Cells and Microscopes
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
topic 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Why are cells typically small in size?
To ensure maximum surface area
The more surface area, the better cells can function
Functions = chemical communication, nutrient absorption, regulation
What happens as cells get larger?
Less surface area
The cell needs to compensate in order to properly function
What is the primary function of microscopy in studying cells?
To magnify objects and reveal details not visible to the naked eye
Who is credited with discovering cells using a microscope in 1665?
Robert Hooke
What does magnification refer to in microscopy?
The ability to make an object appear larger than its actual size
How does resolution work in microscopes?
Smaller resolution values are better for distinguishing separate points in microscopes. larger resolution is better for photos
What is contrast in microscopy?
The ability to distinguish the cell and its parts from the background
Who was associated with the light microscope?
Robert Hooke
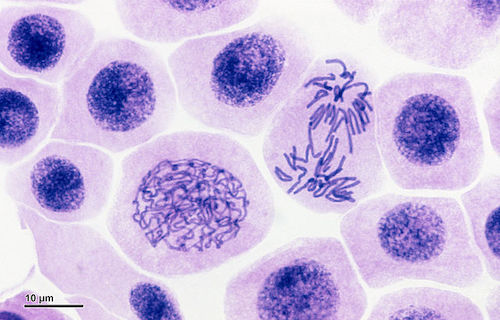
How does a light microscope produce an image?
Light passes through the sample and is absorbed to create a 2D image
magnified by glass lenses
What key features distinguish electron microscopes from light microscopes?
They use electron beams, electromagnetic lenses, and computers for better resolution, cell details, and detect the image
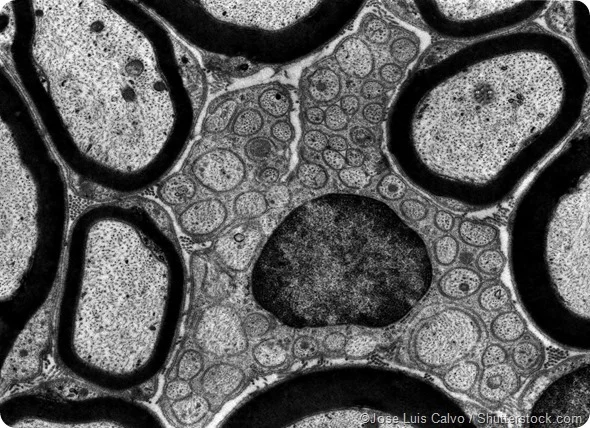
How does a Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) work?
A 2D image with lots of detail (not as much as a SEM), where the electron beam passes through the sample and is detected in order to create an image

What is unique about Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) imaging?
Electrons bounce off the sample's surface for a 3D image with detail, but not internals
Why is staining used to improve contrast in samples?
To selectively highlight certain proteins, genes, or components, making them stand out from the background
How does phase contrast work in microscopy?
Phase shift differences are converted into big brightness differences (not as much detail as DIC)
dark = dense areas
light = less dense areas
What is a phase shift when it comes to microscopy?
The concept that different parts of a cell affect light differently used in phase contrast (dense vs. less dense)
Dense = light slows down more (eg. nucleus)
Less dense = light slows down less (eg. cytoplasm)
What is differential interference contrast (DIC) when it comes to microscopy?
polarized light is used and is split into two beams
the two beams pass through the specimen at slightly diff positions and recombine
same delay = flat image
slower delay (1 beam) = contrast
you see much more detail than within phase contrast
Who is Antonie van Leeuwenhoek known as?
The father of microbiology; first to see live cells and bacteria (microbes) and was able to achieve 200X more magnification than Robert Hooke
What is the challenge when it comes to contrast in microscopy?
Cells are clear/hard to see between the sample and the background since light microscopes pass light through the sample the same way
What are the two solutions to solving the problems regarding contrast in microscopy
Staining (colour or fluorescent) specific to respective proteins/genes
Phase Shift/Contrast and Differential Interference Contrast (DIC)