Cardiovascular System and Cardiac Muscle+ MAP
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what makes up blood
plasma and formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets)_
how many pumps?
two pumps in series
blood flow valves
right atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonary semilunar valve → lungs
left atrium → mitral/bicuspid valve → left ventrice → aortic semilunar valve → systemic circulation
right ventricle becomes weak and fails to eject: where will blood back up?
vena cava
Chordinae tendinae function
attaches AV valves to papillary muscles in ventricular wall: prevents valve from prolapsing into atria when valves are closed during ventricular contraction
ventricular wall heart muscle layers
Pericardium?
Coronary artery with branches into where?
endocardium, myocardium, epicardium
sac around heart
Myocardium
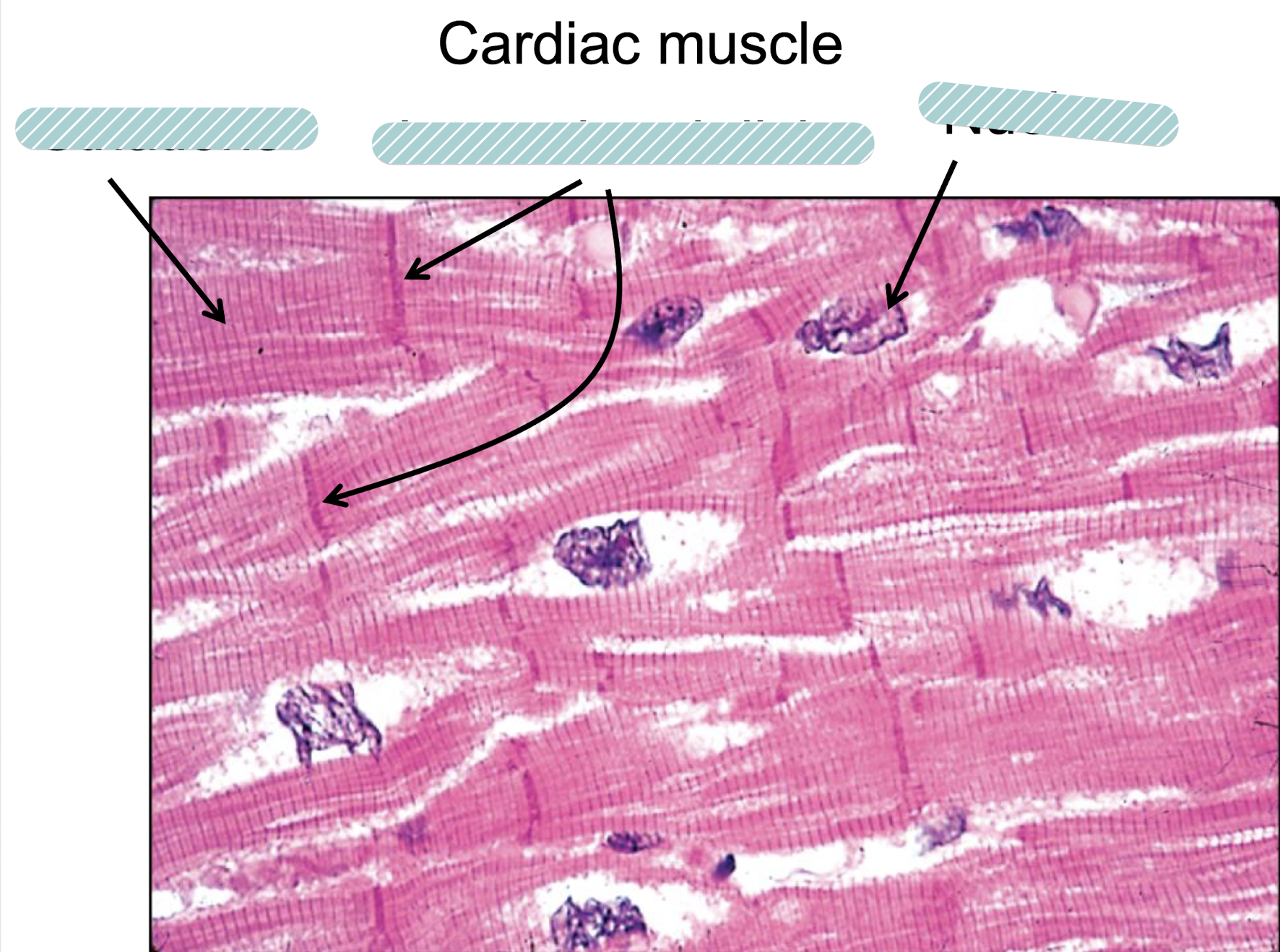
striations, intercalated disc, nucleus
What ensures that all myocytes are involved with each contraction and enables cardiac muscle to act as functional syncytium?
electrically coupled via gap junctions in the intercalated discs
MAP =?
CO * TPR
What is TPR?
resistance in all of systemic blood vessels
What is main controller of TPR?
arterioles
(arterioles and capilaries have highest resistance, but capillaries lack smooth muscle, so cant control)
What can affect TPR?
What about CO?
Anything that will cause constriction or dilation of arterioles
Contraction and relaxation of veins (venous return)
Short term control of TPR, for example standing up
baroreceptor reflex:
Heart control
Rest: PS
SNS
Vasomotor tone: just SNS
standing up → rapid decrease of MAP
Baroreceptros in aortic arch and carotid sinus
increase SNS, decrease PSNS
Baroreceptor response to decrease in MAP: continued: decrease PSNS, increase SNS
symp
Arterioles constrict
Increases TPR
Veins constrict
Increase venous return → increased CO
Increased HR
increased forced of contraction: both lead to increase in CO
in people with hypertension, why doesnt baroreceptor response lower BP?
only for short term