biol 3301 lecture 1
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
what is a microbe
Free-living organism that can only be seen under a microscope (typically <100 microns)
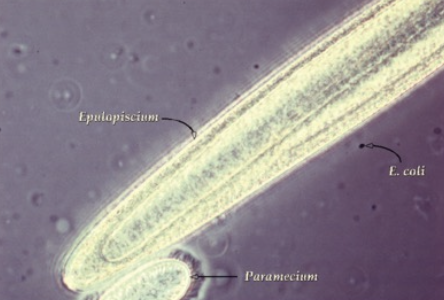
which microbe is not free-living (example)
Chlamydia trachomatis- Causative agent of the most commonly reported sexually transmitted bacterial infection in the US
are viruses alive or cellular?
they are NOT cellular organisms and cant replicate indepentantly
size ranges of microbes
microscopic to macroscopic
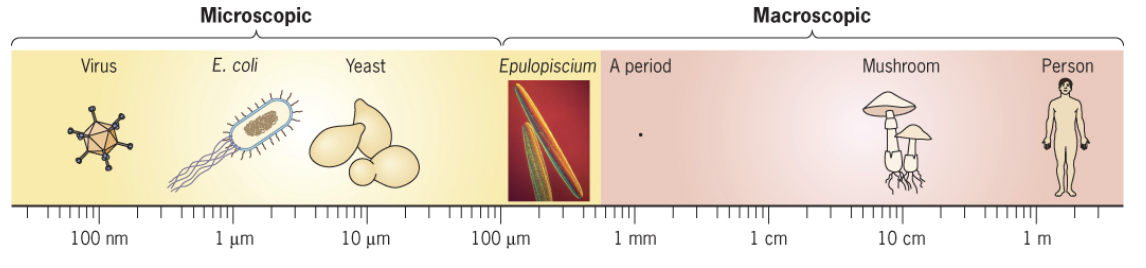
where are microbes most diverse
plants and animals!! they grow virtually everywhere on earth
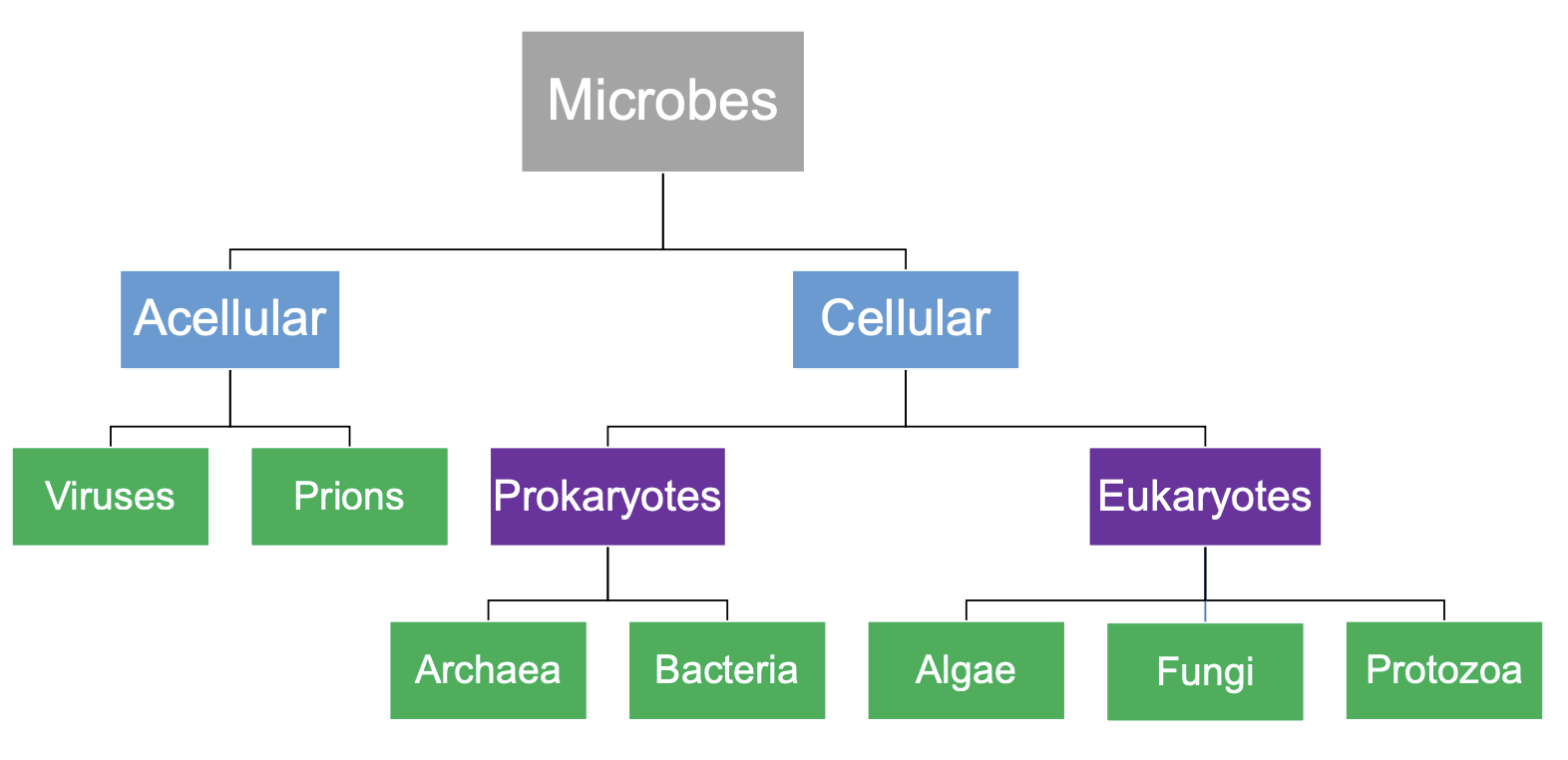
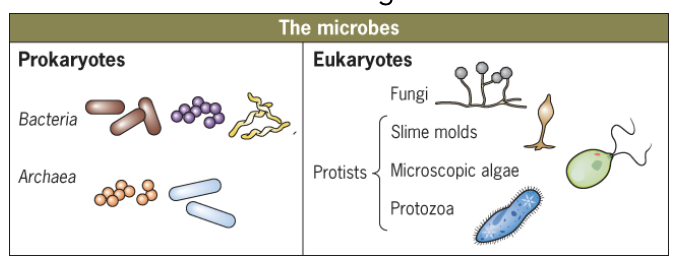
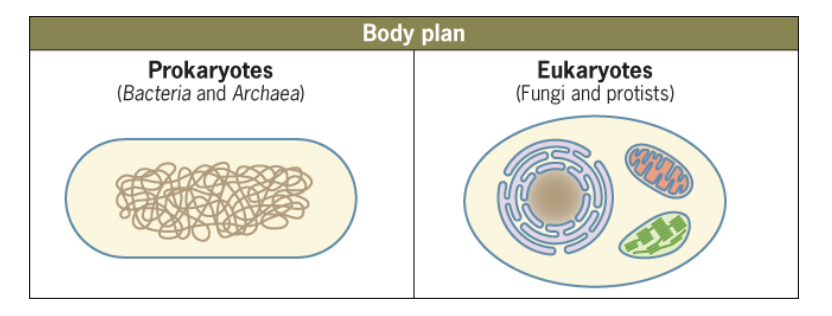
prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
prokaryotes (Bacteria, Archaea) are simple cells lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, with DNA in a nucleoid region, while eukaryotes (animals, plants, fungi, protists) are complex cells with a true nucleus (containing linear DNA) and other membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, ER, and Golgi.
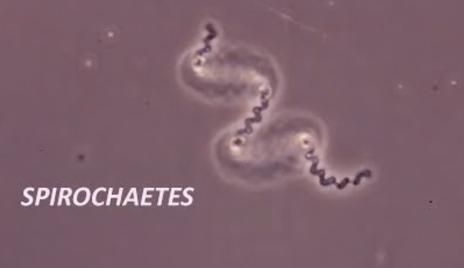
Spirochetes shape
Spirochetes are corkscrew-shaped bacteria that excel at moving in viscous medium (i.e. mud and mucus!)
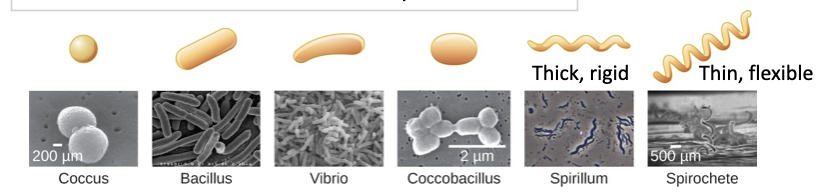
common bacterial cell shapes
coccus, bacillus, vibrio, etc
Prokaryote versus Eukaryote body
p- no true nucleus, thick glob of dna which isnt membrane bound
e-true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles (endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria)
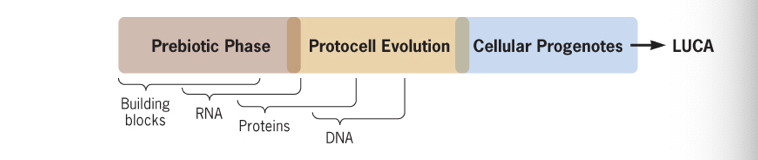
LUCA stands for
Last universal common ancestor
Early on Bacteria and Archaea branched from a common ancestor called
LUCA
proof of shared ancestory lies in..
our DNA
The most useful DNA sequences to reconstruct the evolution of life are those
encoding processes shared by all life forms
what is ribosome- mediated protein synthesis
the cellular process where ribosomes translate messenger RNA (mRNA) into specific chains of amino acids, which then fold into functional proteins, essentially reading genetic code to build life's essential molecules.
WHO compared the relatedness of the small ribosomal RNA genes
carl woese
Why are microbes so good at life?
Answer:
Because they are so small
(and unicellular)
The advantages of being small (volume wise)
The smaller a cell is, the higher its surface-to-volume ratio
Higher surface-to-volume ratio (SA/V) = faster chemical exchange

Why does rapid growth = faster adaptation?
genetic changes aka mutations underlie all adaptations which means small changes in dna sequence (genotype) can result in functional changes (phenotype)
Example in humans: The ability for adults to digest lactose
The ability to digest lactose in adulthood is a result of mutations in the regulatory element of the MCM6 gene that promote continued lactase (the enzyme that breaks down lactose) production.
This adaptation took humans ~20,000 years!
microbes can adapt as LITTLE as
24 hours because they are small in size, they can produce RAPIDLY
Errors (mutations) occur every time DNA is replicated. More replication=more opportunities for adaptive mutation!
Which microbe is the smallest?
Poliovirus
which of the following does the ring of life tree show
eukaryotes arose from area eating a bacteria
Which of the following is NOT a prokaryote?
Yeast
Which organism grows faster?
E. coli
Which environment did LUCA likely call home?
Hydrothermal Vents
cassifying microbes chard