Development of the Muscular System: Derivatives of the Mesodermal Layer
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What is Paraxial Mesoderm
Longitudinal blocks of tissue on either side of the notochord
What does paracial mesoderm give rise to
Axial skeleton and skeletal muscle
What does intermediate mesoderm give rise to
urogenital system
What does the lateral plate mesoderm do
Gives rise to connextive tissue and skelton of the limbs and smooth muscle and viscera and blood vessels
How many somitomeres are there
7
Where are somites
caudal
What is growth/diffrentiation regulated by
HOX
What kind of mesoderm does sclerotome, myotome, and dermatome
Paraxial
What does splanchic somatic extraembroynic
Lateral
What does kidneys and gonad
Intermediate
What does the paraxial mesoderm condense to form
Somites
What model is used to describe somite segmentation
clock and wavefront
What regulates interactions between physically adjacent cells
notch
Where does notch protein accumulate
presomatic mesoderm
When does notch decrease
as the somite is established
What controls the boundaries of somite formation
Retionic acid
What contributes to the regulation of somite formation
FGF8 and WNT3a
Where are FGF8 and WNT3a primarily expressed
caudally
Where is less FGF8 and WNT3a detected
Cranially
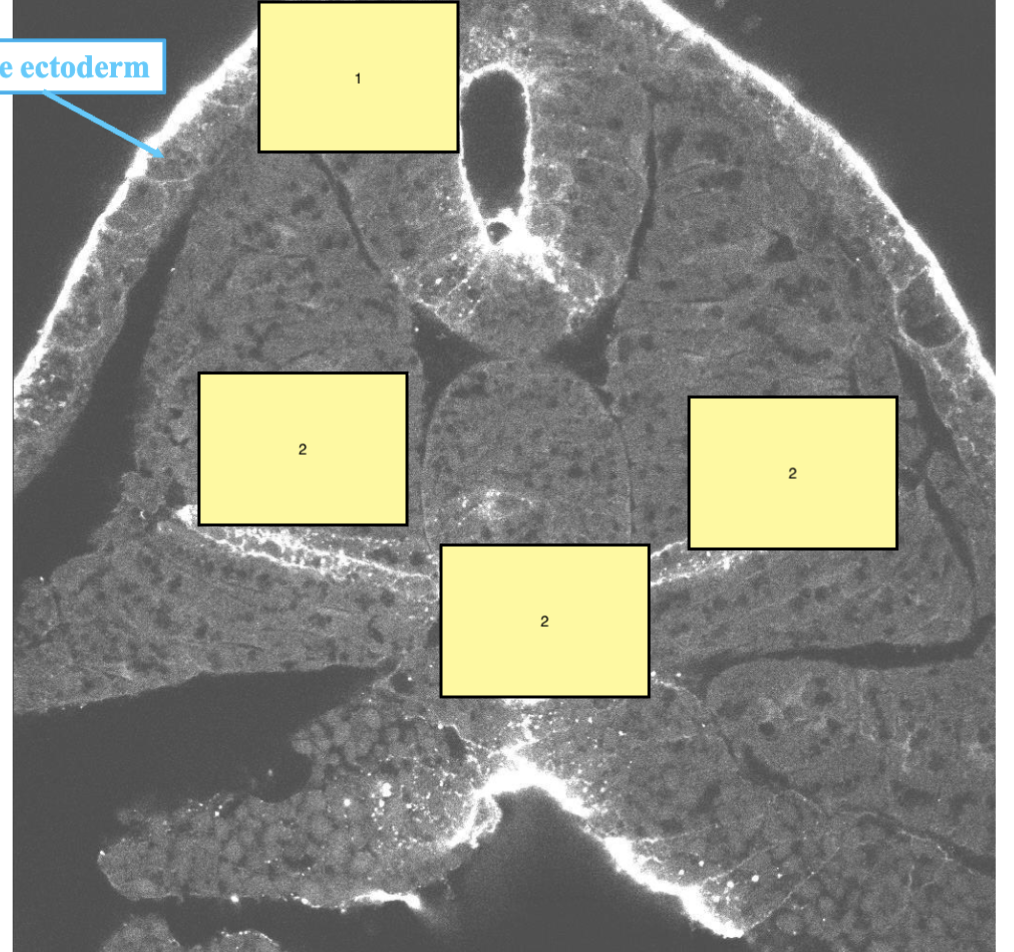
1
neural tube
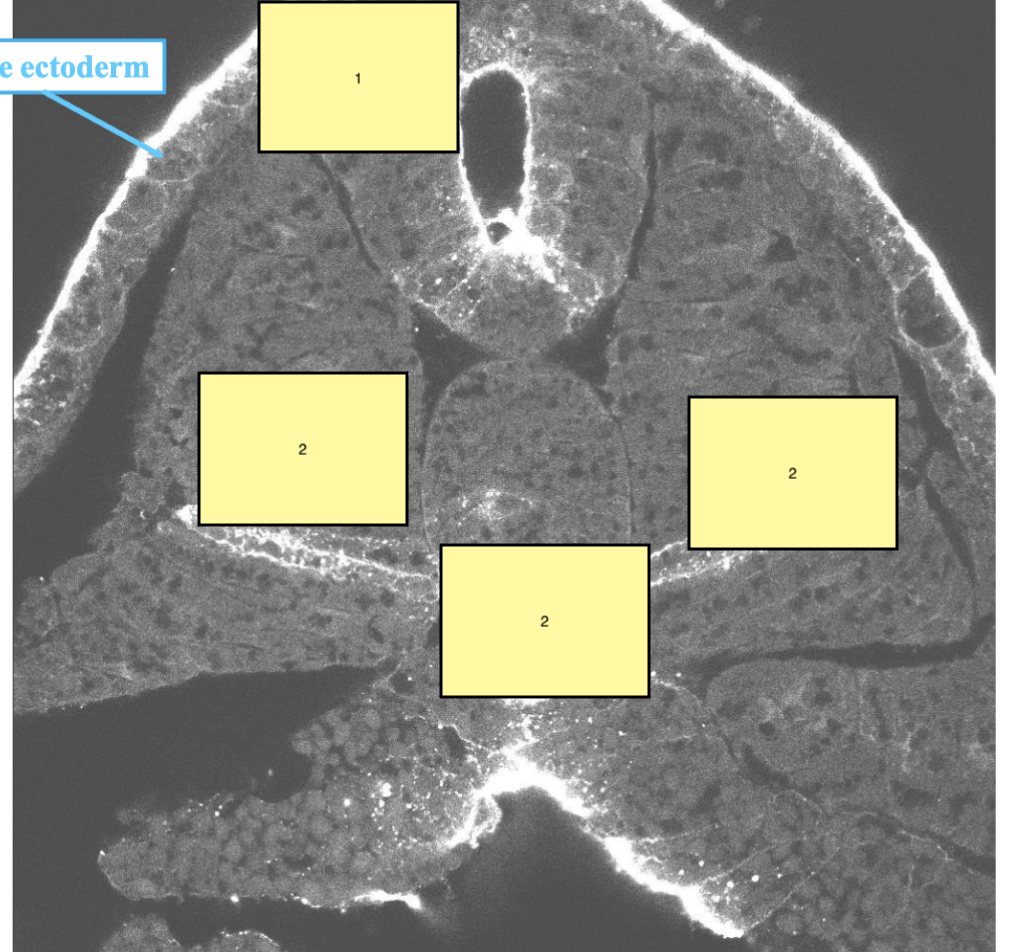
2
Somite
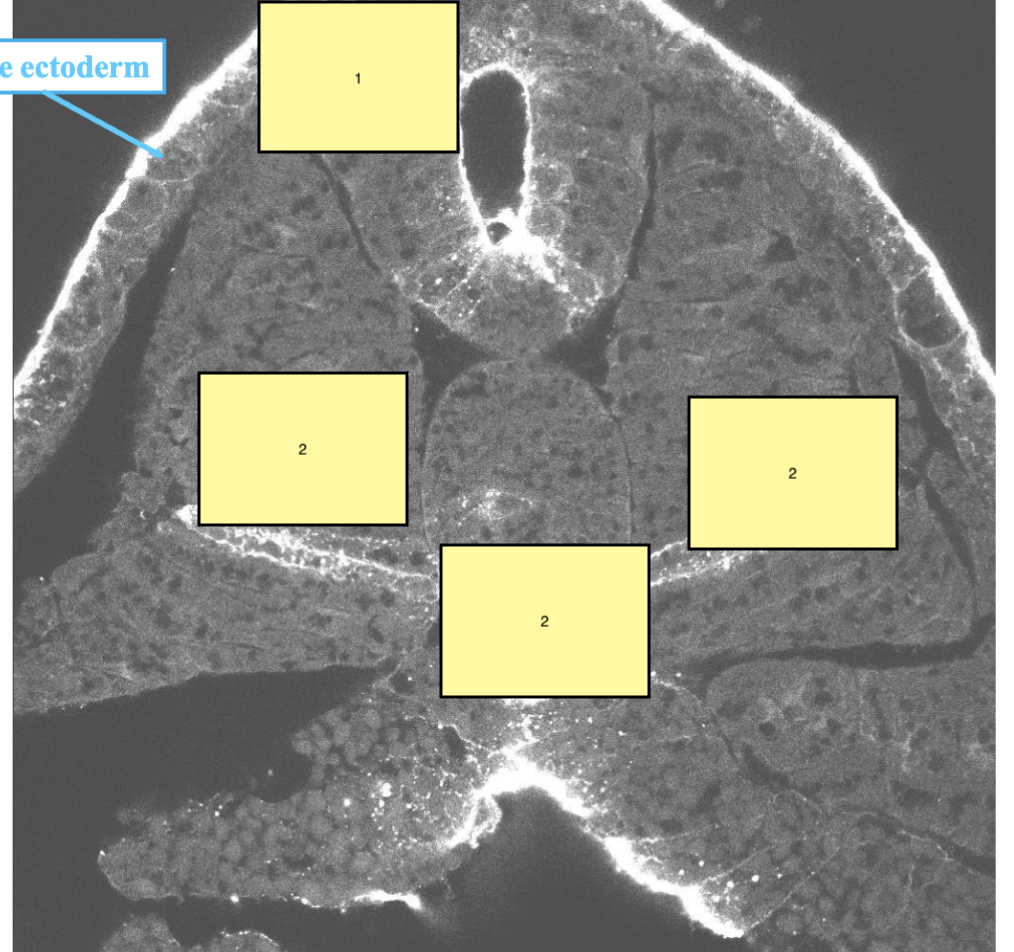
3
notochord
What does the somite divide into
3 parts
What are the parts of a somite
Sclerotome, dermamytome
Where is the sclerotome
Ventromedial part closest to notochord
What does the dermatome become
demis
What does the myotome do
gives rise to muscles
Where do sclerotome cells move
medially
Where do sclerotome cells condense
around notochord
Where does resegmentation take place
only in the sclerotome
What happens to the rostral and caudal halves of somites?
Segregate and refuse with their neighboring halves to form vertebrae
What is bound together
‘c’ of 4, ‘n’ of 5, for example
What forms the vertebrae
the sclerotome
What HOX does cervical
5
what hox does thoracic
69
what hox does lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal
10
Step one of molecular regulation of somite differentiation
Noggin and SHH induce the ventromedial portion of the somite to make a sclerotome
Step two of molecular regulation of somite differentiation
Sclerotome cells express PAX1
What does PAX1 do
Initiates cascade of cartilage and bone forming genes for vertebral formation
What does expression of PAC3 do
Marks dermamytome region of somite
What regulates PAX3
WNT proteins
What is step 4 of molecular regulation of somite differentiation
WNT targets dorsomedial portion of the somite
What does WNT express in the 4th step
MYF5
What does MYF5 form
epaxial muscle
Wgar stimulates MYOD
WNT, BMP4/FGF
Where is MYOD expressed from
dorsolateral somite
What does MYOD form
Hypaxial muscle
What is the midportion directed by
Neurotrophin 3
What does the midportion form
Dermis
What family are MYOD and MYF5 from
Myogenic regulatory factors
What marks dermamyotome region
Expression of PAX3
What do cords contain
root
what does spinal nerve contain
ramus
Where does intermediate mesoderm position itself
posterior abdominal wall
What does the intermediate mesoderm form
Gonads, ducts, accessory glands of urniary and repro tracts
What is sirenomyelia
fusion of lower limbs
What does diabetes do for caudal dysplasia
Increases the chances heavily
Where is somatic
wall of the body cavity
Where is splanchnic
Bisceral (innervated by autonomic)