ECON 2113 Exam 2
5.0(3)Studied by 39 people
Card Sorting
1/63
Earn XP
Last updated 3:59 AM on 2/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
1
New cards
The buyers' willingness to pay can be represented through...
The demand curve
2
New cards
The sellers' costs of producing a good can be represented through..
The supply curve
3
New cards
The consumer surplus benefits the...
Buyer
4
New cards
The producer surplus benefits the...
Seller
5
New cards
What is the total surplus?
The sum of consumer and producer surplus, the total benefit in society/economy
6
New cards
What is welfare economics?
The study of how the allocation of resources affects economic well-being
7
New cards
What is willingness to pay?
Maximum amount that a buyer will pay for a good
8
New cards
How is consumer surplus calculated?
A buyer's willingness to pay minus the price the buyer actually pays
9
New cards
The price on the demand curve represents...
The willingness to pay of the marginal buyer
10
New cards
On the demand curve, the consumer surplus is...
The area below the demand curve and above the price
11
New cards
When the price falls, the consumer surplus...
Increases
12
New cards
What is cost?
The value of everything a seller must give up to produce a good
13
New cards
How is producer surplus calculated?
The amount a seller is paid for a good minus the seller's cost
14
New cards
The price on the supply curve represents...
The willingness to supply by the marginal seller
15
New cards
How is producer surplus represented on the supply curve?
The area above the supply curve and below the price
16
New cards
When price rises, the producer surplus...
Increases
17
New cards
Total surplus is...
The value to buyers + cost to sellers
18
New cards
What is efficiency?
Allocation that maximizes total surplus
19
New cards
What is equity?
Fair distribution of well-being in society
20
New cards
At the market equilibrium price, buyers...
Who value the product more purchase it
21
New cards
A free market allocates goods to buyers with...
The highest willingness to pay
22
New cards
At the market equilibrium price, sellers...
With the lowest costs produce the product
23
New cards
How does a free market affect sellers?
Makes the most efficient sellers to produce
24
New cards
T/F: Total surplus is minimized at the market equilibrium
False. It is maximized at the market equilibrium
25
New cards
If the amount produced is smaller than the equilibrium quantity...
1. The value of the product to buyers is \__________ than the cost to sellers
2. Total surplus would rise if output \____________
1. The value of the product to buyers is \__________ than the cost to sellers
2. Total surplus would rise if output \____________
1. The value of the product to buyers is greater than the cost to sellers
2. Total surplus would rise if output increases
2. Total surplus would rise if output increases
26
New cards
If the amount produced is larger than the equilibrium quantity...
1. The value of the product to buyers is \__________ than the cost to sellers
2. Total surplus would rise if output \__________
1. The value of the product to buyers is \__________ than the cost to sellers
2. Total surplus would rise if output \__________
1. The value of the product to buyers is less than the cost to sellers
2. Total surplus would rise if output decreases
2. Total surplus would rise if output decreases
27
New cards
Markets are efficient when
There are perfectly competitive markets and no externalities
28
New cards
T/F Market equilibrium may not be efficient if perfectly competitive markets and no externalities exist
True
29
New cards
T/F: If there is market failure public policy will not remedy it
False, it can potentially remedy it
30
New cards
Inefficiency means...
Market outcome with less than maximum total surplus, leads to deadweight loss
31
New cards
Examples of public policy are...
Taxes, subsidies, quotas, price ceilings, price floor
32
New cards
What are some effects of market failure?
Underproduction and overproduction
33
New cards
What is underproduction?
Less is traded than determined by the market equilibrium
34
New cards
What is overproduction?
More is traded than determined by the market equilibrium
35
New cards
When the quantity traded is different from the efficient levels, there is...
Deadweight loss
36
New cards
What is deadweight loss?
A decrease in both consumer surplus and producer surplus due to inefficient level of production
37
New cards
If a buyer has to pay a certain dollar for each unit of a good purchased...
It causes a decrease in demand
38
New cards
T/F: The demand curve shifts down by the amount of the tax levied
True
39
New cards
T/F: Taxes encourage market activity
False, they discourage it
40
New cards
T/F: Both buyers and sellers share the burden of taxes
True
41
New cards
What is tax incidence?
How the burden of a tax is shared
42
New cards
How do higher prices due to taxes affect the consumer surplus?
The consumer surplus must go down
43
New cards
How do sellers experiencing lower prices affect the producer surplus?
The producer surplus must go down
44
New cards
T/F: Since buyers send taxes to the government, only the buyer pays for the tax
False, BOTH buyers and sellers pay for tax
45
New cards
T/F: Due to taxes, the buyer has to pay more, and the seller receives less
True
46
New cards
If taxes are added to the supplier, the supply shifts \____________ by \____________
The supply shifts up by the amount of the tax
47
New cards
T/F: Regardless of who pays the tax to the government, the burden to buyers and sellers is the same
True
48
New cards
T/F: The burden of tax is always shared equally, even in inelastic/elastic markets
False, it can depend if the supply is elastic and the demand inelastic, or vice versa
49
New cards
Elastic supply/demand is represented by... (flat/steep curve)
Flat curve
50
New cards
Inelastic supply/demand is represented by... (flat/steep curve)
Steep curve
51
New cards
With elastic supply and inelastic demand, who pays more?
The buyers
52
New cards
With inelastic supply and elastic demand, who pays more?
The sellers
53
New cards
In general, the less elastic side of the market pays \___________
More
54
New cards
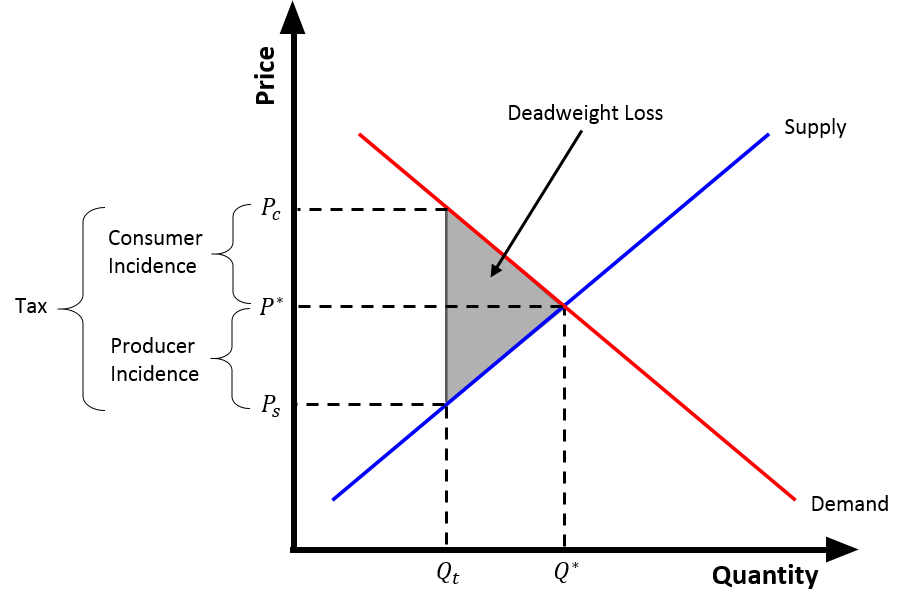
How is the tax wedge calculated?
The buyer's price minus the the seller's price
T \= Pb - Ps
T \= Pb - Ps
55
New cards
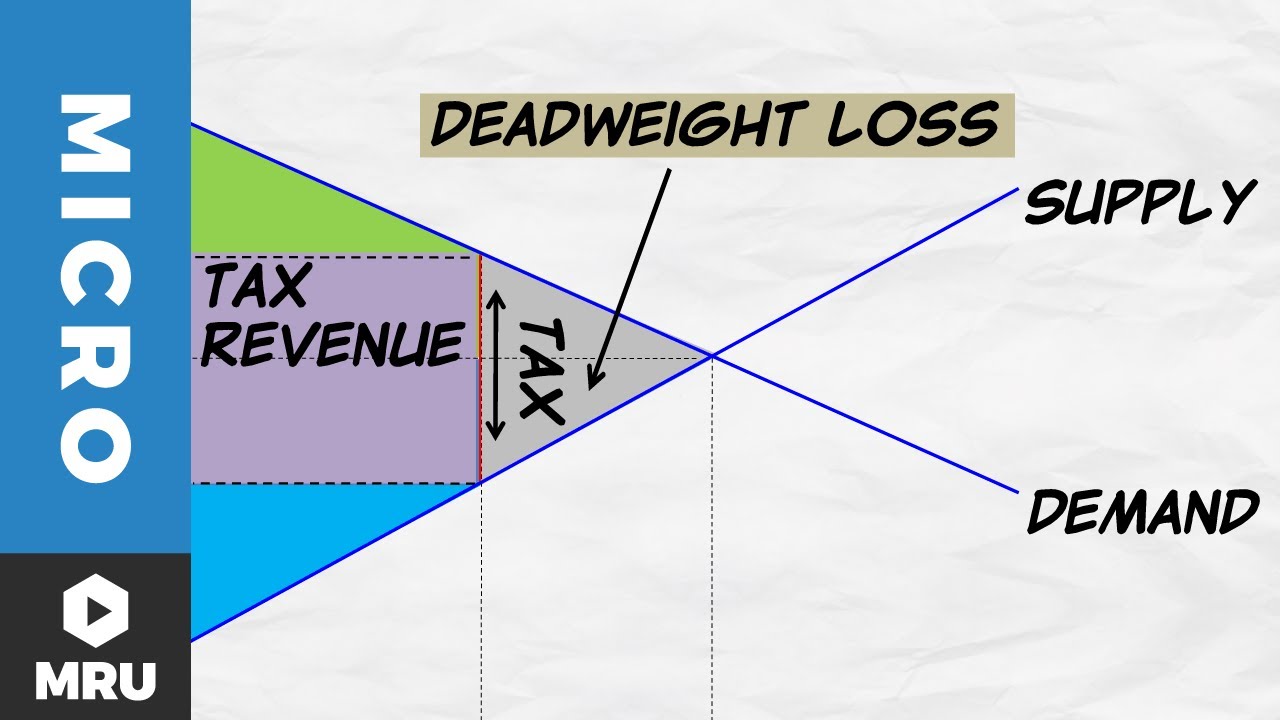
How is tax revenue calculated?
Tax revenue \= T * Q
T \= height of the tax wedge
Q \= quantity sold under the tax
T \= height of the tax wedge
Q \= quantity sold under the tax
56
New cards
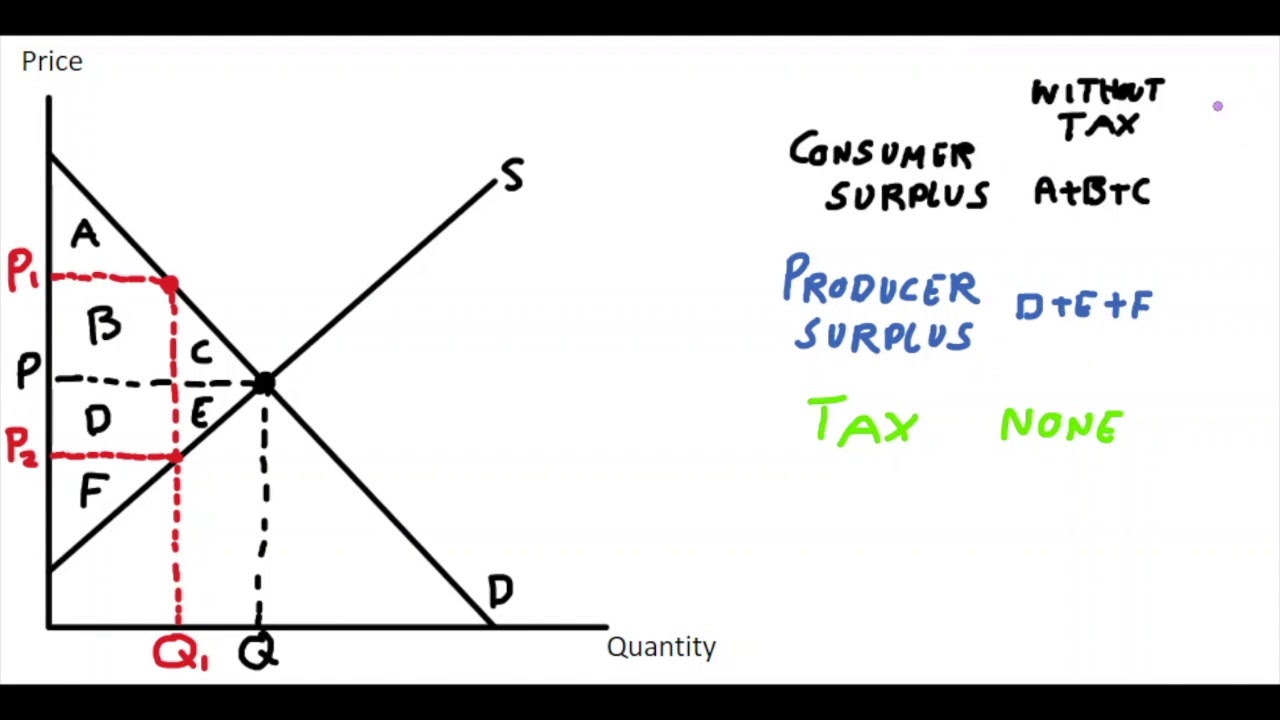
What is A and F on the graph?
A \= Consumer surplus after tax
F \= Producer surplus after tax
F \= Producer surplus after tax
57
New cards
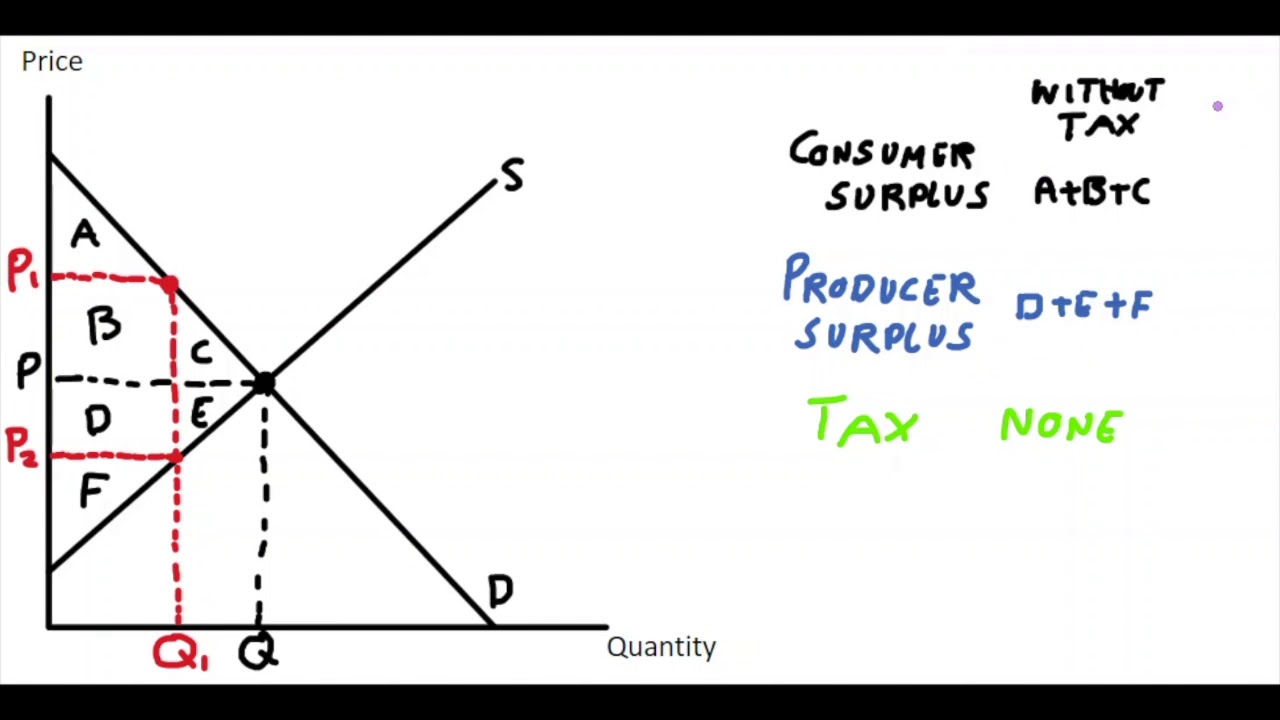
What does the area of A, B, C and D, E, F refer to?
A, B, C \= consumer surplus before tax
D, E, F \= producer surplus before tax
D, E, F \= producer surplus before tax
58
New cards
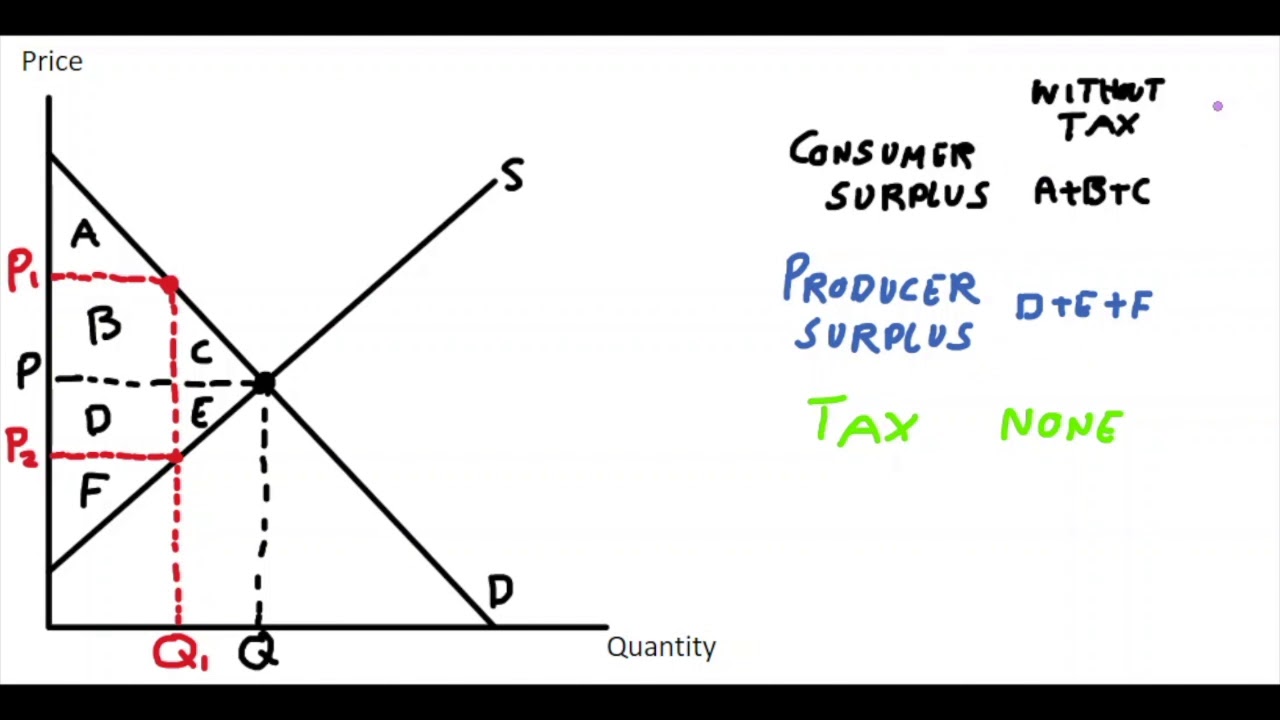
Total surplus (on the welfare analysis graph) is equal to
(A + B + C) + (D + E + F)
59
New cards
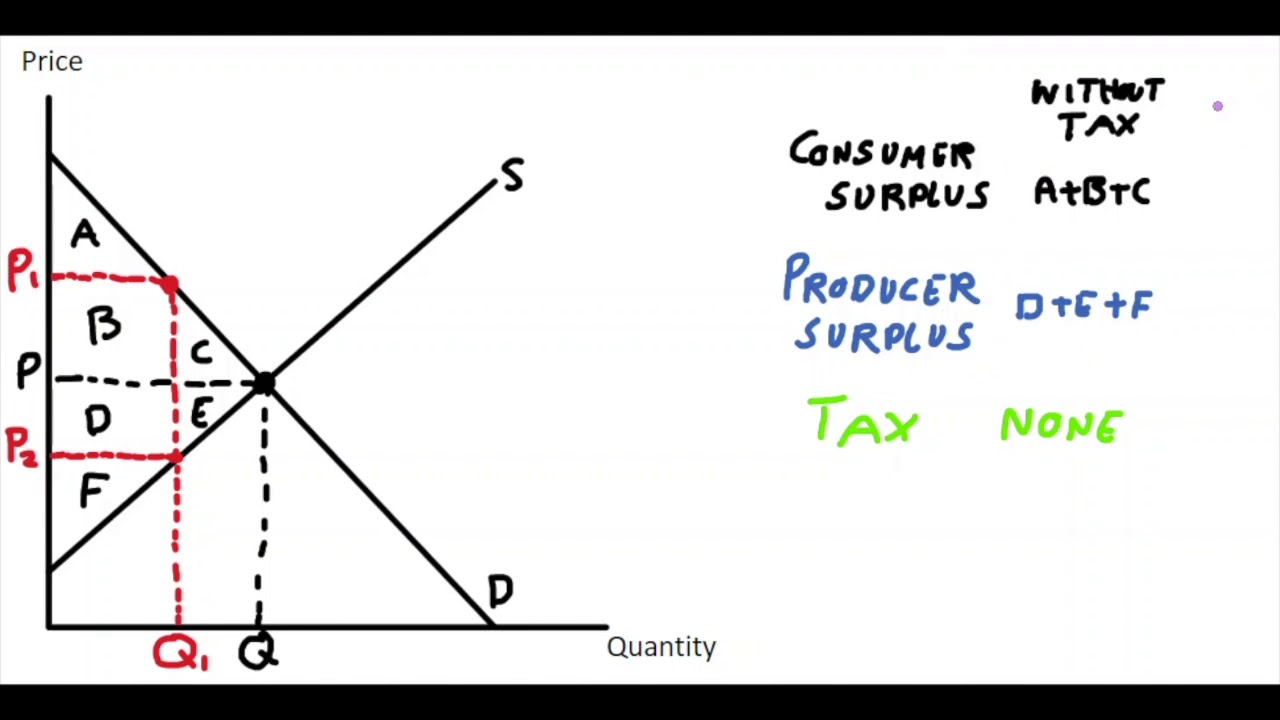
Consumer surplus (on the welfare analysis graph) changes by \____________ after tax
\- B - C
60
New cards
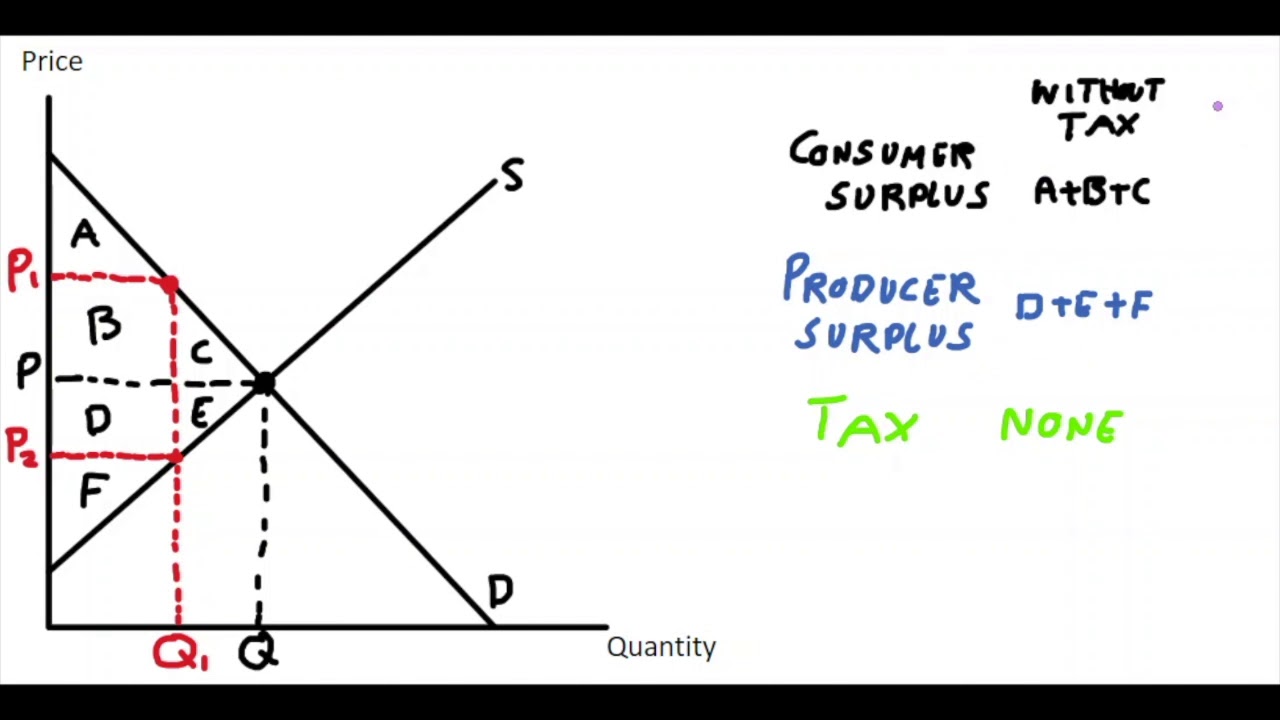
Producer surplus (on the welfare analysis graph) changes by \_____________ after tax
\- D - E
61
New cards
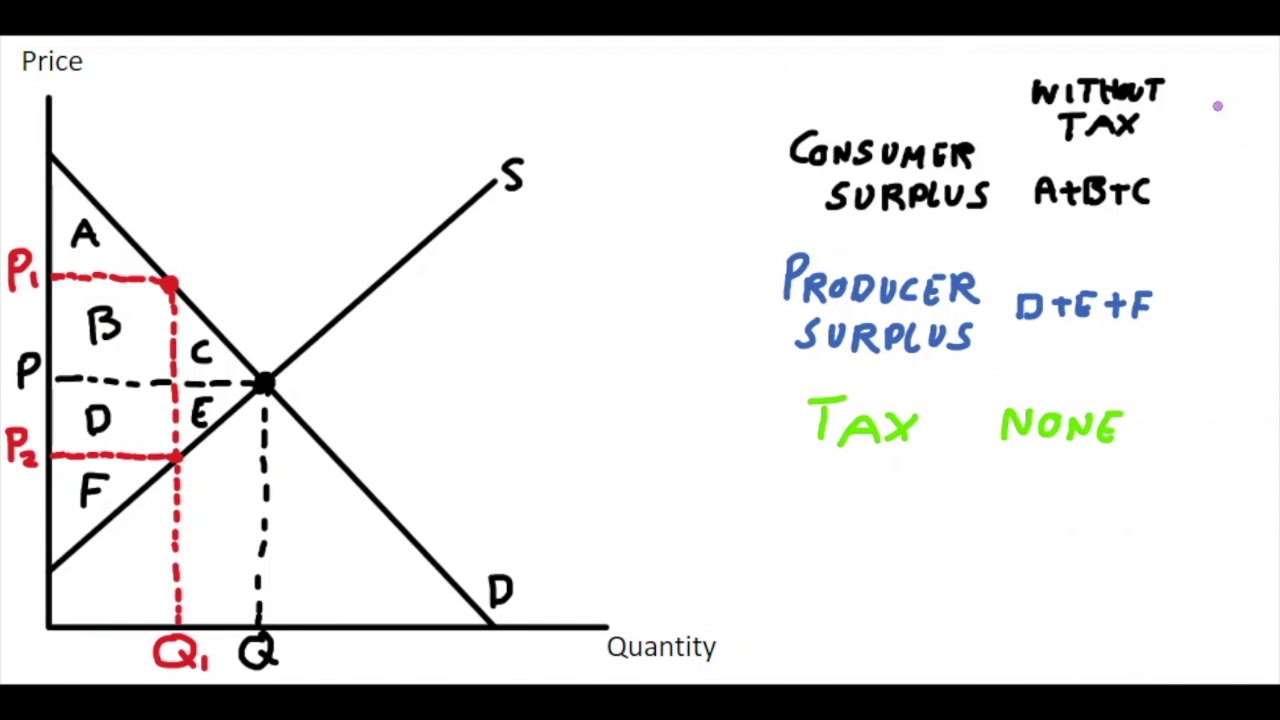
Tax revenue (on the welfare analysis graph) changes by \____________ after tax
\+ B + D
62
New cards
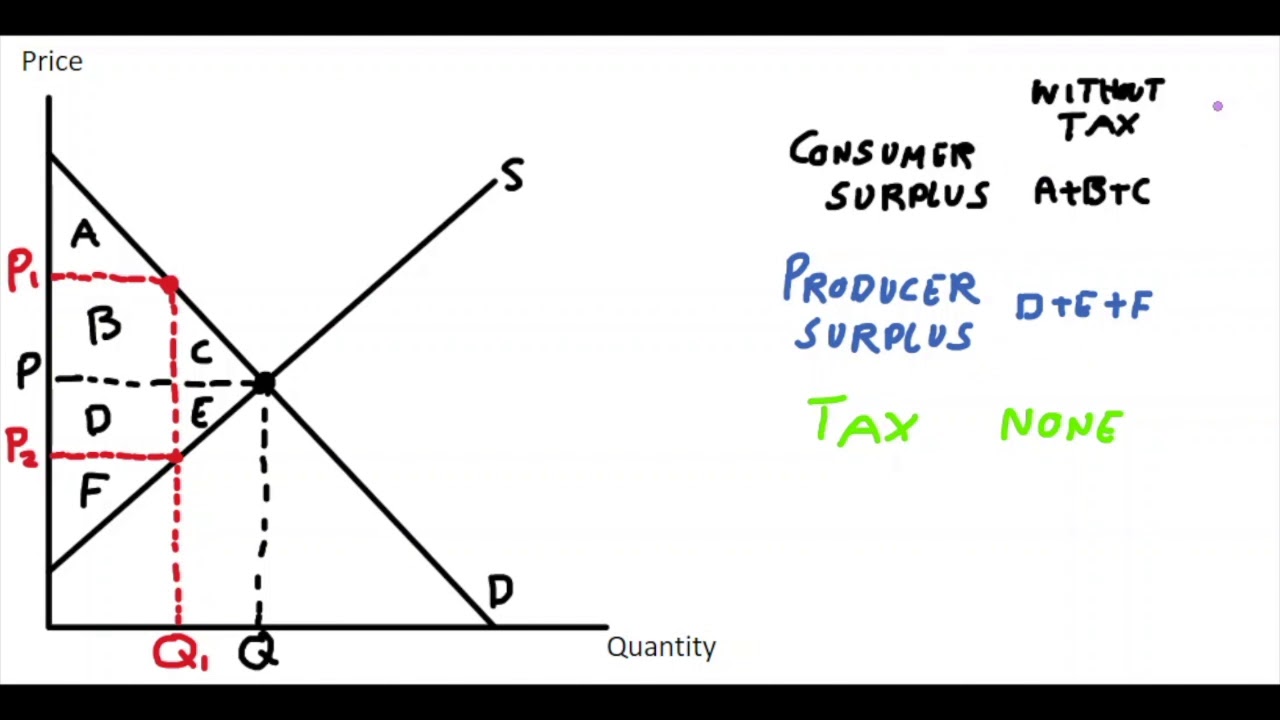
Total surplus changes by \_____________ after tax
\- C - E
63
New cards
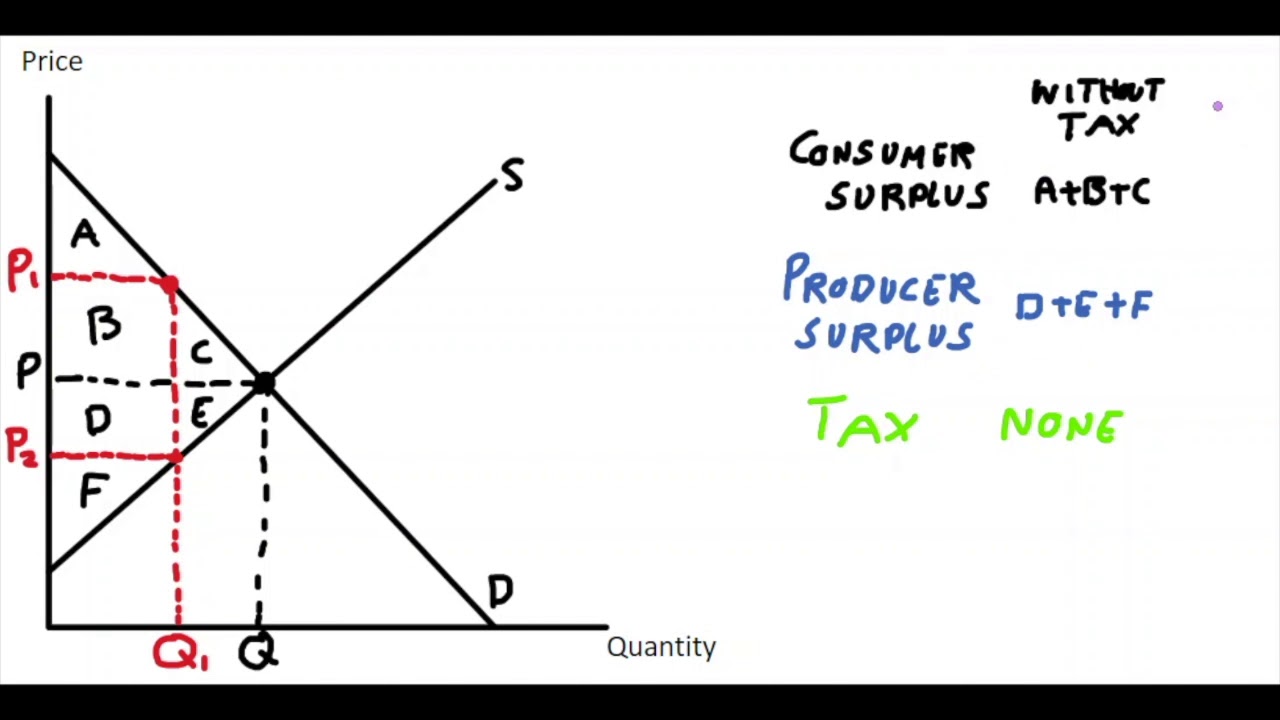
C + E represents....
Deadweight loss
64
New cards
Deadweight loss (in relation to taxes) refers to...
The fall in total surplus that results from a market distortion, such as a tax