Classification of bones | Skeletal, Cranial, Facial Bones
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anatomy & Physiology 12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Long bones
Ex: Arm bones, hand bones, leg bones.
Longer than they are wide.
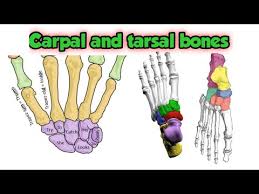
Short bones
Ex: Carpals, tarsals
More cube-shaped.
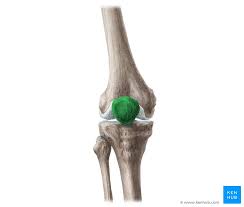
Sesamoid bones
Ex: Knee cap (patella)
A special type of short bone.
Flat/thin bones
Ex: Sternum, scapula, ribs, ilium, cranial bones in the skull
Often have a bit of a curve, Has a large surface area for attaching to muscles.
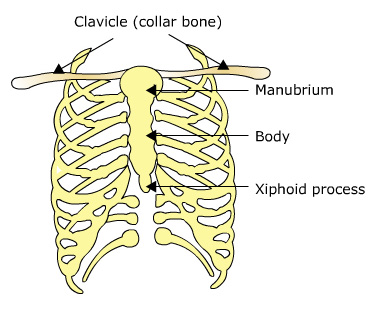
Irregular bones
Ex: Hip bones, vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, sphenoid bone, ethmoid bone
Everything else that does not fit other classifications. Has a specialized shape and structure.
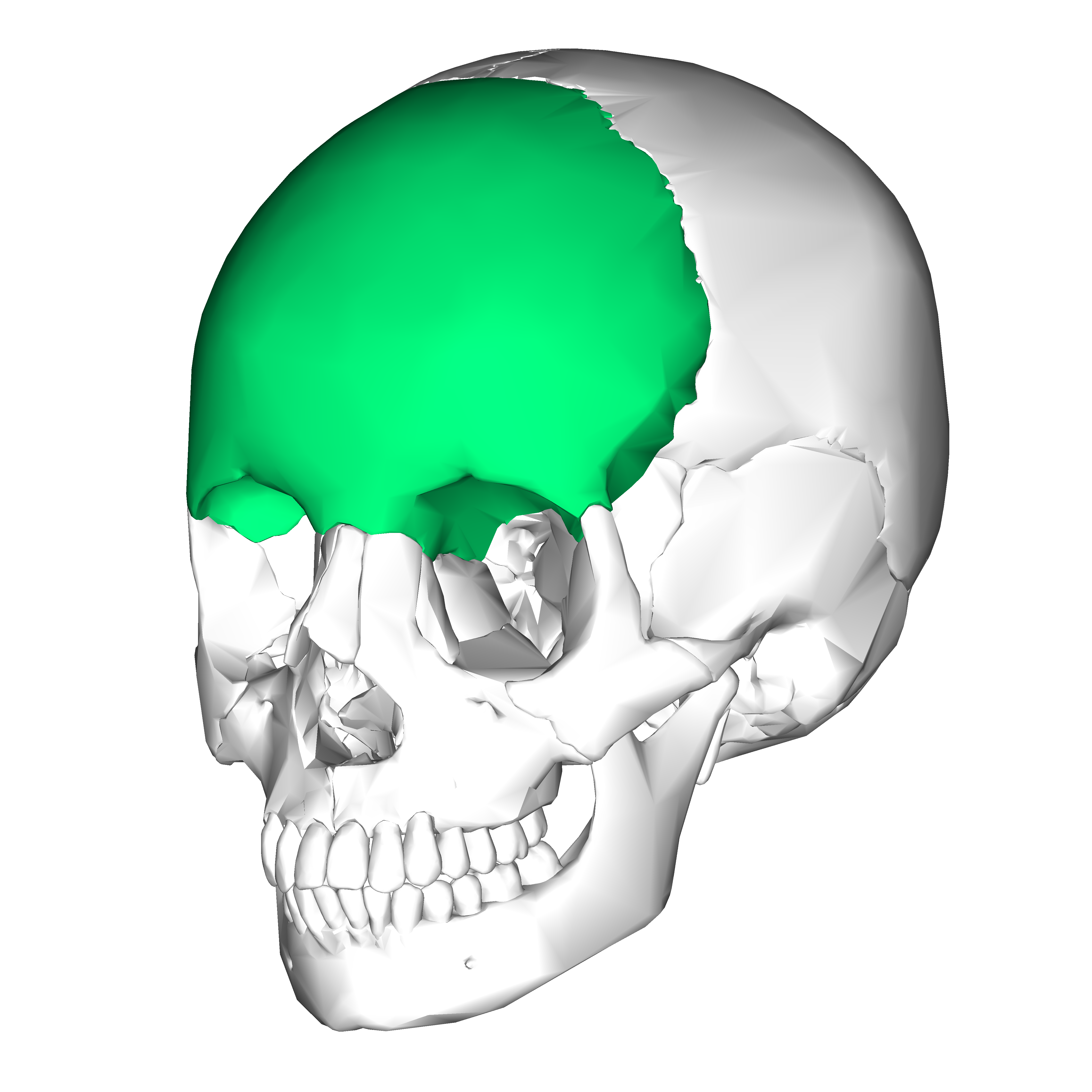
Frontal bone
Anterior wall of the cranium
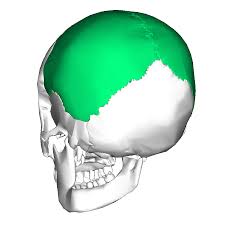
Parietal bones
superior and lateral walls of the cranium
Occipital bone
posterior and inferior wall of the cranium
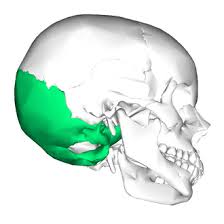
Temporal bones
Interior and lateral walls of the cranium
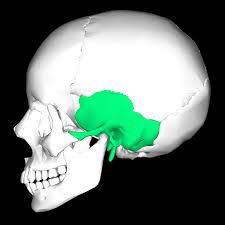
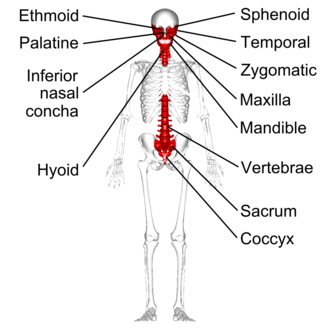
Sphenoid bone
Butterfly shaped bone found in the middle of the cranium; visible in the temples and back of the eye socket (AKA Orbit)
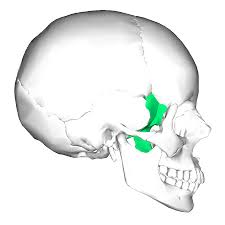
Ethmoid bone
Between the sphenoid bone and bones of the nose; deepest bone of the skull. Forms part of the nasal cavity and orbits.
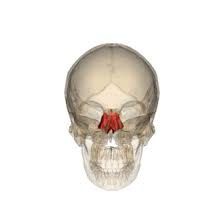
Nasal bones
Forms the bridge of the nose
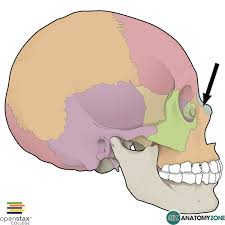
Maxillae
Upper jawbone; all facial bones (except for mandible) touch it; also forms anterior portion of the hard palate
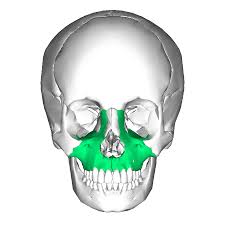
Lacrimal bones
Smallest bones of the face; found in interior corner of each orbit.
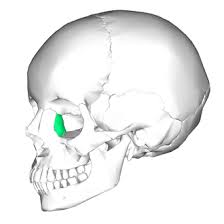
Mandible
Lower jawbone; largest and strongest bone of the face; only bone of the skull that can move
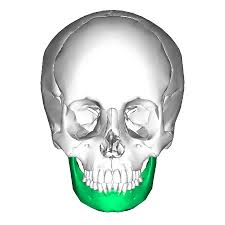
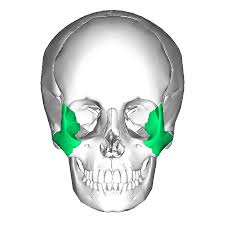
Zygomatic bones
Commonly called the cheekbones; also make up the inferior and lateral walls of the orbits
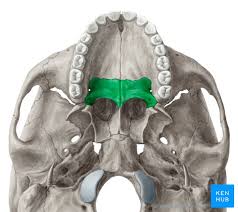
Vomer bone
Together with the ethmoid bone, forms the nasal septum
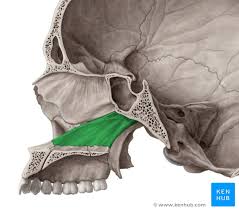
Palatine bones
Forms the posterior portion of the hard palate
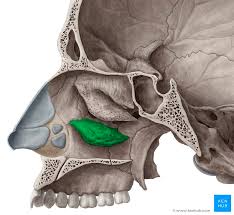
Inferior nasal conche
Curved bones that project from the lateral walls of the nasal cavity.
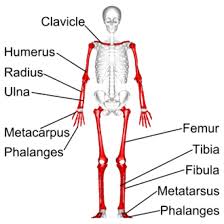
appendicular bones
Limbs and their supporting girdles

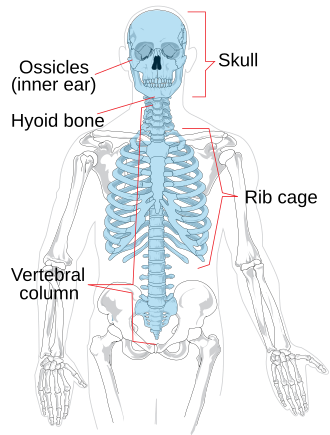
Axial bones
skull, vertebral column, rib cage, hyoid bone, bones of middle ear