Hash Tables
1/20
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is a hash table?
A data structure that implements an associative array (an array where data is stored as a collection of key-value pairs). The position of the data within the array is determined by applying the hash function to the key.
What are the benefits of a hash table?
Allows verfy efficient searching - O(1) / constant time in the best case.
Adding, updating and deleting data is also very efficient.
How are hash tables implemented and why?
They use an array because you have to be able to access each position of the array directly
The positions in the array are called buckets, which are used to store data
The key is stored as part of or alongside the data
How is the load factor of a hash table defined?
load factor = n/k
k is the number of buckets (positions) in the array
n is the number of occupied buckets. Keeping the load factor at around 0.75 is optimal.
What should the load factor be kept at for optimal performance?
0.75
What is a hash function?
An algorithm that converts a hash key to a hash value
What are the key requirements for a good hash function?
It should always produce the same hash value for the same key.
Provide a uniform distribution of hash values i.e. every value has an equal probability of being generated.
Minimise collisions
Be very fast to compute.
What is the name for when two or more different keys produce the same hash value?
A collision
What causes collisions?
When the hash function produces the same hash value for two or more keys.
How do you insert data into a hash table?
Use the hash function to generate the index of the position in the array that will be used to store the data
The data can then be stored at this index
The key must be stored as part of, or alongside, the data.
How do you retrieve a value from a hash table?
Apply the hash function to the key to generate the index at which the data is stored.
The value can be retrieved from this index in the array
What happens when you search for an item in a hash table that does not exist?
The hash function is applied to the key to generate the index at which the data should be stored.
If there is no data at this index in the array, then the item doesn’t exist.
What are two methods of handling collisions when adding to a hash table?
Linear probing (aka open addressing)
Chaining (aka closed addressing)
How does linear probing deal with collisions?
To add the item, move through the table one space at a time to find the next free space.
You then place the data in this free position
How does linear probing work when retrieving an item to a hash table?
Hash the key to generate the index value
Examine the indexed position to see if the key (which is stored together with the data) matches the key of the data you are looking for
If there is no match, check each location that follows (at the appropriate interval) until the matching record is found
If you reach an empty bucket without finding a matching key, the data is not in the hash table.
How does chaining deal with collisions?
Each location stores a pointer to a linked list in which data is stored
When there is a collision, the new item is added to the linked list
Each data item is stored as a node with three attributes:
the key value
the data
a pointer to the next node
The first value to be stored will have a Null pointer as it is the only item in the list.
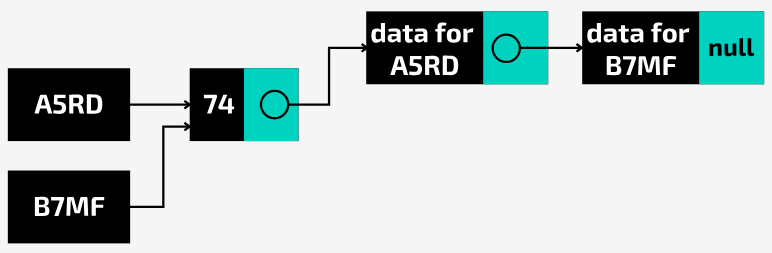
How do you retrieve data from a hash table when chaining has been used?
Hash the key to generate the index value
Examine the indexed position to get the pointer to the node at the head of the list
Examine the key of the node to see if it matches the key of the data you are looking for
If it is not the node you are looking for, follow the linked list until you find the node you are looking for
If you reach the end of the list without finding a matching key (or the head pointer was
null), the data is not in the hash table
When is rehashing used, and why?
Over time, as items are added and deleted from the hash table, it may start to fill up, or have a large number of items which are in the wrong place
This causes the performance of the hash table to degrade.
Rehashing can be used to fix this
Describe the process of rehashing
A new hash table is created (larger if needed).
The key for each item in the existing table will be rehashed and the item will be inserted into the new hash table.
If the new table is larger the hashing algorithm will need to be modified as it will need to generate a larger range of hash values.
How are hash tables used in databases?
Database management systems (DBMSs) make use of hash tables to speed up searching.
The primary key of a table can be hashed to provide a physical location to store the data within a hash table. This makes retrieval using the primary key very fast.
Many DBMSs allow other fields to be indexed. Hash tables will facilitate the high speed retrieval of data based on any field that is indexed.
Why are hash functions used when storing passwords?
Only the hashed password is stored
Since a hash function is ‘one way’, it is easy to hash the password but very difficult to reverse.
As such, even if the hashed password is obtained by a bad actor, they would not be able to get the original password. Without the original password, they can’t gain access to your account, improving security.