APWHM Unit 1
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
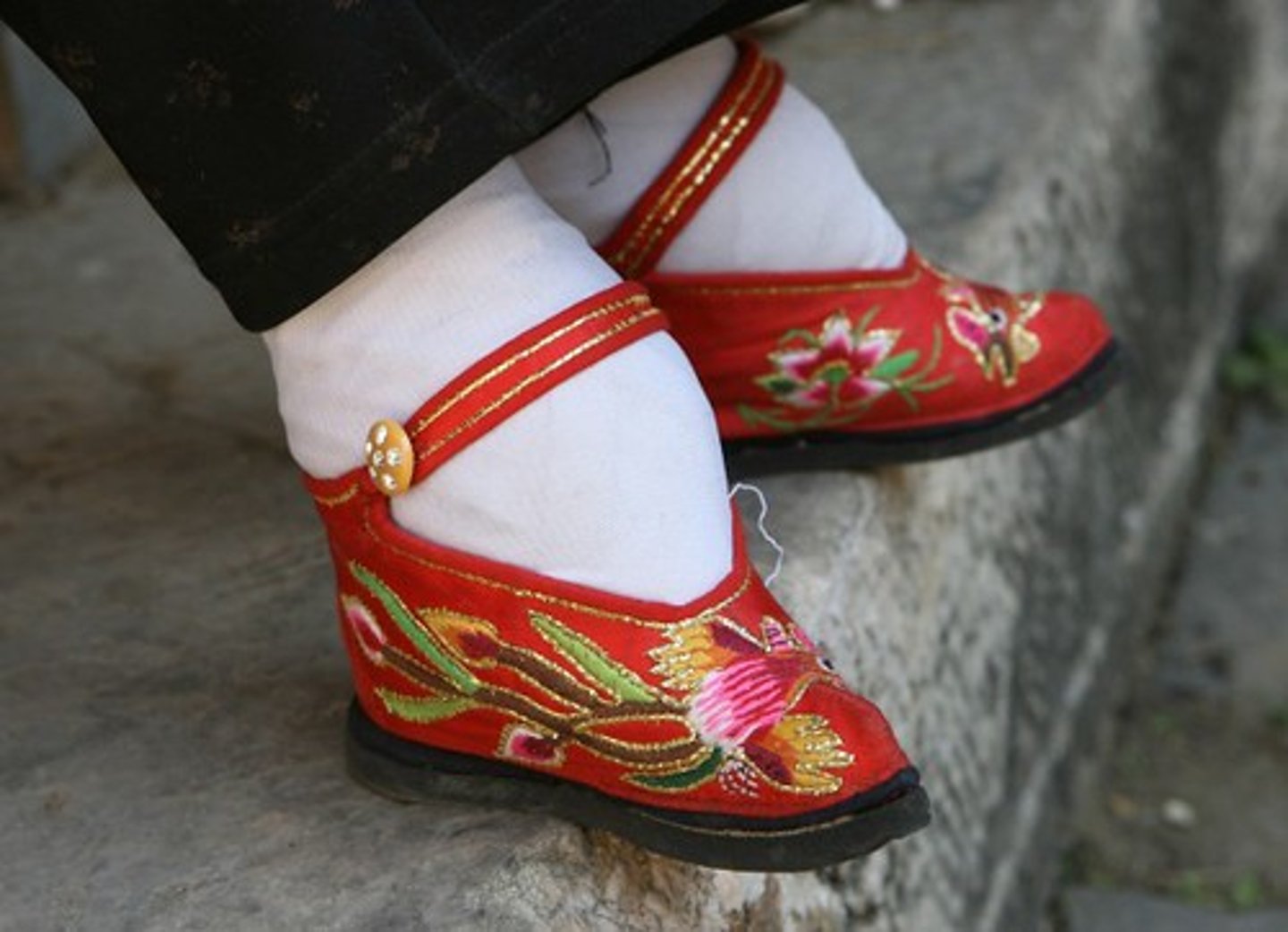
Foot Binding
Practice in Chinese society to mutilate women's feet in order to make them smaller; produced pain and restricted women's movement; made it easier to confine women to the household.

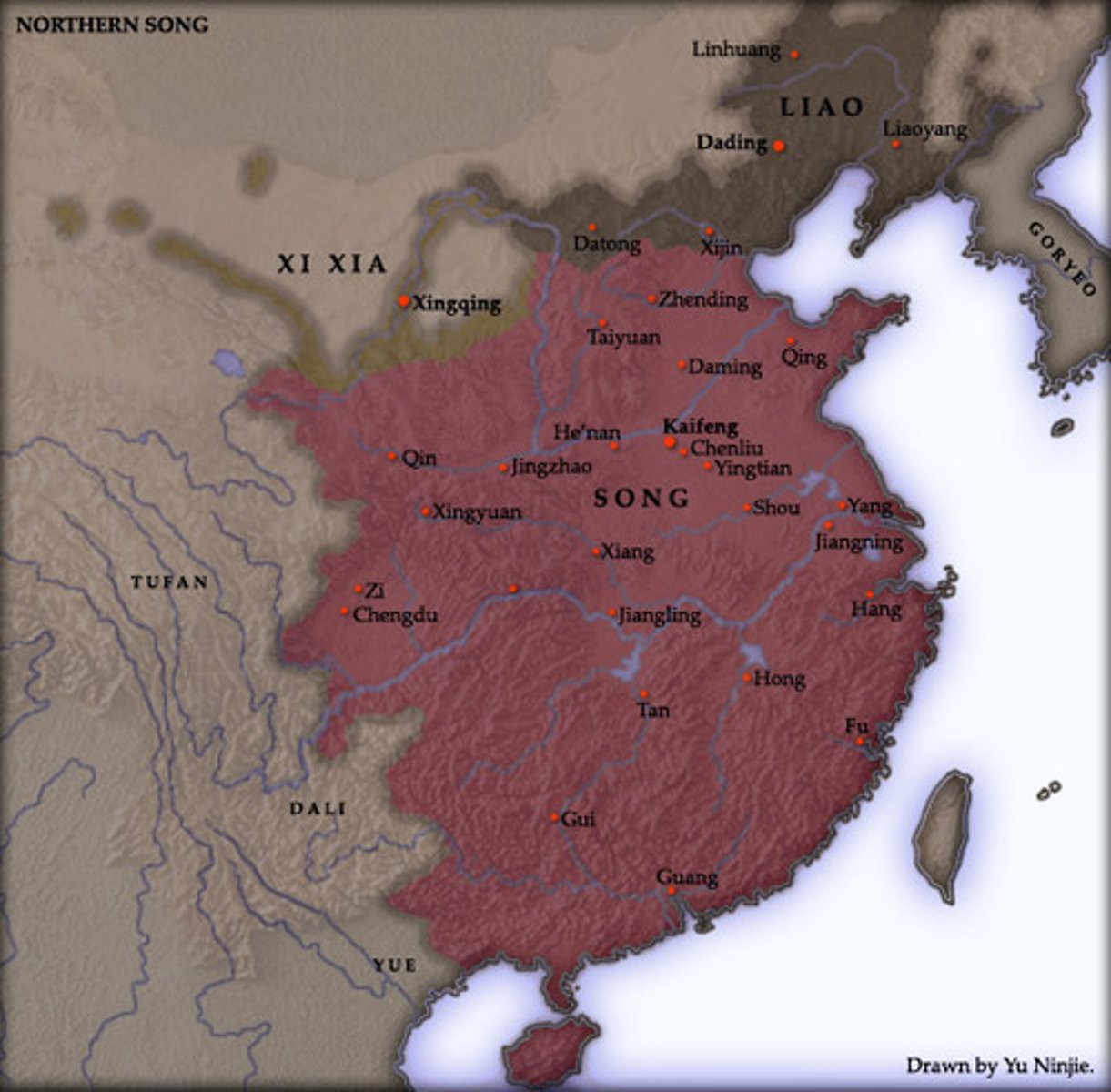
Song Dynasty
During this Chinese dynasty (960 - 1279 AD) China saw many important inventions. There was a magnetic compass; had a navy; traded with india and persia (brought pepper and cotton); paper money, gun powder; landscape black and white paintings
Champa Rice
Quick-maturing rice that can allow two harvests in one growing season. Originally introduced into Champa from India, it was later sent to China as a tribute gift by the Champa state (as part of the tributary system.)
Filial Piety
In Confucian thought, one of the virtues to be cultivated, a love and respect for one's parents and ancestors.

Neo-Confucianism
The Confucian response to Buddhism by taking Confucian and Buddhist beliefs and combining them into this. However, it is still very much Confucian in belief.
Civil Service Exam
In China, it was an exam based on Confucian teachings that was used to select people for various government service jobs in the bureaucracy.
Imperial Bureaucracy
Division of an empire into organized provinces to make it easier to control
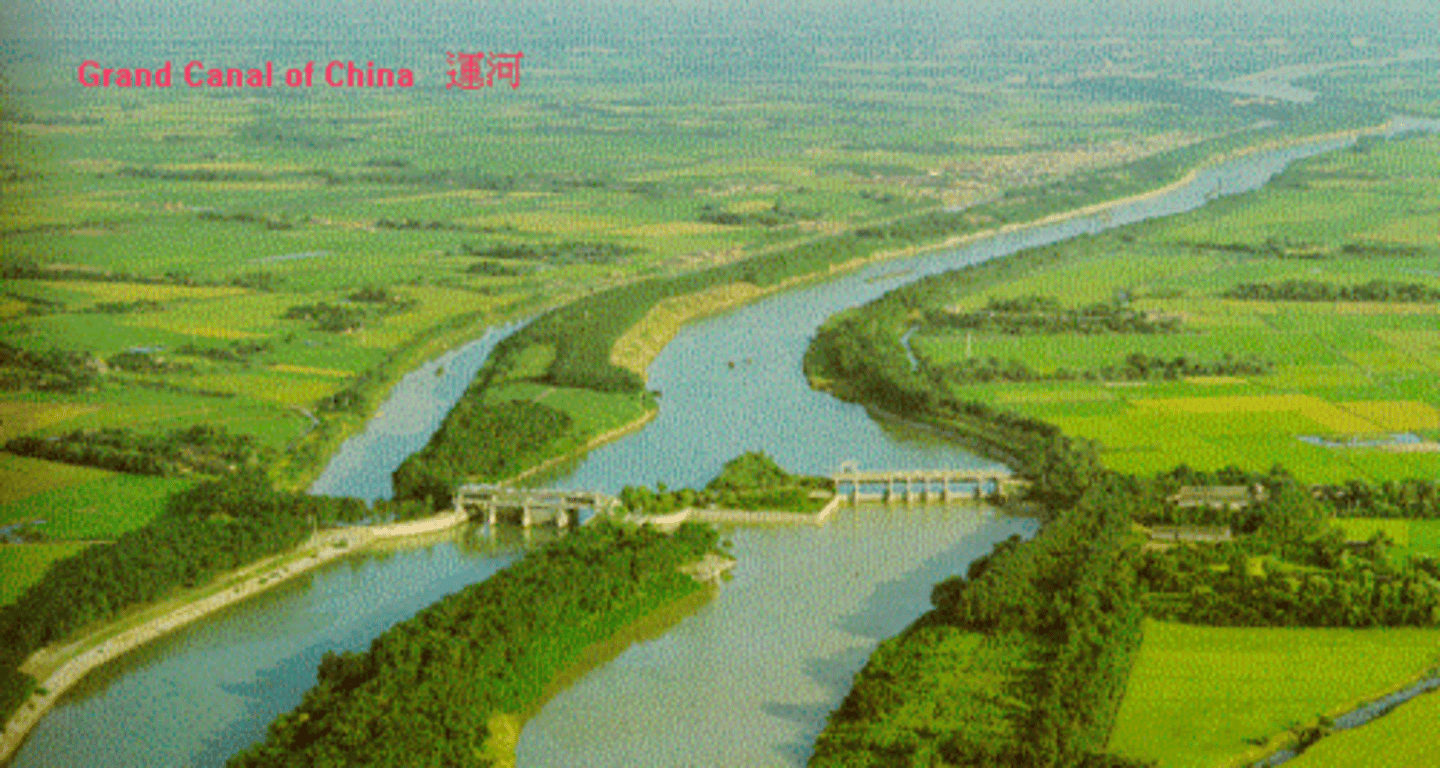
Grand Canal
Built in 7th century during reign of Yangdi during Sui dynasty; designed to link the original centers of Chinese civilization on the north China plain with the Yangtze river basin to the south; nearly 1200 miles long.

Mandate of Heaven
the belief that the Chinese king's right to rule came from the gods
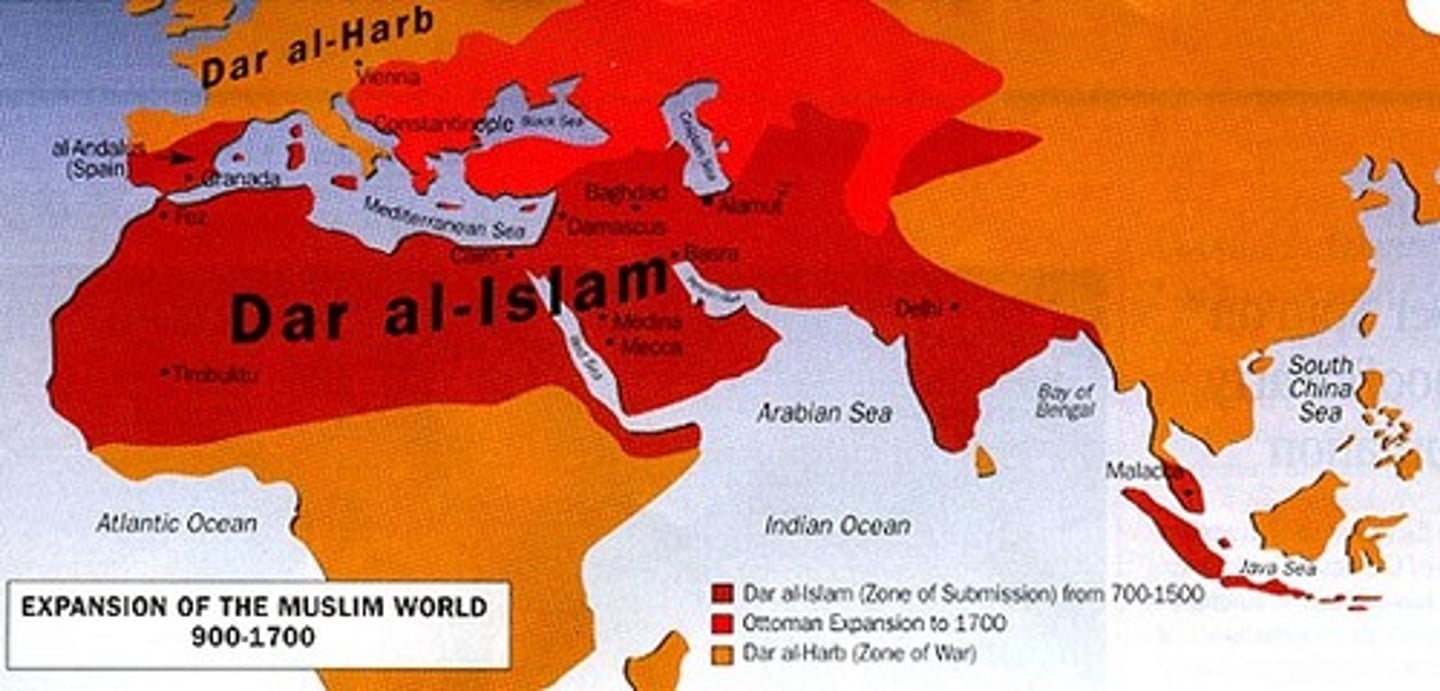
Dar al-Islam
an Arabic term that means the "house of Islam" and that refers to lands under Islamic rule
Seljuk Turkic Empire
An empire of the eleventh and twelfth centuries, centered in Persia and present-day Iraq. Seljuk rulers adopted the Muslim title of sultan (ruler) as part of their conversion to Islam.

Quran
the sacred writings of Islam revealed by God to the prophet Muhammad during his life at Mecca and Medina

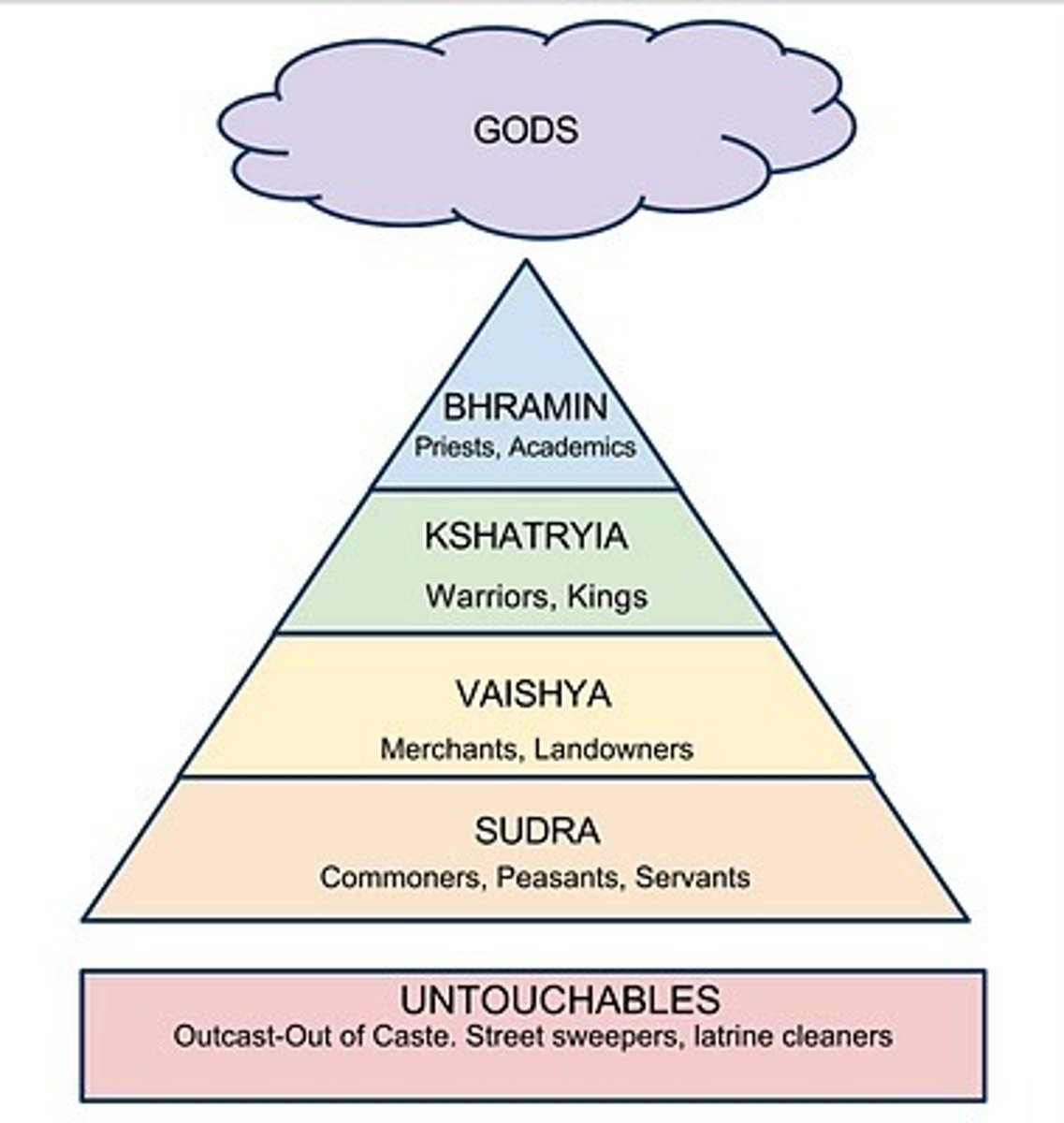
Caste System
a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person's occupation and economic potential, but also his or her position in society
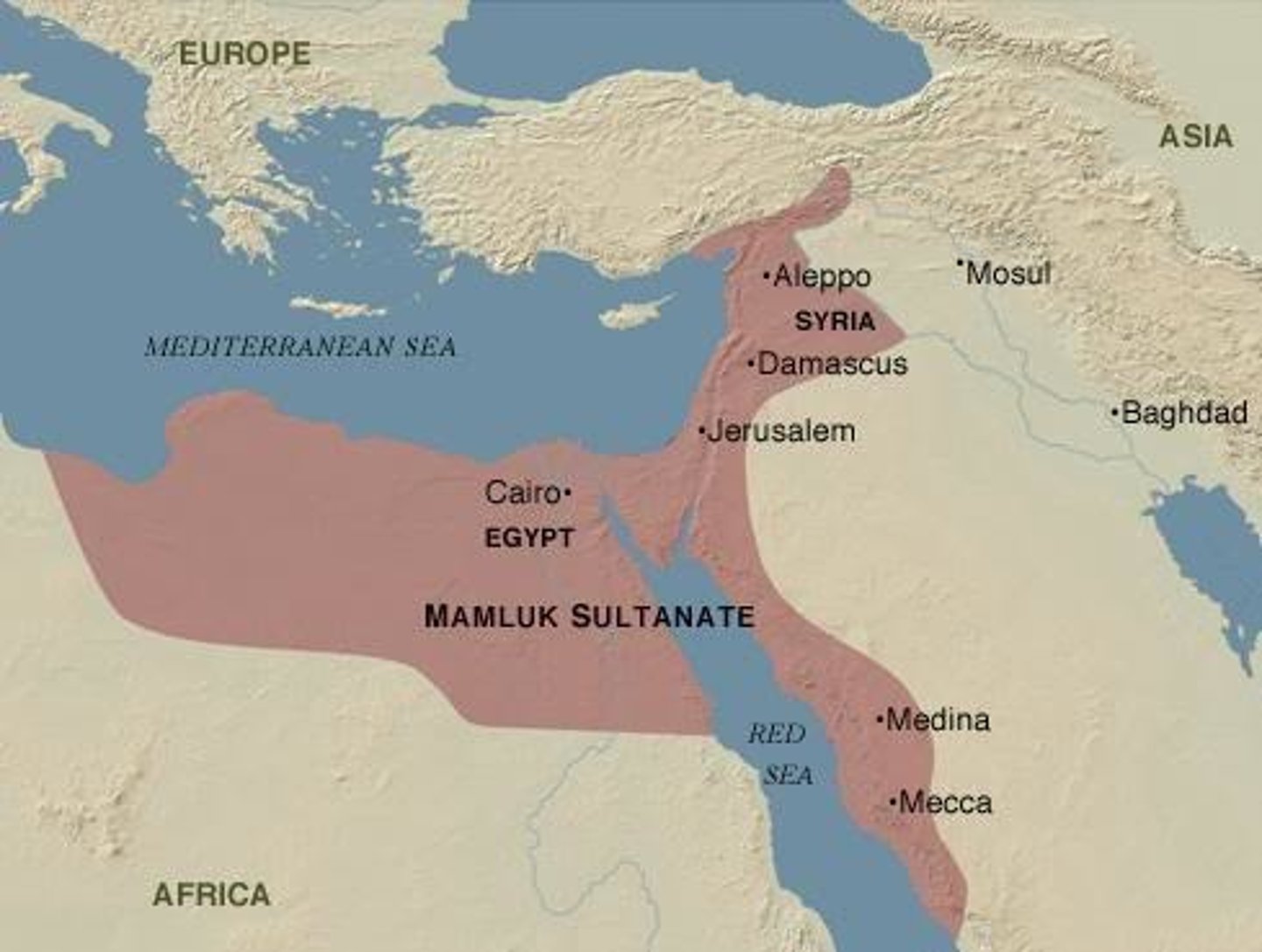
Mamluk Sultanate
Defeated the Mongols and the Ayyubid Sultanate; Did not set up a consistent, hereditary line of succession & failed to adapt to new warfare; Were eventually defeated by the Ottomans
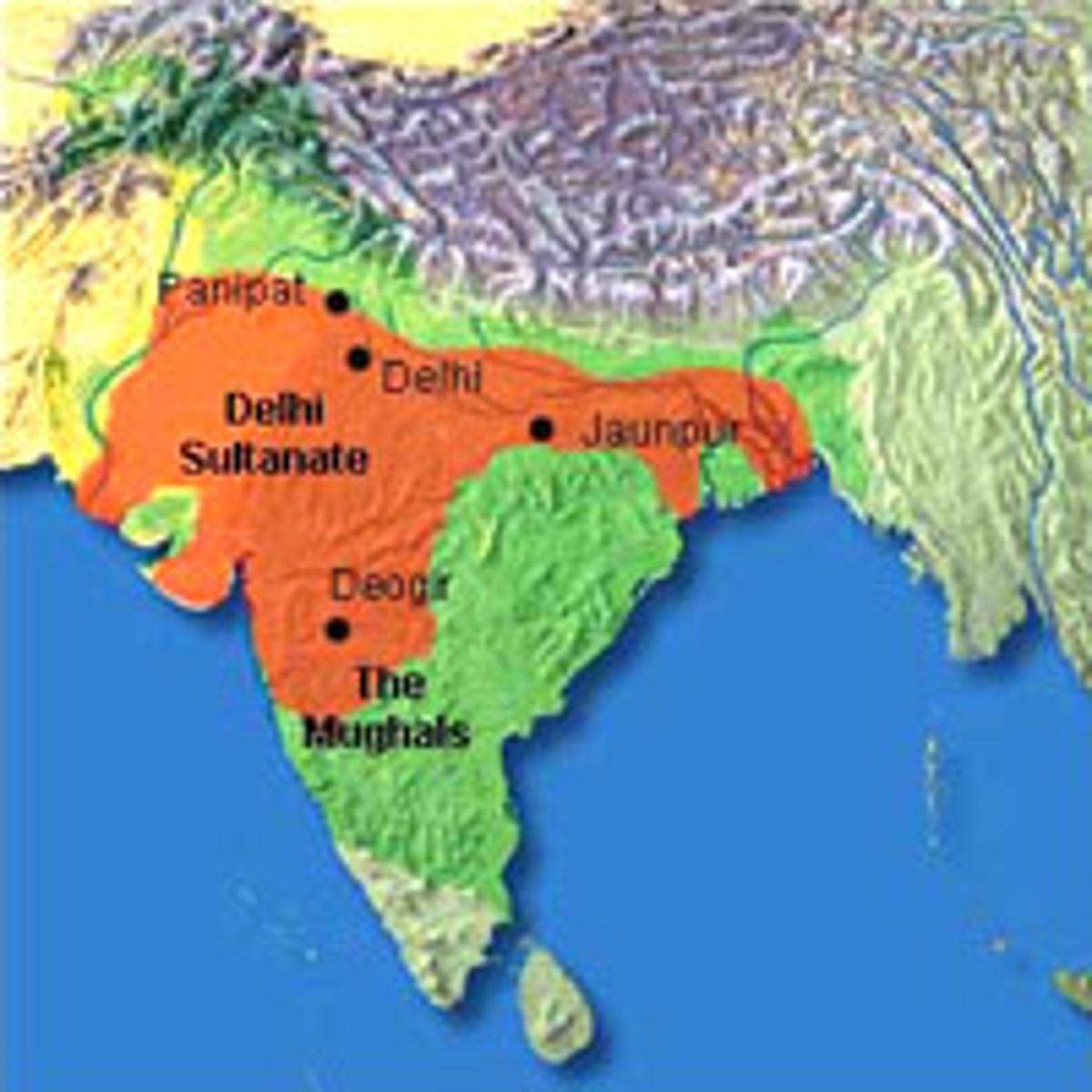
Delhi Sultanate
The first Islamic government established within India from 1206-1520. Controled a small area of northern India and was centered in Delhi.
Sufism
An Islamic mystical tradition that desired a personal union with God--divine love through intuition rather than through rational deduction and study of the shari'a.

Buddhist monasticism
Religious way of life in which one renounces worldly pursuits to devote oneself fully to spiritual work. (The four monastic rules are essentially - don't kill, steal, have sex, or brag.)

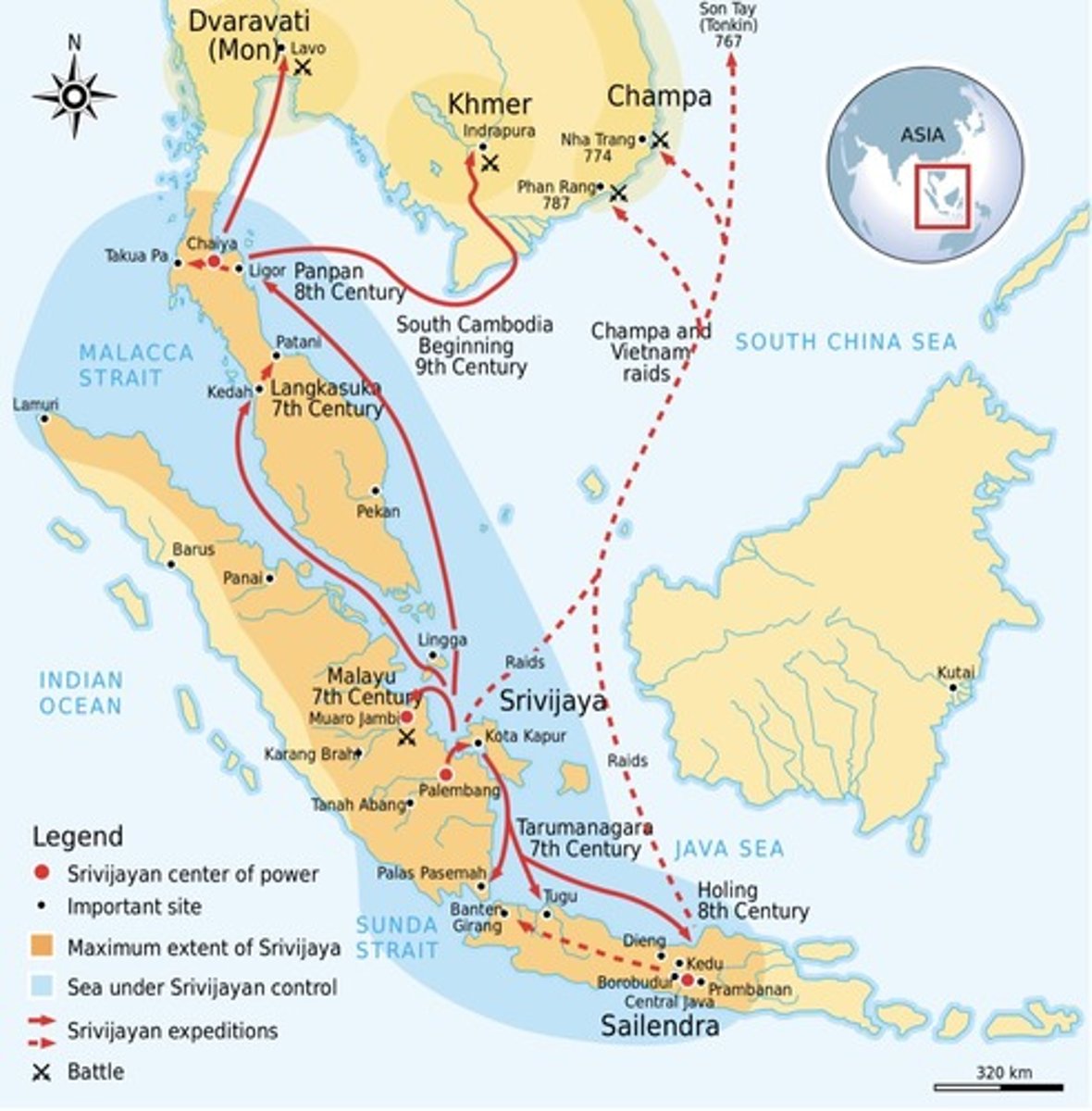
Srivijaya Empire
A maritime empire that controlled the Sunda strait the strait of Malacca between India and China. HS: control strengthened trade routes to China, India, and even Arabia
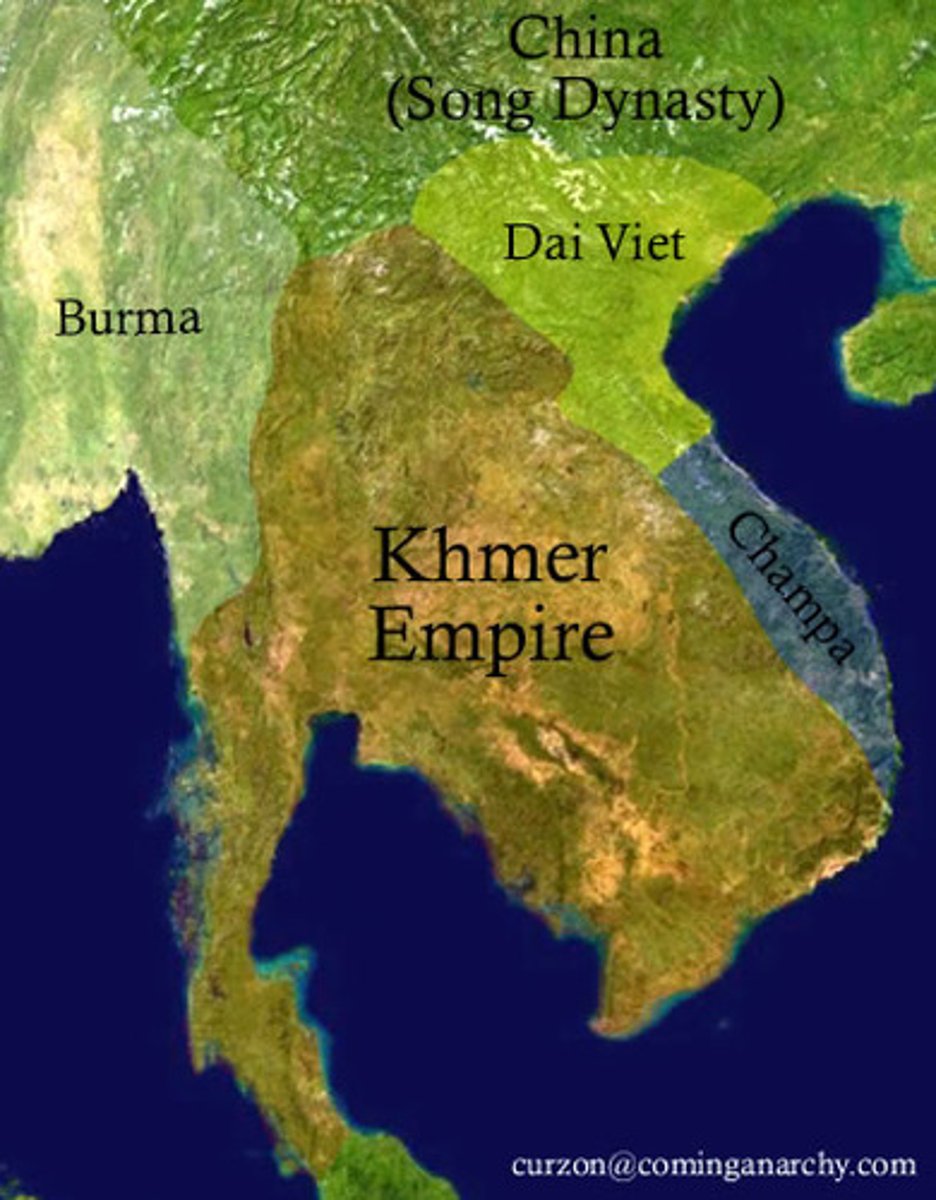
Khmer Empire
The most powerful and longest-lasting kingdom on the mainland of southwest Asia, centering in what is today Cambodia.
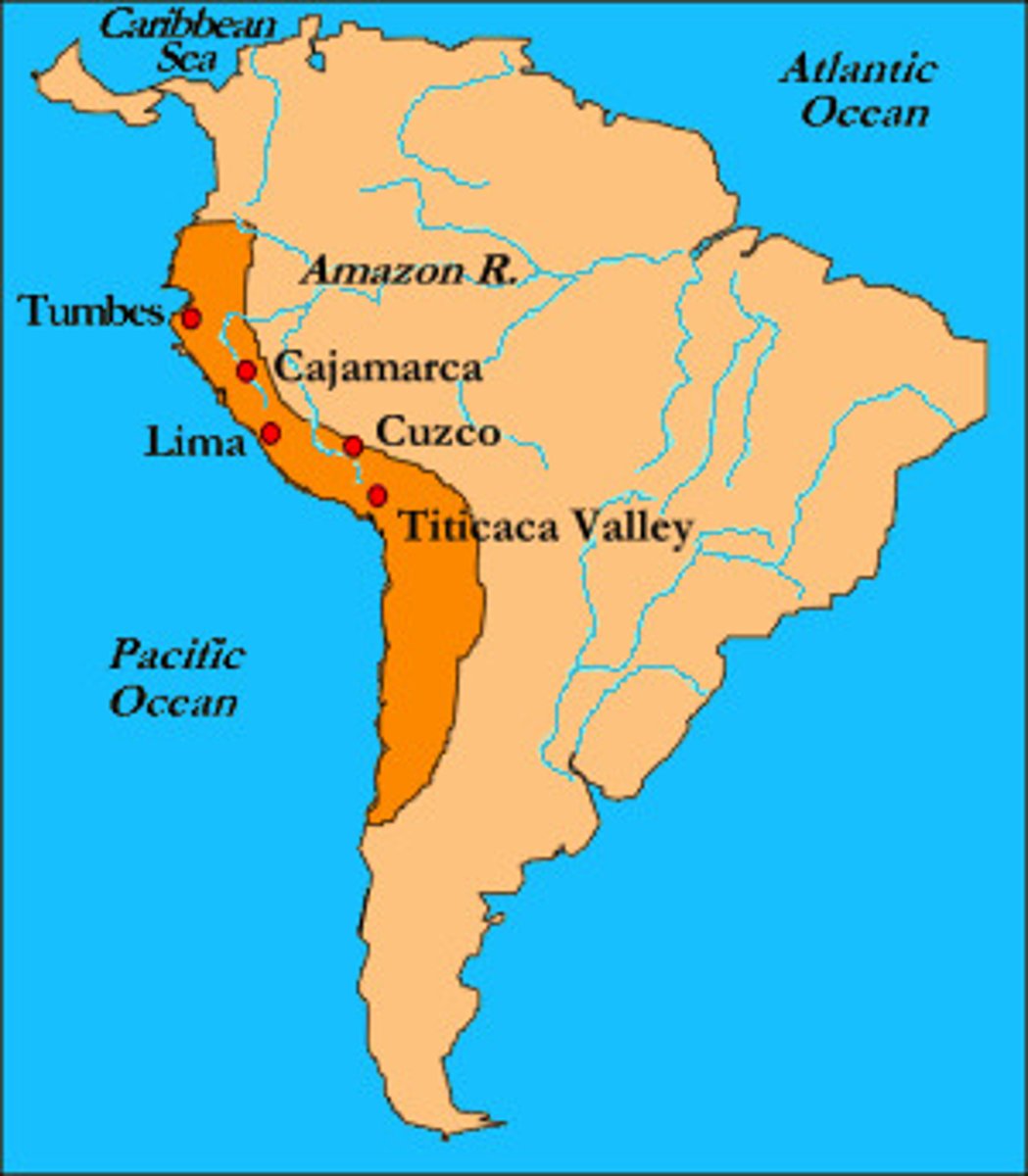
Inca Empire
The vast and sophisticated Peruvian empire centered at the capital city of Cuzco that was at its peak from 1438 until 1532
Mita System
economic system in Incan society where people paid taxes with their labor and what they produced

Aztec Empire
Central American empire constructed by the Mexica and expanded greatly during the fifteenth century during the reigns of Itzcoatl and Motecuzoma
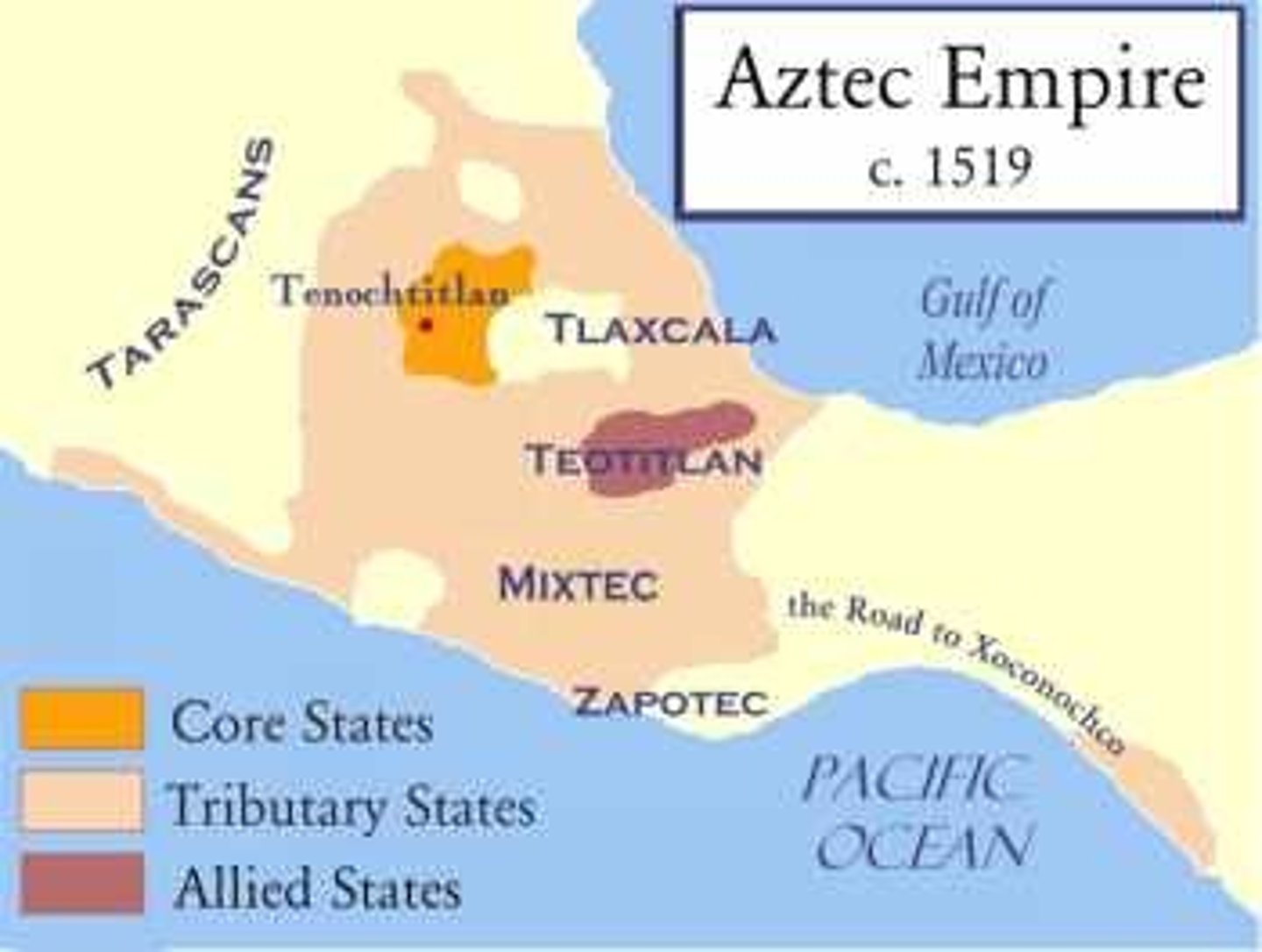
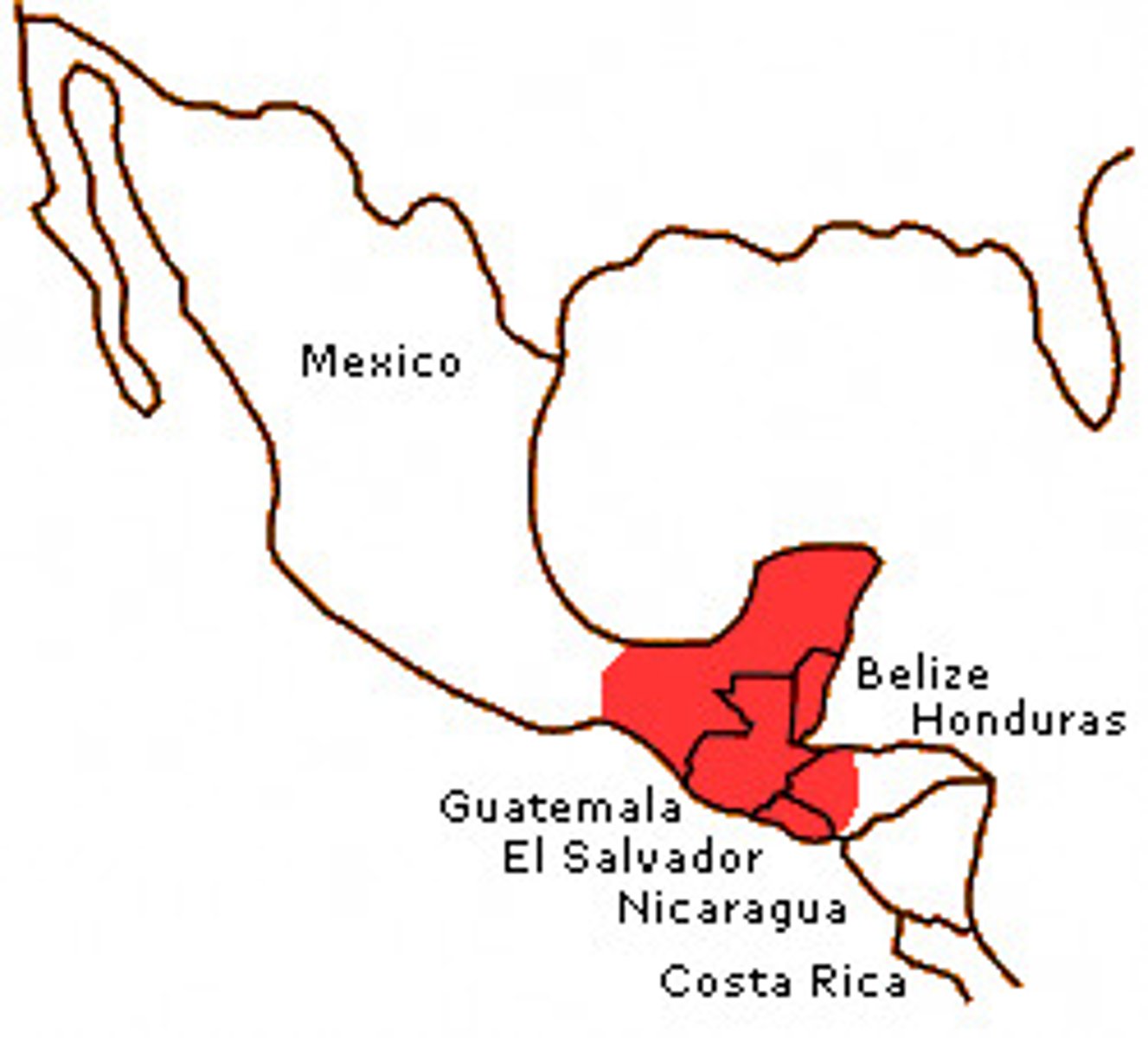
Maya
Mesoamerican civilization concentrated in Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula and in Guatemala and Honduras but never unified into a single empire. Major contributions were in mathematics, astronomy, and development of the calendar.
Cahokia
The dominant center of an important Mississippi valley mound-building culture, located near present-day St. Louis, Missouri; flourished from about 900 to 1250 C.E.

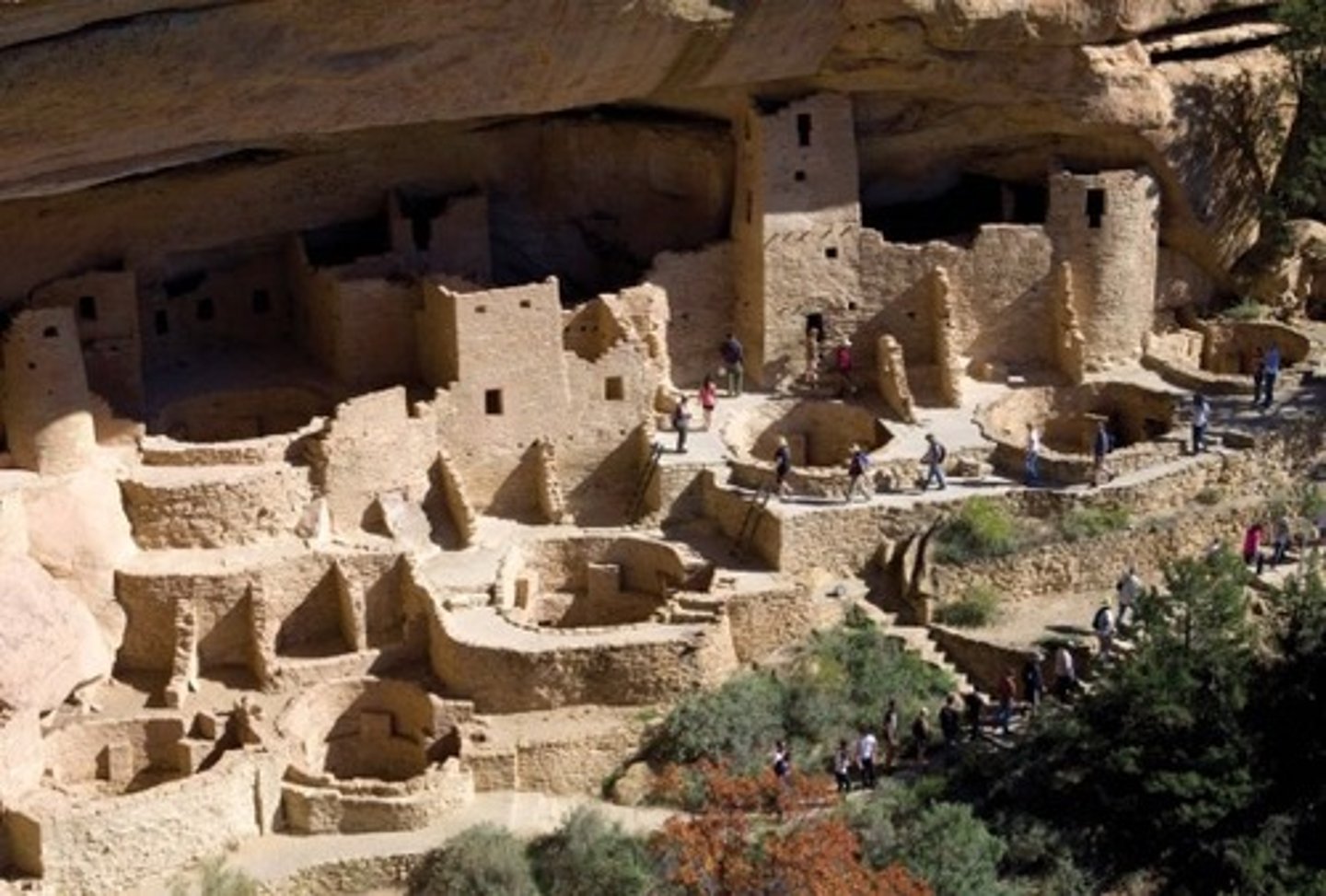
Mesa Verde
The largest complex of Anasazi cliff-dwellings in the United States Southwest, built between about AD 1150 and AD 1300

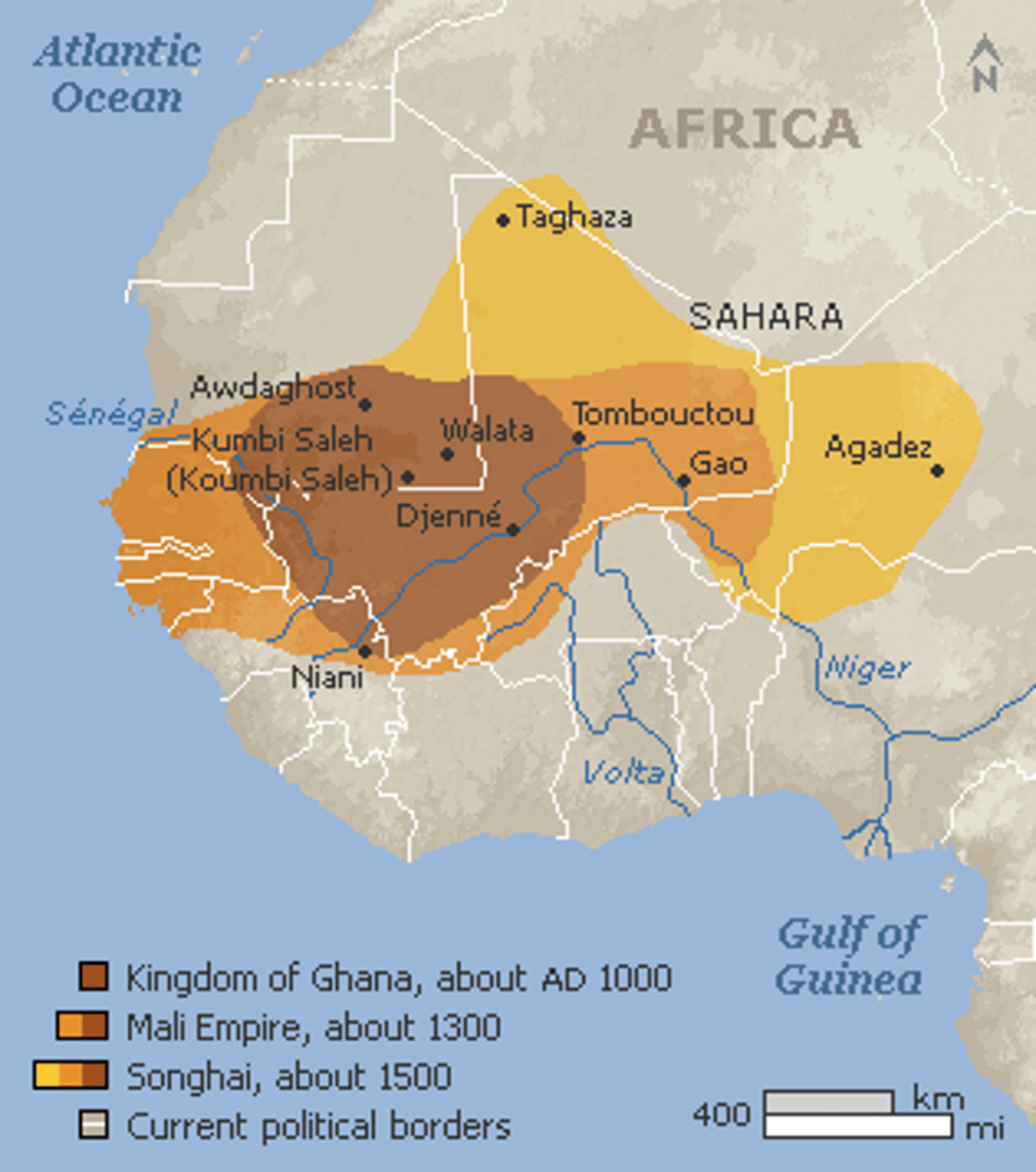
Mali Empire
From 1235-1400, this was a strong empire of Western African. With its trading cities of Timbuktu and Gao, it had many mosques and universities. The Empire was ruled by two great rulers, Sundiata and Mansa Musa. Thy upheld a strong gold-salt trade. The fall of the empire was caused by the lack of strong rulers who could govern well.
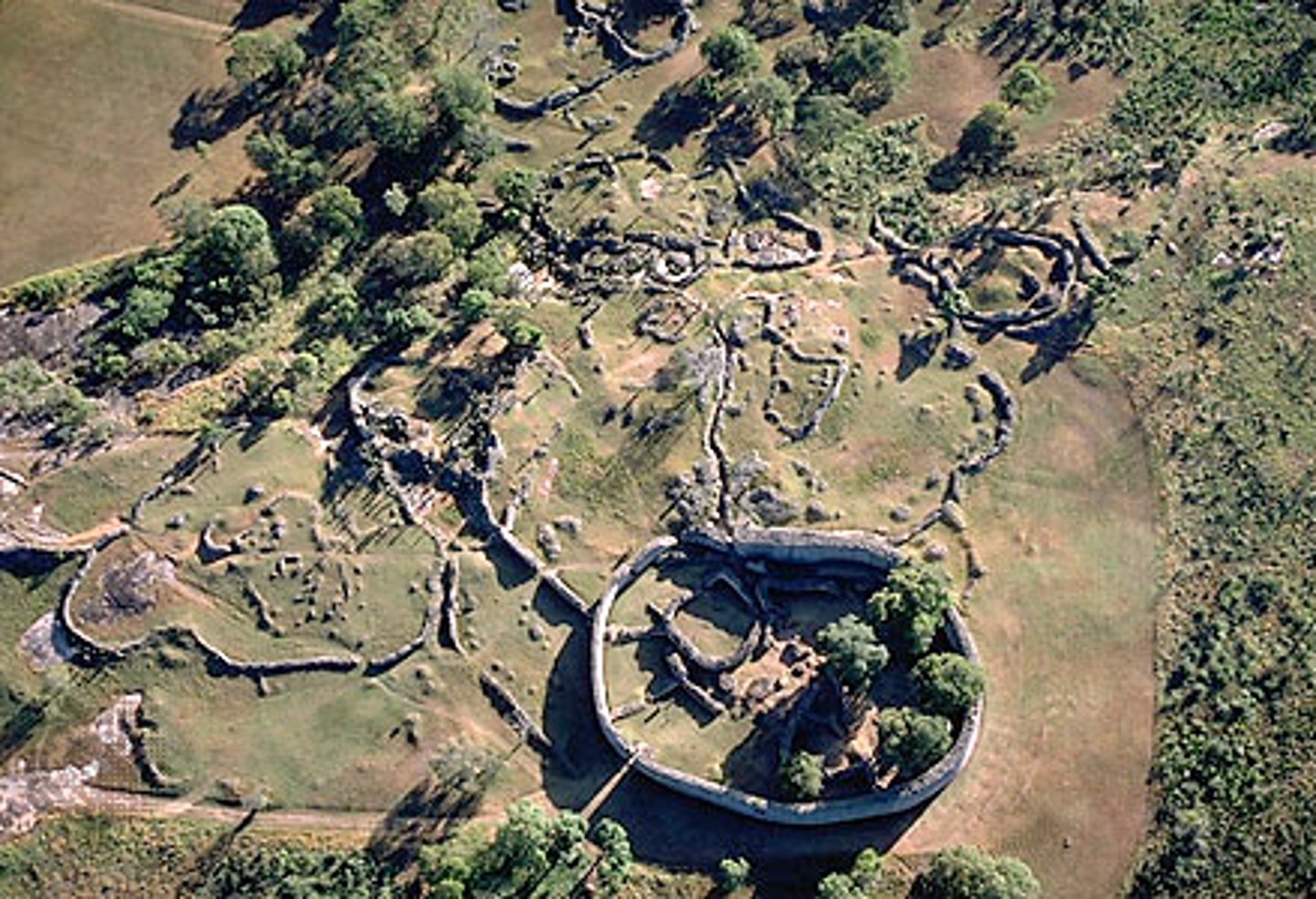
Great Zimbabwe
A powerful state in the African interior that apparently emerged from the growing trade in gold to the East African coast; flourished between 1250 and 1350 C.E.

Ethiopia
A Christian kingdom that developed in the highlands of eastern Africa under the dynasty of King Lalaibela; retained Christianity in the face of Muslim expansion elsewhere in Africa

Hausa Kingdoms
1 kingdom divided into 7 states that were connected through kinship, blood, or ethnic ties; had no main central authority but rather ruled each state separate from one another; mainly benefited economically from the trans-Saharan trade network
Griots
Professional oral historians who served as keepers of traditions and advisors to kings within the Mali Empire

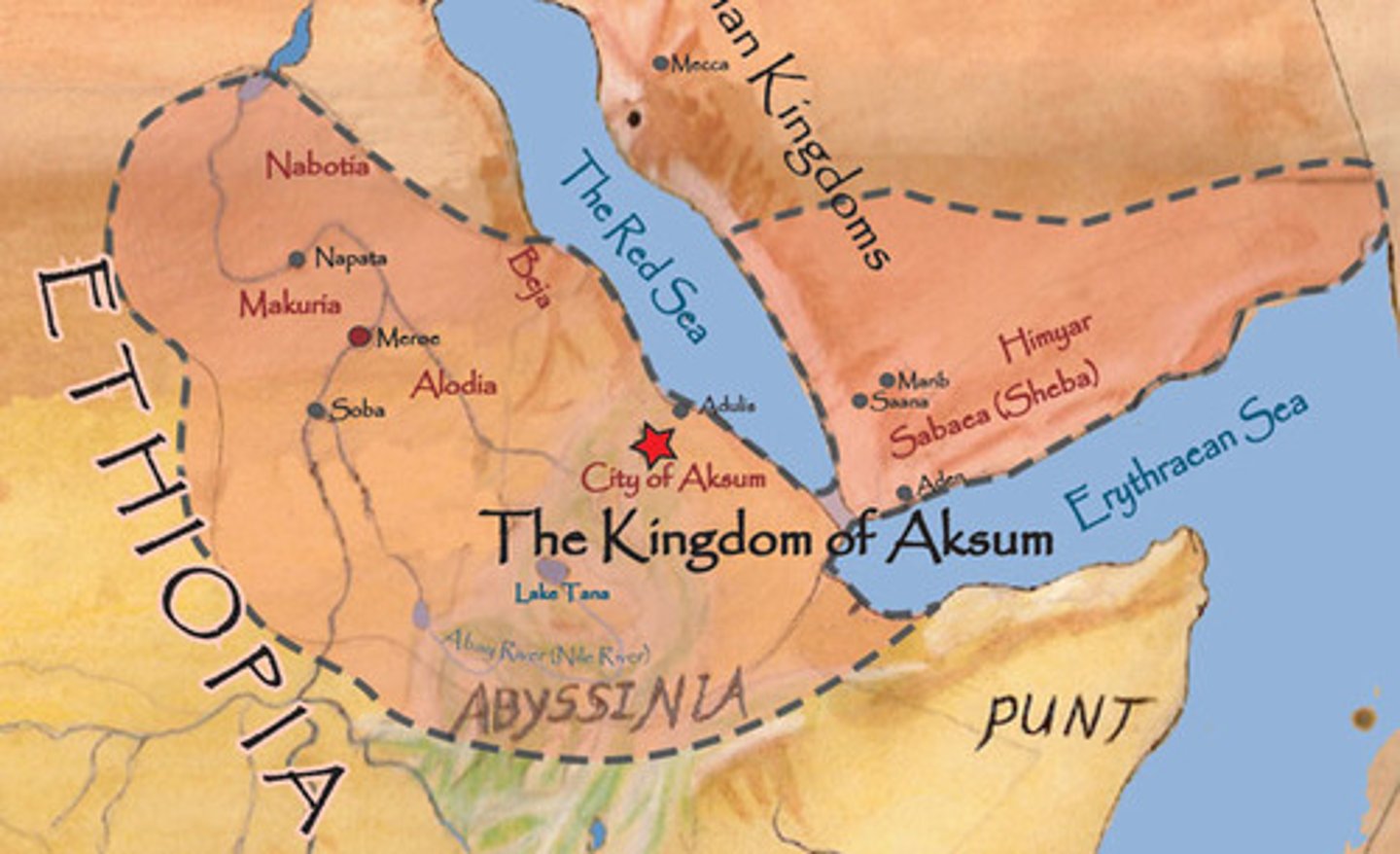
Kingdom of Axum
Founded in the highlands of northern Ethiopia, adopted Christianity, built an empire that included most of Ethiopia as well as Yemen in southern Arabia.
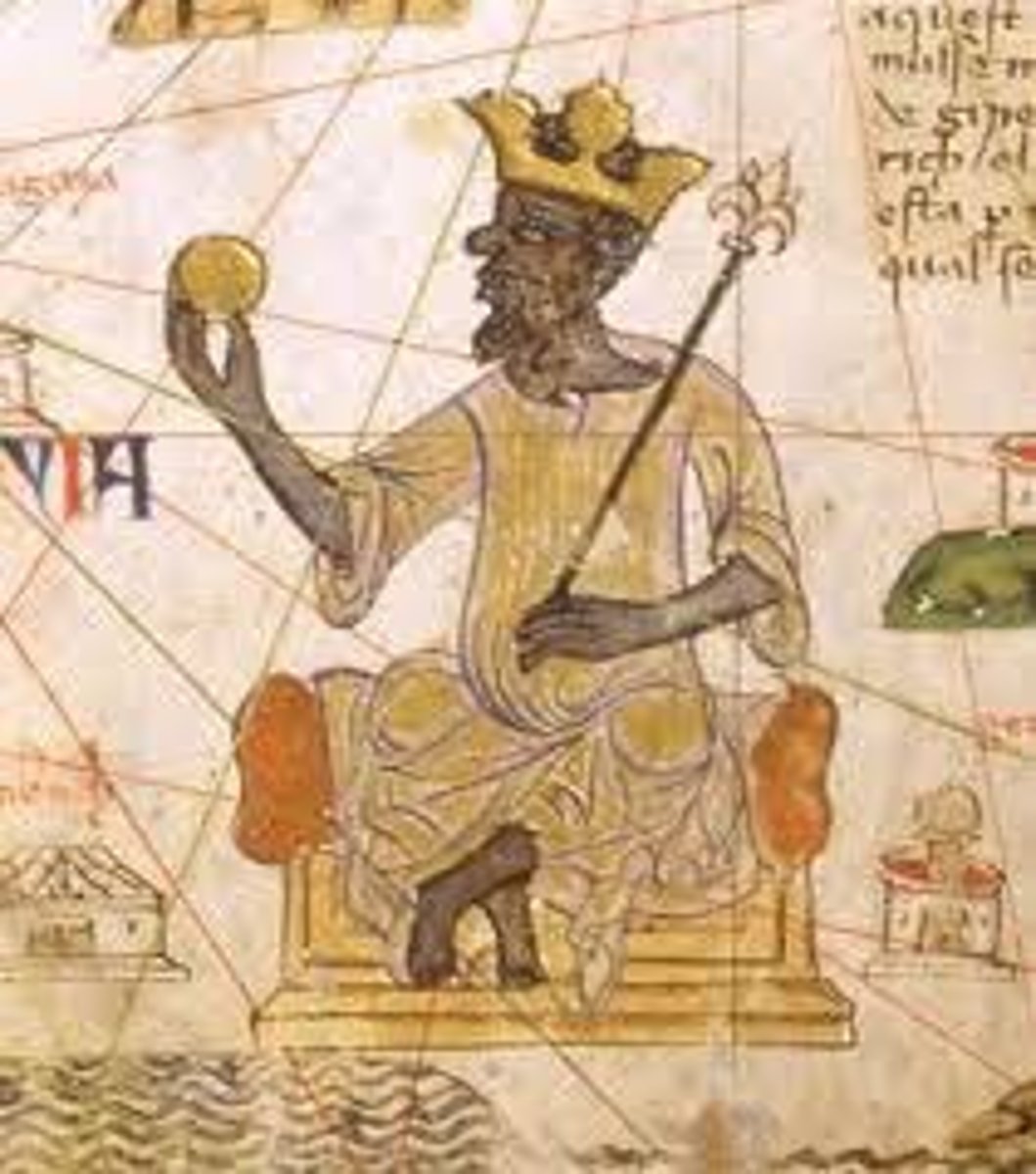
Mansa Musa
Ruler of Mali (r.1312-1337 CE) who made a hajj to Mecca; on the way there, he spread enormous amounts of gold showing the wealth of Mali; on the way back, he brought back education and Islamic culture.

Swahili
Bantu language with Arabic loanwords spoken in coastal regions of East Africa.
Swahili city-states
Waring states that were always competing for control of East Indian trade routes and each other; Many of these city-states were Muslim and very cosmopolitan.
Serfdom
A type of labor commonly used in feudal systems in which the laborers work the land in return for protection but they are bound to the land and are not allowed to leave or to peruse their a new occupation. This was common in early Medeival Europe as well as in Russia until the mid 19th century.
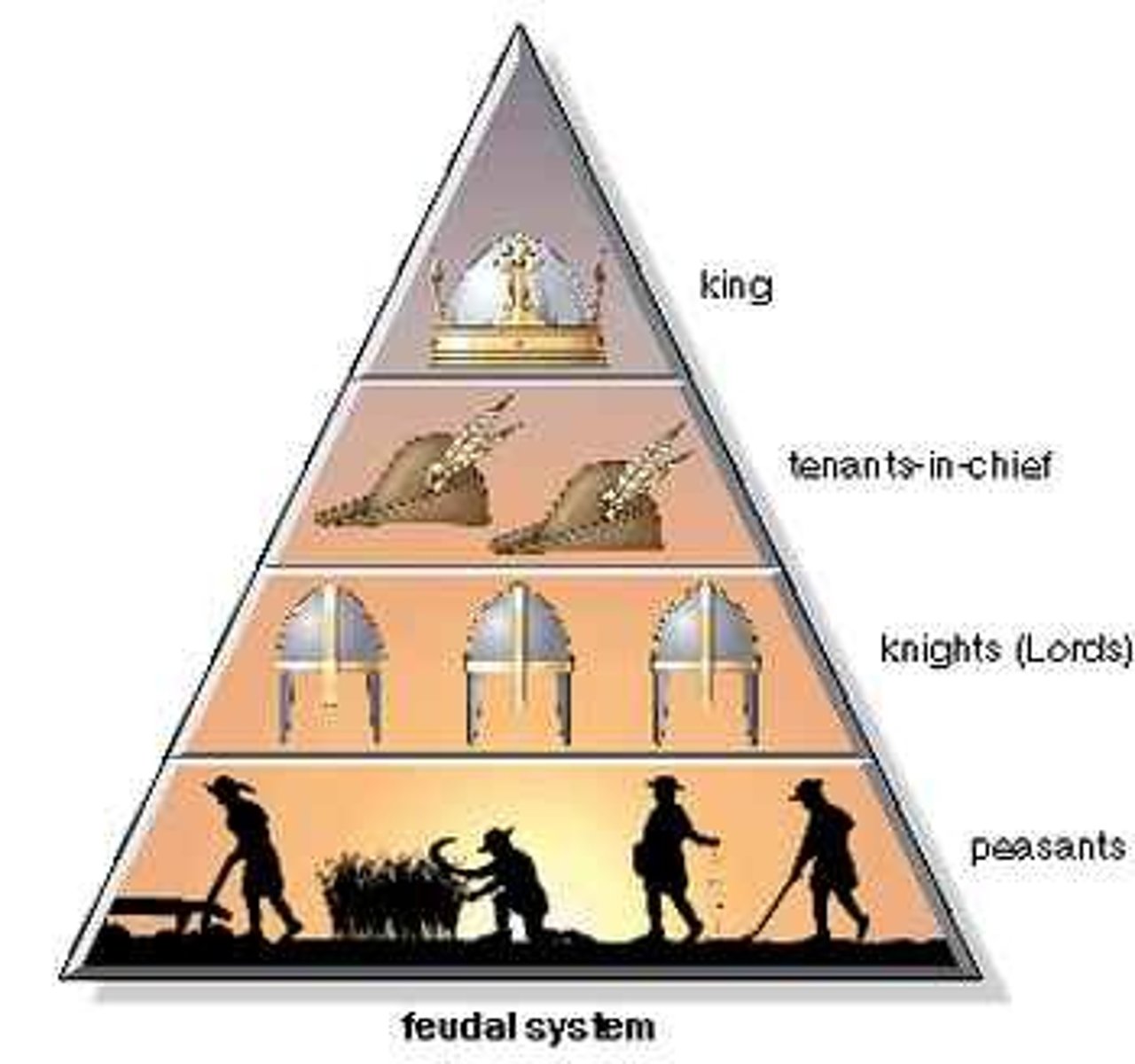
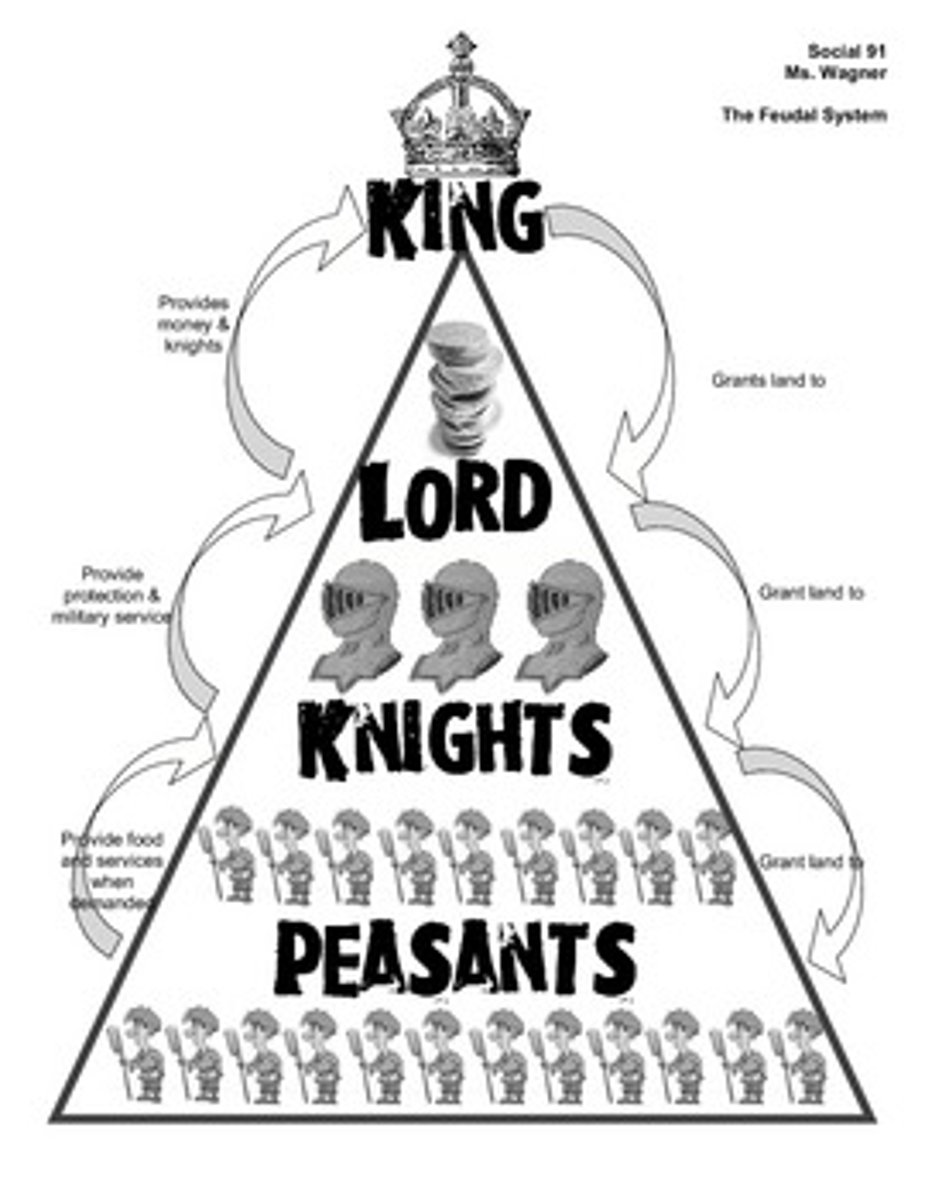
Feudalism
the dominant social system in medieval Europe, in which the nobility held lands from the Crown in exchange for military service, and vassals were in turn tenants of the nobles, while the peasants (villeins or serfs) were obliged to live on their lord's land and give him homage, labor, and a share of the produce, notionally in exchange for military protection.
Bubonic Plague (Black Death)
Deadly disease that spread across Asia, north Africa, & Europe in the mid-14th century, killing millions of people (1/3 of European population); Spread through trade, conquest, uncleanliness
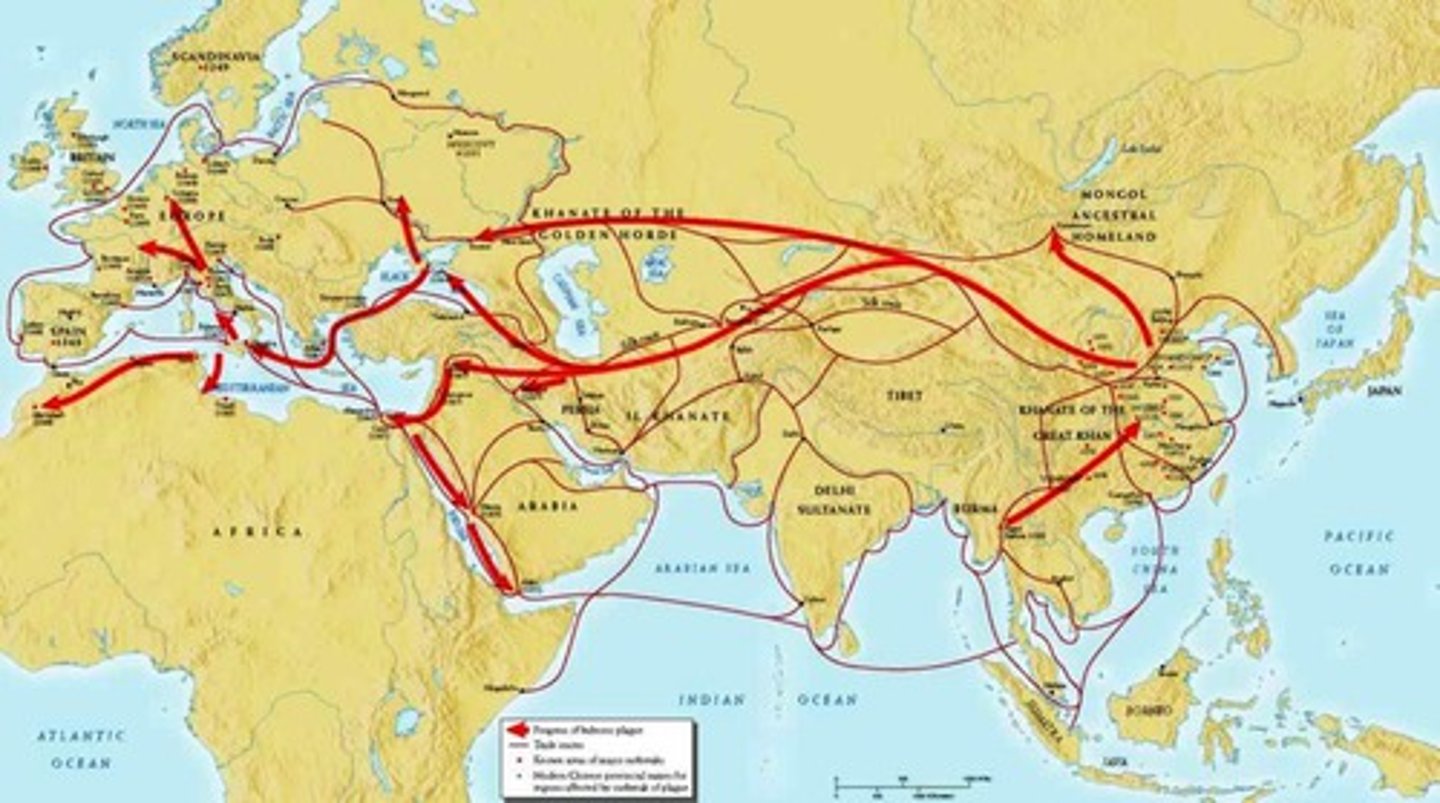
Decentralization
Degree to which decision-making authority is given to lower levels in the political hierarchy.
Manorial System
self sufficient, economic structure that is the relationship b/w the Lord and the peasants or serfs who produced all the necessary goods to keep the manor running
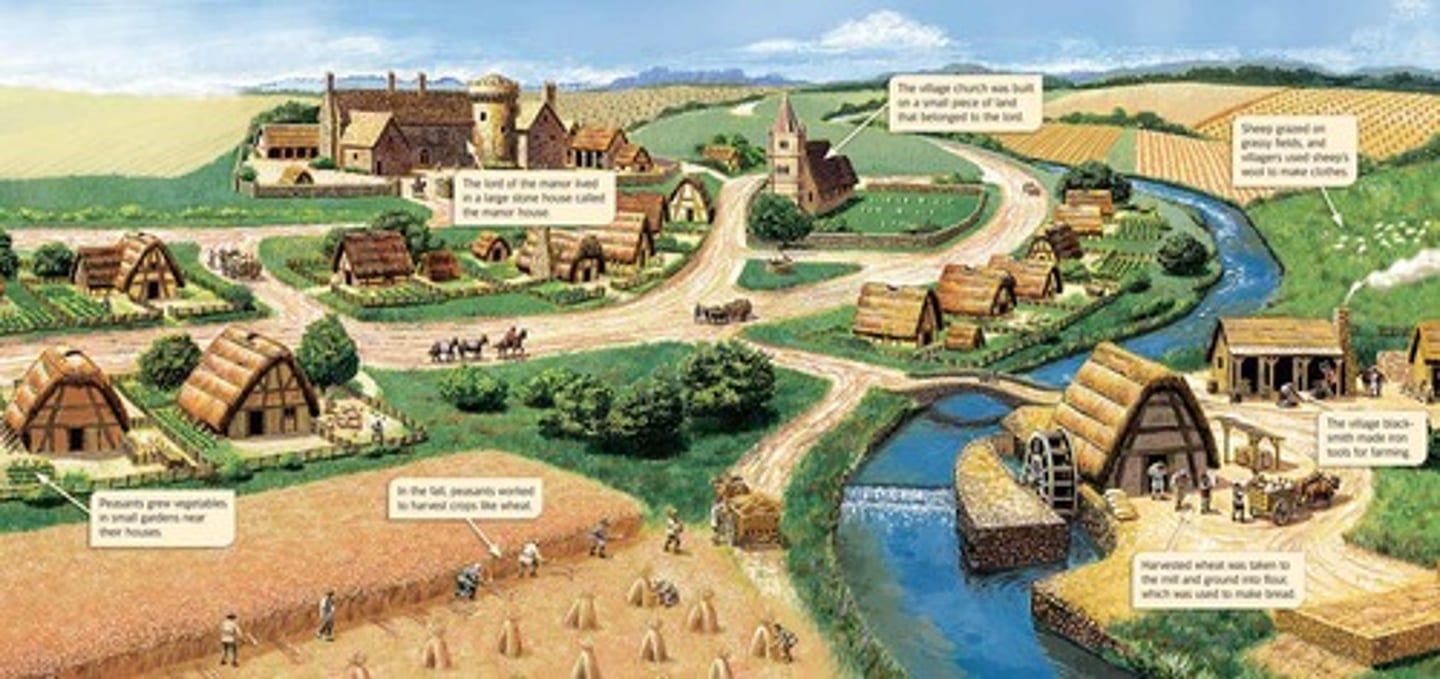
Legitimacy
Source of political authority; often conferred by law, heredity, or the people