Opiates/Opioids
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
Opioid
ANY drug that acts on Opioid Receptors of the Brain/CNS
Short Peptides derived from long precursors
Synthetic Drugs
Opioid Drugs
Opioid Drugs
1. Hydrocodone
2. Oxycodone
3. Fentanyl
4. Heroin
Opiates
opium and its derivatives
NATURALLY derived from the Poppy Plant

Opiate Drugs
1. Morphine
2. Opium
3. Codeine
Term used to describe BOTH Opiates and Opioids
Opioid
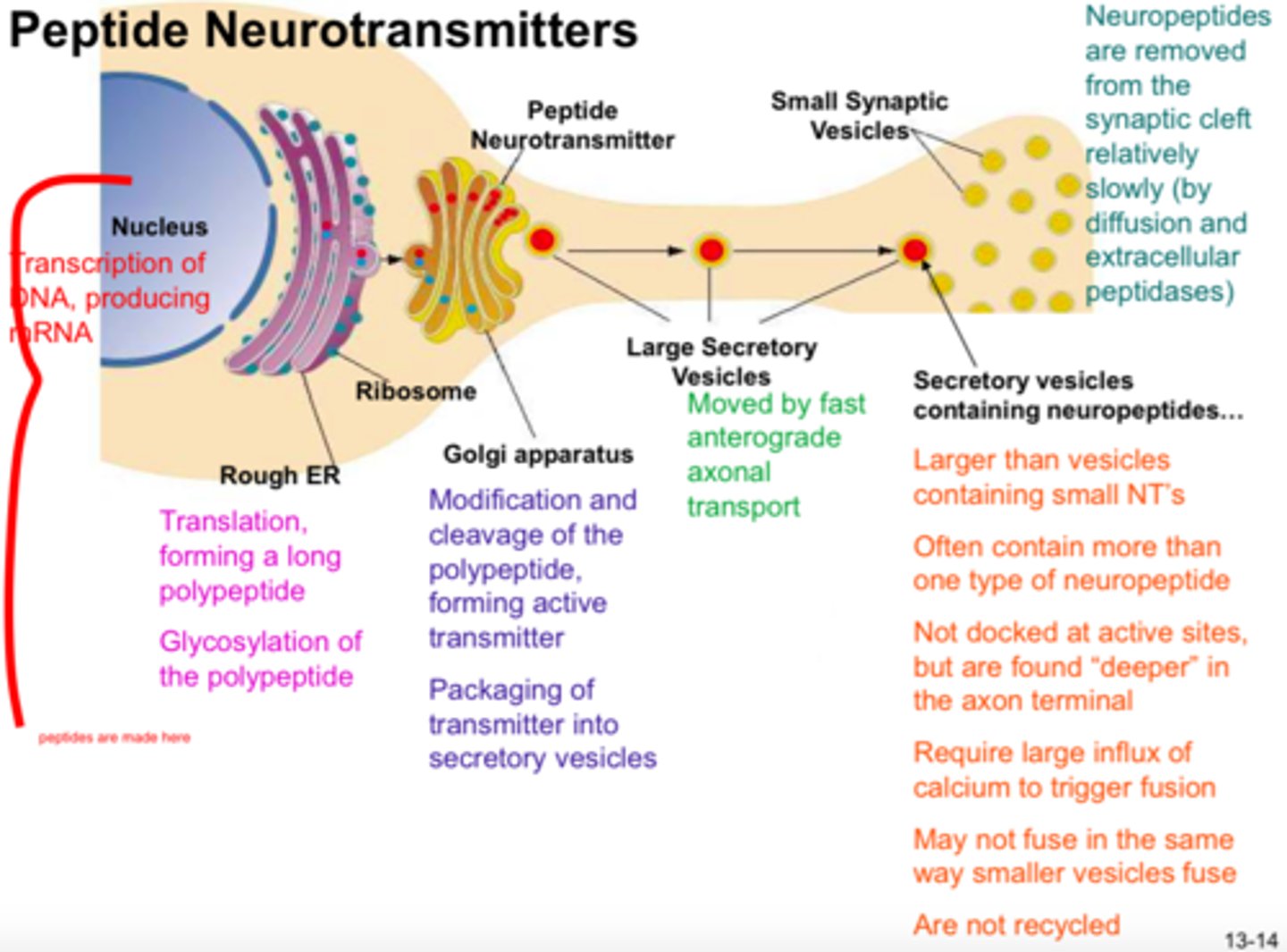
Peptide Neurotransmitters
short chains of amino acids linked together by covalent peptide bonds;
Opioids that are LONGER LASTING
Produce Opioid Short Peptides Endogenously (in the body naturally that bind to Opioid Receptors)
NATURALLY produced in the CNS
Opioid Receptors
mu, kappa, delta
Opioid Receptors are
Metabotropic Receptors (GPCRs)
Opioid Receptors function
Relieve Stress and Pain
--> Why they are targeted by:
1. Analgesics
2. General Anesthetics (some)
3. Drugs of Abuse
Neuromodulator
a naturally secreted substance that acts like a neurotransmitter except that it is not restricted to the synaptic cleft but diffuses through the extracellular fluid
--> Influences activity of other synaptic transmitters
Endogenous Opioid Peptides do this!!
Consensus Opioid Sequence
- Classical opioid peptides have consensus opioid sequence:
Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu/Met
- highly conserved for active site recognition
Three Families/Types of Endogenous Opioid Peptides
1. Enkephalins
2. Endorphins
3. Dynorphins
Note: Generated from longer, Pre-cursor Proteins
Endogenous Opioids that have a UNIQUE Sequence/Structure (test question)
Endomorphins
Tyr-Pro-Trp/Phe-Phe/NH2
Endogenous Opioids Neuromodulator Activity
1. INHIBIT Glutamate Release
2. INHIBIT activation of Spinal Nociceptive Neurons (pain receptors... duhhhh b/c keep us from feeling pain)
Opioid Receptors expressed in the
1. Brain
2. Spinal Cord
3. Peripheral Nerves
Note: Expressed in CNS at sites of PAIN MODULATION
When are Endogenous Opioids released?
During painful states, during stress, and after exposure to rewarding things
Result = Alleviate Pain
Endorphins bind
Delta and Mu Receptor
Enkephalins bind
Delta Receptors > Mu Receptors
NO Kappa binding
Dynorphins bind
Kappa Receptors
Sensitizes Nociceptive Signals in the Dorsal Horn (Test question)
Dynorphins
Endomorphins bind
Mu Receptors ONLY
--> Target for Analgesics
Mu, Delta, and Kappa Receptors are expressed on
1. Primary Afferent/Sensory Receptors --> In the Periphery
2. Nociceptive/Pain Neurons
Presynpatic (Primary Afferent) Expression of Opioid Receptors
ALL Three (Mu, Delta, Kappa)
Post-Synaptic (Nociceptive Neurons) Expression of Opioid Receptors
ONLY Mu Receptors
--> Why Analgesics target these receptors!!
1. Spinal Nociceptive Neurons
2. Peripheral Terminals of Sensory Neurons
Sites of action of opioids on pain transmission: Pre- and Post- Synaptic Mechanisms
1. Spinal Cord
2. Supraspinal Effects (going to the brain)
Sites of action of opioids on pain transmission: Post-Synaptic Mechanisms
Peripheral Terminals
Pathway of Pain Stimulus
1. Pain Stimulus Experienced (Periphery)
2. Primary Afferent Neuron relays information --> Pain Transmission Neuron
3. Pain Transmission Neuron --> Spinal Cord --> Brain
4. Brain perceives Pain and reacts -> Descending Pathway (Modulation)
5. Pain Inhibitory Neuron Activated (once Brain receives Pain signal) --> b/c Pain signal already received by the Brain = Inhibits Transmission of Pain (brain says, "oh yeah, I got it, I am going to do something about it now!)
6. GABA Neurons can inhibit the Pain Inhibitory Neurons --> ALLOWS the brain to receive Pain stimulus!
Regulate/Inhibit Pain Inhibitory Neurons
GABA Neurons --> Hyperpolarization (Chloride Influx)
--> Inhibits Pain Inhibitory Neurons from firing and stopping the pain stimulus from reaching the brain
Endogenous Opioid Agonists
Endorphins
Natural Opioid Agonist
Morphine
Synthetic Opioid Agonist
Fentanyl
MOA of Opioid Drugs (Slide 12-17)
1. Mu, Kappa, Delta Receptors --> Pre-Synaptically when bound
--> GPCR --> Gi protein --> BetaGamma Subunit INHIBITS Voltage-Gated Ca2+ Channel from depolarizing
Result: Glutamate (excitatory neurotransmistter) release INHIBITED --> NO PAIN STIMULUS
Decrease Ca2+ influx, Decrease Glutamate Release
2. Mu Opioid Receptor --> Post-Synaptically when bound
--> GPCR --> Gi protein --> BetaGamma Subunit ACTIVATES GIRK CHANNEL --> K+ EFFLUX --> Hyperpolarization
Result: Signal is NOT PROPAGATED --> NO PAIN STIMULUS
Increase K+ Efflux --> Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential (IPSP)
ACTIVATION OF POST-SYNAPTIC MU RECEPTOR INHIBITS NEURONAL ACTIVATION AND PAIN TRANSMISSION
Primary Therapeutic Target of Opioid Analgesics
Mu Receptors
Effects:
1. Analgesia
2. Euphoria
3. Respiratory Depression
4. Dependence
New Kappa Selective Agonists can cause
DYSHPORIC REACTIONS
--> Anxiety, Pain, Delirium
Activation of Mu Receptors stimulates
Release of Endogenous Opioids (Endorphins, etc.) that activates ALL THREE opioid receptors (mu, delta, kappa)
Kappa Receptors important in these effects (test question)
Sedative and GI effects
Which Opioid Receptor likely contributes to TOLERANCE (test question) --> big problem with opioid drugs and big cause of overdose
Delta Receptors
What kind of Pt should you NEVER give Opioids to? (test question)
1. COPD Pts, Asthma and pts with respiratory disease
--> b/c Mu receptor activation can cause further RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION
2. Elevated Intracranial Pressure
--> b/c opioid activation can increase Intracranial Pressure --> risk of hemorrhaging
Full/Strong Mu Agonists
1. MORPHINE (caps = focus)
2. Hydromorphone
3. Oxymorphone
4. Heroin
5. Methadone
6. Meperidine
7. Fentanyl
8. Sufentanil
9. Alfentanil
10. Remifentanil
11. Levorphanol
12. Dextromethorphan
Partial/Mild Mu Agonists
1. CODEINE
2. Oxycodone
3. Hydrocodone
4. Propoxyphene
5. Diphenoxylate
6. Difenoxin
7. Loperamide
Mixed (Mu and Kappa) Agonist/Antagonists
1. NALBUPHINE
2. Buprenorphine
3. Butorphanol
4. Pentazocine
5. Dezocine
Mu Receptor Antagonists
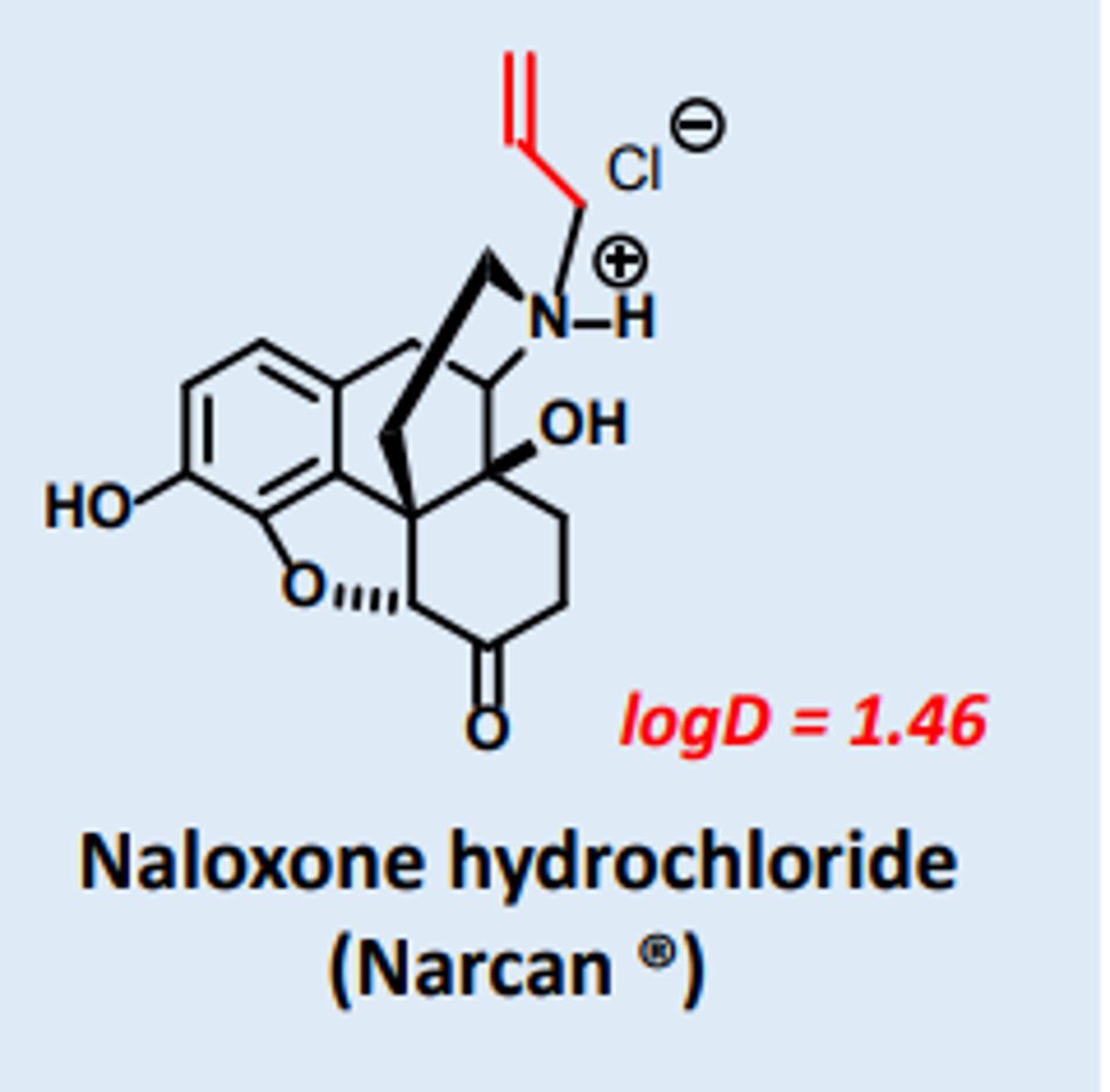
1. NALOXONE
2. Naltrexone
Phenanthrenes
1. Morphine
2. Hydromorphone
3. Oxymorphone
4. Heroin
Phenylpiperidines
1. Meperidine
2. Fentanyl
3. Sufentanil
4. Alfentanil
5. Remifentanil
Phenanthrenes are converted to
NON-active Polar Glucuronides in the Liver
--> Excreted by the kidneys
EXCEPTION: Morphine
Morphine (full agonist) metabolized to ___ and its effect is ___
Morphine-3-glucuronide (M3G) and M6G
Neurotoxic --> SEIZURES
Phenylpiperidines are metabolized by
3A4
Meperidine (full agonist) is demethylated to form ____ that is ____
Normeperidine
Neurotoxic --> SEIZURES
Can trigger Seizures (test question)
1. Morphine
2. Merperidine
Absorption and Metabolism of Opioids
Good absorption
Significant First-Pass metabolism by liver
Do opioids cross the placental barrier?
YES --> Contraindicated in Pregnant Women b/c can be teratogenic
Drug Delivery Methods of Opioids
1. Parenteral formulations
2. Sustained Release
3. Rectal suppositories
4. Transdermal patch
5. Intranasal
6. Buccal transmucosal
Organ System Effects of Opioids: CNS
1. Analgesia --> reduced sensory and emotional pain
2. Euphoria
3. Sedation
4. RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION
5. Miosis (pupil constriction)
6. Truncal rigidity --> increased muscle tone (supraspinal effect (in the brain causes)
7. N & V --> activates Brainstem Chemoreceptor Trigger Zone
Which Opioid causes Cough Suppression?
Codeine and Dextromethorphan
Note: Unknown mechanism
Exception to Miosis Effect (test question)
Meperidine
--> Muscarinic Receptor Blocker (Anticholinergic) --> Mydriasis
Does develop Tolerance to Miosis Effect over time?
NO! --> constantly causes while taking
Organ System Effects of Opioids: Peripheral Effects
1. Bradycardia
2. Hypotension
3. Constipation (Opioid receptors in Enteric System)
4. Reduces Uterine Tone --> Can PROLONG BABY DELIVERY
5. Increased Bladder Tone --> URINARY RETENTION
6. Reduces Renal Function
7. Regulates release of LH, ADH, Prolactin
8. Pruritus (Itchiness) depending on ROUTE of administration
9. Inhibits Natural Killer Cells and Lymphocytes
_____ mostly trigger Pruritus
Mu Opioid Receptor Agonists
Does Tolerance develop with Constipation caused by Opioids?
NO --> persistent constipation in the colon
Opioid that does NOT cause Bradycardia (test question)
Meperidine --> Tachycardia b/c Muscarinic Antagonist
Clinical Use of Opioids
1. Analgesia
a) Severe Acute Pain
b) Chronic Pain
Concern: Tolerance and Dependence
c) Terminal Illness
d) Labor and Delivery
e) Pre-operative as sedative
f) During surgery to complement anesthetics
g) Surgically implanted pump for chronic pain
2. Acute Pulmonary Edema
3. Diarrhea
4. Cough Suppression
Dependence NOT a major issue
Terminal Illness
Regional (specific location) Analgesia is delivered via
Epidural Delivery to the Spinal Column!
1. Morphine
or
2. Fentanyl with Local anesthetics
Note: Respiratory Depression can still occur!
Epidural Headache
If the needle goes through arachnoid mater, then cerebrospinal fluid can leak out and the loss of this fluid can cause enormous brain pain.
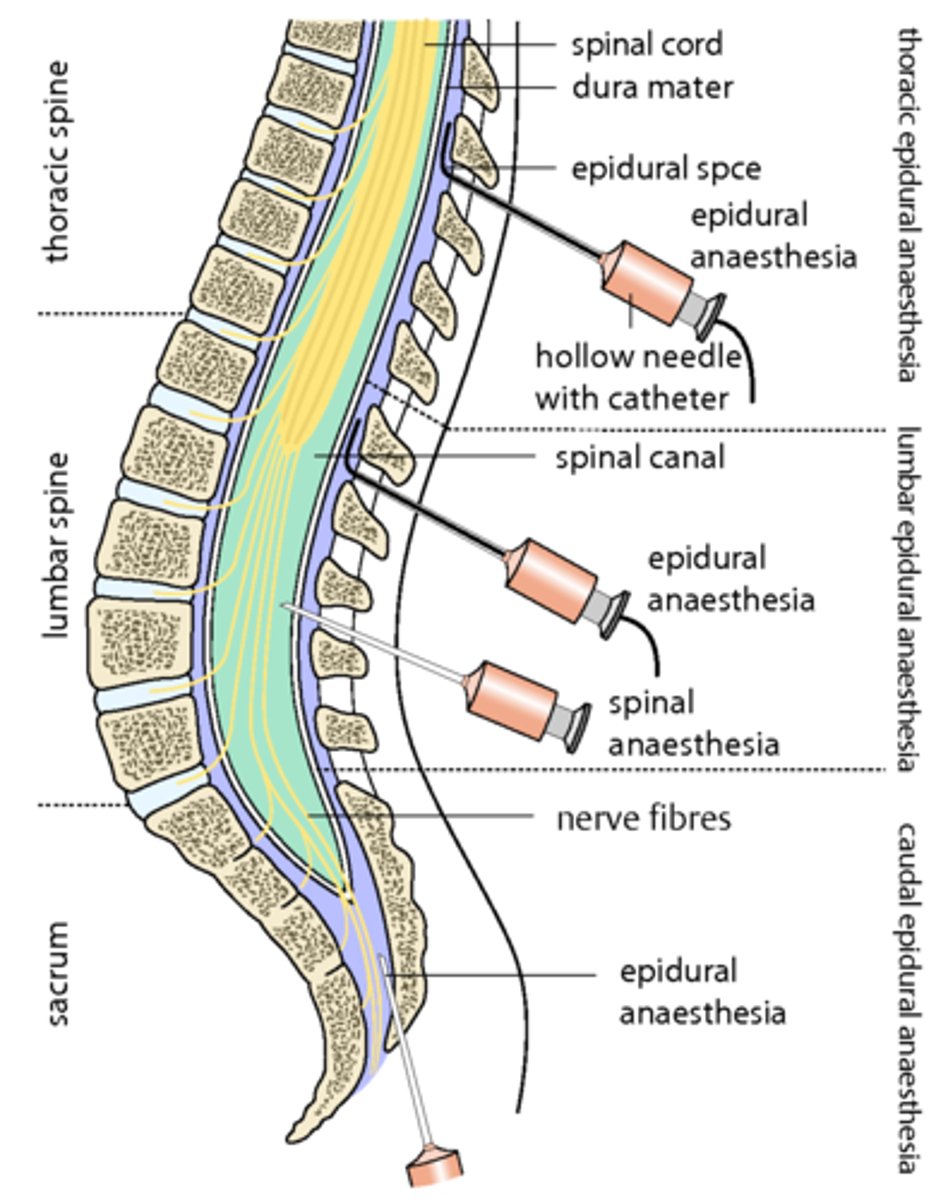
Opioid used in Labor and Delivery
Meperidine
Note: Fetus closely monitored for Respiratory Depression b/c opioids cross the placental barrier
Acute Pulmonary Edema is alleviated by
Morphine (not clear how)
The dyspnea is alleviated
Opioids that treat Diarrhea are
1. Diphenoxylate
2. Difenoxin
3. Loperamide
Partial/Mild Mu Agonists with FEW CNS side effects --> low risk for abuse
Low Solubility --> Low CNS penetration --> NOT used as analgesics
ALL ____ have high potential for Physical Dependence and Addiction
Full Agonists
1. Morphine
2. Hydromorphone
3. Oxymorphone
4. Heroin
Used to treat SEVERE PAIN only
Potencies of Phenylpiperidines
Sufentanil > Fentanyl > Alfentanil
Avoid using Meperidine in pts with
1. Tachycardia
2. Decreased RENAL function
b/c Muscarinic Blocker (Anticholinergic) --> further increases heart rate and reduced renal function --> MI and Kidney Failure can result
Used to treat Opioid Use Disorder (OUD)
Methadone
b/c LONGER DOA --> used for DETOX --> Lessens Withdrawal Severity
Methadone effect on Heroin
Blocks rewarding effects of Heroin
--> Used for Maintenance/Relapse Prevention
Methadone MOA
Blocks NMDA Receptors and Monoaminergic Uptake
Morphine Alternative in Opiate Rotation
Methadone
--> can be used as a Therapeutic Analgesic! NOT just for withdrawal
Should partial/mixed agonists be given to patients receiving full agonists?
NO
--> b/c Partial Agonist will COMPETE with full agonist and hinder it from reaching the MAXIMUM EFFECT --> pt will be in more pain as a result
Insufficient for Extreme Pain
Propoxyphene
Mixed Agonists partially bind
ALL 3 receptors (mu, kappa, delta)
Variable efficacy as analgesics --> due to not being full active
ALL Mixed agonist have potential for
Negative Psychotogenic Effects
--> Delusion and HALLUCINATIONS
Mixed Agonists
1. Nalbuphine
2. Butorphanol
3. Pentazocine
Nalbuphine activity
Kappa Agonist
Mu Antagonist
Butorphanol activity
Kappa Agonist
Partial Agonist at Mu Receptor
Pentazocine activity
Kappa Agonist
Weak Mu Antagonist
Buprenorphine activity
Mixed Agonist
Partial Mu Agonist
Antagonist at Delta and Kappa Receptors
Long Acting Partial Mu Agonist
Buprenorphine
Detox and Maintenance for Addictions
Buprenorphine
Which has Lower Risk, Methadone or Buprenorphine?
Buprenorphine b/c Partial Mu Agonist
LOWER Respiratory risk than Methadone (full mu agonist)
Used for Detox and maintenance for addictions and functions as an Analgesic
Tramadol MOA
Serotonergic Analgesic (SERT Blocker)
--> Increases Serotonin levels in synapse
Weak Mu Receptor Agonist
Tramadol adverse effects
Seizures, Nausea, Serotonin Syndrome
Tapentadol MOA
NET Block (Inhibits NE Reuptake)
Weak Mu Receptor Agonist
Cough Suppressant that is a Partial Mu Agonist
Codeine
--> sub-analgesic doses
Cough Suppressant that is a Full Mu Agonist
Dextromethorphan
NON-HABIT FORMING and LESS constipating than Codeine
Partial Agonists noteworthy Adverse Effects
May PRECIPITATE Withdrawal Symptoms in patients receiving Full Agonists
--> b/c not receiving full analgesic dose
Pre-Existing Intracranial Pressure or Head Injury
Opioids should NOT be used
Respiratory Depression --> CO2 Retention --> Vasodilation --> More IOP
Mild Fetal Withdrawal Syndrome
Diazepam controls
Severe Fetal Withdrawal Syndrome
Methadone controls
Contraindications for Opioid Use
1. Elevated IOP
2. Pre-Existing Pulmonary Impairments
3. Impaired Renal or Hepatic Function
--> Dosage should be REDUCED if given
4. Hypothyroidism or Low Adrenal Activity
--> Opioids effects are exaggerated
Opioid Antagonists have a High Affinity for
Mu Receptors
Opioid Antagonists are ____ in the absence of an ___
Inert
Opioid Agonist (ex: Fentanyl)
Opioid Antagonists use
acute opioid overdose