Ecosystems and material cycles
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What is an ecosystem?
All the living organisms and the environment in which they live
What is a community?
All the organisms that live and interact in an area
What does interdependence mean?
All animals and plants in an ecosystem interact and depend on each other for food, shelter and so on
\-Pitfall trap
\-Quadrats
\-Belt transect
How do you use a belt transect?
The method involves laying out a transect line and then placing quadrats over the line at regular intervals, starting the quadrat at the first marked point of the line.
Any consistent measurement size for the quadrat and length of the line can be chosen, depending on the species.
Changes in factors such as temperature and light intensity are also recorded making it easier to link a change in distribution with a physical change
What are parasites?
An organism that lives in or on an organism of another species (its host) and benefits by deriving nutrients at the other's expense.
What is mutualism?
A type of symbiotic relationship where all species involved benefit from their interactions
What are the stages of the water cycle?
Transpiration/Evaporation: Water evaporates from the sea, land and plants and becomes water vapour
Condensation: As air rises it cools and condenses forming clouds
Precipitation: Water droplets become heavy and start to fall as rain or snow and the water is returned to Earth
Some of the water evaporates again and some runs off the surface into the sea or rivers
Some water filters down into the ground to underground natural reservoirs
Infiltration: Ground water from natural reservoirs finds its way to rivers through soil and rock
Rivers flow into lakes and will return to the ocean
Steps of the carbon cycle
Plants use sunlight and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere for photosynthesis
Photosynthesis produces oxygen and an organic carbon source. The carbon source is eaten by animals.
Plants and animals use glucose and oxygen to carry out cellular respiration they release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere
Animals and plants that die that are not broken down by decomposers such as bacteria and fungi form fossil fuels.
Factory emissions burn fossil fuels and release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere
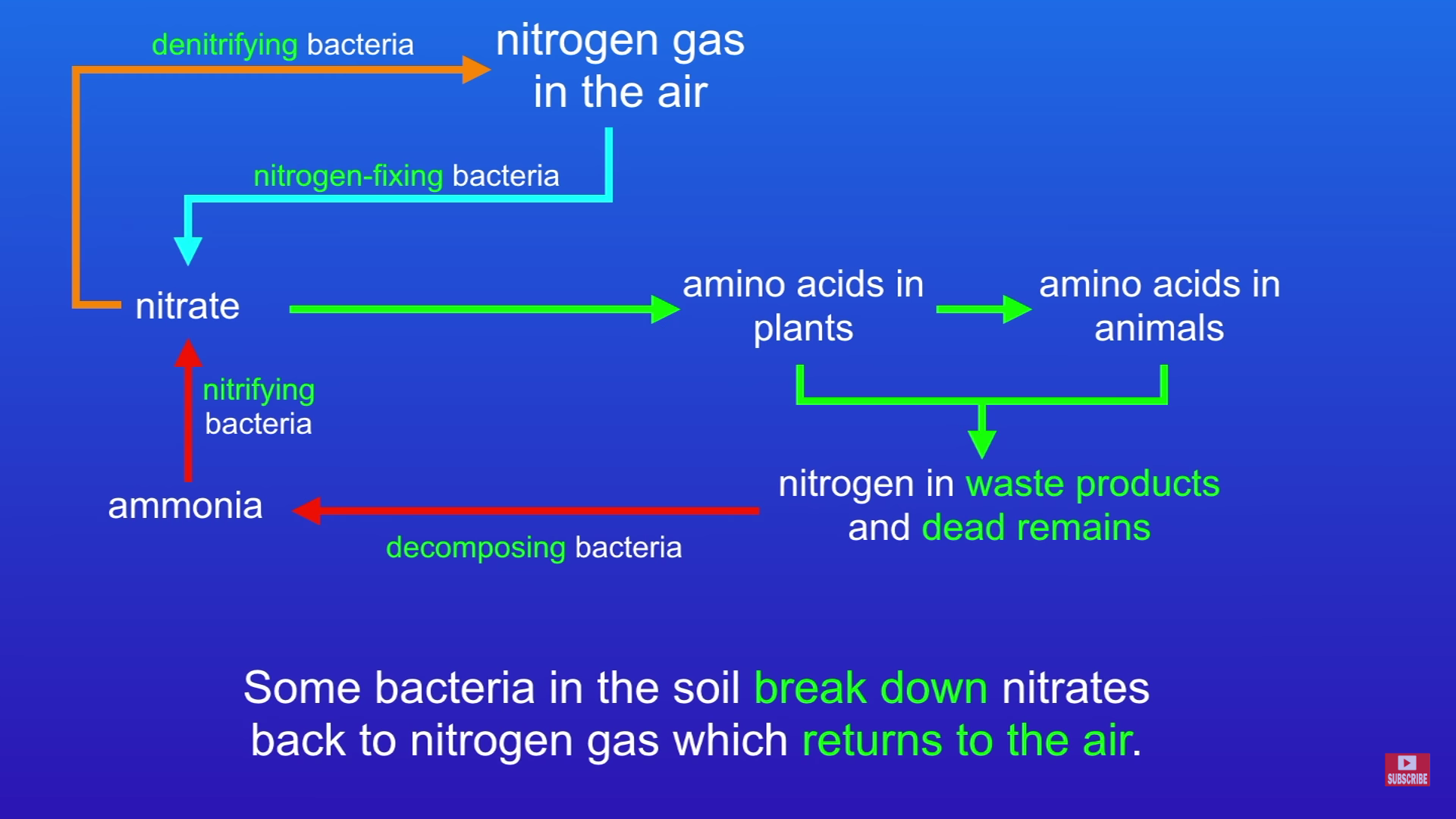
What happens in the Nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen in the air is converted to nitrates in the soil by nitrogen fixing bacteria
The nitrates are absorbed by plants and made into amino acids
Animals eat some of these plants and the amino acids are passed into animals
When plants and animals die (or through animal excrement) there is nitrogen in their remains
Decomposing bacteria turn this into ammonia
Nitrifying bacteria then converts the ammonia to nitrates to be absorbed into plants again
Denitrifying bacteria breaks down some of the nitrates into nitrogen which goes back into the air
Advantages of fertilisers?
They are quick in providing plant nutrients and restoring soil fertility.
They are portable and easy to transport.
Plants easily absorb fertilizers.
Fertilizers improve and increase the productivity of many crops such as wheat, maize, and rice
Increases crop yield
* They harm the microbes present in soil.
* They reduce soil fertility.
* They are expensive.
* They provide only short term benefits.
* They change the nature of soil, making it either too acidic or too alkaline.
What is algal bloom in eutrophication?
Fertiliser from fields is washed away by rain into a body of water
Algal bloom is when the algae absorb all the nutrients from the fertiliser and grow and rapidly
Why is algal bloom a problem in eutrophication?
Because the algal bloom will absorb all the sunlight from the surface and the plants underneath will not get enough sunlight to do photosynthesis and will die. The algae will also die when all the nutrients are used up and they have no food.
After algal bloom, what begins to break down the dead plants and algae?
Bacteria
What does breakdown of plants and algae cause in eutrophication?
More nutrients being released which leads to the algal bloom cycle continuing
Why does the water become anoxic in eutrophication?
Because the bacteria are growing and respiring which uses oxygen.
What happens if the water become anoxic in eutrophication?
all non-bacterial life in the water, including fish and other animals, will die.
What is an organism?
A single living individual
What is distribution affected by?
Factors in the environment
What are some living environmemtal factors that affect distribution?
Prey
Competitor
Predator
What are some non-living environmental factors that affect distribution?
Light
Average temperature
Average rainfall
Oxygen levels in water
Pollution
What is a pollutant?
Energy or a chemical that has an effect on living organisms
What are oxygen levels like in polluted water?
In polluted water they are low whereas in unpolluted water they are high
What are some ways organisms protect themselves from predators?
Some display they are poisonous with very bright colours
Some animals use colours to make them look more frightening
Some plants have large thorns
Other plants are poisonous
How does competition arise in an ecosytem?
Organisms need a supply of materials from their surroundings and sometimes other organisms so they can survive and reproduce
This causes competition for materials in short supply
What do plants compete for?
Light
Space
Water
Nutrients
What do animals compete for?
Food
Mates for reproduction
Territory
How do parasites use their hosts?
Some like fleas and had lice suck the blood from animals
Some like tapeworms live in the animals small intestine where the absorb nutrient from the digested food in the intestine
Some like mistletoe grow roots into tress to absorb water and nutrients
What are some ways mutualism benefits both organisms?
One animal will feed off the dead skin and parasites from another organism
This means that the first organism will get food and the second benefit from the loss of dead skin and parasites
Nitrogen fixing bacteria in root nodules are protected from the environment and get food from the plant they are on and the legume plant will get nitrogen compounds for healthy growth from the bacteria
How do we use quadrats?
Coordinates are made for an areas in the field
A system can be used to produce a random coordinate in this area for the quadrat to be placed in
The number of organisms is counted in each area
How are the number of organisms in an area estimated with quadrats?
Mean number of organisms in one quadrat x total area/area of quadrat
Why do we use samples to estimate population or distribution?
The areas we want to analyse are too large to count every individual organism
What do we use to study the affect of biotic or abiotic factors on organisms?
Belt transect
Where is energy stored in an organism?
In it’s biomass
What are trophic levels?
The feeding levels in a food chain or food web
What happens to energy as it is stored as biomass in the next trophic level?
Not all energy from one trophic level is stored as biomass in the next
Some of the energy is transferred to the environment
Energy lost as heat is not as useful as it cannot be converted to biomass again
How do energy transfers happen in plants?
Energy transferred by light during photosynthesis
Energy stored in new plant biomass which can be transferred to herbivores in their food
Energy from respiration transferred to the surroundongs
How do energy transfers happen in animals?
Energy stored in biomass from food
Energy stored as new animal biomass which can be transferred to carnivores in their food
Energy is stored in substances like faeces and urine
Energy from respiration transfers energy to surroundings as heat
What are pyramids of biomass?
A diagram that shows he amount of biomass at each trophic level
The producer is the bottom bar and the other show the trophic levels in order
The amount of biomass at each trophic level gets smaller as some energy is transferred to heating the environment
These are usually only 4 or 5 levels because the biomass at the top is not enough to provide the energy needed for another level
What is biomass?
The mass of an organisms body tissue
What is fish farming?
Growing one kind of fish in an area
The fish are fed and the waste they produce are removed from their tanks
What are the advantages and disadvantages of fish farming?
Waste can pollute the local area, changing conditions which could cause some species to die out
Diseases from the farmed fish can spread to wild fish and kill them
Farming fish reduces the fishing of wild fish
What are the positives and negatives of introducing a non-indigenous species into an area?
They may reproduce rapidly as they have no natural predators
They may out-compete native species for food and other resources
They may provide food for native species
What reasons do humans have for maintaining biodiversity?
Morality: Humans should respect other living organisms
Aesthetic: People enjoy seeing the variety in an ecosystem
Ecosystem structure: Some organisms have important roles to play and if the planet loses species, the food chain becomes more unstable
Usefulness: Some organisms such as plants that produce life saving drugs are very important to humans
What is reforestation?
Replanting forests where they have been destroyed
What are the advantages of reforestation?
Restores habitat for species that are endangered
Reduces concentration of carbon dioxide in the air through photosynthesis
Tree roots bind the soil together and reduce the effects of soil erosion
Affects local climate, for example reducing the range of temperature variation
What is food security?
Having a reliable and adequate food supply
Increasing human population need greater food security
As people become more well off, there is a higher demand for meat and fish
What are the effects of increased food demand?
Increasing human population means more food is needed
Increased demand of meat and fish means more land is used for farming and a has greater impact on wild fish population either due to wild fishing or fish farming
Movement of people and goods introduces pests into an area, damaging local crops and animals
Increased waste is produced, leading to pollution
How does human activity affect availability of land and food?
Environmental impacts caused by humans such as global warming reduces availability for land to farm on due to rising sea levels, which the leads to less food being produced
Why is the carbon cycle important?
Carbon dioxide is limited and must be recycled
It recycles carbon dioxide released in respiration to plants in photosynthesis, to make organic molecules in living animals
Why do plants need nitrates?
To grow well
Nitrogen is needed to make proteins for healthy growth
What is crop rotation?
Growing different crops each year, on a rotation basis
How does crop rotation improve soil fertility?
Different crops remove different nutrients from the soil
Plants such as clover have nitrogen fixing bacteria in their roots, and can be ploughed back into the soil, to add nitrates
What are indicator species useful for?
Assessing levels of pollution
Why is assessing levels of pollution important?
Some species are well adapted to living in polluted conditions
Other species can only live if there is no pollution
Changes in the abundance of these species can show changes in the level of pollution
How do some species of lichen work as an indicator of air pollution?
Some species of lichen can only grow where there is no pollution
Other species can grow where there is air pollution
The species of lichen growing on trees can tell you if the air has been polluted
How does blackspot work as an indicator of air pollution?
Blackspot is a fungus that infects roses
The fungus is damaged by sulfur dioxide in the air
Where there is air pollution, the roses are clear of the fungus
How do bloodworms and sludgeworms work as indicators of water pollution?
They can live in water that contains very little oxygen so they are found in polluted water
How do stonefly larvae, mayflies and some caddisflies work as indicators of air pollution?
They can only live in water that contains a lot oxygen
This means they are indicators of unpolluted water
What is decay?
The break down (digestion) of materials by microorganisms
What is the rate of decomposition affected by and why?
Warm temperatures because this increases enzyme activity in microorganisms
Water content because microorganisms need water for many cell processes to work
Oxygen availability because microorganisms need oxygen for respiration
How can we prevent the decay of food?
Refrigeration cools food down and the temperature is too cold for most microorganisms to grow quickly
Salting food causes water to move out of bacterial cells by osmosis, so there is not enough water in the microorganism’s cells to grow
Packing food in nitrogen means there is no oxygen for microorganisms to respire
How do we recycle kitchen and garden waste?
Kitchen and garden waste can be used to make compost
Conditions in compost should encourage the growth of decay microorganisms, which grow and digest faster in conditions that are: moist, warm and aerobic (oxygen present)
How do we calculate the rate of decay?
Rate of decay = (Loss in mass in grams)/time in days
What does potable water mean?
Drinkable water
What is desalination?
Producing drinking water from salty water
This can be done by distillation
Why is desalination important?
Some countries where it is very hot and dry suffer from drought
They do not get enough drinking water from precipitation as their source of potable water