QA Quizzes - Midterm
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is the role of CMS in clinical laboratory setting?
to impose sanctions for clinical laboratories that do not follow CLIA guidelines
What does CLIA stand for?
Clinical Laboratory and Improvement Amendments
True or False: the relationship between CLIA and CMS is that CMS enforces CLIA regulations and certification of laboratories
true
What is the role of OSHA in regards to clinical laboratory testing?
to regulate the safety of clinical laboratory workers
Which entity has the authority to impose sanctions and penalties for noncompliance with CLIA regulations?
CMS
What is the main purpose of CLIA?
to establish quality standards for clinical laboratory testing
What does CAP stand for?
College of American Pathologists
What does FDA stand for, and what is the role of the FDA in the clinical laboratory?
Food and Drug Administration; to regulate the safety and efficacy of clinical laboratory testing equipment and reagents
True or False: the purpose of CLIA is to establish standards for laboratory testing
true
What does OSHA stand for?
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
True or False: laboratories are not required to be CLIA certified
false
What does the Joint Commission stand for?
Joint Commission on Accreditation of Health Care Organizations
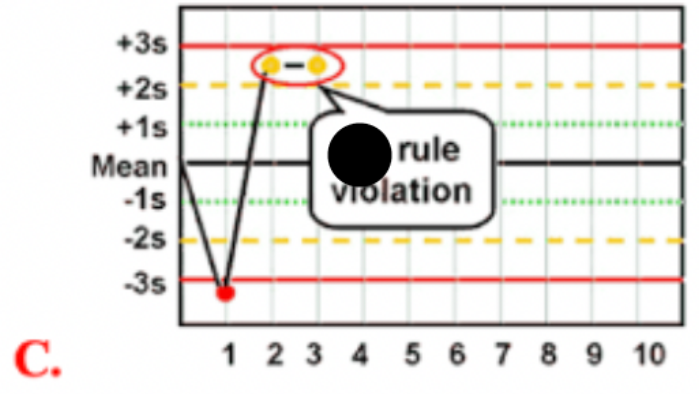
Use the photo to select the correct Westgard rule:
2 2S
Precision in the laboratory refers to
the ability to produce the same result when repeated
What is a sigma metric?
a tool used to assess the performance of laboratory testing processes
Which of the following represents the correct order of the total testing process?
pre-analytical, post-analytical, analytical
What is the purpose of a quality management plan in the clinical laboratory?
to establish policies and procedures for ensuring quality of testing
True or False: Matrix compatibility refers to the ability of QC materials to behave similarly to patient specimens in terms of their composition and performance
true
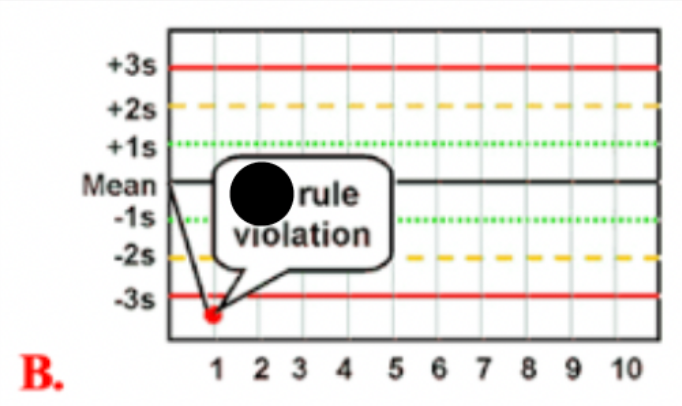
What is a (1 2S) Westgard QC rule violation
indicates 1 control measurement exceeding 2 SD control limits
What is a (2 2S) Westgard QC rule violation
indicates when 2 consecutive control measurements exceed the +/- 2 SD control limit
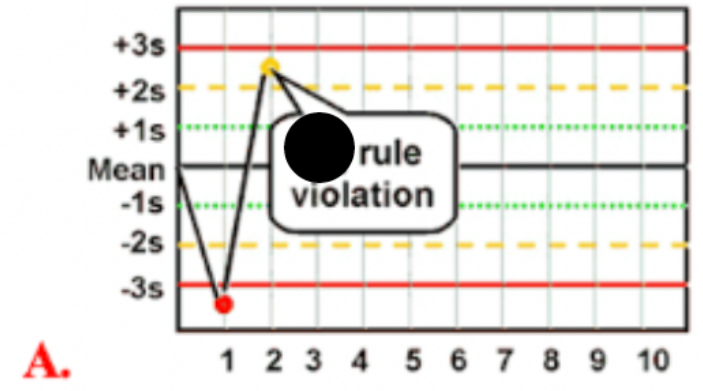
What is a (1 3S) Westgard rule violation
indicates 1 control measurement exceeding 3 SD control limits
What is a (R 4S) Westgard rule violation
two consecutive control measurements have a difference of more than 4 SD form the mean
What is a (10x) Westgard rule violation
a single result is more than ten times the SD away from the mean
What is a (4S) Westgard rule violation
four consecutive results fall more than 1 SD away from the mean in the same direction
Use the photo to select the correct Westgard rule:
1 3S
True or False: the primary purpose of conducting a root cause analysis (RCA) in the laboratory is to identify underlying cause(s) of errors, problems, or incidents
true
Which of the following are components not an outcome of a successful quality control program?
Training and competency assessment of staff
Answer,
Documentation and Record Keeping
Incorrect answer:
Treatment Protocols
Selected Answer - Incorrect
Incorrect answer:
Patient satisfaction survey
What is a Westgard rule?
a set of rules for detecting errors in laboratory test results
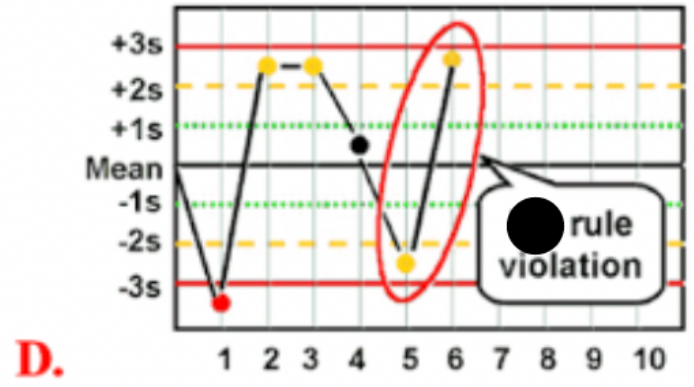
Use the photo to select the correct Westgard rule:
R 4S
Accuracy in the laboratory refers to
the closeness of a measured value to the true value
Use the photo to select the correct Westgard rule:
1 2S
True or False: According to CAP the retention period for personnel records such as competency and training is 1 year
false
True or False: A sigma value of 6+ is considered excellent, which indicates a low probability of errors and a high level of quality assurance
true
Proficiency testing records should be retained for a minimum of how many years?
2 years
What is a key feature of a document control system?
managing and organizing documents
What are 3 major components of a quality management plan?
quality management, quality assurance, and quality control
What is proficiency testing?
a process by which laboratory personnel demonstrate their ability to perform specific laboratory tests
What is the purpose of a Quality Management Plan?
to ensure quality standards and continuous improvement
CMS Regulated analytes aim to ensure:
regulatory compliance in clinical testing, continuous improvement in laboratory processes, accuracy and reliability in testing
What is the purpose of Sigma Metrics in the clinical laboratory?
to assess laboratory performance in clinical testing
True or False: the notation N=2, R=2 indicates 2 control measurements are needed in a single run
false
According to CAP the retention period for validation and verification of method performance specifications is:
2 years after discontinuation of the test
What are the components of verification?
accuracy, precision, reportable range
True or False: Validation and verification are essential components of quality assurance in clinical laboratory testing
true
True or False: Analytical Specificity evaluates the methods ability to detect and measure low concentrations of analytes
false
For a given QC material for cholesterol, if the mean is 200mg/dL and the SD=4mg/dL, what are the 2SD QC limits?
192, 208
Qualitative Methods that result in positive, negative, present, or absent can be utilized in which laboratory department(s)?
blood bank, microbiology, HIV testing
True or False: An IQCP should be used whenever the lab is following the manufacturers QC instructions
false
True or False: Laboratory Developed Tests are diagnostic tests that are developed, validated, and performed by a specific laboratory for in-house use
true
Verification of performance specification is required for what instances?
prior to reporting patient test results, when a test system or analyte is introduced to the lab, when multiple instruments are used to perform the same test