
Causes vaginitis; moves via flagella; phylum: Archaezoa
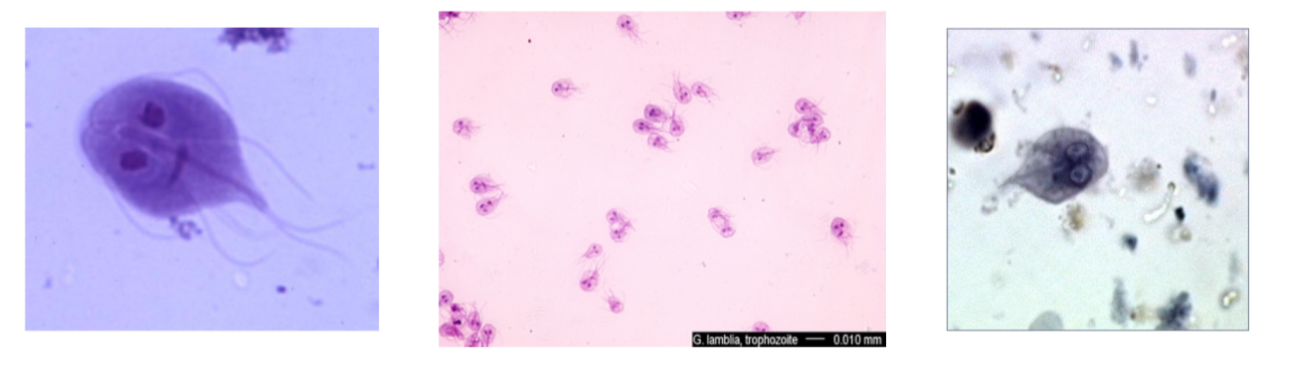
What is the name of this organism?
Giardia lamblia
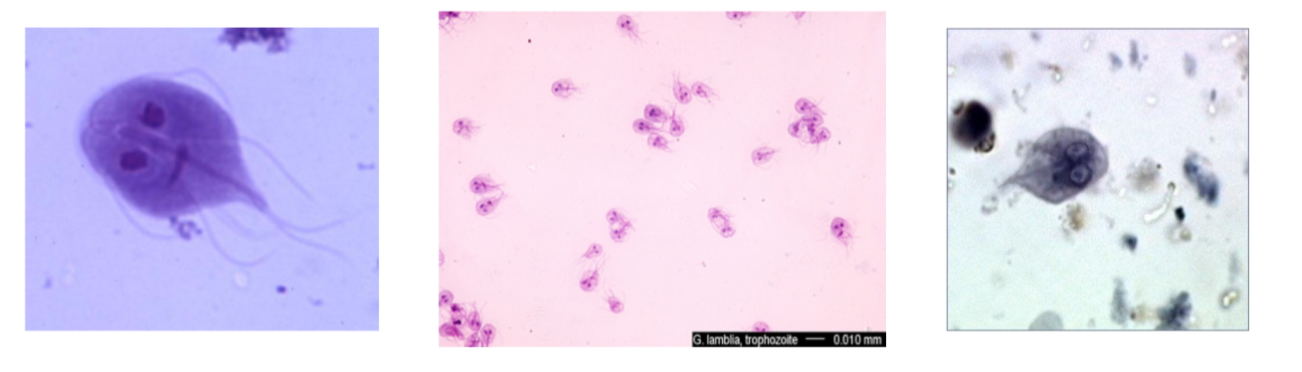
Giardia lamblia —
What disease does it cause?
What is it’s method of motility?
What phylum does it belong to?
Severe diarrhea
Move via flagella (visible)
Archaezoa
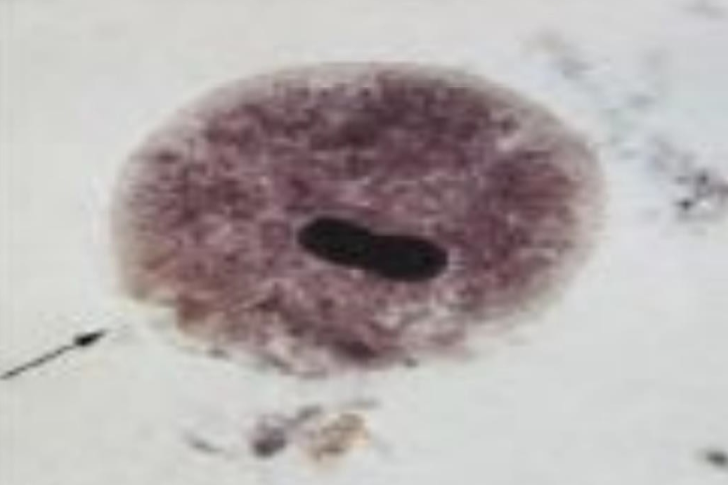
What is the name of this organism?
Balantidium coli
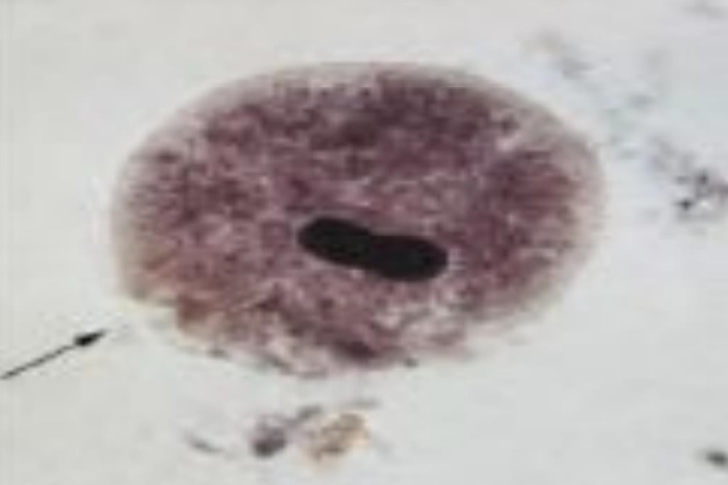
Balantidium coli —
What are it’s key features?
What disease does it cause?
What is it’s method of motility?
What phylum does it belong to?
Bean/Bar/Kidney-bean nucleus
Causes severe diarrhea
Move via cilia
Ciliata Phylum
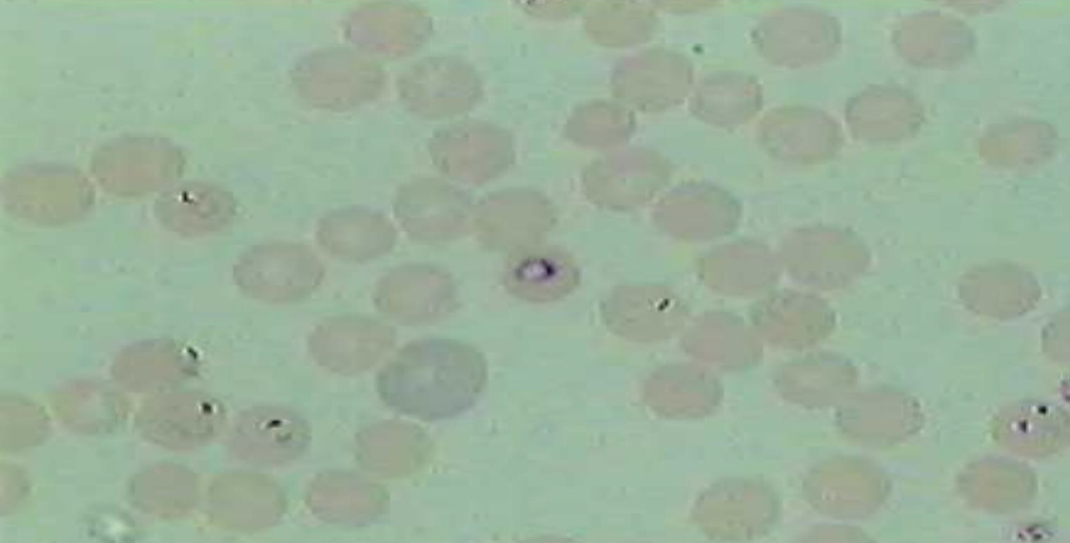
What is the name of this microbe?
Plasmodium spp.
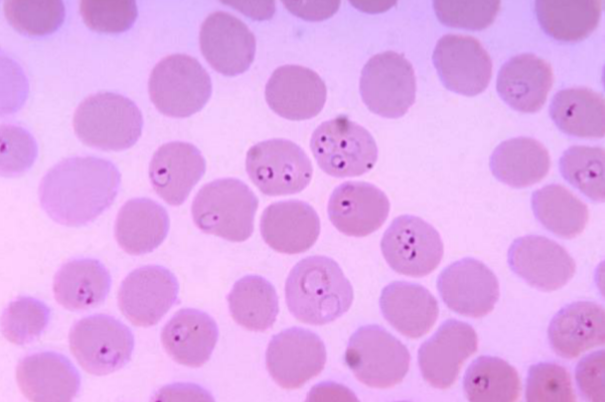
Plasmodium —
What disease does it cause?
How is it transmitted?
What is it’s method of motility?
What phylum does it belong to?
Causes malaria;
Transmitted by Anopheles mosquito
No Motility (Apicomplexa)
What is the name of this organism?
Paramecium
Paramecium —
What kind of reproduction is going on here?
Is this activity sexual OR asexual?
What is it’s method of motility?
Binary fission (asexual) if they’re facing towards each other
Conjugation (sexual) if they’re next to each other
Cilia for motility
Fluke vs Tapeworm reproductive status?
Fluke = monoecious (one organism, both sexes)
Tapeworm = monoecious too.
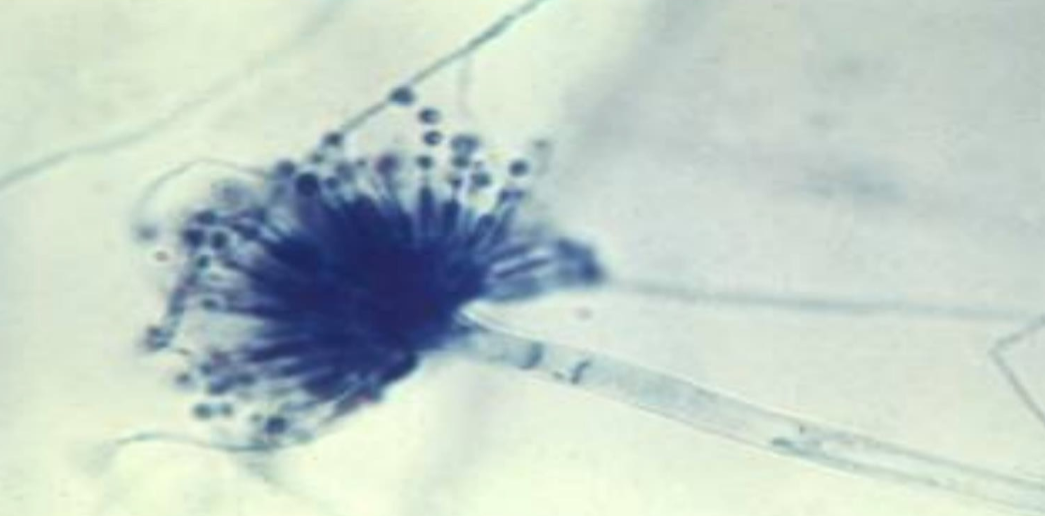
Aspergillus —
What is it’s spore structure name?
Conidiospores - Conidia (finger-like) - asexual

What is the genus name of this organism?
What name is given to this spore-bearing structure?
Aspergillus
Conidiospores - Conidia

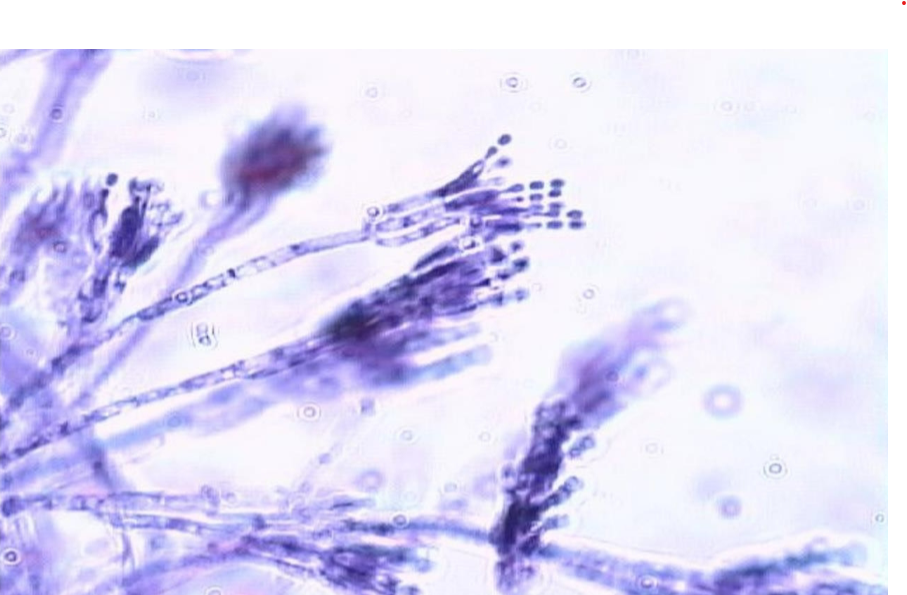
What is the genus name of this organism?
What name is given to this spore-bearing structure?
Rhizopus
Sporangium
Rhizopus —
What is it’s spore structure name?
Sporangium (enclosed capsule)
What is the genus name of this organism?
What name is given to this spore-bearing structure?
Penicillium
Conidiospores (Conidia)

Penicillium — spore structure name?
Conidia (same as Aspergillus).
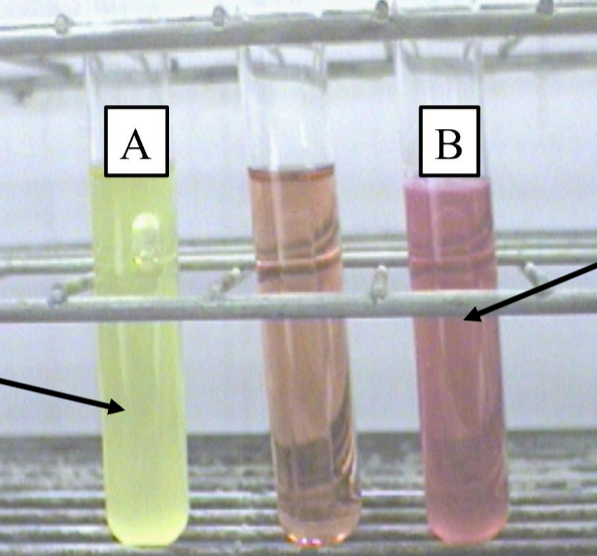
What is the name of the test with a Durham tube and yellow color?
Phenol Red test.
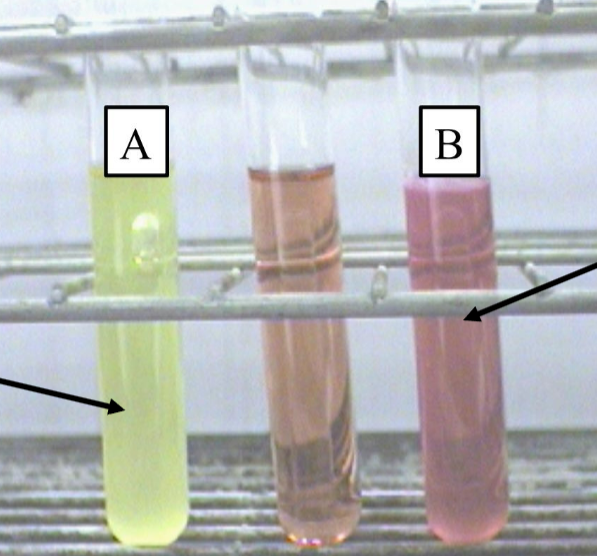
What does yellow color mean?
Acid production (positive fermentation).
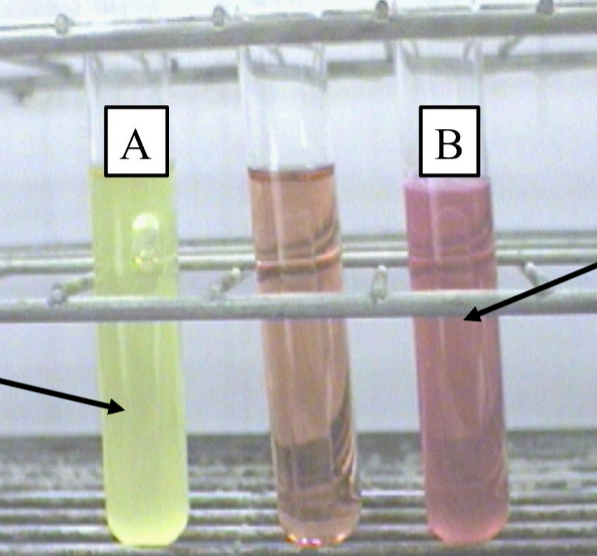
What is the Indicator used in phenol red test?
Phenol red (yellow = acid, pink = base).

What is the name of this test?
Indole Test
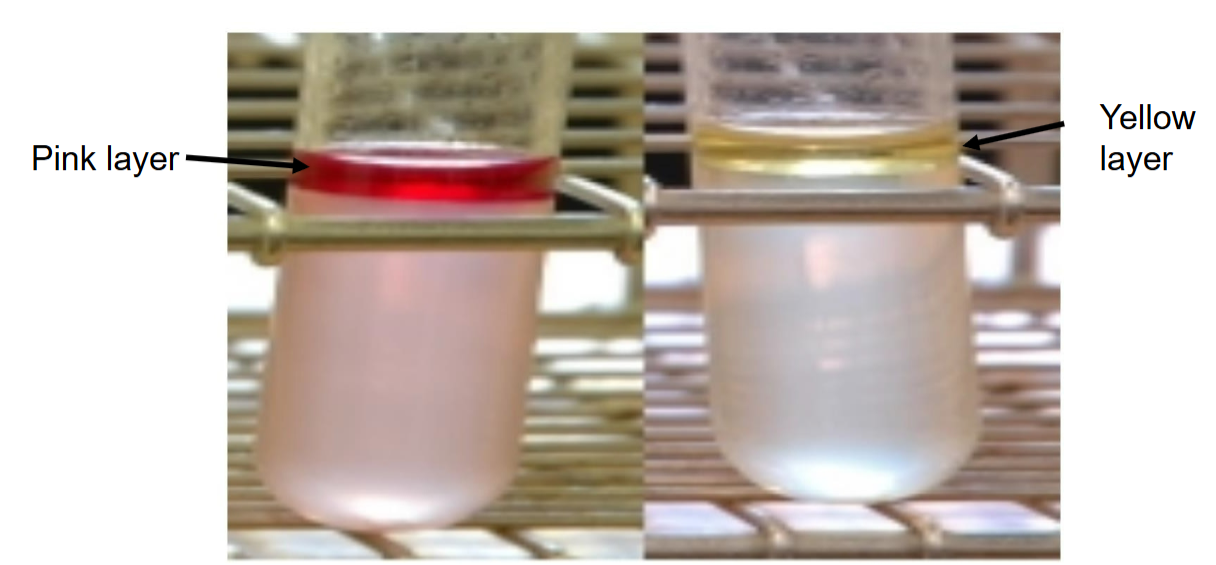
Indole Test —
What reagent is added to detect indole?
Which test tube is a positive reaction?
Is this test part of IMVIC?
Kovac’s reagent
Pink layer at top (indole produced from tryptophan).
Yes — Indole, Methyl Red, Voges-Proskauer, and Citrate

What is the name of this test?
Methyl Red (MR) Test

Methyl Red (MR) Test
Which test tube is positive?
What does a positive Methyl Red test mean?
Red
Mixed acid fermentation (pH drops; turns red).
What does a positive Voges-Proskauer test mean?
2,3-butanediol fermentation; red color after reagents
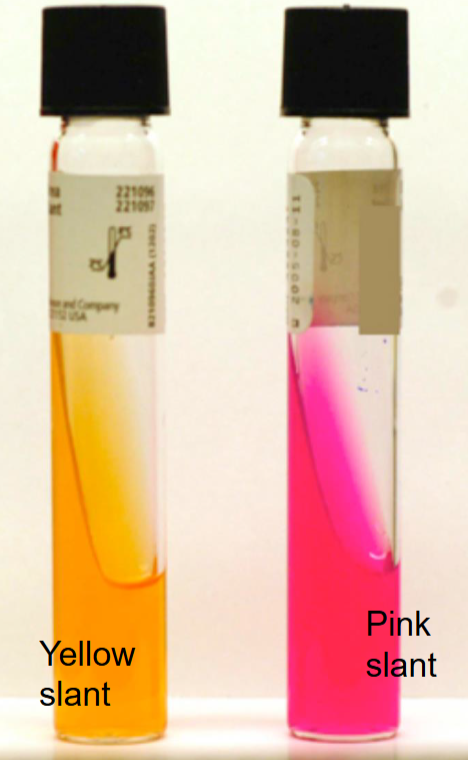
What is the name of this test?
Urea Agar (Urease) Test
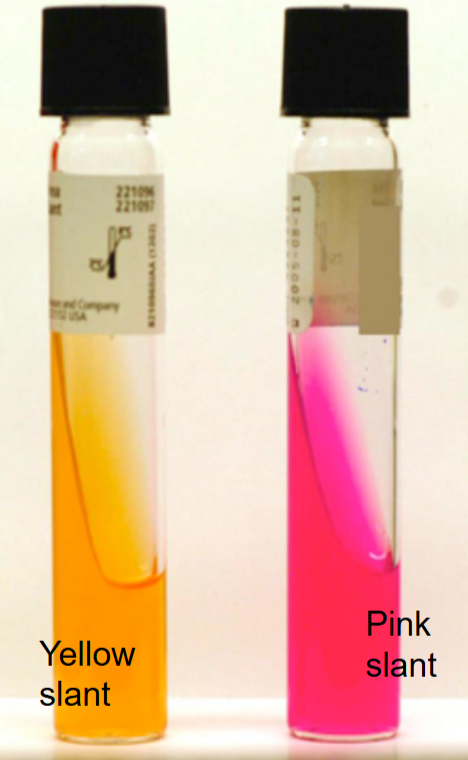
Urea Agar (Urease) Test
What is this test detecting for?
What is the indicator?
Which test tube shows a positive reaction?
Detects urease enzyme that breaks down urea → ammonia + CO₂ (alkaline).
Indicator: Phenol red.
Positive: Pink (alkaline, urease present) b/c ammonia produced, base increases pH
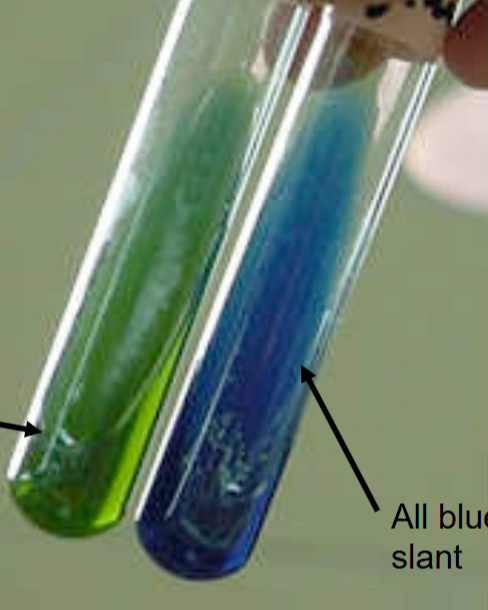

What is the name of this test?
Citrate Test
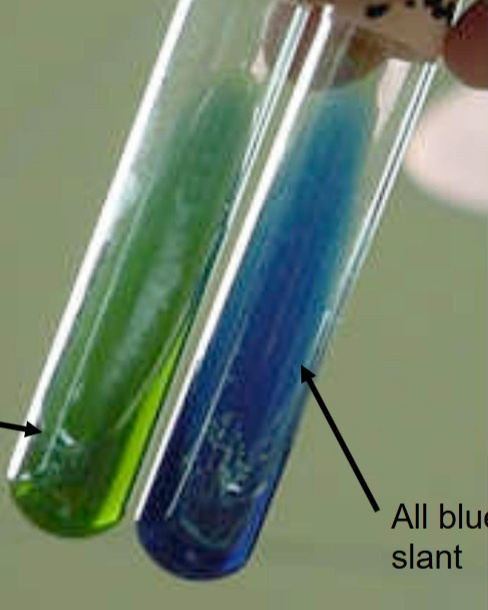

Citrate Test
What indicator is used in this test?
What does a positive result look like?
Bromothymol blue.
Blue slant → citrate used; ammonia hydroxide (alkaline byproducts) produced → raises pH.
What is the name of this test?
Catalase Test
Catalase Test
What enzyme does it detect and causing the bubbles to form?
What is the Reagent used in this reaction?
What does a positive reaction look like?
What is an example of Catalase positive + Catalase negative?
Which are probably Streptococcus?
Detects catalase enzyme that breaks down H₂O₂ → H₂O + O₂
3% hydrogen peroxide.
Positive: Bubbling (oxygen released).
Catalase-positive: Staphylococcus.
Catalase-negative: Streptococcus.
Negative: no bubble formation
What does blackening of media indicate?
Positive; sulfur compound formation.
What indicates a positive DNA test?
Clearing around streak = DNA hydrolysis
Blood Agar Plate (BAP): Green discoloration on BAP indicates what type of hemolysis?
Alpha hemolysis (partial RBC breakdown).
Complete clearing around colonies?
Beta hemolysis.
EMB Plate (Eosin Methylene Blue): What does metallic green sheen indicate?
E. coli — strong lactose fermenter.
What is EMB plate selective/differential for?
Selective for Gram-negative; differential for lactose fermentation.
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA): Selective and differential ingredients?
Selective = 7.5% NaCl; Differential = Mannitol & Phenol Red
Yellow result on MSA means?
Acid from mannitol fermentation; likely Staph aureus.
Red result but growth means?
Staph epidermidis (salt tolerant, non-mannitol fermenter).
TSI (Triple Sugar Iron) Test
What does red slant/yellow butt mean?
Only glucose fermented.
TSI (Triple Sugar Iron) Test
Yellow/yellow?
All sugars fermented
TSI (Triple Sugar Iron) Test
Red/red?
No fermentation; amino acid deamination
Kirby-Bauer Test
What agar is used?
Mueller-Hinton agar.
Kirby-Bauer Test
How to interpret results?
Measure zone of inhibition → compare to chart for resistant/susceptible
Gel Electrophoresis
DNA charge and migration direction?
DNA is negatively charged; moves toward positive electrode
What differentiates DNA bands on a gel?
Size — smaller fragments move farther.
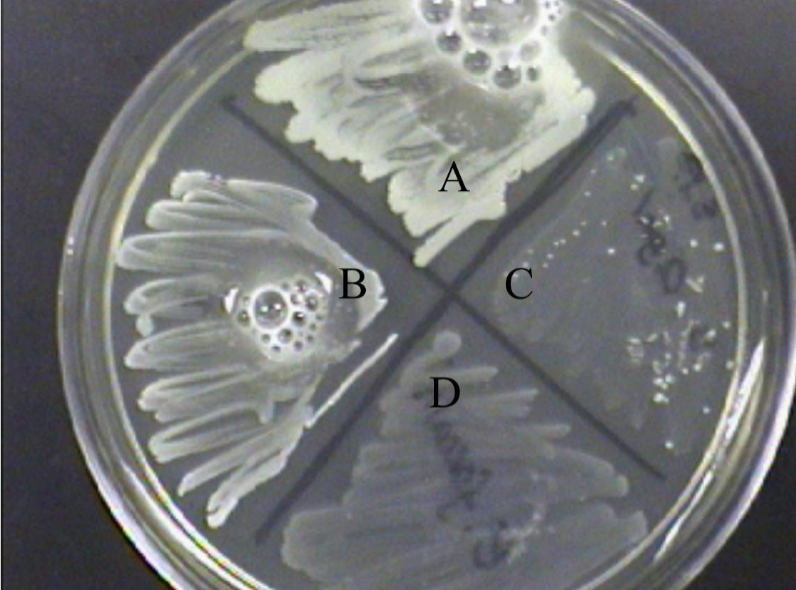
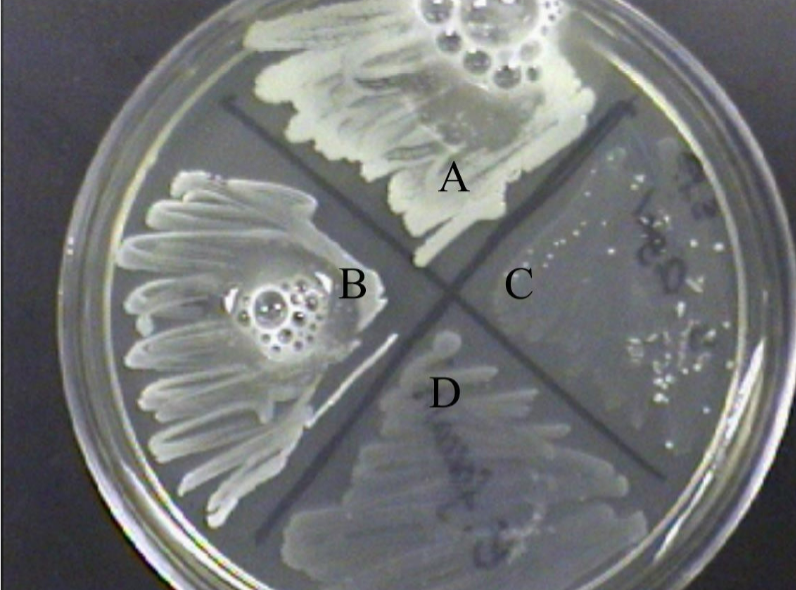
What is the streak plate method used for?
Isolating pure colonies (not quantification).
What method is used to determine concentration?
Spread plate method.