Psychodynamic approach
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are the assumptions of the psychodynamic approach?
The unconscious = key determinate of how we behave
We have innate ‘drives’/‘instincts’ that ‘energise’ our minds to motivate behaviour as we develop through our lives
Our personality (the psyche) is made up of the ID, ego + superego
Childhood experiences = v important in determining our personality when we reach adulthood
Psychodynamic approach
What are the levels of consciousness according to Freud?
Conscious → What we’re are aware of at any given time → Eg: seeing/hearing/smelling/thinking in the moment)
Preconscious → Thoughts that may become conscious at some point → Eg: through dreams/Freudian slips
Unconscious → the part we are unaware of
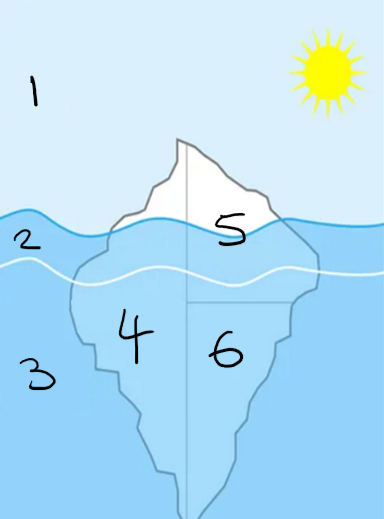
Psychodynamic approach
Iceberg analogy:
Conscious
Preconscious
Unconscious
Superego
Ego
ID
Psychodynamic approach
What is the role of the unconscious according to Freud?
It’s the driving, motivating force behind our behaviour/personality - crucial to understanding human behaviour, containing:
Our biological instinct + drives that influence behaviour (eg: survival/sexual instincts including aggression)
Childhood memories can become part of it later on
Protects the conscious self from trauma + conflict (eg: repression)
Psychodynamic approach
What are the ways that Freud claims we can get insight into the unconscious mind?
Freudian slips can give insight to unconscious (when we make a mistake in our speech that reveals our unconscious thoughts/desires)
Analysing dreams → said they were ‘disguised fulfilments of repressed wishes’
Personality (Psychodynamic approach)
The ID:
When does it develop?
What is it, and what principle does it obey?
What level of consciousness is it in?
When does it develop?
By around 6 months
What is it, and what principle does it obey?
The innate, selfish part of personality → contains aggressive + sexual instincts (the libido)
Wants to do what will give pleasure w/o regard for consequences → obeys the ‘pleasure principle’
What level of consciousness is it in?
Unconscious
Personality (Psychodynamic approach)
The ego:
When does it develop?
What is it, and what principle does it obey?
What level of consciousness is it in?
When does it develop?
By age 3
What is it, and what principle does it obey?
Acts as rational part of mind - 'reality principle'
Mediates b/w the conflict of the ego/super-ego
What level of consciousness is it in?
Both the conscious/unconscious
Personality (Psychodynamic approach)
The superego:
When does it develop?
What is it, and what principle does it obey?
What level of consciousness is it in?
When does it develop?
By around five
What is it, and what principle does it obey?
Sense of right and wrong (conscience + morality) passed onto by parents/society → if we fail to live up to this = feel guilt/shame
Tries to supress the urges of the ID (conflict)
Morality principle
What level of consciousness is it in?
Both the conscious/unconscious
Personality (Psychodynamic approach)
What happens if the ID or super-ego are dominant?
What would a person with a dominant ID develop to be?
What would a person with a dominant superego develop to be?
What happens?
Leads to unhealthy psychological states (eg: anxiety)
Dominant ID
Highly impulsive
Lack self-control
May be involved in criminal
Dominant super-ego
Judgmental, critical + self righteous
Highly anxious/depressed at failure to meet standards of super-ego
Psychosexual stages
What does how parents raise a child affect?
how much pleasure is obtained through that stage (eg: how strict they are when potty training, and what type of role models they are)
Psychosexual stages
How do people pass through the psychosexual stages?
What happens if a person is unable to do (the answer to above)?
How?
Each stage has a conflict that must be resolved
What happens w/ unresolved conflict?
Become 'fixated' at that stage → it’s repressed into the unconscious, but influences adult personality/behaviour
Psychosexual stages
What could severe fixations lead to?
A psychological disorder
Name the stages of development (psychosexual stages) in order + the ages they occur:
oral - 0-1
anal - 1-3
phallic - 3-6
latent - 6-12
genital - 12+
Psychosexual stages
The oral stage:
Where is libido/pleasure directed towards?
What conflict needs to be resolved?
What causes a fixation?
What is the fixation?
Libido/pleasure:
Mouth → first area associated w/ pleasure + satisfaction (mainly bcs of feeding)
Conflict:
Weaning → child must become less dependent on caregiver for food (eg: breast feeding) + transition to other foods
Cause of Fixation:
If child's oral needs not met enough/excessively met (eg: weaned to early/late) -> difficult to adjust to new habits -> oral fixation
Fixation:
Oral fixation (eg: smoking, nail biting, chewing gum, alcoholism → to gain oral stimulation)
Psychosexual stages
What part of the personality develops during the oral stage?
ID
Psychosexual stages
The anal stage:
Where is libido/pleasure directed towards?
What conflict needs to be resolved?
What causes a fixation?
What is the fixation?
Libido/pleasure:
Controlling bowel movements (withholding/expelling faeces)
Conflict:
Toilet training → enables them to develop control + independence
Cause of Fixation:
If parents are not supportive + encouraging while potty training (eg: punishing the child + making them feel shame/embarrassed if made mess)
Fixation:
Anal expulsive personality → messy, wasteful, unorganised, cruel
Anal-retentive → excessively: organised, tidy, obsessive, + concerned w/ bodily cleanliness
Psychosexual stages
What part of the personality develops during the anal stage?
Ego
Psychosexual stages
The phallic stage:
Where is libido/pleasure directed towards?
What conflict needs to be resolved?
What causes a fixation?
What is the fixation?
Libido/pleasure:
Genitals
Conflict:
Oedipus/Electra complex → when resolved:
Boys identify w/ their father + adopt a male role
Girls identify w/ their mother + adopt a female role
Then go onto internalise the moral values + standards of their same-sex parent (in super-ego)
Cause of Fixation:
Not resolving the Oedipus/Electra complex
Fixation:
Being overly dependent of their mother/father
Confusion w/ gender identity
Psychosexual stages
What part of the personality develops during the anal stage?
Super-ego
Psychosexual stages
What is the Oedipus complex?
In boys
Sexual desire towards mother + resentment/rivalry w/ father
Due to a fear of castration
Psychosexual stages
What is the Electra complex?
In girls
Sexual desire towards father + resentment/rivalry w/ mother
Due to penis envy (assume they used to have a penis + have been castrated so resent their mother for this loss)
Psychosexual stages
The latency stage:
Where is libido/pleasure directed towards?
What conflict needs to be resolved?
What is the fixation?
Libido/pleasure:
Dormant/not active
Conflict:
Generally calm + conflicts from earlier stages = repressed
Defence Mechanisms develop
Fixation:
Fixation does not usually develop at this stage, BUT could be immaturity
Psychosexual stages
The genital stage:
Where is libido/pleasure directed towards?
Libido/pleasure:
Becomes more active w/ onset of puberty
Develop strong sexual desires w/ opposite sex
Psychodynamic approach
What are defence mechanisms?
Name them:
What are they?
Unconscious methods the ego uses to help us deal w/ memories/experiences we find too traumatic/disturbing
Done as part of mediating b/w the super-ego + ID → reduces anxiety from conflict b/w them (bcs ID wants instant satisfaction + superego wants to impose morals) → stops us from feeling eg: guilty
Names:
Repression
Denial
Displacement
Psychodynamic approach - defence mechanisms
What is repression?
Give an example:
What is it?
The ego pushes unwanted + possibly painful thoughts out of the conscious
BUT still influences our behaviour unconsciously
Example:
Forgetting about being mugged bcs was too traumatic
Psychodynamic approach - defence mechanisms
What is denial?
Give an example:
What is it?
A threatening event/unwanted reality is simply ignored + the person refuses to acknowledge it in order to avoid dealing w/ painful feelings that may be associated w/ it
Example:
Someone grieving may deny their loved one has died
Psychodynamic approach - defence mechanisms
What is displacement?
Give an example:
What is it?
We transfer feelings from true source of distressing emotion onto a substitute figure bcs the real source is too abstract/powerful/distant etc
Example:
Redirecting anger towards friends/family bcs angry at boss
Psychodynamic approach - defence mechanisms
What is projection?
Give an example:
What is it?
Place our negative emotions/feelings about something onto another figure
Example:
You are a jealous/controlling person → accuse your partner of being jealous/controlling → protects the superego from feeling guilty
Psychodynamic approach - Case study/Oedipus complex
Little Hans:
5y/o boy developed a phobia of horses - was observed by his father who made notes of Hans's dreams/stuff he said + gave them to Freud for analysis
Hans was afraid of horses because he thought they might bite him or fall on him
He developed an interest in his penis - his mum told him not to play with it or she'd castrate him
Hans told his dad about a dream where he was married to his mum and his dad was now his grandfather
Freud concluded that:
Hans's phobia was his repressed fear of his father was displaced onto horses → horses = metaphor for repressed fear of castration bcs of Oedipus complex
Psychodynamic approach
Evaluation of Little Hans:
Pros:
Supports Freud’s Phallic stage
Cons:
results based entirely on observation + interpretation, so can’t establish cause/effect relationship
Alt interpretations/explanations to Freud’s conclusions (eg: the phobia was developed bcs of classical conditioning due to study Hans fright from witnessing a horse falling down in the street)
Freud analysed information from Hans's father, so the results could be biased
Psychodynamic approach:
Evaluation: application
It led to development of psychoanalysis/psychotherapy → modern psychiatry still uses Freudian psychoanalytic techniques, eg: any hesitations/avoidance during therapy are explored as potential signs of deeper unconscious conflict BUT unsuitable for some disorders (eg: schizophrenia) bcs delusions/hallucinations may struggle w/ self-reflection/insight/verbal expressions of thoughts/emotions or even be counter-productive SO may be ineffective or potentially harmful → increased confusion/worsening of symptoms
Psychodynamic approach:
Evaluation: unfalsifiable
unfalsifiable bcs can’t be empirically tested → many of Freud's concepts supposedly occur in unconscious (cannot be operationalised) → impossible to test → falsifiability means psychodynamic approach = often called pseudoscience
Psychodynamic approach:
Evaluation: Anecdotal evidence
use of case studies as supporting evidence → approach doesn’t use controlled experiments to collect empirical evidence → considered far less scientific than other approaches → hard to generalise to gen pop bcs low pop val
Psychodynamic approach:
Evaluation: gender bias
Androcentric - theories of female psychosis = underdeveloped + suggest route of female issues = not being a male (penis envy)
Psychodynamic approach:
Evaluation: formed the basis for lots of other theories
psychodynamic approach = v influential on psych + helped explain variety of behaviours eg: before this disorders cause thought to be physical/things like possession by evil spirits → one of first approaches suggesting may be linked to unresolved conflicts + suggest a connection b/w childhood + future development → a basis for the IWM of attachment → SO although major limitations, = important for psycho to develop