Lesson 1.1 (REVIEW OF IMPORTANT CONCEPTS) Introduction to Pharmaceutical and Medicinal Organic Chemistry
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Alkene
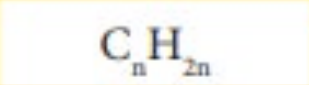
Alkyne
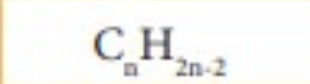
Alkyl Halide

Alkyl Halide
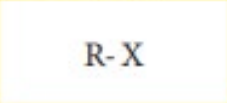
Alcohol
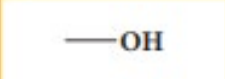
Alcohol
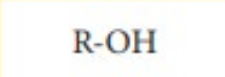
Ether
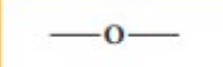
Ether

Aldehyde
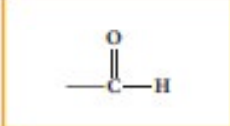
Aldehyde

Ketone
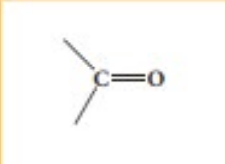
Ketone
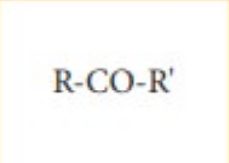
Carboxylic Acid
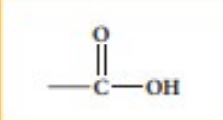
Carboxylic Acid
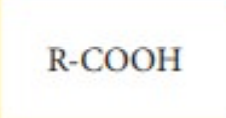
Ester
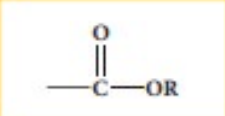
Ester

Acid Anhydride
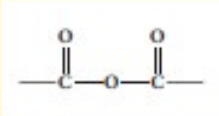
Acid Anhydride
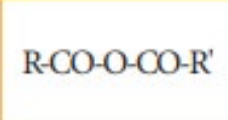
Acyl halide
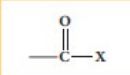
Acyl halide
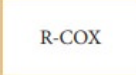
Sulphonic acid
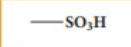
Sulphonic acid

nitro alkane
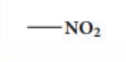
nitro alkane
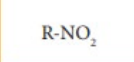
amine
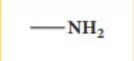
amine
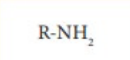
amide
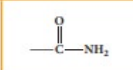
amide
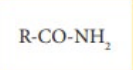
Open-chain
not cyclic or linear structures
Cyclic
ring structure
monocyclic, bicyclic, etc.
classification of cyclic based on # of rings
Homocyclic and Heterocyclic
classification of cyclic based on ring atoms
oxo
means oxygen
aza
means nitrogen
thia
means sulfur
Phenol
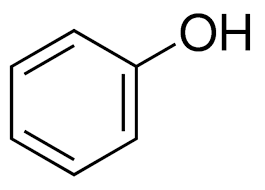
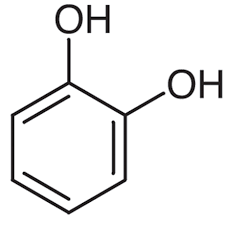
Catechol
IV preparations
Catechol is a benzene derivative that is used for _____________
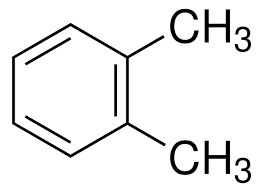
Xylene
can be ortho, meta, para
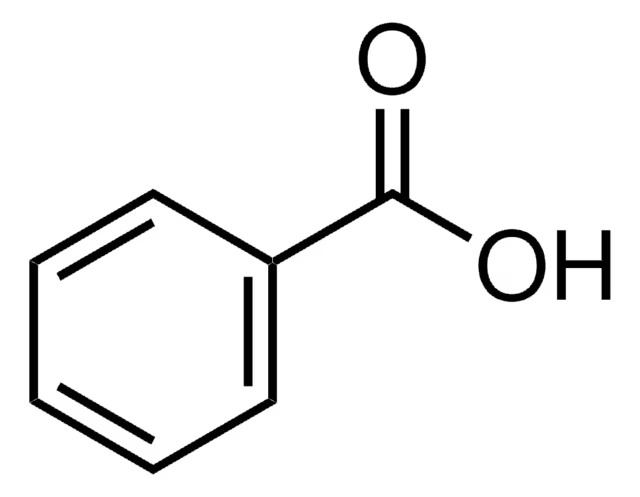
Benzoic Acid
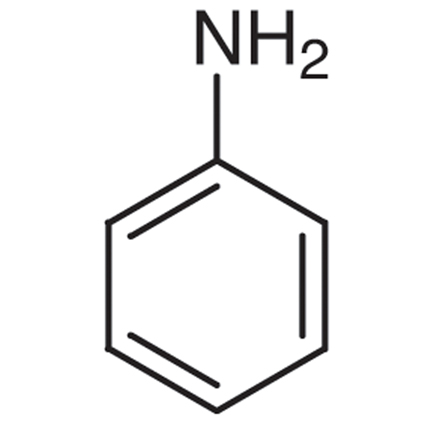
Aniline
Resorcinol
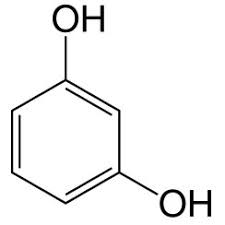
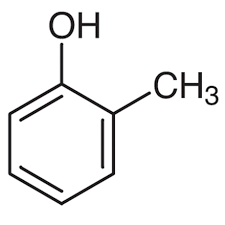
Cresol
can be ortho, meta, para
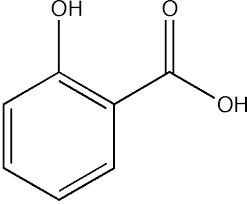
Salicylic Acid
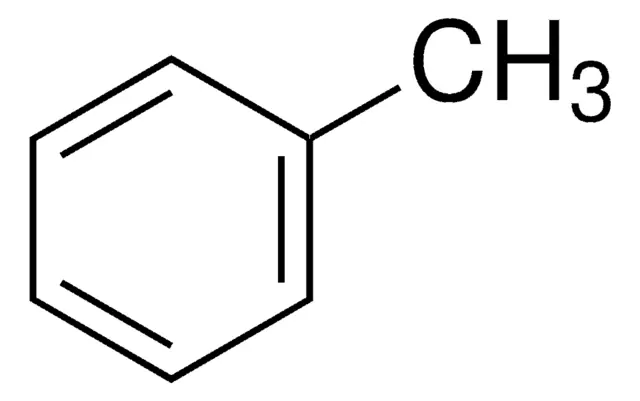
Toluene
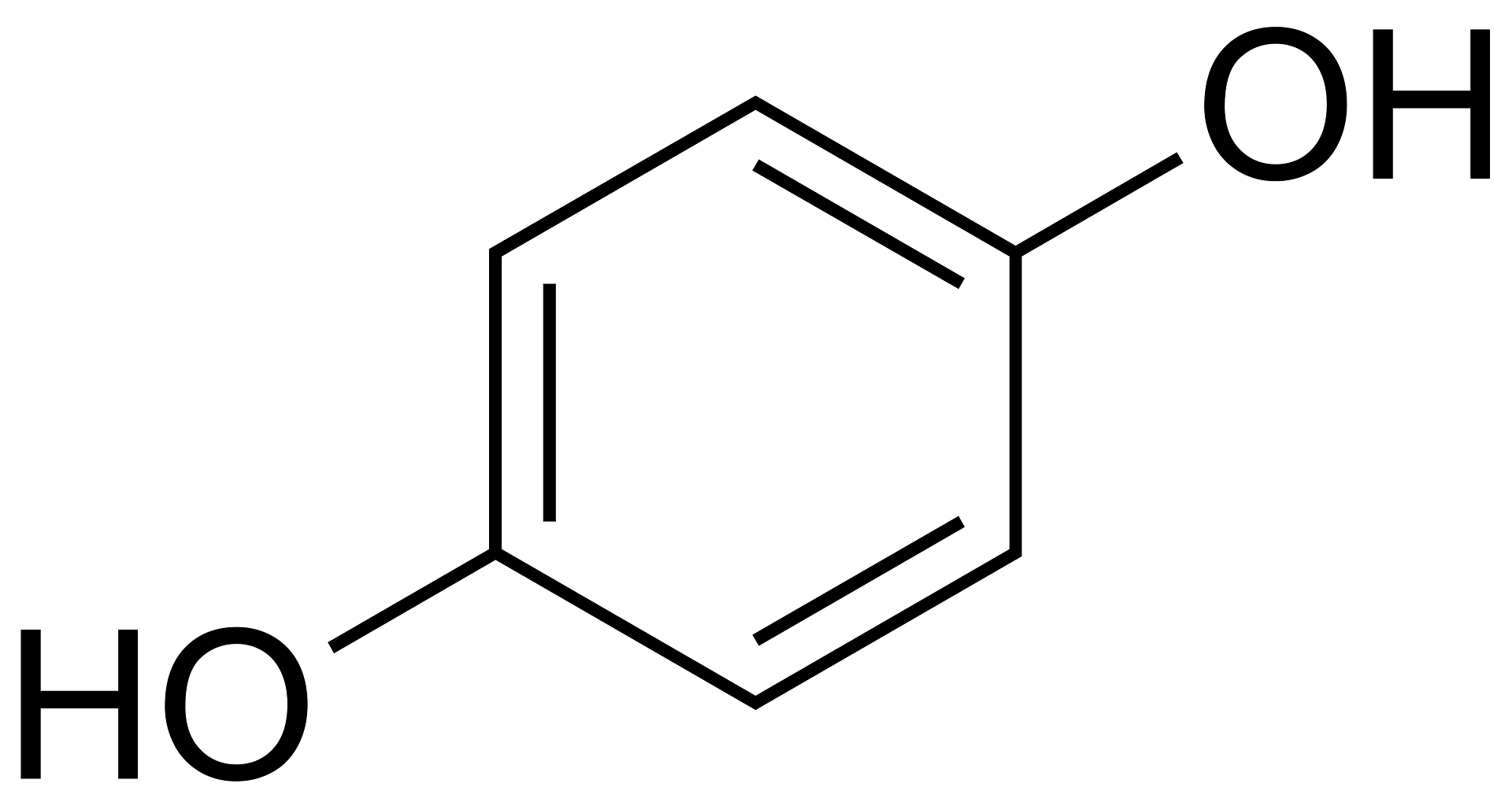
Hydroquinone
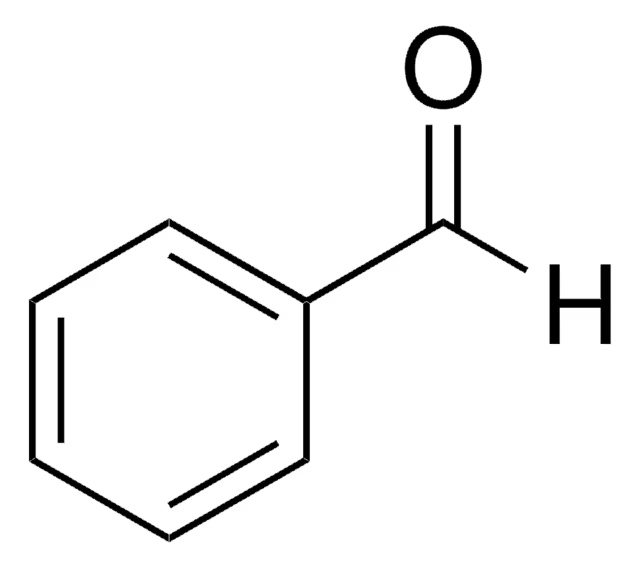
benzaldehyde
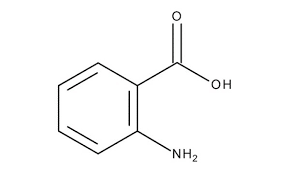
Anthranilic Acid
mefenamic acid
______________ has anthranilic acid as its structure
Anthracene
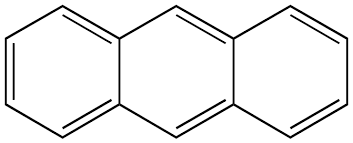
linear three fused rings (tricyclic)
structure of anthracene
Phenanthrene
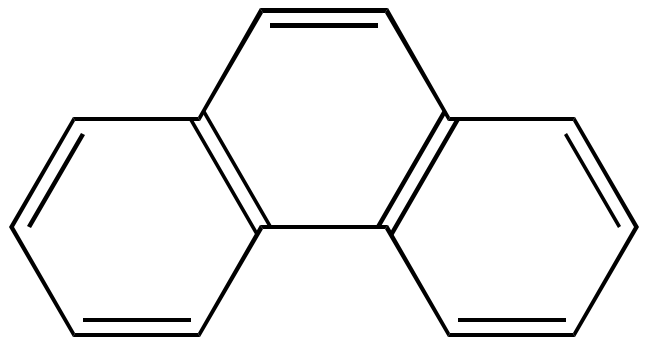
non-linear three fused rings (tricyclic)
structure of phenanthrene
benzo [a] pyrene
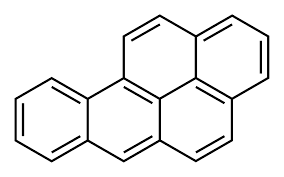
five fused rings (pentacyclic)
structure of benzo [a] pyrene
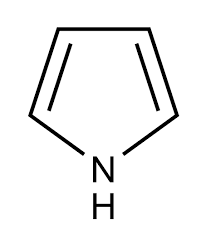
Pyrrole
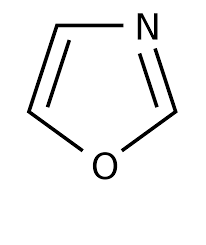
oxazole
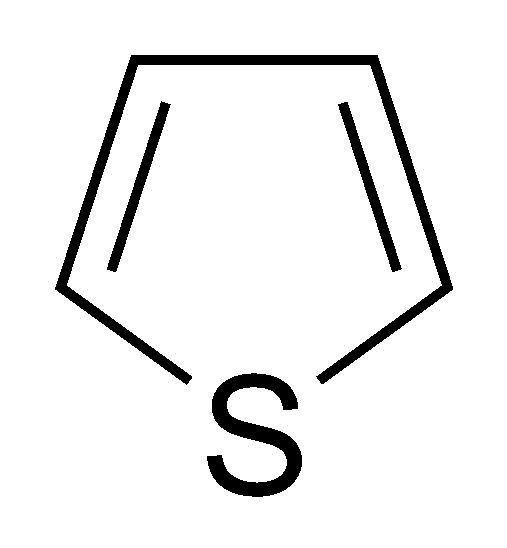
thiophene
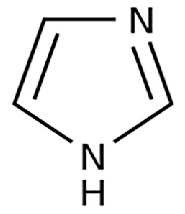
Imidazole
cimetidine
An example of Imidazole is ______________ for hyperacidity, but this one has restrictions
-ole
suffix for 2 double bonds present in a five sided figure
imidazoline
suffix for 1 double bond present in a five sided figure
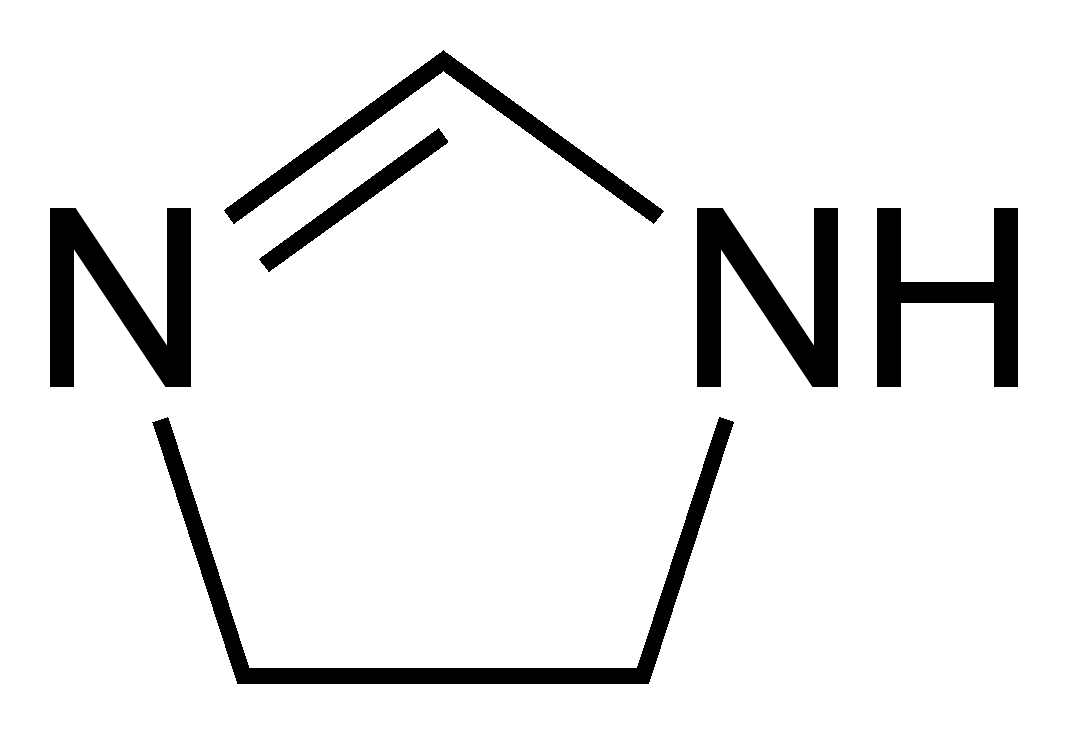
-oline
suffix for 1 double bond present in a five sided figure
imidazolidine
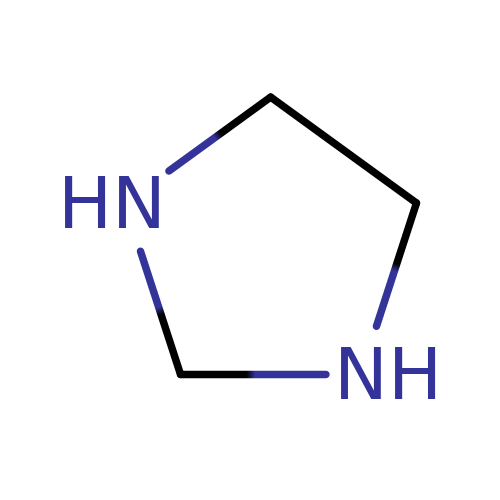
-olidine
suffix for no double bond present in a five sided figure
Furan
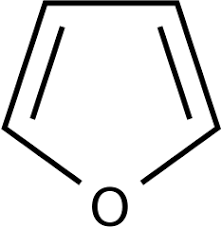
Ranitidine
An example of furan is _____________________ for acidity but there are no restrictions
Thiazole
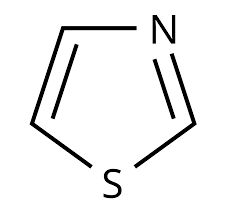
famotidine
An example of Thiazole is _______________ which is for hyperacidity, specifically for GERD or acid secretion, for nocturnal
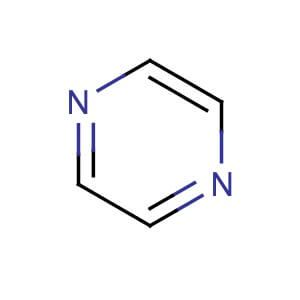
Pyrazine
Pyridine
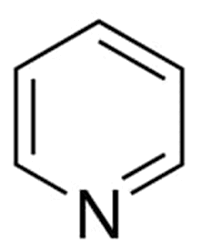
CNS Drug
Pyridine is a __________
Piperidine
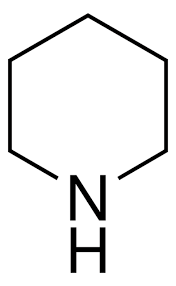
CNS Drug
Piperidine is a ____________
Piperazine
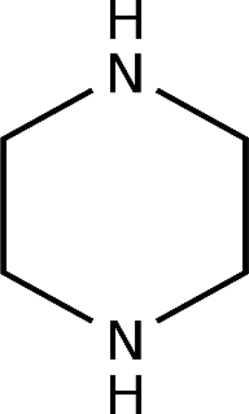
Quinoline
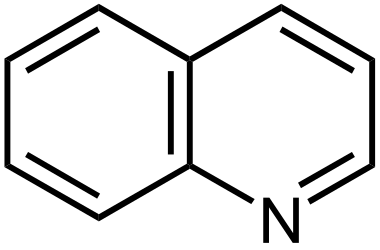
NSAID drugs
Quinoline is a __________
Indole
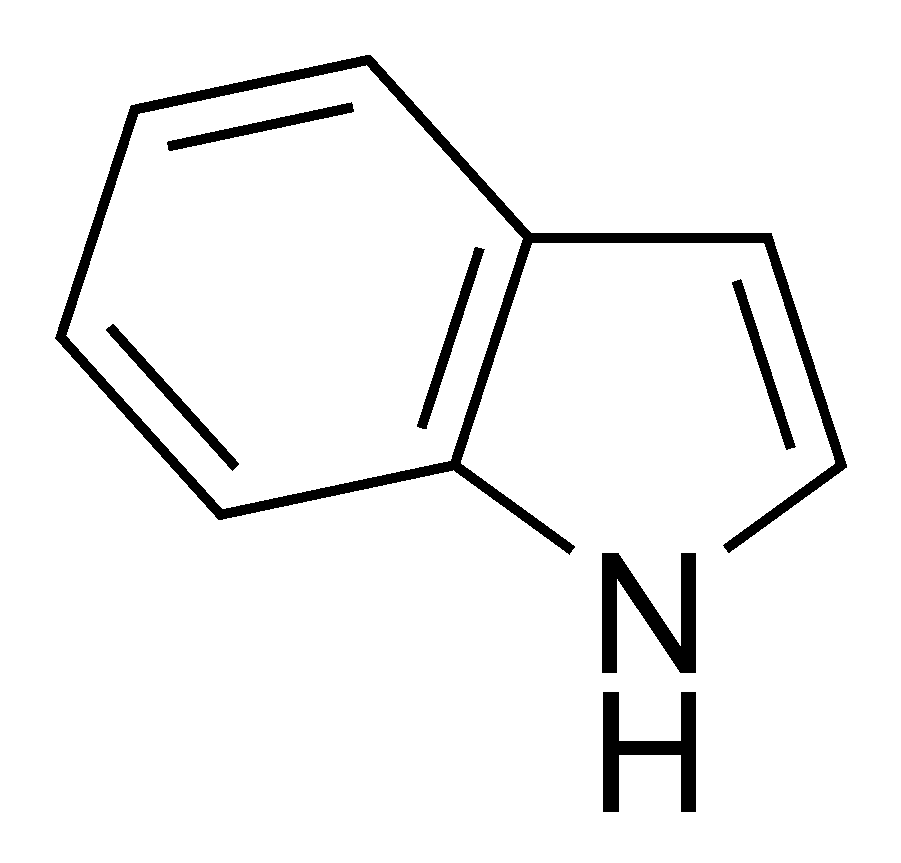
NSAID drugs
Indole is a __________
Isoquinoline
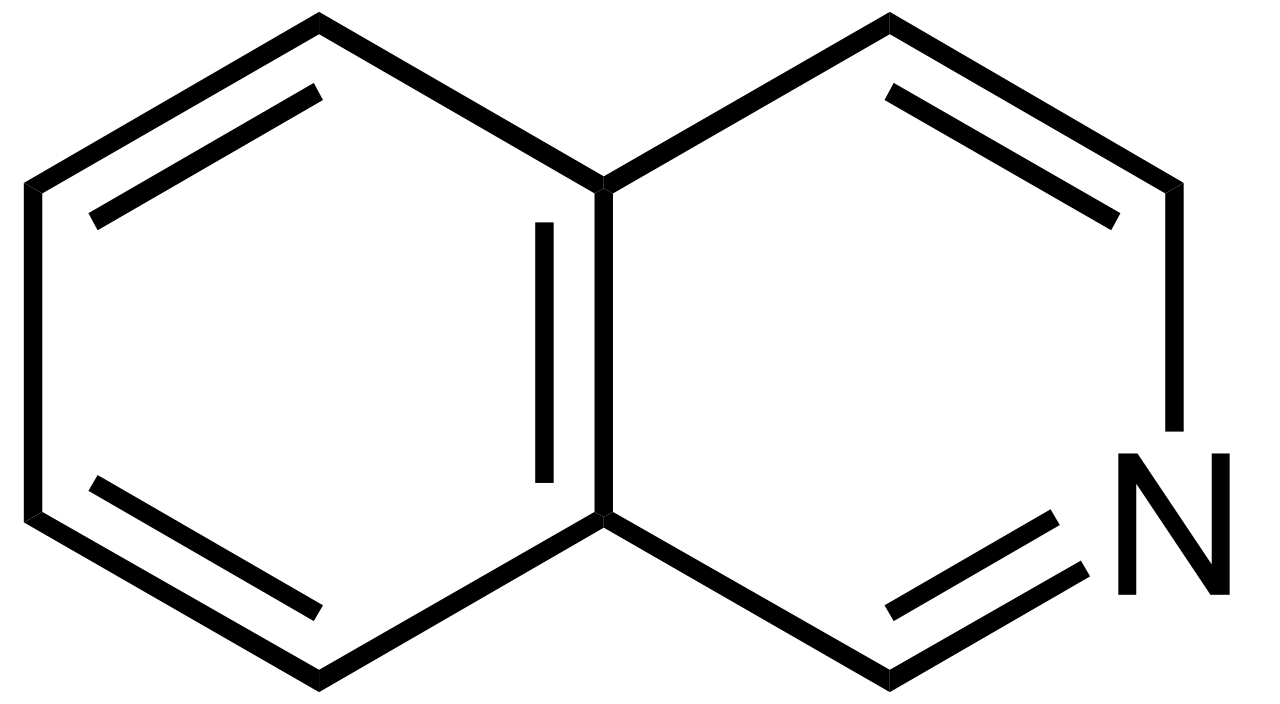
NSAID drugs
Isoquinoline is a _________________
Purine
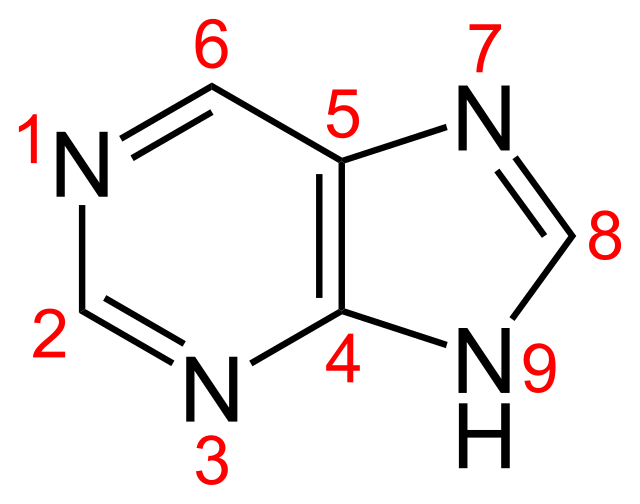
gout
Purine is used for ________
Conjugated
contains 2 or more C-C double bonds separated by single bonds (alternating)
Saturated
contains C-C bonds which are purely single bonds (sigma bonds)
Unsaturated
contains at least 1 C-C double or triple bond (sigma and pi bonds)
Alpha Carbon
carbon atom directly attached to a functional group
Vinylic/Olefinic Carbon
carbon atom directly holding a double bond
Allylic Carbon
Allylic Carbon
Benzylic Carbon
carbon atom positioned next to a benzene
ortho
1,2 patterns around a benzene ring
meta
1,3 patterns around a benzene ring
para
1,4 patterns around a benzene ring
Polarity, Solubility, and Net Dipole
plays a role in the formulation and pharmacokinetics of drugs
Polar
It is more ______________, if it contains a lot of oxygen, -OH, COOH, C=O
water
Polar is ________ soluble
topical
Polar subs are used in ____________ preparations
non-polar
It is more ______________, if it contains a lot of carbon
lipid
Non-polar subs are __________ soluble