Cell Evolution
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
1
New cards
Major Cell Type
Eukaryotes - Eukaryotes (have a nucleus and
membrane-bounded organelles)
Archaea - prokaryotes, no nucleus
Bacteria - prokaryotes, no nucleus, most diverse and widespread prokaryotes
\
3 major domains - eukarya, archaea, bacteria all derived from a common ancestor
phylogenies show evolutionary relationships
membrane-bounded organelles)
Archaea - prokaryotes, no nucleus
Bacteria - prokaryotes, no nucleus, most diverse and widespread prokaryotes
\
3 major domains - eukarya, archaea, bacteria all derived from a common ancestor
phylogenies show evolutionary relationships
2
New cards
What was needed for the first life to form?
First unicellular organism - 3.5BYA
\
Organic (macro)molecules
* nucleic acids
* proteins
* lipids
* Polysaccharides
Self replication
* RNA
Enclosed spaces (protocells)
\
Organic (macro)molecules
* nucleic acids
* proteins
* lipids
* Polysaccharides
Self replication
* RNA
Enclosed spaces (protocells)
3
New cards
Approaches to classify organisms
Molecular approaches to define the different types of life
The more related an organism the more similar their DNA
Based on genetics: ribosomal RNA and other genes AND morphology
The more related an organism the more similar their DNA
Based on genetics: ribosomal RNA and other genes AND morphology
4
New cards
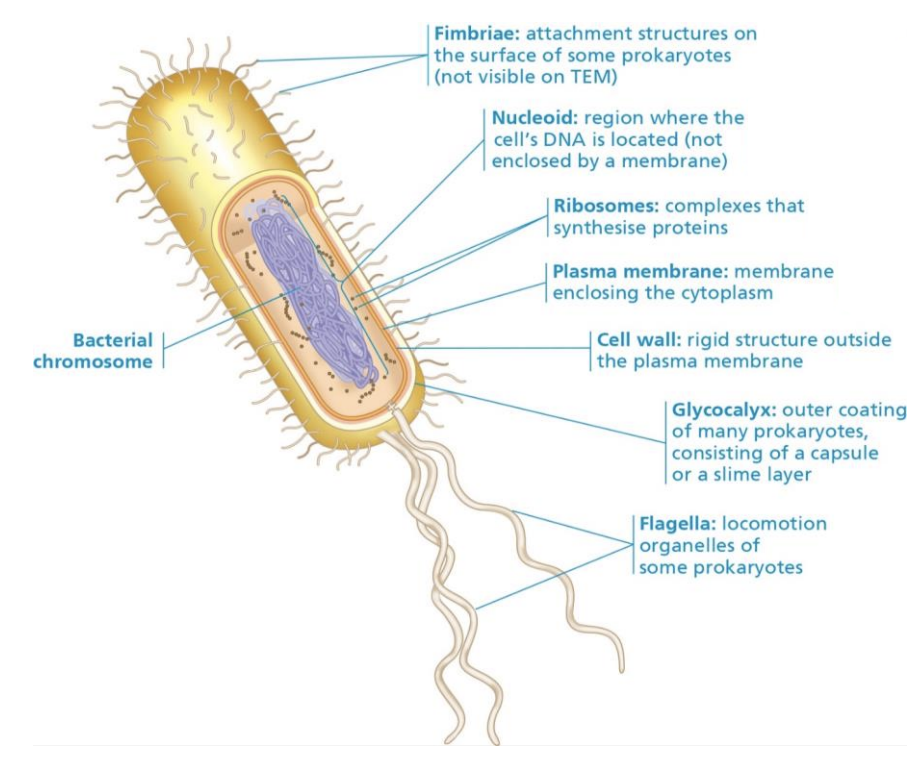
Prokaryotes
* Mostly single celled (cocci, bacilli, spirilla)
* Size 1-5 micrometre
* Can aggregate to form colonies
* DNA is circular in chromosomes and plasmids
* Can be motile - flagella
* Peptidoglycan in cell wall
* no nucleaus or membrane bound organelles
\
Features
* Binary fission - reproduction
* Fimbriae - attachment
* Capsule - protection, adherence
* Flagella - motility
* Ubiquitous - everywhere
* If removed by antibiotic treatment, pathogens may fill the empty niche
\
* Most bacterial species can’t cause disease
* Many are beneficial (antibiotics and food production, e.g. Streptomyces, Lactobacillus)
* Free-living soil bacteria and cyanobacteria perform many essential functions in the biosphere, (e.g. Rhizobium and nitrogen fixation)
* Size 1-5 micrometre
* Can aggregate to form colonies
* DNA is circular in chromosomes and plasmids
* Can be motile - flagella
* Peptidoglycan in cell wall
* no nucleaus or membrane bound organelles
\
Features
* Binary fission - reproduction
* Fimbriae - attachment
* Capsule - protection, adherence
* Flagella - motility
* Ubiquitous - everywhere
* If removed by antibiotic treatment, pathogens may fill the empty niche
\
* Most bacterial species can’t cause disease
* Many are beneficial (antibiotics and food production, e.g. Streptomyces, Lactobacillus)
* Free-living soil bacteria and cyanobacteria perform many essential functions in the biosphere, (e.g. Rhizobium and nitrogen fixation)
5
New cards
Bacterial Cell Walls
**Gram positive**
* Retains violet dye - purple
* Peptidoglycan layer on outside
**Gram negative**
* Dye washes out - pink
* Peptidoglycan layer on inside
* Retains violet dye - purple
* Peptidoglycan layer on outside
**Gram negative**
* Dye washes out - pink
* Peptidoglycan layer on inside
6
New cards
DNA transfer in bacteria
Circular DNA free floating forming the nucleoid region
Small genomes
Contain Plasmids: multiple small circular DNA fragments
Plasmids: extra, useful genes, e.g. encoding antibiotic resistance
Small genomes
Contain Plasmids: multiple small circular DNA fragments
Plasmids: extra, useful genes, e.g. encoding antibiotic resistance
7
New cards
Archea
* Small size
* Rapid reproduction
* Mutations
* Diverse adaptation
* Rapid evolution
* Rapid reproduction
* Mutations
* Diverse adaptation
* Rapid evolution
8
New cards
Bacteria Vs Archea
Membrane lipids with branched hydrocarbons
Cell wall - NOT peptidoglycan
Grow at extreme temperatures
Cell wall - NOT peptidoglycan
Grow at extreme temperatures
9
New cards
Extremophiles
\
* High salt
* Extreme temperatures - hot or cold
* Extreme acidity
* Methanogens
* High salt
* Extreme temperatures - hot or cold
* Extreme acidity
* Methanogens
10
New cards
Eukaryotes
* Nucleus - DNA enclosed in a membrane
* Membrane bound organelles
* Commonly classified into 4 kingdoms: protists, animalia, fungi and plantae
* Single celled or multi celled
* Autotrophic: contain chloroplasts
* Heterotrophic: no chloroplasts
* Membrane bound organelles
* Commonly classified into 4 kingdoms: protists, animalia, fungi and plantae
* Single celled or multi celled
* Autotrophic: contain chloroplasts
* Heterotrophic: no chloroplasts
11
New cards
Domain Eukarya
**SAR**
*Stramenopila*
* Large, extremely diverse lineag
* Grouping based on whole genome sequencing
*Alveolata*
* Membrane-lined sacs regulate diffusion across plasma membrane
* Red tides (carotenoids), bioluminescence
* Parasites
*Rhizaria*
* Many species are amoebas
* Move and feed by pseudopodia
*Excavata*
* Diverse, often groove on bodies
* Often modified/reduced mitochondria (dysfunctional)
* Parasitic, predatory and photosynthetic species
*Stramenopila*
* Large, extremely diverse lineag
* Grouping based on whole genome sequencing
*Alveolata*
* Membrane-lined sacs regulate diffusion across plasma membrane
* Red tides (carotenoids), bioluminescence
* Parasites
*Rhizaria*
* Many species are amoebas
* Move and feed by pseudopodia
*Excavata*
* Diverse, often groove on bodies
* Often modified/reduced mitochondria (dysfunctional)
* Parasitic, predatory and photosynthetic species
12
New cards
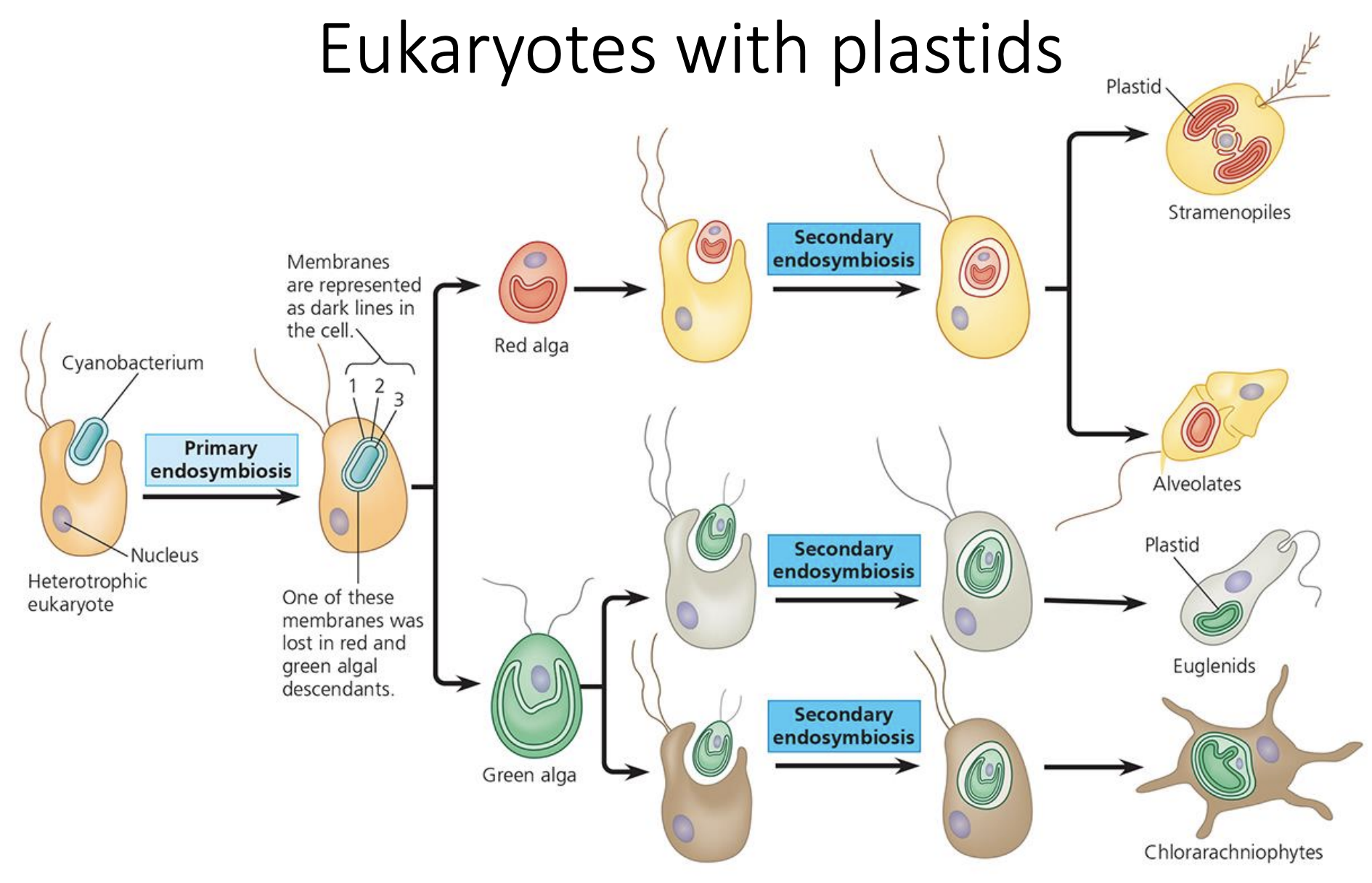
Endosymbiosis