astro final
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Suppose that one year you put 10 kilograms of a radioactive isotope in a cabinet in your laboratory. The stuff has a half-life of 10 years. If 30 years later you stumble across that stuff, you will find that you still have how much of the radioactive isotope?
a. 7.5 kilograms
B. 5.0 kilograms
C. 2.5 kilograms
D. 1.25 kilograms
E. 0.625 kilograms
D. 1.25 kilograms
Oxygen has atomic number = 8
The “ion” O+5 has a net charge of +5. How many electrons are in the “cloud” around the nucleus of O+5?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 5
E. 8
C. 3 electrons
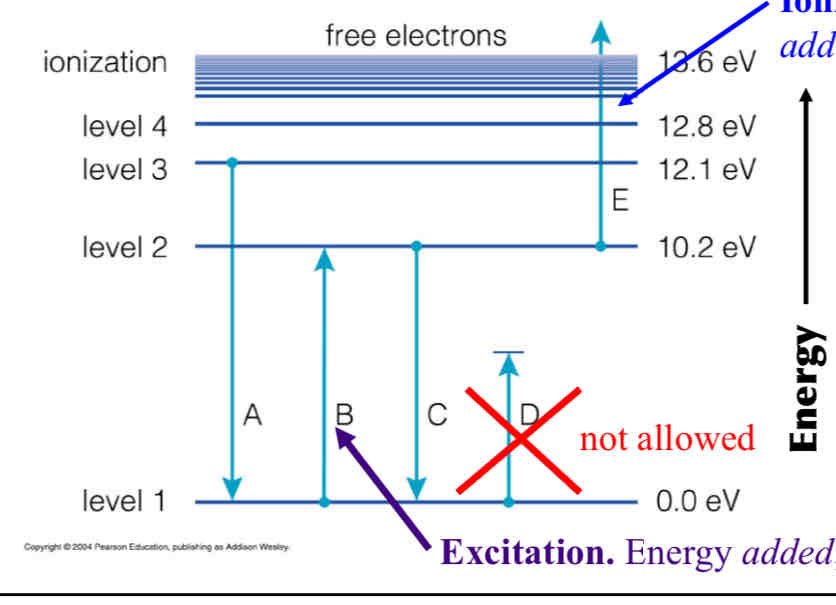
Atom energy levels are often depicted in a simple way as shown below. Clicker Question! Atoms often spontaneously emit radiative energy (light). Which of the electron transitions shown below (A, B, C, D, or E) would cause the atom to emit light?
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
5. E
6. A and B
7. A and C
8. A, B, C
9. A, B, C, D
10. All of them
A and C
Opposite charges attract, but similar charges repel each other. The nucleus of helium contains two positive protons and two neutral neutrons. Why don’t the similarly-charged protons in this nucleus push each other away?
A. There is a strong chemical bond inside the
nucleus.
B. The attraction of the negatively-charged electrons holds the protons together.
C. There is a force that is even stronger than the charge force that holds the nucleus together, but it only acts on short distance scales, i.e., when particles are quite close together.
C. There is a force that is even stronger than the charge force that holds the nucleus together, but it only acts on short distance scales, i.e., when particles are quite close together.
iClicker question. The tablecloth trick is all about manipulating:
A. gravity
B. the electromagnetic force
C. the nuclear strong force
D. the nuclear weak force
B. the electromagnetic force
(the electromagnetic force is trillions of times stronger than gravity)
Which of the following is least likely to be accelerating?
A. A car driving down a winding, narrow mountain road.
B. A racecar driver.
C. A car driving through Texas on the interstate highway.
D. A bumper car at a county fair.
E. A planet orbiting a star.
C. A car driving through Texas on the interstate highway.
• The mass of Jupiter is approximately 30,000 times greater than the mass of the Moon.
• The distance from the Earth to Jupiter is 1500 times greater than the distance from the Earth to the Moon.
Which of these objects exerts a stronger force of gravity on the Earth?
A. Jupiter
B. The Moon
the moon
When a rocket blasts off, it pushes off the ground in order to launch itself into the air.
A. TRUE
B. FALSE
B. false
(rockets are based on the conservation of momentum)
You are a shuttle astronaut returning to the shuttle after attempting to fix the International Space Station with a hammer. As you are jetting back to your shuttle, your lifeline breaks, your jets run out of fuel, your radio goes dead, and you miss the shuttle. To get back safely, you should:
A. use a swimming motion with your arms and legs
B. throw the hammer at the shuttle to get someone’s attention
C. throw the hammer away from the shuttle
D. make a hammering motion in the direction of the shuttle
E. make a hammering motion away from the shuttle
C. throw the hammer away from the shuttle
To steer a bicycle, you just move the handlebars.
A. TRUE
B. FALSE
B. false
(To steer a bicycle, you must control and manipulate the angular momentum in the spinning wheels. To change directions, you must lean your body around to manipulate the angular momentum)
Which part of Newton’s physics of motion could be used to point the Hubble Space Telescope at an interesting object? This could be accomplished various ways, but a frequently used method is to employ:
A. Newton’s 1st Law
B. Newton’s 2nd Law
C. Newton’s 3rd Law
D. Conservation of linear momentum
E. Conservation of angular momentum
E. Conservation of angular momentum
Three balls in space near a planet Suppose an astronaut places three equal mass balls next to each other out in space above some planet as shown on the previous screen. The balls are initially at rest. After some time, the balls will
A. still be the same (i.e., nothing will have changed).
B. all be falling toward the planet at the same speed.
C. all be falling toward the planet with ball 3 moving fastest.
D. all be falling toward the planet with ball 1 moving fastest.
C. all be falling toward the planet with ball 3 moving fastest.
If the Sun suddenly collapsed into a black hole with the same mass but 10 times smaller diameter, how would the Earth’s orbit change?
A. It would become 10 times smaller.
B. It would become 100 times smaller.
C The Earth would plunge into the black hole.
D. The Earth would spiral into the black hole.
E. Nothing would change.
E. nothing would change
Tides are readily apparent in the oceans because liquid water flows more readily than rock. Can tidal effects be observed easily on planets that have no water?
A. No, tidal effects are too subtle if there aren’t oceans.
B. Yes.
B. yes
In the 1800s, physicists showed that there is no “ether” filling space, so light must propagate through an (pretty much) an empty vacuum.
SURVEY QUESTION: which of the fundamental forces has a profound connection to light? There is a relationship between light and the fundamental forces in our universe….
A. The force of gravity
B. The electromagnetic force
C. The nuclear “strong” force
D. The nuclear “weak” force
B. The electromagnetic force
A red fire truck is red because:
A) it only emits frequencies corresponding to red
B) it only reflects frequencies corresponding to red
C) it only transmits frequencies corresponding to red
D) it only absorbs frequencies corresponding to red
B) it only reflects frequencies corresponding to red
A red neon sign is red because:
A) it only emits frequencies corresponding to red
B) it only reflects frequencies corresponding to red
C) it only transmits frequencies corresponding to red
D) it only absorbs frequencies corresponding to red
A) it only emits frequencies corresponding to red
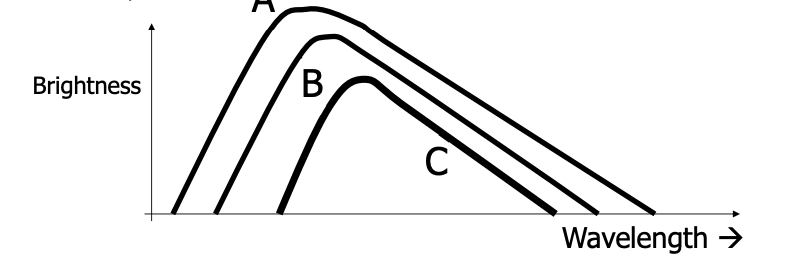
The graph below shows the blackbody spectra of three different stars. All three stars have the same size. Which of the stars is at the highest temperature?
A) Star A
B) Star B
C) Star C
A) Star A
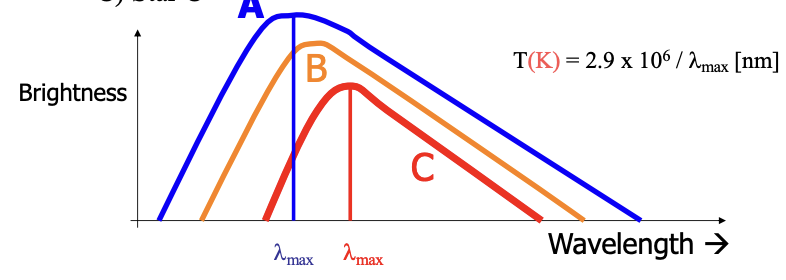
The graph below shows the blackbody spectra of three different stars. All three stars have the same size. Which of the stars is at the highest temperature?
A) Star A
B) Star B
C) Star C
A) Star A
Uranus is almost 20 times farther from the Sun than the Earth. Consider one of the moons of Uranus that has no atmosphere. How much colder is the surface of that moon compared to the surface of the Earth’s Moon?
A. 20 times colder
B. 40 times colder
C. 200 times colder
D. 400 times colder
E. 1000 times colder
D. 400 times colder
At the present time, the inside of the Earth is
A. Entirely molten rock, i.e., “magma”
B. Entirely solid rock
C. Mostly magma with a small amount of solid rock
D. Mostly solid rock with a small amount of molten rock
D. Mostly solid rock with a small amount of molten rock
(In its early days, the interior of the Earth was mostly molten (liquid) rock. As time passed, this cooled off and turned solid, and only a small liquid region remains…)
Consider a gas cloud in space, such as the one shown at right. Suppose that it starts to collapse suddenly
What will happen to the temperature of the cloud as it collapses?
A. The cloud will cool down.
B. The cloud will warm up.
C. The cloud temperature will remain the same.
D. This cannot be answered without additional information.
B. The cloud will warm up.
Consider a balloon full of air. Inside that balloon, which of the following elements will move the slowest?
A. Hydrogen (atomic weight = 1)
B. Helium (atomic weight = 4)
C. Nitrogen (atomic weight = 14)
D. Oxygen (atomic weight = 16)
D. Oxygen (atomic weight = 16)

Look carefully at this picture. What might you conclude about the way that Saturn formed?
A. Tidal forces due to encounters between Saturn and comets/asteroids are the main origin of the rings
B. Saturn is a “mini solar system”. The physics that led to the formation of the rings are the same as those that formed the Sun and its planets, etc.
B. Saturn is a “mini solar system”. The physics that led to the formation of the rings are the same as those that formed the Sun and its planets, etc.
The basic idea at the core of the nebular theory of solar system formation is that
nebulae are clouds of gas and dust in space. | ||
the planets each formed from the collapse of their own separate nebulae. | ||
it is a discarded idea in which planets formed as a result of a near collision between our Sun and another star. | ||
our solar system formed from the collapse of an interstellar cloud of gas and dust. | ||
All of the Above |
our solar system formed from the collapse of an interstellar cloud of gas and dust.
What is the definition of the "frost line" in the context of solar system formation theory?
It marks the special distance from the sun at which hydrogen compounds became abundant; closer to the Sun, there were few or no hydrogen compounds. | ||
It is the altitude in a planet's atmosphere at which snow can form. | ||
The frost line is the distance from the Sun beyond which the temperature in the protosolar nebula was low enough for ices to condense. | ||
It is another way of stating the temperature at which water freezes into ice. |
The frost line is the distance from the Sun beyond which the temperature in the protosolar nebula was low enough for ices to condense.
According to nebular theory, what are asteroids and comets?
Chunks of rock or ice that were originally in interstellar space but were captured by the solar system. | ||
They are leftover planetesimals that never accreted into planets. | ||
They are the shattered remains from collisions between planets. | ||
All of the Above |
They are leftover planetesimals that never accreted into planets.
What do we mean by the period of "heavy bombardment" in the context of the development of our solar system?
The time before planetesimals finished accreting into planets, during which many growing planetesimals must have shattered in collisions. | ||
The first few hundred million years after the planets formed, which is when most impact craters were formed. | ||
The time during which heavy elements condensed into rock and metal in the protosolar nebula. | ||
The period about 65 million years ago, when an impact is thought to have led to the extinction of the dinosaurs. |
The first few hundred million years after the planets formed, which is when most impact craters were formed.
According to modern scientific dating techniques, approximately how old is the solar system?
10,000 years | ||
14 billion years | ||
4.6 billion years | ||
4.6 million years |
4.6 billion years
Which of the following best explains why the vast majority of the mass of our solar system consists of hydrogen and helium?
Hydrogen and helium are produced in stars by nuclear fusion. | ||
All the other elements escaped from the protosolar nebula before the Sun and the planets formed. | ||
All the other elements were swept out of the solar system by the solar wind. | ||
Hydrogen and helium are the most common elements throughout the Universe because they were the only elements that were formed when the Universe was extremely young. All other elements were subsequently synthesized inside stars, which is an inefficient process. |
Hydrogen and helium are the most common elements throughout the Universe because they were the only elements that were formed when the Universe was extremely young. All other elements were subsequently synthesized inside stars, which is an inefficient process.
What is the primary basis upon which we divide the ingredients of the protosolar nebula into four categories (hydrogen/helium, hydrogen compounds, rock, and metal)?
The locations of various materials in the protosolar nebula. | ||
The amounts of energy required to ionize various materials. | ||
The temperatures at which various materials will condense from gaseous form into solid form. | ||
All of the Above |
The temperatures at which various materials will condense from gaseous form into solid form.
The rigid rocky material of the crust and uppermost portion of the mantle is called the
lithosphere
True or false? Smaller worlds generally have thinner lithospheres
false
Which of the following is an example of convection?
Heating that occurs when gravitational potential energy is converted to heat when dense materials sink into the middle of a terrestrial planet. | ||
Different kinds of material separating by density, like oil and water | ||
Warm air expanding and rising while cooler air contracts and falls | ||
A rock sinking in water |
Warm air expanding and rising while cooler air contracts and falls
Which terrestrial world has the greatest difference in temperature between its "no atmosphere" temperature and its actual temperature?
AND
What causes this difference?
Venus, Carbon Dioxide
Suppose that the Earth's atmosphere had no greenhouse gases. In this case, the Earth's average surface temperature would be
slightly warmer, but still below the boiling point of water. | ||
some 30 degrees celcius cooler, i.e., well below the freezing point of water. | ||
slightly cooler, but still above freezing. | ||
about the same as it is now. |
some 30 degrees celcius cooler, i.e., well below the freezing point of water.
Which planet or planets have an atmosphere that consists mostly of carbon dioxide?
Venus only | ||
Venus and Mars | ||
Venus, Earth, and Mars | ||
Mars only |
Venus and Mars
In essence, the flat shape of the Solar System results from
rotation of the original cloud from which it formed. | ||
intense magnetic fields generated by the Sun during the early days of the Solar System. | ||
a collision of the early solar system with another cloud that squashed it. | ||
All of the Above | ||
None of the Above |
rotation of the original cloud from which it formed.
The cratered surfaces on many planets and moons are evidence that
volcanic activity was common in the early Solar System. | ||
gravity was much stronger in the past than it is now. | ||
remnant planetesimals and their fragments bombarded the surfaces of these objects. | ||
aliens waged nuclear war in the early Solar System. |
remnant planetesimals and their fragments bombarded the surfaces of these objects.
he statements below make comparisons between the Jovian and the terrestrial planets. Which of these statements is NOT true?
The Jovian planets have greater masses than the terrestrial planets. | ||
The Jovian planets have higher densities than the terrestrial planets. | ||
The Jovian planets have larger diameters than the terrestrial planets. | ||
The Jovian planets have more satellites than the terrestrial planets. | ||
None of the Above |
The Jovian planets have higher densities than the terrestrial planets.
The atmosphere of Mars is mostly
hydrogen. | ||
molecular nitrogen. | ||
hydrogen compounds such as methane and ammonia. | ||
CO2 (carbon dioxide). | ||
None of the Above |
CO2 (carbon dioxide). |
Condensation in the protosolar nebula probably led to the formation of
rocky silicate grains near the present orbit of Earth. | ||
icy grains beyond the present orbit of Jupiter. | ||
metallic grains near the present orbit of Mercury. | ||
All of the Above | ||
None of the Above |
All of the above
The amount of gravitational potential energy released as an object falls depends on
its mass and its speed at the time it begins falling. | ||
only the distance it falls. | ||
its mass and the distance that it falls. | ||
only its mass. |
its mass and the distance that it falls. |
Consider an atom of gold in which its nucleus contains 79 protons and 118 neutrons. What is its atomic number and atomic weight?
atomic number = 79 and atomic weight = 197 | ||
atomic number = 118 and atomic weight = 79 | ||
atomic number = 79 and atomic weight = 118 | ||
atomic number = 118 and atomic weight = 197 |
atomic number = 79 and atomic weight = 197
True or false? If you double the mass of fusion material in a hydrogen bomb, you quadruple the amount of energy generated
False
Which object has the most kinetic energy?
A 1-ton car moving at 100 km/hour | ||
A 2-ton car moving at 50 km/hour | ||
A 1-ton car moving at 50 km/hour | ||
A 10-ton boat moving at 10 km/hour |
A 1-ton car moving at 100 km/hour
The planets never travel in a straight line as they orbit the Sun. According to Newton's second law of motion, this must mean that
the planets will eventually fall into the Sun. | ||
planetary motions cannot be predicted. | ||
a force is acting on the planets. | ||
the planets have angular momentum. |
a force is acting on the planets. |
If one object has a large redshift and another object has a small redshift, what can we conclude about these two objects?
The one with the large redshift is hotter and therefore is putting out more radiation. | ||
The one with the large redshift is moving away from us, and the one with the small redshift is moving toward us. | ||
The one with the large redshift is moving away from us faster than the one with the small redshift. | ||
The one with the large redshift is moving toward us faster than the one with the small redshift. |
The one with the large redshift is moving away from us faster than the one with the small redshift.
What is the ecliptic plane?
The plane of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. | ||
The plane of the Sun's equator. | ||
The plane of the Milky Way. | ||
The plane of the Earth's equator. |
The plane of the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
Suppose that we observe two distant galaxies: Galaxy 1 is twice as far away as Galaxy 2. In that case,
Galaxy 1 must be twice as big as Galaxy 2. | ||
we are seeing Galaxy 1 as it looked at an EARLIER time in the history of the universe than the time at which we are seeing Galaxy 2. | ||
we will observe a Doppler shift of the spectrum of Galaxy 2 but not of Galaxy 1. | ||
we are seeing Galaxy 1 as it looked at a LATER time in the history of the universe than the time at which we are seeing Galaxy 2. |
we are seeing Galaxy 1 as it looked at an EARLIER time in the history of the universe than the time at which we are seeing Galaxy 2. |
If the Moon is setting at 6AM, the phase of the Moon must be
third quarter. | ||
new. | ||
first quarter. | ||
full. |
full
True or false? The Milky Way can only be seen from the Northern Hemisphere.
False
Which of the following is NOT one of, nor is a direct consequence of, Kepler's Laws?
The force of attraction between any two objects decreases with the square of the distance between their centers. | ||
More distant planets orbit the Sun at slower speeds. | ||
As a planet moves around its orbit, it sweeps out equal areas in equal times. | ||
The orbit of each planet about the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus. |
The force of attraction between any two objects decreases with the square of the distance between their centers.
Which of the following was not observed by Galileo?
Phases of Venus | ||
Four moons orbiting Jupiter | ||
Stellar parallax | ||
Mountains and valleys on the Moon |
Stellar parallax
Which of the following balloons is most likely to pop?
A balloon filled with a gas with density = 5 grams/cm3 and temperature = 10o C | ||
A balloon filled with a gas with density = 10 grams/cm3 and temperature = 20o C | ||
A balloon filled with a gas with density = 20 grams/cm3 and temperature = 20o C | ||
A balloon filled with a gas with density = 5 grams/cm3 and temperature = 20o C |
A balloon filled with a gas with density = 20 grams/cm3 and temperature = 20o C
Your seat belt prevents you from crashing forward into the dashboard when your car suddenly stops. Your forward motion before your belt saves you is an example of
Newton's 2nd law of motion | ||
Newton's law of gravity | ||
Newton's 1st law of motion | ||
Newton's 3rd law of motion | ||
None of the Above |
Newton's 1st law of motion
One reason the ancient Greeks rejected the idea that the Earth moves around the Sun was that they
thought the Earth was flat and unable to move. | ||
could see no shift in positions of nearby stars compared to distant stars (parallax) over the course of the year. | ||
thought that the Earth was much bigger than the Sun. | ||
observed retrograde motion. | ||
All of the Above |
could see no shift in positions of nearby stars compared to distant stars (parallax) over the course of the year.