Geology Quiz Questions
1/403
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
404 Terms
one that can satisfy its needs without jeopardizing the needs of future generations
What is a sustainable society?
Birth rate - death rate
What is the formula for population growth rate?
Japan
Which country has an essentially stable population?
The Sun
Which of the following is NOT a component of the hydrosphere?
in steady state
If transfers of energy and matter into and out of an open system are about the same, the system is said to be:
all living organisms on Earth
What is the biosphere made of?
by measuring the number of species, or groups of specie
How is biodiversity measured?
allow only energy (not mass) to move in and out of the system
Closed systems:
Solar Power
What is an example of a renewable energy resource?
it explains a large set of observations and relationships that have been independently verified by many researchers
What is true about a scientific theory?
is a tentative explanation consistent with what researchers know about a situation
What is true about a scientific hypothesis?
Geosphere
Rock and sediment belong to which component of the Earth System?
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
Which is the correct order of the planets in our solar system, going from closest to the sun to farthest from the sun?
Nebula
A vast cloud of dust and gases that contracted approximately 4.5 billion years ago to form our solar system.
Crust, mantle, outer core, inner core
Which is the correct order of Earth's compositional layers, going from the surface (where we mostly live) down into the interior of the planet.
Continental crust
Granite is a rock that is typical of the:
Oceanic crust
Basalt is a rock that is typical of the:
Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, and Thermosphere
Four distinct atmospheric layers are defined based on the vertical temperature distribution in the atmosphere. Going up from Earth's surface (the bottom of the atmosphere) to the upper atmosphere, these atmospheric layers are:
Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon
Excluding water, what are the top three most abundant gases in the atmosphere today, from most abundant to least abundant?
Oxygen
Which of the following gases was likely NOT a major part of Earth's early (or first) atmosphere?
Stratospheric ozone
It helps living organisms on Earth's surface by blocking most incoming ultraviolet radiation; this radiation can damage DNA in living tissue.
Hydrosphere
Which component of the Earth System includes the water in ice sheets, glaciers, rivers, lakes, underground, and in the oceans?
Water cycle
a cycle that describes how water moves among various reservoirs such as the oceans, the atmosphere, on land, and below land's surface, in groundwater
Ice sheets and glaciers
Where is most of Earth's fresh water located?
Fossils
Preserved worm burrows, preserved animal tracks, shells, dinosaur bones
sometime between 4.2 and 3.5 billion years ago
Approximately when did life on Earth begin?
Natural selection
the principle mechanism behind evolutionary change in the biosphere
Georges Cuvier
Who recognized that some vertebrate fossils represent the remains of organisms that no longer exist?
½
What is the ratio of parent to total atoms (P/T) when exactly one half-life has elapsed
1/16
What is the parent to total atoms (P/T) ratio when exactly 4 half lives have elapsed?
Cross-cutting
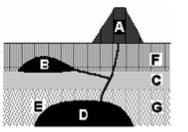
Which relative time principle assumes that rock unit D is younger than rock unit G?
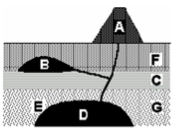
Superposition
Which relative time principle assumes that rock unit F is younger than rock unit C?
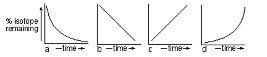
a
Which graph below (a-d) best illustrates the change in the proportion of unstable (parent) radioactive isotope with time?
65 million years ago
Approximately when did dinosaurs, exclusive of birds, become extinct?
The rock unit is younger than the inclusion
What must be true of a rock unit has an inclusion?
542 million years ago
Approximately when did large numbers of fossils first appear in the geologic record?
False
True or False: Relative dating involves estimating how many half lives of a given radioactive isotope have elapsed since a sample formed.
Their half-lives do not change over time - they are not sensitive to changes in environmental conditions
Why can radioactive elements be used to determine the ages of rocks?
True
True or False: The geologic time scale was originally developed using relative time principles and fossil correlation.
d
Which of the images below best represents the boundary between the Nazca and South American plates, on the western side of South America?
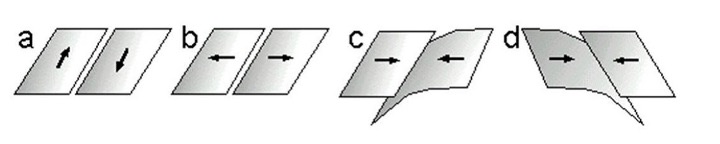
b
Which of the images below would most likely be associated with the creation of new oceanic crust?
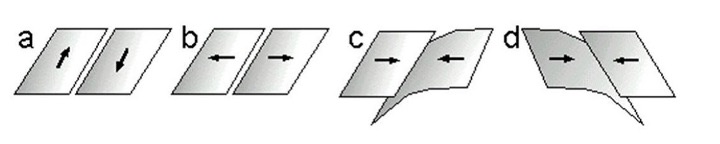
a
Which of the images below best represents the plate boundary between the North American and Pacific plates along the San Andreas Fault?
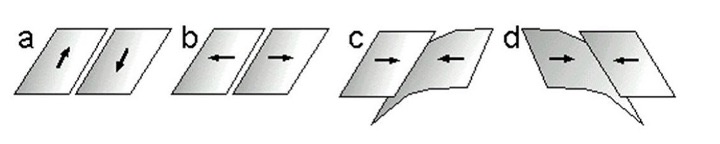
200 million years old
Approximately how old is the oldest ocean crust scientifically dated to be?
Subduction zone
Where one lithospheric plate is dragged or pushed beneath another lithospheric plate.
Wegener did not offer a plausible explanation for how the continents move
When it was first proposed, Alfred Wegener's continental drift hypothesis was heavily criticized by earth scientists. What was one of their primary objections to the continental drift hypothesis?
B
Which site below is the location of continent-continent collision, a type of convergent plate boundary?
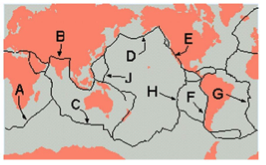
G, H, C, A
All of these sites on the map below are mid-ocean ridges.
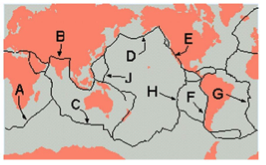
Near mid-ocean ridges
Where do we find the youngest oceanic crust?
Continental drift and seafloor spreading
Which two ideas were eventually combined to form the theory of plate tectonics?
Pangaea
What was the name of the super-continent landmass proposed to have existed approximately 250 million years ago?
Continental rifting
Continents pull apart from each other
Igneous
Jello begins as a liquid mixture of boiling water and flavored gelatin. After it cools it forms a solid (but wobbly) material. This could be seen as an analog for the formation of what type of rock?
Metamorphic rocks
Rocks that are formed by the crystallization of new minerals in the solid state (i.e. without melting) due to heat and/or pressure are
Sedimentary
Rocks formed at the Earth’s surface from the breakup of other rocks, followed by lithification, are:
Sugar
Which is not a mineral: Ice, Diamond, Sugar, Salt
Neutrons; protons
The different isotopes of a particular element have different numbers of _______ and the same number of _______ in their respective nuclei.
Oxygen, silicon, aluminum
The three most common elements in continental crust are, from most abundant to least:
Silicates
Muscovite, Biotite, Quartz, Feldspar, Pyroxene and Olivine are all part of which mineral group
Silica; iron & magnesium
Felsic rocks and minerals have relatively more ______ and relatively less ______ & ______ than mafic rocks and minerals.
Clastic
Sandstone is what type of sedimentary rock?
False
True or False: The mineral grains of plutonic (or intrusive) rocks are usually small compared to those of volcanic (or extrusive) rocks.
Silicosis
A disease from the inhalation of silicate minerals
Marble
Metamorphosed limestone is:
Iron and magnesium
Oceanic crust has more of these elements than the continental crust:
Sulfide
What type of mineral is pyrite?
Gabbro is more crystalline
What is the difference between basalt and gabbro?
Plutonic igneous
What type of rocks are gabbro and granite?
Oxygen, iron, silicon, magnesium
What are the four most common elements in the Earth's geosphere (i.e., for the whole planet)?
Geosphere
Where did most of the carbon-dioxide in our 2nd atmosphere go?
Photosynthesis
What process lead to the high amount of oxygen in our atmosphere today, relative in Earth’s 2nd atmosphere?
Thermosphere
Highest layer - greatest in elevation above Earth's surface. Where charged particles coming from the sun interact with the upper atmosphere, generating the colored light shows known as auroras
Mesosphere
Second highest - the layer below the highest layer. Where most meteors burn up, generating so-called shooting stars
Stratosphere
Second lowest layer - the layer just above the lowest layer. Where the ozone layer blocks most UV light from reaching Earth’s surface
Troposphere
Lowest layer - the layer we mostly live and breath in. Where most non-aquatic life exists, and where most weather occurs.
2.8%
What percentage of today's hydrosphere is the form of freshwater (ice, groundwater, surface water)?
97.2%
What percentage of today's hydrosphere is the form of ocean water (salty-water occupying the ocean basins)?
Precipitation & evaporation
What are the two most important processes involved in exchanging water between the larger liquid portions of the hydrosphere, and the much smaller amount of water vapor in the atmosphere?
71%
Approximately what percentage of Earth’s surface is covered by ocean water?
Antarctica
What continent currently possesses the largest accumulation of ice? (Hint, this continent is not an autonomous dependency of the Kingdom of Denmark)
Sedimentary
Rock that has formed from lithification of any type of sediment, including clastic or chemical sediments, or organic remains.
Weathering
The destructive processes that, through both physical disintegration and chemical decomposition, change rock that has been exposed at Earth’s surface.
Protolith
The original rock from which a metamorphic rock formed.
Magma
Molten rock beneath the planet’s surface.
Erosion
The transportation of weathering products by wind, water flow, or ice flow.
Igneous
Rock produced by solidification of molten material, either lava or magma.
Metamorphic
Rock that formed by the crystallization of new minerals in the solid state (i.e. without melting) due to heat and/or pressure.
Lava
Molten rock that has reached the planet’s surface.
Granite
Origin/Texture: plutonic or intrusive, phaneritic. Composition: felsic.
Basalt
Origin/Texture: volcanic or extrusive, aphanitic. Composition: mafic.
Diorite
Origin/Texture: plutonic or intrusive, phaneritic. Composition: intermediate.
Gabbro
Origin/Texture: plutonic or intrusive, phaneritic. Composition: mafic..
Andesite
Origin/Texture: volcanic or extrusive, aphanitic. Composition: intermediate.
Rhyolite
Origin/Texture: volcanic or extrusive, aphanitic. Composition: felsic.
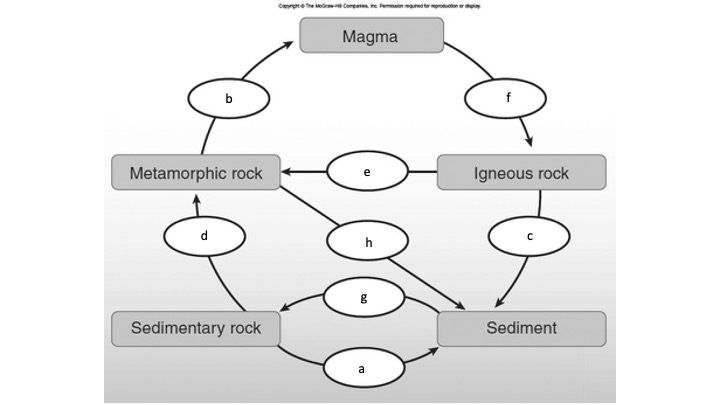
Heat and pressure causing metamorphism
What is d?
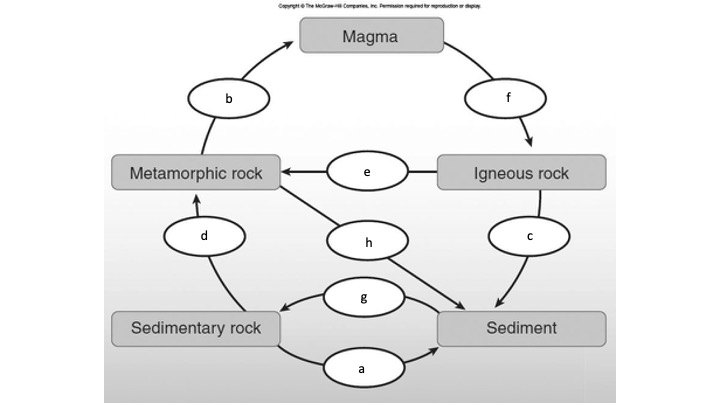
Melting
What is b?
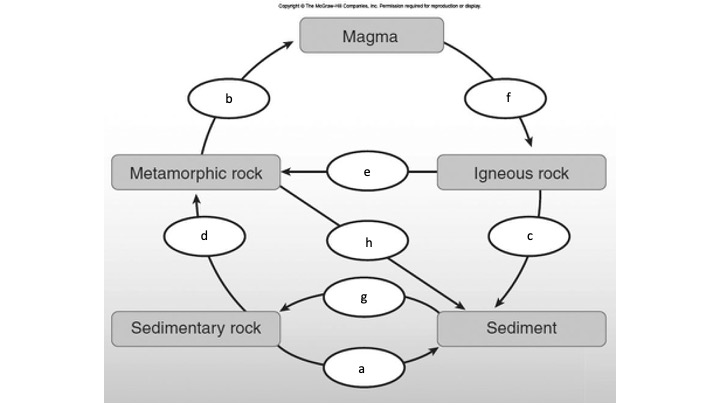
Cementation and compaction (lithification)
What is g?
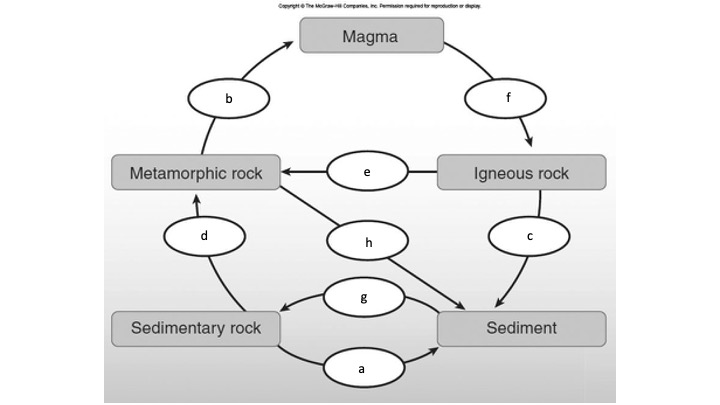
Weathering, erosion, and deposition
What is c?
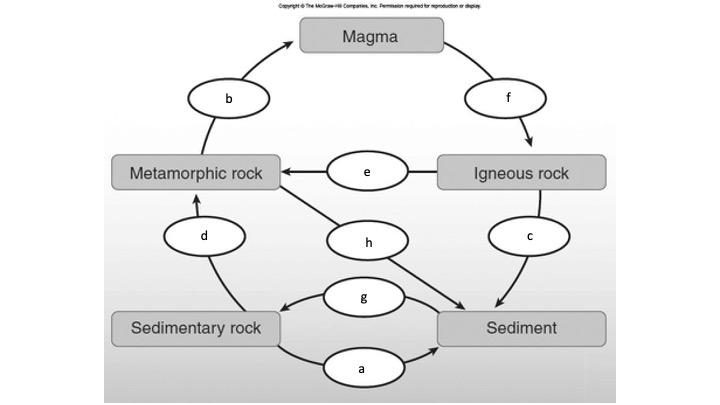
Cooling and solidification
What is f?
Felsic
More silica; Granite; Feldspar and Quartz; light-colored minerals; Less dense
Mafic
Less silica; More Mg & Fe; Basalt; Dark-colored minerals; Denser