chemistry - separate chemistry: qualitative analysis (5.8 - 5.18)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
concentration definition
amount of solute dissolved in a stated volume of solution
5.8 calculate concentrations of solutions in mol dm-3
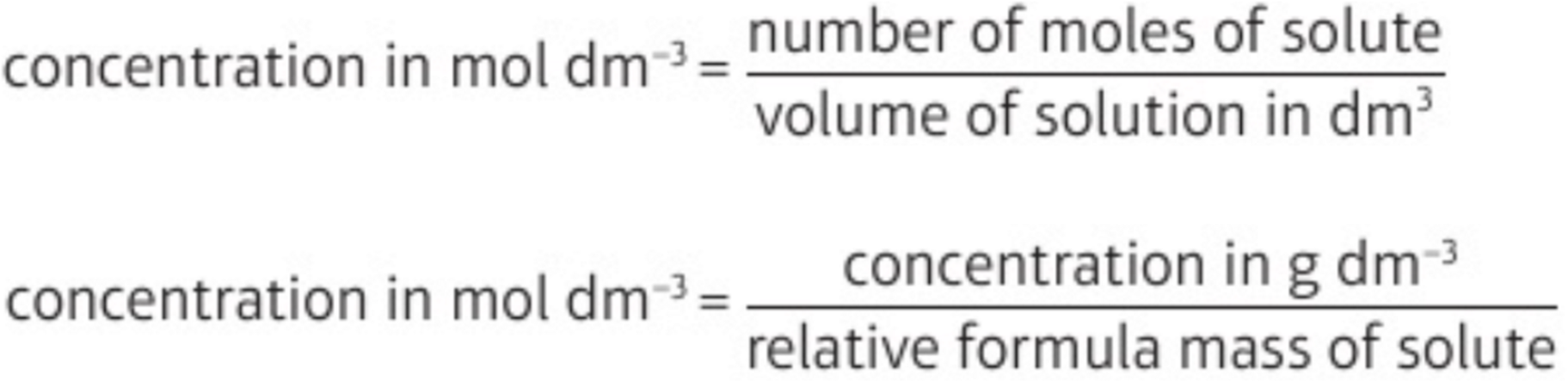
5.8 convert concentration in g dm-3 → mol dm-3 & vice versa
g dm-3 → mol dm-3: ÷ relative formula mass of solute
mol dm-3 → g dm-3: x relative formula mass of solute
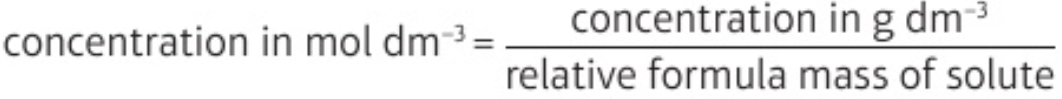
what’s the purpose of acid-alkali titrations?
find exact volume of acid that neutralises specified volume of alkali or vice versa
5.9 core practical: accurate acid-alkali titration, using burette, pipette & suitable indicator
rinse burette with hydrochloric acid
fill burette with the acid - ensure jet below tap is also full
record initial volume of acid in burette
rinse pipette with sodium hydroxide solution
fill pipette to 25cm3 mark & empty solution into conical flask
add few drops of methyl orange indicator to flask
place flask on white tile under burette
add acid to sodium hydroxide solution while swirling flask
when indicator starts to change colour, rinse tip of burette & sides of flask with small amount of distilled water from wash bottle to ensure all acid in mixture, then add acid drop by drop until end-point reached
record final volume acid in burette
repeat experiment (don’t repeat initial rinsing of burette & pipette) until concordant results obtained
5.11 percentage yield formula
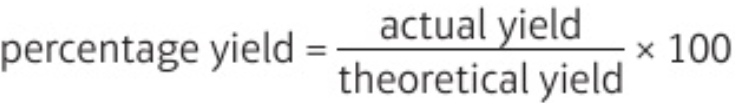
5.12 is actual yield of reaction usually less/more than theoretical yield?
actual yield usually less than theoretic yield
5.12 why is actual yield of reaction usually than theoretical yield?
incomplete reactions
practical losses during experiment
competing, unwanted reactions (side reactions)
5.13 atom economy definition
shows percentage by mass of useful products (formed by reactants)
5.14 atom economy formula
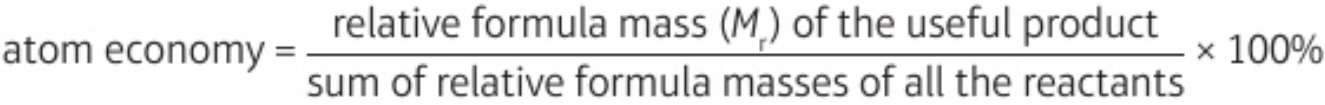
5.15 why is particular reaction pathway chosen to produce specified product?
chosen based on factors:
atom economy - high
yield - high
rate of reaction - fast
equilibrium position - lies to right (favours product formation)
usefulness of by-products - useful
(percentage yield - no indication of amount of waste products)
5.16 molar volume of any gas at room temp. & pressure
volume occupied by one mole of molecules of any gas at room temp. & pressure = 24dm3 (or 24000cm3)
5.17 molar volume equation
volume of gas = amount of gas (mol) x molar volume
volume = moles x 24