Photosynthesis
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
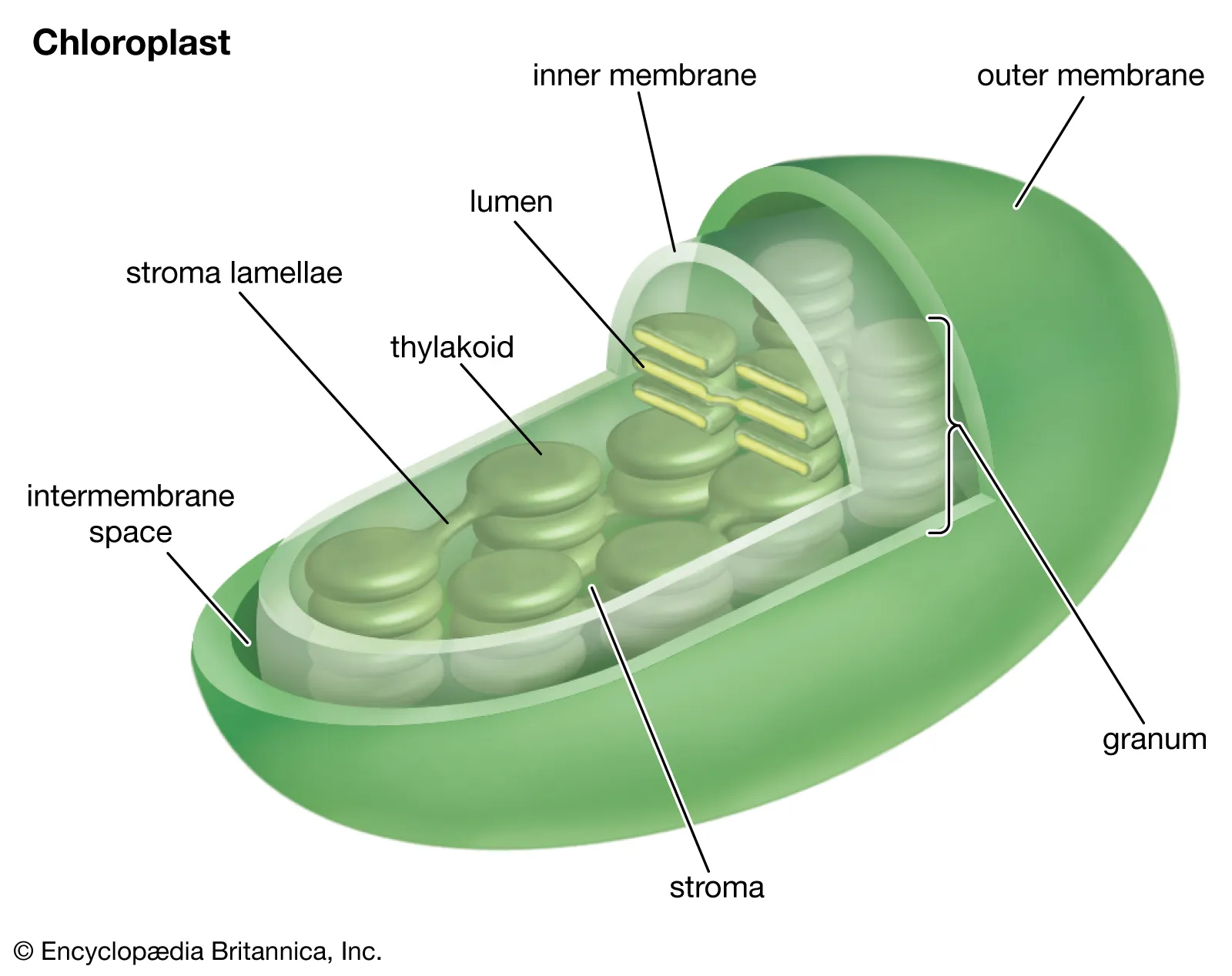
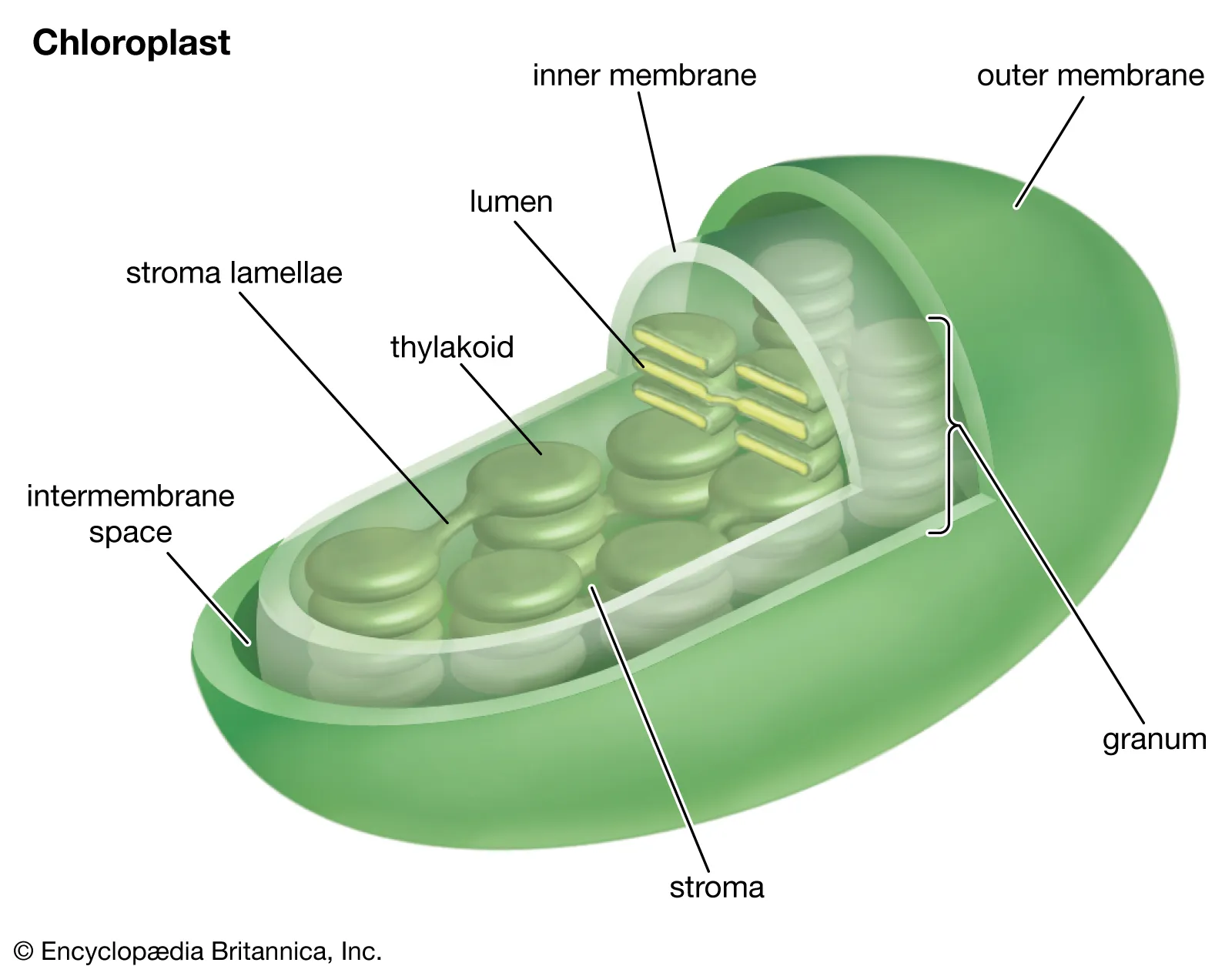
stroma
central liquid space within chloroplast, contains enzymes to reduce CO2 to carbohydrates
chlorophyll
pigment in green plants: absorbs light in photosynthesis to reflect green
chloroplasts
organelles carrying out photosynthesis, located in the middle of a plant’s leaves
thylakoid
membrane-bound structures within chloroplasts where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur; contain chlorophyll
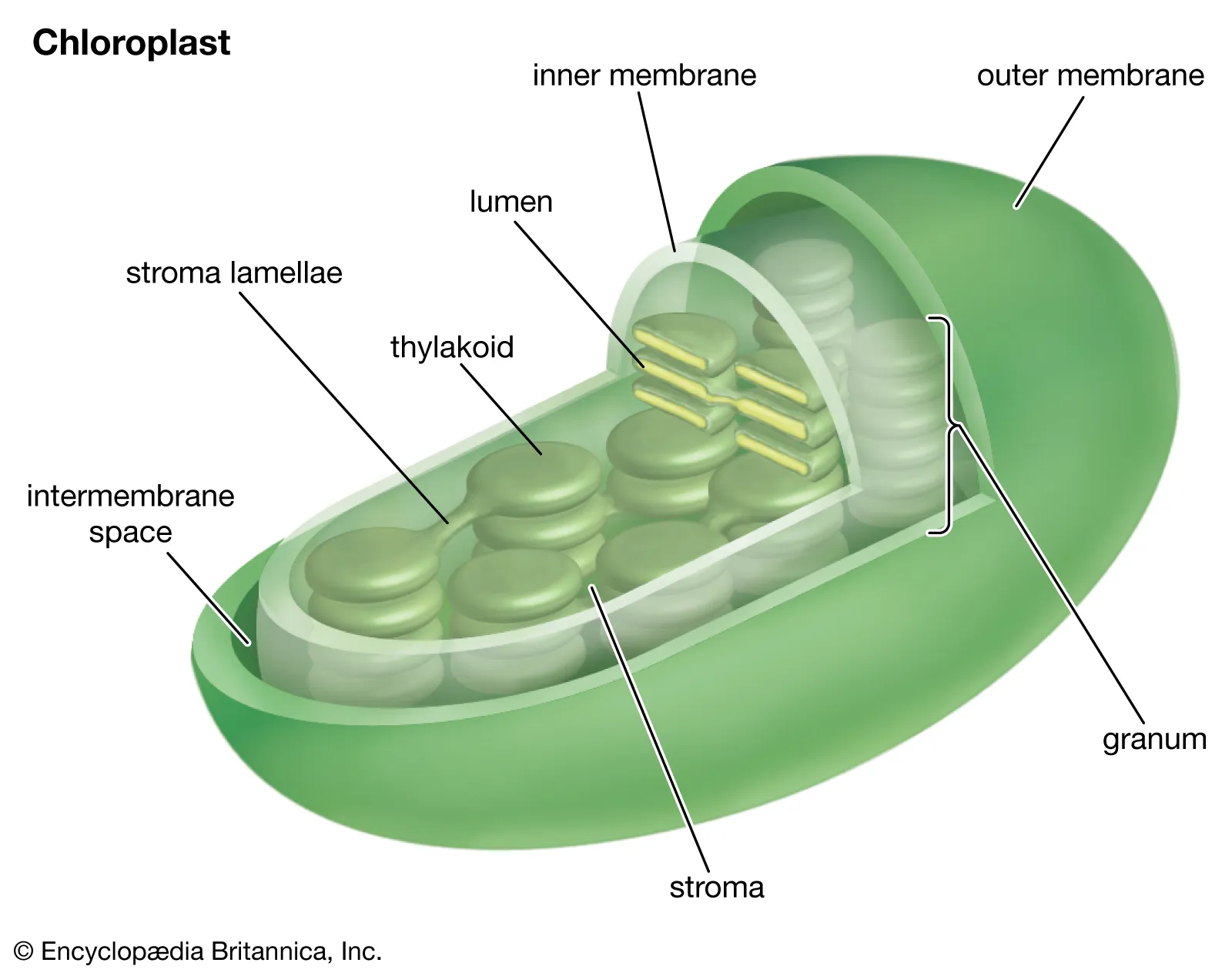
grana
stacks of thylakoid membranes
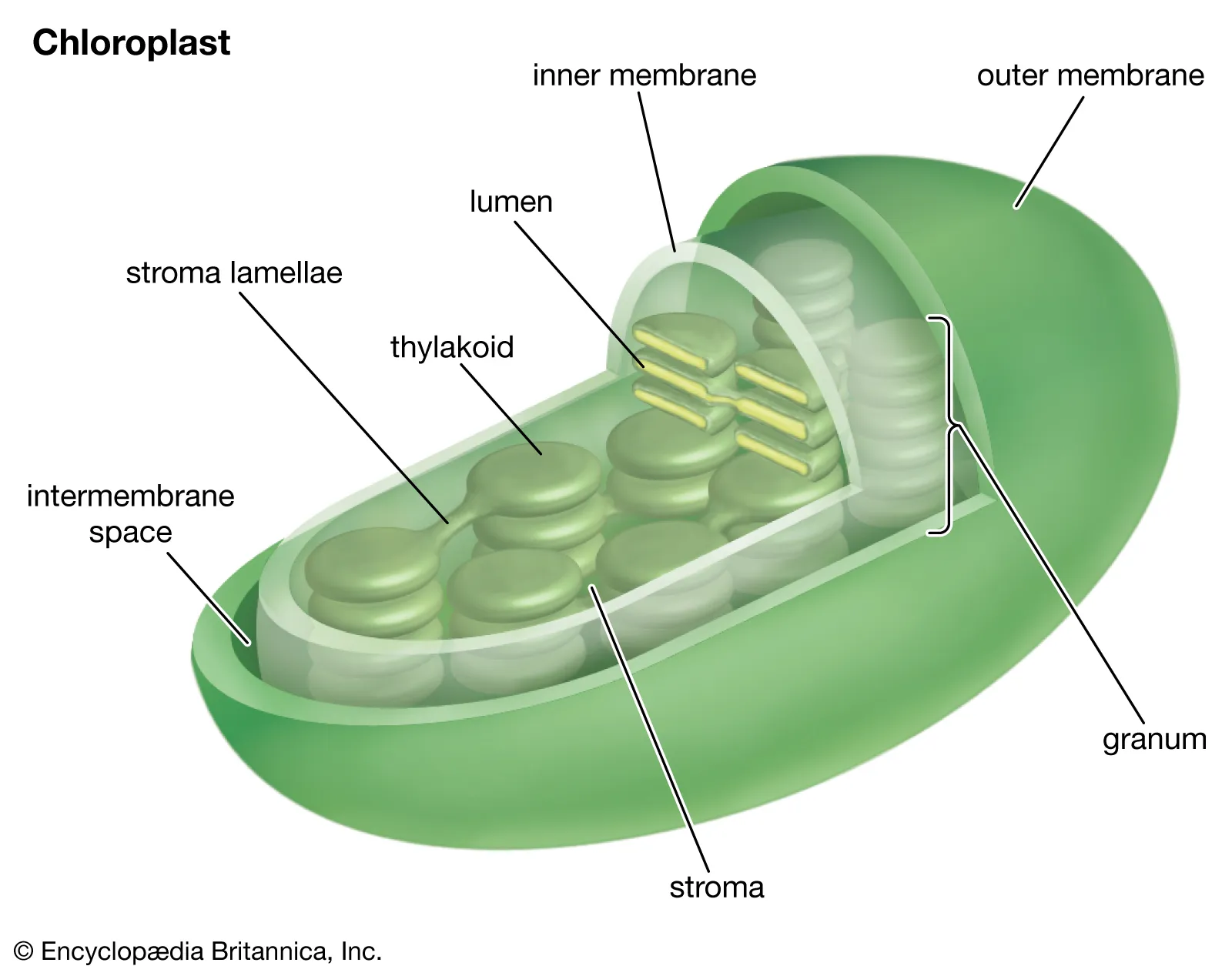
stomata
pores on the surface of leaves, allow CO2 to ENTER and O2 to EXIT
photosystem II
first protein complex, generates ATP
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + solar energy —> 1 C6H12O6 + 6 O2
photosynthesis equation
photolysis
splits water (H2O) into H+ ions, electrons (e-), and oxygen (O2)
thylakoid membranes contain:
chlorophylls, other pigments, protein carriers
light-dependent reactions
convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of NADPH and ATP
where do light-dependent reactions occur
thylakoid space
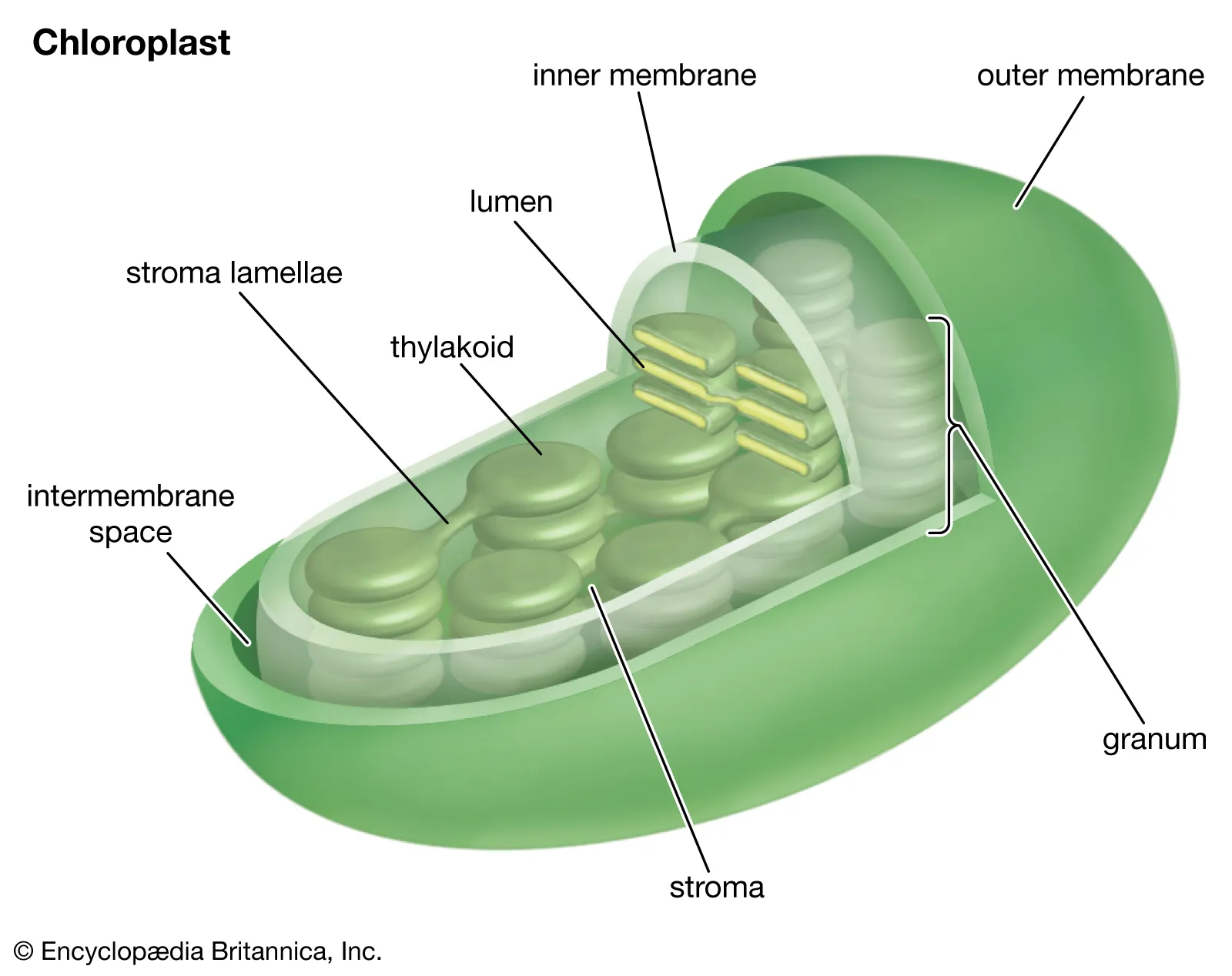
where does photolysis occur
chloroplast (granum)
light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle)
NADPH and ATP used to reduce CO2 into sugar
how many times does the Calvin cycle repeat
6
photosystem I
second protein complex, generates NADPH
how do plants produce ATP into the night
cellular respiration
rubisco
enzyme that attaches carbon to an organic molecule to generate G3P during the calvin cycle
why is chlorophyll green
reflects green light, absorbs red and blue
carbon fixation
incorporation of carbon into organic compounds, later being reduced to a carbohydrate
when does carbon fixation occur
during the calvin cycle
what makes up a photosystem
a reaction-center complex surrounded by several light-harvesting complexes
what is a reaction-center complex
association of proteins holding a special pair of chlorophyll a molecules and a primary electron acceptor
what is a light-harvesting complex
consists of various pigment molecules bound to proteins. proteins holding chlorophyll pigments and other accessory pigments absorb a broader spectrum of colors all together
carotenoids
accessory pigments that are shades of yellow and orange, absorb violet and blue-green light. these pigments broaden the colors able to be absorbed by photosystems
what are photons
particles with a fixed quantity of energy
function of photons during photosynthesis
excite electrons to a higher energy level through energy transfer
how many times does the calvin cycle occur per G3P molecule
3
first phase of sugar production
carbon fixation: CO2 attached to RuBP, results in 2 3-phosphoglycerate
second phase of sugar production
reduction: 3-phosphoglycerate receives phosphate group from ATP, and NADPH reduces the product into G3P
third phase of sugar production
regeneration of RuBP: 5 molecules of G3P rearranged into 3 RuBP, spending 3 ATP while the light reactions regenerate ATP. G3P is starting point for synthesis of molecules like glucose
how many G3P synthesize 1 glucose
2
light-dependent reactions
convert solar energy to chemical energy
light-independent reactions
convert chemical energy (ATP, NADPH) into sugar
what is the purpose of NADPH
carries the captured energy after being reduced into NADPH to the light-independent reactions, reducing an electron acceptor and providing energy, thus allowing CO2 to be reduced into G3P
antennae pigments function
gather more light than just blue/red to transfer to reaction center
examples of antennae pigments
chlorophyll b, carotenoids
where are the ATP synthase complexes located in a plant cell
thylakoid membrane and plasma membrane