Units 1-9
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Industrial revolution
The revolution spurred urbanization, altered labor systems, and improved transportation with railways and steamships. While it boosted economic growth and innovation, migration, it also brought challenges like poor working conditions, child labor, and environmental degradation, and replaced existing energy sources with fossil fuel, laying the groundwork for modern industrial society.
The first Industrial Society
Great Britain. The British textile industry played a huge role in this because it created a huge boom in production, innovations transformed textile production, and shifted it to factory’s.
The British Aristocracy
They didn’t suffer materially, owned ½ of cultivated land in Britain. but eventually lost ground to emerging middle classes and industrialists.
The middle class society
Benefited most from ind rev. Mostly factory/ mine/ business owners. Lived aristocratic life. They were liberals who pushed for male suffrage. ¨ideology of domesticity¨ (men work woman stay home). Woman not working was viewed as status. Woman slowly reentered workplaces, ind rev economy created job opportunists for woman+men.
The labouring classes
Benefited least from ind rev. Made up 70% of Britain. Worked in mines/factories/construction ect, desperate for jobs. Resided in overcrowded/ polluted city’s as result of ind rev. Factories favored girls/unmarried woman bc they accepted lower wage and were believed to be good for simple tasks. Meanwhile men were in more skilled supervisory positions. Woman not allowed in unions, later worked as domestic servants for upper middle class (until marriage)
Social Protest
Ind life was uninhabitable for laboring classes so they made their own accommodations. Created self help groups ¨friendly society’s¨ Revolted by burning down the mills/machinery that took their jobs. Socialist challenged capitalism, a prominent socialist was Karl Marx. Nationalism eroded working class radicalism by creating a shared identity of all social classes.
Europeans in motion
Ind rev prompted huge migratory process where ½ of euro moved to country side/city’s. 20% left Europe entirely for Africa, North/Latin America, Australia and New Zealand. Unlike Latin america, the US was affordable and had job opportunities, but the native people there were protestants and hated the new Catholics/Jews, viewed them as ¨un-american¨. In Russia after the freeing of serfs, 13 million russians migrated to Siberia which caused lots of population pressure there, the russian gov encouraged Europeans to migrate there as well because it encouraged the dispersion of people.
Industrialization in the US and Russia
Rev eventually spread from Britain- W Europe- the rest of the world. Effects were new tech and energy sources, urbanization, change in class structures (ex Middle class became more popular and respected), trade unions, socialism ect. Ind rev most prominent in US/Russia. Appeared differently in every country. Russia became first out put of global communism.
The US industrial Rev without socialism
Socialism in US was very weak bc of conservative union organization, and diverse workforce in skilled labor. American industrialization began in New England textile factories which grew explosively due to resources. Also assisted by gov which gave tax breaks and public land for railroads. Political changes in response to capitalist industrial abuses, ex small farmers ralied against existing money system/ monopolies. And progressives who pushed for wage/hour and sanitation reforms. Socialism was viewed as un american.
Russia: Industrialization and revolution
US exuberant democracy and Russia’s absolute monarch heavily contrasted. Russia only had nobility (land owners, gov officials, military officers ect.) Most were peasants/serfs. Nobility spoke french as result of westernization, viewed as status. Economic differnces aswell. US farmers/busness men could operate in politcs to generate more fair change. Russias change was state genrated. Working class found marxist socialism, revolts led to Russian rev of 1905. But still change was limited and contitions of WW1 led to Russian rev of 1917.
After independence in Latin America
Latin america didnt expirence ind rev, but the second hand impacts were inevitable. Destructive struggle for independence led to a post independent country with decreased livestock, population and an empty national treasury. The 4 major administrative units turned into 18 separate countrys. Lots of international/local conflict. Conservatives vs. Liberals. Those two violently opposed groups allowed the millitary strongmen ¨caudillos¨ to gain power as defenders. Not much social change (woman not in politics, slavery mostly abolished, mulitracial middle class ect.)
Facing the world economy
In 19th cent Latin american politcal consolidation led to stability. Latin america was driven into world economy due to ind rev. They increased exports (Latin american export boom) provided ½ of worlds silver, guano (fertalizer) in return the imported textiles/machinary/tools. Large scale investment of foreign capital (great britain, US europe)
Becoming like europe
As economy and polulation and urbanization increased Latin america became more keen on becoming like europe and the US. To do so they expanced white population (recruited poor europeans with promise for better living) in hopes of atracting them. Only Middle and Upper class benifited from export boom. The lower class suffered and engaded in stikes which resulted in consecuences as grave as slaughter. These revolts formed the Mexican revelution which never caught on to rest of Latin america. Economy soared (financed from abroad) ¨aka ¨depended development¨ which was a form of colonization
Industrial revolution
The revolution spurred urbanization, altered labor systems, and improved transportation with railways and steamships. While it boosted economic growth and innovation, migration, it also brought challenges like poor working conditions, child labor, and environmental degradation, and replaced existing energy sources with fossil fuel, laying the groundwork for modern industrial society.
The first Industrial Society
Great Britain. The British textile industry played a huge role in this because it created a huge boom in production, innovations transformed textile production, and shifted it to factory’s.
The British Aristocracy
They didn’t suffer materially, owned ½ of cultivated land in Britain. but eventually lost ground to emerging middle classes and industrialists.
The middle class society
Benefited most from ind rev. Mostly factory/ mine/ business owners. Lived aristocratic life. They were liberals who pushed for male suffrage. ¨ideology of domesticity¨ (men work woman stay home). Woman not working was viewed as status. Woman slowly reentered workplaces, ind rev economy created job opportunists for woman+men.
The labouring classes
Benefited least from ind rev. Made up 70% of Britain. Worked in mines/factories/construction ect, desperate for jobs. Resided in overcrowded/ polluted city’s as result of ind rev. Factories favored girls/unmarried woman bc they accepted lower wage and were believed to be good for simple tasks. Meanwhile men were in more skilled supervisory positions. Woman not allowed in unions, later worked as domestic servants for upper middle class (until marriage)
Social Protest
Ind life was uninhabitable for laboring classes so they made their own accommodations. Created self help groups ¨friendly society’s¨ Revolted by burning down the mills/machinery that took their jobs. Socialist challenged capitalism, a prominent socialist was Karl Marx. Nationalism eroded working class radicalism by creating a shared identity of all social classes.
Europeans in motion
Ind rev prompted huge migratory process where ½ of euro moved to country side/city’s. 20% left Europe entirely for Africa, North/Latin America, Australia and New Zealand. Unlike Latin america, the US was affordable and had job opportunities, but the native people there were protestants and hated the new Catholics/Jews, viewed them as ¨un-american¨. In Russia after the freeing of serfs, 13 million russians migrated to Siberia which caused lots of population pressure there, the russian gov encouraged Europeans to migrate there as well because it encouraged the dispersion of people.
Industrialization in the US and Russia
Rev eventually spread from Britain- W Europe- the rest of the world. Effects were new tech and energy sources, urbanization, change in class structures (ex Middle class became more popular and respected), trade unions, socialism ect. Ind rev most prominent in US/Russia. Appeared differently in every country. Russia became first out put of global communism.
The US industrial Rev without socialism
Socialism in US was very weak bc of conservative union organization, and diverse workforce in skilled labor. American industrialization began in New England textile factories which grew explosively due to resources. Also assisted by gov which gave tax breaks and public land for railroads. Political changes in response to capitalist industrial abuses, ex small farmers ralied against existing money system/ monopolies. And progressives who pushed for wage/hour and sanitation reforms. Socialism was viewed as un american.
Russia: Industrialization and revolution
US exuberant democracy and Russia’s absolute monarch heavily contrasted. Russia only had nobility (land owners, gov officials, military officers ect.) Most were peasants/serfs. Nobility spoke french as result of westernization, viewed as status. Economic differnces aswell. US farmers/busness men could operate in politcs to generate more fair change. Russias change was state genrated. Working class found marxist socialism, revolts led to Russian rev of 1905. But still change was limited and contitions of WW1 led to Russian rev of 1917.
After independence in Latin America
Latin america didnt expirence ind rev, but the second hand impacts were inevitable. Destructive struggle for independence led to a post independent country with decreased livestock, population and an empty national treasury. The 4 major administrative units turned into 18 separate countrys. Lots of international/local conflict. Conservatives vs. Liberals. Those two violently opposed groups allowed the millitary strongmen ¨caudillos¨ to gain power as defenders. Not much social change (woman not in politics, slavery mostly abolished, mulitracial middle class ect.)
Facing the world economy
In 19th cent Latin american politcal consolidation led to stability. Latin america was driven into world economy due to ind rev. They increased exports (Latin american export boom) provided ½ of worlds silver, guano (fertalizer) in return the imported textiles/machinary/tools. Large scale investment of foreign capital (great britain, US europe)
Becoming like europe
As economy and polulation and urbanization increased Latin america became more keen on becoming like europe and the US. To do so they expanced white population (recruited poor europeans with promise for better living) in hopes of atracting them. Only Middle and Upper class benifited from export boom. The lower class suffered and engaded in stikes which resulted in consecuences as grave as slaughter. These revolts formed the Mexican revelution which never caught on to rest of Latin america. Economy soared (financed from abroad) ¨aka ¨depended development¨ which was a form of colonization
Silk Roads
Routes of trade stretching from Europe to Asia, luxury goods, mostly silk, which became valuable from of currency and showed status. Did not only affect elite, peasants began to play part in silk making as it grew popularity, giving up crop cultivation. Prompted spread of Buddhism.
Dunhuang
Major Central Asian Commerce city
Chinggis Khan
Created the major Mongol empire. Born poor, small alliance/military victory’s, became supreme leader. Launched Mongol World war. Well acomplished
Temujin Khan
Former name of Chinggis Khan
Mongol World War
Half a century of war which started as attack on China launched by Chinggis Khan.
Khubili Khan
Grandson of Chinggis Khan, Chinas Mongol ruler (1271-1294) kind, Confucianism-inspired.
Ming Dynasty
Followed that of the Mongol, but by this time Mongols had retreated to their homeland. During this dynasty they enforced Confucian/gender values to erase Mongol impact
Black Death
Origen: China. Transported by rodents transmitted by fleas. Emerged 1331 in NE China, reached middle east/W Europe bu 1347. 50-90% death rates of pop. Middle east -1/3 ; Europe -1/2
Sea Roads
Caused by desire for foreign goods. Indian ocean commerce. Lower transportation costs than silk because ships could carry more than camels. Used monsoons. Enabled by spread of Islam, which was a religion friendly to trade.
Great Zimbabwe
Powerful state. Peaked 1250-1350 due to trade in cold and wealth derived from cattle. Labor power; build big walls.
Melaka
City on S edge of Malay Peninsula, founded by prince from Sumatra, became capital of Malay Muslim sultanate. By 15th cent had largest pop of SE Asia. Part of growing role of Islam, center for Islamic learning. Merchants moved there. Monopolized trade by selling things for 3 times the cost to China.
Zheng He
Muslim captain of Chinese maritime expeditions Sought to bring foreigners to Chinese tribute system.
Sand Roads
Commercial networks of trade spreading across Sahara desert, connected N Africa to Mediterranean. Major international trade route that fostered contact between distant peoples.
Arabian camel
Turning point for sand roads bc it made it possible to travel across due to camels not drinking for 10 days. Initiated trans-Saharan commerce.
House of Wisdom
Academic center for research and translation in Baghdad.
Crusades
“holy wars“ between Arab Empire and Christian Byzantine Empire (Islam vs. Christendom) Arab captured Byzantine and laid siege unsuccessfully on Constantinople. Began in 1095 and were intermittent for next 200 years.
American web
Spread of culture and art/technology and Commerce throughout the Americas (not nearly as intricate as Eurasian/African webs)
Chaco Phenomenon
5 major pueblos emerged 2500 sq miles in NW New Mexico.
Pochteca
Merchants in Aztec society who took on large trading missions, usually private businessmen. Legally commoners but super wealthy.
Caravanserai
Inns and guest houses along the silk roads designated for merchants to rest at and nourish their animals and exchange with locals
Song Dynasty
It was a dynasty that ruled over ancient Chinese civilization; considered “golden age“ of arts and literature. Elite upper class exams. Stable political rule. (1960-1279)
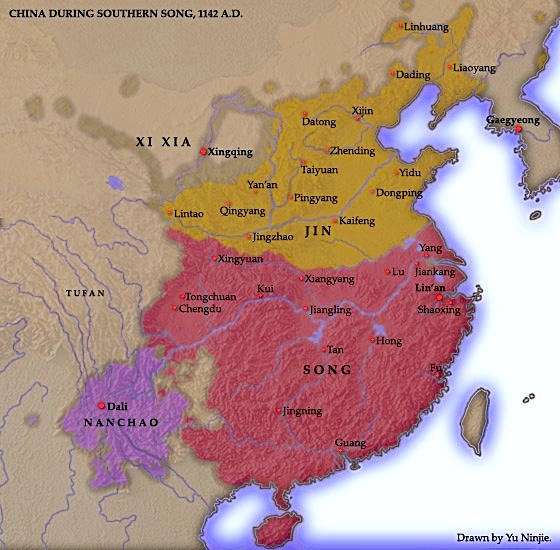
China’s economic revolution
Made song dynasty most successful country. Population spiked. Adoption of Champa rice from Vietnam. Many agricultural achivments
Hangzhou
Capital of Song Dynasty. Home to over 1 million people.
Foot Binding
Began among dancers and courtesans in 10th or 11th century. Process of wrapping young girls feet which prevented growth symbolizing fragility and femininity (before and after song Dynasty)
Bushido
“the way of the warrior“. Samurai’s values which included loyalty honor ect. Samurai warriors would choose death over surrendering.
Tribute system
Showing respect other country’s rulers in order to establish a good relationship and secure peace/ trading opportunities.
chu nom
(southern script) Vietnam’s writing system that was developed from Chinese writing.
Srivijaya
SE Asia. Early example of commerce connection. Region shaped by early Indian ocean trade and small sea ports success gave rise to Malay Kingdom. Employed Indians. Buddhism was very prominent and gave rulers a higher level of magic.
Madjapahit
Largest state on Island of Java. Influenced by Hinduism. Hindu-Javanese cultural blend. Peaked in mid 1300’s.
Angkor Wat
Stunning architectural temple representation of Hinduism built by Khmer Kingdom of Angkor. Largest religious structure of its time.
Abbasid Caliphate
And Arab dynasty that ruled over Islamic world (in theory) since 790. Built capital of Baghdad but lost control to Turkic speaking pastorialists and converted it to the Seljuk Turkic empire.
Seljuk Turkic empire
Participated greatly in the Islamic middle east. Turks became major sustainers of Islam as it warriors and peoples converted. Taken over my mongols (pastoral people) and ended in 1258
Ottman Empire
Created by Turkic warrior groups who migrated to Turkey and established, and protracted the life and power of the Islamic middle east. Extended control over time. Sought to bring unity to Islamic world.
Constantinpole
Capital of Roman empire
jizya
a tax targeted towards non muslims, which encouraged the conversion of non muslims
al-andalus
Muslims name for Spain. Site of cross cultural encounters with Christian western Europe. Muslims, Christians and Jews were able to mix freely. Most prosperous agricultural economy in Europe. Christians eventually became inferior to Muslims.
Swahili Civilization ( East African Civilization)
A set of Commercialized city states along east African coast. Began as farming/fishing people but developed do to trade with Arabian, Greek and Roman. Urban society, politically independent.
West African Civilization
Emerged driven by commercial exchange; penetration of Islam. Hausa speaking people of N Nigeria created many independent city/states which resembled that of Swahili. Flourishing commercial culture. Began integrating with international commerce which prompted hierarchy’s, which viewed powerful woman as dangerous. Most slaves were woman.
trans-Sahara slave trade
5,500 enslaved people traveled across dessert to word for the wealthy in the Islamic North. (1100-1400)
Timbuktu
One of west Africans urban commercial centers, some of which became manufacturing centers.
Byzantine Empire
Most sophisticated and powerful Christian empire for century’s. It was a continuation of the Roman empire. Declined terminally in 1200. However its traditions remained influenced by Rus (emerging civilization in Europe)
Ottoman seizure of Constantinople
Over time Turks and Western Europeans began to destabilize Byzantine territory. And finally did so permanently when they took the Capital City and Empire.
Kievan Rus
A culturally diverse region which included Finnic and Baltic people emerged in 9th century. Was a society of opposite ends of social class. ex. freemen and enslaved people.
Eastern Orthodox Christianity
affiliated with Byzantine empire, which was in search of unifying religion that would connect it to exchange. Created unified identity.
Western Christianity/christiendom
On margins of world History distinctly until 1000. Its geographic location made trade extremely difficult, which made political unity challenging and divided it. Referred to as Roman Catholic whom’s church linked entire region. Large church community with both competitive/uplifting relationship.
Feudalism
Lower ranking lords/knights pleaded alligence to higher ranking ones.
Roman Catholic empire
By 1450 Christianity had been embraced by almost all of western Europe. The Roman Catholic church became the link of the entire region in order to distinguish itself. It was represented by someone in nearly every community.
European Renaissance
Beginning in commercial sites of Italy, between 1350-1500) it sought inspiration for art and literature from ancient Greece and Rome “returning to the sources.” Although some religious content, most themes were contemporary references from ancient mythology. Prompted more individualism which caused capitalist economy. Created new future from its own past.
Maya Civilization
Civilization where Guatemala and Yucatan are currently, incredible intellectual and artistic accomplishments. Temples, pyramids, murals, palaces ect. Most elaborate writing systems in the Americas.
Aztec Empire
Population of 5-6 million. Loosely structured, local people rebelled often. Required labor from its people. Sacrifice was a huge ritual and used enslaved people. Because of this the empire took off, establishing dominance and respect.
Inca empire
Great geographic location which supported agriculture and trade. Empire located along Aldes Mountains. Quickly became rich. Recorded data of population in their “quipus“. People were mostly free religiously, people they conquered learned Quechua and every family was required labor service (mita)
Korea’s relationship with China
Neighbors, they were invaded by China therefore their trading wasn’t always as lenient and more pressure from China. They adopted Confucianism which replaced their flexible lifestyle. Developed alphabet and became distinctive society as the stopped traveling to China. Developed their own military (samurai)
Vietnam’s Relationship with China
Shaped by encounters with China. Borrowed lots (Confucianism, Buddhism, Daoism, art/lit ect.). Their cultural heartland was fully incorporated into China yet they still maintained it despite it having been there for <1000 years. Remained politically independent and took inspiration from China but kept their own traditions. As it grew from China it took on more Orthodox Confucianism which gave woman more freedom.
Constantinople
Capital of Roman empire
Serfdom
Given way to by Roman style slavery. Enslaved people were not personal property and were able to live in families.
Upanishads
Sacred texts written by anonymous people (hinduism)
Hinduism
Largest and oldest religion in India. No founder, spread from India - southwest Asia. Valued truth, peace, love ect. Originated in Inus River valley (modern day Pakistan)
Brahman
Cast that valued sacrifice/ offerings that deities required
Buddhism
Modest and moral lifestyle. Meditation, understanding of reality. Founded by Sidartha Gualama. Enlightenment (Nirvana).
Founded Buddism
Siddhartha Guatama: prince who found sick old man then went on quest for enlightenment and became the Buddha.
Theravada Buddism
(teaching of the elders) portrayed Buddha as very wise but not divine. No help achieving Nirvana
Mahayana Buddism
more accessible practice, Nirvana was possible for everyone. Spread throughout central Asia, China, Japan, Kora, SE
Tibetan Buddhism.
Gave special authority to teachers , dissapeared in India then took place in Asia, due to high wealth of monostarys separation of people and competition against Islam.
Bhakti Movement
Began in S Korea and moved North. Involved devotion to particular deity. Pushed against caste/gender hierarchys.
Islam
Founder: Muhhamed. 3rd Religion of Abrahamic family of faiths. Turned marginal nomadic Arabs into huge empire and central role in history.