Pt 1 - intro to Cells
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Cell Theory
all living organisms are made of one or more cells
cells are the basic unit of all living organisms
cells arise from pre-existing cells
Miller-Urey Experiments
recreated the conditions that are believed to have existed in the primitive earth
7 simple molecules: H2O, N2, NH3, CO, CO2, CH4, H2
Observations: With each round of the experiment, increasingly complex organic molecules were formed
Nucleic acids are necessary for______
reproduction and evolution
Central Dogma of Genetics
flow of genetic information
The first genetic system on earth was _____ based.
RNA
Evidence for RNA world:
some RNA molecules have enzymatic activity. aka Ribosomes
RNA can catalyze the polymerization of nucleotides, using itself as the template
Why are cells so small?
smaller cells have larger surface area : volume ratio.
smaller cells can interact with their surroundings more efficiently
Prokaryotes
lack a nuclear envelope, organelles, and a cytoskeleton
bacteria & archaea
most diverse groups of cells
Eukaryotes
have a nuclear envelope, nucleus, organelles, and a cytoskeleton
Coliform Bacterium (E. Coli)
no nucleus
no organelles
single chromosome
cell wall
capsule
Chemosynthetic bacteria
can fix CO2 without sunlight
ex: Beggiatoa
What is the defining feature of eukaryotic cells?
Nucleus
Operational Genes
meant for metabolism and other cell functions
informational genes
meant for cell division an gene expression
independent, free living cell
Single cell living
aggregation of cells of the same species but no division of functions
Colonial Living
Aggregation of cells of the same species with different somatic and reproductive functions, but not recognized true multicellularity b/c cell functions can be reversed
Colonial Living with Division of Functions
Division of functions (somatic & reproductive), terminal cell identities, and multicellularity
True Multicellularity
cells that are tightly bound by junctions and form sheets that cover the body surfaces and form the lining of the internal organs
Epithelial cells
Types of Connective Tissues
fibroblasts
bone
cartilage
adipose tissue
areolar tissue
Blood Cell types
red - transport O2
white - immune responses
Mouth Epithelial Cells
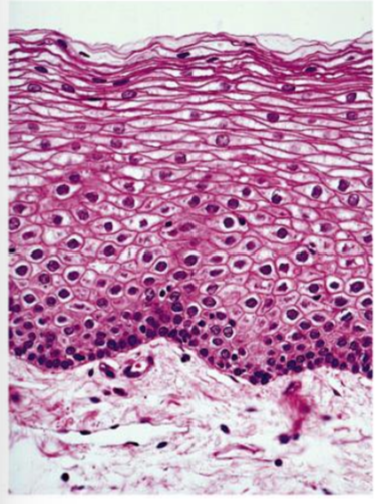
Bile Duct Epithelial Cells
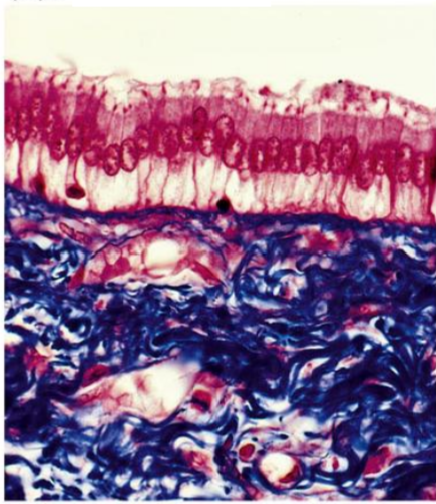
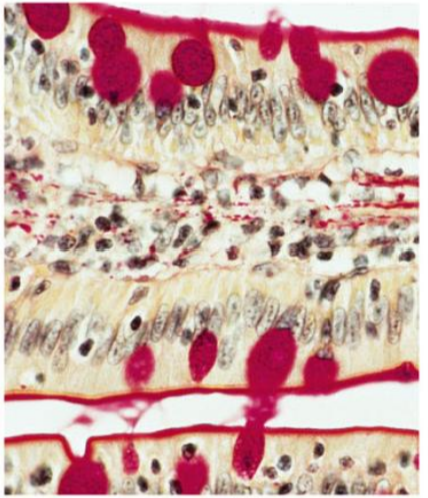
Intestine Epithelial Cells
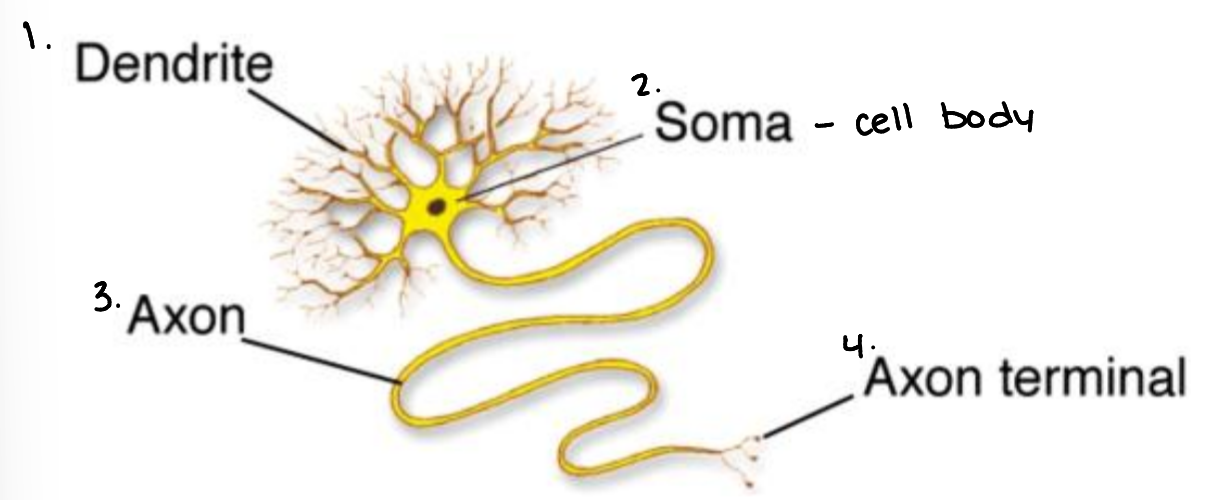
cells that receive and transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the body & are capable of generating electrical activity
Neurons
long, multinucleated cells that generate force & movement
Muscle Cells
Giardia
example of a eukaryotic cell that is anaerobic
no mitochondria no chloroplasts
exists before endosymbiosis
Syncytium
a multinucleated cell that is the product of the fusion of mononucleated myoblasts
Basic Properties of Cells:
What distinguishes living cells from other non-living entities?
Complexity
genetics
replication
metabolism
Biochemistry
Function
response
Self-regulation
Which experiment demonstrates the origin of biologically important molecules?
Miller -Urey
→ suggested that organic molecules could form under the conditions that existed in the primitive earth