Ecology Study Set: Key Terms & Definitions in Biology
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
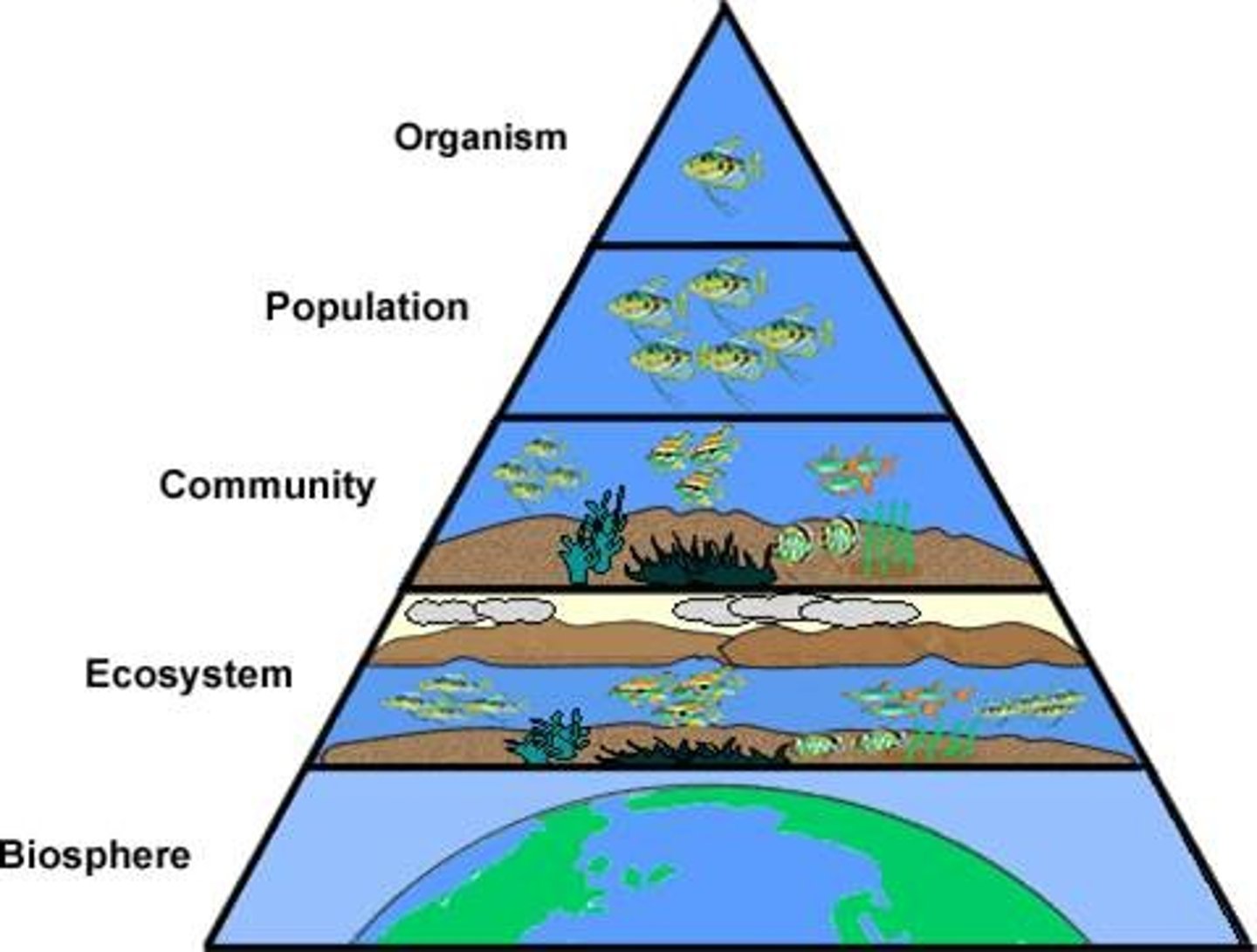
What is ecology?
The study of interactions between organisms and their environment
What is organismal ecology?
how an organism's structure, physiology, and behavior meet environmental challenges

What is population ecology?
the study of populations in relation to their environment

What is community ecology?
study of interactions among all populations in a common environment

What is ecosystem ecology?
study of the flow of energy and cycling of chemical elements within an ecosystem
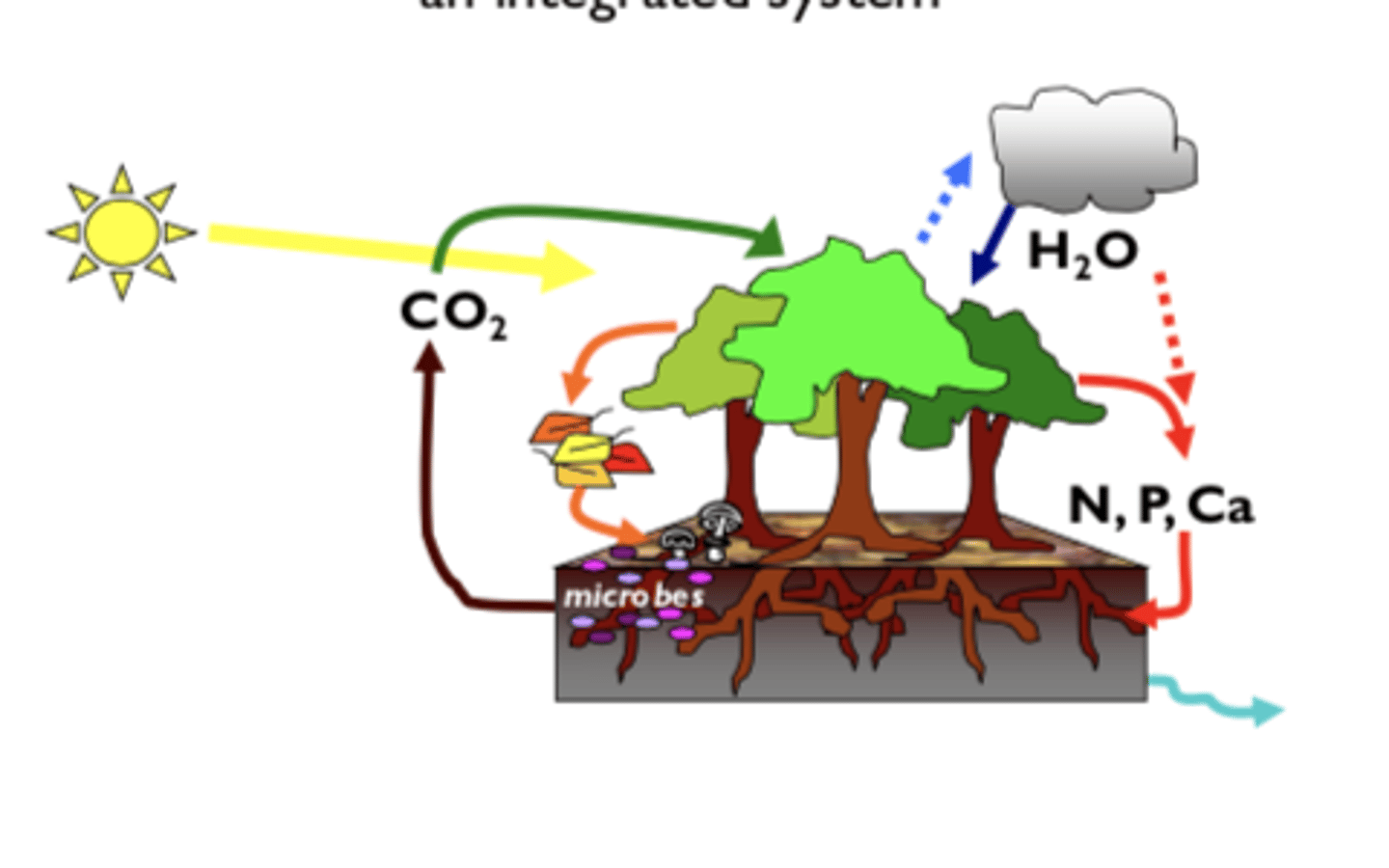
What is biosphere ecology?
the sum of all the planet's ecosystems
What is an invasive species?
A species that lands in a new place and can be harmful to their environment.
What is coevolution?
process in which two or more species evolve in response to changes in each other.
What is the difference between ecology and environmental science?
Environmental science has a larger human focus, looks into the impacts of pollution and degradation, and human impacts on ecosystems and biodiversity. Ecology is the study of the interactions between organisms and the environment.
What is a niche?
The role of an organism in its habitat which is due to biotic and abiotic factors
What is a habitat?
the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism.
What is a population?
group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area
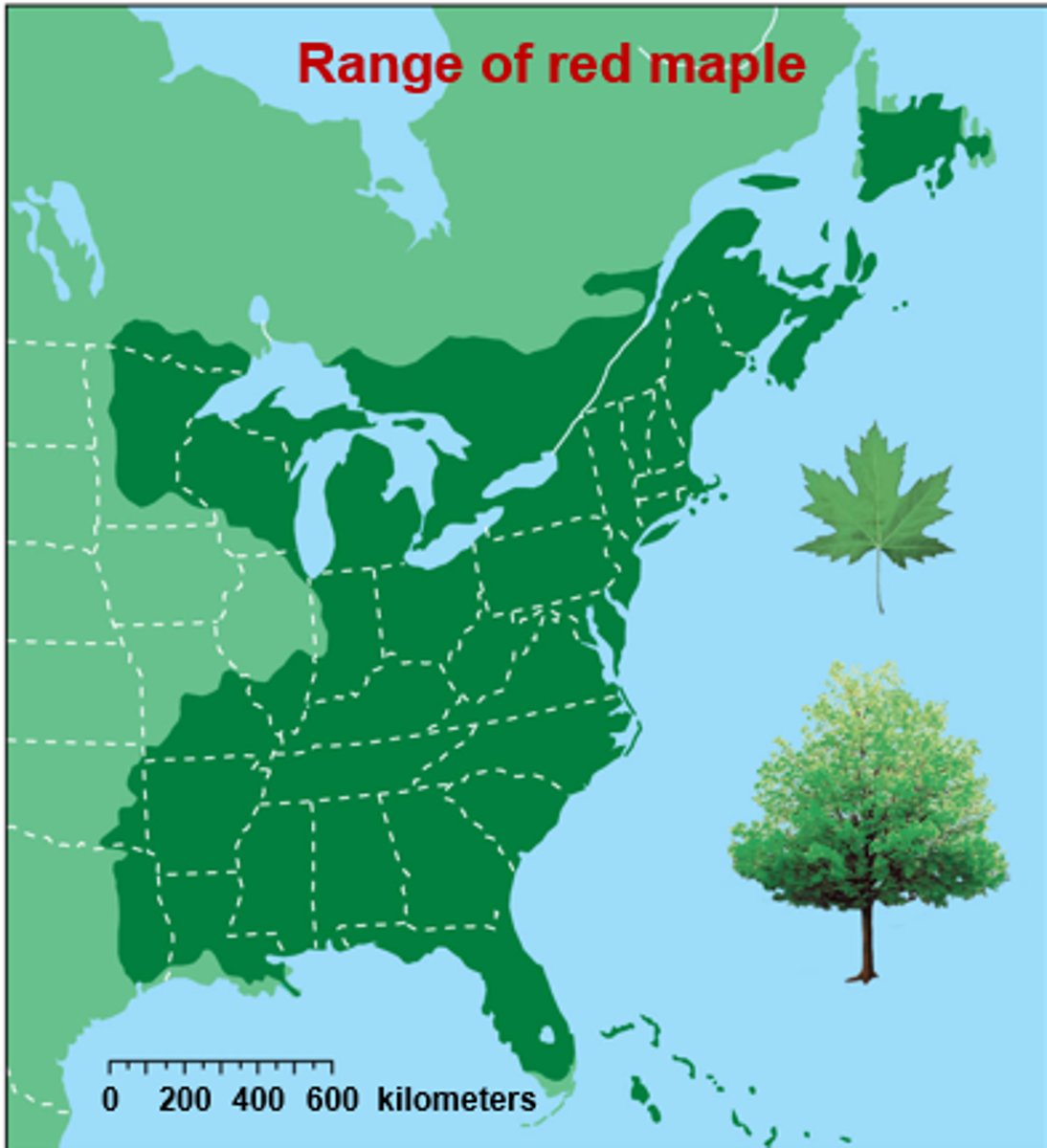
What is geographic range?
a measure of the total area covered by a population
What is abundance?
how many individuals in defined area
What is density?
how many individuals divided by area or volume
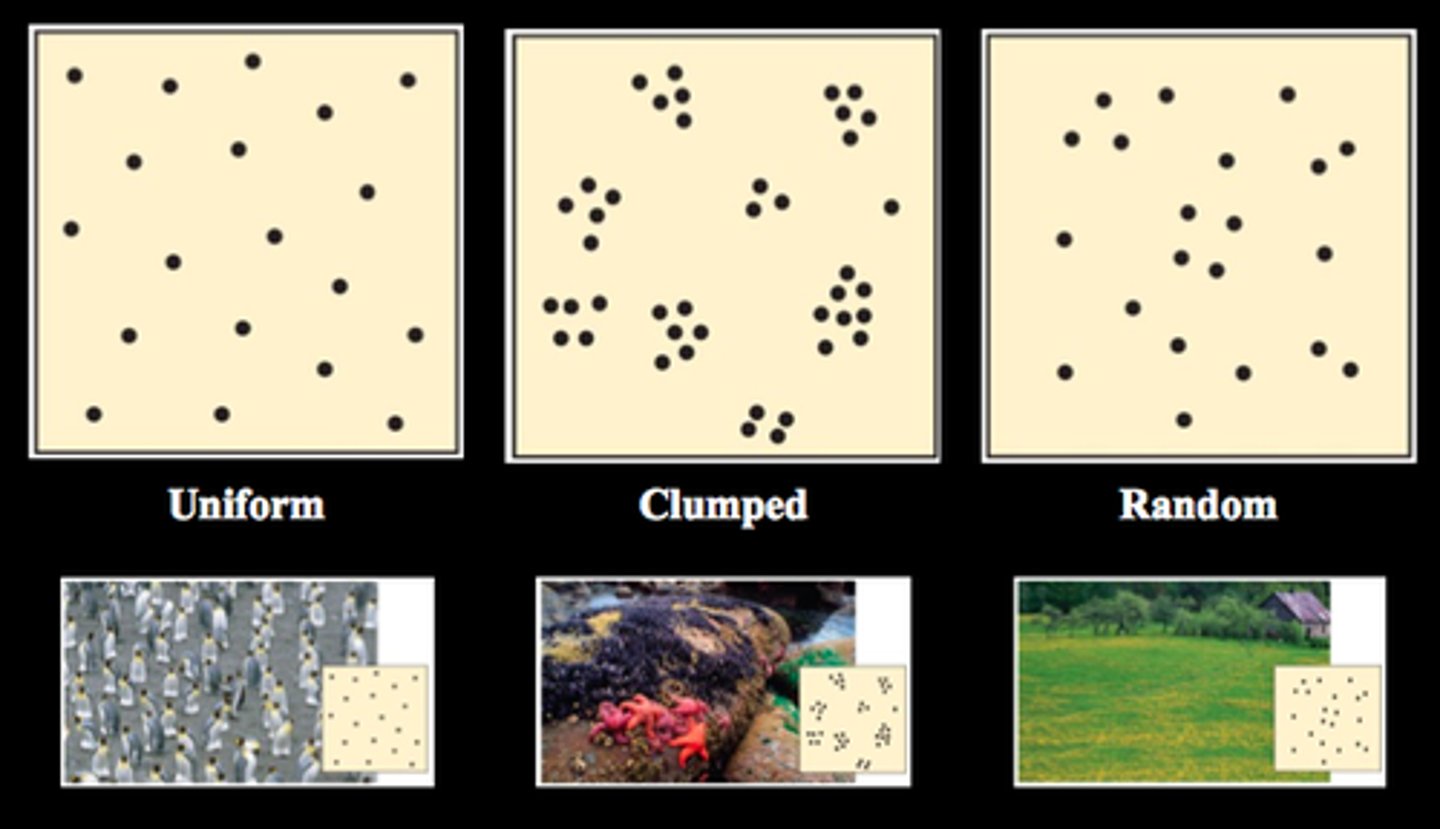
What is dispersion?
the pattern of spacing among individuals within the boundaries of the population

What is dispersal?
the movement of organisms from one place to another
What is an endemic species?
species found in one place and nowhere else
What is a cosmopolitan species?
A species with a distribution that ranges across all or most of the world in appropriate habitats
What is an exponential growth curve?
- Population starts out growing slowly, but then begins to grow fast.
- ex. human population growth
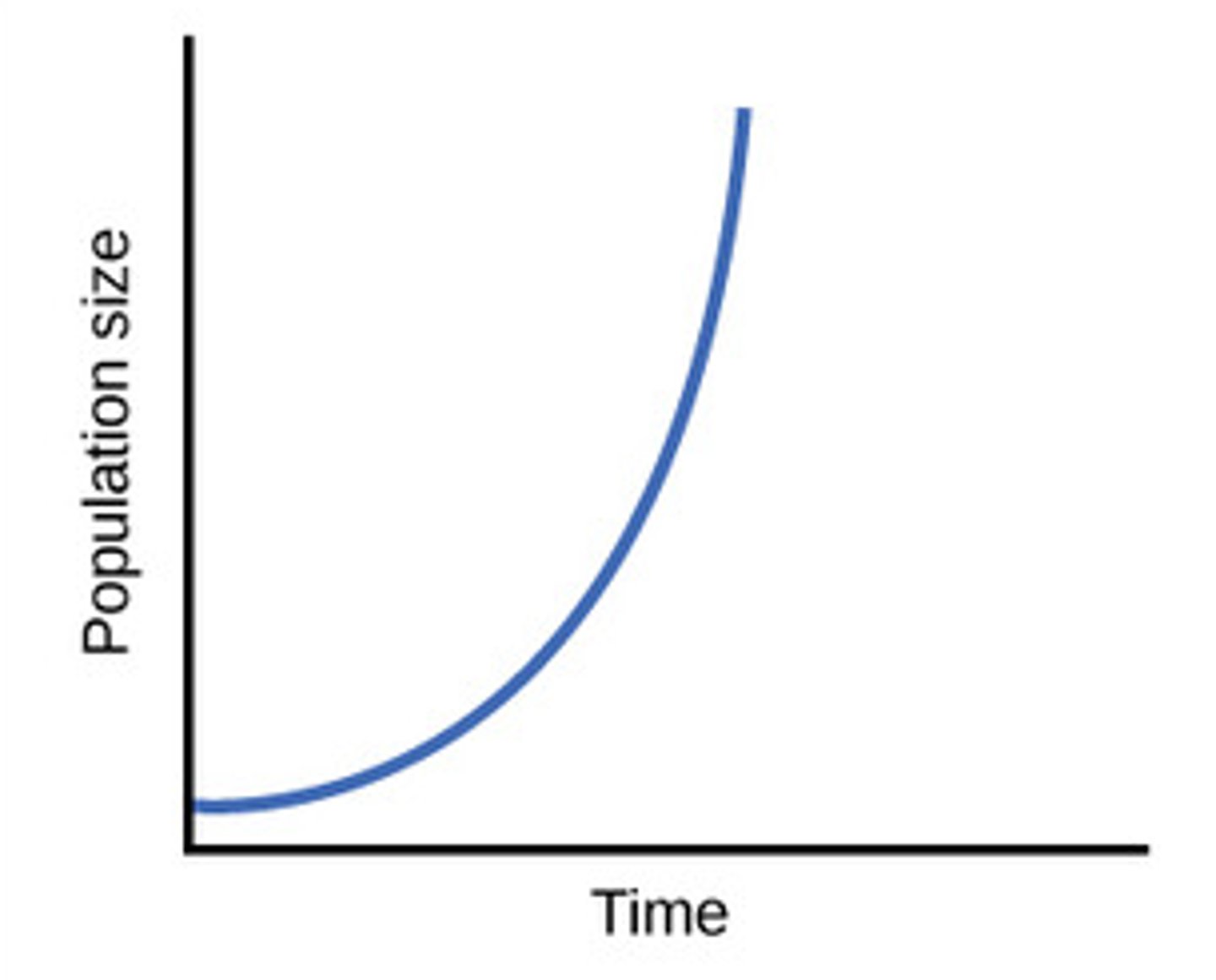
Can populations grow forever or not?
No, because resources will eventually run out.
What is logistic growth? (S shape)
Logistic growth occurs when a population's growth slows and then stops, following a period of exponential growth.

What is a community?
A group of populations living and interacting in an area.
What is species richness?
the number of different species in a community
What is species abundance?
How many of each species are there
What is species distribution (evenness)?
relative abundance: number of each species/total
What is species diversity?
The number of different species (richness) and the number of individuals of each species (distribution/evenness) within any one community.
(higher diversity considered better)
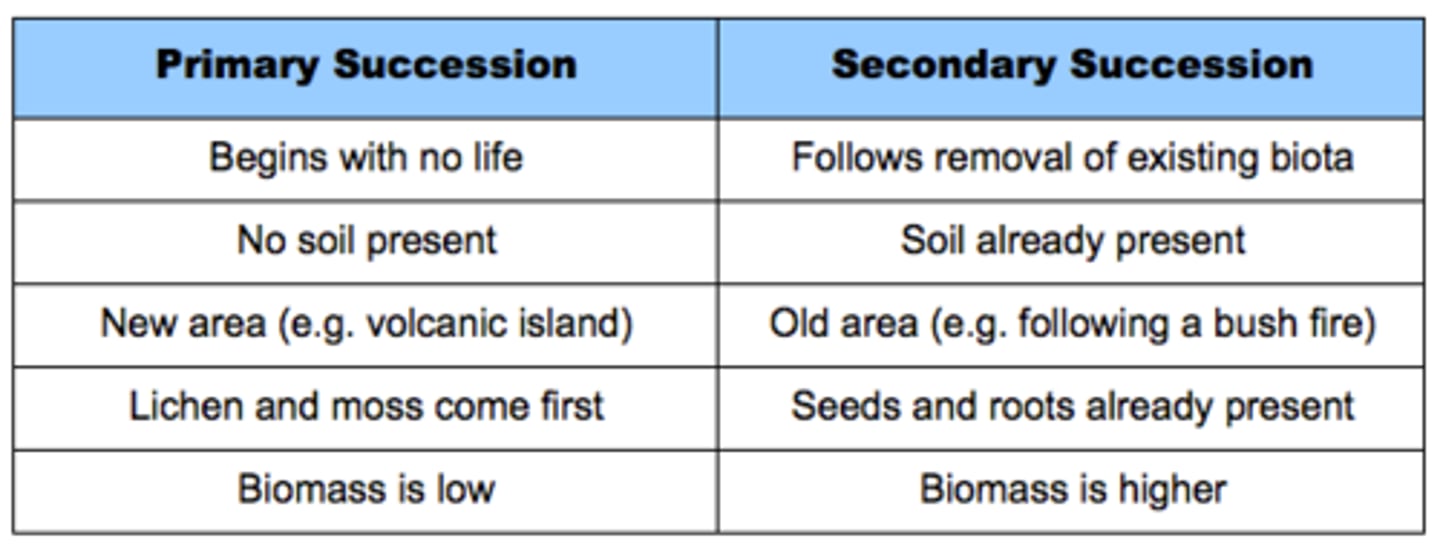
What is community succession?
change in species composition of a community after a disturbance
What is primary succession?
succession that begins in an area with no remnants of an older community

What is secondary succession?
Succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil
What is competition?
the struggle between organisms to survive as they attempt to use the same limited resources

What is interspecific competition?
competition between different species
What is intraspecific competition?
competition within a species
What is the law of the minimum?
The nutrient in least supply is the one that limits growth
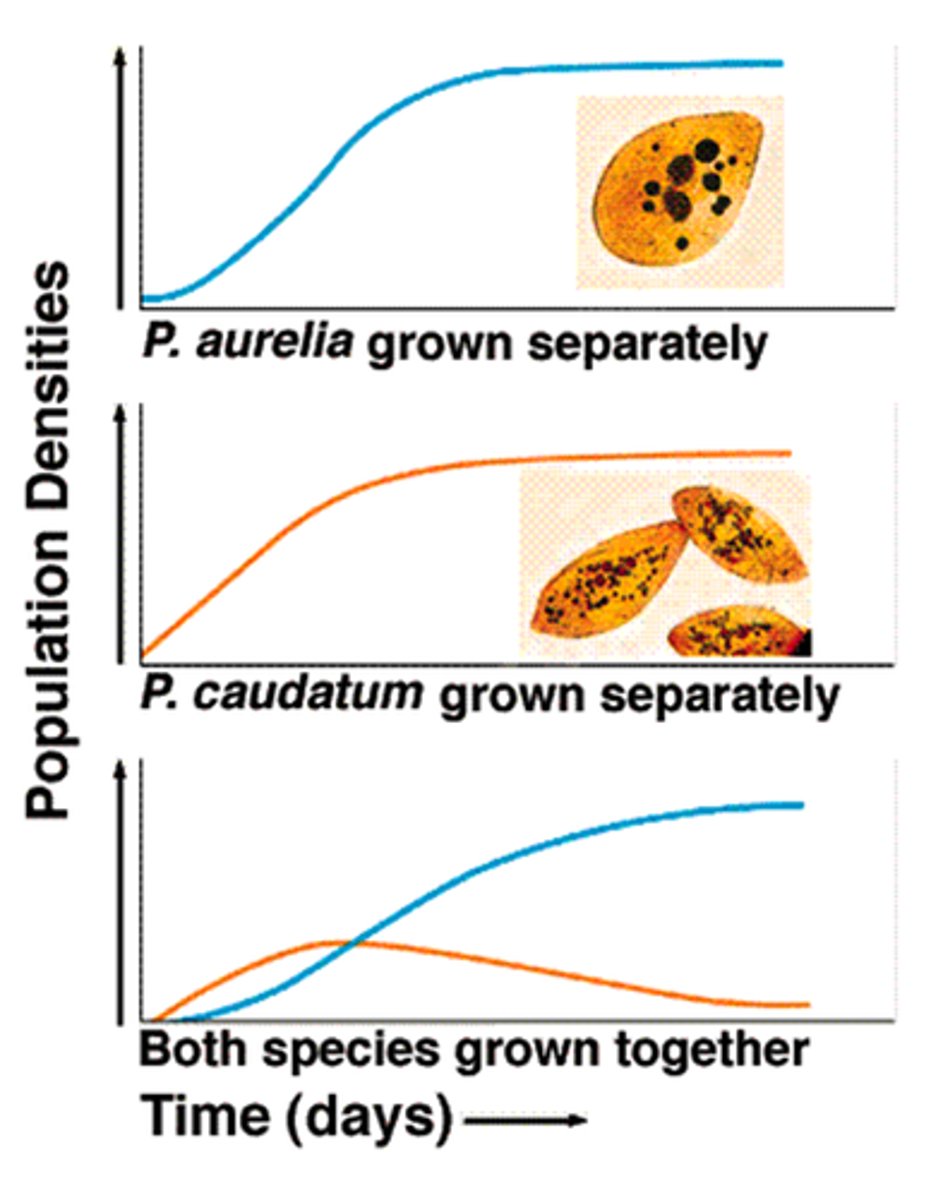
What is the competitive exclusion principle?
states that no two species can occupy the same niche in the same habitat at the same time
What is mutualism?
both organisms benefit
What is facultative mutualism?
both species can survive alone (not mandatory)
What is obligate mutualism?
where one species cannot survive without the other (required)
What is a generalist mutual?
Any organism can provide the necessary benefit
What is specialist mutual?
requires only a single specie to provide the necessary benefit
What is ammensalism?
One species harmed, the other unaffected
(ex. grass being stepped on)

What is commensalism?
one organism benefits and the other is unaffected

What is parasitism?
one species benefits and the other is harmed
- endoparasites = inside host
- ectoparasites = live on the host (external)
What is an ecosystem?
all of the living and nonliving things interacting in an area
What does biotic mean?
living organisms
What does abiotic mean?
Non-living things
What is the greenhouse effect?
The process by which gases hold heat in the atmosphere.
ex. permafrost melting, polar region warmed up 7F in 50 years