chemistry - separate chemistry 2: qualitative analysis: test for ions (9.1 - 9.9)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
9.1 why must test for any ion be unique?
test for ion should only detect that ion
couldn’t know which ion is present if more than 1 ion gave same result
9.2 flame test to identify lithium ion (Li+) in solid
red
9.2 flame test to identify sodium ion (Na+) in solid
yellow
9.2 flame test to identify potassium ion (K+) in solid
lilac
9.2 flame test to identify calcium ion (Ca2+) in solid
orange-red
9.2 flame test to identify copper ion (Cu2+) in solid
blue-green
identifying cations - adding sodium hydroxide
add few drops at a time to test solution
9.3 test to identify aluminium ion (Al3+) in solid/solution
add sodium hydroxide solution
white precipitate
to distinguish between calcium ions & aluminium ions (both produce white precipitates): add excess sodium hydroxide solution - turns colourless
9.3 test to identify calcium ion (Ca2+) in solid/solution
add sodium hydroxide solution
white precipitate
to distinguish between calcium ions & aluminium ions (both produce white precipitates): add excess sodium hydroxide solution - stays white
9.3 test to identify copper ion (Cu2+) in solid/solution
add sodium hydroxide solution
blue precipitate
9.3 test to identify iron (II) ion (Fe2+) in solid/solution
add sodium hydroxide solution
green precipitate
9.3 test to identify iron (III) ion (Fe3+) in solid/solution
add sodium hydroxide solution
brown precipitate
9.3 test to identify ammonium ion (NH4+) in solid/solution
add sodium hydroxide solution
warm mixture - ammonia gas produced
ammonia turns damp red litmus paper → blue
9.4 chemical test for ammonia
place damp red litmus paper in ammonia gas
turns blue
9.5 test to identify carbonate ion (CO32-) in solid/solution
add dilute hydrochloric acid
bubble gas produced through limewater - turns cloudy if CO2 present
positive result = lime water cloudy
9.5 test to identify sulfate ion (SO42-) in solid/solution
add dilute hydrochloric acid - removes carbonate ions that might give precipitate in test
add barium chloride solution
positive result = white precipitate forms
9.5 test to identify chloride ion (Cl-), bromide ion (Br-), iodide ion (I-) in solid/ solution
add nitric acid - removes carbonate ions that might give precipitate in test
add silver nitrate solution
chloride positive result = white precipitate forms
bromide positive result = cream precipitate forms
iodide positive result = yellow precipitate forms
9.6 core practical: identify ions in unknown salts using tests for specified cations & anions - flame tests for metal cations
light Bunsen burner & open air hole to give hot blue flame
pick up small sample of solid salt using clean wire loop/damp wooden splint
hold sample in edge over flame
observe & record colour
9.6 core practical: identify ions in unknown salts using tests for specified cations & anions - hydroxide precipitate tests for metal cations
dissolve a little salt in test tube using distilled water
add few drops dilute sodium hydroxide solution one drop at a time
record colour of any precipitate formed
if white precipitate forms, add excess dilute sodium hydroxide solution to see if it will disappear to leave clear solution
9.6 core practical: identify ions in unknown salts using tests for specified cations & anions - testing for ammonium ions
dissolve a little solid salt in test tube using distilled water
add dilute sodium hydroxide solution
warm gently
remove from flame, hold damp red litmus paper near mouth of test tube
record what happens to its colour
9.6 core practical: identify ions in unknown salts using tests for specified cations & anions - testing for carbonate ions
put a little salt in test tube & add few drops of dilute acid
record whether any effervescence occurs
use limewater to check if bubbles contain carbon dioxide
9.6 core practical: identify ions in unknown salts using tests for specified cations & anions - testing for sulfate ions
dissolve a little solid salt in test tube using distilled water
add a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid
add a few drops of barium chloride solution
record whether white precipitate forms
9.6 core practical: identify ions in unknown salts using tests for specified cations & anions - testing for halide ions
dissolve a little solid salt in test tube using distilled water
add a few drops of dilute nitric acid
add a few drops of silver nitrate solution
record colour of any precipitate formed
9.8 other methods of analysis
instrumental methods of analysis (machines) available
9.8 what do instrumental methods of analysis improve?
sensitivity - detect much smaller amounts
accuracy - give values closer to true values
speed of tests
what does a flame photometer do?
measures light intensity of flame colours metal ions produce
determines conc. of metal ion in dilute solution
9.9 evaluate data from flame photometer - determine conc. of ions in dilute solution using calibration curve
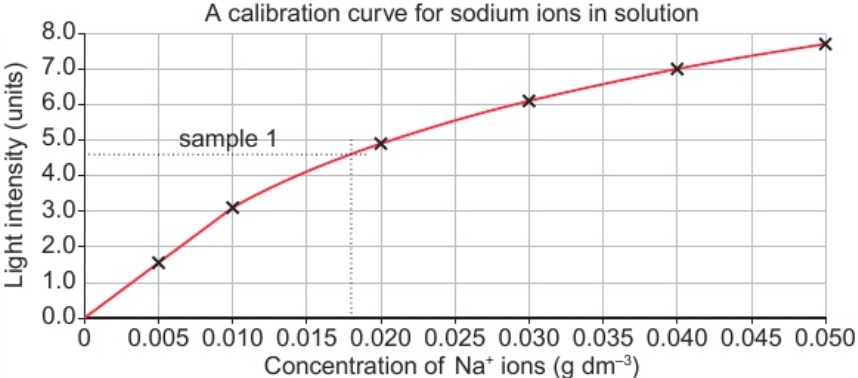
9.9 evaluate data from flame photometer - identify metal ions by comparing data with reference data
colour of light we see in flame test usually mixture of diff. colours
flame photometer separates out these colours - produces spectrum of light emitted by each metal ion
diff. metal ions produce diff. emission spectra
identify metal ion in unknown solution - match its spectrum to spectrum from known metal ion