Parasitology All Labs (BMS171)
1/143
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Parasitology labs. goodluck
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
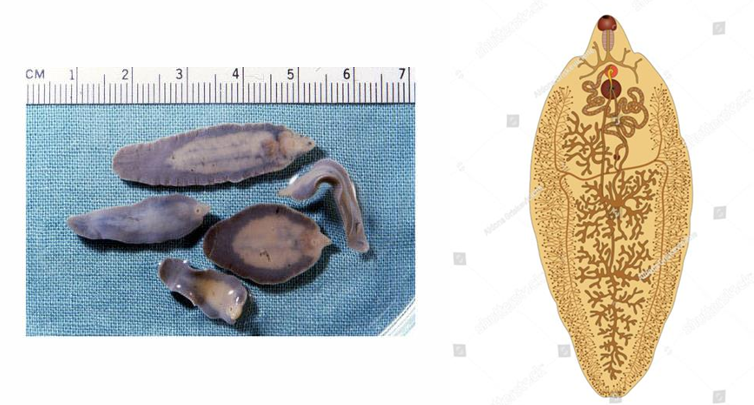

Flattened unsegmented leaf-like = Trematodes
Flattened segmented tape-like = Cestodes
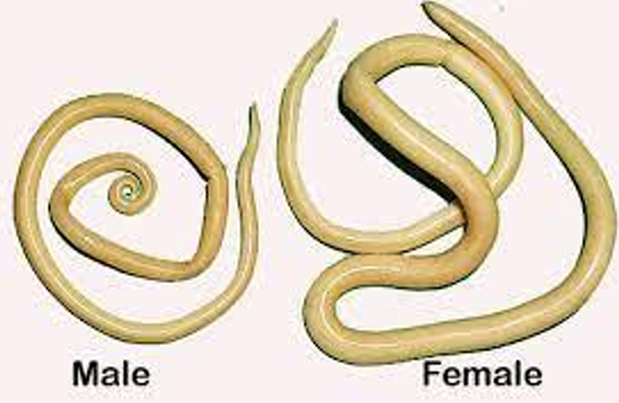

Cylindrical rounded unsegmented = Nematodes

Adult Taenia worm in Jar

Adult Ascaris in jar
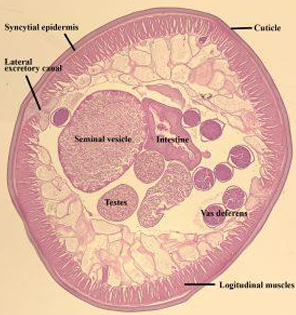
Cross section in Ascaris male
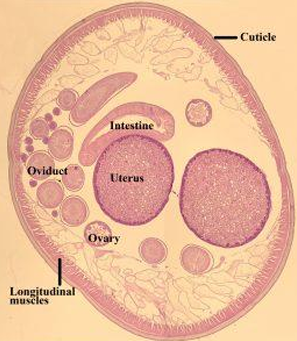
Cross section in Ascaris female
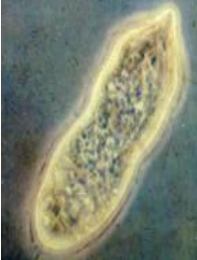
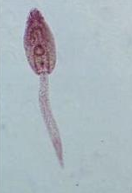
Miracidium

Miracidium of schistosomes
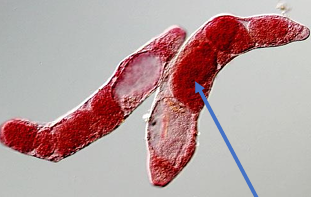
Sporocysts
Arrow: Daughter sporocysts
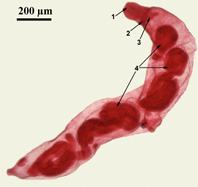
Sporocyst
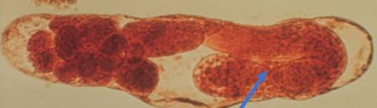
Arrow: Redia
Redia
Leptocercus cercaria: with Simple tail
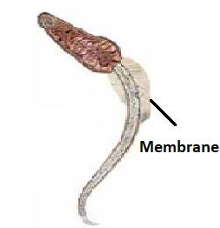
Lophocercus cercaria: tail is surrounded by a membrane
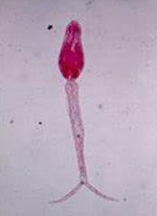
Furcocercus cercaria: with forked tail
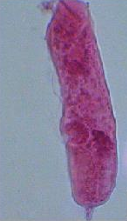
Microcercus cercaria): tail is a a knob like structure
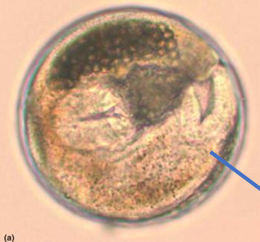
Encysted metacercaria
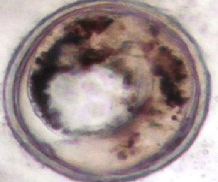
Encysted metacercaria
Encysted metacercaria
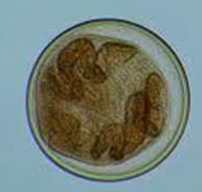
Cysticercoid
Cysticercus larva
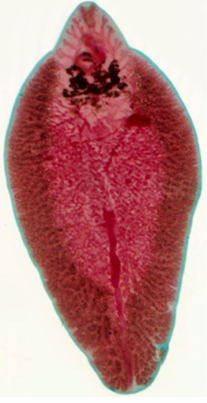
Fasciola Adult
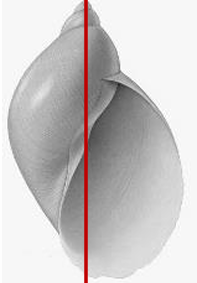
Snail Intermediate host of Fasciola spp, what is it called?
Lymnaea cailliaudi
Dextral, Thin, fragile Prominent apex Short spire, few whorls Aperture 2/3 of length Fresh water IH of Fasciola gigantica Surface feeder Susceptible to molluscicides
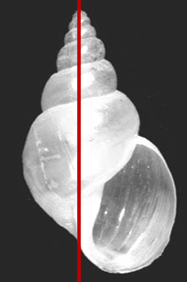
Snail Intermediate host of Fasciola spp, what is it called?
Lymnaea truncatula
Dextral, Thin, fragile Prominent apex Few whorls Aperture 1/2 of length IH of Fasciola hepatica Fresh water Surface feeder Susceptible to molluscicides
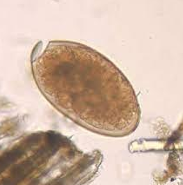
Fasciola Egg (diagnostic stage)
Oval Thin 150 x 70 µ Yellow immature Operculated
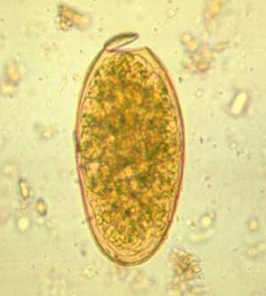
Fasciola Egg (diagnostic stage)
Oval Thin 150 x 70 µ Yellow immature Operculated

Leptocercus cercaria: with Simple tail
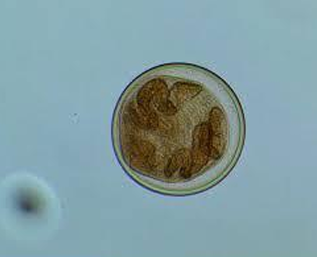
Fasciola encysted metacercaria (infective stage)

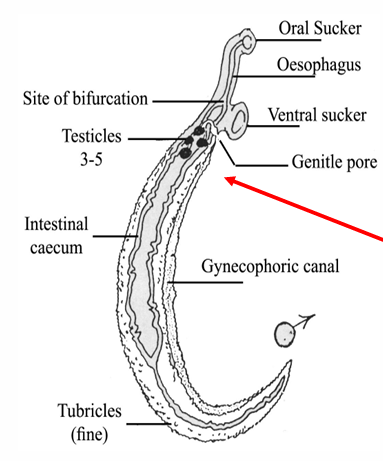
Schistosoma
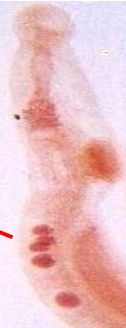
Schistosoma haematobium male
Schistosoma haematobium male
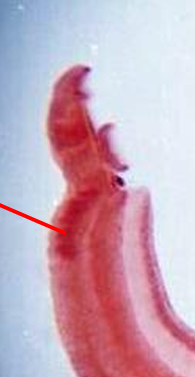
Schistosoma mansoni male
Schistosoma mansoni male
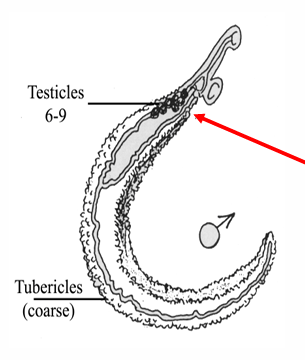
Schistosoma haematobium adult female
Schistosoma haematobium adult female
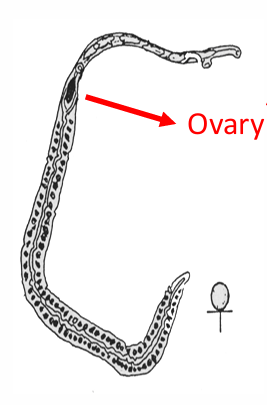
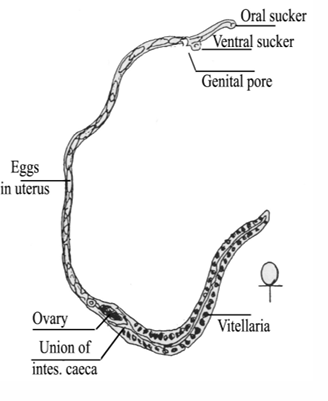
Schistosoma mansoni adult female
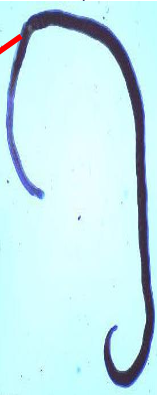
Schistosoma mansoni adult female
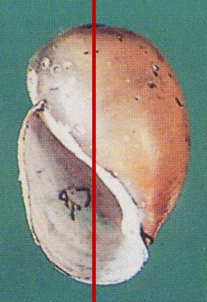
Snail Intermediate hosts of Schistosoma spp
Bulinus truncatus
Sinistral Blunt apex with shoulder With umbilicus IH of Schistosoma haematobium Fresh water Various level of water Susceptible to molluscicides

Snail Intermediate hosts of Schistosoma spp
Biomphalaria alexandrina
Sinistral Discoid IH of Schistosoma mansoni Fresh water Surface feeder Susceptible to molluscicides
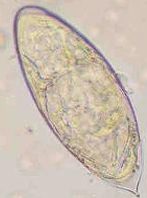
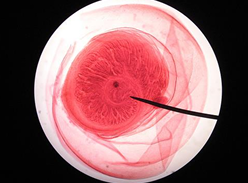
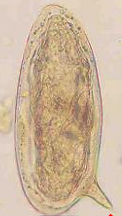
Schistosoma Egg, Terminal Spine
Shape: oval
Shell: Thin
Color: Colorless
Content: Mature with fully formed miracidium
Pass in urine, rarely in stool
Schistosoma Egg, Lateral Spine
Shape: oval
Shell: Thin
Color: Yellow
Content: Mature with fully formed miracidium
Pass in STOOL, rarely in urine
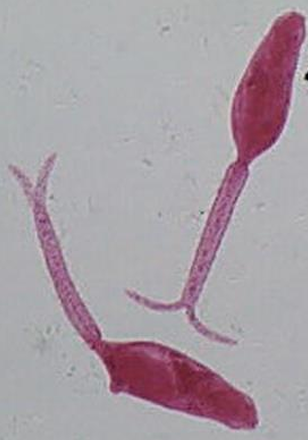
Furcocercus cercaria (infective stage) of schistosoma
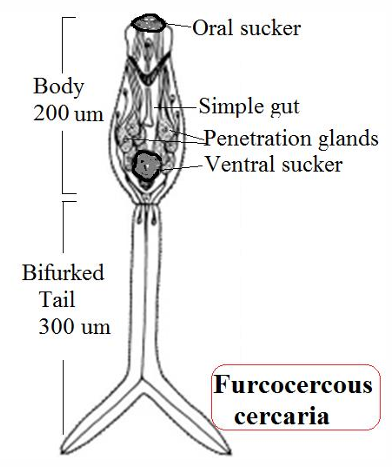
Furcocercus cercaria (infective stage) of schistosoma

Scolex of cestoda - Pseudophyllidea
arrow pointing at Bothria
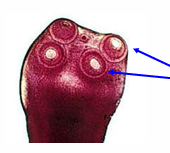
Scolex of cestoda - Cyclophyllidea
arrow pointing at suckers
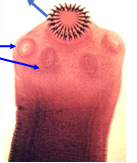
Scolex of cestoda - Cyclophyllidea
arrow pointing at suckers
4-cup shaped suckers-with rostellum and hooks

Reproductive system of Pseudophyllidea (Mature Segment)
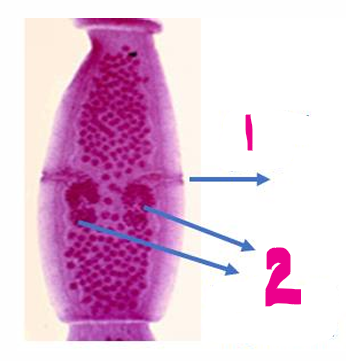
Reproductive system of Cyclophyllidea (Mature Segment)
1- Genital pore
2- Double set of genitalia
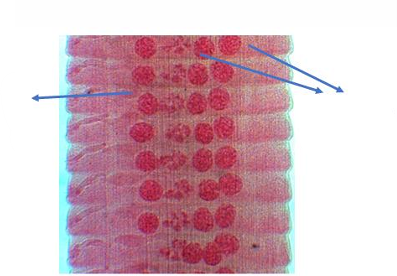
Reproductive system of Cyclophyllidea (Mature Segment)
arrows = testis
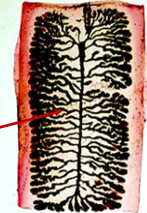
Reproductive system of Cyclophyllidea
Lateral Branches
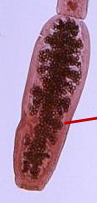
Reproductive system of Cyclophyllidea
Lateral Pouches
Reproductive system of Cyclophyllidea
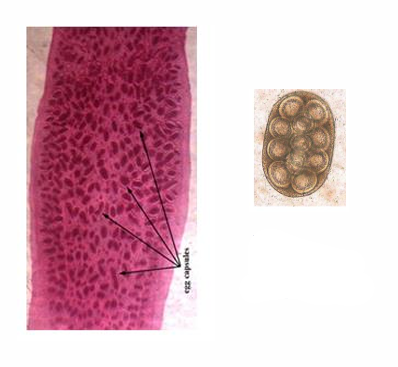
Egg Capsules
Developmental stages of Pseudophyllidea
Egg

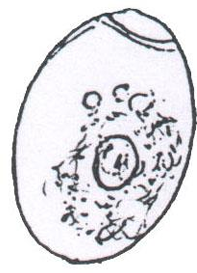
Developmental stages of Pseudophyllidea
Coracidium
Developmental stages of Pseudophyllidea
Procercoid

Developmental stages of Pseudophyllidea
Plerocercoid
Developmental stages of Cyclophyllidea
Egg
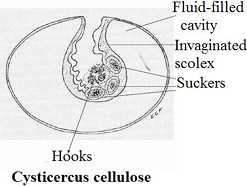
Developmental stages of Cyclophyllidea
Cycticercus
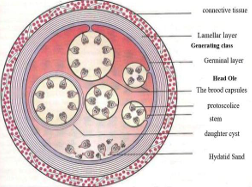
Developmental stages of Cyclophyllidea
Larva; Hydatid Cyst
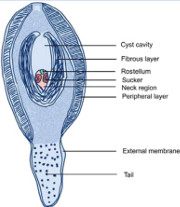
Developmental stages of Cyclophyllidea
Cysticercoid
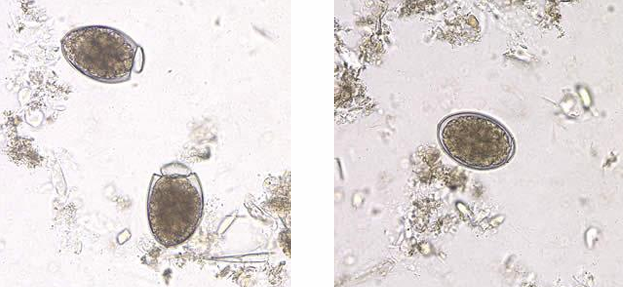
Eggs of Pseudophyllide
Eggs are immature, they are not infective to man

IH of Pseudophyllide
Cyclops
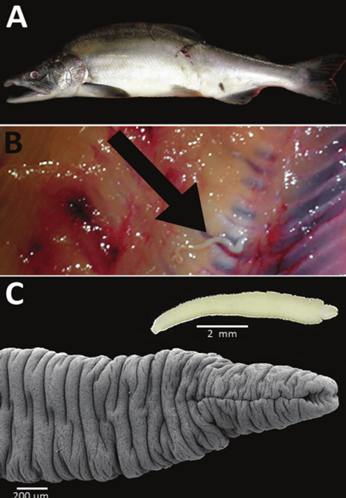
Infective stage of Pseudophyllide
Plerocercoid in fish muscle

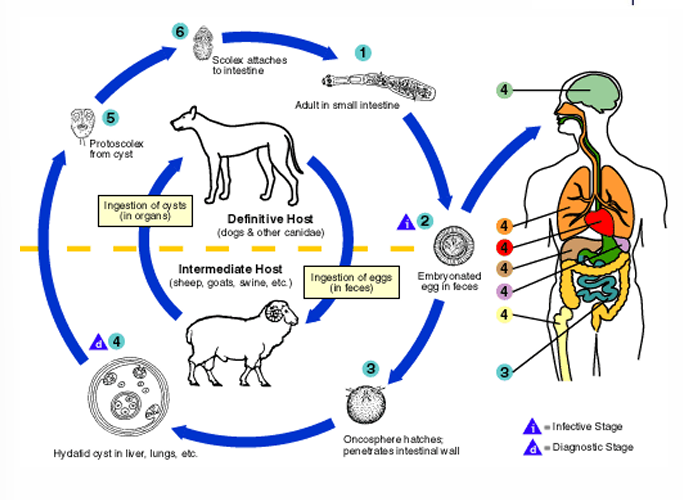
Echinococcus granulosus adult
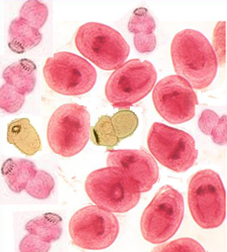
Hydatid sand (Diagnostic Stage of Cyclophyllidea)
Hydatid sand is many miniature tapeworm scolices (heads), these will form adult tapeworms in the DH (dog)
What’s the infective stage of Cyclophyllidea?
Egg
What’s the mode of infection of Cyclophyllidea?
Eating food contaminated by excreta of dogs
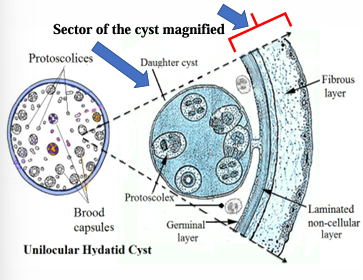
Wall of Unilocular Hydatid Cyst
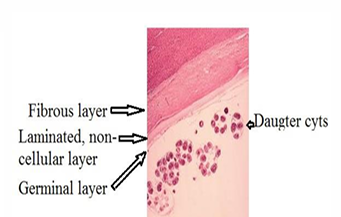
part of wall of Unilocular Hydatid Cyst
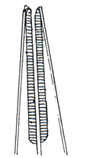
Nematode Cylindrical Myosyringata (Muscular oesophagus)
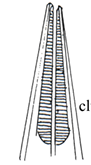
Nematode Club-Shaped Myosyringata (Muscular oesophagus)
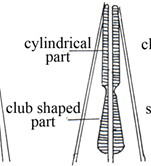
Nematode Rhabditiform Myosyringata (Muscular oesophagus)
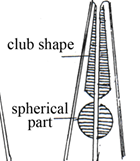
Nematode Double-bulbed Myosyringata (Muscular oesophagus)
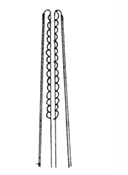
Nematode Cellular Oesophagus Trichosyringata

Ascaris lumbricoides
(Giant Intestinal Roundworm)

Ascaris lumbricoides
(Giant Intestinal Roundworm)

Ascaris lumbricoides
(Giant Intestinal Roundworm)
Ascaris lumbricoides
egg
Diagnostic Stage

Ascaris lumbricoides
egg
Diagnostic Stage

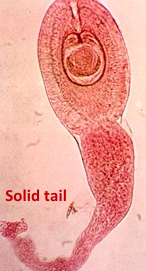
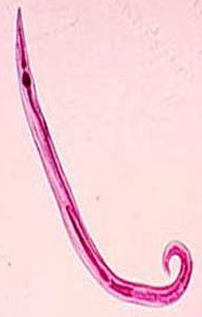
Enterobius vermicularis (Oxyuris, Pinworm)
Female
pointed tail hence the name pinworm
Enterobius vermicularis (Oxyuris, Pinworm)
Male
curved ventrally carries a single spicule.
Infective stage of Enterobius vermicularis?
Mature egg (egg containing larva)
Mode of infection of Enterobius vermicularis?
Autoinfection: Ingestion of eggs lodged on contaminated fingers of the infected persons
Ingestion
Inhalation
Retro Infection: Re-entrance of larvae that sometimes hatch from eggs on the peri anal skin to the large intestine
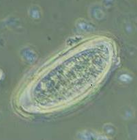
Eggs of Enterobius vermicularis
Plano-convex, flattened on one side and curved in the other (D shaped).
Thick colorless shell
Doubly refractive wall
50 x 25 um
Mature, immediately infective

Eggs of Enterobius vermicularis
Plano-convex, flattened on one side and curved in the other (D shaped).
Thick colorless shell
Doubly refractive wall
50 x 25 um
Mature, immediately infective
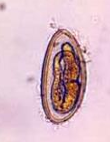
Eggs of Enterobius vermicularis
Plano-convex, flattened on one side and curved in the other (D shaped).
Thick colorless shell
Doubly refractive wall
50 x 25 um
Mature, immediately infective
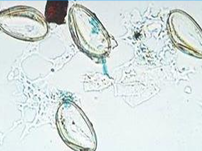
Eggs of Enterobius vermicularis
Plano-convex, flattened on one side and curved in the other (D shaped).
Thick colorless shell
Doubly refractive wall
50 x 25 um
Mature, immediately infective
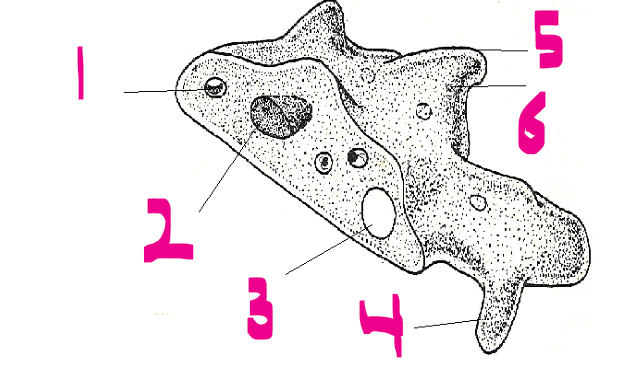
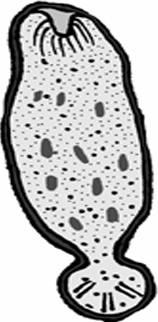
General Characters of Protozoa
1- Food vacuole
2- Nucleus
3- Contractile vacuole
4- Pseudopodium
5- Ectoplasm
6- Endoplasm
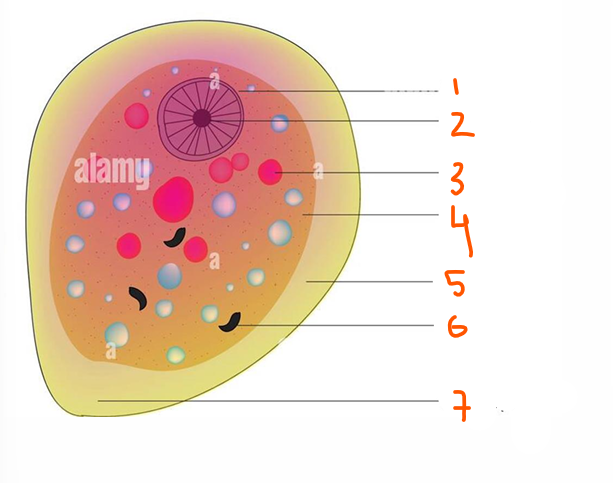
1- Nucleus
2- Endosome
3- Ingested RBC
4- Endoplasm
5- Ectoplasm
6- Ingested bacteria
7- Pseudopodium

Reproduction of Protozoa
Asexual: Binary fission
It occurs either longitudinally or transversally. Mitotic division of nucleus is followed by division of the cytoplasm.
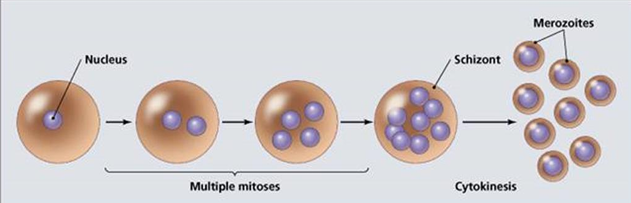
Reproduction of Protozoa
Asexual: Multiple fission or schizogony
The nucleus undergoes several successive divisions within the schizont to produce large number of merozoites
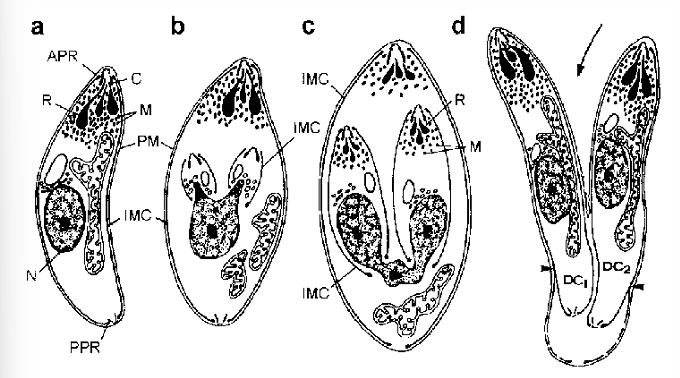
Reproduction of Protozoa
Asexual: Endodyogeny
Two daughter cells form within the parent cell —> Ruptures —> the smaller progeny grow to full size before repeating the process
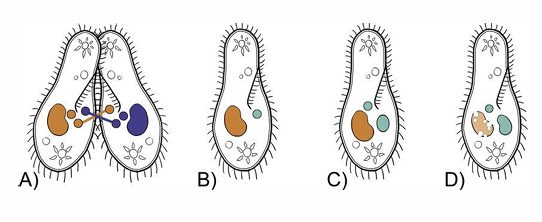
Reproduction of Protozoa
Sexual: Conjugation
where two organisms fuse together and exchange nuclear matter as in Balantidium coli.

Locomotion of protozoa
Flagella
long thread-like cytoplasmic extensions. • Arises in the endoplasm from basal body • Kinetoplast is at the base of the basal body of the flagellum • It consists of a curved, electron-dense structure containing DNA

Locomotion of protozoa
Cilia
Numerous short hair-like threads covering the whole organism. Each arises from a basal granule just below the surface of the cell
Locomotion of protozoa
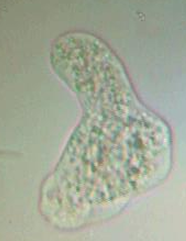
Pseudopodia
Extension of the ectoplasm followed by the endoplasm resulting in amoeboid movement
Functions: 1- locomotion 2-Engulfing of food
Pseudopodia
Extension of the ectoplasm followed by the endoplasm resulting in amoeboid movement
Functions: 1- locomotion 2-Engulfing of food
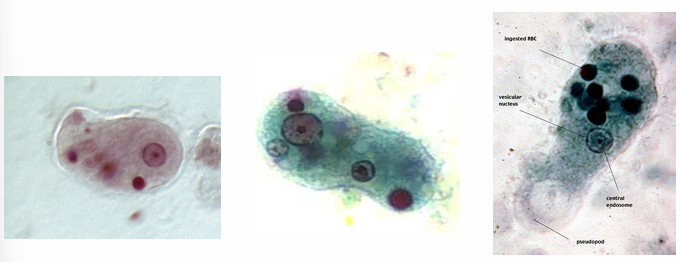
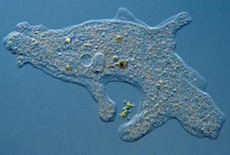
Entamoeba histolytica tissue form (Magna form)
It DOSEN’T form precyst or cyst
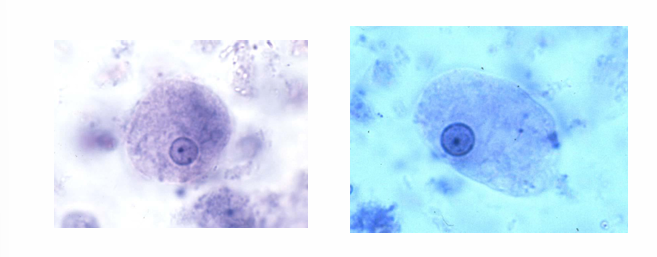
Entamoeba histolytica lumen form (Minuta form)
It DOES form precyst or cyst
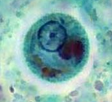
Cyst of Entamoeba histolytica
Rounded with well developed cyst wall, 12-15 µ, it contains 1-4 nuclei, glycogen and chromatoid bodies