h
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Syn addition
Two groups added to the same face of alkene
Anti addition
Two groups added to opposite faces of alkene
HBr addition
syn and anti (random)
acid-catalyzed hydration
syn and anti (random)
Bromination/bromohydrin formation
anti addition
oxymercuration reduction
anti addition (only for first step)
Pd-catalyzed hydrogenation
syn addition
hydroboration/oxidation
syn addition
methylene chloride
CH2Cl2
butyl bromide
CH3CH2CH2CH2—Br
isopropyl iodide
(CH3)2CH—I
allyl chloride
H2C=CH—CH2—Cl
benzyl group
Ph—CH2—
HCCl3
Chloroform
HCBr3
Bromoform
HCI3
Iodoform
alpha-carbon
Carbon bonded to the halogen or oxygen
methoxy and methylthio
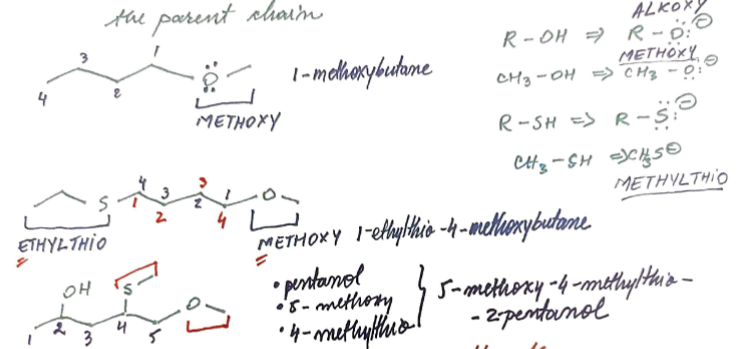
Furan
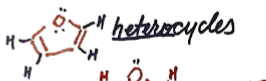
Tetrahydrofuran
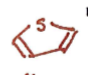
Thiophene
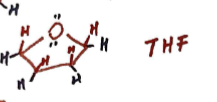
Dioxane
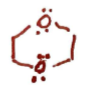
Oxirane
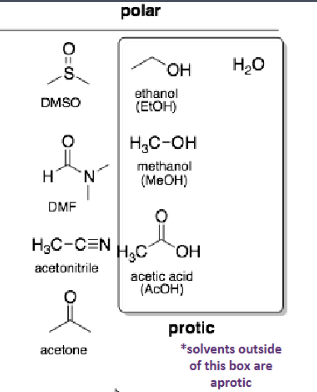
non-polar solvents
alkanes, benzene, diethyl ether, toluene
moderately polar solvents
THF, ethyl acetate, chloroform, methylene chloride
polar solvents
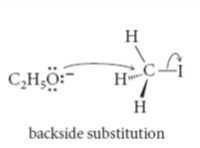
Sn2 mechanism
leaving group: I>Br>Cl
E2 mechanism
must be anti
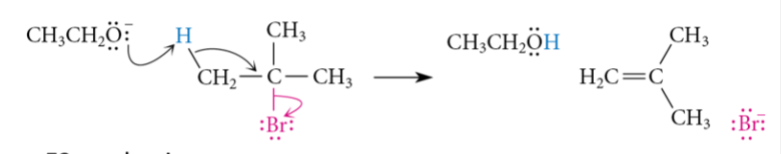
Strong Nucleophile and Strong Base
Sn2 and E2: NaOH, NaOMe, NaOEt
Strong Nucleophile but weak base
Sn2: NaN3, NaCN, NaSPh, NaI, NaBr
Weak nucleophile but strong base
E2: NaOtBu (RMgBr and RLi)
Weak nucleophile and weak base
Sn1 and E1: NaF, NaCl, ROH, H2O, CH3COONa
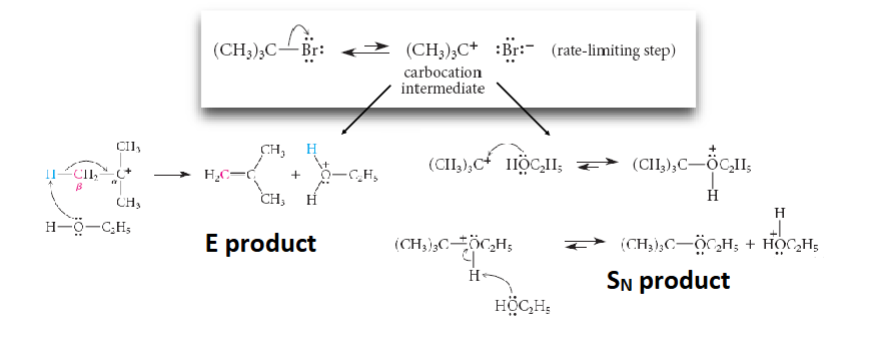
Sn1 and E1 mechanism
most rapid with tertiary, slower with secondary, never with primary, C+ chift to more stable position
Carbene mechanism
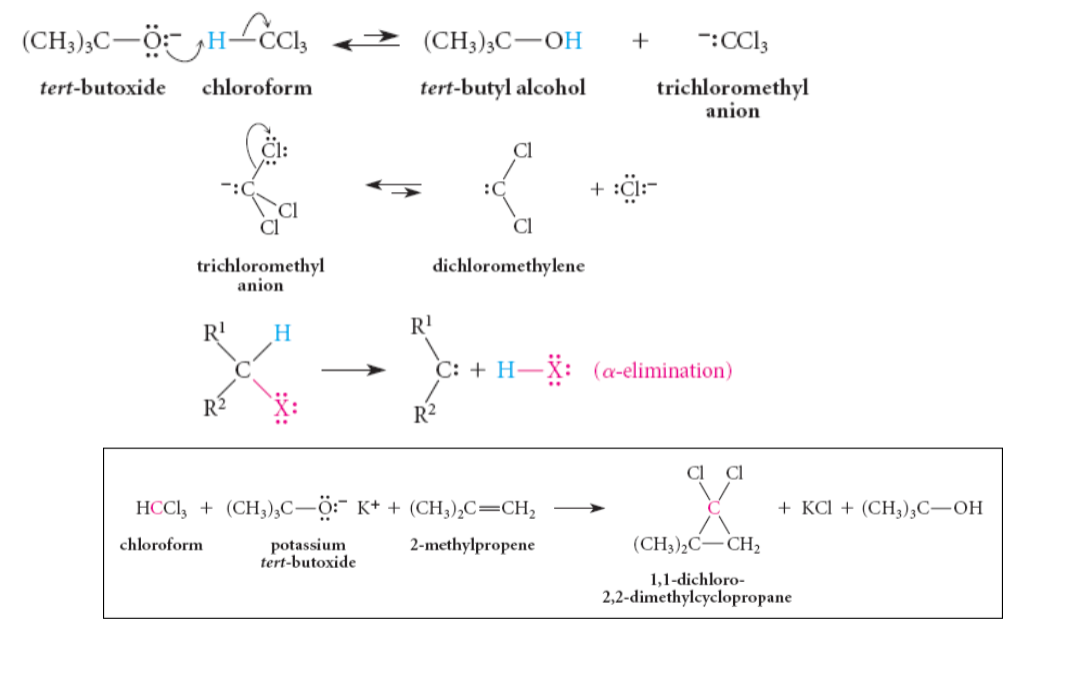
Simmons smith Rx
CH2I2 with Zn-Cu couple