Thunderstorms, Tornadoes, And Flooding
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Based mainly on my class notes from my Introduction To Weather class at Suffolk County Community College.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Moisture, Lift, And Instability
The three ingredients that all thunderstorms need in order to be created.
Maritime Tropical
Air mass thunderstorms usually develop in_________air masses.
Lifting Mechanism
Differential heating is an example of a possible__________in an air mass thunderstorm, which is one of the primary requirements in their formation.
Not Associated With
Air mass thunderstorms are generally___________the passage of a front.
Cumulus, Mature, Dissipating
The Three Stages Of Air Mass Thunderstorms
Updrafts, Warm, Moist, Transported Upward
In the cumulus stage of air mass thunderstorms, the storm is dominated by only________, in which______,_______air is__________
Most Intense
During the mature stage of an air mass thunderstorm, the storm is the________out of all the stages.
Updrafts, Downdrafts
In the mature stage of an air mass thunderstorm, there is both______of warm air, and_______of cool air.
Entrainment, Cool, Dry, Pulled Into
__________helps strengthen downdrafts in the mature stage of air mass thunderstorms, which is the process in which surrounding______,______air is_________the cloud.
Downdrafts, Cool, Transported Downward
In the dissipating stage of air mass thunderstorms, the storm is dominated by_______, in which_______air is________
Gust Front (Outflow Boundary)
Mesoscale boundary separating thunderstorm-cooled air from the surrounding warmer air, creating similar weather conditions to a cold front.
Shelf Clouds
Low-horizontal wedge shaped cloud formations that mark the passage of a gust front.
Mid-Late Afternoon, Late Spring, Summer, Early Fall
The time of day that air mass thunderstorms are most likely to form is in the_______, and the time of year they occur is during the_______,________,and________
Florida
State that experiences the most thunderstorms in an average year.
Hail At Least 1 Inch In Diameter, Wind Gusts Of At Least 58 MPH, Or A Tornado
Criteria needed for a thunderstorm to be classified as severe.
Supercell
The most destructive of all thunderstorm types that are known for producing large and long-lived tornadoes.
Single, Powerful, Tropopause, Stratosphere
Supercell thunderstorms consist of a______,______cell that can extend to the____________and even “overshoot” into the____________
Squall Line
Line of thunderstorms that is known for producing heavy wind that blows from the same direction, often causing damage. It also can produce short-lived and generally weaker tornadoes.
Mesoscale Convective Complex
A large, long lived cluster of thunderstorms that produce heavy rainfall, often causing flooding, and can also cause damaging wind.
Great Plains
Mesoscale Convective Complexes most commonly form in the__________region.
Slow
Mesoscale Convective Complexes move at a________speed.
Oval/Circular
Mesoscale Convective Complexes are organized into a____________shape.
Ice
In order for lightning and thunder to develop in a storm, it must contain particles of….
Leader
Channel of ionized air that forms a path for the lightning to travel along.
Stepped Leader
Nearly invisible short burst of ionized air coming from a cloud towards the Earth.
Return Stroke
Bright visible flash that we see during lightning. It electrically extends upwards from the ground to the cloud.
Explosive Expansion, Heated, Sound Waves
Thunder is produced due to the_________of the_______air by lightning, which produces_________
Not Heard, Heat Lightning
Thunder is typically______when lightning is more than 20 km (12.4 miles) away. This is often referred to as________
Sheet Lightning
Flash of lightning within a cloud that illuminates it.
5 Seconds, Estimate Your Distance From Lightning
Sound waves travel one mile in around_______, and knowing this helps us in storms to________
Wind Shear
Radical shift in wind speed and direction that quickly occurs over a very short distance.
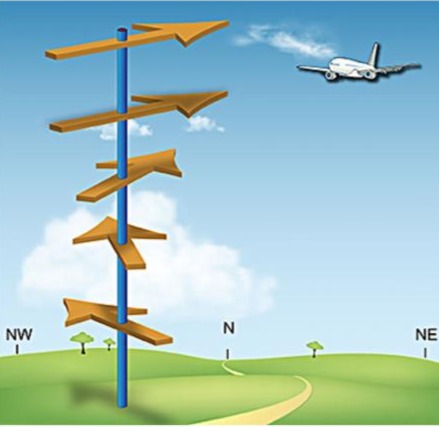
Directional Shear
The type of wind shear that can be seen in this diagram.
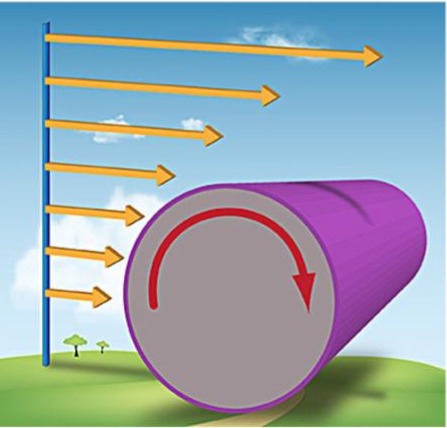
Speed Shear
The type of wind shear that can be seen in this diagram.
Vertical Wind Shear
The occurrence of___________within the environment of a thunderstorm is required in the formation of a tornado.
Tornado
Violent windstorm with at least one rapidly rotating column of air, or vortex.
Varies, A Single Vortex, Multiple Vortices
The amount of vortices in a tornado________. They can have either________or________
Late Afternoon, Evening, Any Time Of Day
The time of day that tornadoes most commonly form are in the________and the________. However, they have the ability to form in__________
Updrafts
A type of wind known as______occur inside tornadoes, which helps grow the tornado and makes it more intense.
Northeast
Most tornadoes travel to the…..
May
Month in which tornadoes are the most likely to occur in the United States.
Fujita Scale
Scale for rating tornado intensity. It has several degrees of damage that are applied, primarily based on the level of destruction caused by the Tornado.
Tornado Watch
When the formation of a tornado is possible and the conditions for its creation are favorable, a_________is issued.
Tornado Warning
When a tornado is sighted or detected by weather radar, a________is issued.
Doppler Weather Radar And Storm Spotters
These are what are commonly used to issue tornado warnings in the United States.
Much Larger, Several States, Much Longer
A tornado watch usually covers a___________area than a tornado warning and can cover__________. They also usually take place for a__________period of time.
1/5 inch
Hail is precipitation of ice pellets that are larger than________in diameter.
Large And Damaging
It is very rare to see hail that is________produced by air-mass thunderstorms.
Stronger
The larger the size of the hail, the_______the updrafts.
Cumulonimbus, Small Ice Pellets, Upward, Updrafts, Downward, Downdrafts
Hailstones are formed in________clouds, where they initially begin as_________. They are then propelled________throughout the cloud by_______, which help them grow, and they also move________as a result of__________
Flash Flood
Rapidly rising water over a short period of time, usually associated with heavy rainfall.
Ponding
A type of flooding, often classified as a flash flood, that results from water piling up at or near the point of where it falls because rainfall rates exceed drainage capacity. It often occurs in relatively flat areas.
Urban Flooding
A type of flood, often classified as a flash flood, that occurs when large amounts of runoff from concrete and asphalt collect in low spots in roads, poor drainage areas, intersections, and underpasses.