C.1.2 Cell Respiration
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
what does cellular respiration break down?
This energy (in the form of ATP) is produced during cellular respiration by breaking down nutrients and food (organic compounds) using enzymes into CO2, H2O and ATP.
what are organic compounds
Organic compounds are the initial source of energy. Organic compounds are molecules which contain carbon-carbon or carbon-hydrogen bonds such as glucose or fatty acids.
how is the energy taken out of these organic compounds
Through a number of metabolic steps the molecules are oxidized and potential energy stored in the compounds is transferred to ATP.
whats the source of organic compounds?
The source of organic compounds broken down in cell respiration is the food that we eat. Carbohydrates (sugars or starch) and lipids (fatty acids), but also proteins are used for energy production in cell respiration.
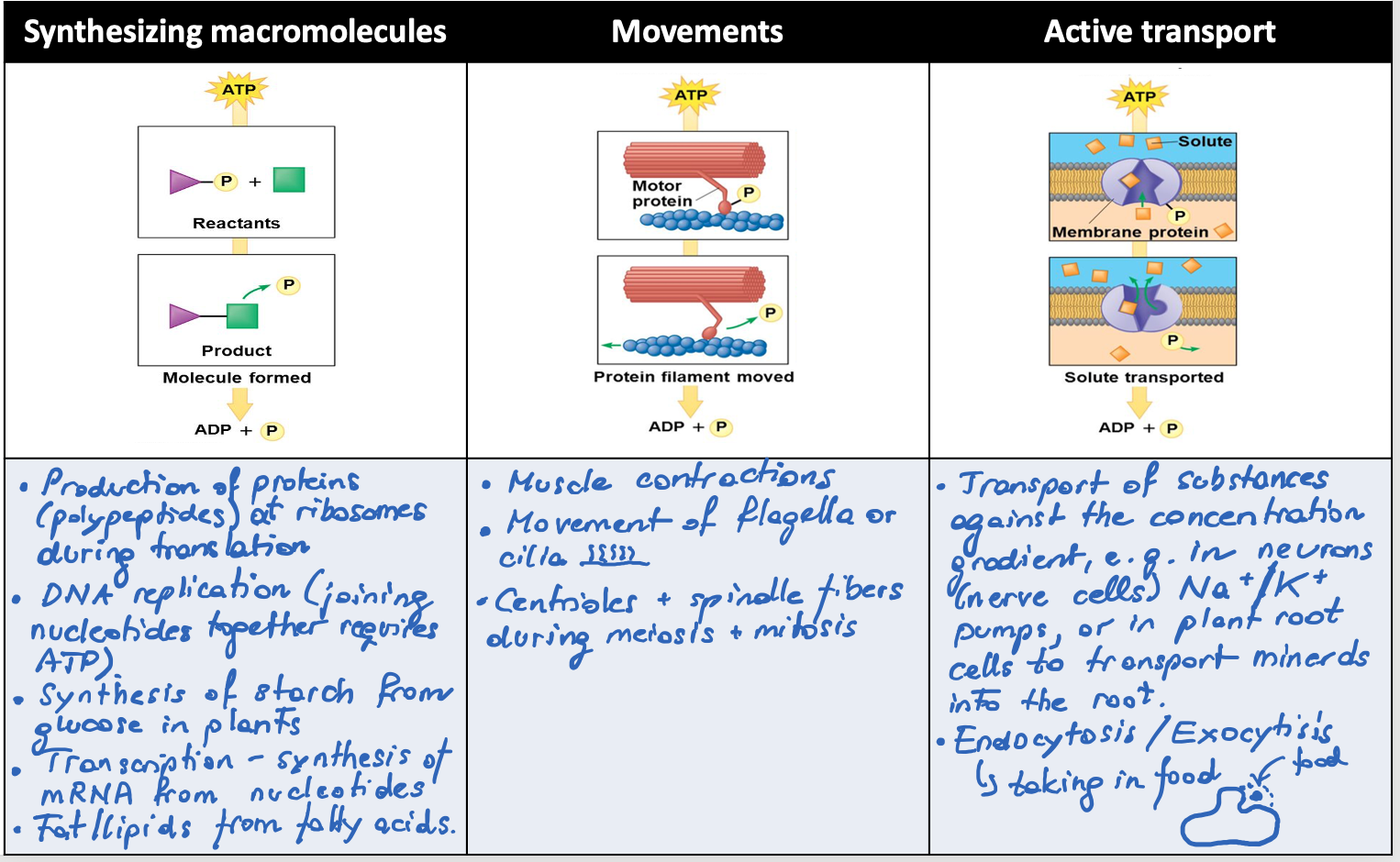
How is atp produced
ATP is produced by attaching a phosphate group to ADP. This step requires energy – ultimately coming from food. The covalent bond created stores energy until it is released again for processes required by cells. ADP is therefore recycled again.
Cellular Respiration is not the same as Breathing!
1- Breathing is the intake of oxygen into the lungs and release of carbon dioxide from the lungs to enable gas exchange and to provide the body with oxygen for cellular respiration.
2- Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds to produce ATP. It takes place in the mitochondria of all cells.
how is energy released in cellular respiration
Energy in cellular respiration is transferred in small quantities rather than one big release. If energy would be all given out in one go most of it would be lost as heat to the surrounding. Instead, energy is transferred to ATP in many small steps with only little heat loss.
whats the universal energy currency
ATP (Adenosine triphosphate)
What properties make ATP suitable as an energy source?

Why does ATP phosphorylate metabolites during metabolic reactions, and what is the effect of this phosphorylation?
ATP transfers a phosphate to form phosphorylated intermediates, which become more reactive and able to participate in the next step of the metabolic pathway.
What is phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is when a molecule gains a phosphate group, usually from ATP, which makes the molecule more reactive or changes its activity.
what is dephosphorelation
Dephosphorylation is when a phosphate group is removed from a molecule, often turning the molecule “off” or reducing its activity.
How is ATP formed during cellular respiration?
Energy from food is used to join ADP and Pi to form ATP.
What do energy-requiring processes in the body use as their energy source?
They use ATP (with enzymes), which is converted back into ADP.
What is the name of the process that forms ATP from ADP and Pi and releases water?
Condensation
What happens during the hydrolysis of ATP?
ATP is split into ADP by removing one phosphate group using water.
Why does ATP hydrolysis release energy?
Because breaking the covalent bond holding the phosphate group releases stored energy.
How does ATP hydrolysis enable muscle contraction involving actin and myosin filaments?
When muscles contract, they shorten in length as a result of actin and myosin protein filaments in muscle cells sliding in and out of each other. The sliding depends on the hydrolysis of ATP and the energy released is used for the “power stroke”.
steps of muscle contractions

what can chemical energy
Chemical energy (ATP) produced by an organism through cellular respiration can be converted into a number of different forms of energy with only little being lost to heat:
Chemical energy (ATP) produced by an organism through cellular respiration can be converted into a number of different forms of energy with only little being lost to heat:
kinetic energy during muscle contractions
light energy in bioluminiscence
into other forms of chemical energy in the synthesis of molecules or when transporting materials.
uses of atp in your body
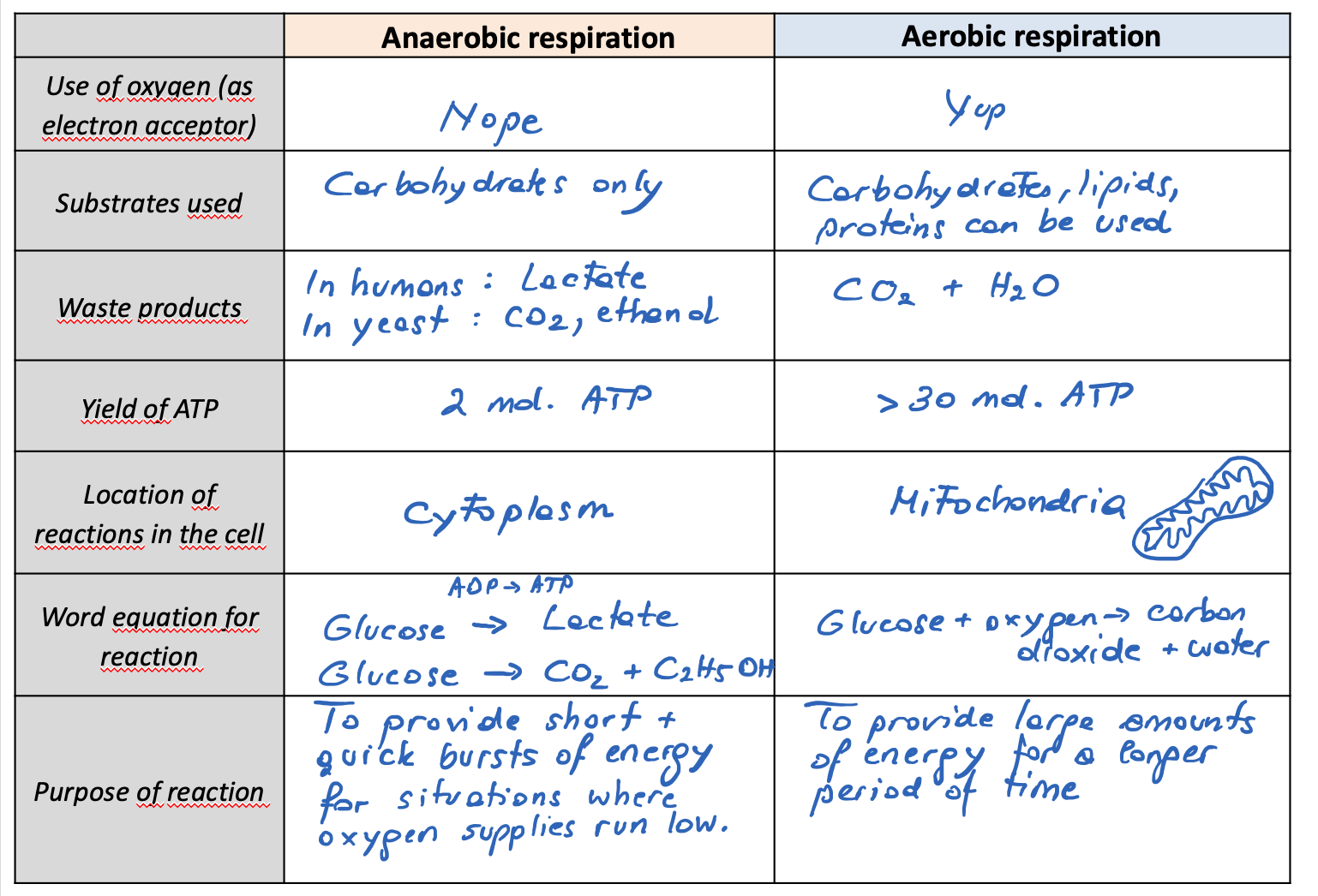
steps of anaerobic and aerobic cell respiration
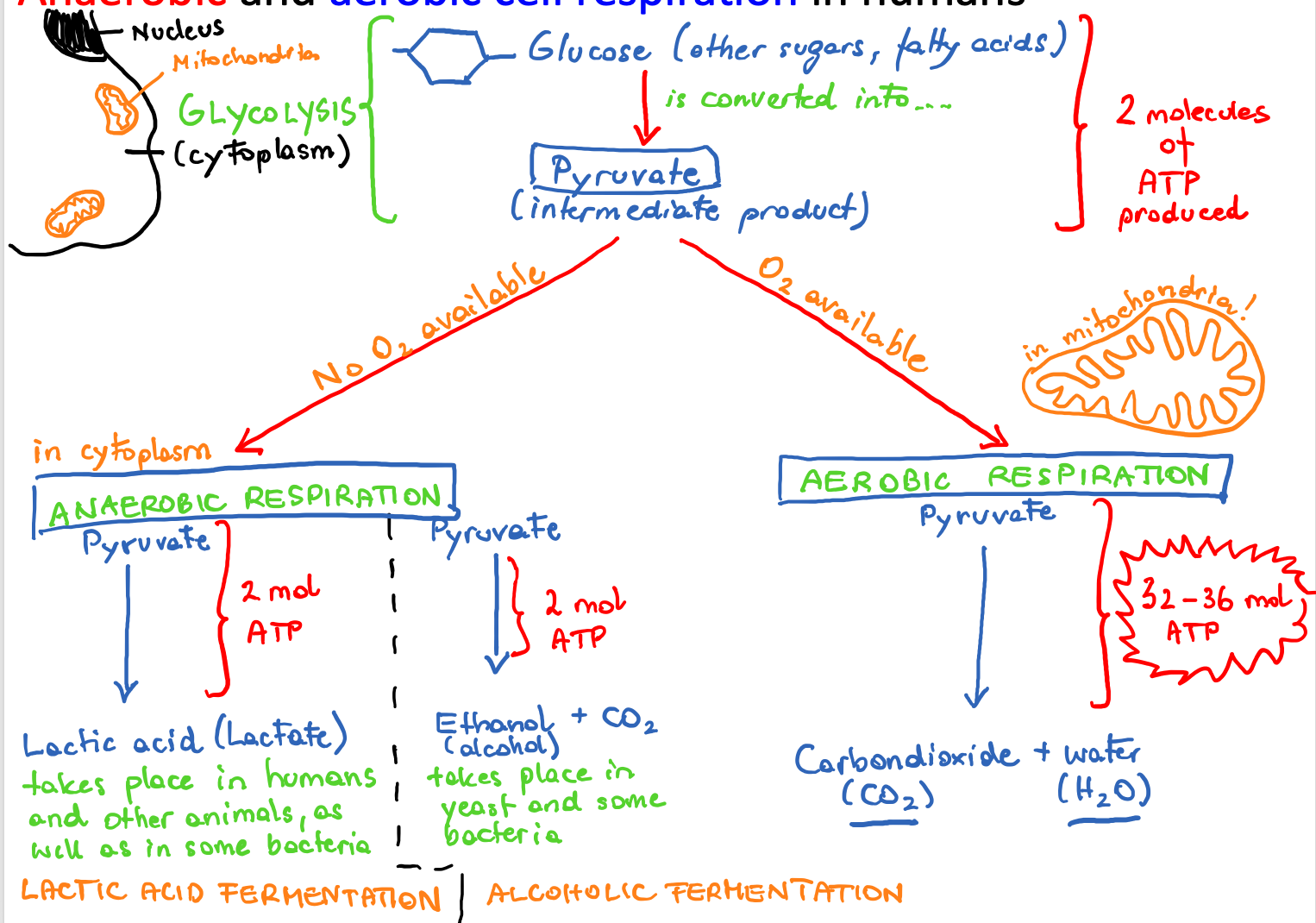
Anaerobic and aerobic cell respiration in humans.
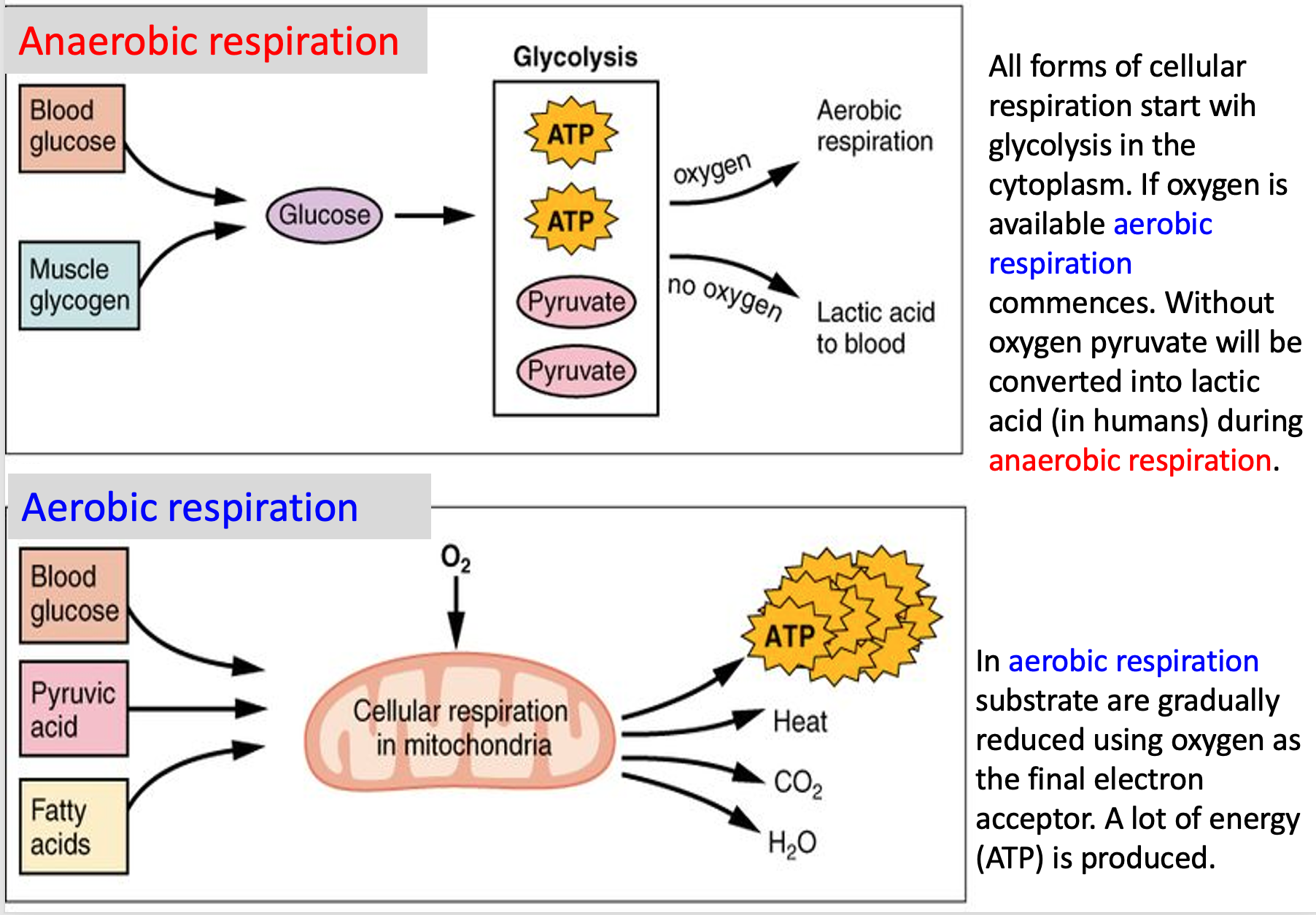
when is anaerobic respiration used.
•When a short and rapid burst of ATP is needed
•When oxygen supplies run out in respiring cells
•In environments which are oxygen deficient (e.g. waterlogged soil)
why is anaerobic respiration used in high intensity exercise such as sprinting, boxing or weight-lifting require anaerobic respiration?
What is produced?
This is because….
•There is not enough time to deliver O2 to the cells for aerobic respiration.
•The supply of energy needs to be fast and quickly available so that power can be maximized.
Lactate and a small amount of ATP is produced in this process. This process is only sufficient to produce ATP. Hydrogen ions (H+) accumulate and prevent further anaerobic respiration
if oxygen is avaliable, what respiration will be used? explain the products.
If oxygen is available, the intermediate product pyruvate is absorbed by mitochondria
Inside the mitochondrion the pyruvate is gradually broken down (reduced) into carbon dioxide, water and 36-38 molecules of ATP. Aerobic cell respiration therefore has a much higher yield of ATP per gram of glucose than anaerobic cell respiration.
steps of aerobic respiration
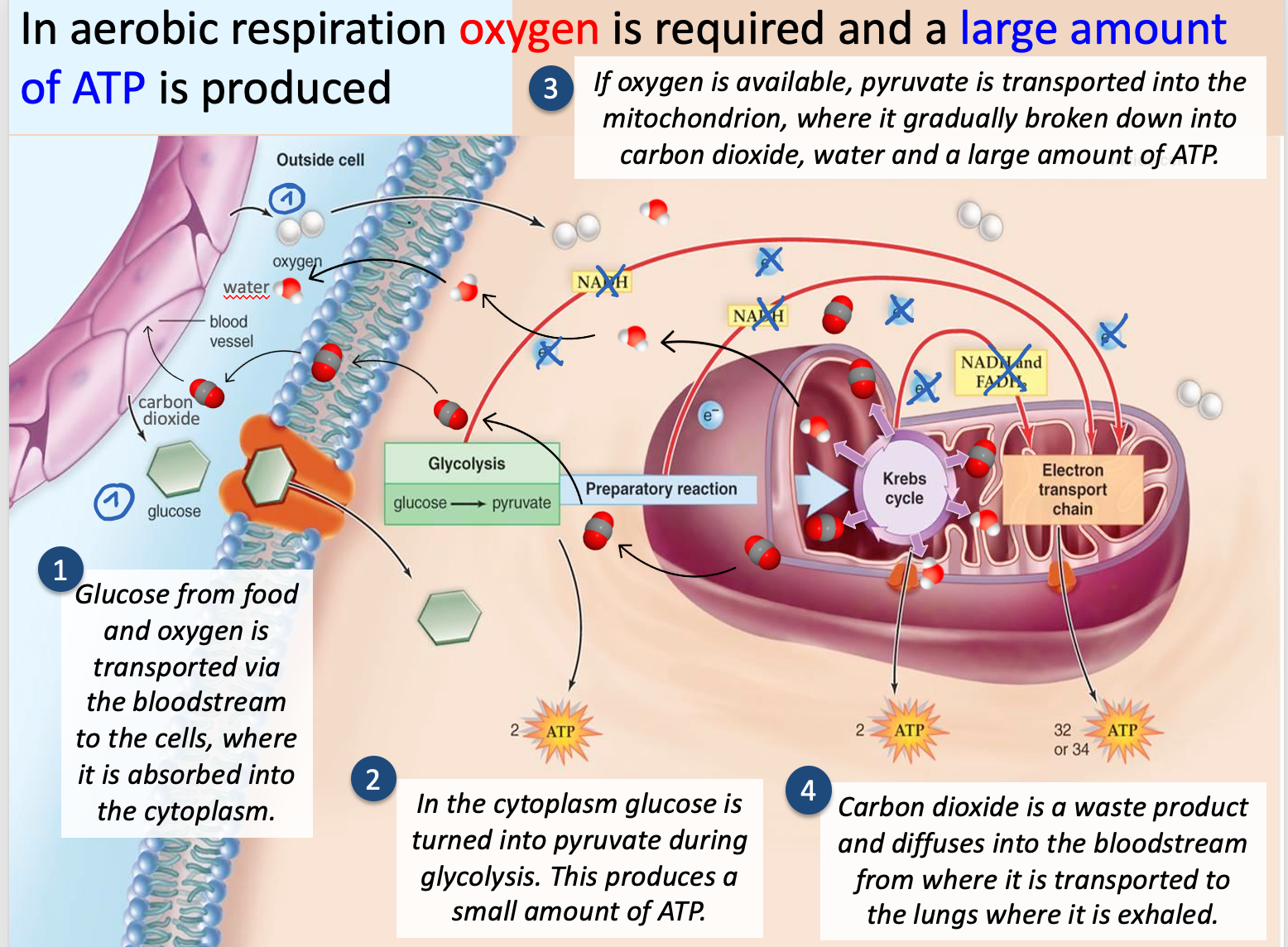
compare between anaerobic and aerobic respiration
whats a respirometer
A respirometer is a simple device that is used to measure respiration rate.
A respirometer usually involves…
The use of a sealed glass container in which the organism is places.
A substance which absorbs CO2 produced by cell respiration.
A capillary tube containing fluid which allows the changes in pressure to be monitored.
Label

