Lecture 22 - Cell communication and cell signaling II
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Many G protein activate membrane-bound _____ that produce small messenger molecules
enzyme
What are the secondary messengers of GPCR pathways
cAMP
IP3/Calcium
What does cAMP stand for
cyclic adenosine monophosphate
What was the “original messenger” that was discovered
cAMP
What promotes the formation of cAMP
adenylyl cyclase (followed by the binding of ligands)
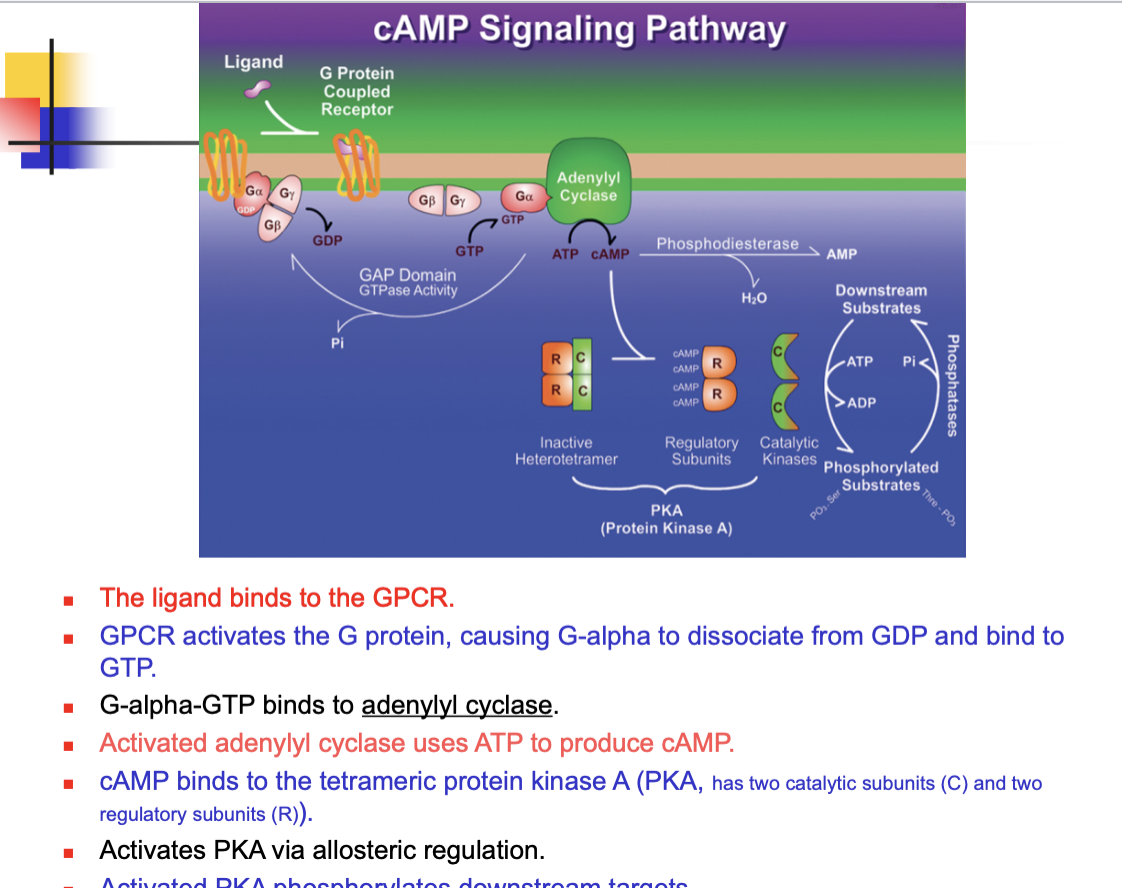
can you list all 7 steps of the GCPR signaling pathway?
(yes)
The cAMP pathway is considered a … response
fight or flight
cAMP is inactivated through …
hydrolysis to AMP
What enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of cAMP to AMP
PDE/ phosphodiesterase
What is the effect of caffeine in cAMP pathway
inhibits PDE
cAMP levels remain higher
sustained activation of PKA
What is the activation of PKA do
increases glucose availability for increasing metabolism
enhances neurotransmitter release
Cytosolic concentration of Ca is very __
low
The cytosolic Ca concentration is about _____ time lower than in the extracellular space
10,000
The ___ stores intracellular Calcium
ER
GPCR pathways can also generate _____ _____ that carries a signal to adjacent cells
dissolved gas
Most hydrophilic secondary messengers such as cAMP, IP3, and calcium cannot …
pass through the membrane and function only within the cell that produces them
Purpose of gas messengers
can pass through the membrane and carry signal to nearby cells
What is the downstream effect of the binding of acetylcholine
ACh binds to GPCRs —> production of IP3 and calcium
Ca activates ____ ____ synthesis from arginine
nitric oxide (NO)
When NO diffuses into smooth muscle cells in the adjacent vessel wall, the blood vessels _____
dialate
2 components of enzyme-coupled receptors
transmembrane proteins with ligand-binding domains (on cytosolic surface)
Enzyme coupled receptors act as ____ _____ at ___ ______
local mediators; low concentration
Dimerization
binding of an extracellular signal causes two receptor molecules to dimerize
What is the largest class of enzyme-coupled receptors
receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)
What do RTKs respond to (4)
mitogens
EGFRs
INSRs
VEGF
Each phosphorylated tyrosine acts as a _____ ____ for specific signaling proteins → relaying the signal to the cell interior
docking site
Most RTKs activate the protein
Ras
What is Ras
monomeric GTPase
What is a mitogen
signals that stimulate mitosis
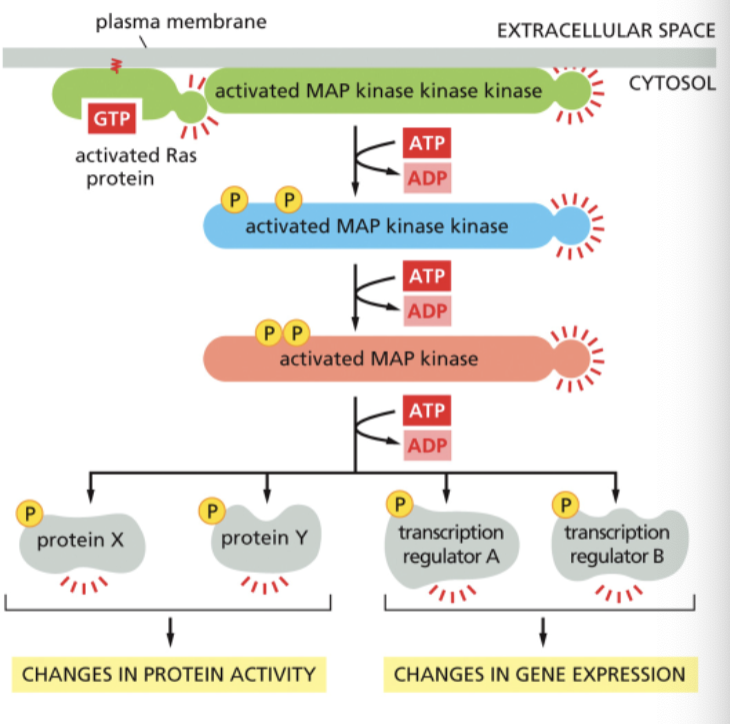
Activated Gas activates ____
MAP3K (MAP kinase kinase kinase)
__ of human cancers contain Ras mutation
30
(T or F) Ras is considered a proto-oncogene
true
Example of Ras pathway
EGF pathway
Monoclonal antibody-based drugs that block EGFR will ___ effective in colon cancer patients with Ras mutation
not be
Some small, hydrophobic ____ _____ bind to intracellular receptors that act as transcription regulators
steroid hormones
Example of steroid hormones (3)
cortisol, estradiol, and testosterone
intracellular receptors can also be found on the _____
nucleus
Which 2 intracellular pathways crosstalk with eachother
GCPRs and RTKs
Which molecules are used to crosstalk between the GCPR and RTK (3)
IP3, phospholipase C, and calcium
Crosstalk between intracellular pathways is mediated by ____ _____
protein kinase
Why are there so many signal transduction pathway?
Allows cell to respond to a wide variety of extracellular signals
the amplification process can increase a signal by ___ to ___fold
10^6 to 10^9
What are there so many steps in each signal transduction pathway
multiple points for crosstalk (integrate)
signal diversification (distribution)
feedback regulation (modulate)