Bot-Lab (Sem-1) - Chapter 11: Plant Tissues
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
spermatophyte
gymnosperms and angiosperms; any plant that produces seeds; made up of many cells that form tissues that occur in all primary organs such as roots, stems, and leaves
meristematic; permanent
two types of basic tissues of plants
meristematic tissues
cells that facilitate growth during the development of a plant embryo and then into a seedling; two types: primary/apical and secondary/lateral
primary/apical meristem
a type of meristem responsible for primary growth in all plants; reason behind plant totipotency; two types: shoot apical meristem (SAM) and root apical meristem (RAM)
totipotency
the ability of a single cell to give rise to all of the differentiated cell types that build the conceptus
shoot apical meristem (SAM); root apical meristem (RAM)
two types of primary/apical meristem
apical meristem; primary meristem (protoderm; procambium; ground meristem)
parts found in both the shoot apical meristem (SAM) and root apical meristem (RAM)
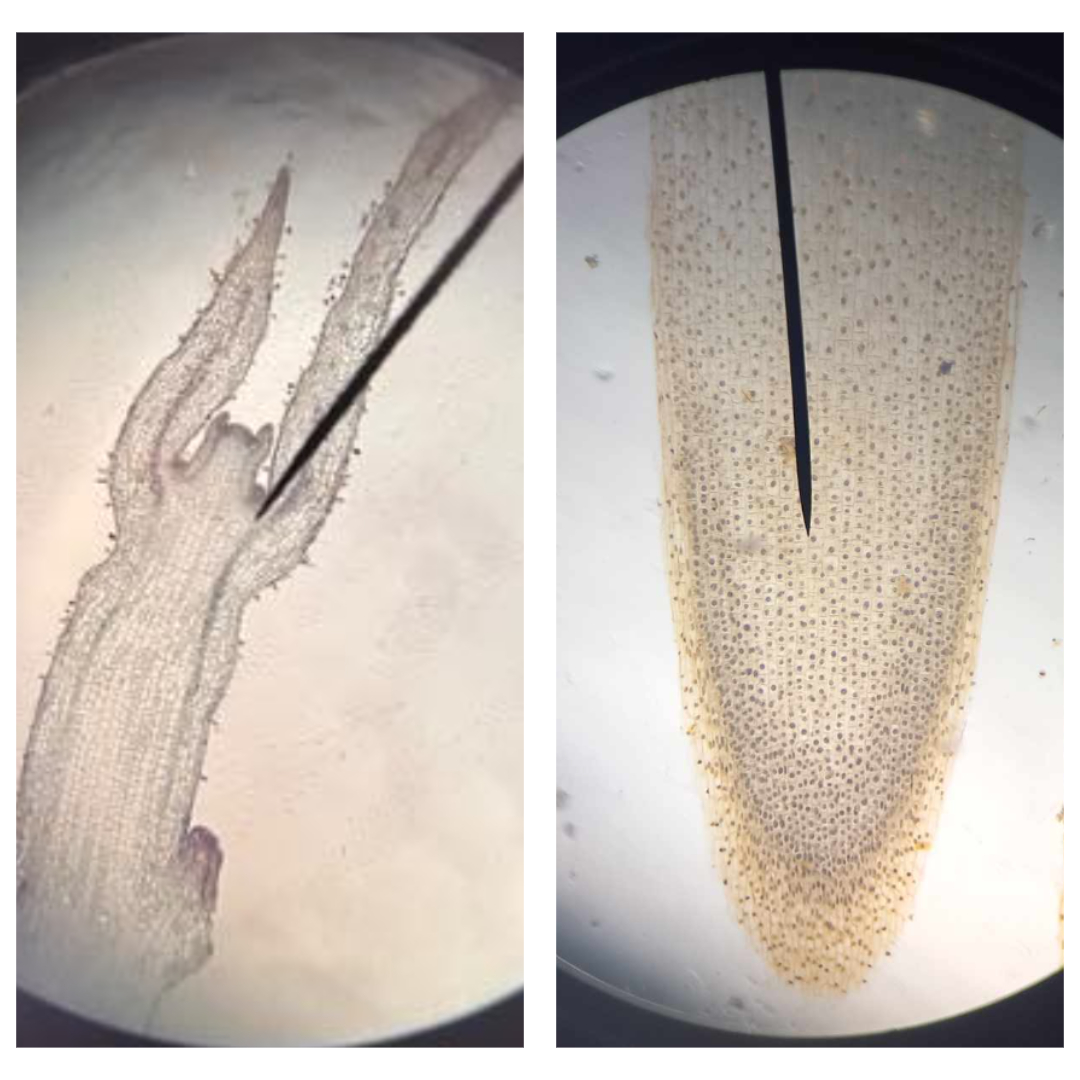
apical meristem/promeristem
part of SAM and RAM under microscope; occur at the tip of a growing shoot
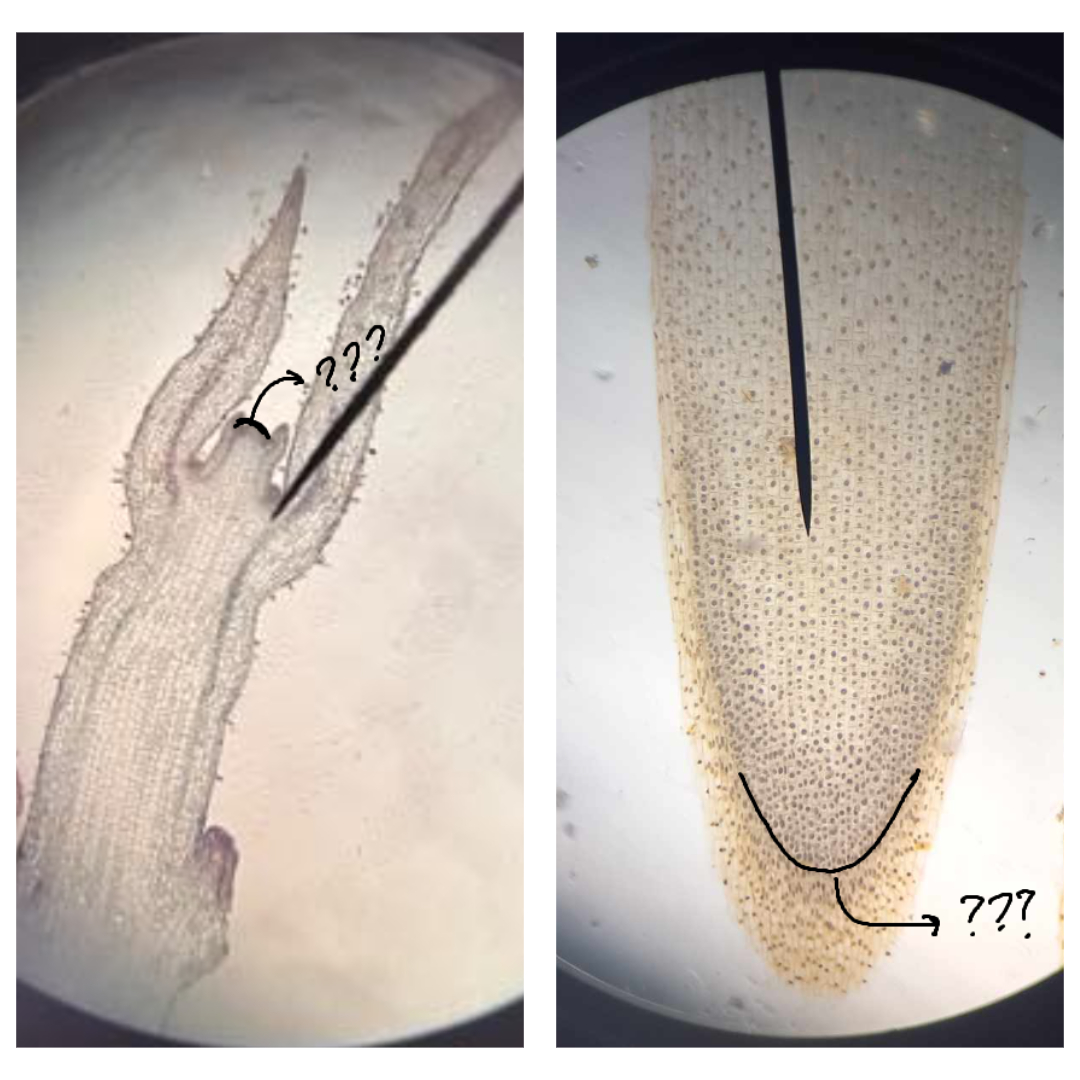
primary meristem
part of SAM and RAM under microscope; composed of three different regions: protoderm; procambium; ground meristem
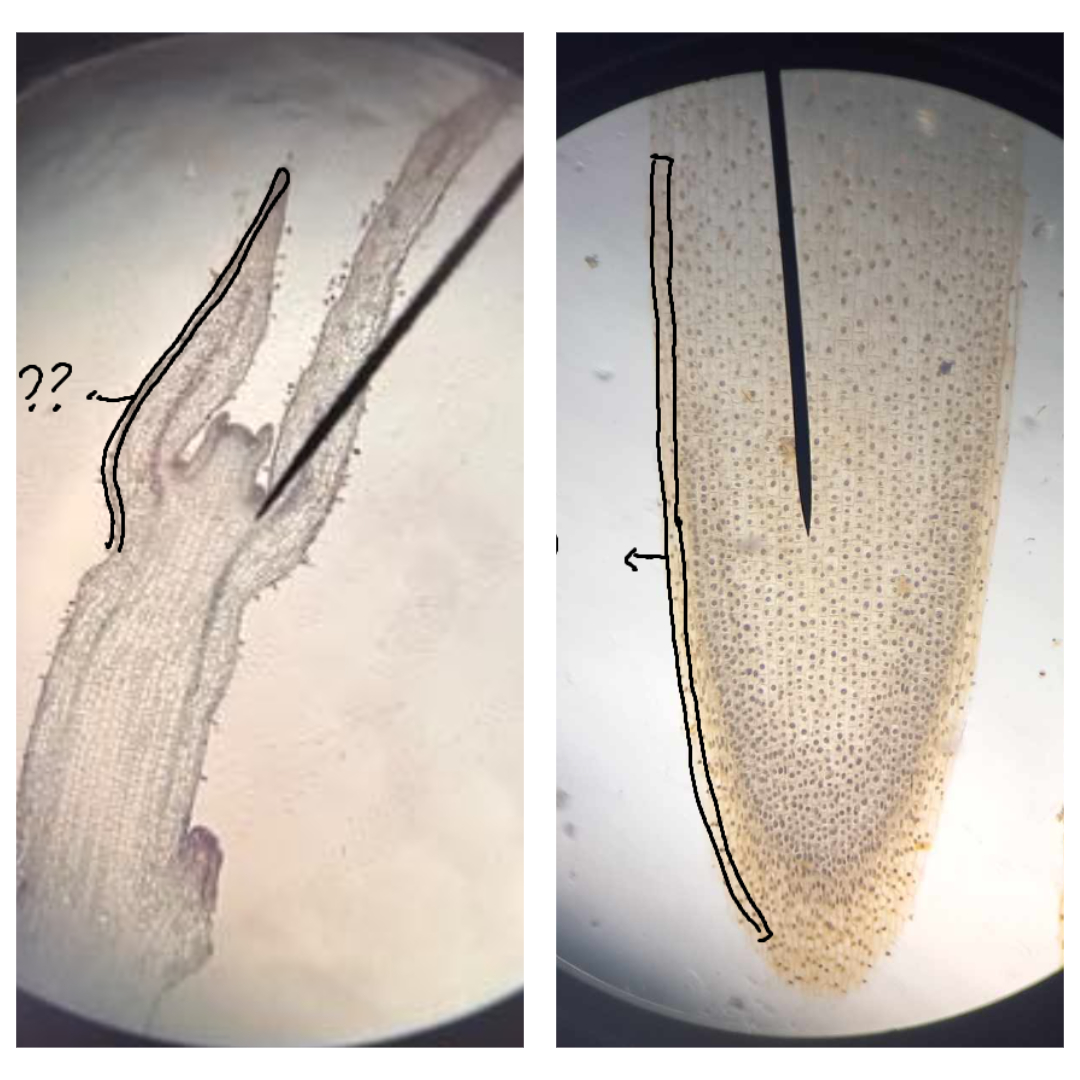
protoderm
part of the primary meristem; gives rise to the epidermis (dermal tissue)
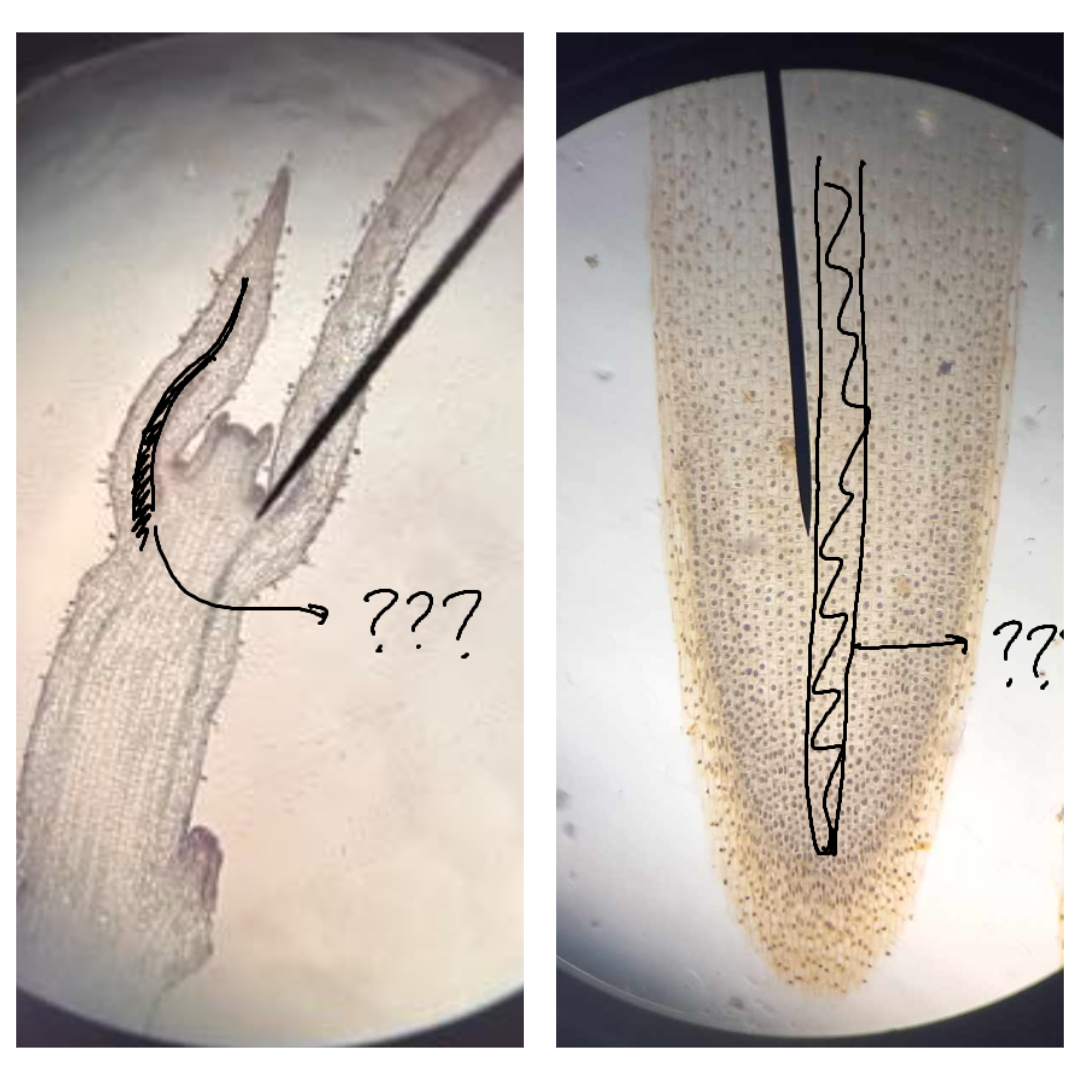
procambium
part of the primary meristem; gives rise to the vascular tissues (primary xylem and primary phloem)
ground meristem
part of the primary meristem; gives rise to the cortex (ground tissue)
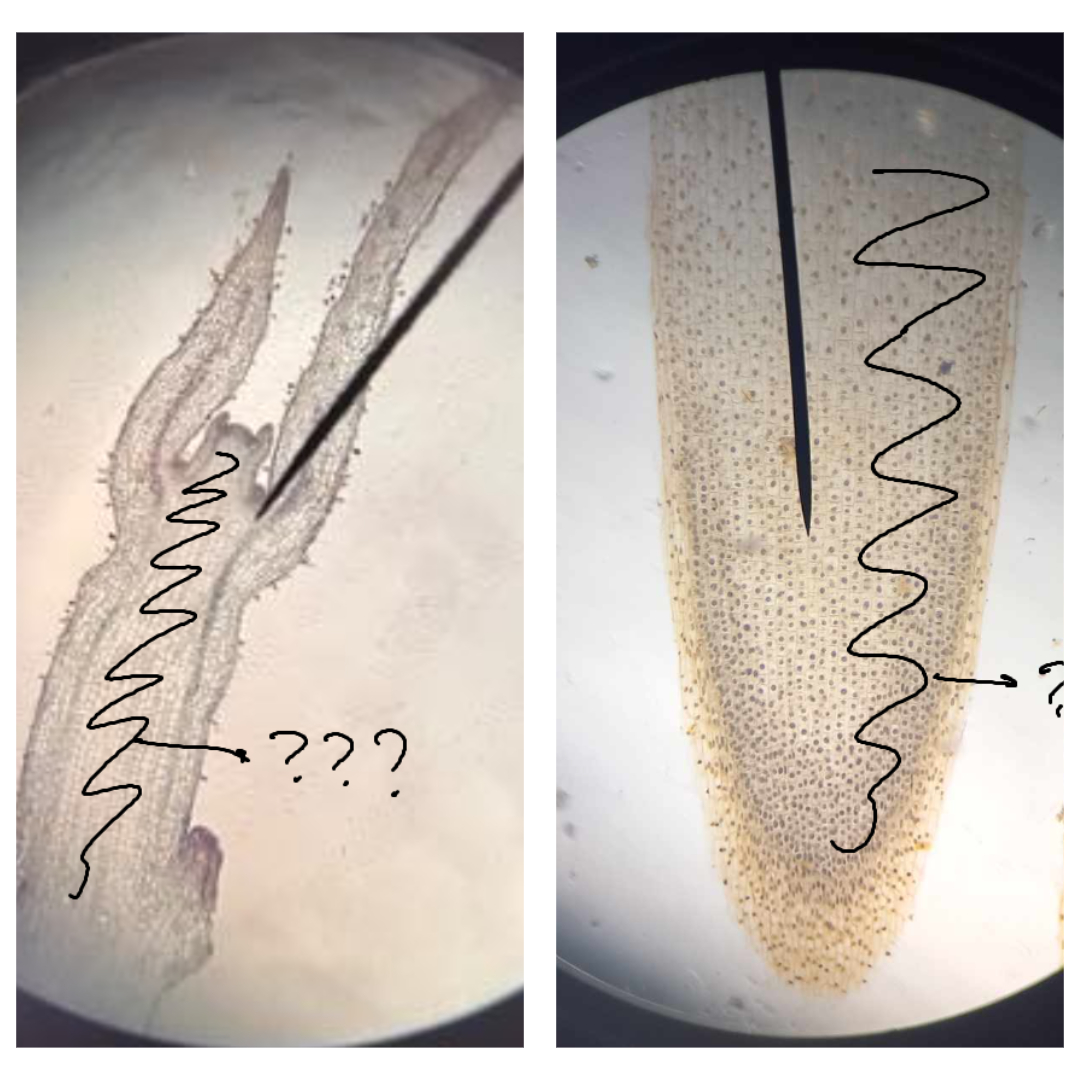
shoot apical meristem (SAM)
primary meristem that produces leaves, buds, and stem; generates above-ground aerial organs throughout the lifespan of higher plants
Coleus blumei
mayana
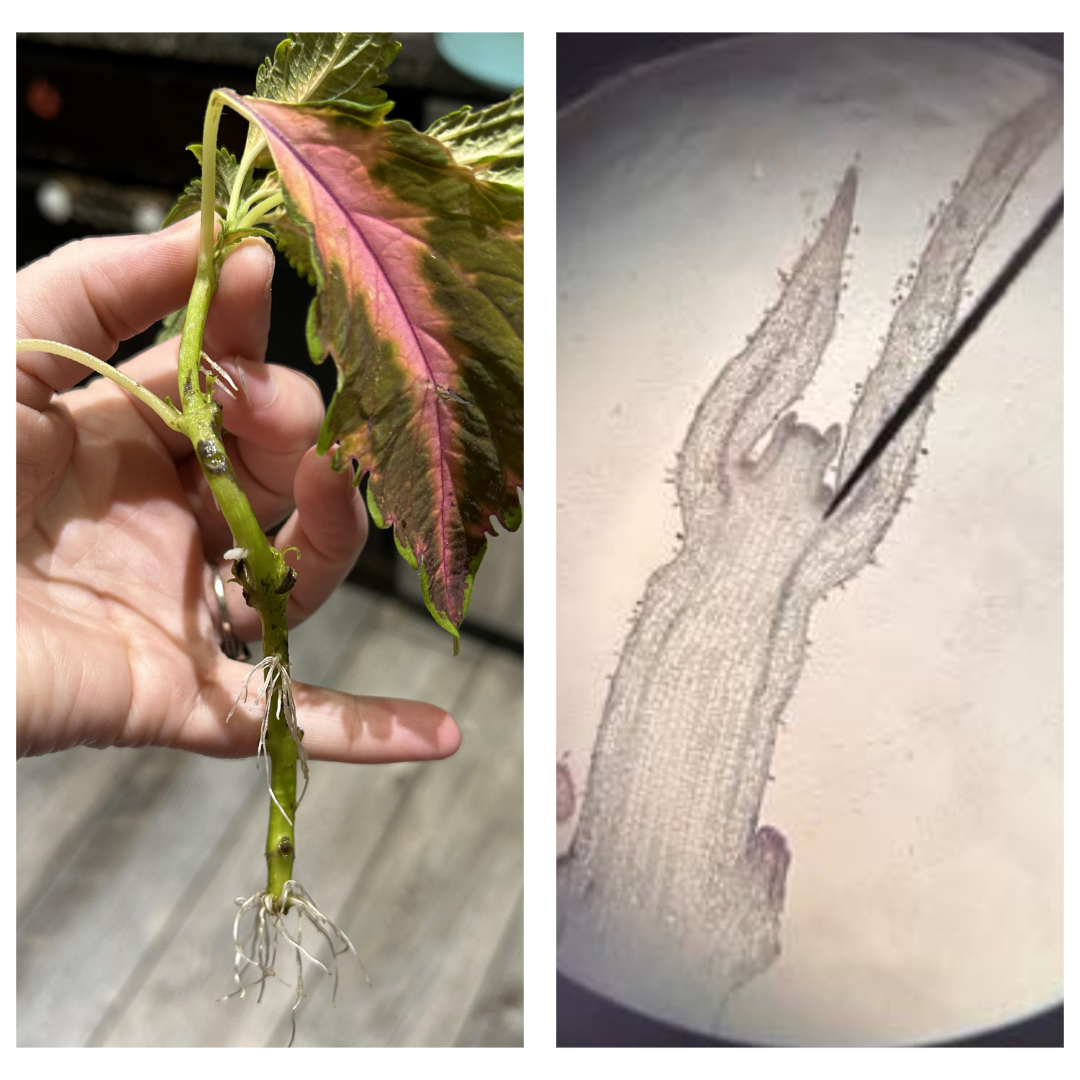

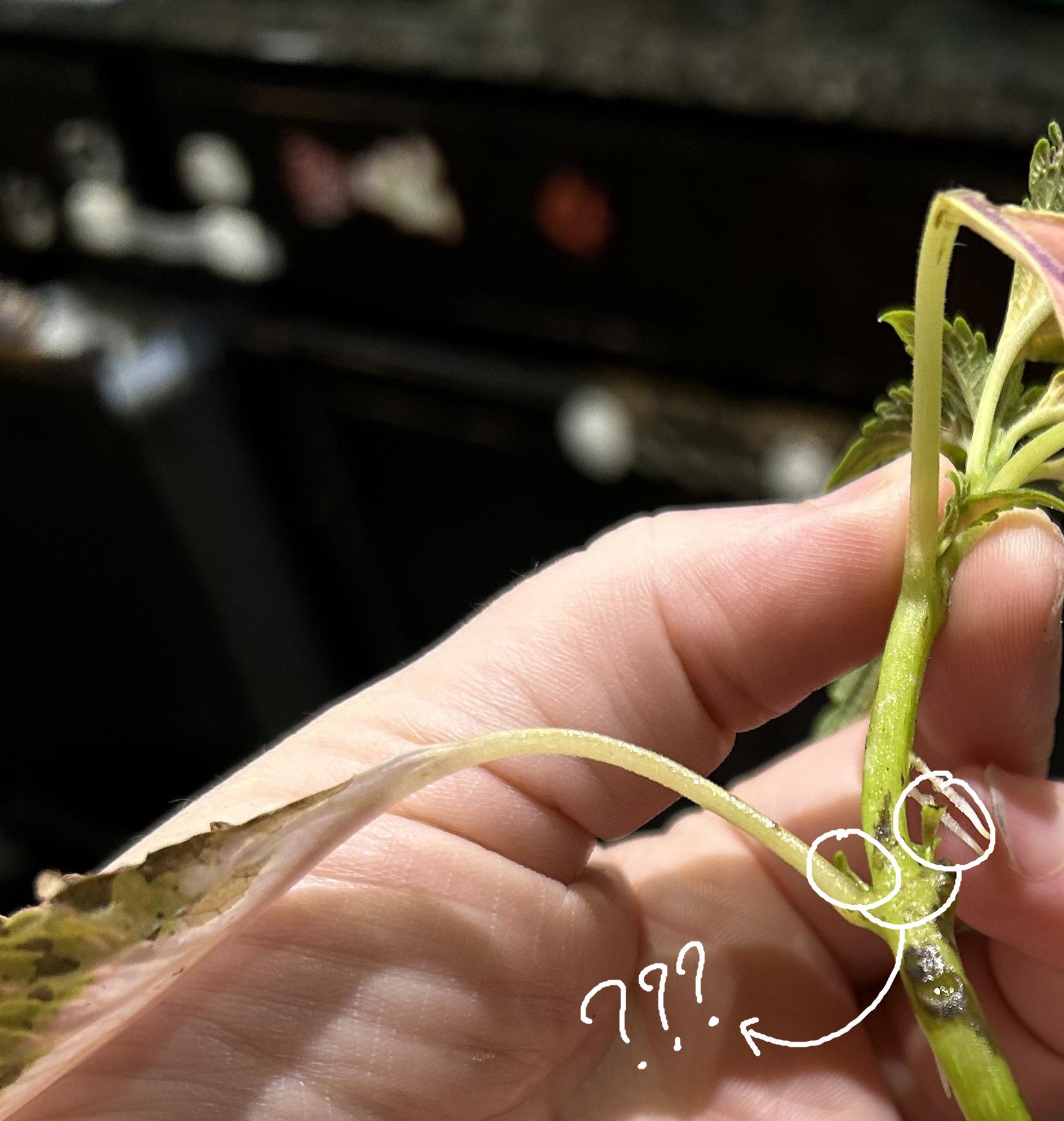
nodes; internodes; bud leaf axils; leaf; shoot tip
parts of a shoot apical meristem (SAM) live specimen
nodes
where leaves are attached
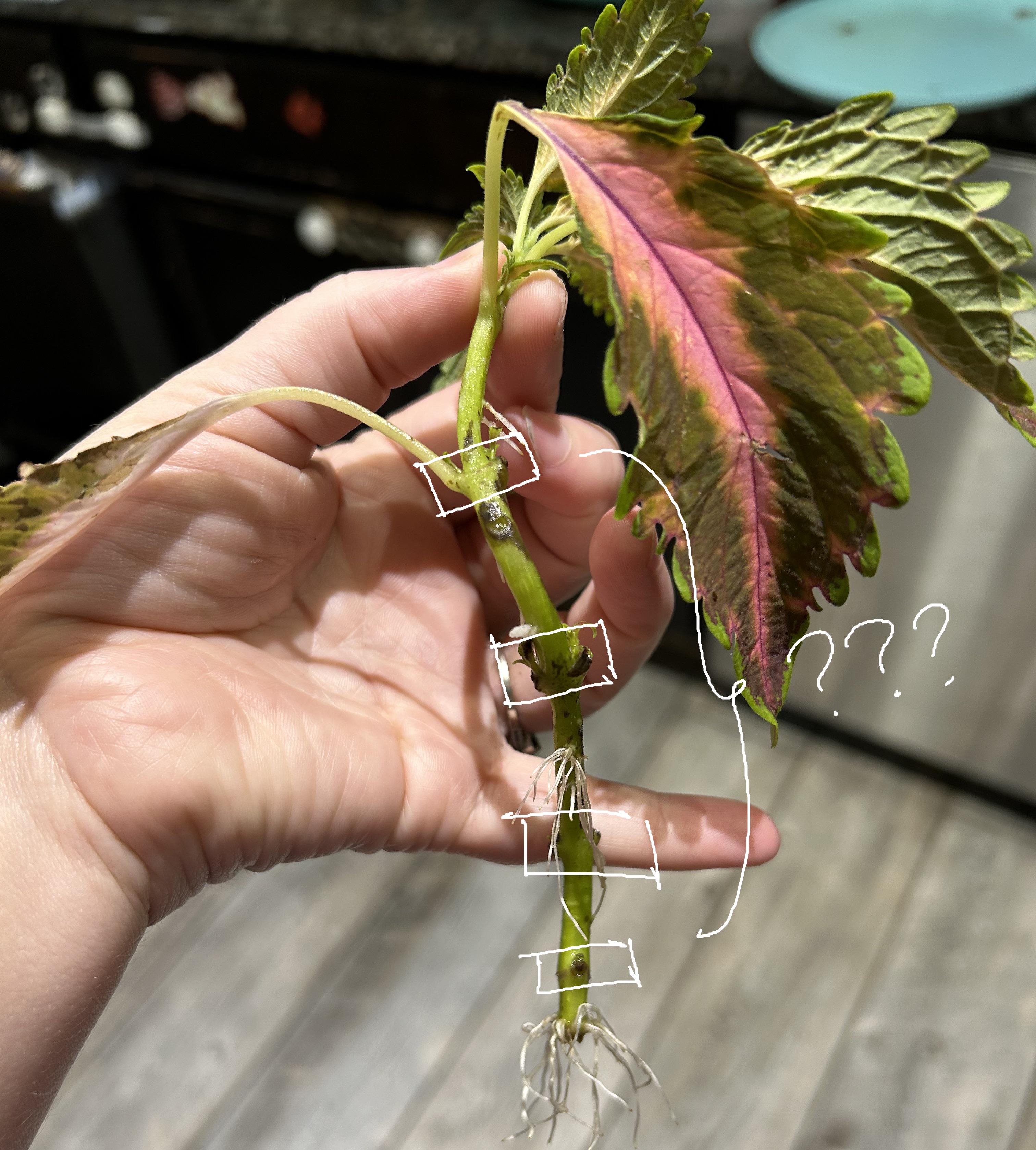

internodes
regions between nodes
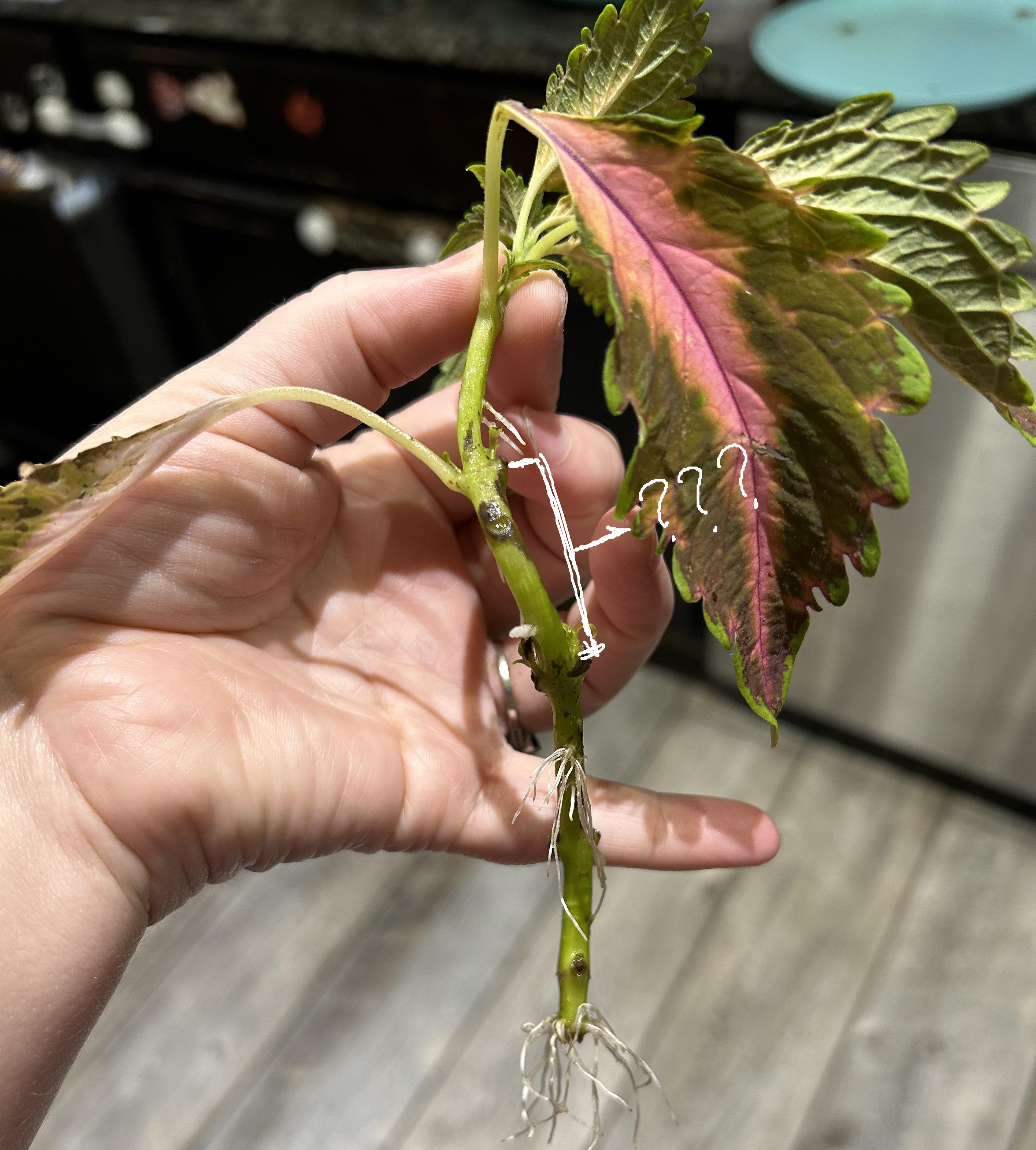

bud leaf axils
buds found above the point where the leaf is attached

leaf
plant organ specialized for photosynthesis
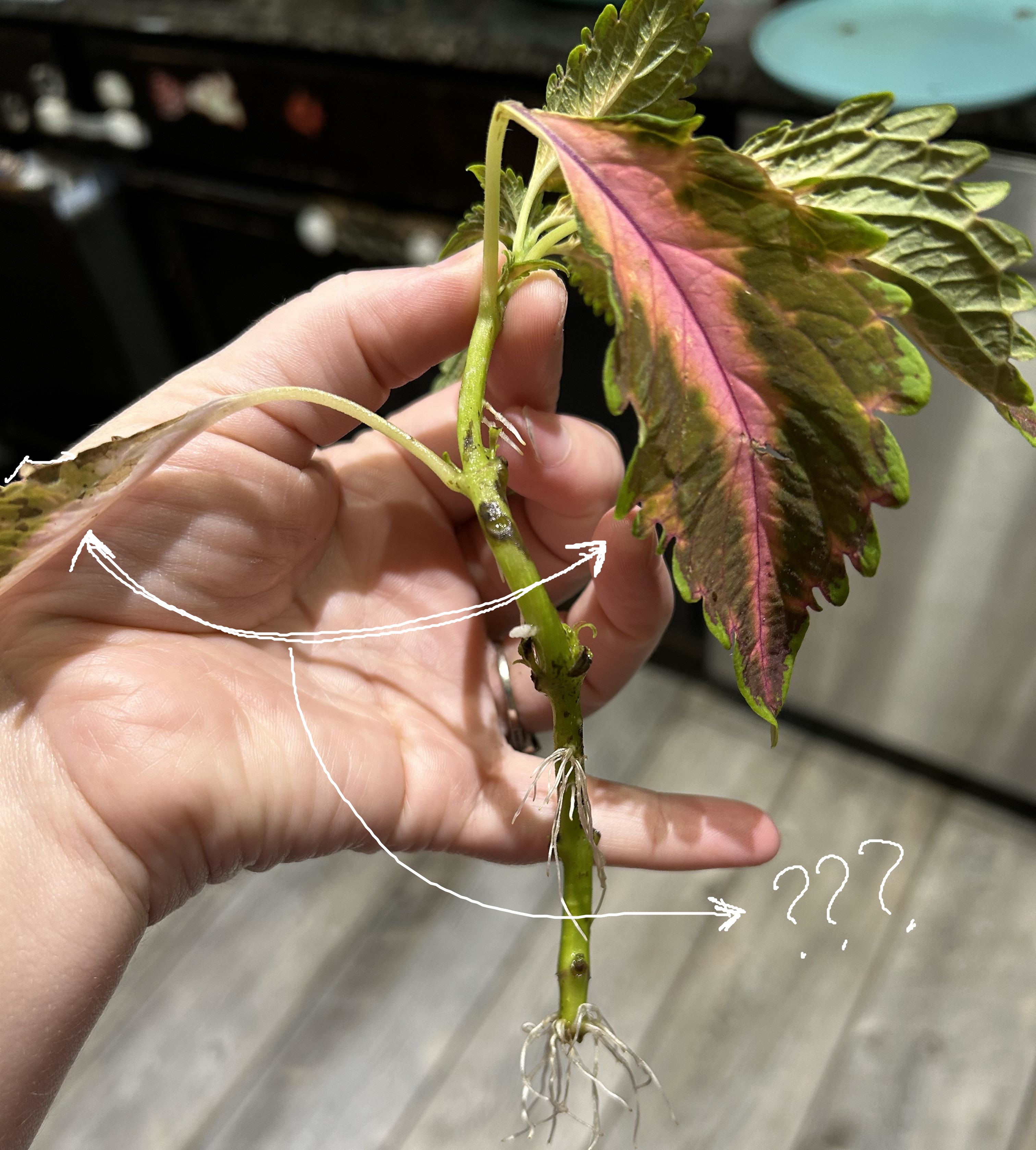

shoot tip
organized tissues composed of an apical dome and several leaf buds
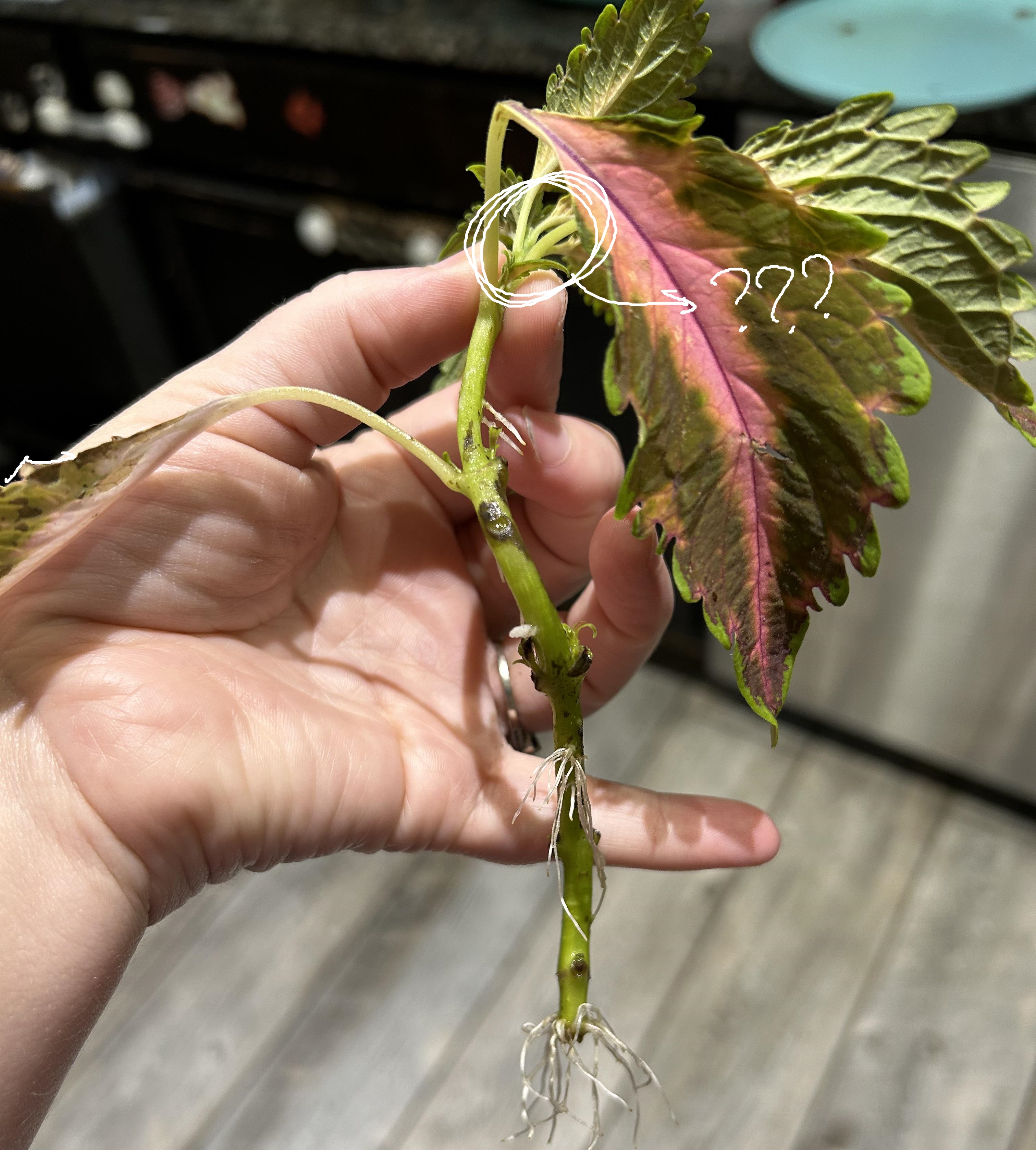

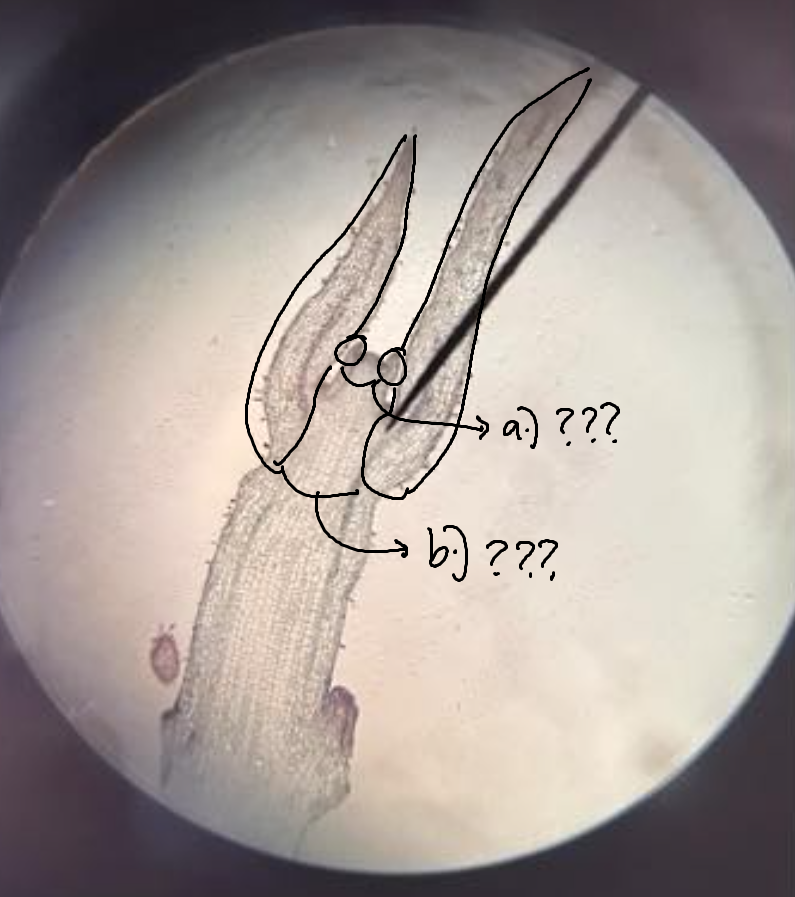
leaf buttress; leaf primordia
parts of a shoot apical meristem (SAM) under microscope
leaf buttress
part of SAM under microscope; a slight bulge that continues to grow into a leaf primordium
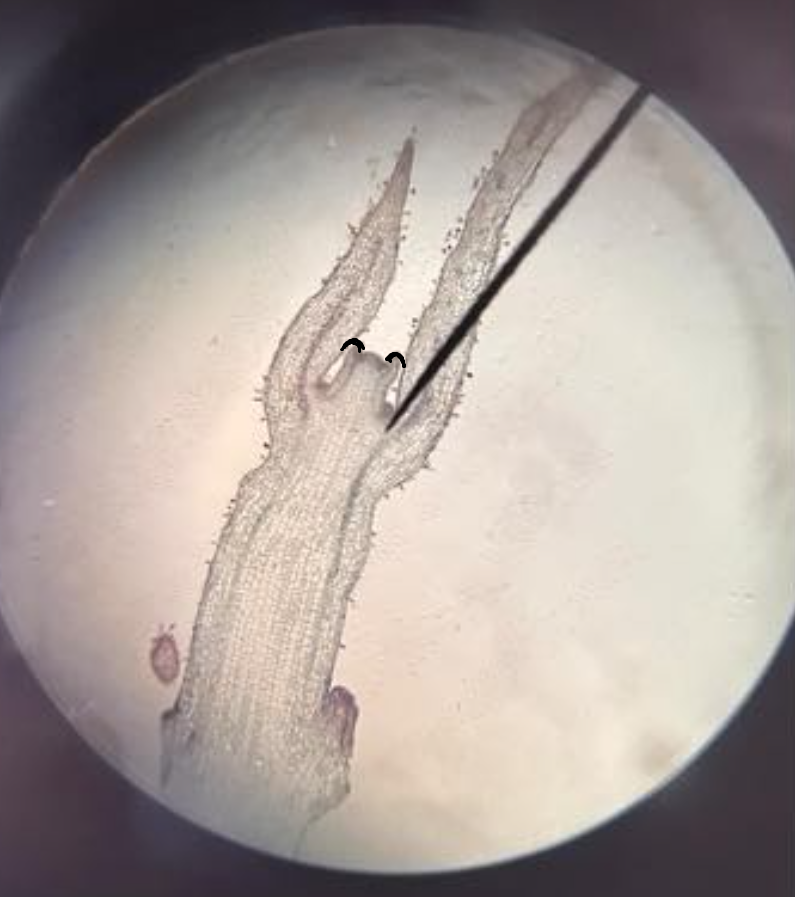
leaf primordia
part of SAM under microscope; groups of cells that will form into new leaves; can be young (smaller) or old (bigger)
root apical meristem (RAM)
primary meristem that produces the root and responds to gravitational cues
Allium cepa
onion
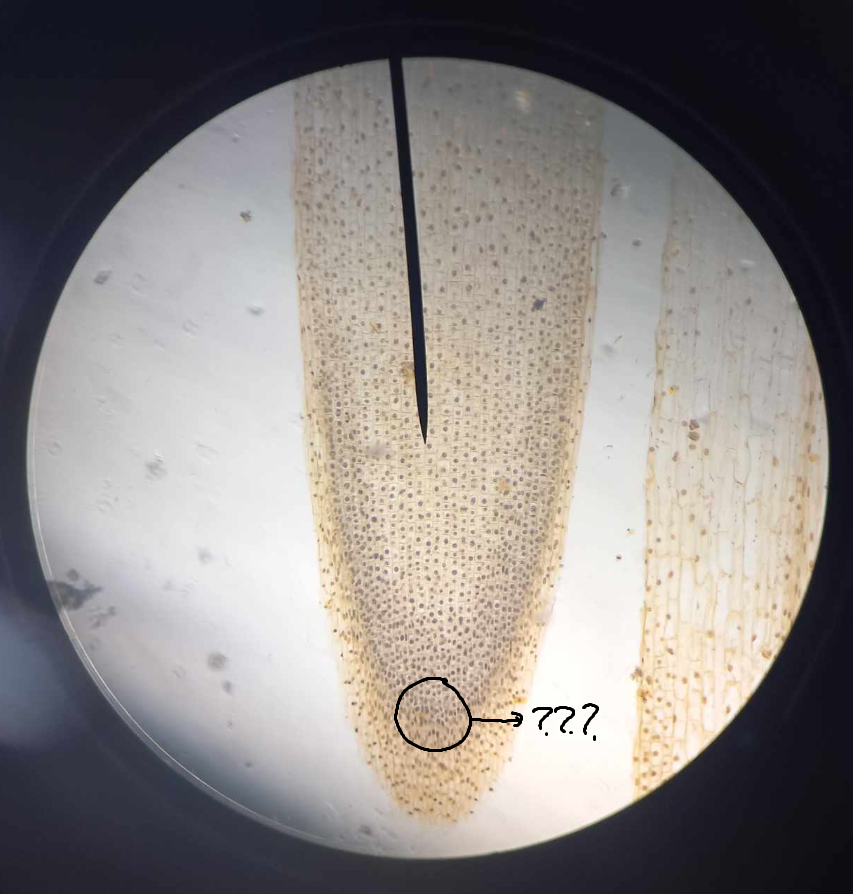
root cap; quiescent center
parts of a root apical meristem (RAM)
root cap
part of RAM; protective tissue located at the tip of every root
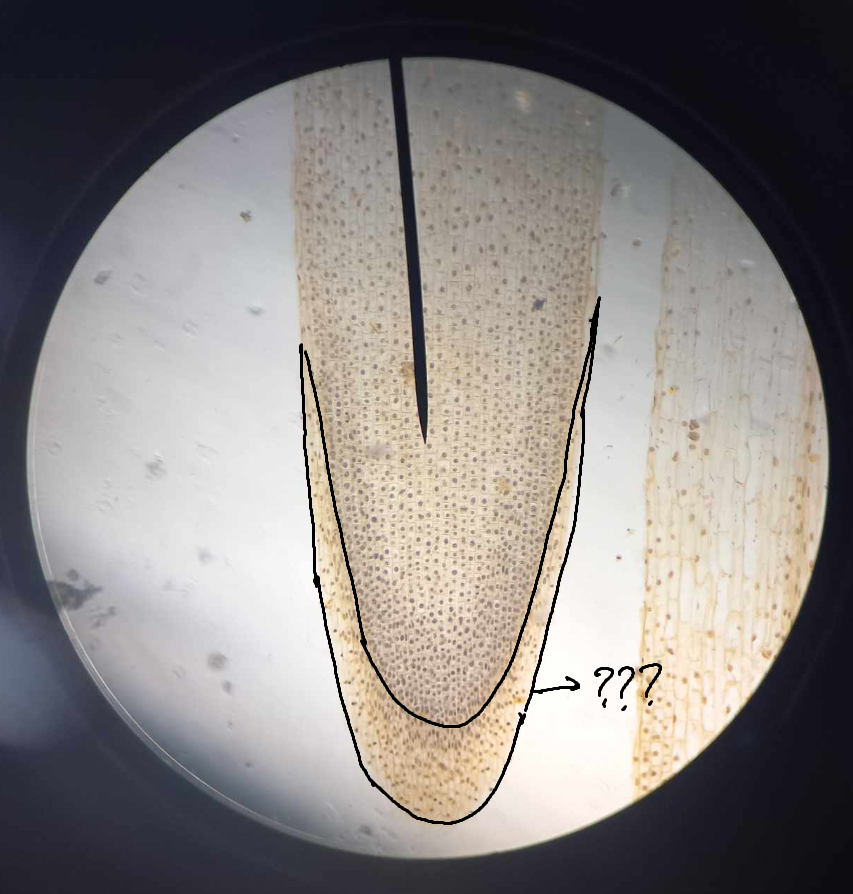
quiescent center
part of RAM; a group of cells, up to 1,000 in number, in the form of a hemisphere, with the flat face toward the root tip of vascular plants
secondary/lateral meristem
a type of meristem responsible for continuing meristematic activity produce secondary tissues for taxa with secondary growth
herbaceous plants
usually monocots; non woody; seldom undergo secondary growth
woody plants
usually gymnosperms and eudicots; grow tall with sturdy trunks as a result of secondary growth
Anonna squamosa
atis; custard apple
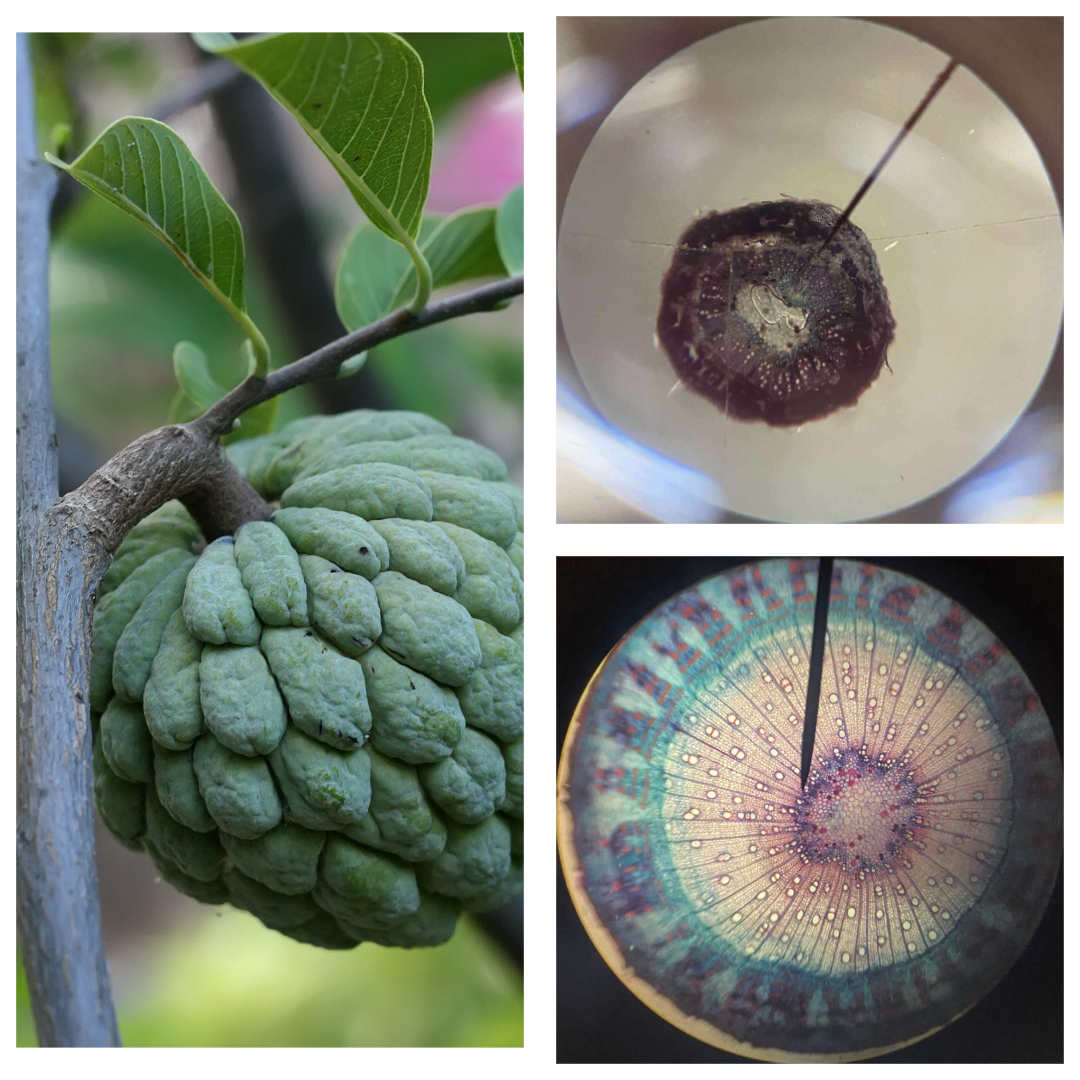

vascular cambium
secondary meristem responsible for increasing the diameter of stems and roots and for forming woody tissue
fascicular cambium; interfascicular cambium; vascular bundle
parts of the vascular cambium
fascicular cambium
cambium that is located within the vascular bundles in plants, between the xylem and phloem
interfascicular cambium
cambium that is located between vascular bundles
vascular bundles
composed of xylem, phloem, and sometimes a layer of cambium cells
cork cambium (phellogen)
secondary meristem; a single layer of thin-walled cells that continue to divide and produce phelloderm and phellem (dead cork cell layers) on the outside of the stem
phelloderm
inside of cork cambium; composed of living parenchyma cells
phellem
dead cork cell layers
permanent tissues
vary in form and function and the types of component cells; two types in terms of cell composition: simple or complex; three types: dermal; ground; vascular
simple tissues
range from the common cell type (parenchyma) to some more specialized ones (collenchyma and sclerenchyma)
complex tissues
vascular tissues composed of conductive elements and non-conducting cells
dermal; ground; vascular
three types of permanent tissues
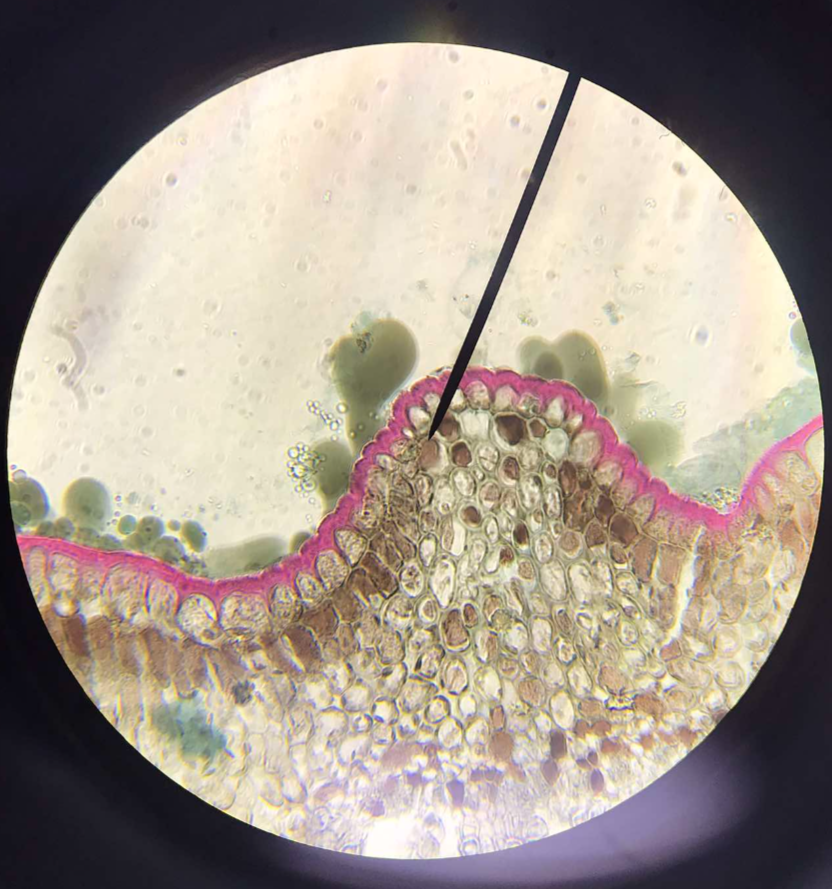
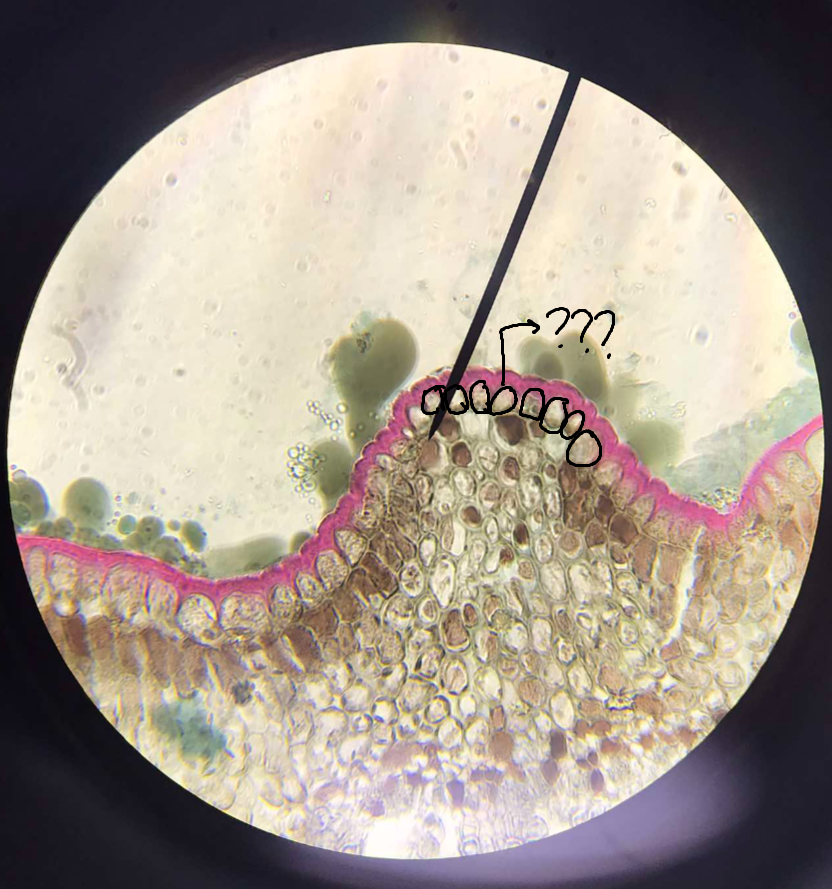
dermal tissues
permanent tissue; surface tissues of the plant body; composed of the epidermis and periderm
epidermis
dermal tissue; the outermost cell layer of the plant body; two types: uniseriate and multiseriate
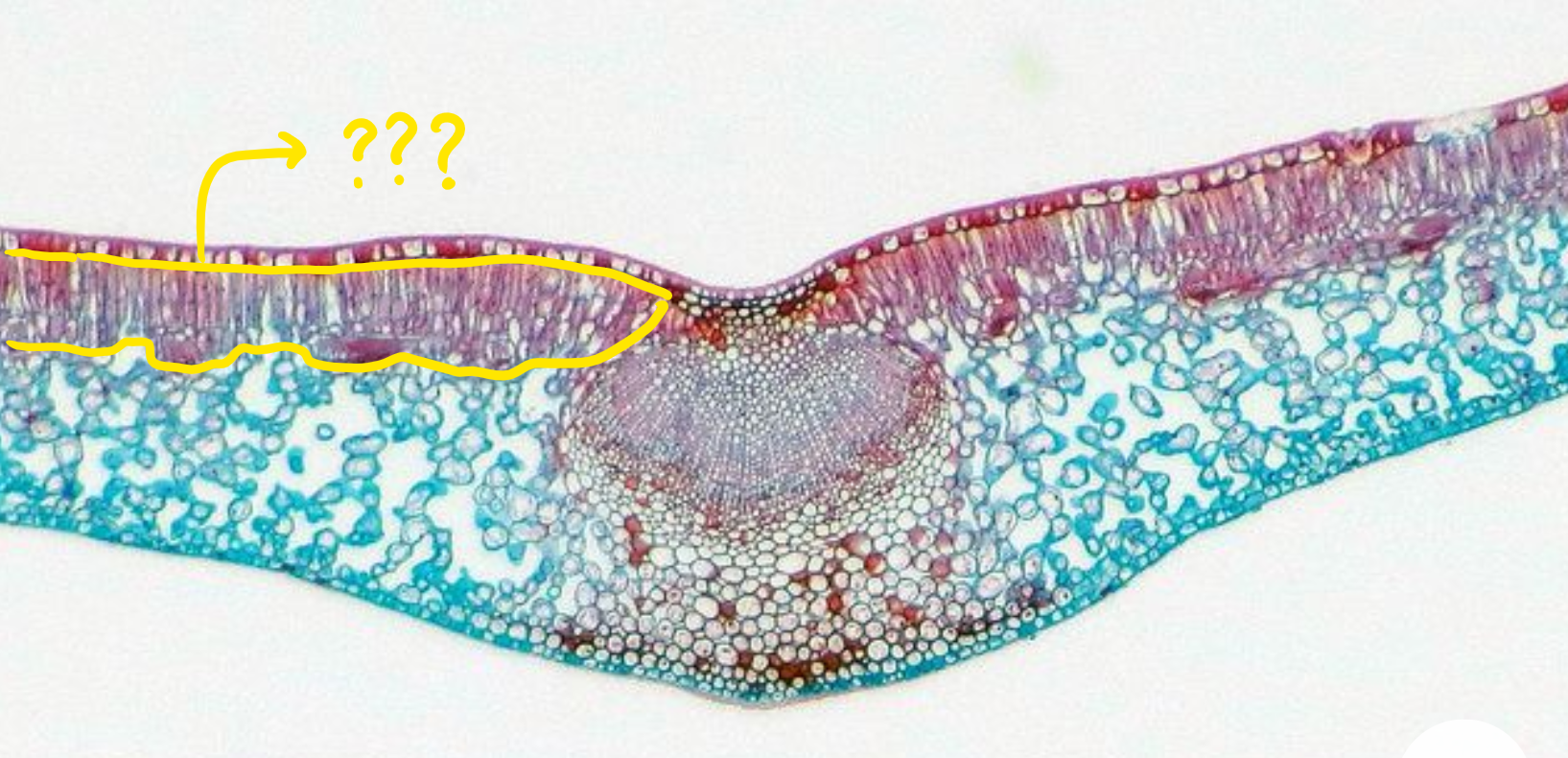
adaxial epidermis
upper surface of the leaf
palisade mesophyll
nearer the adaxial side of the epidermis; oblong in shape, densely packed and contact with each other; maximize energy production during photosynthesis
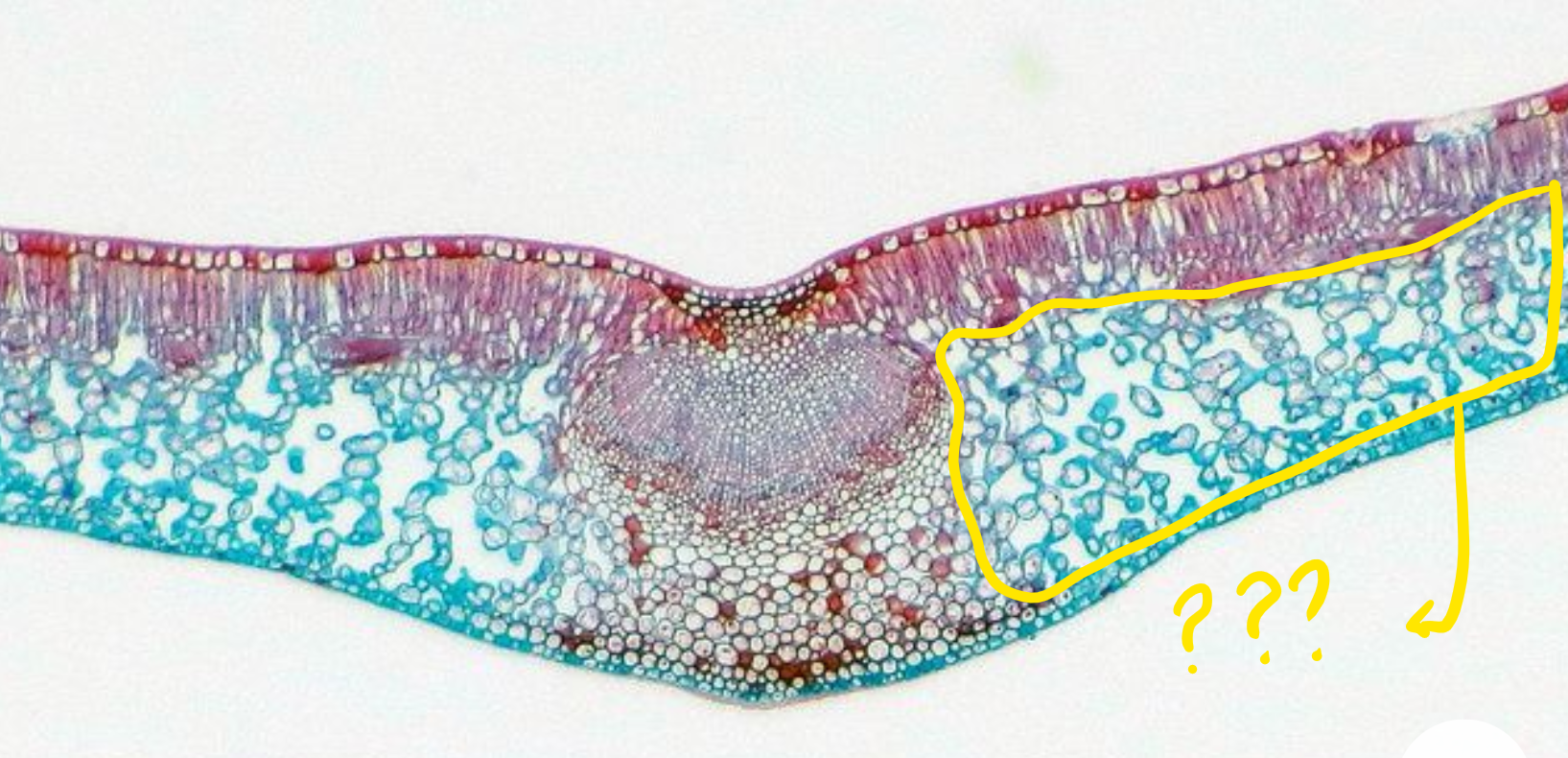
abaxial epidermis
lower surface of the leaf
spongy mesophyll
nearer the abaxial side of the epidermis; uneven in shape and have air spaces between them; facilitate the exchange of gases essential to the process of photosynthesis
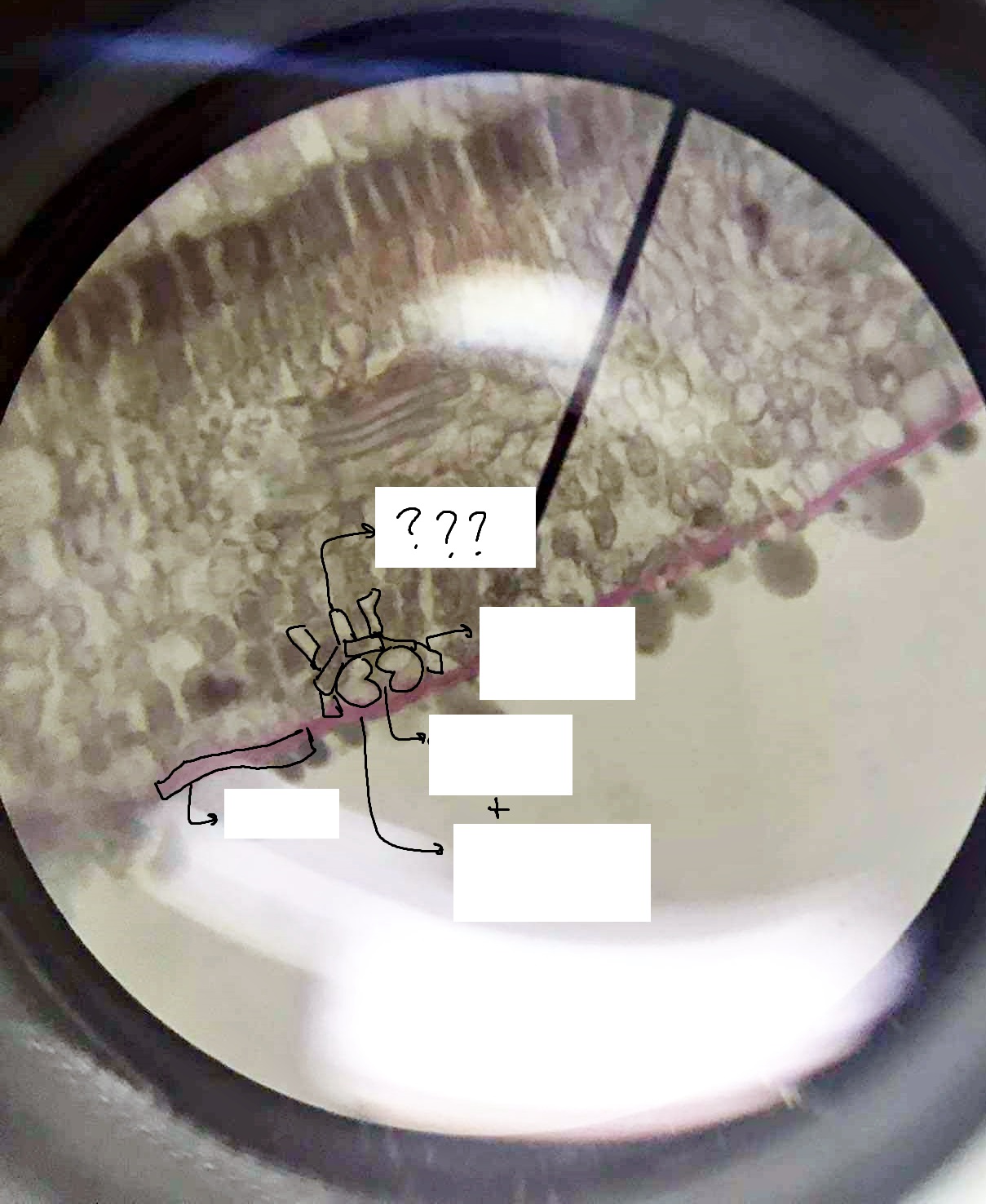
cuticle; guard cells; ordinary epidermal cell; stomatal pore; subsidiary/accessory cell; substomatal chamber
parts of the epidermis
cuticle
a protecting film covering the outermost skin layer (epidermis) of leaves, young shoots and other aerial plant organs
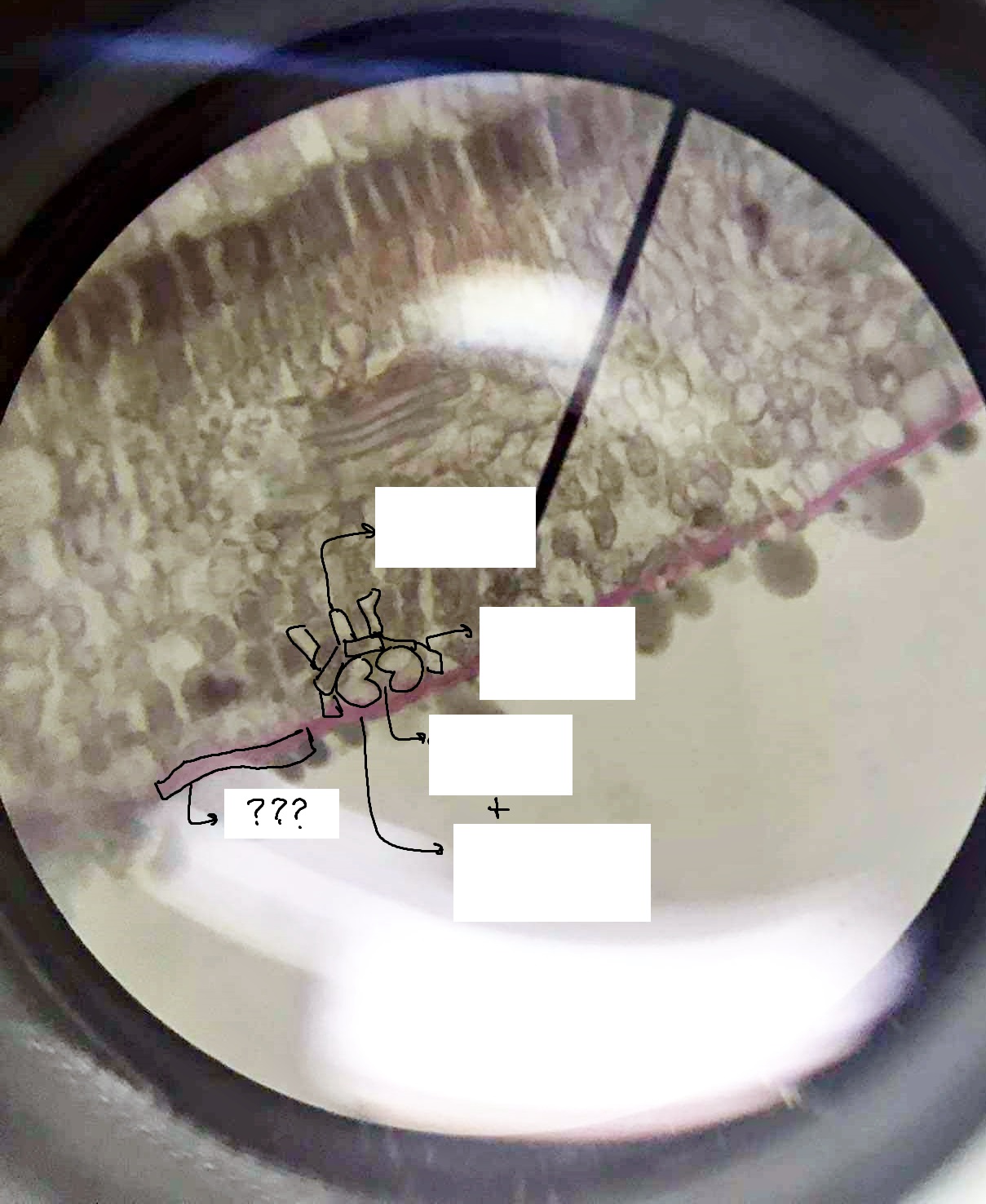
stoma
a pore flanked by guard cells found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange between the internal air spaces of the leaf and the atmosphere
guard cells
part of the epidermis and stoma; help to regulate the rate of transpiration by opening and closing the stomata
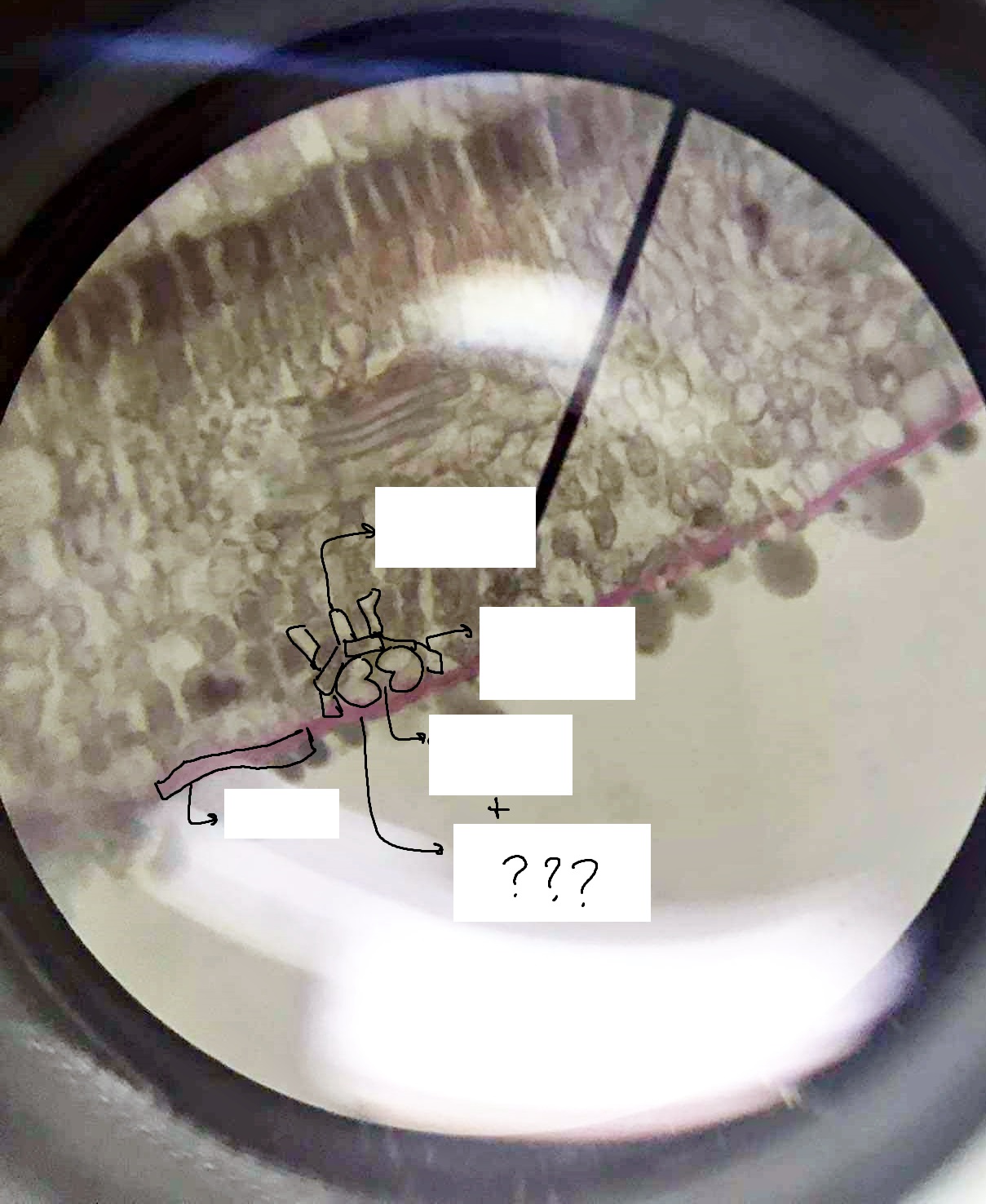
stomatal pore
microscopic holes in the leaves and stems of plants that allow for gas exchange with the environment
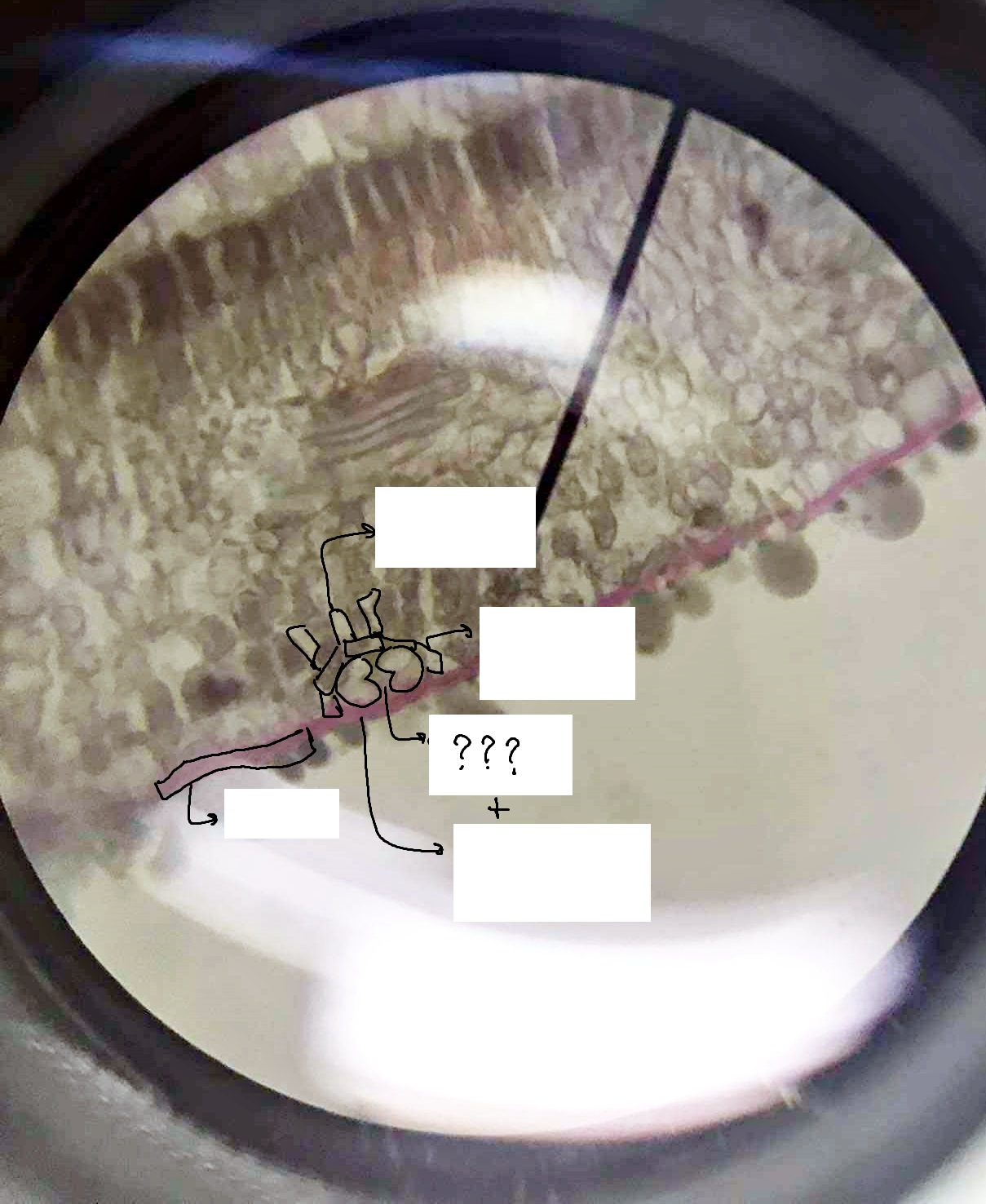
ordinary epidermal cell
cells that lie between the more specialized cells of the epidermis
subsidiary/accessory cell
part of the epidermis; surround and support guard cells
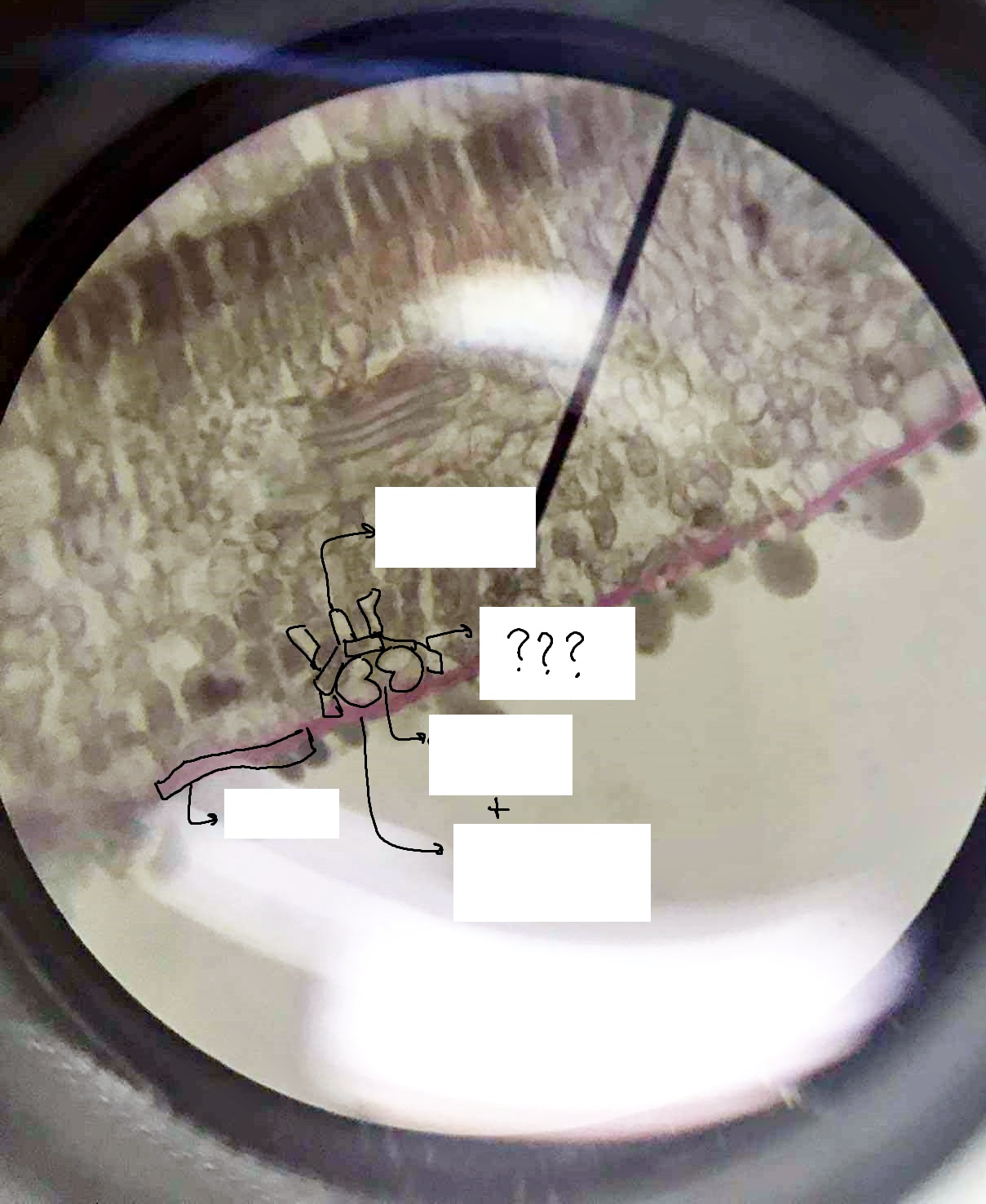
substomatal chamber
the cavity located immediately proximal to the stoma
uniseriate
epidermis with one cell layer
Ixora
santan; West Indian jasmine
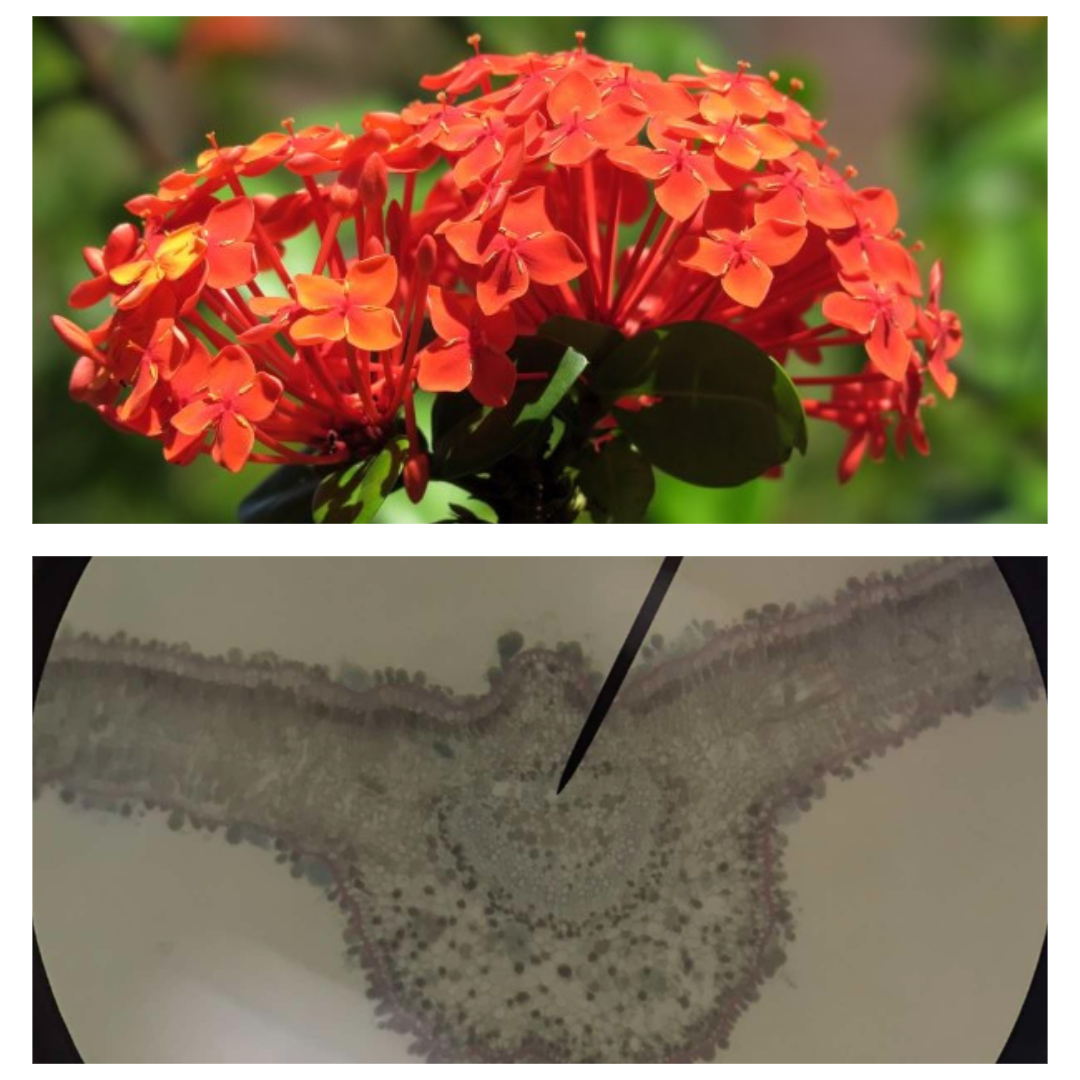

multiseriate
a.k.a. multiple epidermis; epidermis with more than one cell layer; one or more layers beneath the outermost are derived from the protoderm by periclinal divisions and may be morphologically and physiologically distinct from the deep-lying ground tissues
cystoliths
calcium carbonate deposits inside cells
lithocysts
cells that bear cystoliths