Cell Bio Chapter 4 The Structure and Function of the Plasma Membrane
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Compartmentalization
Separates cellular activities for regulation.
Scaffold for biochemical activities
Framework for effective molecular interactions.
Selectively permeable barrier
Controls movement of substances in and out.
Transporting solutes
Mechanisms for moving substances across membranes (against concentration and ion gradient)
Signal transduction
Process of responding to external signals.
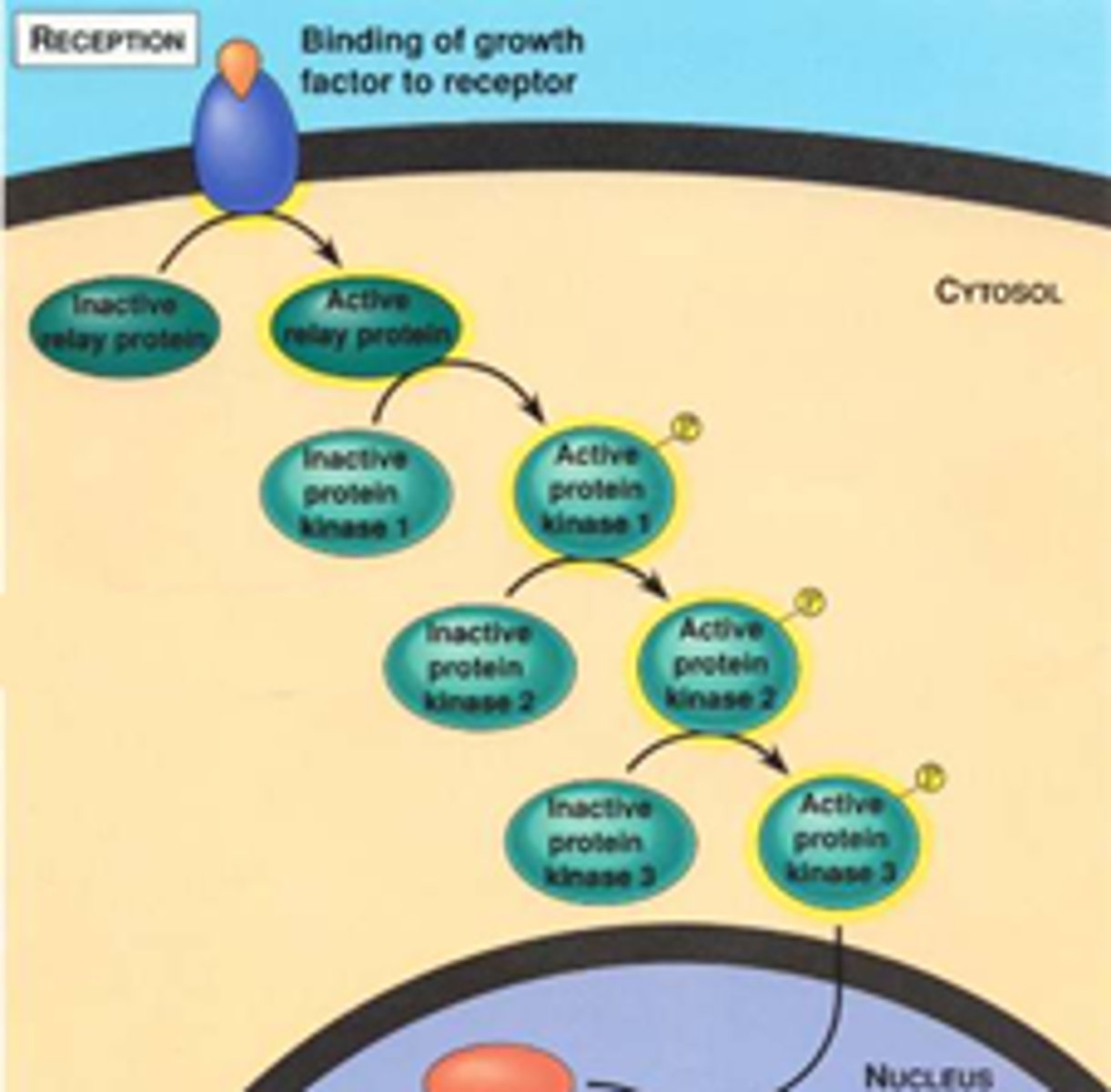
Receptor
Molecule that recognizes and responds to stimuli.
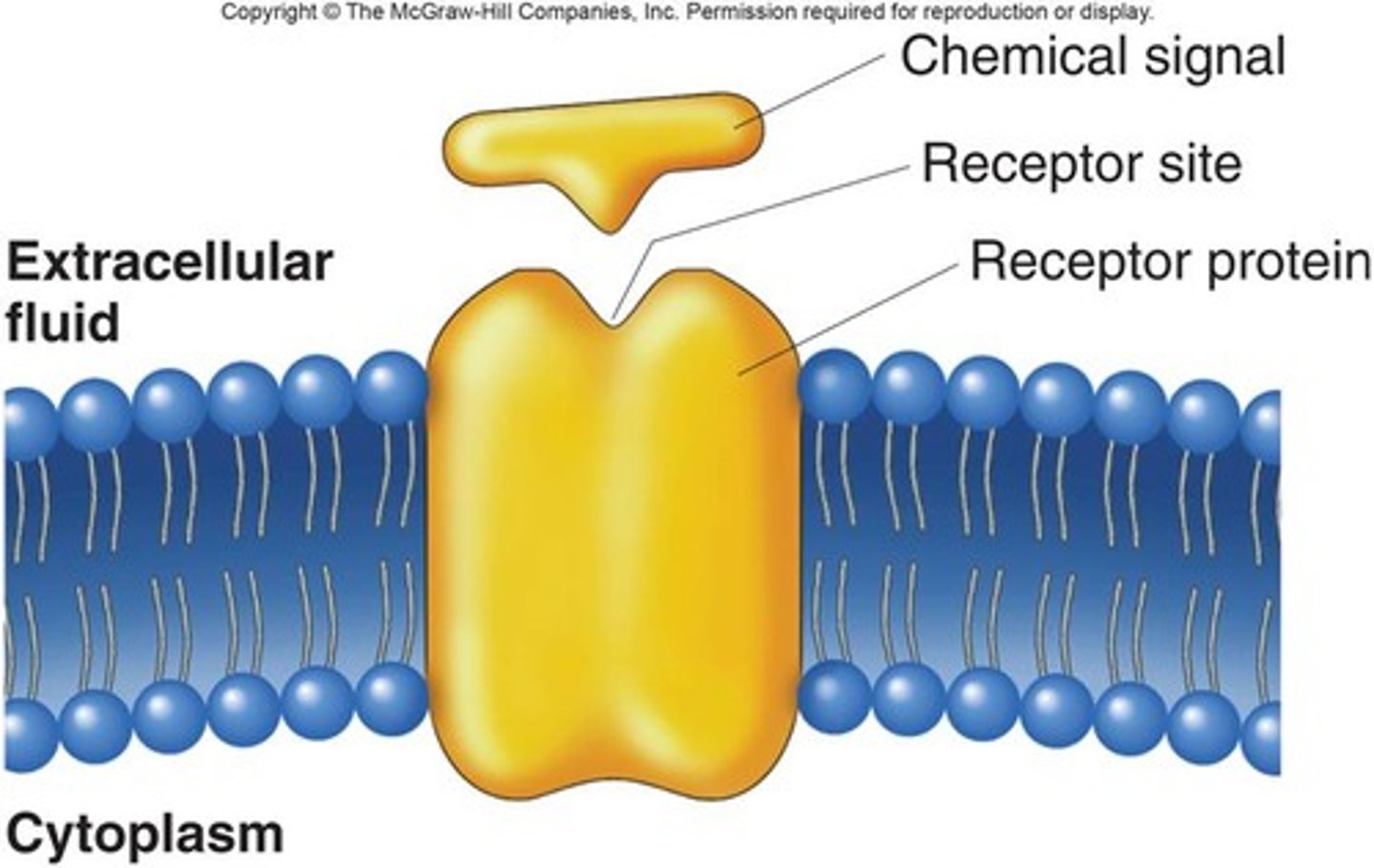
Ligand
Type of stimulus recognized by receptors.
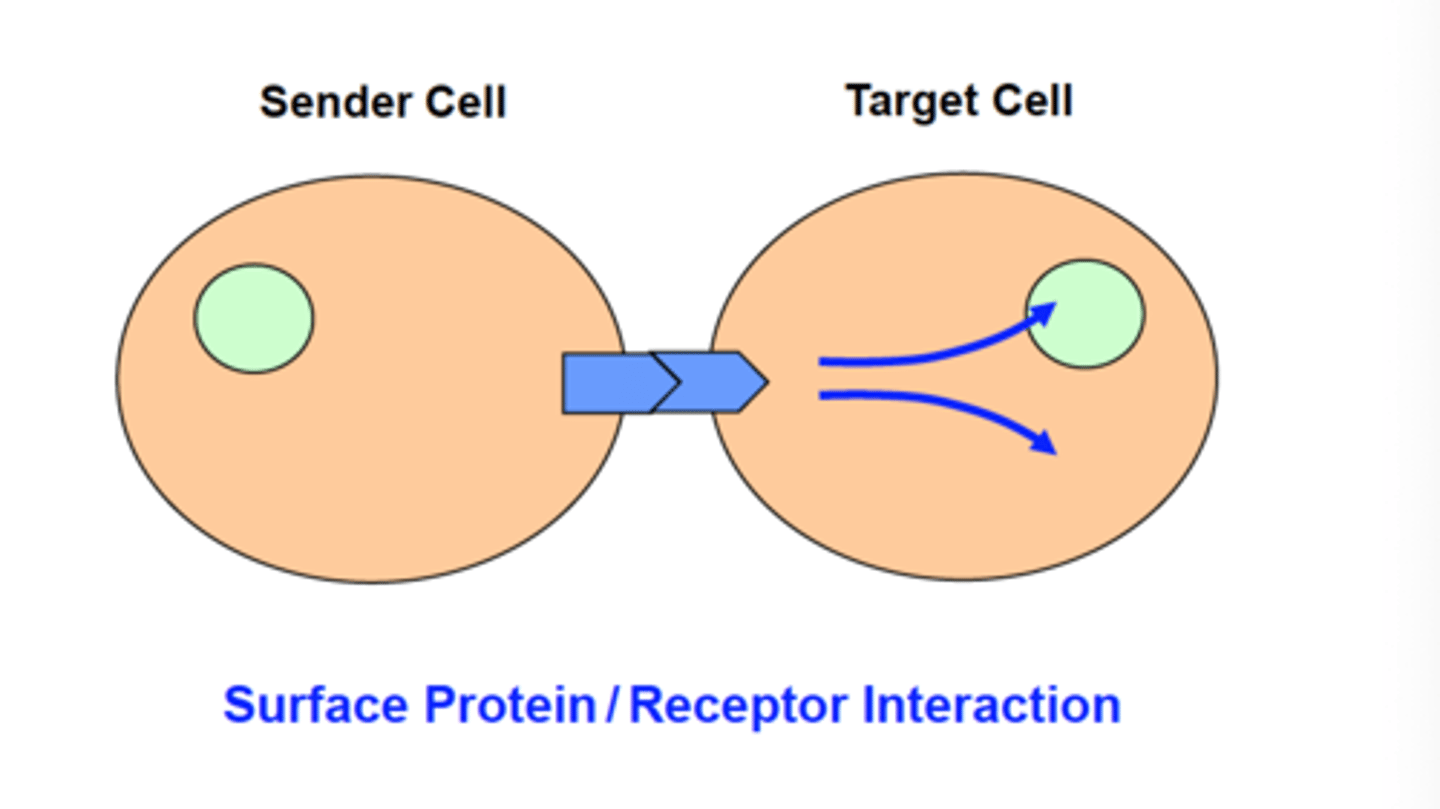
Intercellular interaction
Cell membranes facilitate communication between cells.
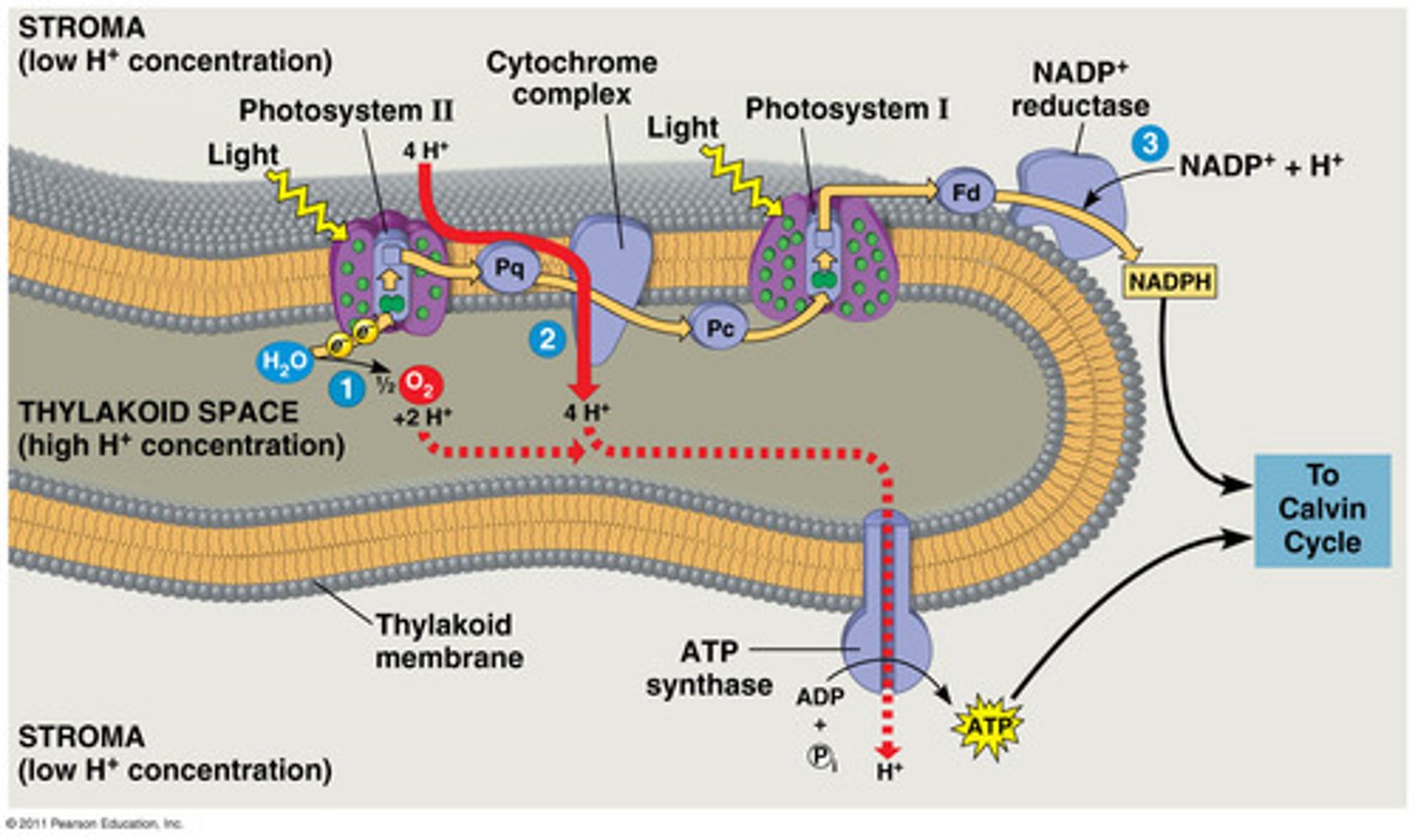
Energy transduction
Conversion of energy to chemical forms (ATP).
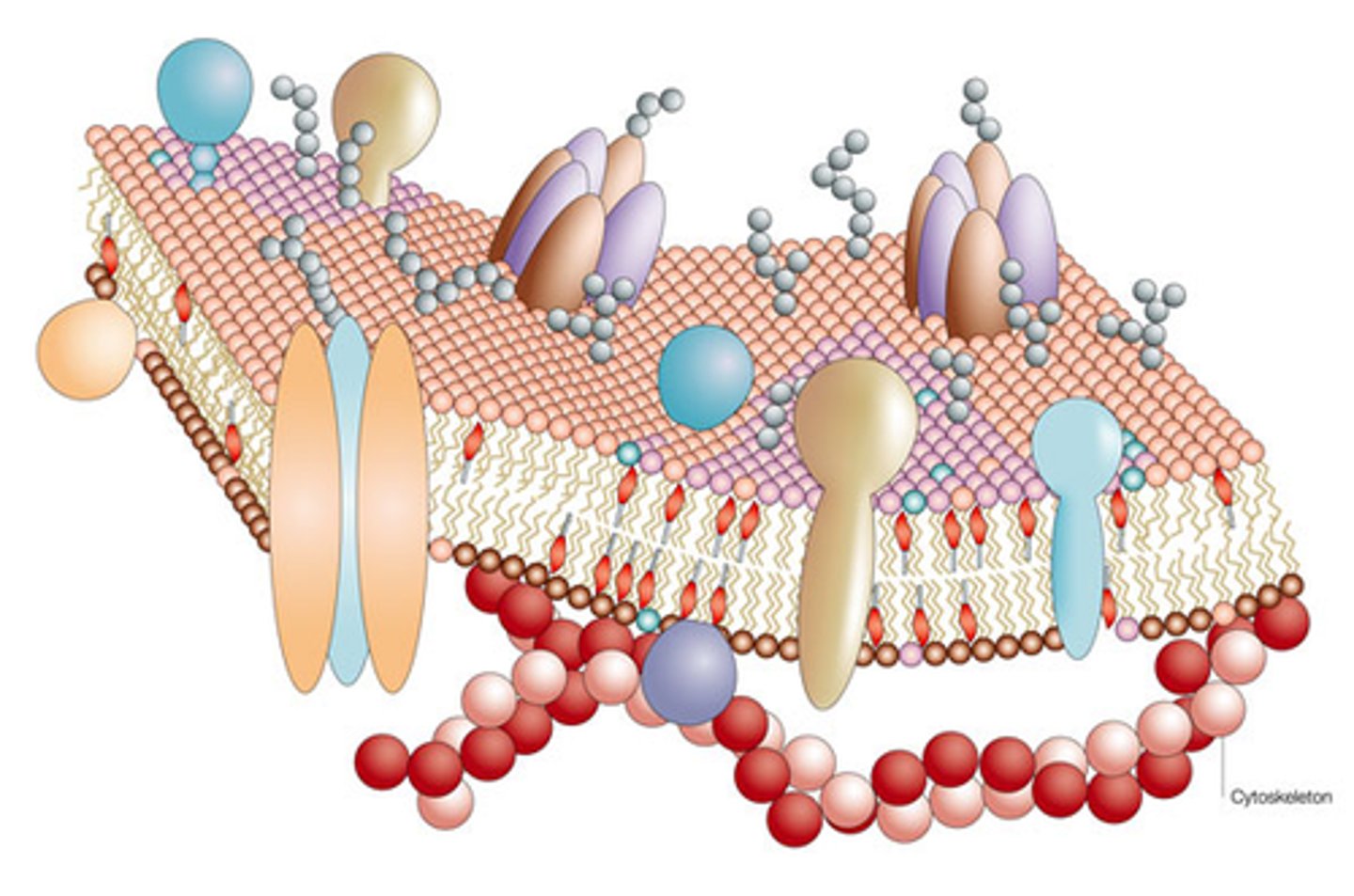
Fluid-mosaic model
Describes membrane structure as dynamic and varied.
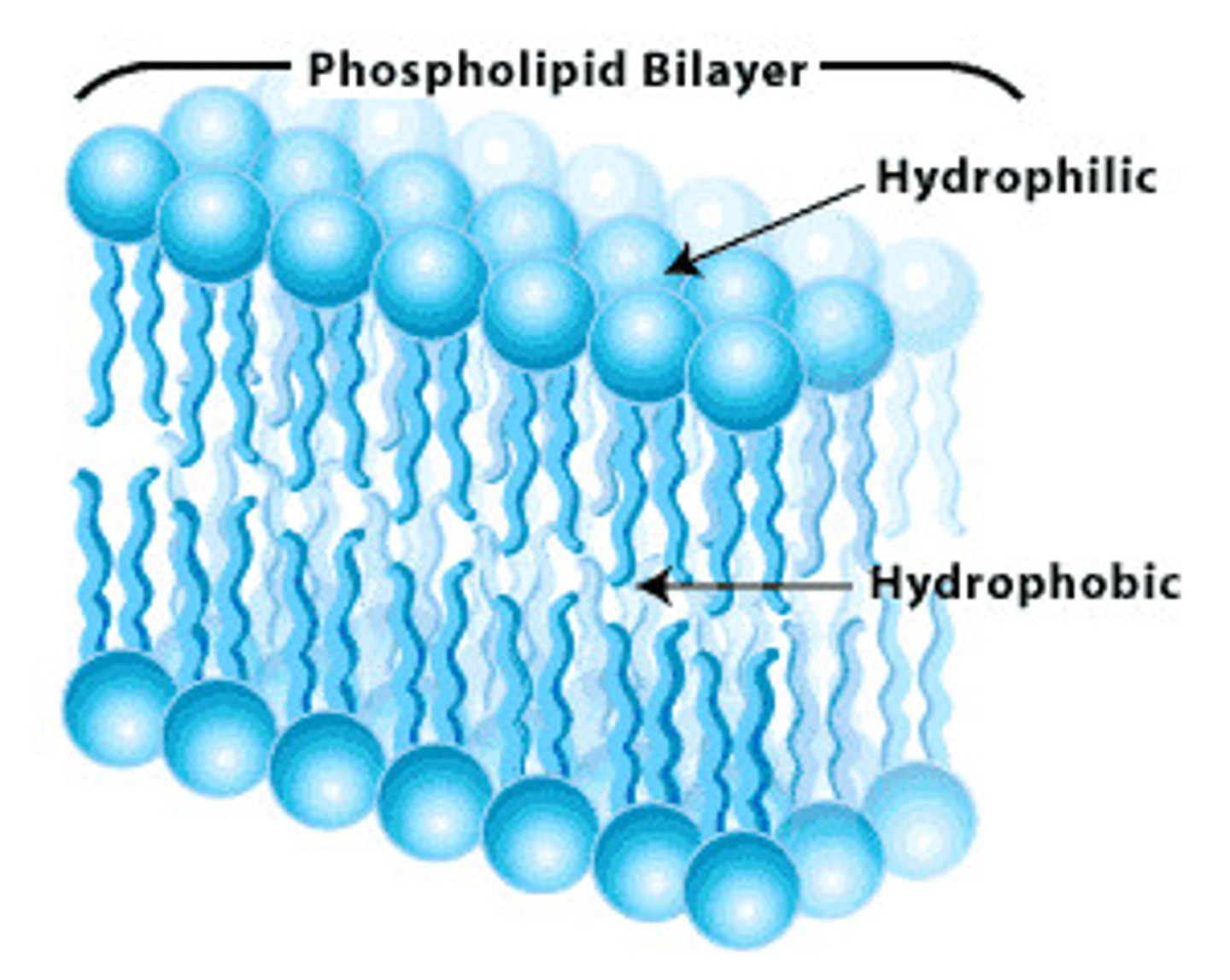
Amphipathic lipids
Molecules with hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
Structural backbone of Membranes
Lipid bilayer
Part of the membrane that specifies determination
Proteins
3 main types of membrane lipids
phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, cholesterol
Phosphoglycerides
Diacylglycerides with phosphate-linked head groups.
Sphingolipids
Ceramides formed from sphingosine and fatty acids.
Cholesterol
A smaller and less amphipathic membrane lipid found only in animals.
Membrane lipids can differ in:
Types of lipids, nature of the head groups, and the particular species of fatty acyl chains
Hydrophilic region
Water-attracting part of an amphipathic lipid.
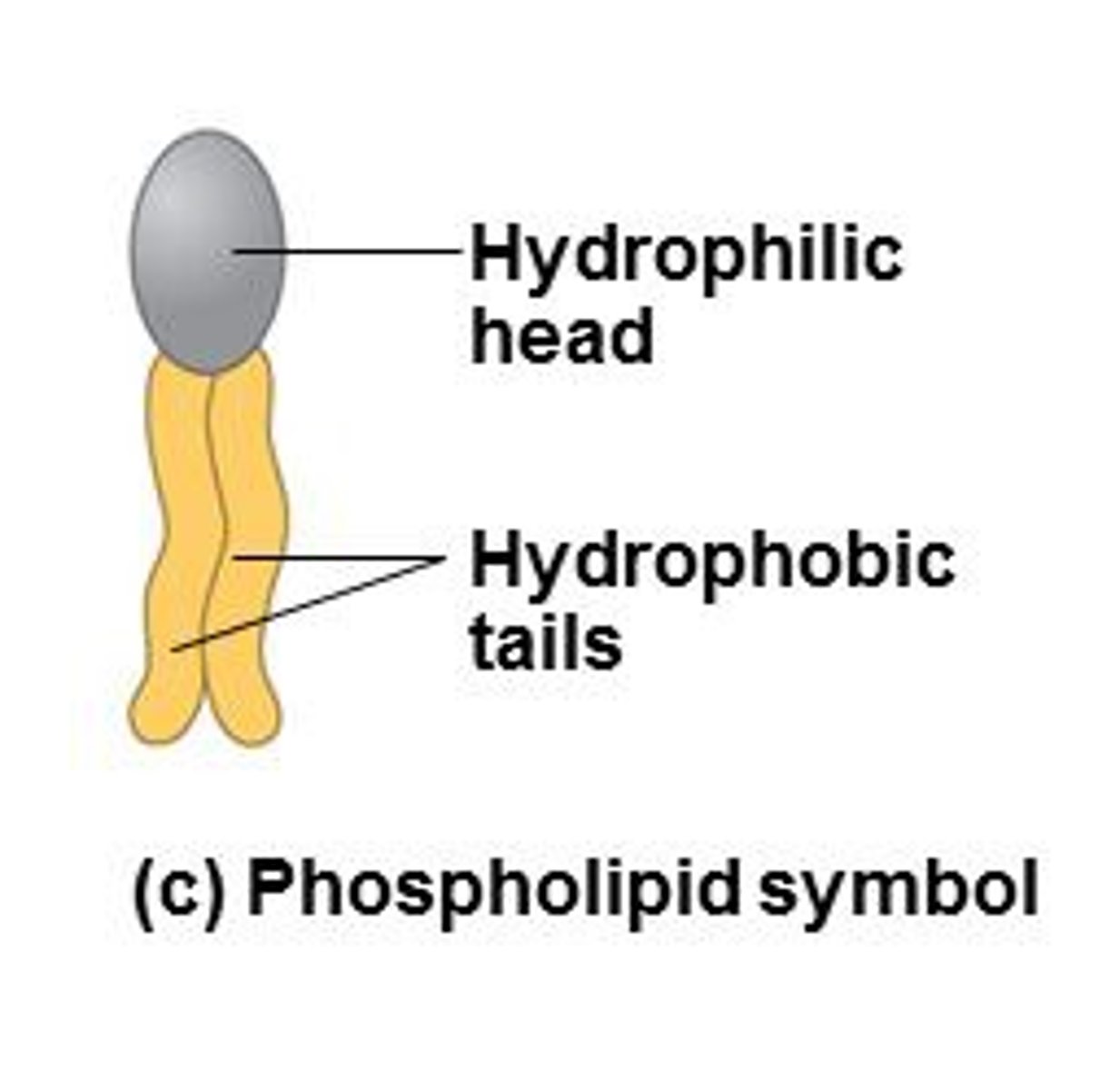
Hydrophobic region
Water-repelling part of an amphipathic lipid.
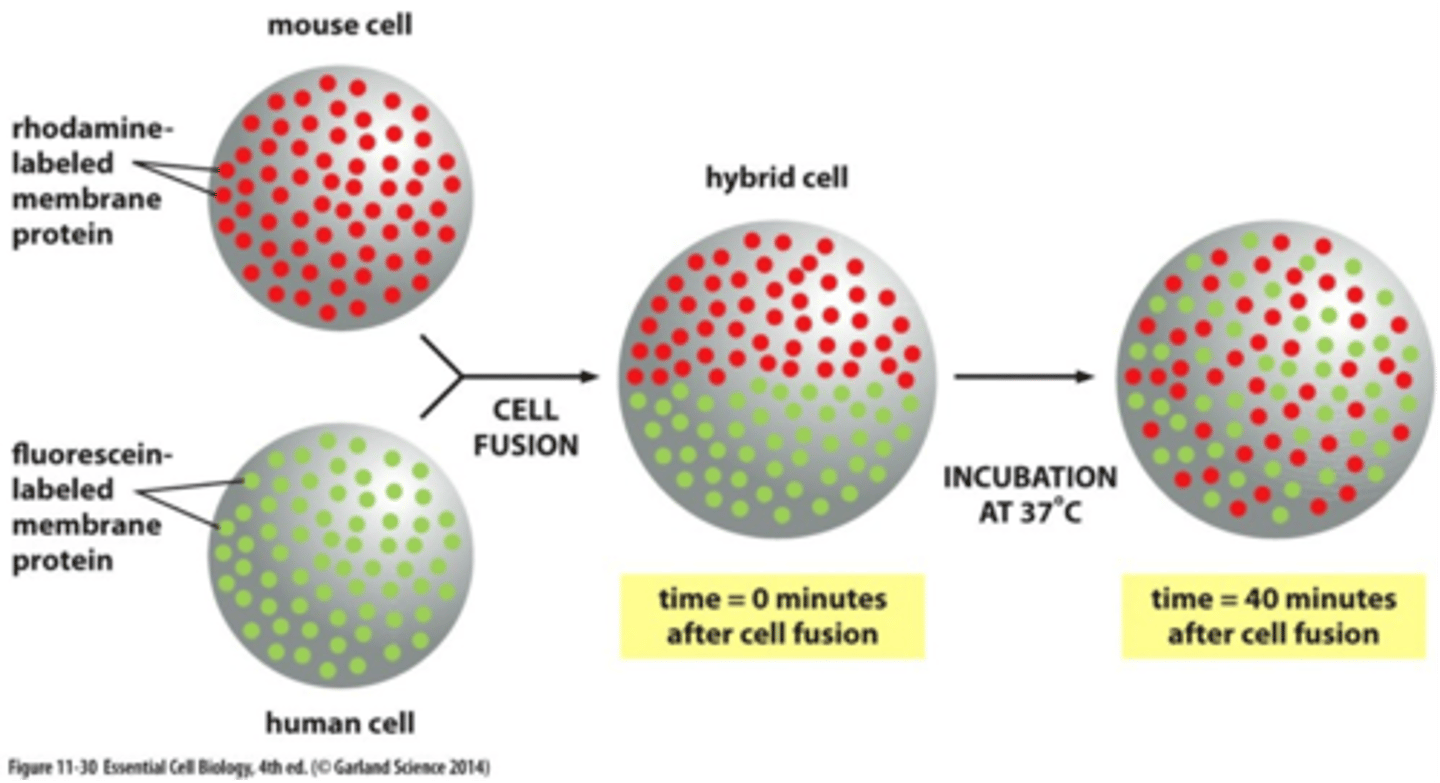
Cell Fusion
A technique whereby two different types of cells, or cells from two different species, can be fused to produce one cell with a common cytoplasm and a single, continuous plasma membrane.
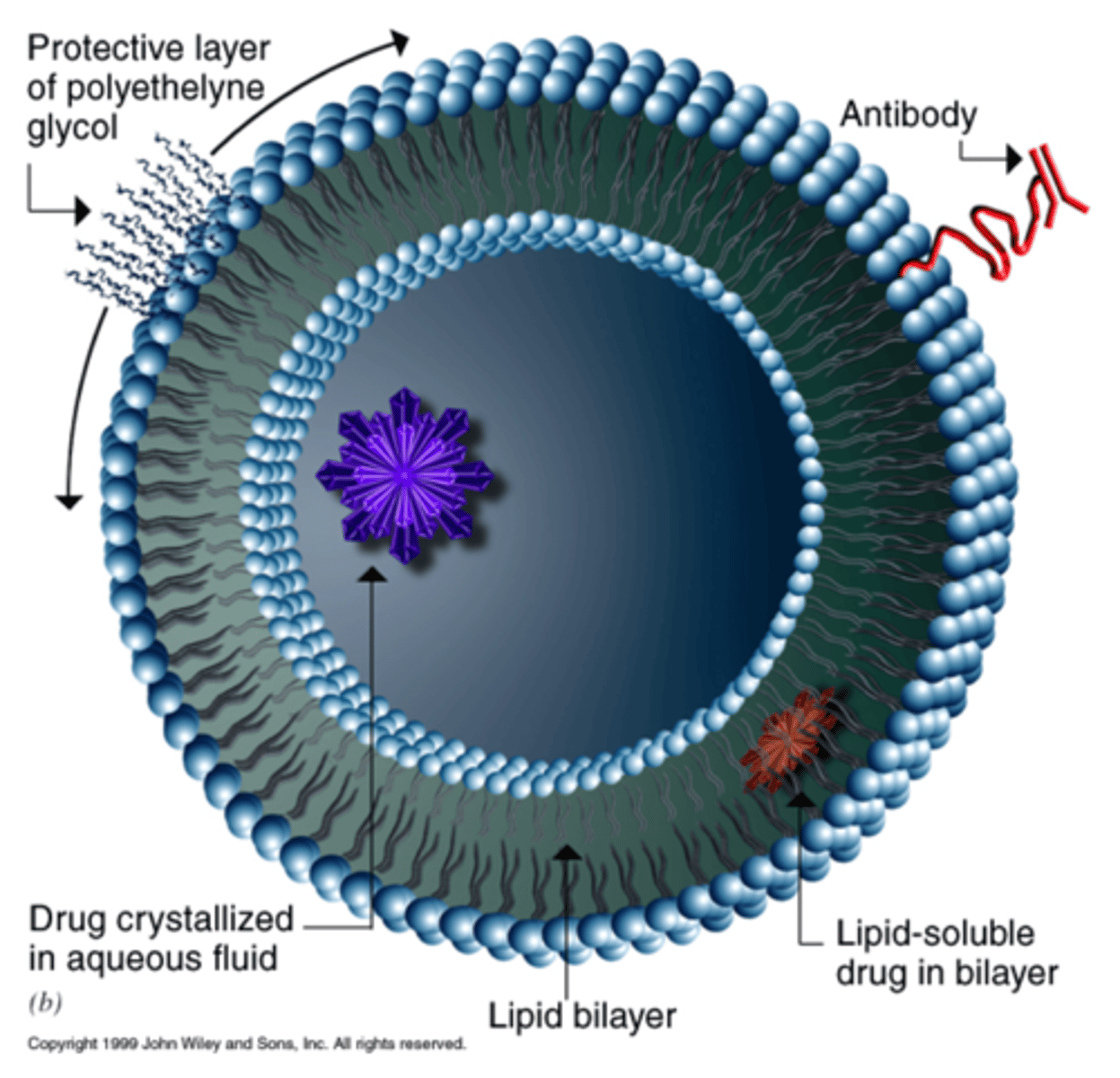
Liposomes
An artificially prepared spherical vesicle composed of a lipid bilayer that is Invaluable in membrane research.
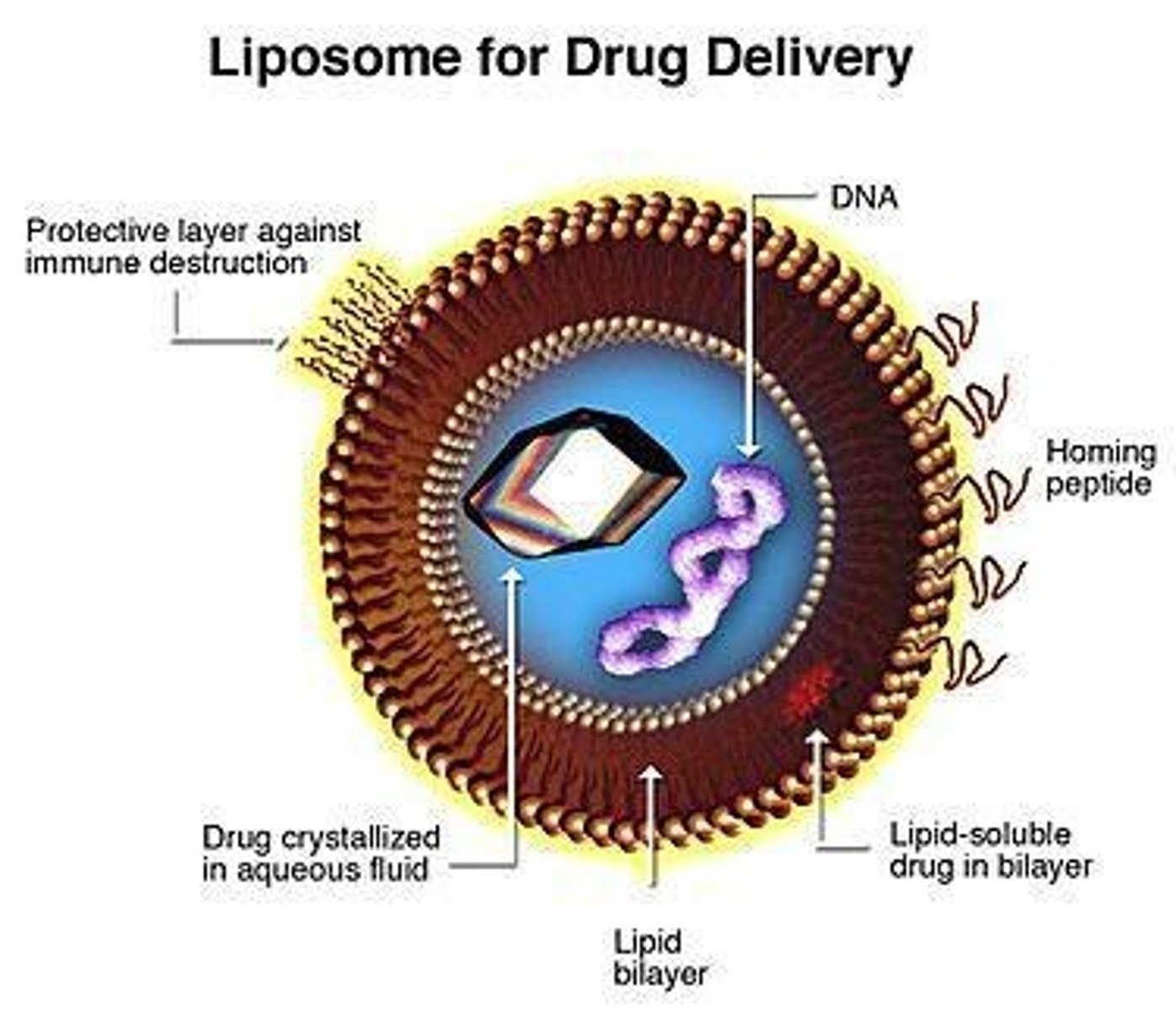
liposomes function
Act as vehicles for drugs to a specific location or DNA delivery and protect drugs from the immune system.
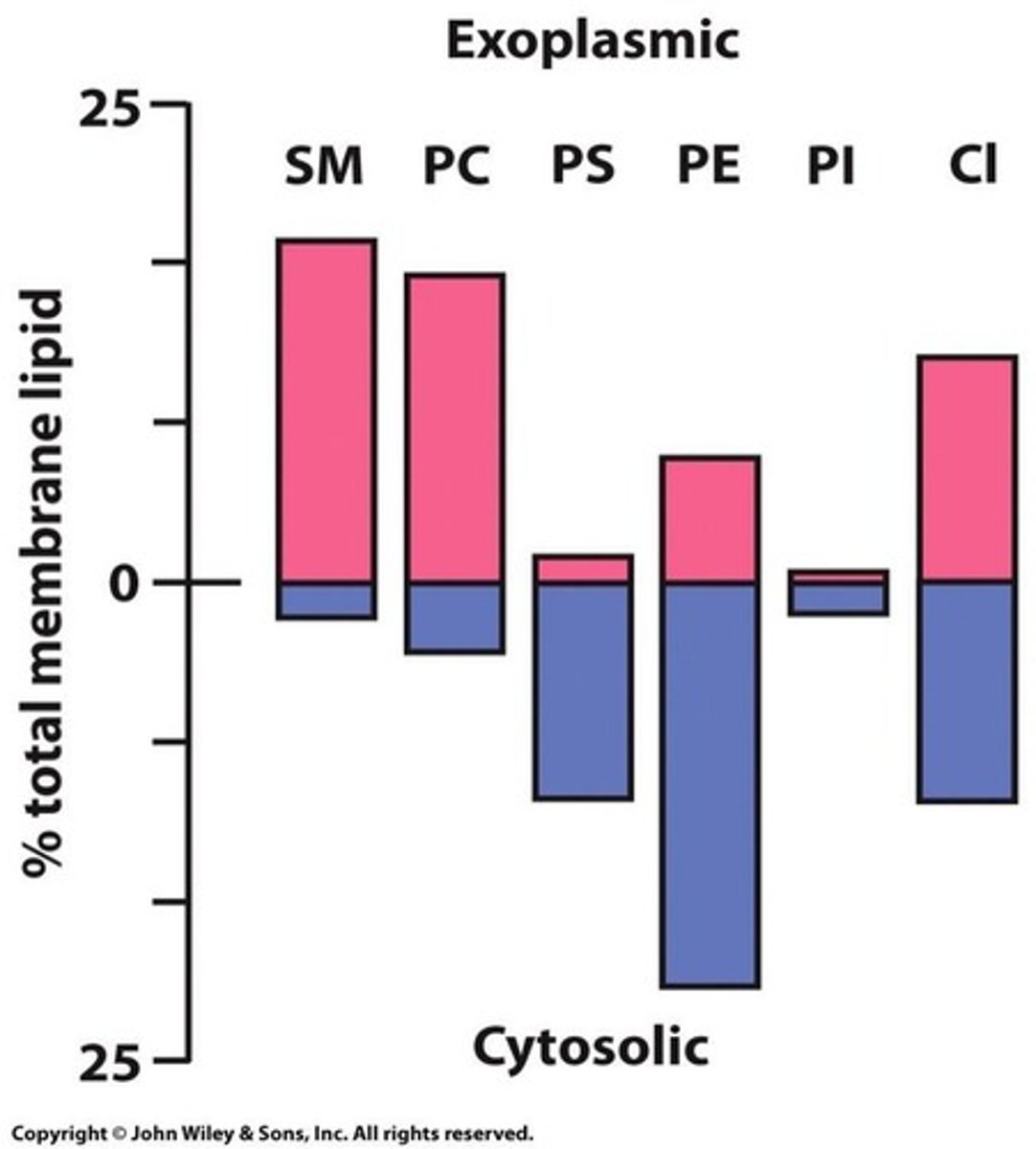
Membrane Asymmetry
Different lipid compositions in inner and outer leaflets.
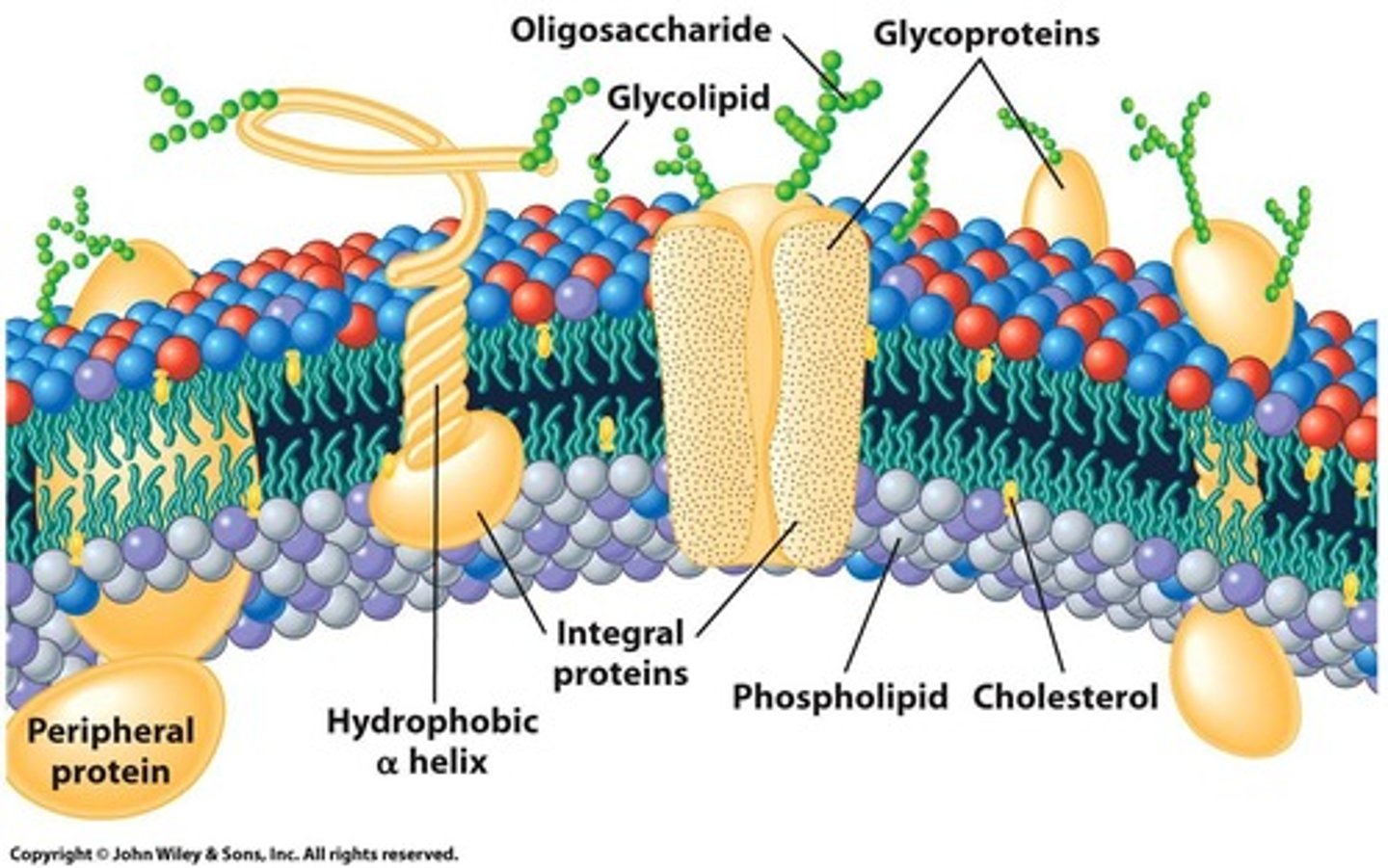
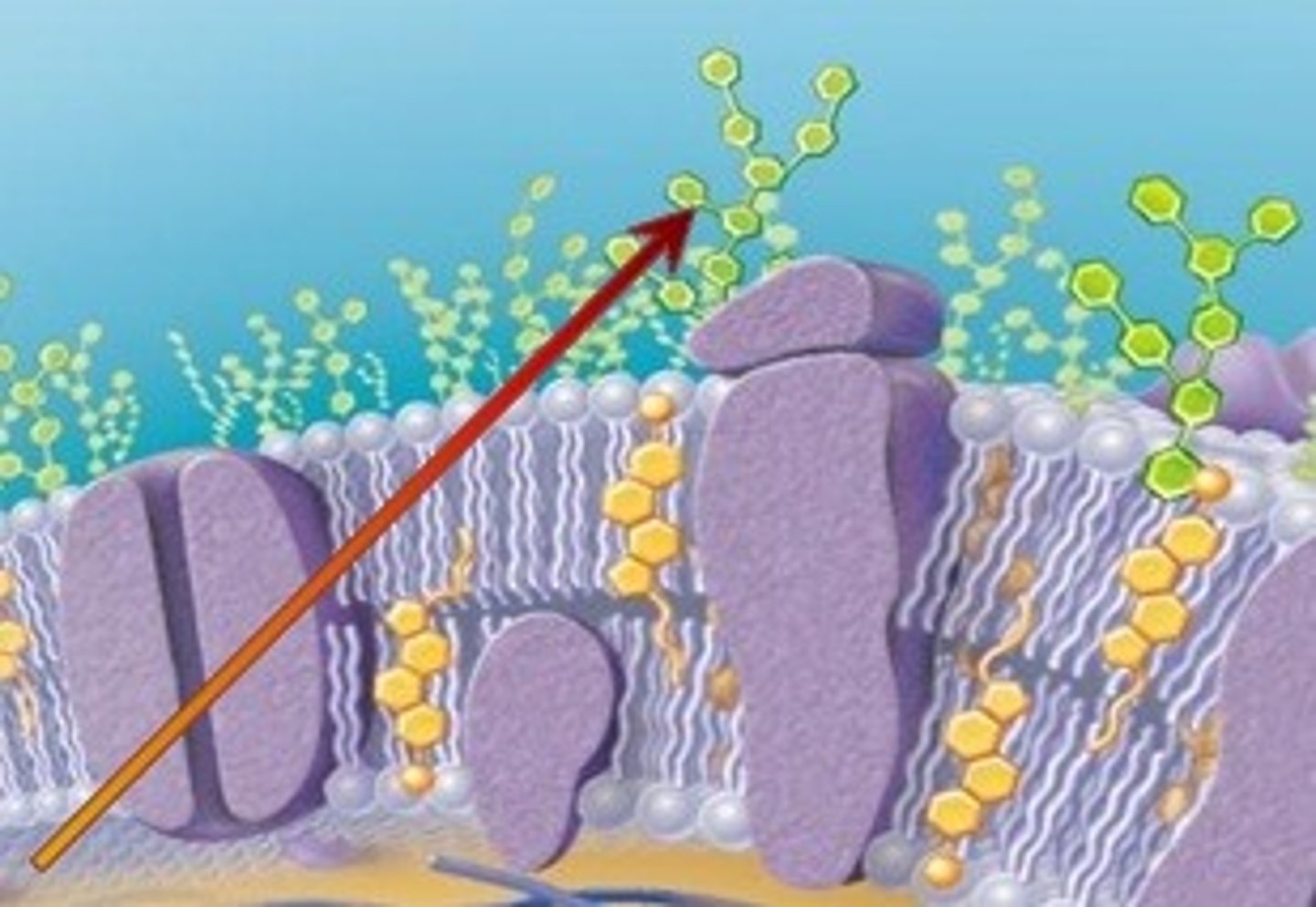
Membrane Carbohydrates
Account for 2-10% of the eukaryotic plasma membrane, covalently linked to lipids and proteins on the extracellular surface of the bilayer.
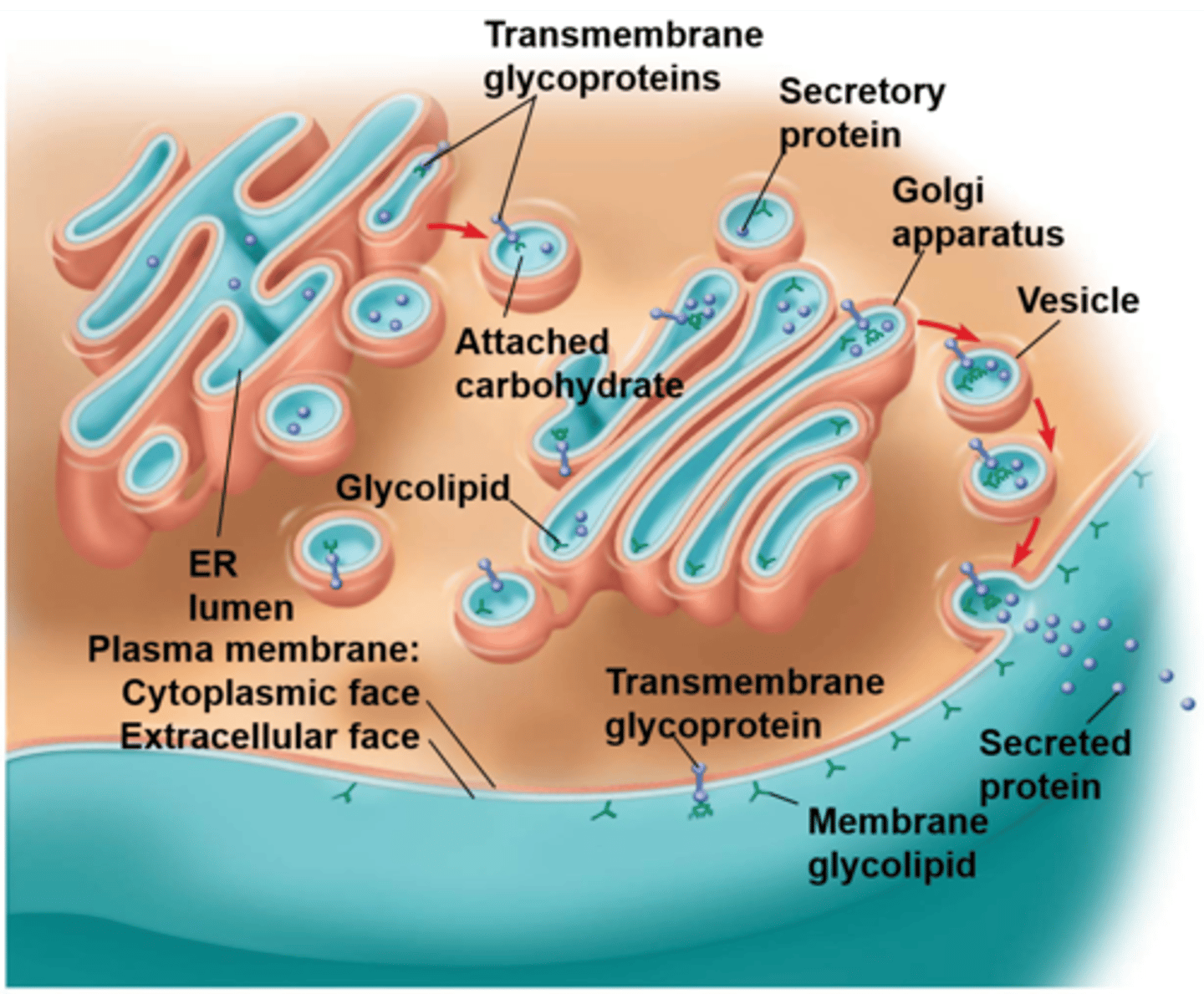
Glycoproteins
Carbohydrates linked to proteins on the membrane surface. It makes up more than 90% of membrane carbohydrates and is used for interaction with other cells.
Glycolipids
Carbohydrates linked to lipids. They make up more than 10% of membrane carbohydrates and are used as sites of cell-to-cell recognition.
Membrane Sidedness
Asymmetry of the membrane bilayer resulted from different membrane proteins attached to the bilayer.
Types of membrane proteins
integral(transmembrane), peripheral, lipid-anchored
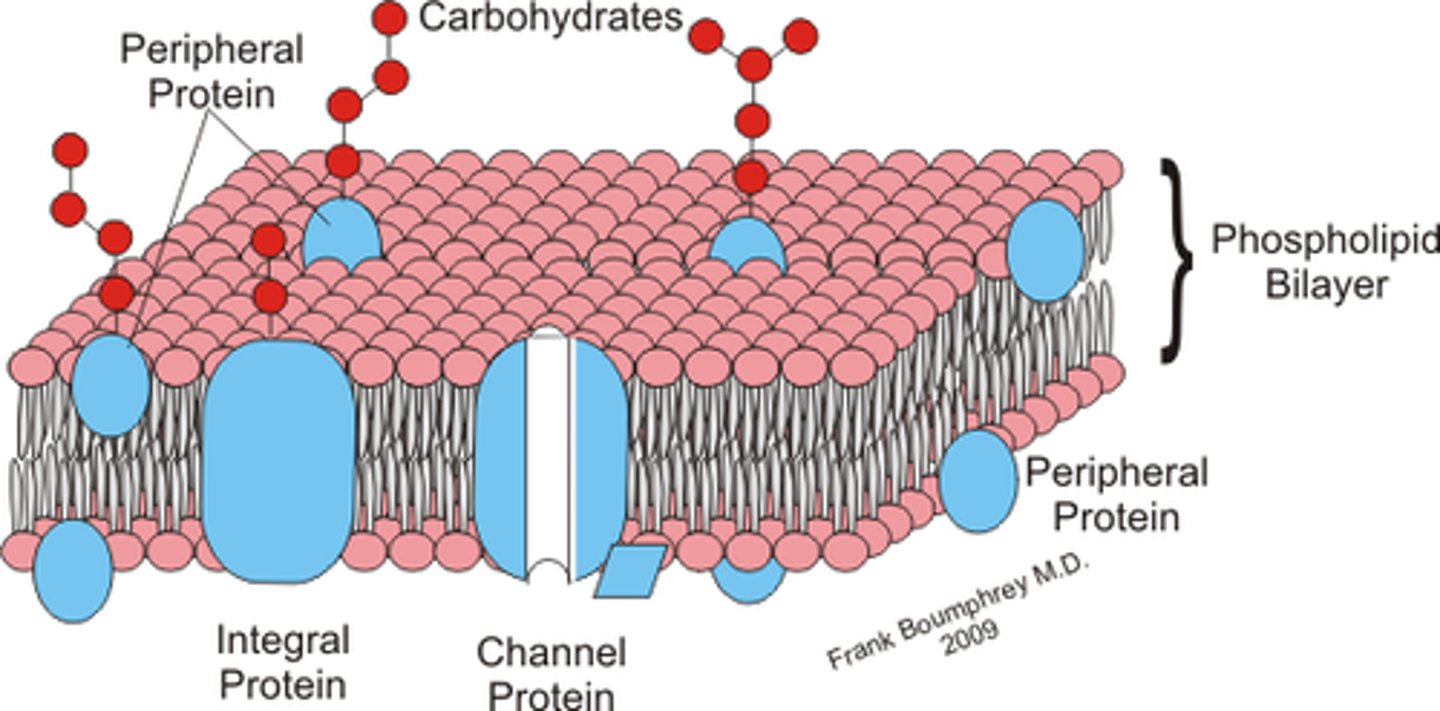
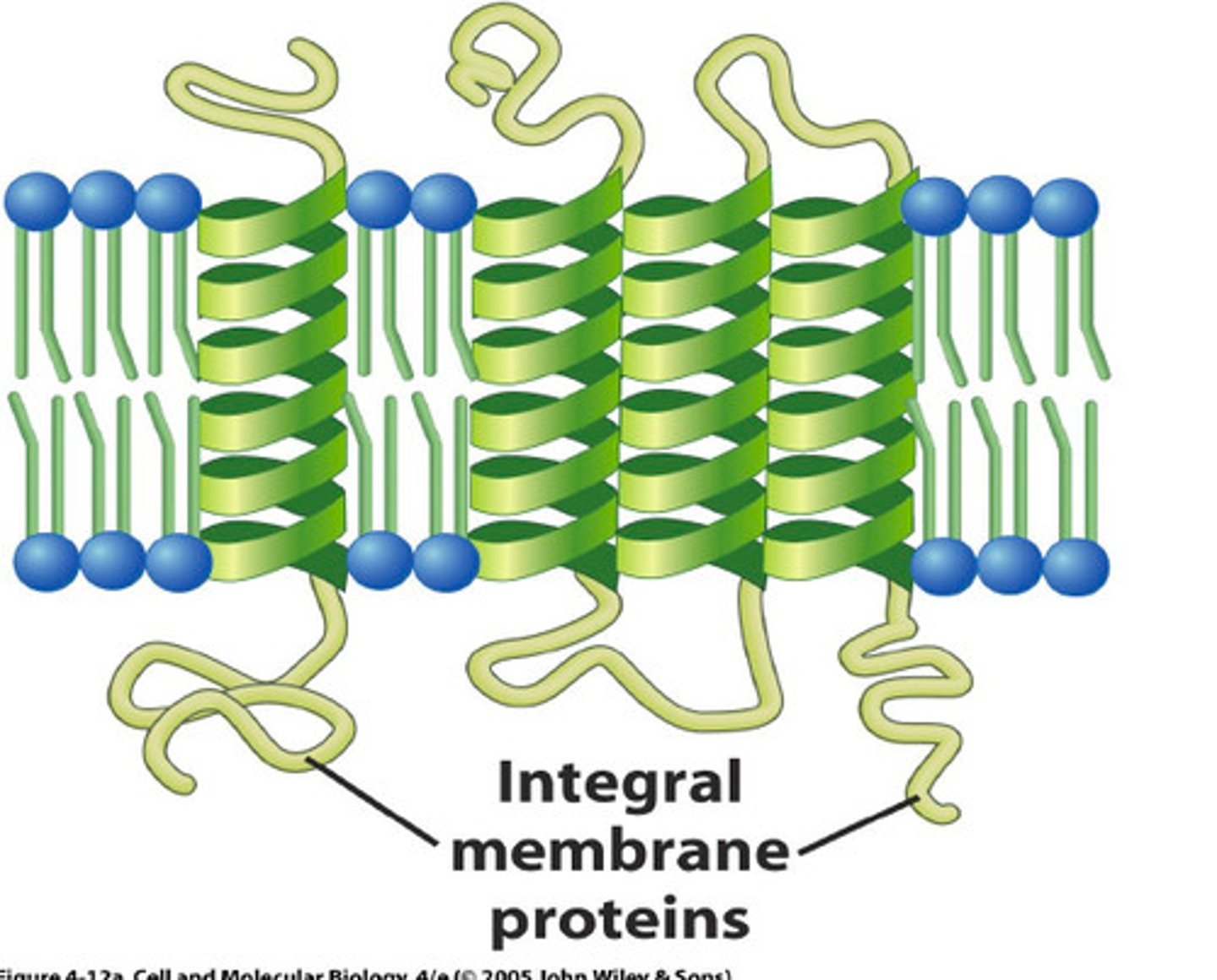
Integral Proteins (transmembrane proteins)
Proteins spanning the entire lipid bilayer.
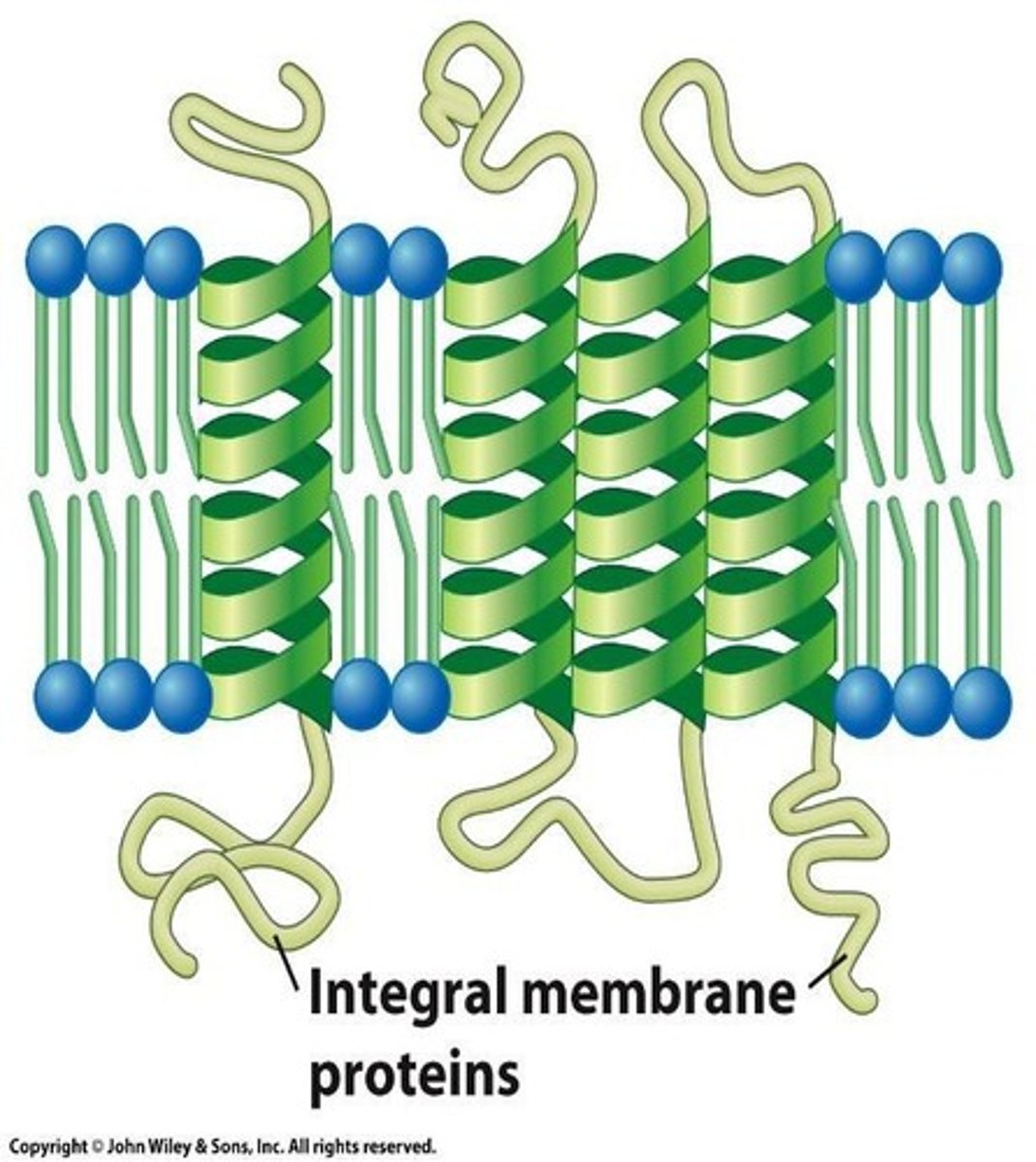
Integral Proteins Functions
Transport proteins (channels and carriers), Receptors that respond to stimuli, and Agents that transfer electrons.
Peripheral proteins
Located entirely outside of the bilayer on either the extracellular or cytoplasmic side, associated with non-covalent bonds.
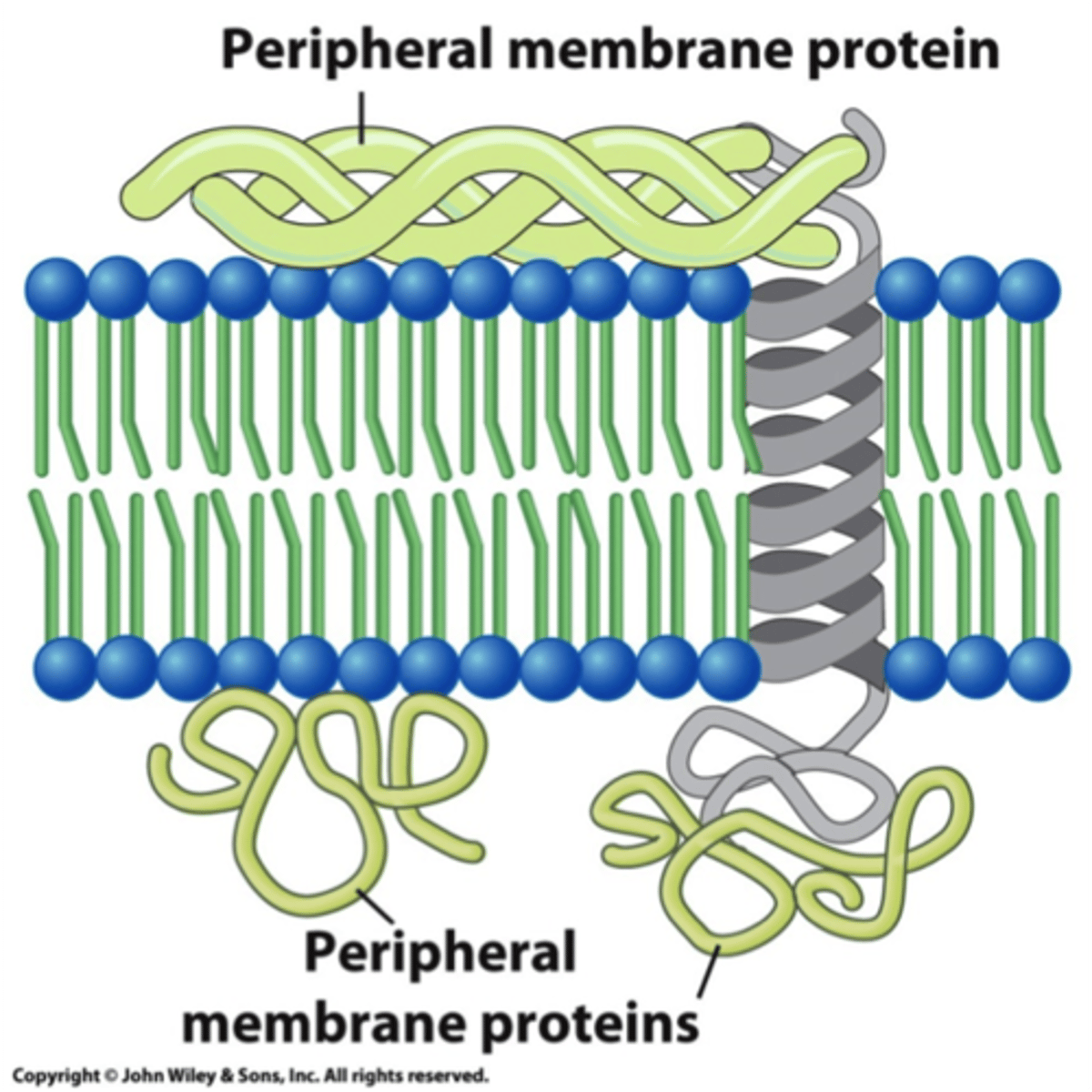
Functions of peripheral proteins
Provide mechanical support, specialized coats, anchor integral proteins, act as enzymes, and transmit signals.
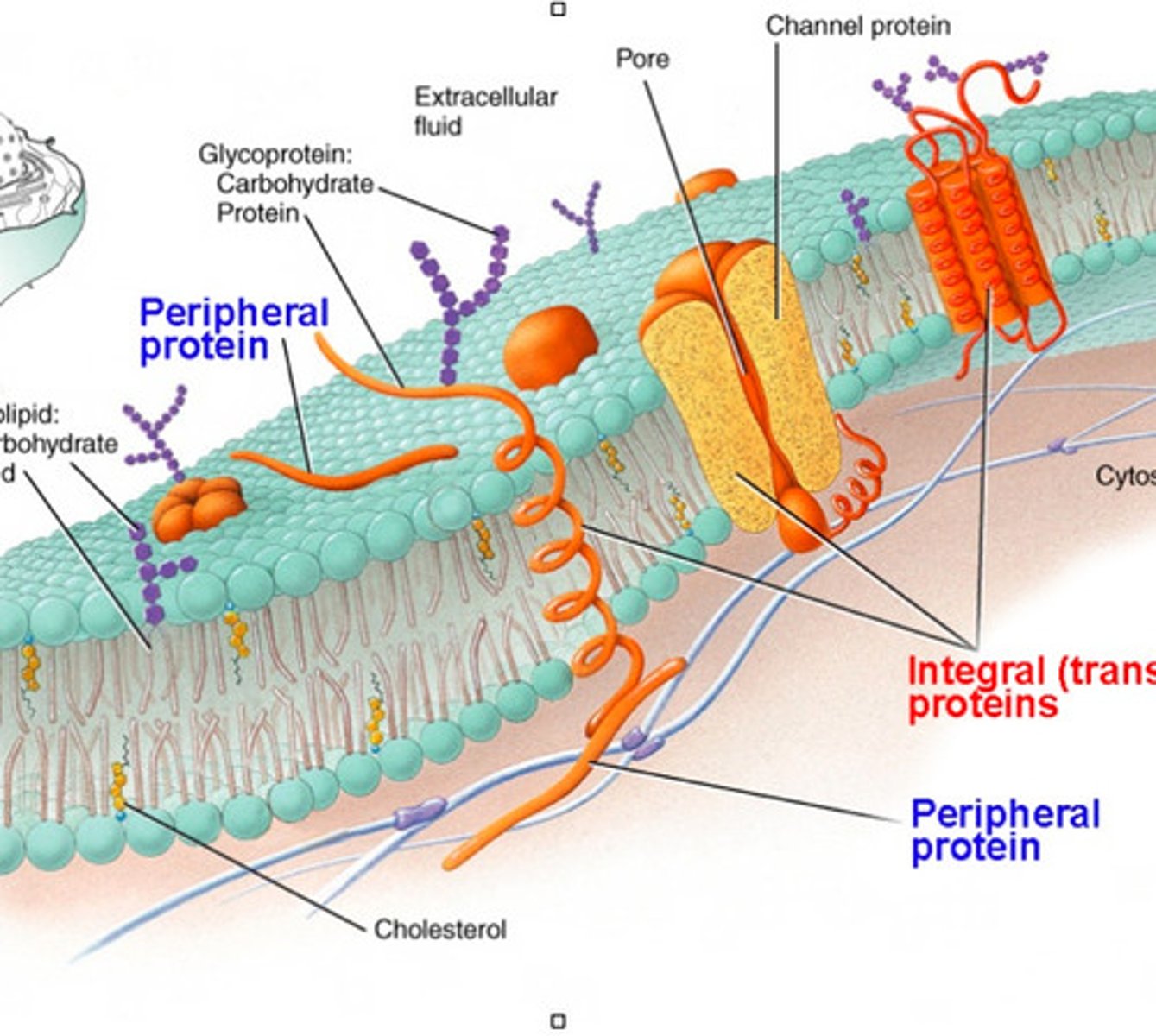
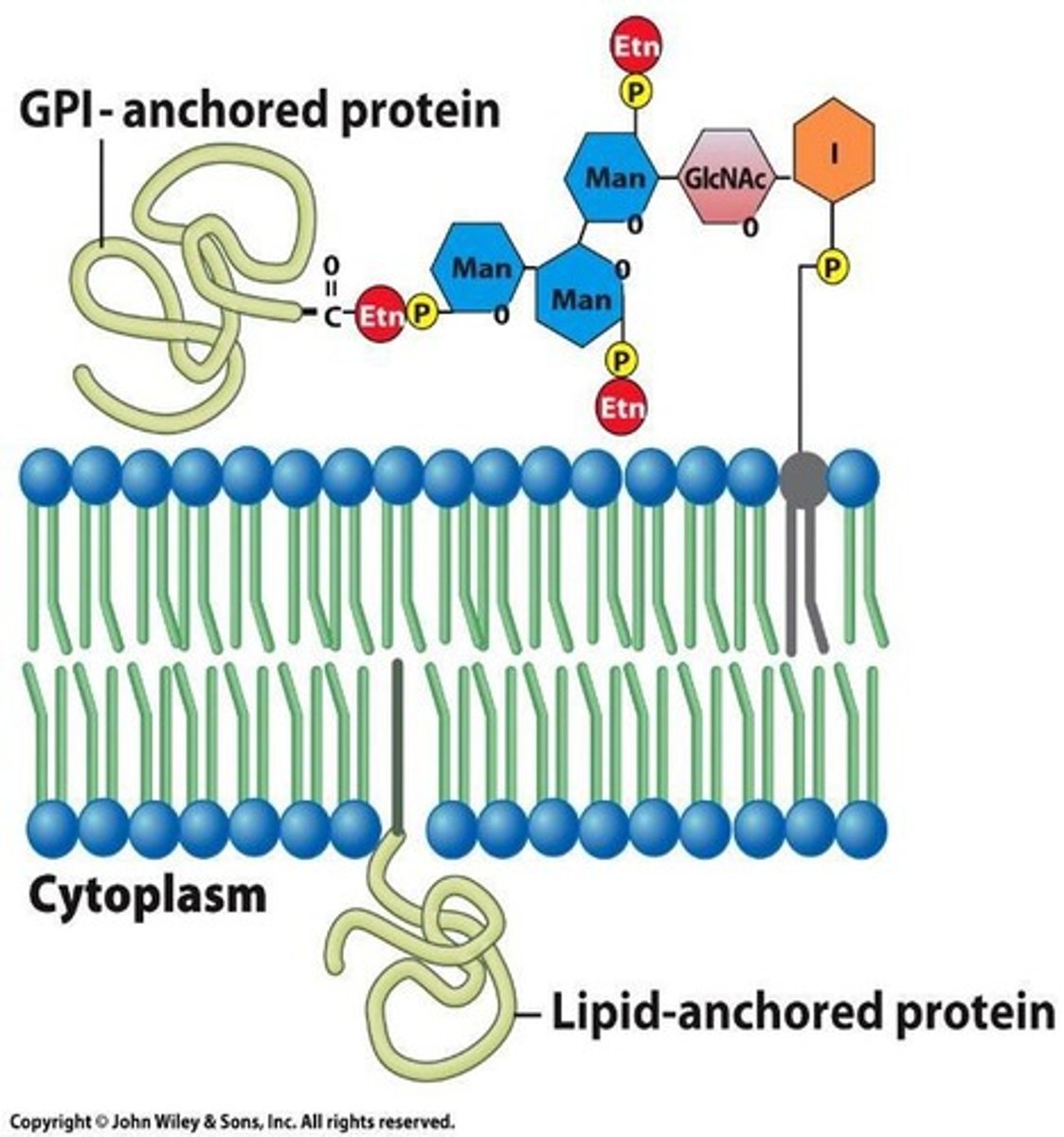
Lipid-anchored proteins
Located outside the lipid bilayer, on either the extracellular or cytoplasmic surface, it is covalently linked to lipids outside the bilayer.
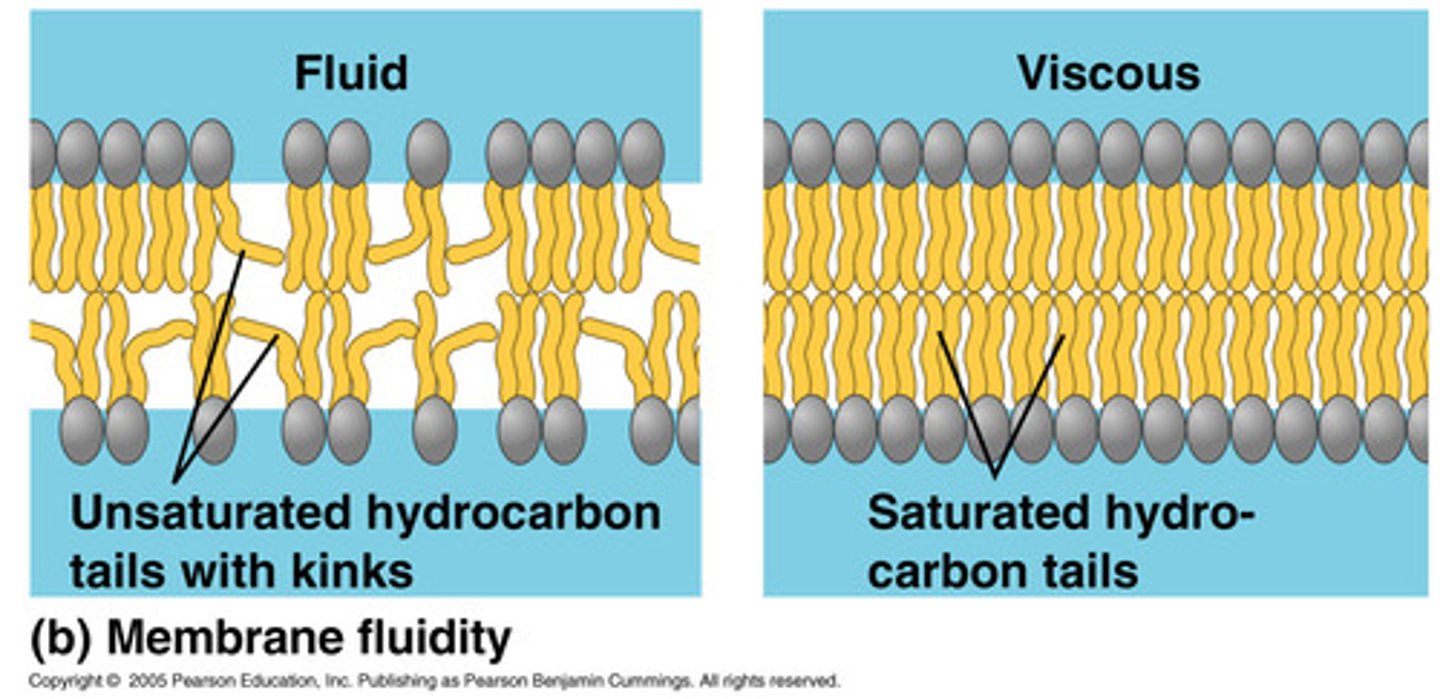
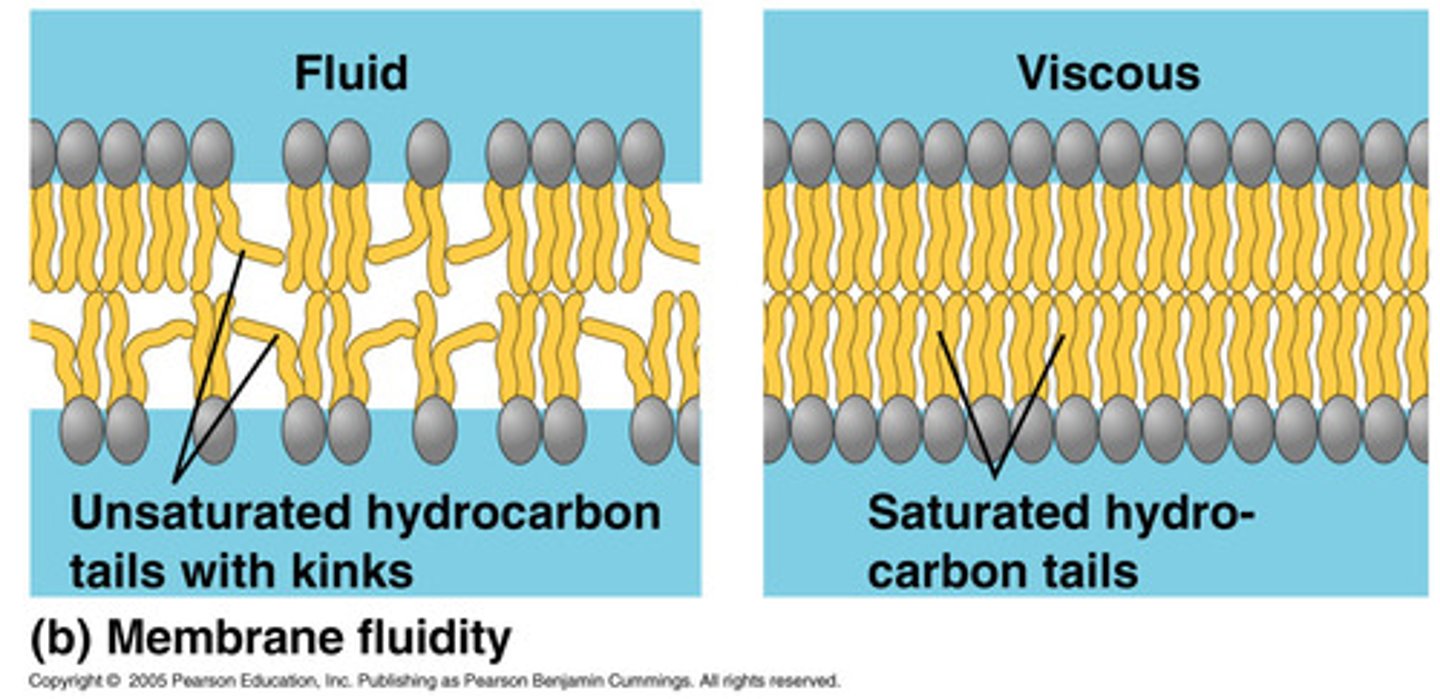
Fluidity (Viscosity)
Physical state of lipid molecules
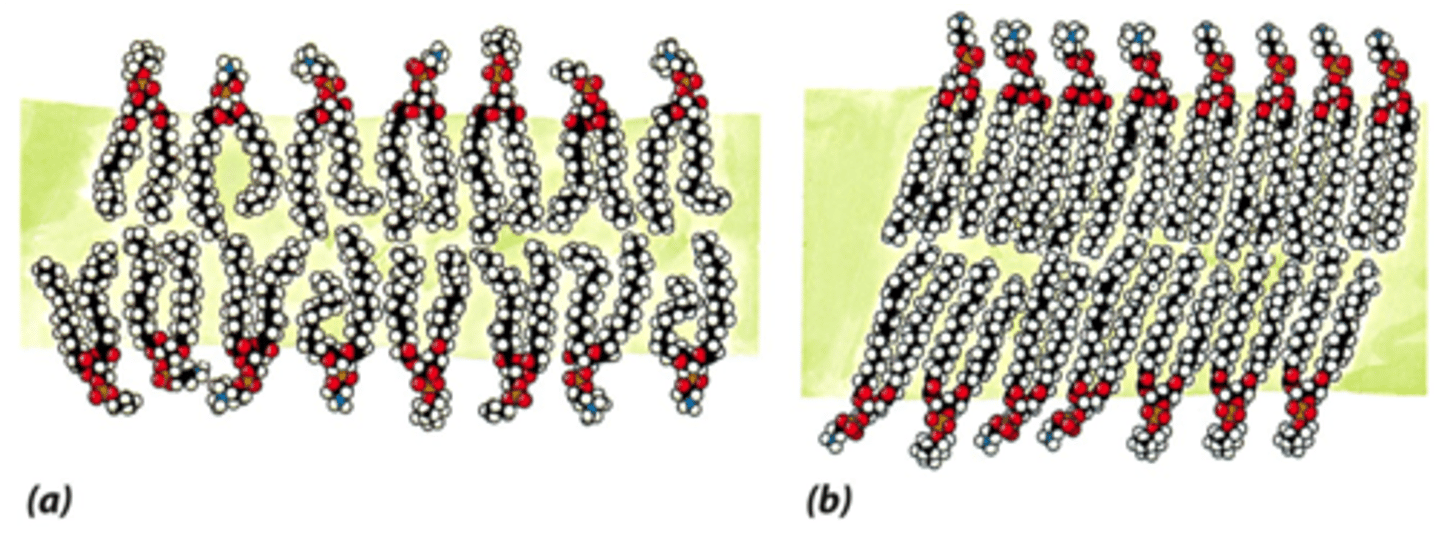
Liquid-crystal phase
Lipid molecules can rotate and move laterally.
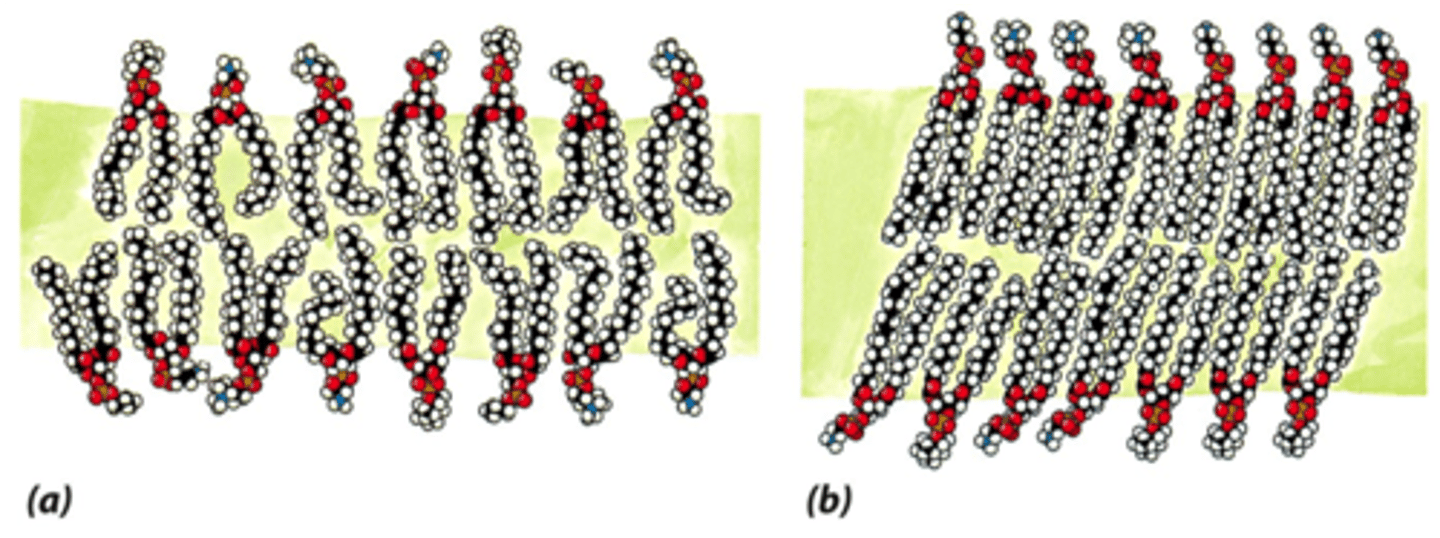
Solid-crystal (gel) phase
Lipid movement is greatly restricted.
What determines the fluidity of lipid molecules?
Temperature
Transition temperature (TT)
Temperature where lipid phase changes from liquid to gel.
Higher than TT
Liquid phase
Lower than TT
Gel phase
Determinants for TT
Saturation, length of fatty acids, and cholesterol presence.
Saturation of fatty acids
More unsaturated fats lower the transition temperature.
Length of fatty acids
Shorter chains lower the transition temperature.
Cholesterol's role in TT
More cholesterol lowers the transition temperature.
Importance of membrane fluidity
Balances rigidity and fluidity for membrane function.
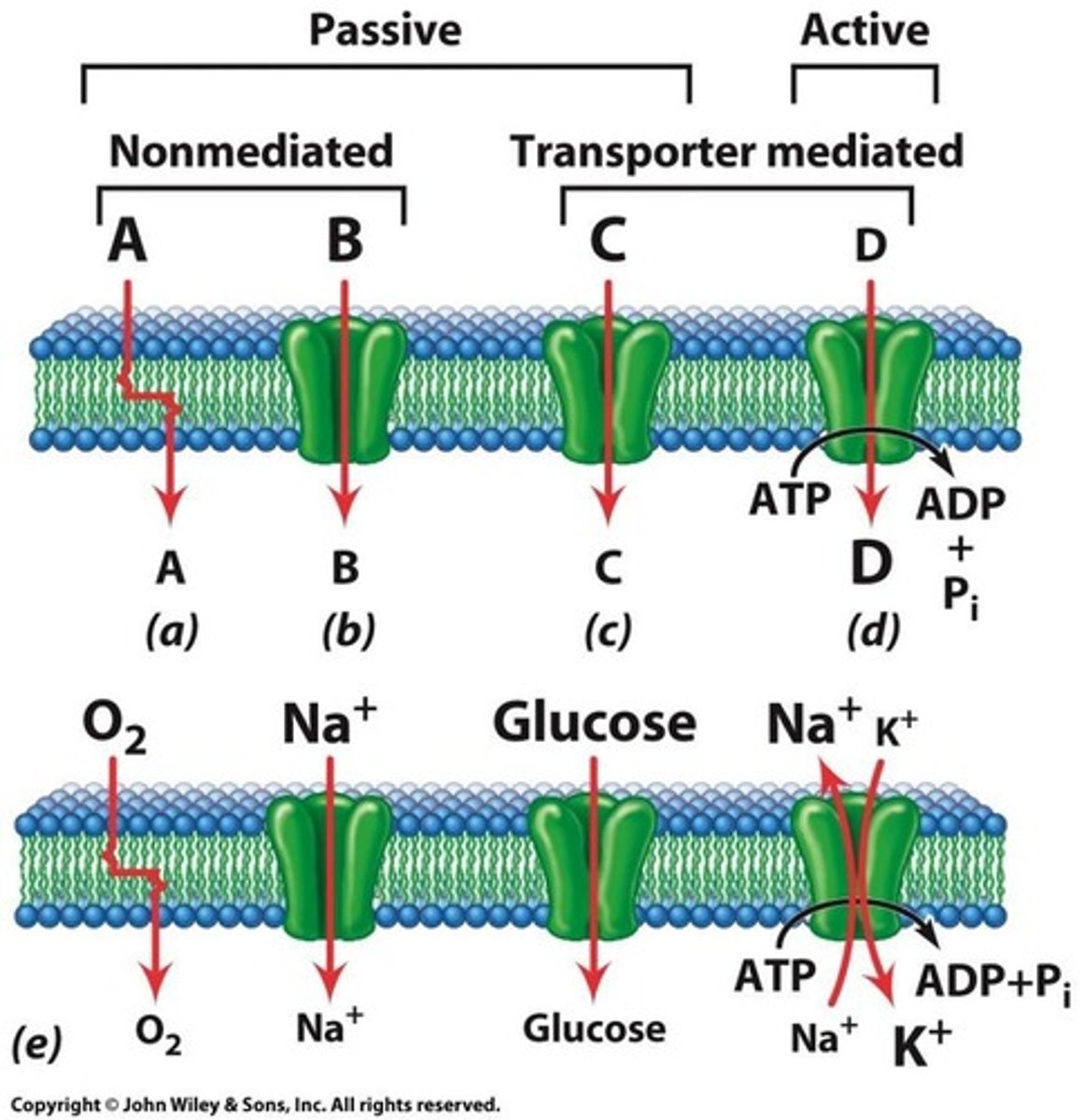
Simple diffusion
Movement of substances(water and ions) with/without protein channels.
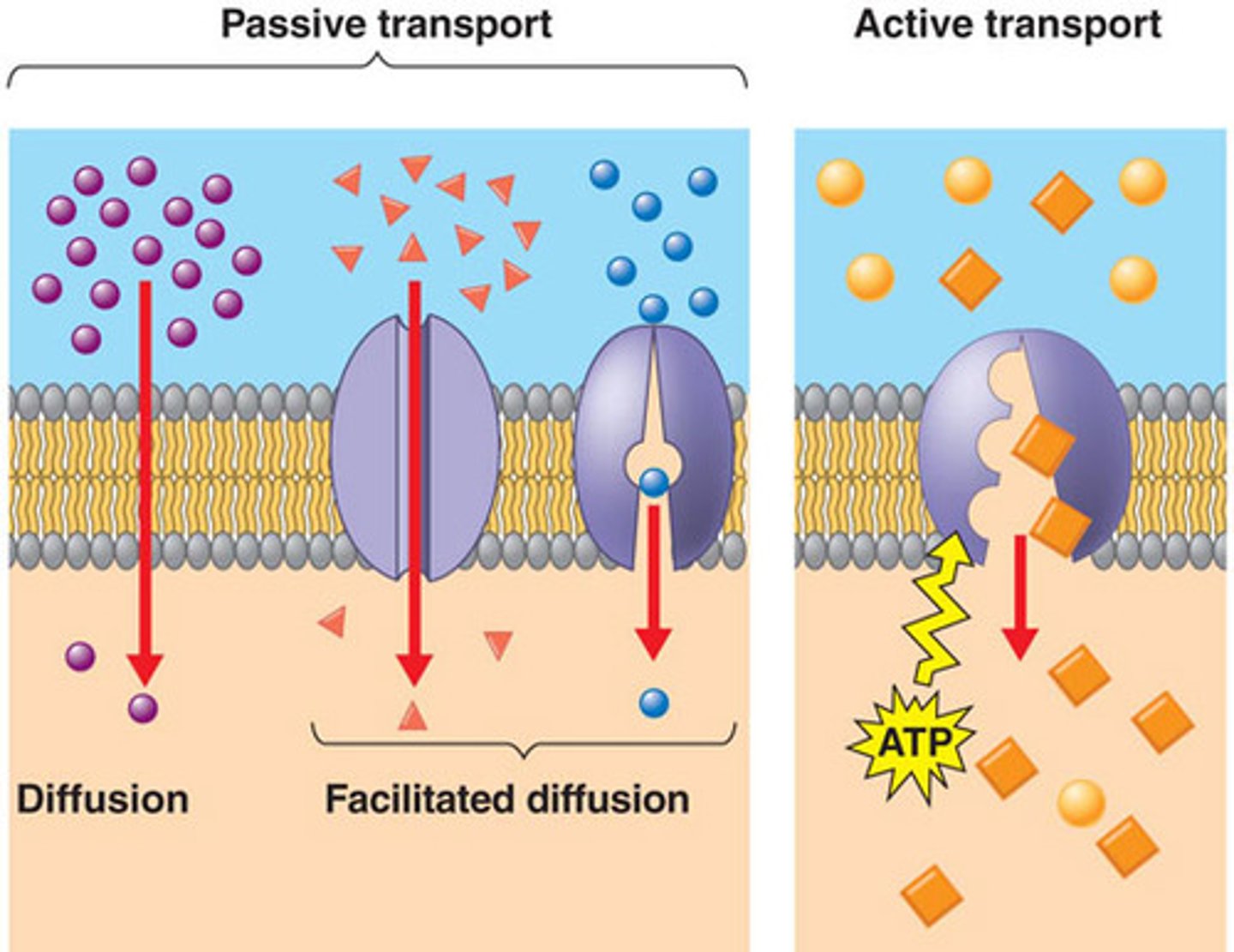
Facilitated diffusion
Requires specific binding to protein transporters.(Glucose transporter)
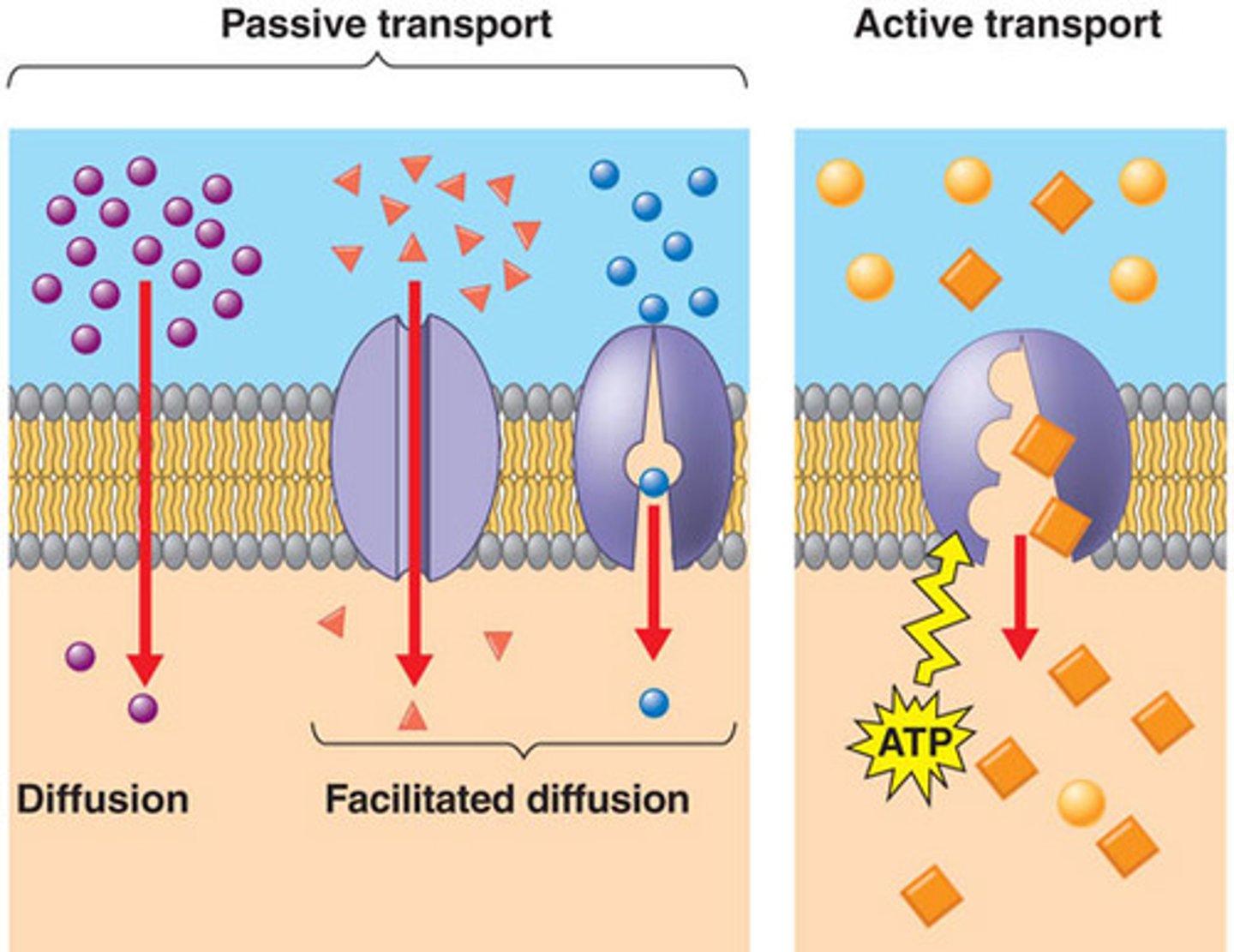
Active transport (primary and secondary)
Requires ATP, moves against concentration gradient.
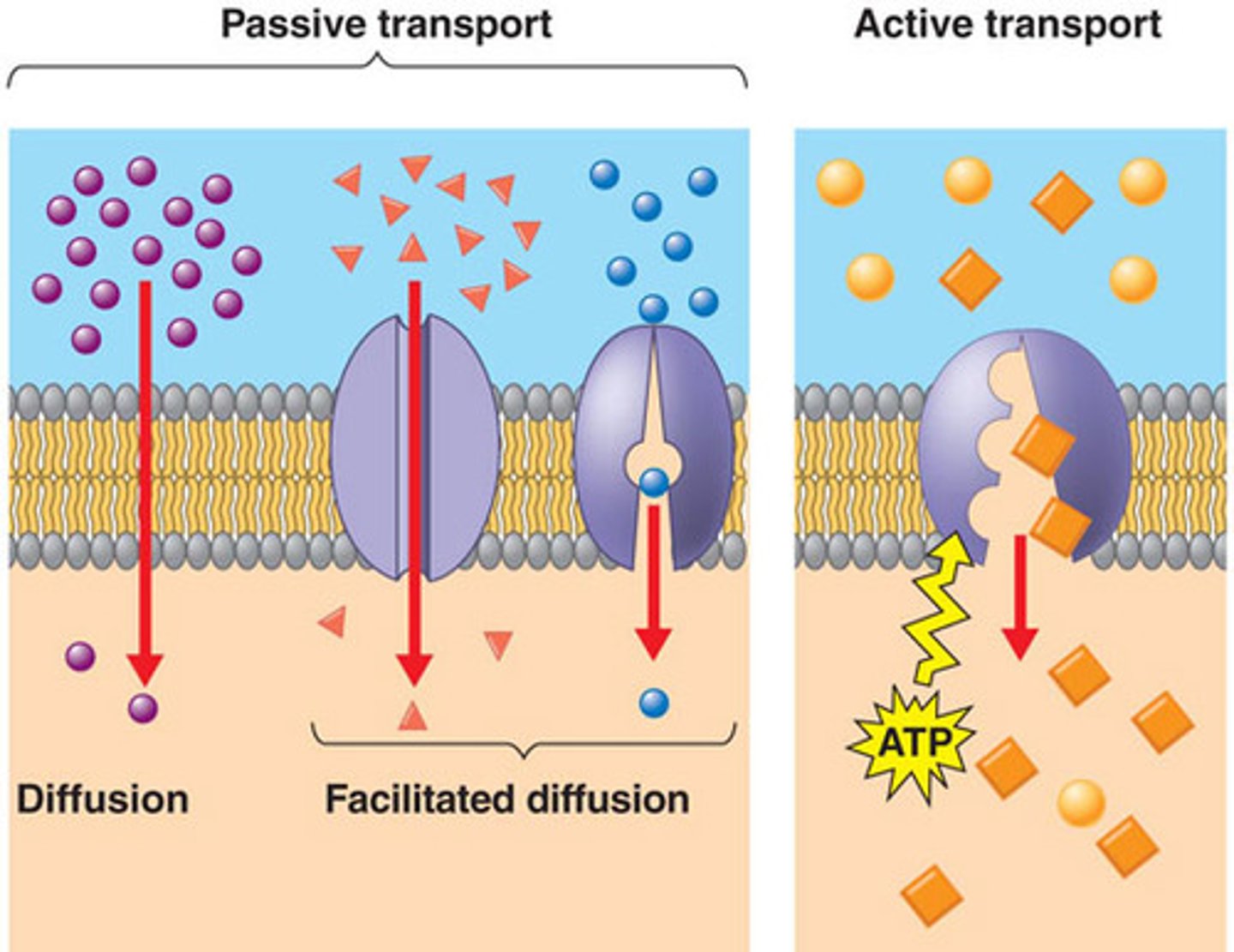
Selective permeability
Allows separation and exchange of materials across membranes.
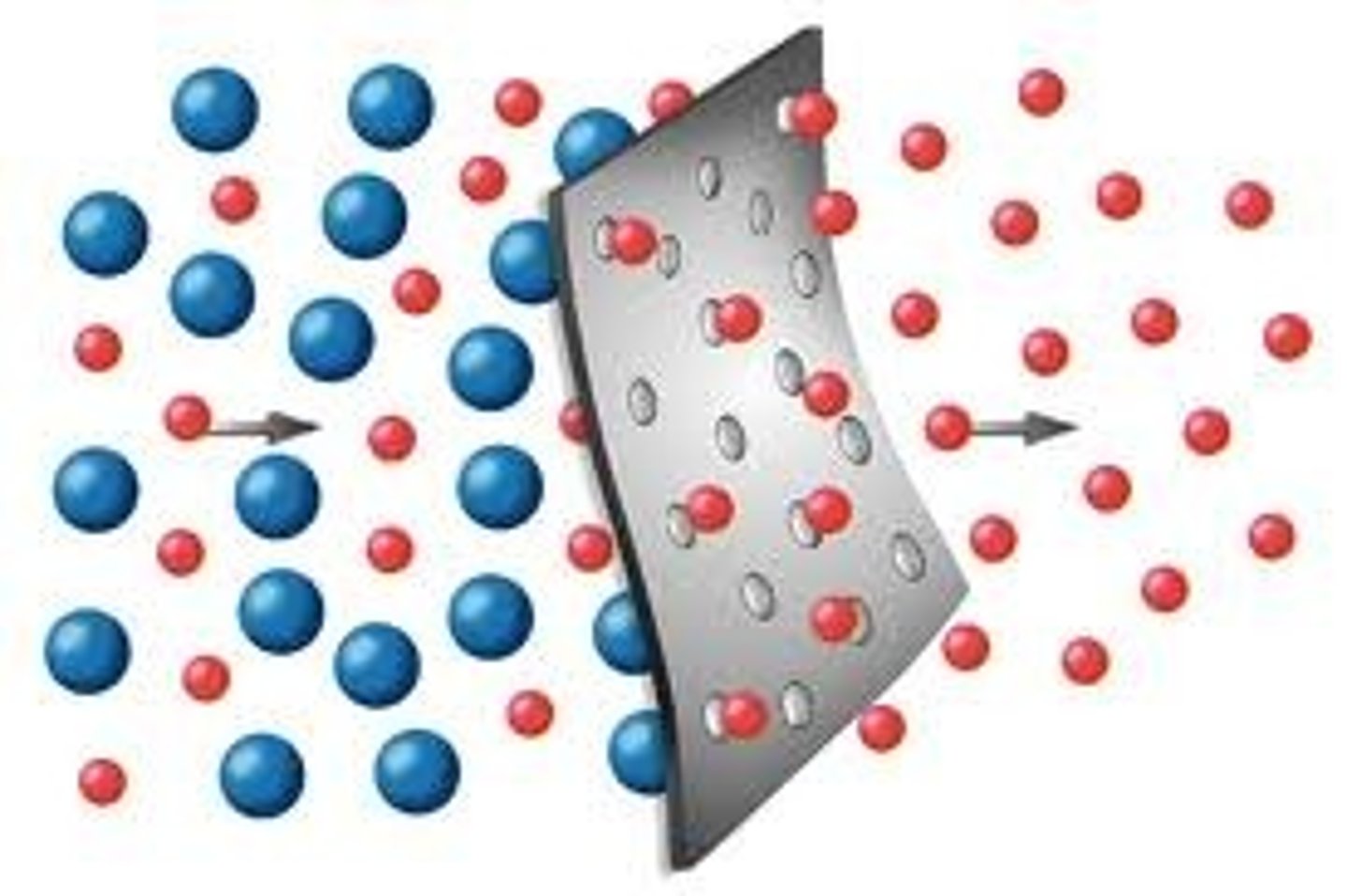
Net flux
Difference between influx and efflux of materials.
Diffusion
Spontaneous movement from high to low concentration.
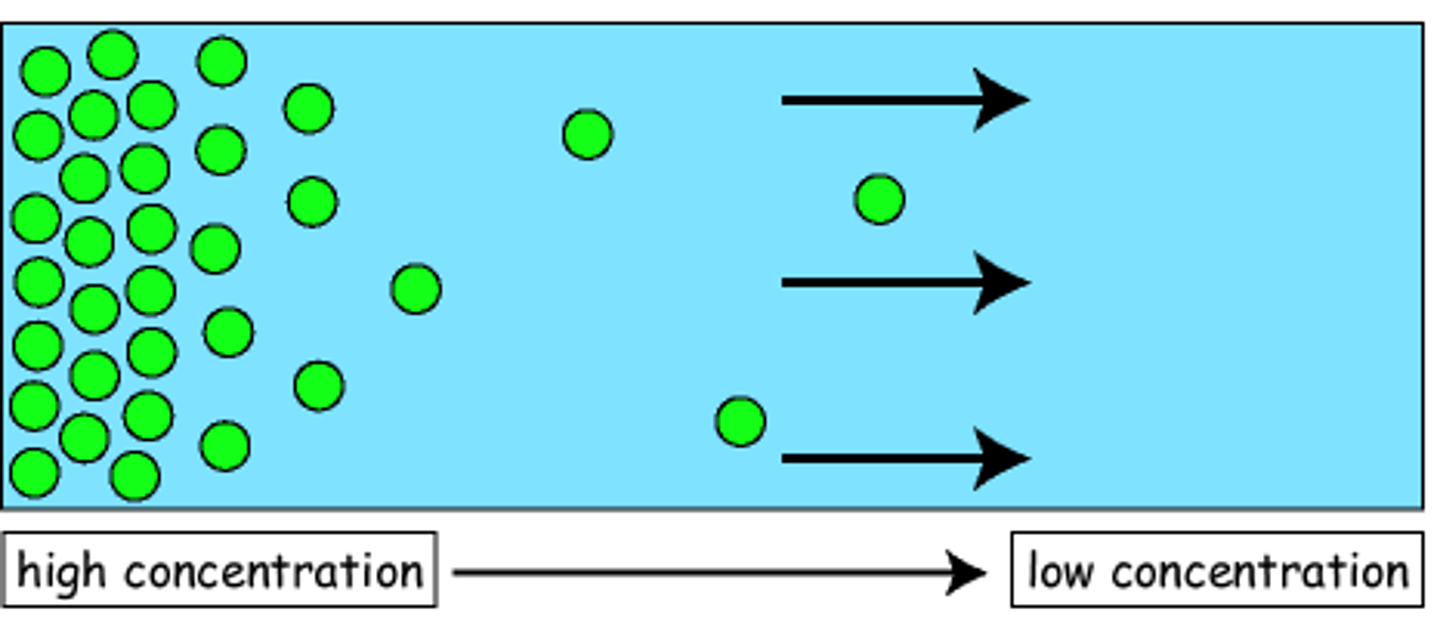
Diffusion of nonelectrolytes
depends on the concentration gradient
Diffusion of electrolytes
depends on the electrochemical gradient
Determinants of simple diffusion rate
polarity and molecular size
Partition coefficient
The ratio of a substance's solubility in a nonpolar solvent compared to its solubility in water.
Partition coefficient and polarity
Less polar, larger partition coefficient (faster penetration)
Size Effect on Diffusion
Smaller molecules penetrate membranes faster.
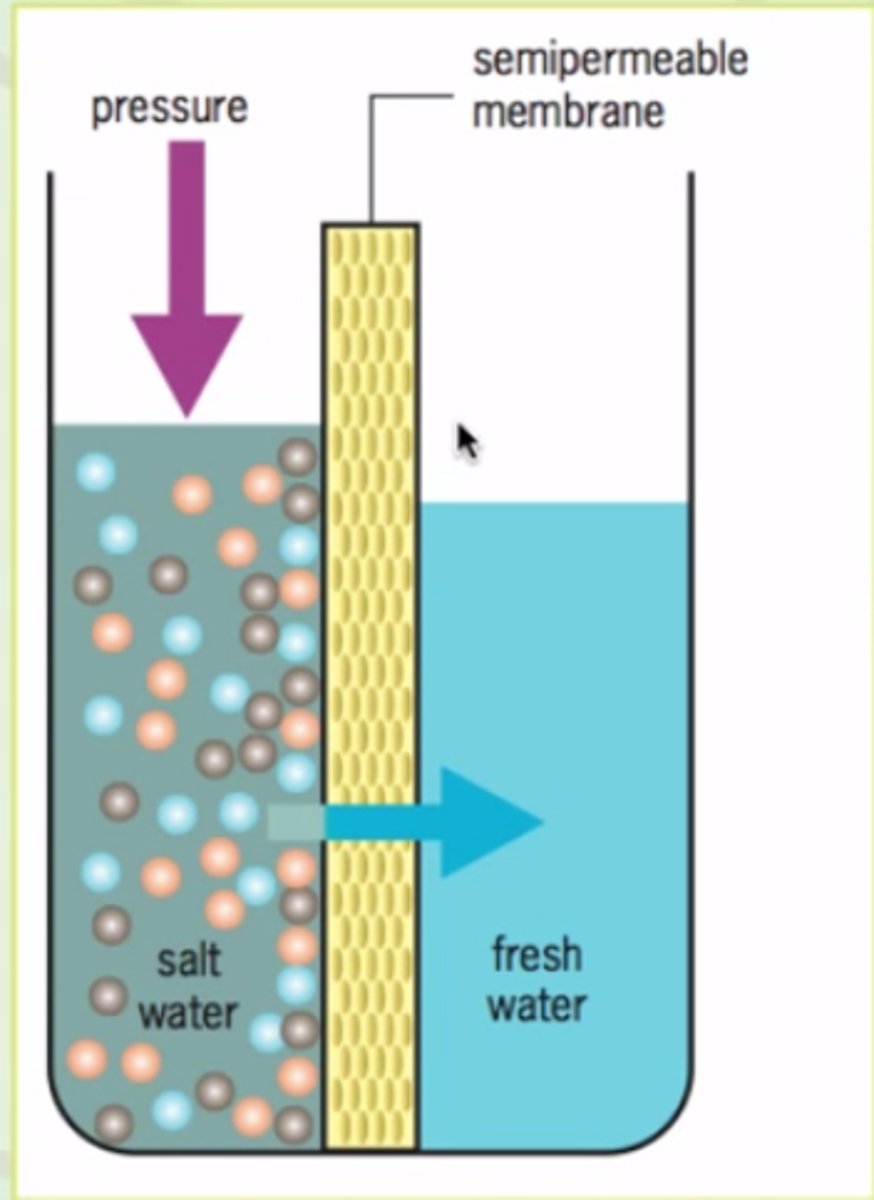
Osmosis
the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane. (low to high concentration)
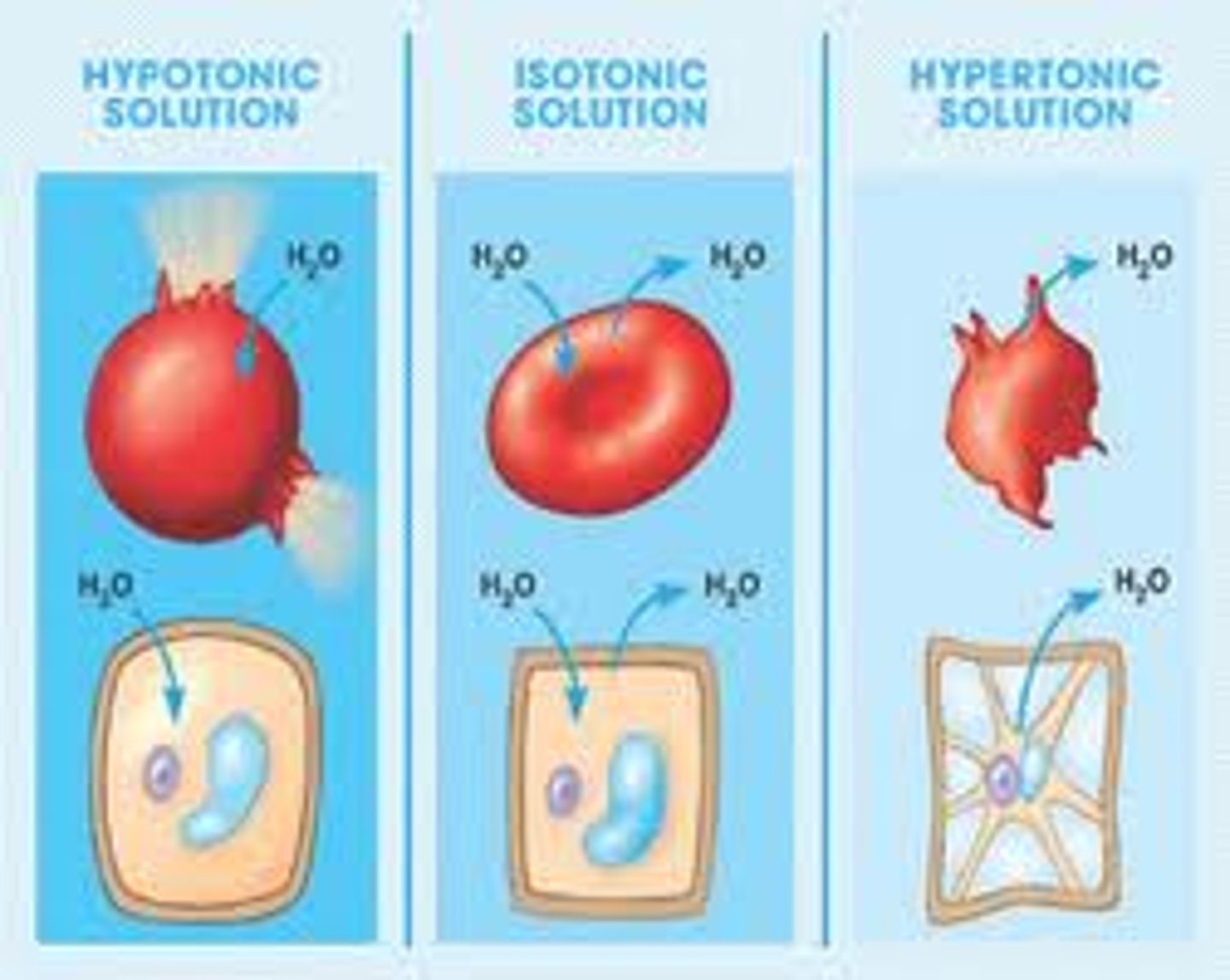
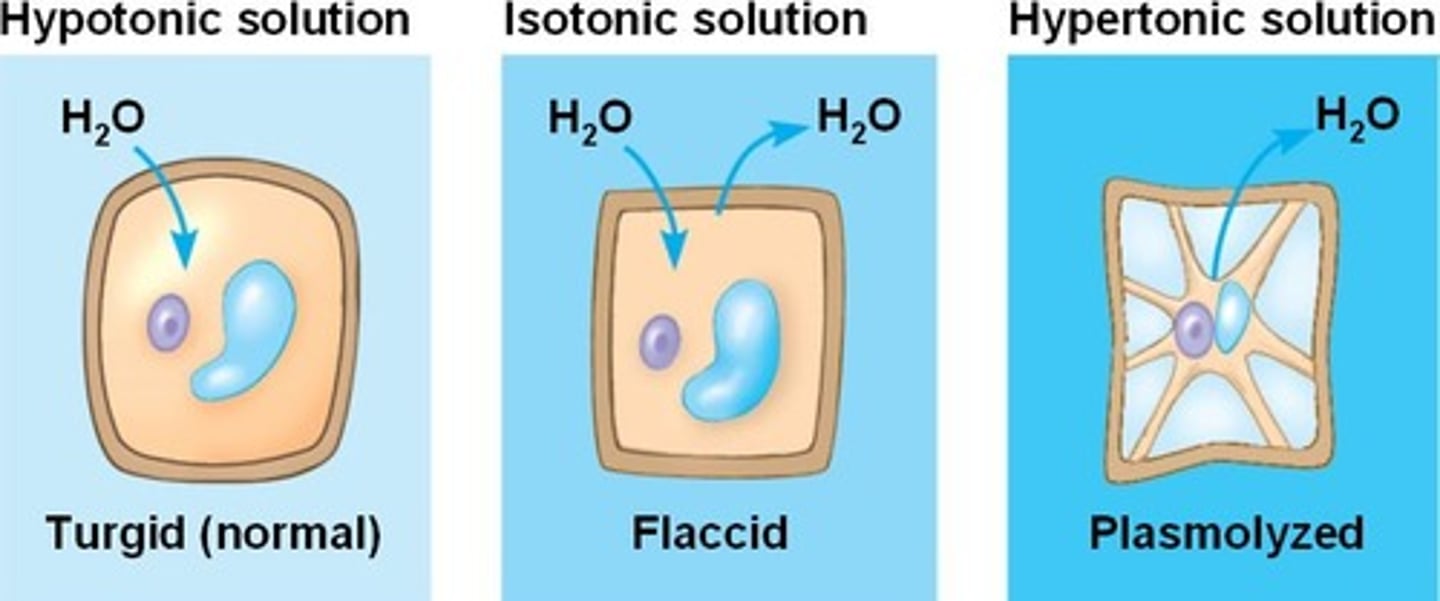
Hypotonic Solution
Lower solute concentration; cells swell; lose ions
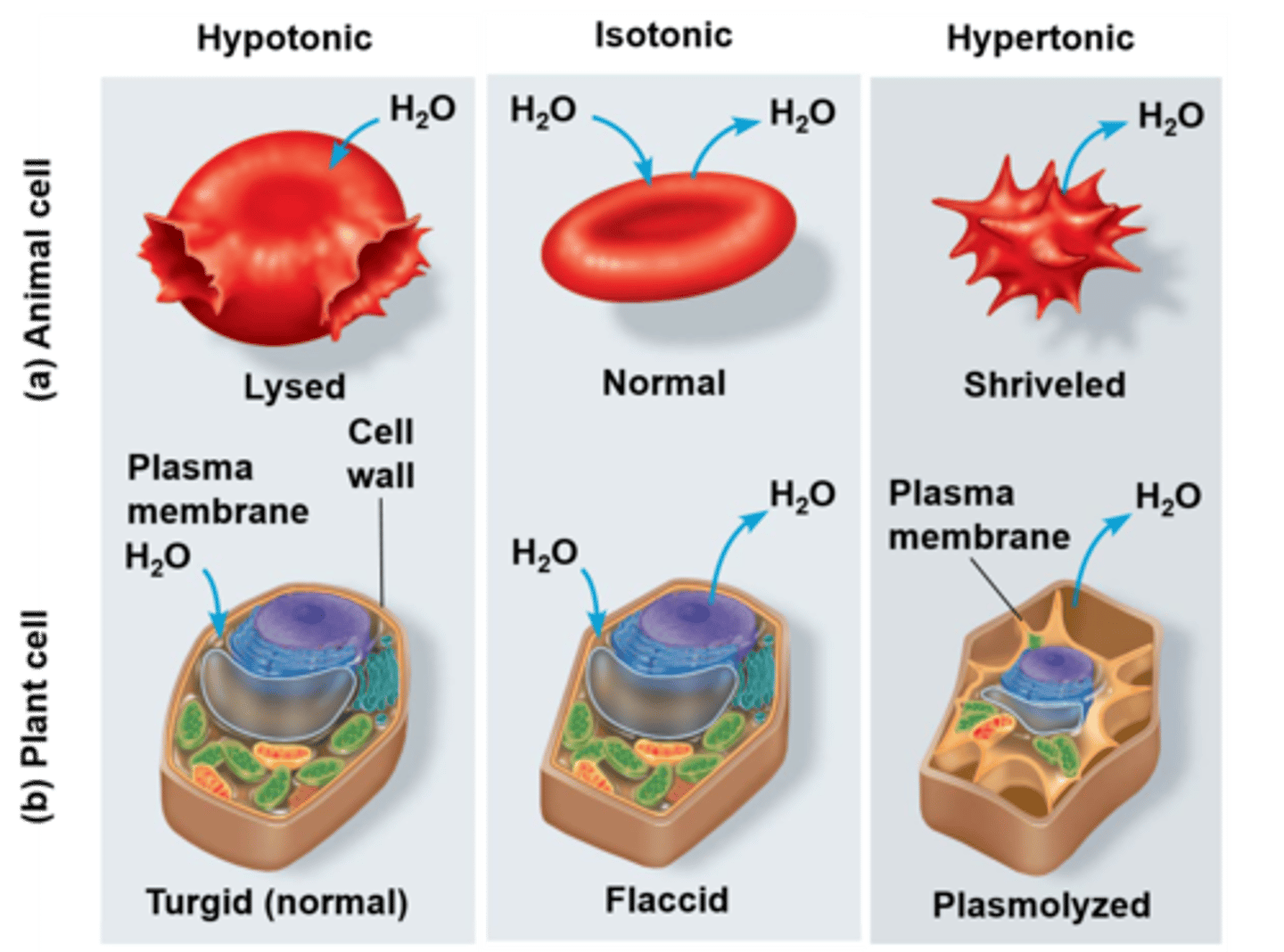
Hypertonic Solution
Higher solute concentration; cells shrink; gain ions
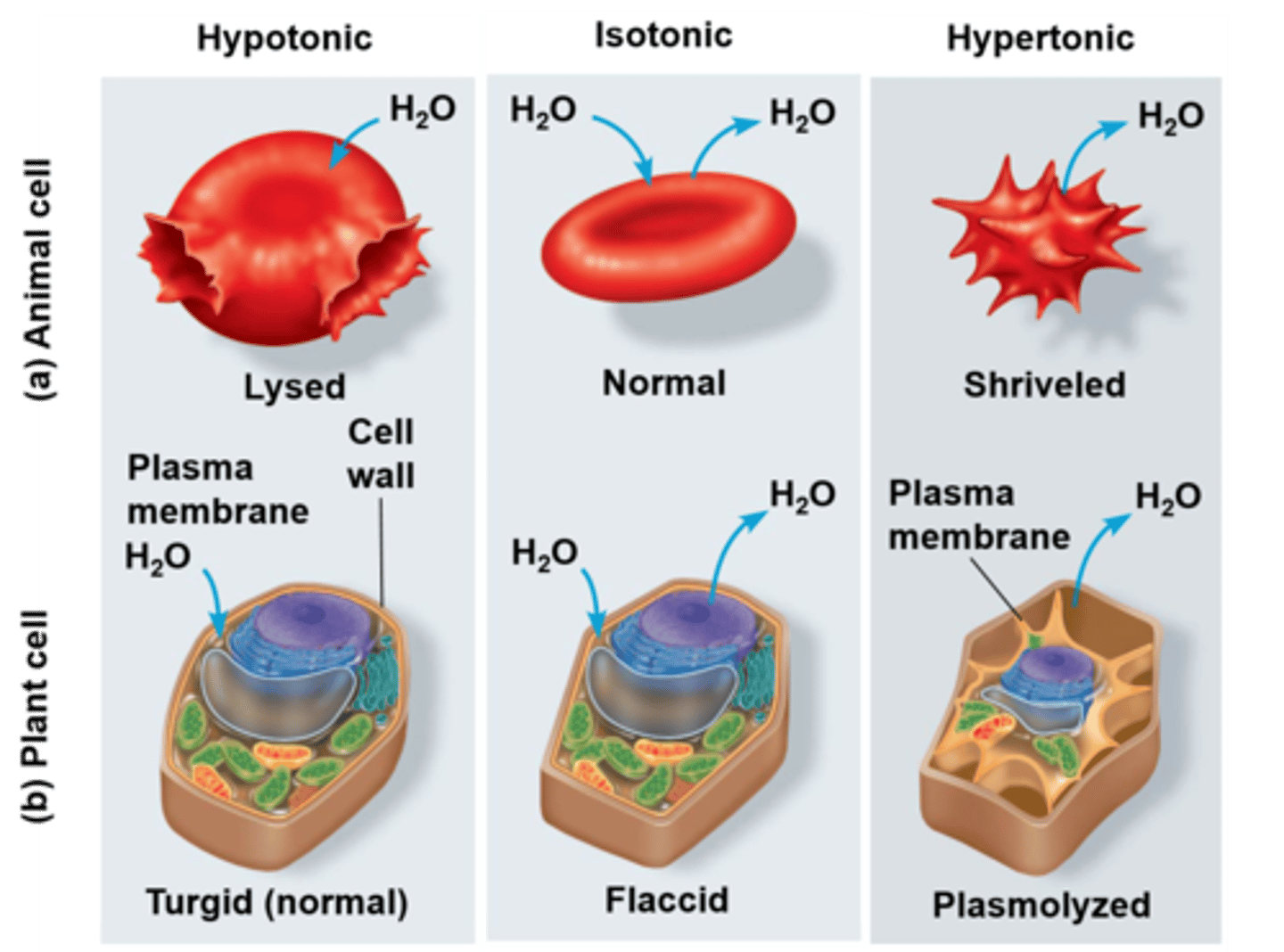
Isotonic Solution
Equal solute concentration; cells unchanged.
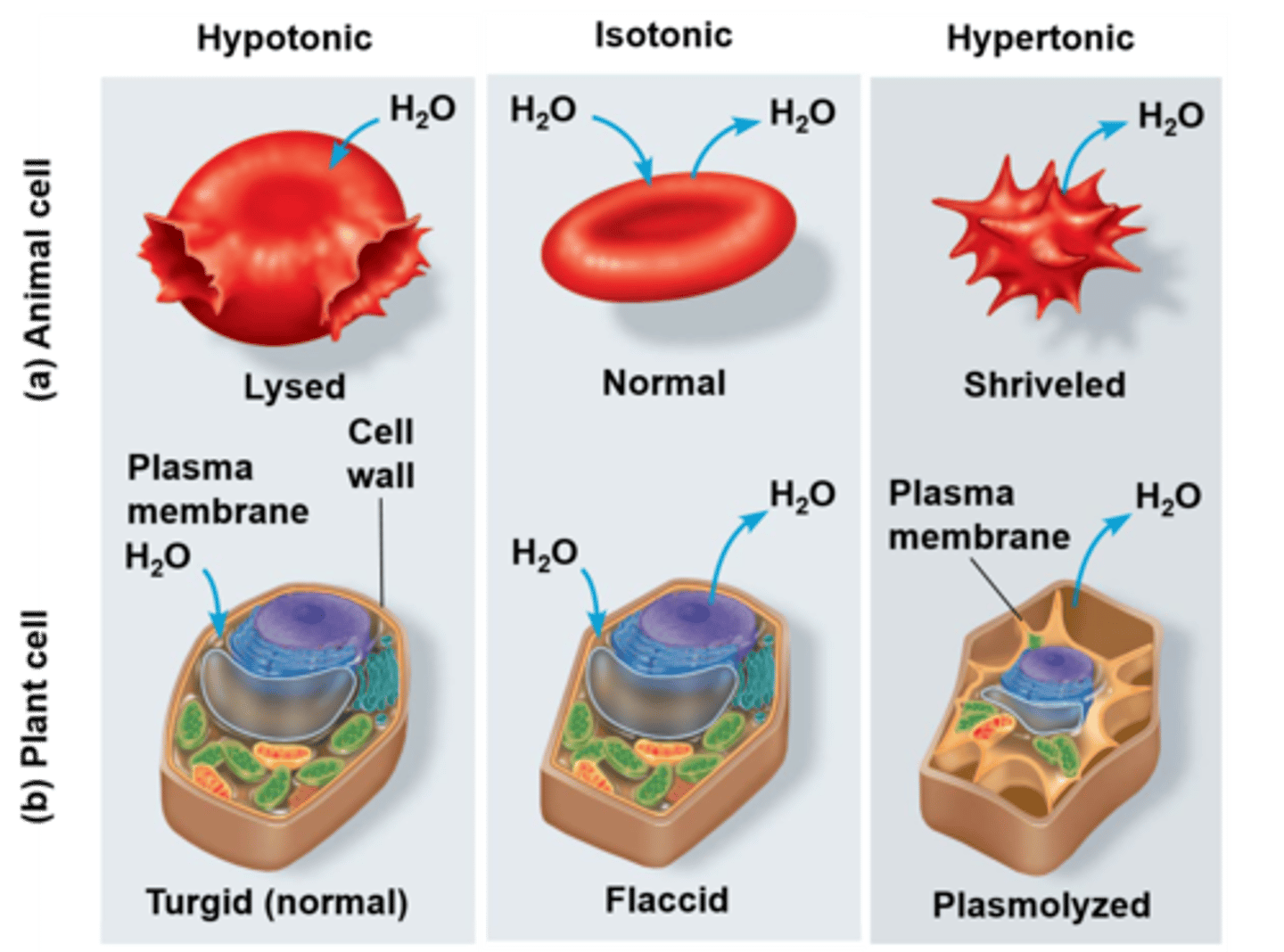
Turgor Pressure
Pressure in plant cells preventing swelling.
Plasmolysis
Plant cell shrinkage in hypertonic solutions.
Aquaporins
Proteins facilitating rapid water movement.
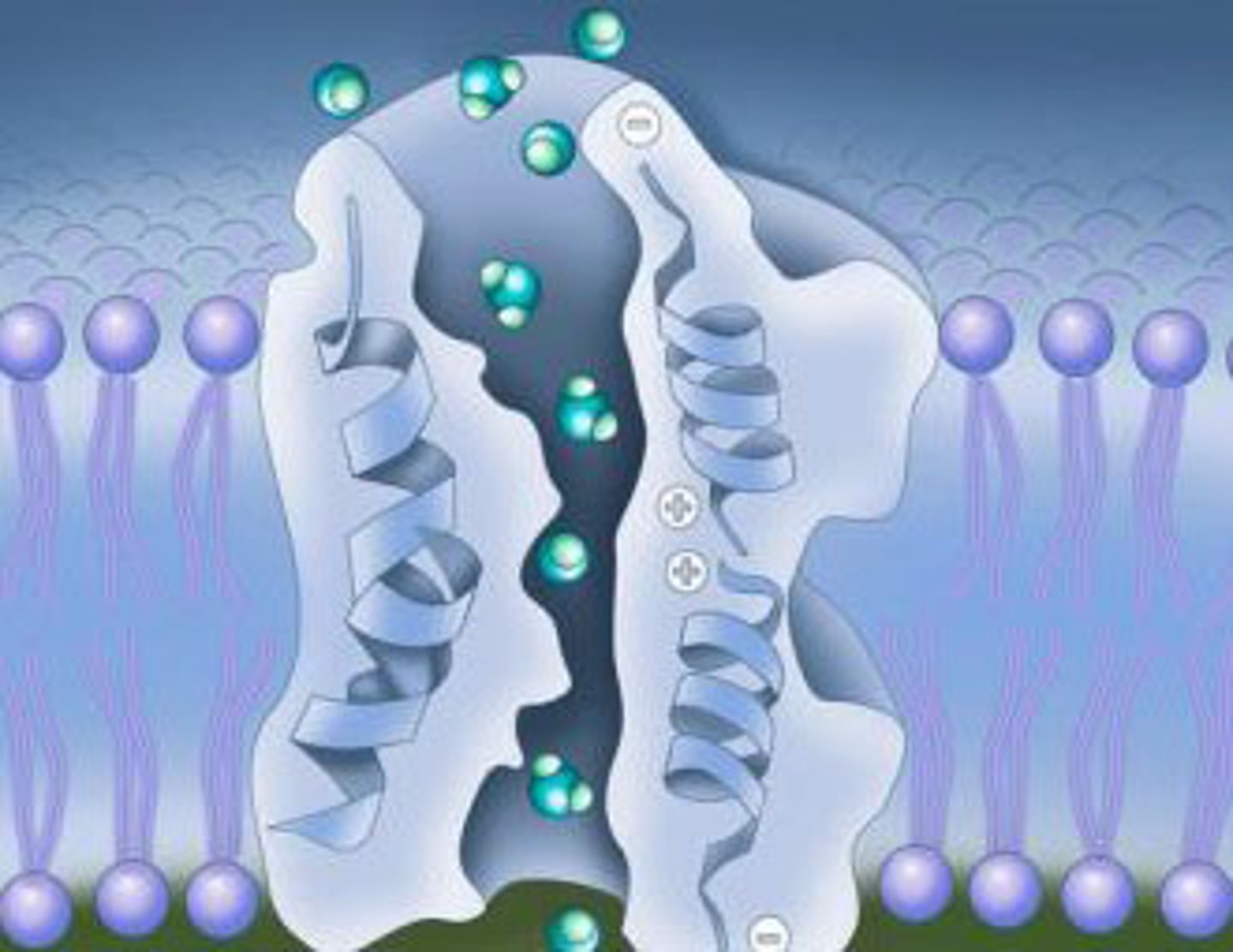
Ion Channels
Proteins allowing specific ion passage across membranes.
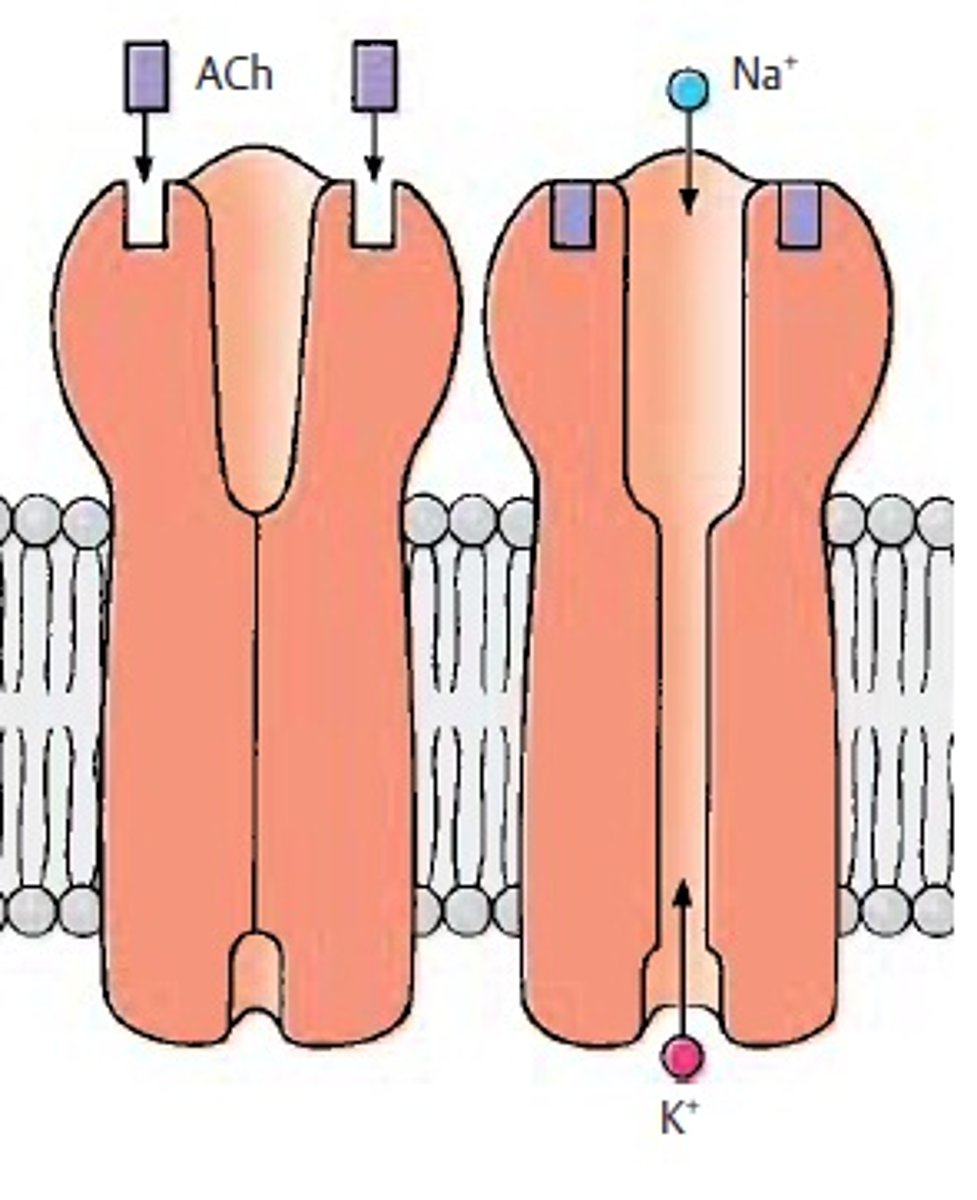
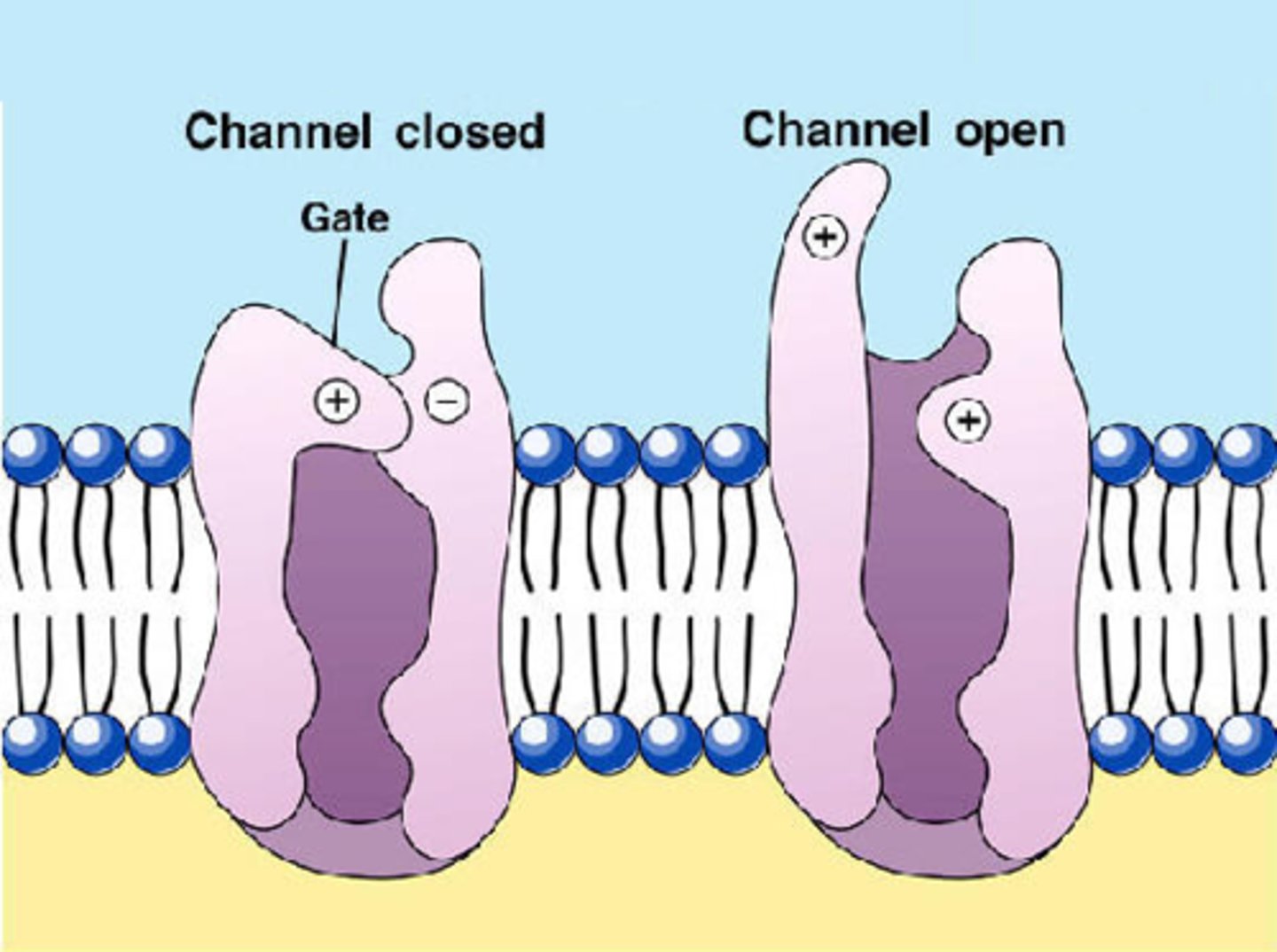
Gated Channels
Ion channels that can open or close.
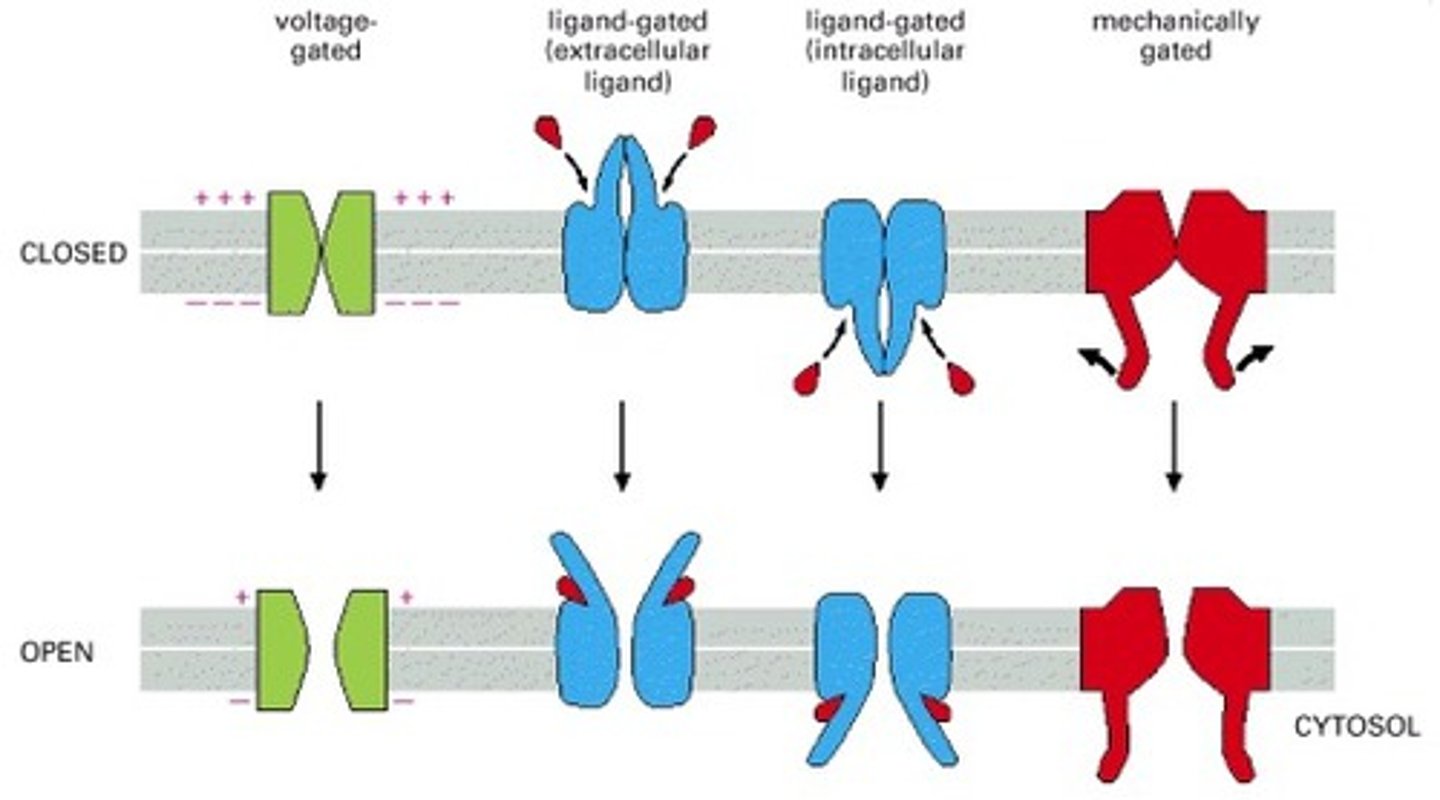
Voltage-Gated Channels
Open in response to membrane potential changes (ionic charge).
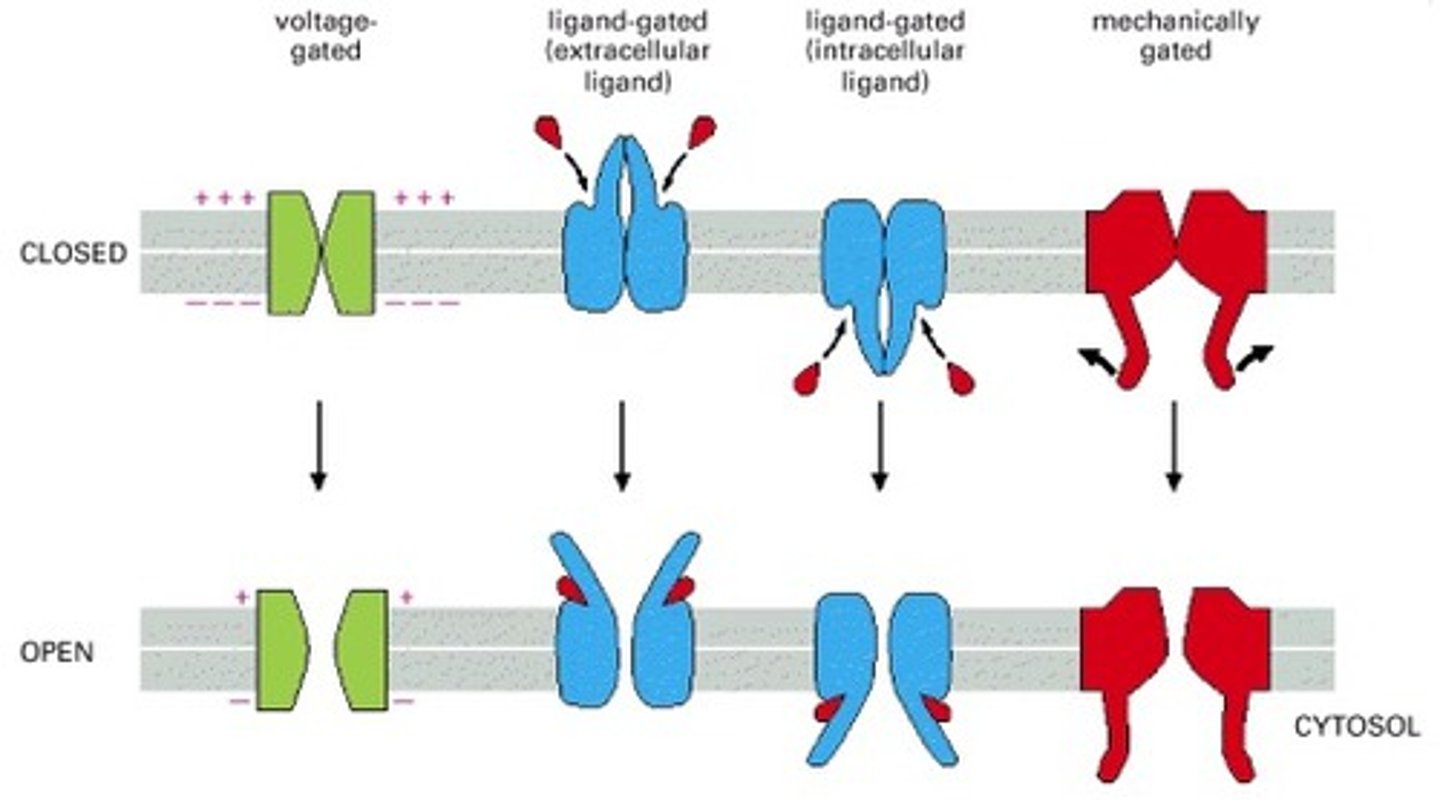
Ligand-Gated Channels
Open when a specific molecule binds.
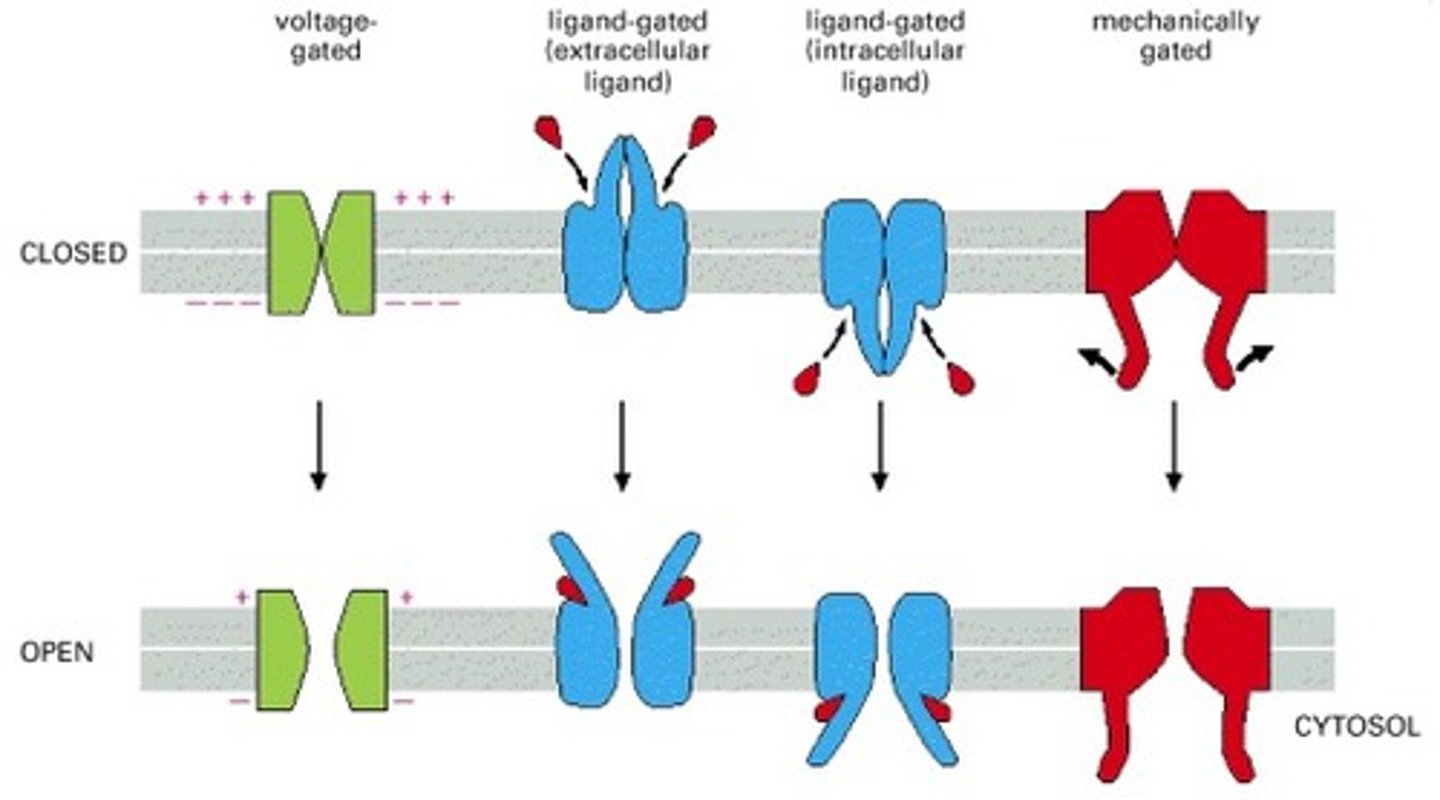
Mechano-Gated Channels
Open in response to mechanical forces.
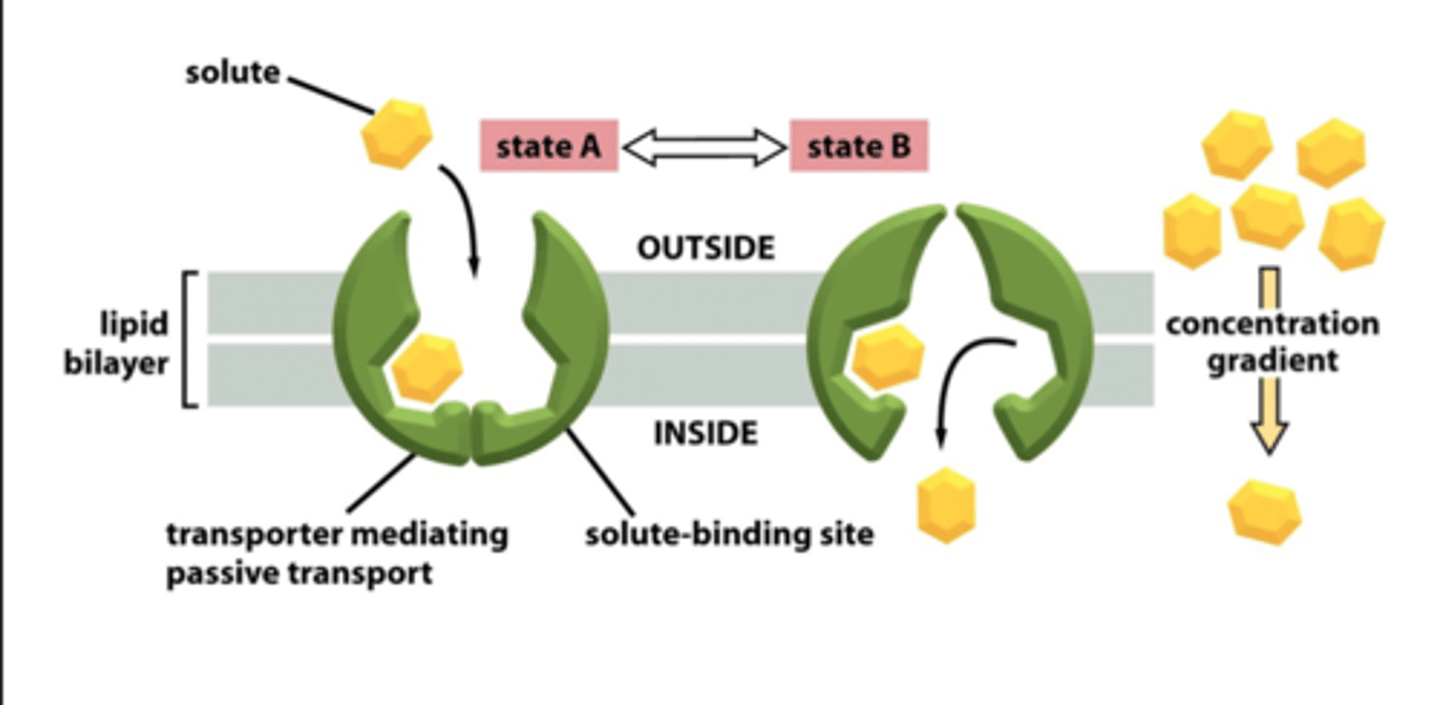
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive transport via specific transporter proteins.
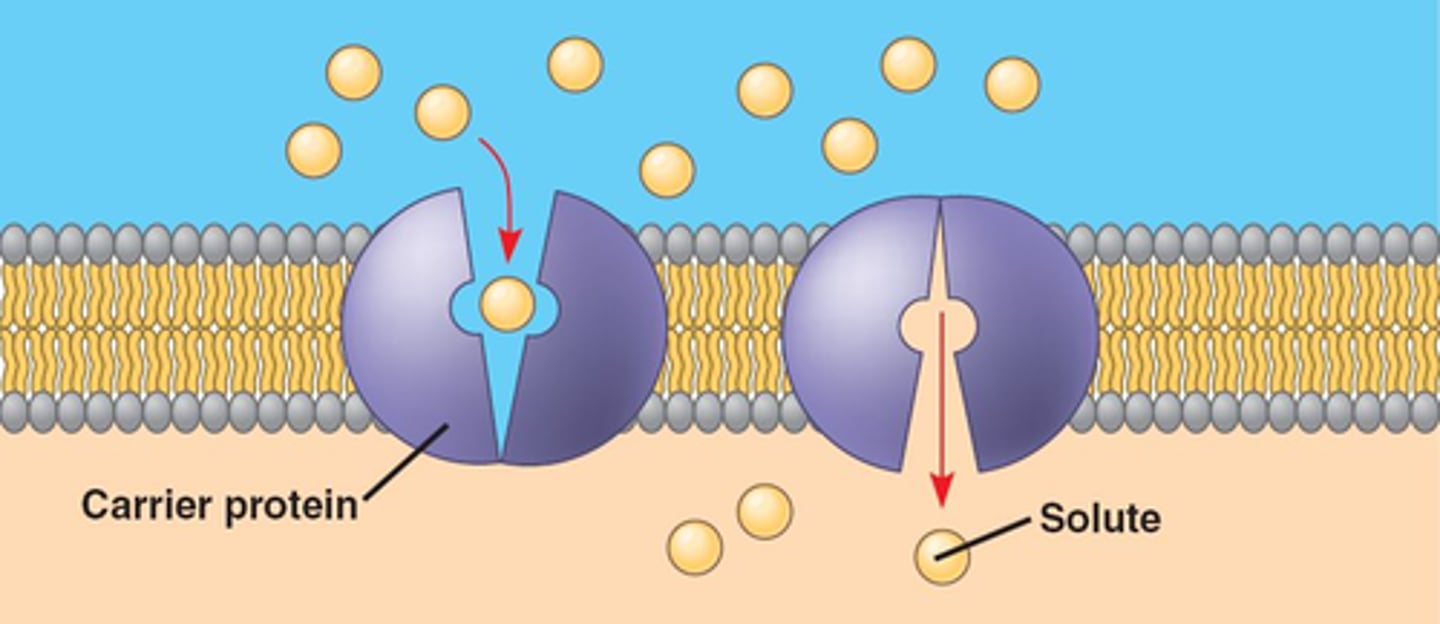
Saturation Kinetics
Transport limited by available transporter proteins.
Conformational Change
An alteration of the structure of the protein that impacts that protein's function
Active Transport
Movement against a concentration gradient using energy. (low to high concentration)
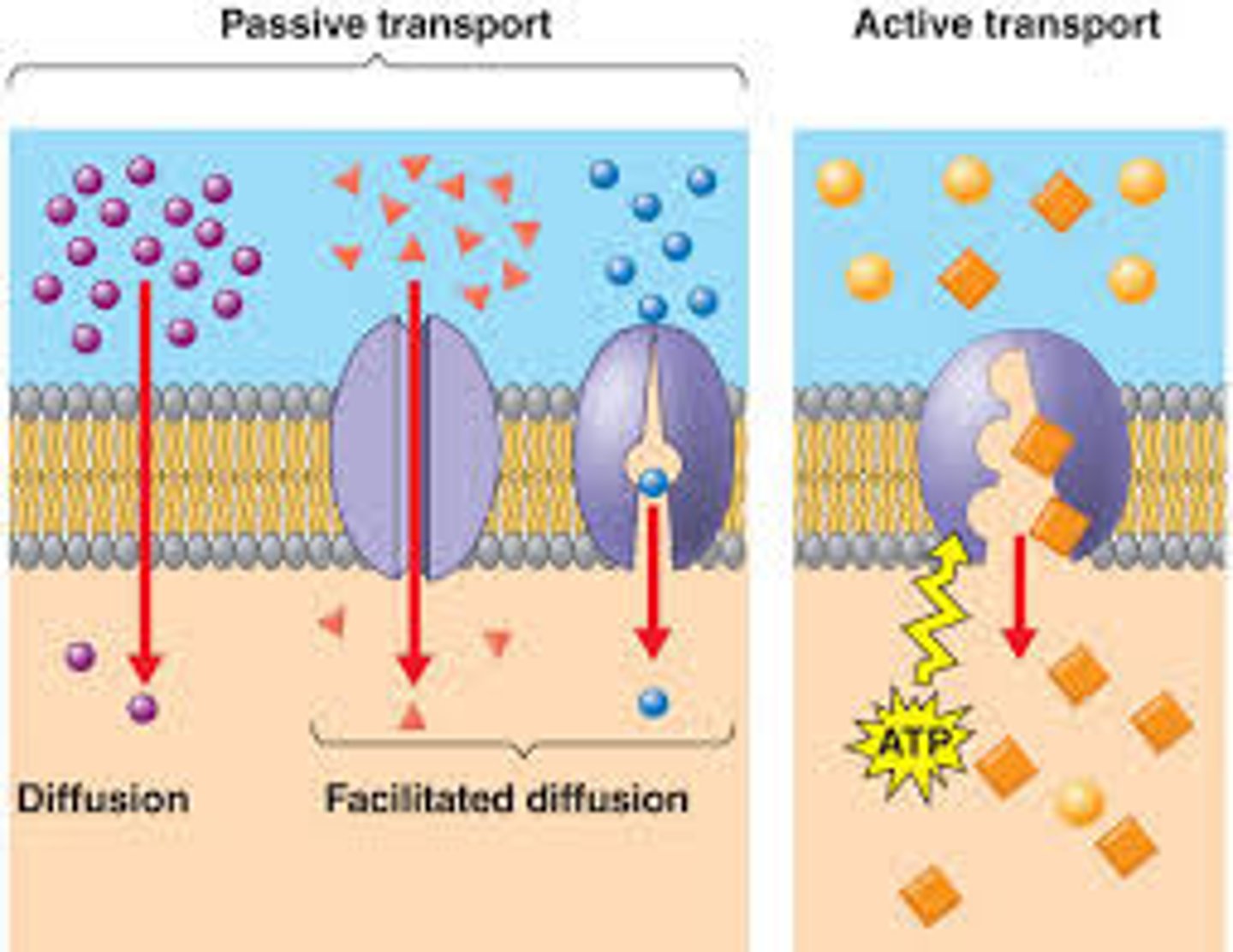
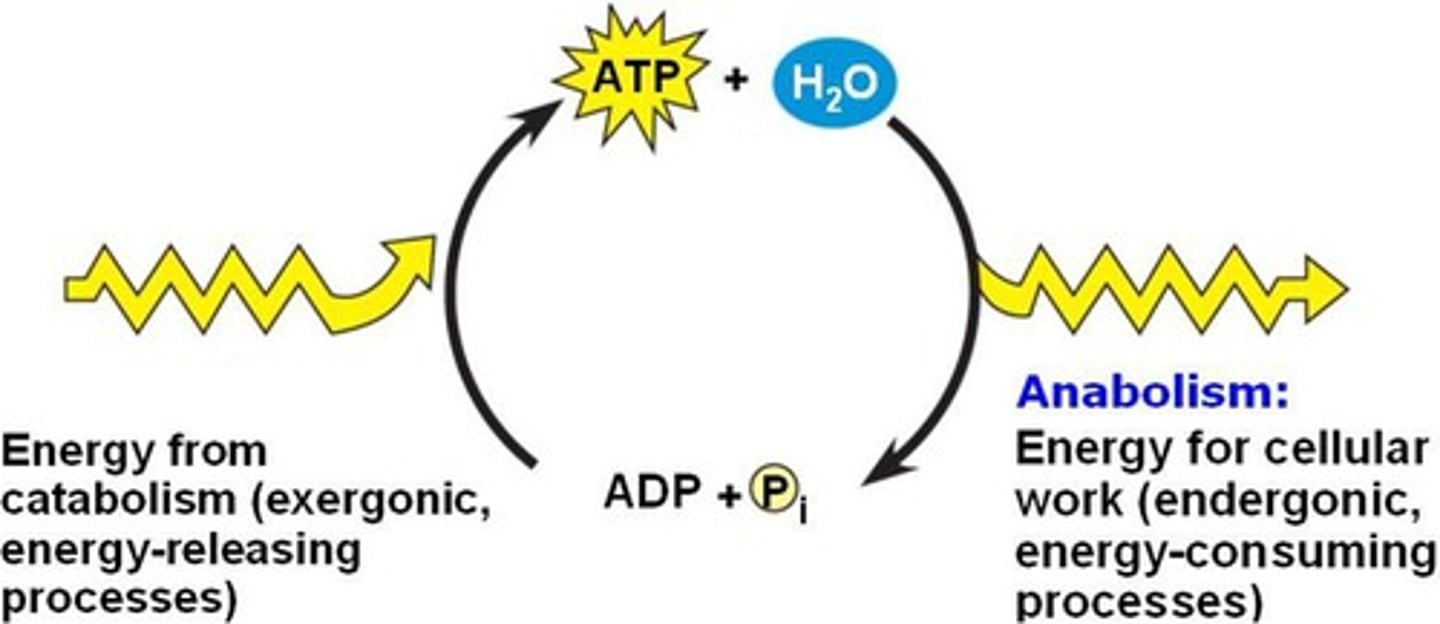
Hydrolysis of ATP
Exergonic process coupled with active transport releases energy by breaking phosphate group off.
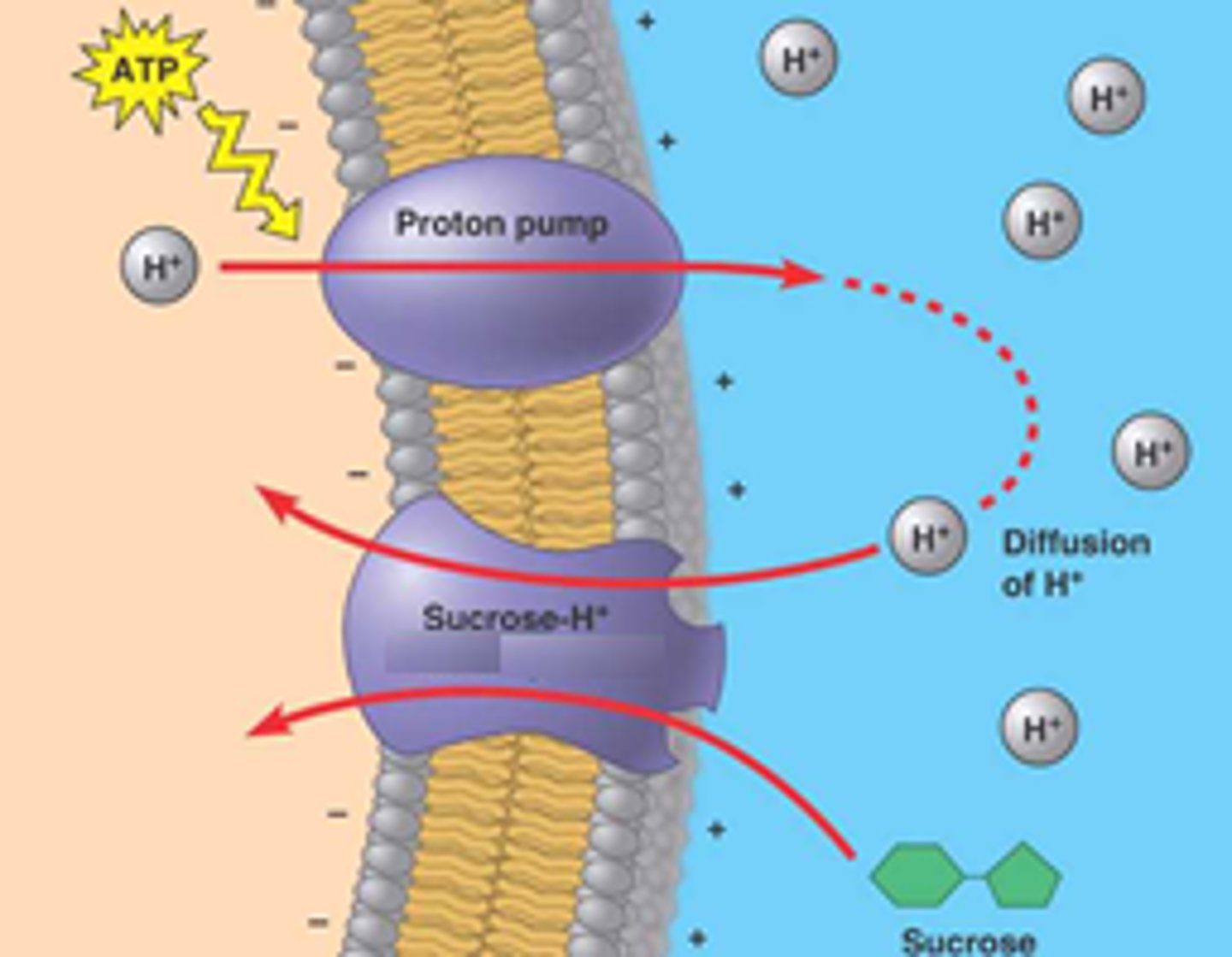
Primary Active Transport
Direct use of ATP to transport substances.
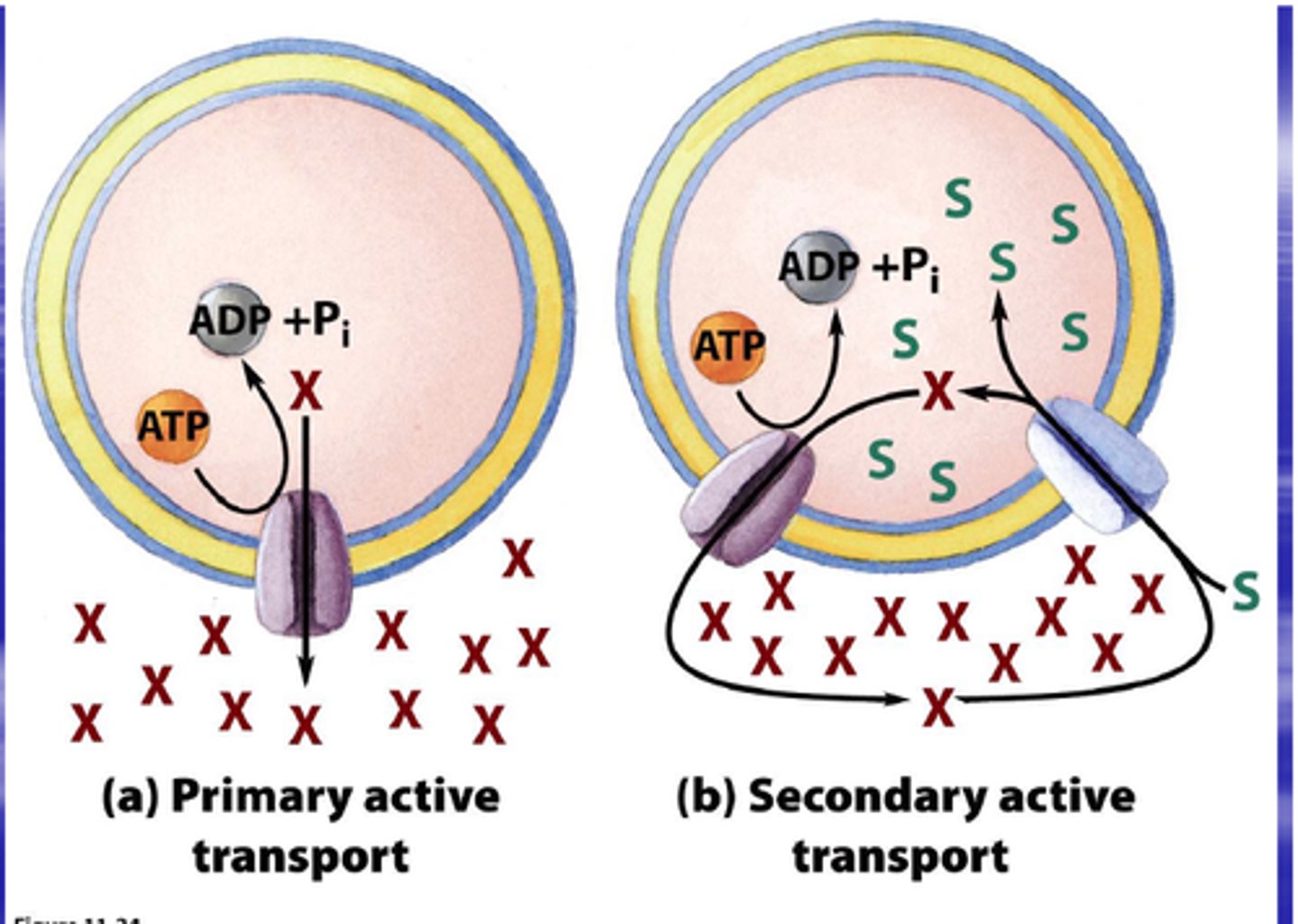
Secondary Active Transport
Uses existing gradients from primary active transport to transport other solutes.
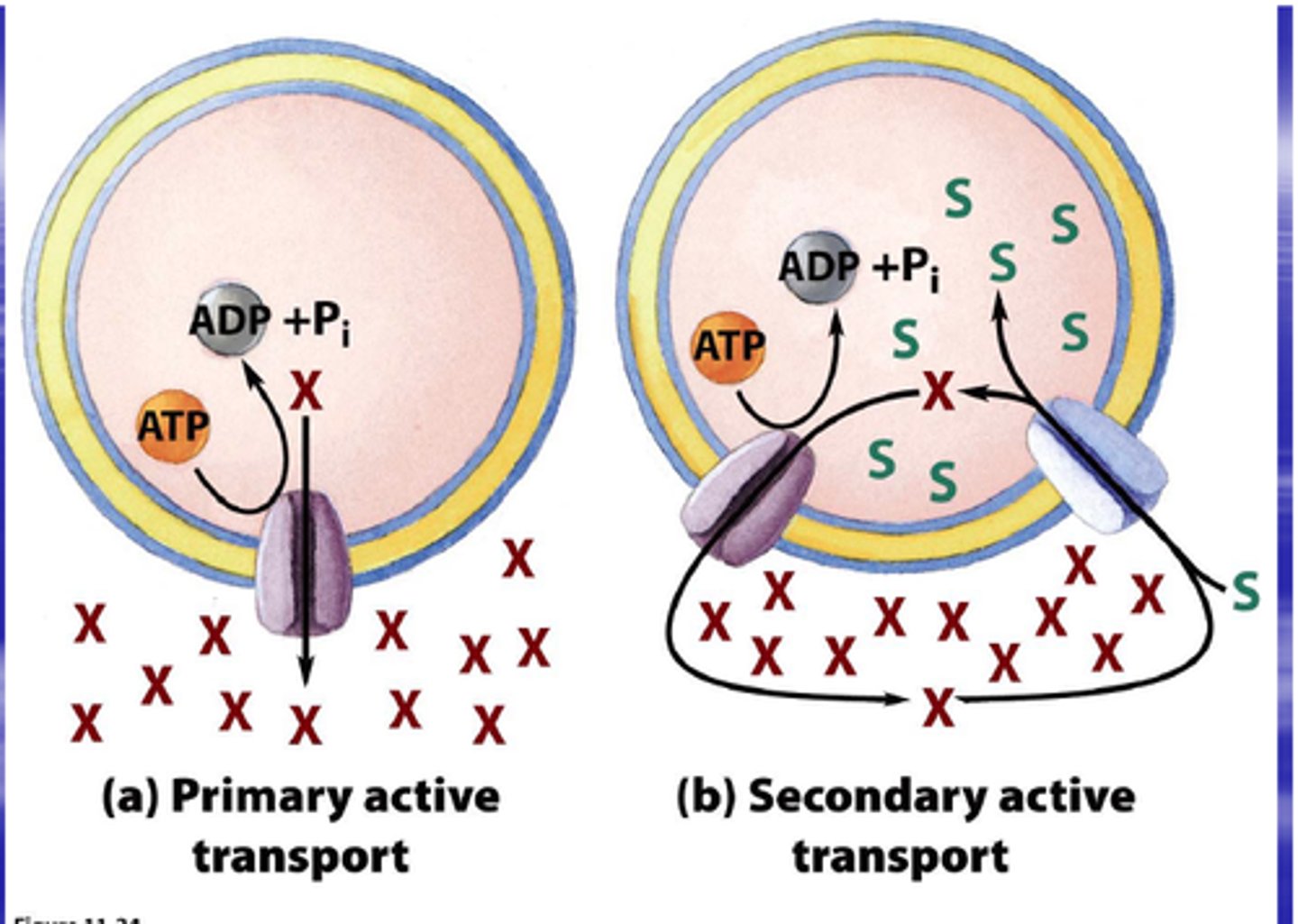
Cotransport
Simultaneous transport of two substances across membranes.