UC A&P1 Hedderson - CH 3
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
true
T or F: Cells are responsible for all structural and functional properties of a living organism
true
T or F: understanding cells is important for understanding workings of the human body, mechanisms of disease, and rationale of therapy
Cells
____ are the simplest structural and functional unit of life
cell theory
The idea that all living things are composed of cells and that all cells come from other cells defines
true
T or F: Cells of all species exhibit biochemical similarities
200
about how many types of cells are found in the human body?
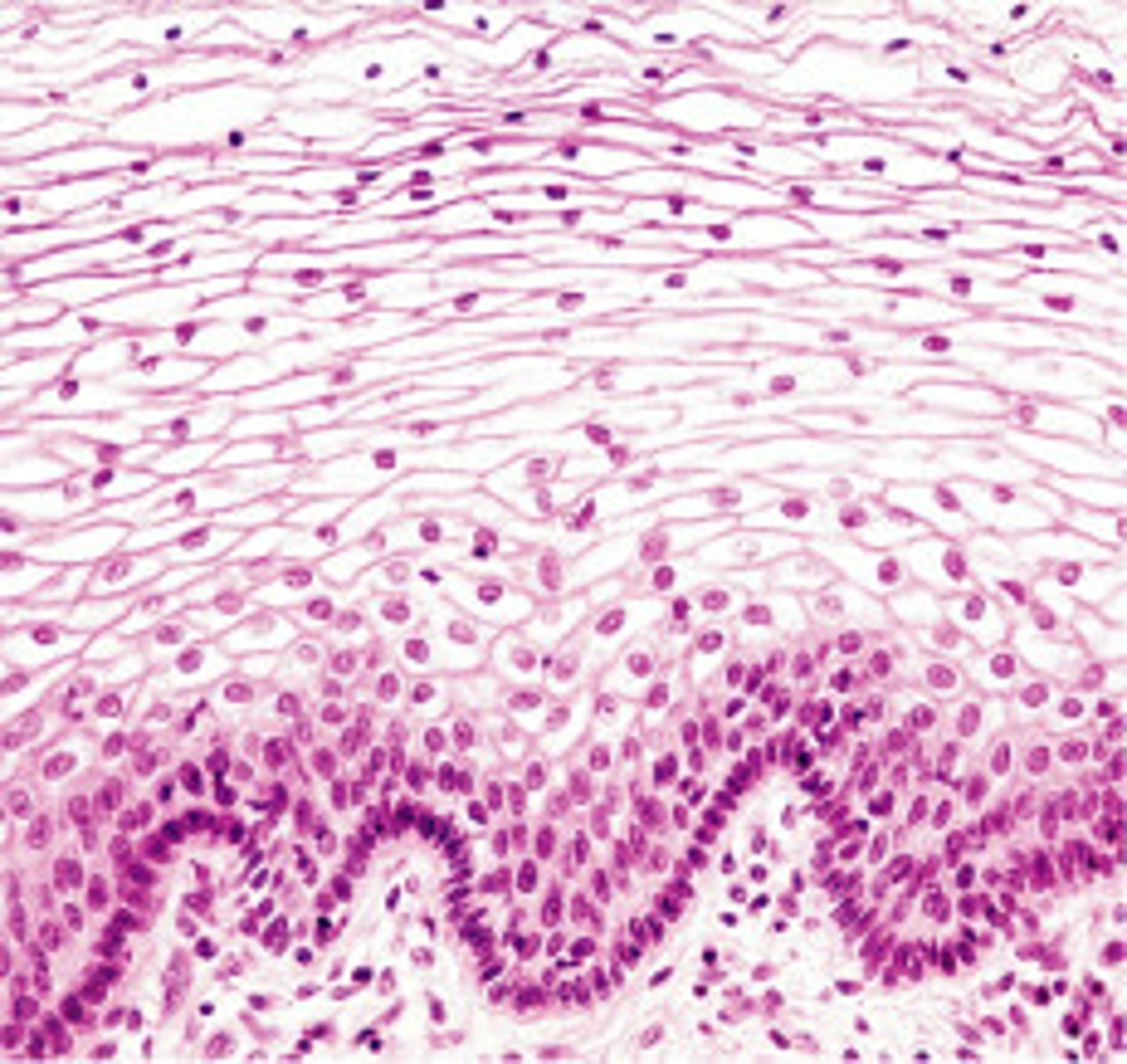
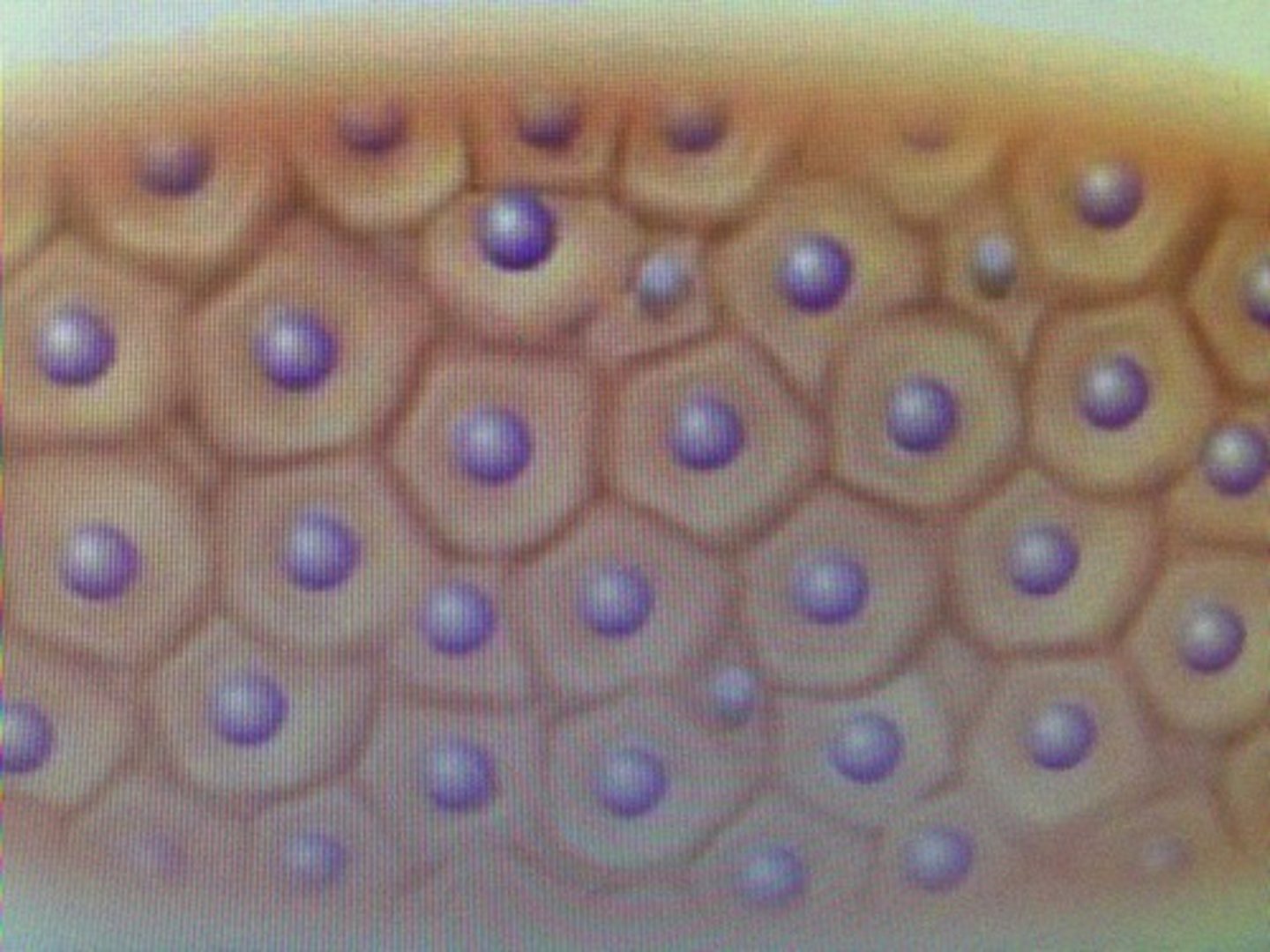
squamous
(type of cell) thin, flat, scaly
cuboidal
(type of cell) square looking
Columnar
(type of cell) taller than wide

polygonal
(type of cell) irregularly angular shapes, multiple sides
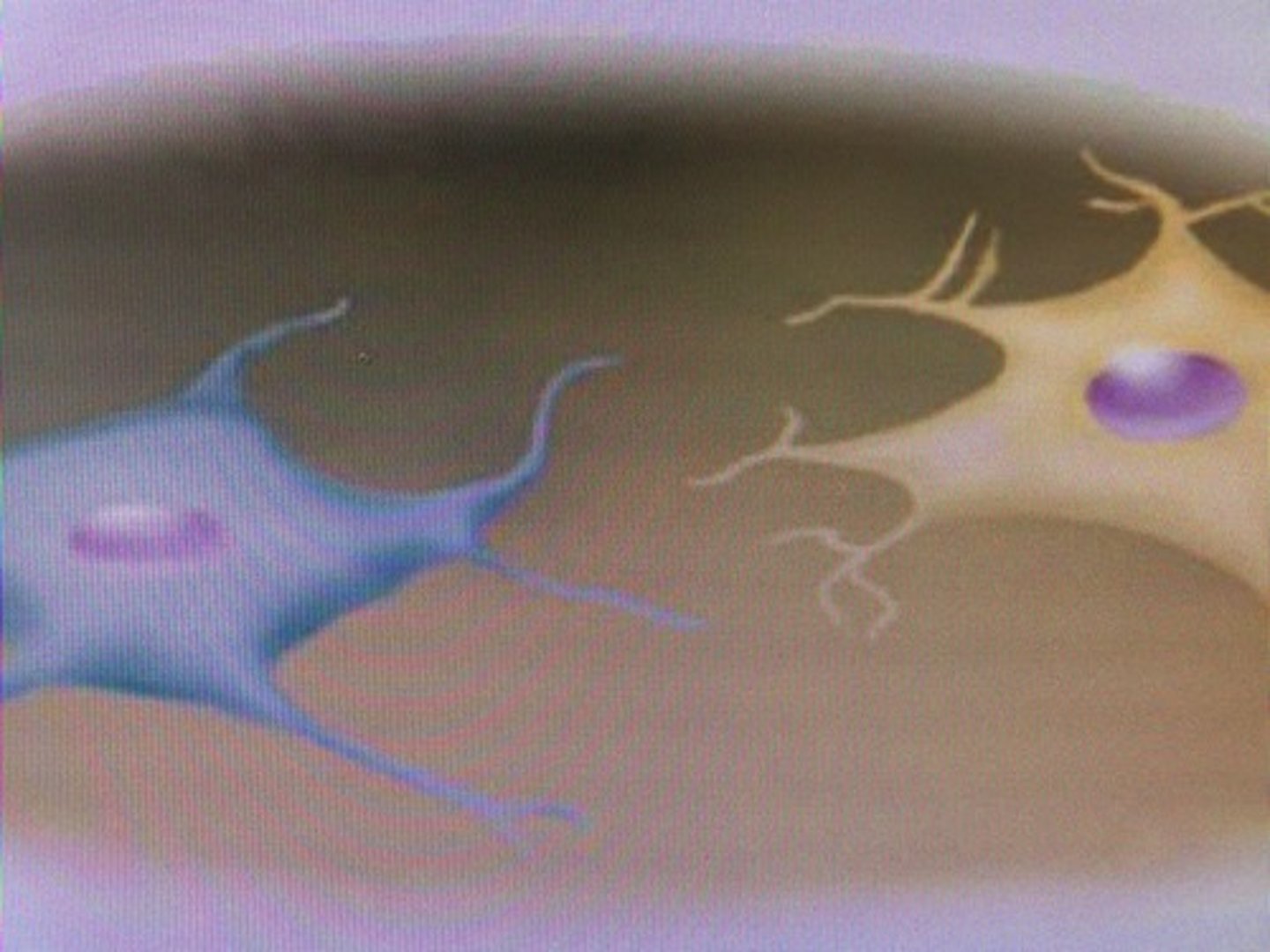
stellate
(type of cell) star-like
spheroid to ovoid
(type of cell) round to oval
discoidal
(type of cell) disc-shaped
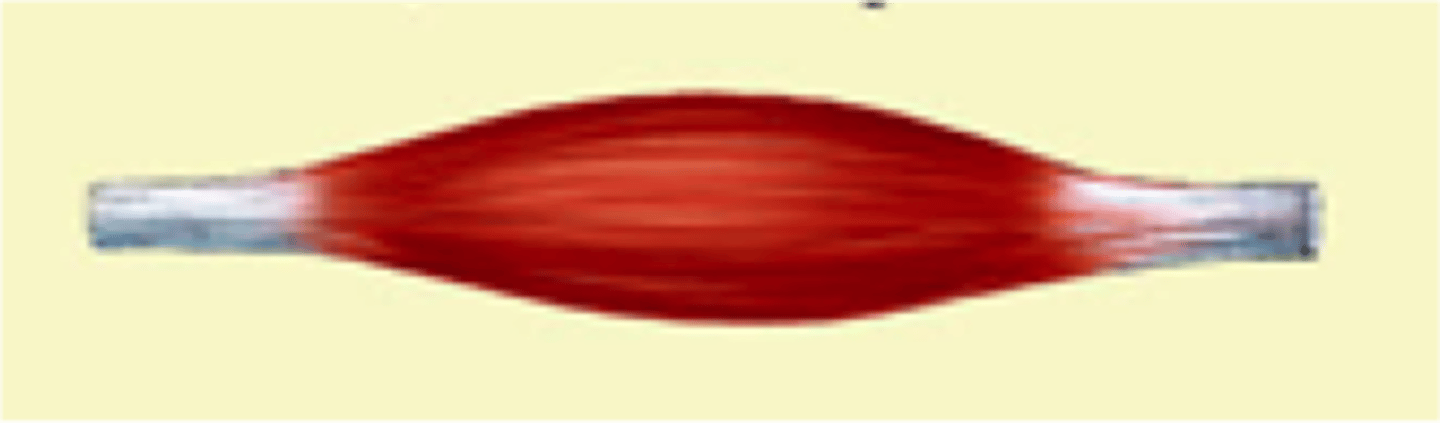
fusiform
(type of cell) thick in the middle, tapered towards the ends

fibrous
(type of cell) thread-like
plasma membrane
border of the cell; surrounds cell, defines boundaries, made of proteins and lipids
cytoplasm
A cytosol fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended, and where the cytoskeleton and inclusions are found.
cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
extracellular fluid
Fluid outside of cells includes tissue (interstitial) fluid
false
T or F: the plasma membrane has only an intracellular face
function of plasma membrane
-defines cell boundaries
-governs interactions with other cells
- controls passage of materials in and out of cell
lipids
98% of the plasma membrane molecules are ____
75%
percentage of membrane lipids that are phospholipids
Amphipathic
phospholipids are ______, meaning that they have a hydrophilic head and a portion of hydrophobic tails
20%
percentage of plasma membrane lipids that are cholesterol
cholesterol
_____ holds phospholipids still and can stiffen the plasma membrane
5%
percentage of plasma membrane lipids that are glycolipids
glycolipids
phospholipids with short carbohydrate chains on extracellular face
glycocalyx
the carbohydrate coating on a cell's surface
integral, peripheral
membrane proteins consist of ____ proteins and _____ proteins
integral
____ proteins are those that penetrate the membrane and pass completely through
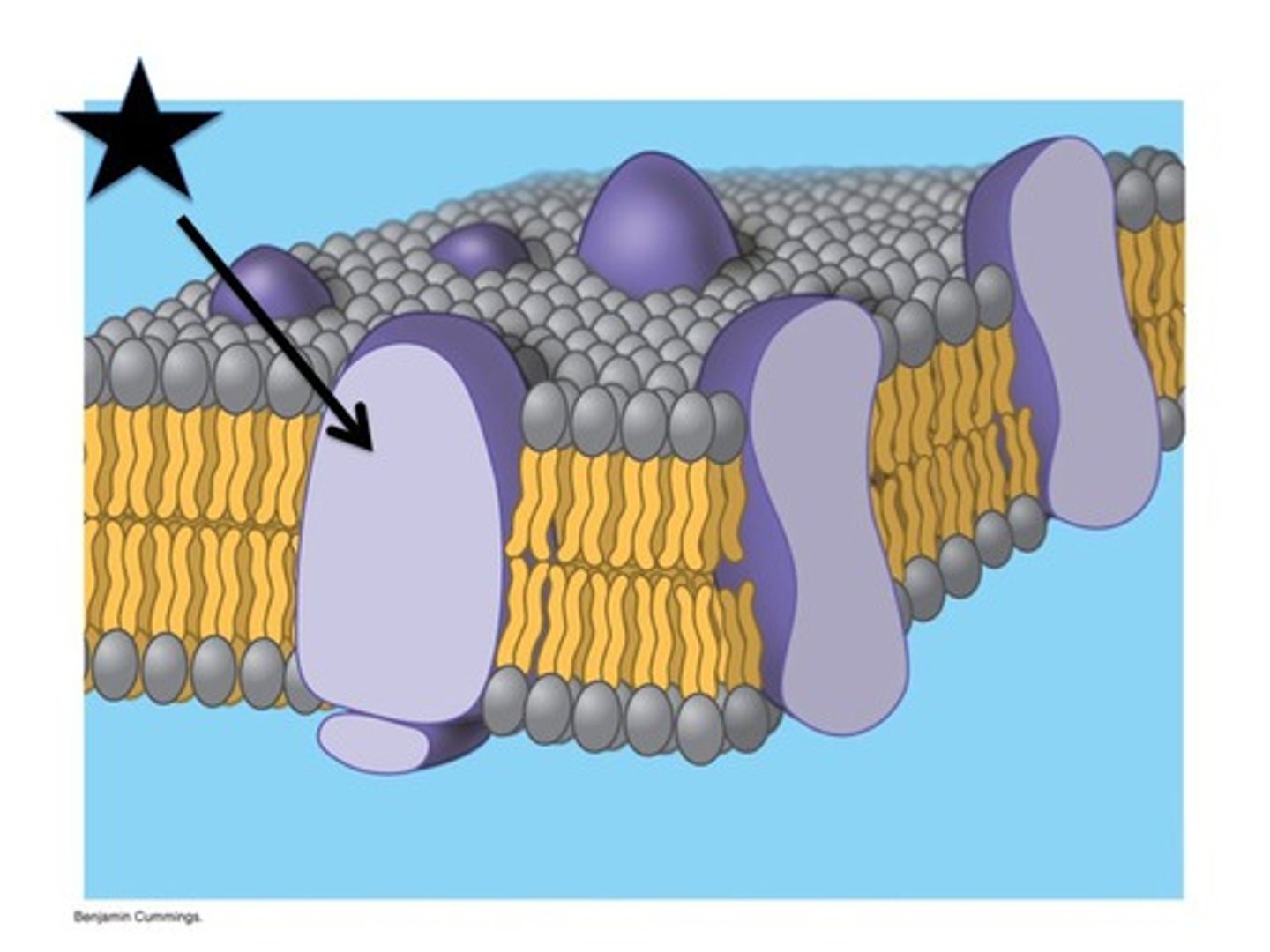
amphipathic
integral proteins are ______ since they have hydrophilic regions that contact cytoplasm and extracellular fluid, and a hydrophobic region that passes through the lipid membrane
true
T or F: some integral proteins drift in the membrane while others are anchored to the cytoskeleton
peripheral
_____ proteins adhere to one face of the plasma membrane and are usually tethered to the cytoskeleton
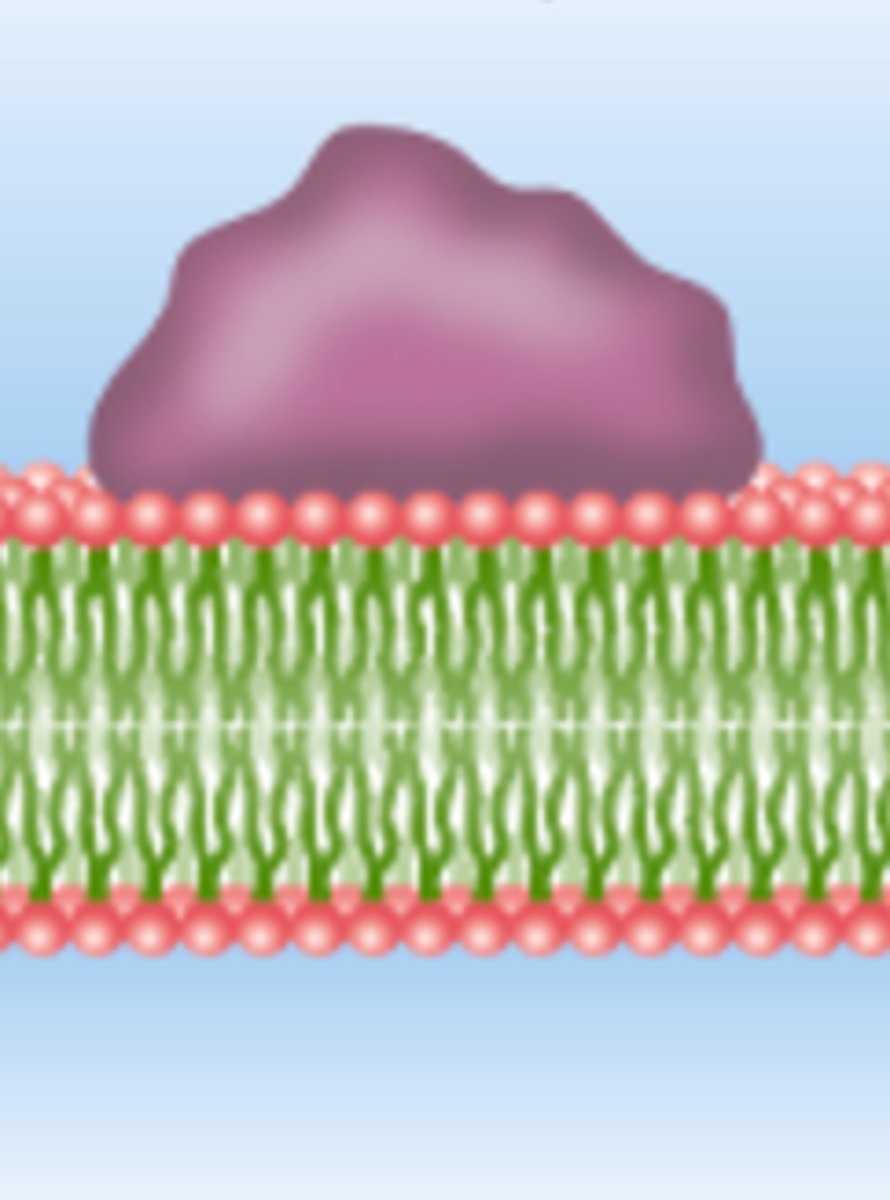
membrane proteins
functions of ____ include:
- receptors, second-messenger systems, enzymes, channels, carriers, cell-identity markers, cell-adhesion molecules
receptor
(membrane protein) binds chemical signals
second messenger systems
(membrane protein) communicate within the cell receiving chemical message
enzymes
(membrane protein) catalyze reactions including digestion of molecules
enzymes
responsible for the production of secondary messenger systems
channel proteins
(membrane protein) that allow hydrophilic solutes and water to pass through the membrane, some are gated and some are always open
ligand-gated
_____ channels respond to chemical messengers
voltage-gated
____ channels open or close in response to changes in membrane potential / charge changes
mechanically gated
____ channels that respond to physical stress on the cell and receptors
nerve, muscle
channel proteins are crucial to ___ and ___ function
carrier
___ proteins bind solutes and transfer them across membranes
pumps
carrier proteins that consume ATP
cell-identity markers
glycoproteins acting as identification tags
cell-adhesion molecules
mechanically link cell to extracellular material
cAMP
main secondary messenger
G
the ____ protein relays a signal to adenylate cyclase which converts ATP to cAMP
cAMP
____ activates cytoplasmic kinases
phosphate groups
kinases add _______ to other enzymes to turn some on and some off
Glycocalyx
carbohydrate coating on cell surface
glycocalyx functions
Functions:
- protection, cell adhesion, immunity to infection, fertilization, defense against cancer, embryonic development, transplant compatibility
microvilli
extensions of the plasma membrane that serve primarily to increase a cell's surface area by 15-40x
absorption
the best developed microvilli specialized in ___
actin filaments
protein fibers of microvilli that are tugged toward the center of the cell to milk absorbed contents into the cell
cilia
Hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane
function of cilia
to act as antenna for monitoring nearby conditions, help with balance in inner ear, and light detection in retina
sensory cells of the nose
multiple nonmotile cilia are found on the _____
ciliopathies
defects in structure and function of cilia
motile cilia
cilia found in respiratory tract, uterine tubes, ventricles of brain, ducts of tests
motile cilia
usually 50-200 of these on each cell that help sweep materials across cell surface
axoneme
core of motile cilium
axoneme structure
2 central microtubules surrounded by a ring of 9 pairs that anchor cilium to the cell as part of the basal body
dynein arms
responsible for the bending of cilium that uses ATP as energy
cyctic fibrosis
hereditary disease in which cells make chloride pumps but fail to install them in the plasma membrane, thick mucus plus pancreatic ducts and respiratory tract
chloride pumps
responsible for creating adequate saline layers on the cells surface for cilia to function correctly
30
what is life expectancy for cystic fibrosis?
incomplete digestion of nutrients and absorption of oxygen, chronic respiratory infections
what is the result of thick mucus plugs on pancreatic ducts and respiratory tract in individual's with cystic fibrosis?
flagella
whiplike tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement
flagella
tail of sperm is a _____
false
T or F: cilia are much longer than flagella
true
T or F: flagella are stiffened by coarse fibers that support the tail
true
T or F: flagella movement has no power stroke, unlike cilia
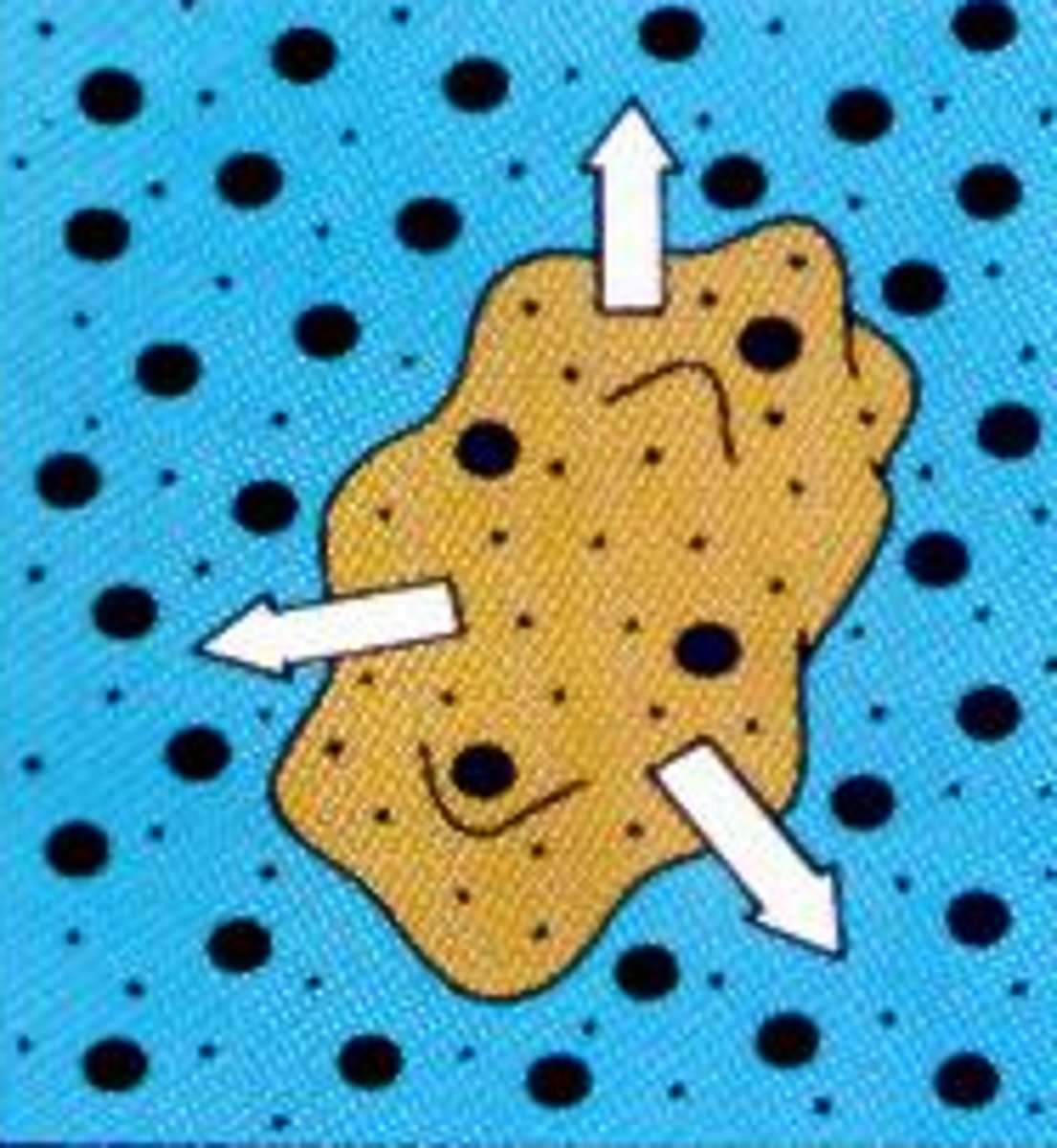
pseudopods
continually changing extensions of the cell that vary in size and shape, utilized in cellular locomotion and capturing foreign particles
selective permeability
A property of a plasma membrane that allows some substances to cross more easily than others
Passive
____ mechanisms require no ATP since the random motion of particles provides necessary energy
filtration, diffusion, osmosis
examples of passive membrane mechanisms
active
_____ mechanisms require active transport and vesicular transport and consume ATP for membrane transport
carrier-mediated
_____ mechanisms use a membrane protein to transport substances across a membrane
filtration
particles are driven through membrane by physical pressure
true
T or F: filtration of water and small solutes through gaps in capillary walls allows for the delivery of water and nutrients to tissues and removes waste from capillaries in the kidneys
simple diffusion
net movement of particles from place of high concentration to place of lower concentration
down
substances diffuse ___ their concentration gradient
increase
_______ diffusion rate through a membrane due to:
- increased temp/increase motion of particles
- decreased MW
- bigger concentration difference
- more membrane surface area
- more permeability
osmosis
net flow of water through a selectively permeable membrane from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration
diarrhea, constipation, edema
Name three symptoms of osmosis imbalance.
aquaporins
channel proteins that facilitate the passage of water
osmotic pressure
hydrostatic pressure required to stop osmosis
false
T or F: the osmotic pressure decreases as the amount of nonpermeating solutes rises
reverse osmosis
process of applying mechanical pressure to overide osmotic pressure
Tonicity
The ability of a solution surrounding a cell to affect the cells fluid volume and pressure in the cell
nonpermeating solutes
Tonicity depends on the concentration of _______
hypotonic solution
Solute concentration is less than that inside the cell; cell gains water
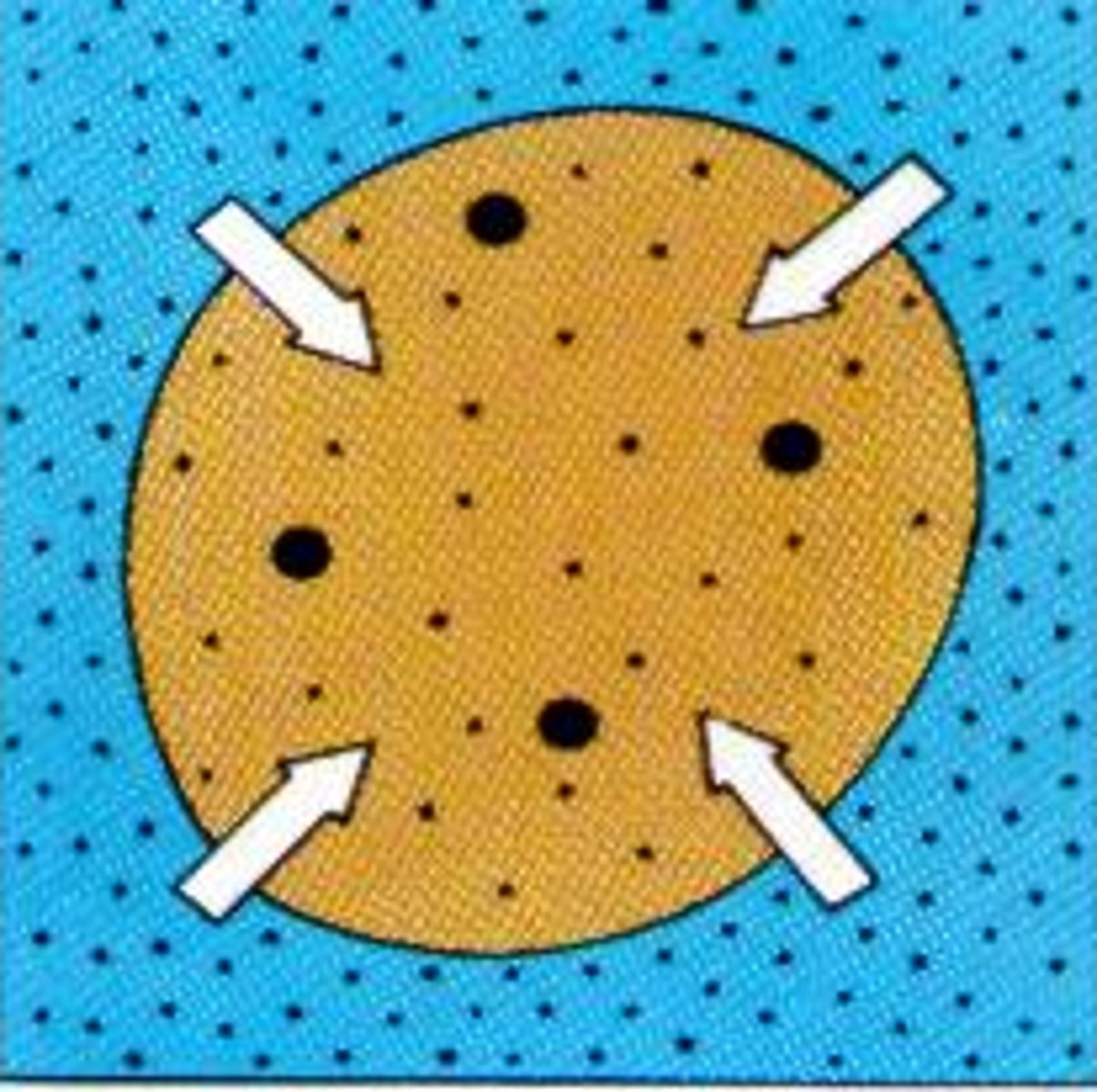
hypertonic solution
Solute concentration is greater than that inside the cell; cell loses water

isotonic solution
a solution whose solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside a cell; no cell change
False
T or F: when a solute is released from the carrier protein on the opposite side of the membrane, the solute is changed
true
T or F: transport proteins are specific for particular solutes where the solute binds to a receptor site on a carrier protein
increases
as the solute concentration increases, the rate of transport _____ but only to a certain point