ESCI 130 - Human Impacts
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Marine Pollution
Any harmful substance or energy put into the oceans by humans
Pollution
The presence of a substance where it should not be or at concentrations above background
Contamination
Contamination that results in adverse biological effects to resident communities.
Assimilative Capacity
The maximum amount of input of fresh water, dissolved substances, and organic matter without harming the oceans.
Main Types of Marine Pollution
Petroleum, Sewage sludge, DDT and PCBs, Mercury, Non-point-source pollution & Trash, Biological 'pollution'
Petroleum Pollution
Oil spills often from transport accidents, extraction, or loading/unloading accidents.
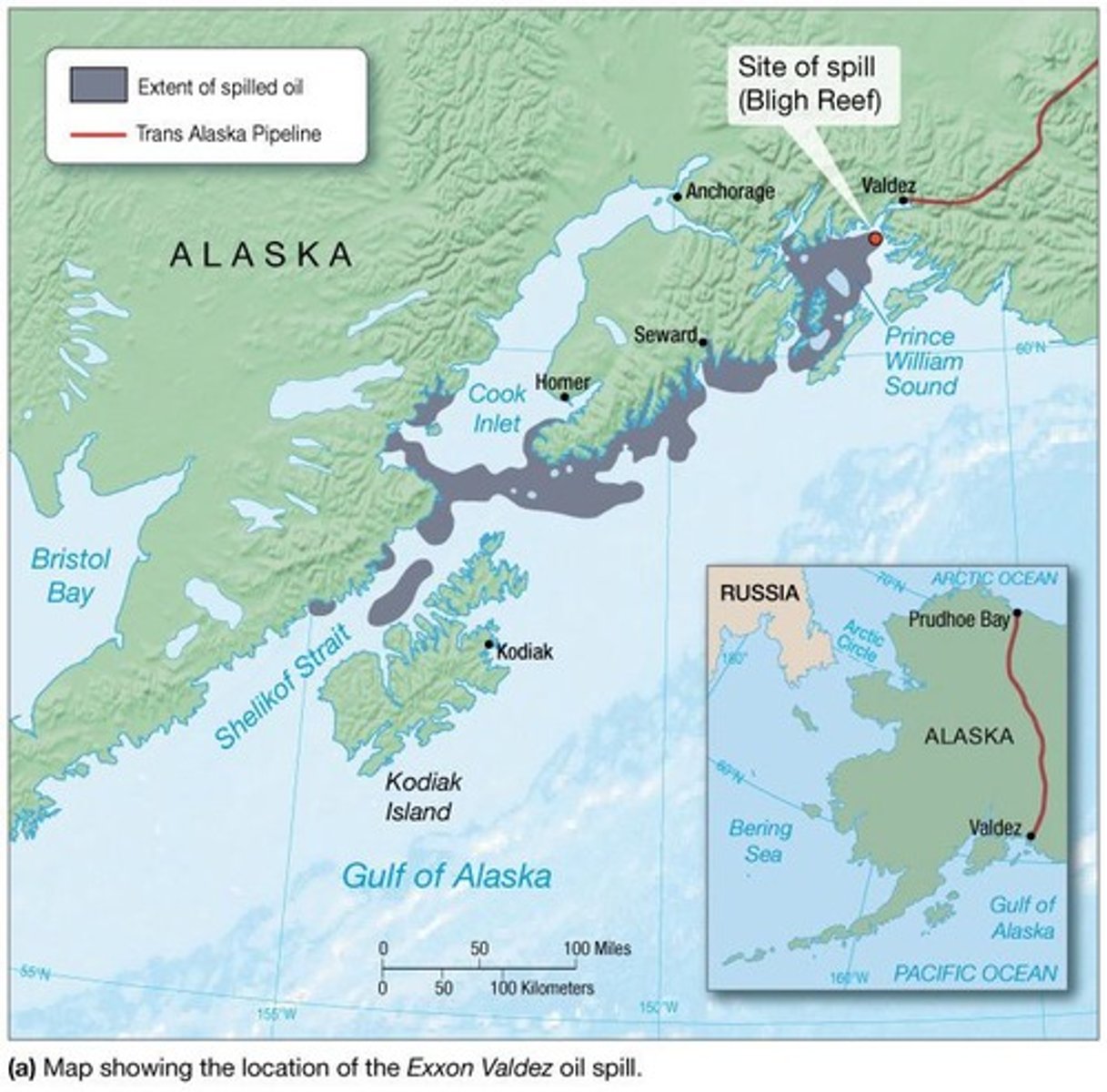
Exxon Valdez Oil Spill
On March 29, 1989, almost 44 million liters (11.6 million gallons) of oil spilled into Prince William Sound, AK.
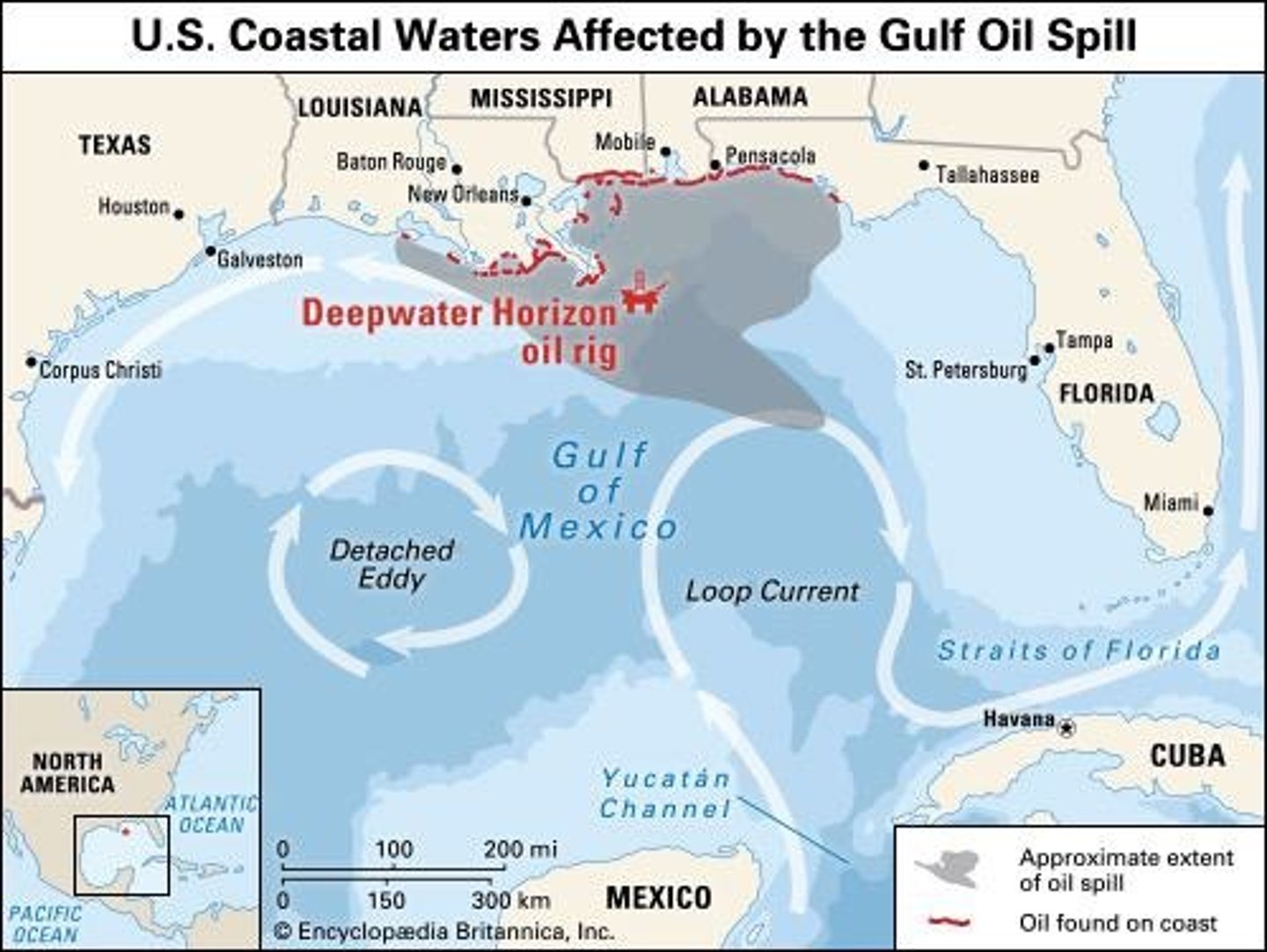
Deepwater Horizon
The world's largest accidental ocean oil spill, which spilled more than 780 million liters (206 million gallons) from April 20 to July 15, 2010.
Toxic Compounds in Petroleum
Petroleum contains various hydrocarbons and toxic compounds that can sicken humans, animals, and plants in small doses.
Long-term Impacts of Petroleum Pollution
Can change gene expression, cause developmental abnormalities, and decrease embryo survival.
Environmental Bioassay
A widely used technique for determining how particular pollutants affect marine organisms.
Drawbacks of Environmental Bioassay
Does not predict long-term effects of pollution, does not account for pollutants combining with other substances, and is time-consuming and organism-specific.
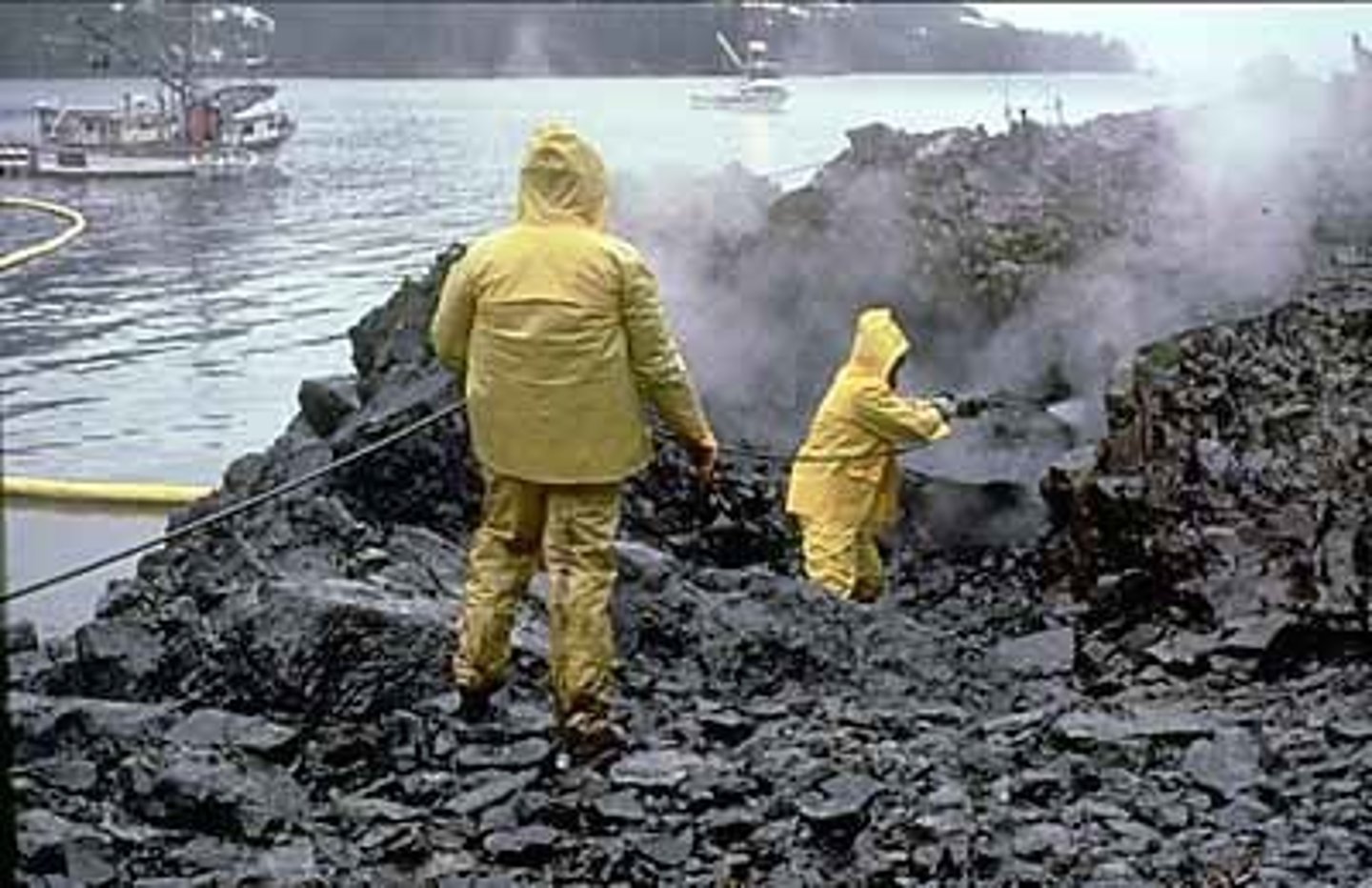
Oil Spill Cleanup Methods
Workers using high-pressure, hot-water washing to clean an oiled shoreline.

Surface Oil Decline
The amount of surface oil visible at NOAA's study sites in Prince William Sound followed a decline in the years after the Exxon Valdez spill (1989 to 1997).
Oil Spill Consequences
Many animals, including birds and otters, were killed outright, and long-term consequences remain unknown.
Hydrocarbons
Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon found in petroleum.
Biodegradability of Petroleum
Petroleum is organic and can be biodegraded.
Oil Spill Dates
Deepwater Horizon spill date was from April 20 to July 15, 2010, with the well officially sealed on September 19, 2010.
Petroleum Pollution Sources
Includes oil spills from transport accidents, extraction, and loading/unloading accidents.
Biological Pollution
Refers to the introduction of invasive species or pathogens into marine environments.
Mercury Pollution
A type of marine pollution that poses risks to marine life and human health.
BP Oil Spill
An environmental disaster that killed 11 people and devastated the coast.
Oil Pollution Act of 1990
Legislation that barred single-hulled tankers from U.S. ports and restricted their operation near France and Spain.
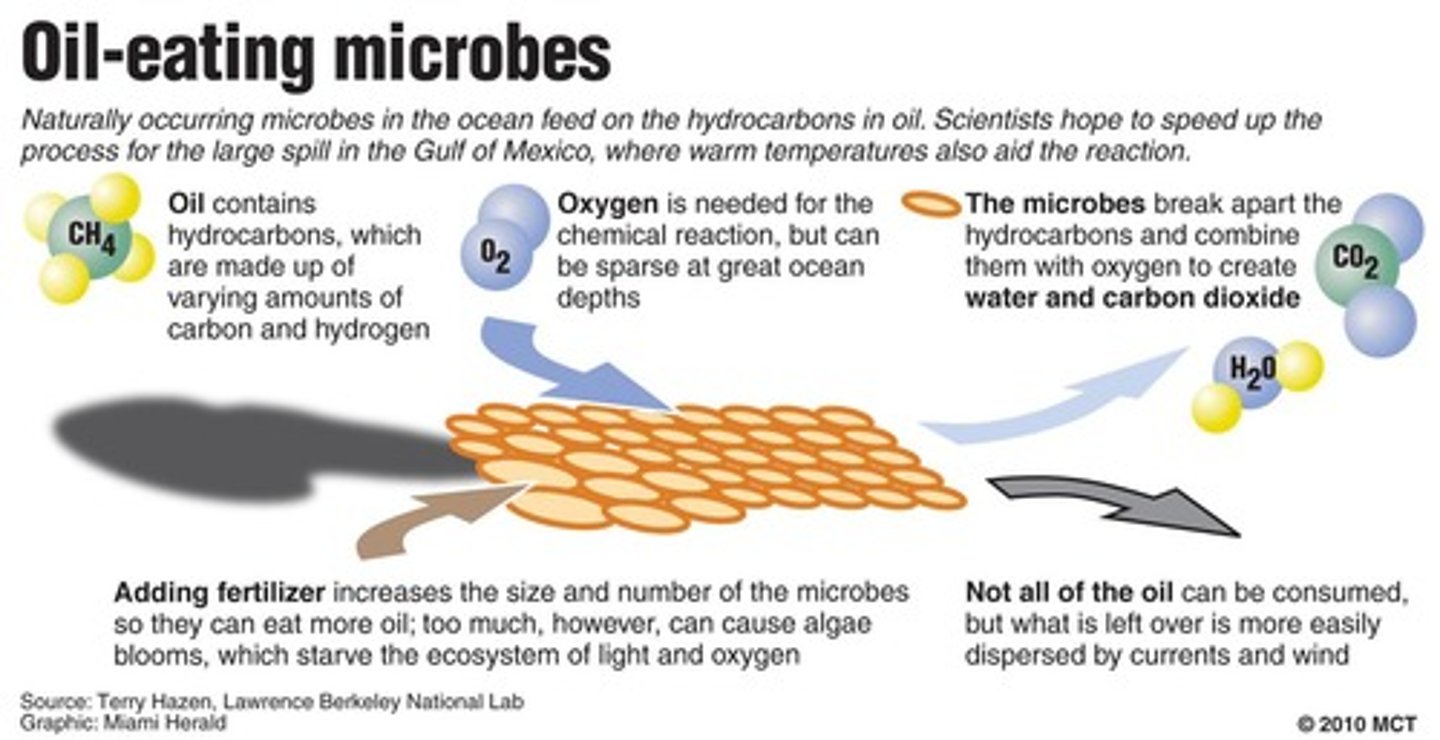
Bioremediation
A cleanup method that uses microorganisms to break down pollutants.
Sewage Sludge
A semisolid byproduct of sewage treatment containing human waste and various chemicals.
Clean Water Act, 1972
Legislation that prohibited the dumping of sewage sludge in the ocean after 1981.
New York's Sewage Sludge Disposal at Sea
A project that initially used shallow-water sites for sludge disposal, later moving to deeper-water sites.
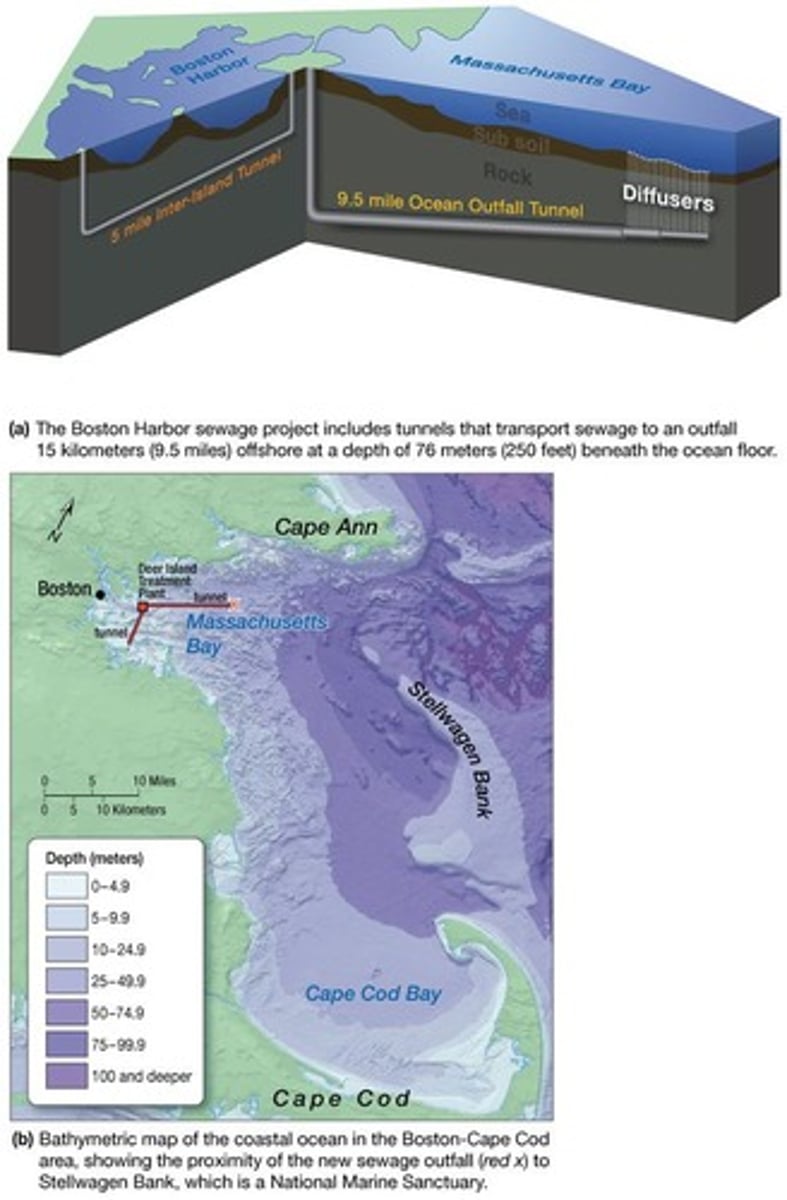
Boston Harbor Sewage Project
A court-ordered cleanup project for Boston Harbor that involved treating sewage and releasing it into deep water.
DDT
A pesticide that caused a decline in bird populations and was banned in the U.S. in 1972.
PCBs
Industrial chemicals that are toxic, have a long life in seawater, and accumulate in fatty tissues.
Thin eggshells
A consequence of DDT exposure leading to reduced bird populations.
Long Island osprey
A bird species affected by DDT, leading to population decline.
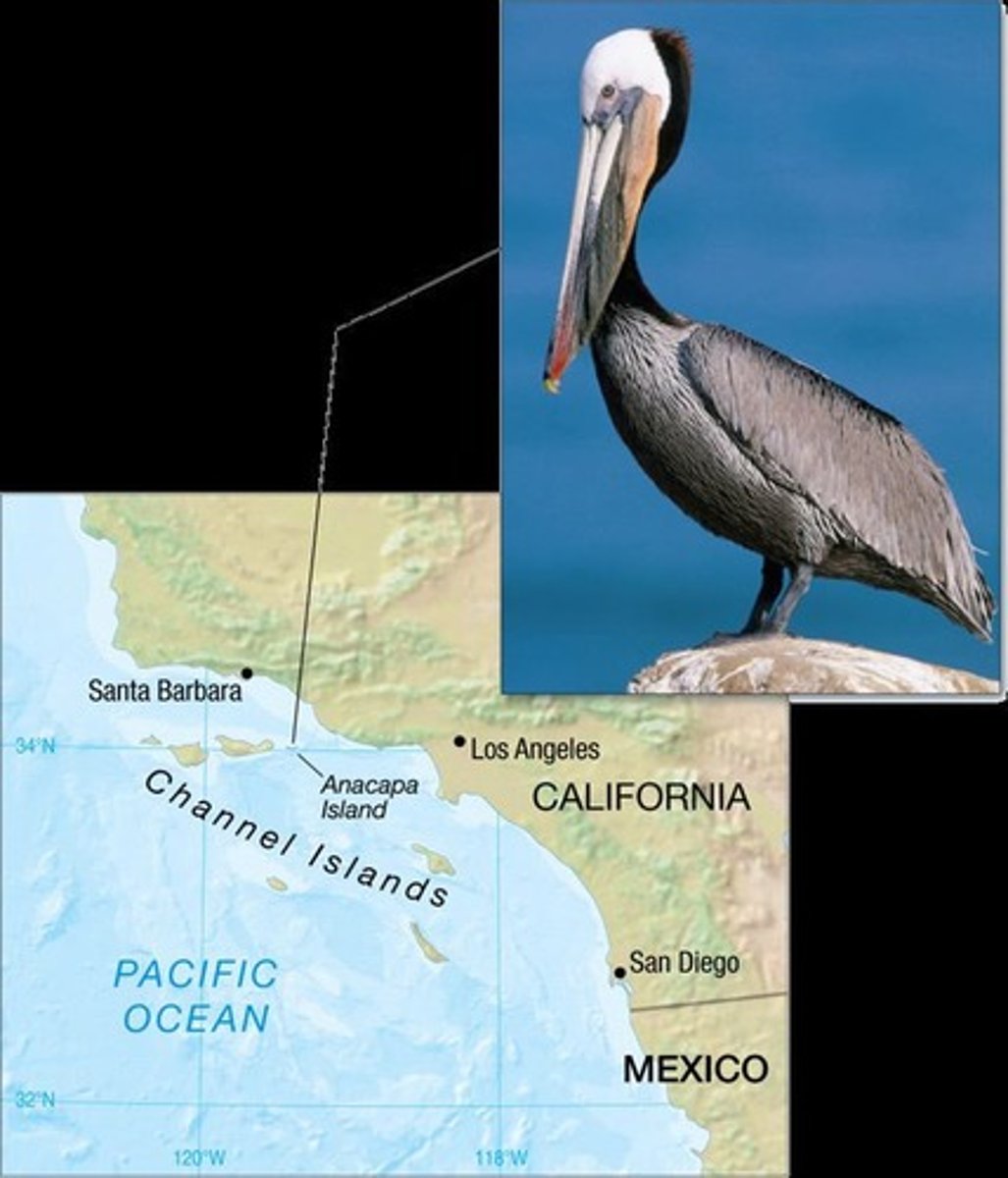
California brown pelican
A bird species that experienced population decline due to DDT.
Accumulation in food chain
The process by which toxic substances like DDT and PCBs build up in organisms at different trophic levels.
DO NOT EAT Fish
White Croaker, Barracuda, Black Croaker, Barred Sand Bass, and Topsmelt due to contamination from DDT, PCB, and mercury.
Adverse effects on fish
Negative impacts on fish populations due to sewage sludge disposal.
Bacteria counts during wet weather
A measure indicating the level of bacteria in water, with lower counts being preferable.
Oil initially floats
The physical property of oil that allows it to remain on the surface of water.
Oil and water mix to form mousse
A phenomenon where oil combines with water to create a thick, foamy substance.
Redesigning ships
An approach to improve tanker safety and reduce oil spills.
Single-hulled tankers
Vessels that are barred from U.S. ports due to safety concerns.
Double-hulled tankers
Safer vessels designed to prevent oil spills.
Methyl mercury
Toxic to most living organisms; released by a chemical plant in Minamata Bay, Japan, in 1938; first reported ecological changes in 1950.
Minamata Disease
Neurological disorder caused by mercury poisoning.
Safe levels of mercury
Determined by the rate of fish consumption by people, mercury concentration in fish consumed, and minimum ingestion rate of mercury to cause damages.
Non-point-source pollution
Pollution that enters the ocean from multiple sources, making it difficult to pinpoint origin.
Marine debris
Vast majority of marine debris is plastics; 80% of marine debris from land sources.
Plastics
Entangle fish, marine mammals, and birds; plastic bags choke turtles mistaking them for jellyfish.
Nurdles
Small pre-production plastic pellets found in the ocean and all beaches due to spillage.
Microbeads
Plastics between 1 and 5 millimeters (0.04 and 0.2 inches) that transport pollutants and are eaten by fish.
Laws Regarding Ocean Dumping
In 1988, the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL) proposed a treaty banning disposal of plastics and regulating other trash dumping at sea.
Non-Native Species
Originate elsewhere, introduced by humans intentionally or accidentally; outcompete and dominate native populations.
Invasive species
Cause extensive damage annually; have invaded the Great Lakes of North America and altered the ecology of freshwater lakes and streams.
Mare Liberum
Free sea; assumed fish supply to be inexhaustible.
Territorial sea
De Dominio Maris - 1702; every country has ownership over a 3-mile territorial limit from shore.
United Nations Conference on the Law of the Sea
First Meeting: 1958, Geneva, Switzerland; controls prospecting and mineral mining on the continental shelf under the control of the country owning nearest land.
Marine plastic particles
Increasing significantly; regions of floating trash are evident.
Ecological changes
First reported in 1950 due to mercury pollution.
Trash
Includes pesticides and fertilizers, road oil; washed down storm drains to ocean.
Floating plastics
Break into smaller pieces, contributing to marine debris.
Chemical plant in Minamata Bay
Released mercury in 1938, leading to significant ecological and health impacts.
Plastic pollution
Includes various forms of plastic waste, which are harmful to marine life.
Convention on the Territorial Sea and Contiguous Zone
(1964)
Convention on the Continental Shelf
entry into force (1964)
Convention on the High Seas
(1962)
Convention on Fishing and Conservation of Living Resources of the High Seas
(1966)
Baseline
is drawn between the outermost points of the outermost islands
Maritime Zones
from mean low tide line inland
Extension of land
out to the edge of the continental shelf or 200 km, whichever is greater
1994 Agreement
Eliminate production controls on sea floor mining
Overfishing
harvesting too much marine life at a rate that is greater than the reproductive rate
Causes of Overfishing
Efforts in the mid 1900s to increase the availability and affordability of protein-rich foods caused an increase in fishing hauls
Change in fishing methods
favor large catches with increased bycatch
Open access fisheries
a cause of overfishing
Poor fisheries management
a cause of overfishing
Illegal fishing
a cause of overfishing
Subsidies
a cause of overfishing
2006 study in Science
predicted that all of the world's fisheries would collapse by 2048 if no changes occurred
UN Food and Agriculture Organization Study (2006)
showed various states of fishery depletion
Overfishing of top predators
disrupts the marine ecosystem
System collapse
overfishing + pollution + climate change + habitat destruction + ocean acidification
Sustainable fisheries
what can be done to address overfishing