Chemistry 1 exam lecture 1-7
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
noble gases increase boiling pressure why?
higher boiling point is a result of stronger IMF. noble gases only have dispersion forces.
why low vapor pressure in IMF
is due to weak intermolecular forces. This leads to fewer molecules escaping into the gas phase.
Capillary action
a physical effect caused by the interactions of a liquid with the walls of a thin tube. The capillary effect is a function of the ability of the liquid to wet a particular material.
Viscosity
is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow, influenced by intermolecular forces and temperature. Higher viscosity indicates thicker fluids that flow more slowly.
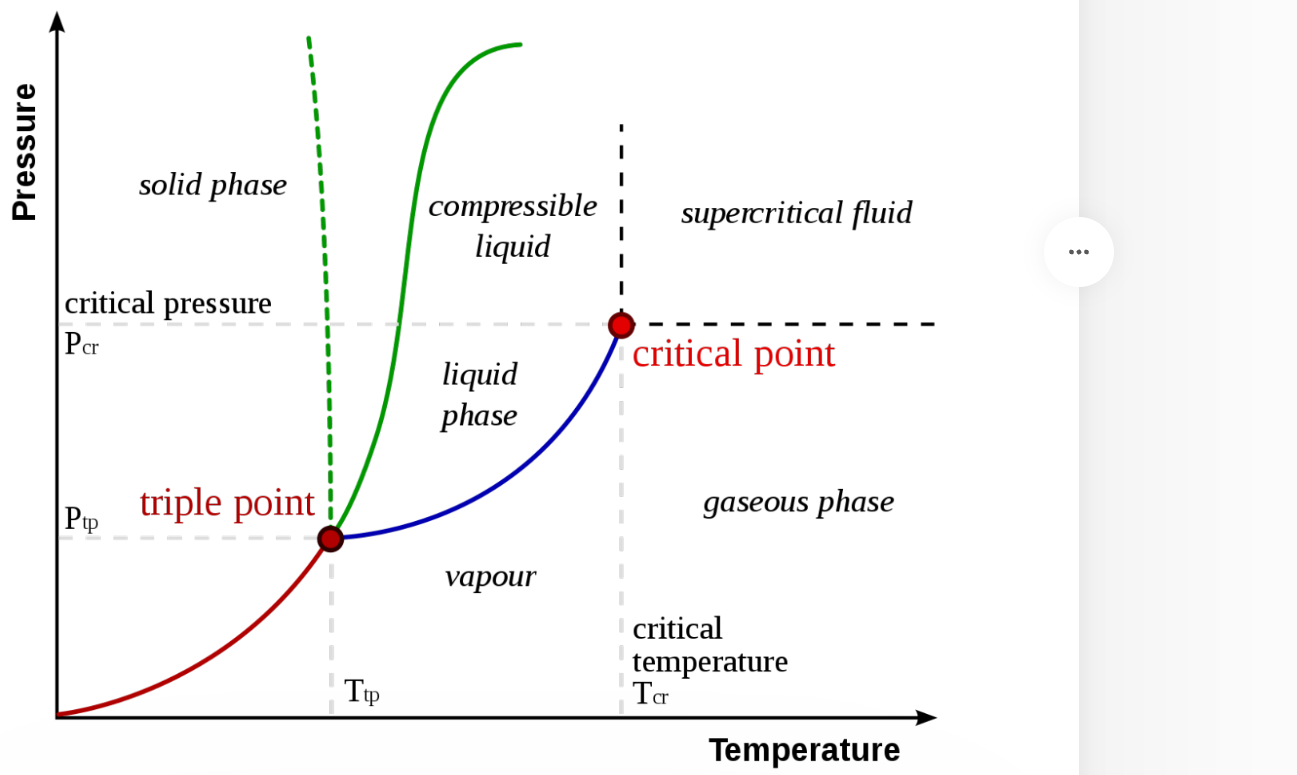
what is phase diagram
the diagrams shows at what temperatures and pressures a substance will be a solid, liquid or gas.
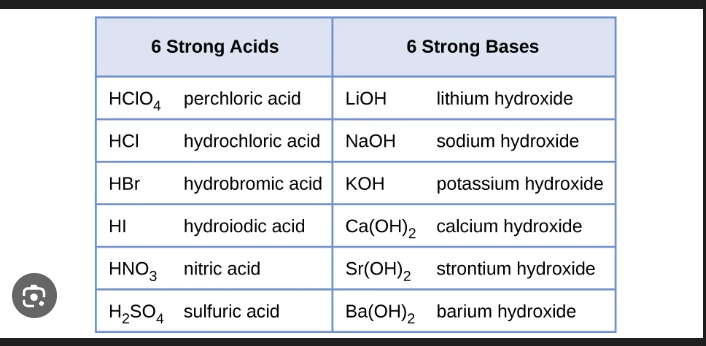
what are strong electrolytes
a solute that completely dissociates or ionizes into ions when dissolved in water or in a molten state
Ion-dipole
Interaction of an ion (cation or anion) with a polar molecule
Dissolving any ionic compound in water
Dipole-dipole
Interaction of polar molecules with other polar molecules
Examples: Acetone with acetone, triethyl amine in acetone
Hydrogen bonding
Special case of dipole-dipole when there is a H bonded to a N, O, or F.
Examples: Water, acetic acid, acetone in water
Dipole-induced dipole
A polar molecule interacting with a nonpolar one(which induces a dipole)
Examples: Carbon dioxide in water (note: this may not be a good example because we could envision hydrogen bonding occurring), carbon dioxide in ethylene
Surface tension
tries to minimize the surface area, resulting in liquids forming spherical droplets and allowing insects to walk on the surface without sinking.

1.91 atm
gas to diamond
Lowering temp and raising pressure
Vaporization
the process of converting a liquid into a gas
breaking IMF
The stronger the intermolecular forces that are holding a liquid together, the more energy that will be required to pull them apart. What this means in practical terms is that a liquid with strong intermolecular forces will have to be heated to a higher temperature before it will evaporate.
water havp
ΔHvap of 40.7 kJ/mol and methane has a ΔHvap of 8.2 kJ/mol. Methane is actually a gas at room temperature because of its low heat of vaporization.
Condensation
the process by which a gas changes phases into a liquid.
Vapor pressure i
a measurable quantity that exists when a liquid and its vapor are in equilibrium. vapor pressure is also dependent on the temperature of the system
formula for vp

The clausius-clapeyron equation

A Super Critical Fluid and critical point
A Super Critical Fluid (SCF) is defined as a substance above its critical temperature (TC) and critical pressure (PC). The critical point represents the highest temperature and pressure at which the substance can exist as a vapor and liquid in equilibrium.



solid held
held together by ionic or strong covalent bonding, and the attractive forces between the atoms, ions, or molecules in solids are very strong.
Ionic Solids
Are made up of positive and negative ions and held together by electrostatic attractions. They’re characterized by very high melting points, brittleness, and are poor conductors in the solid state. An example of an ionic solid is table salt, NaCl.
Molecular Solids
Are made up of atoms or molecules held together by London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, or hydrogen bonds. Characterized by low melting points, flexibility, and are poor conductors. An example of a molecular solid is sucrose.
Covalent-network (also called atomic) Solids
Are made up of atoms connected by covalent bonds; the intermolecular forces are covalent bonds as well.
Metallic solids
Are made up of metal atoms that are held together by metallic bonds. Characterized by high melting points, can range from soft and malleable to very hard, and are good conductors of electricity.
cube numbers in atom
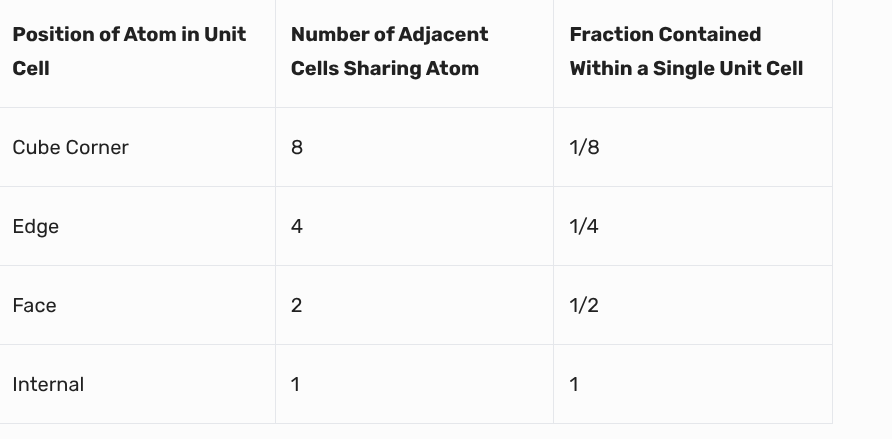



desnsity unit cell
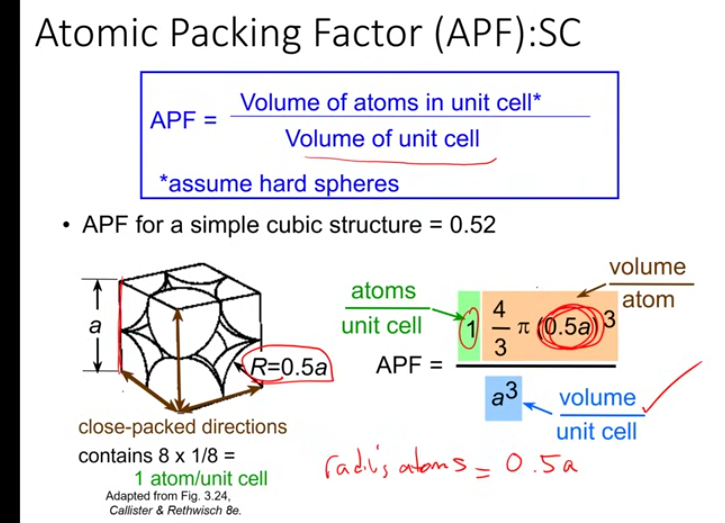
atomic packing




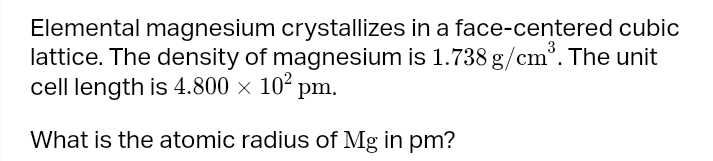
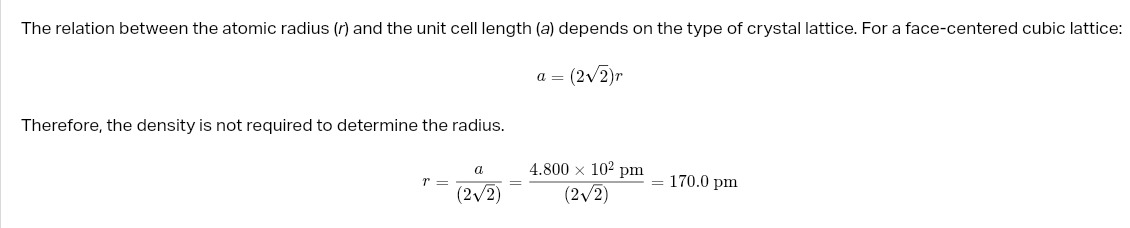
solvent
it is the molecule in the mixture with the highest concentration
solute
is the compound in a mixture with a lower concentration.
solution process
When we place solutes and solvents together,

saturation

supersaturation

heat solution formula
Δ Hsoln = Δ H1 + ΔH2 + ΔH3.
ΔHhydration exo or endo
exo
h solution formula
Δ HSolution = -ΔHLattice + ΔHHydration
how does decrease solubility act in gases
Solubility decreases as temperature increases. The physical reason for this is that when most gases dissolve in solution, the process is exothermic. This means that heat is released as the gas dissolves
temp increasing effect on gas solubility
As the temperature increases, the solubility of a gas decreases as shown by the downward trend in the graph.
Decrease in solubility with temperature:
If the heat given off in the dissolving process is greater than the heat required to break apart the solid, the net dissolving reaction is exothermic
increase in solubility with temperature:
If the heat given off in the dissolving reaction is less than the heat required to break apart the solid, the net dissolving reaction is endothermic.
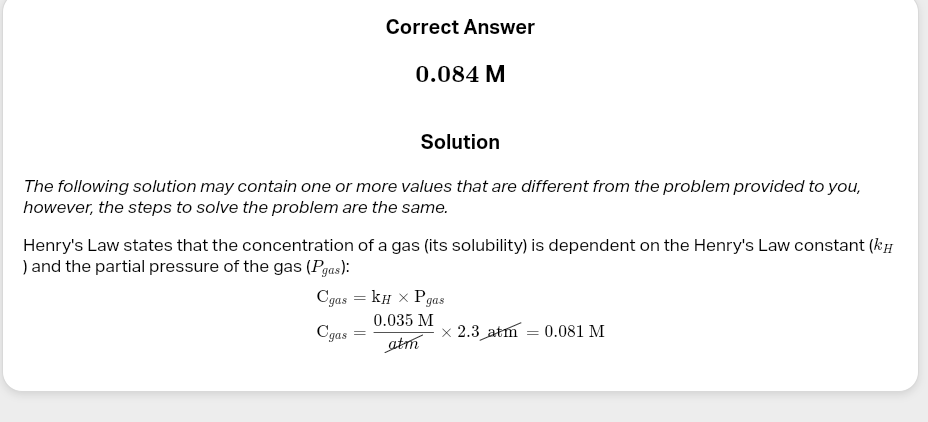
Henry's Law:
Sg=kH×Pg




henry’s law meaning
