topic 1 - biological molecules
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
What does beta glucose + beta glucose make?
When the OH groups aren't next to each other the bond can form diagonally
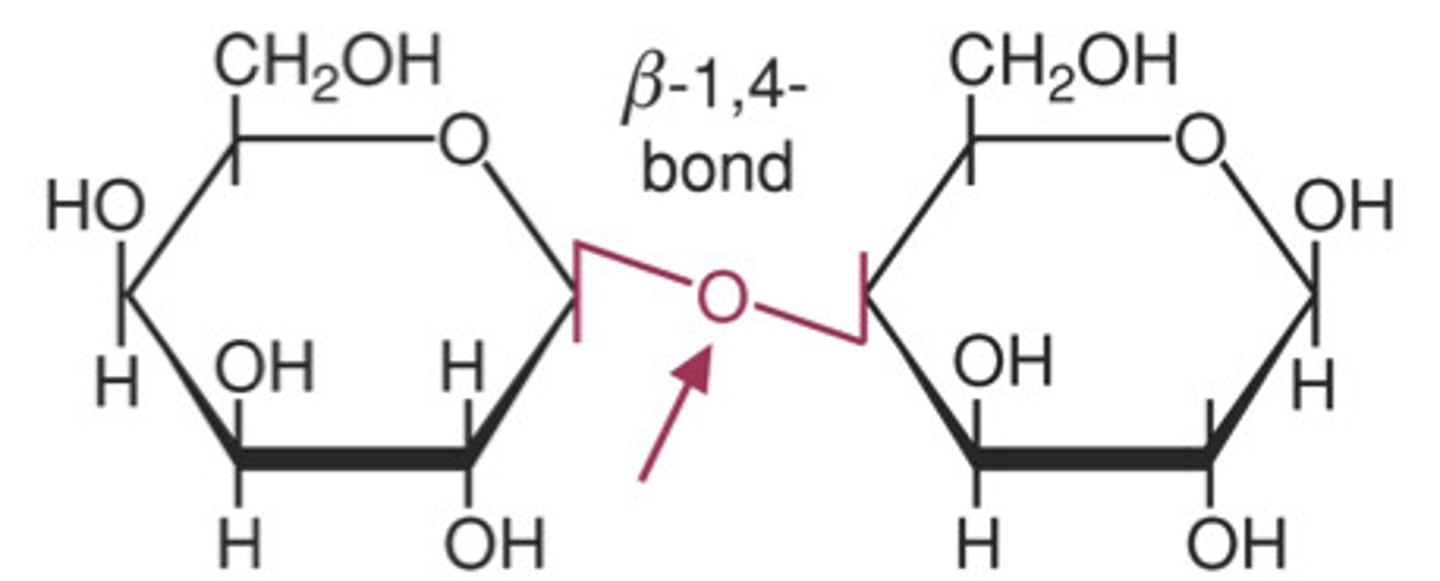
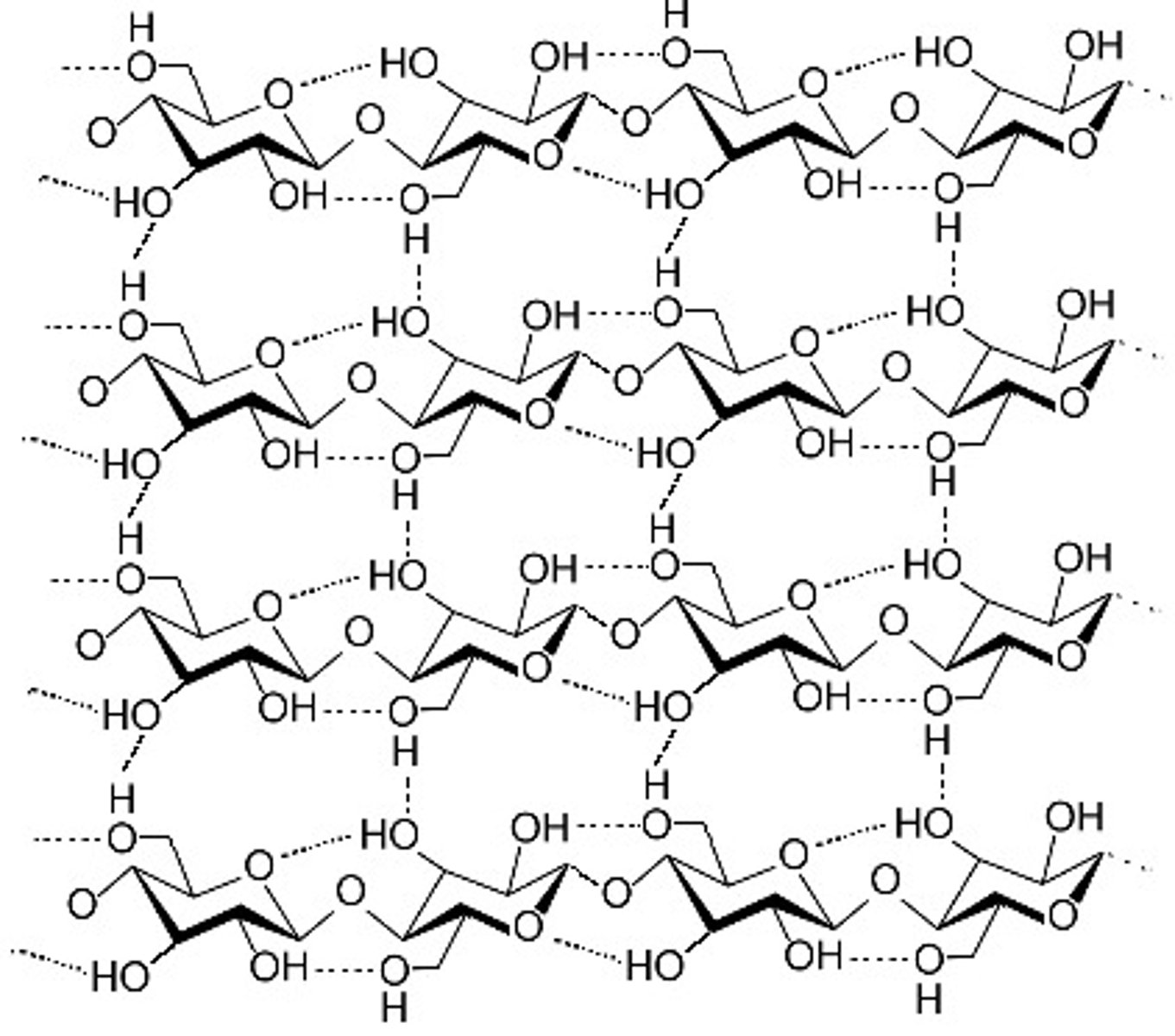
What is cellulose?
- polysaccharide in cell walls made out of beta glucose
- mechanically very strong so has a slow decomposition
- 1 to 4 links but in each one beta glucose molecule is inverted
-the structure also has many hydogen bonds linking the chains and making microfibrils
---> these are why cellulose is so straight and strong
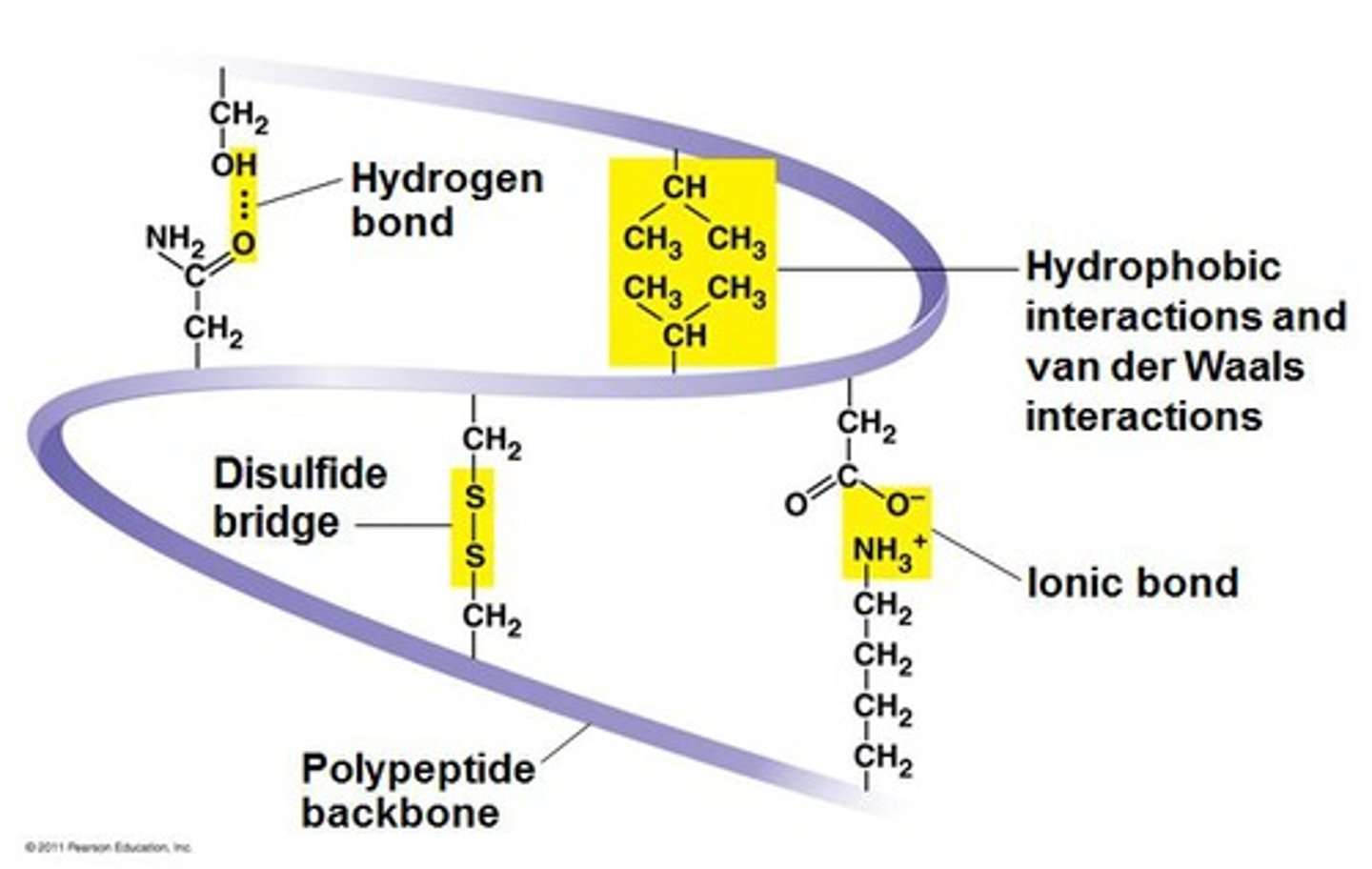
What are the different bonds that can be formed in the tertiary structure?
Disulphide - between 2 R groups which have sulphurs
Ionic bonds - between an acidic R group and a basic R group
Hydrogen bonds - between slightly charged carboxyl and amine groups
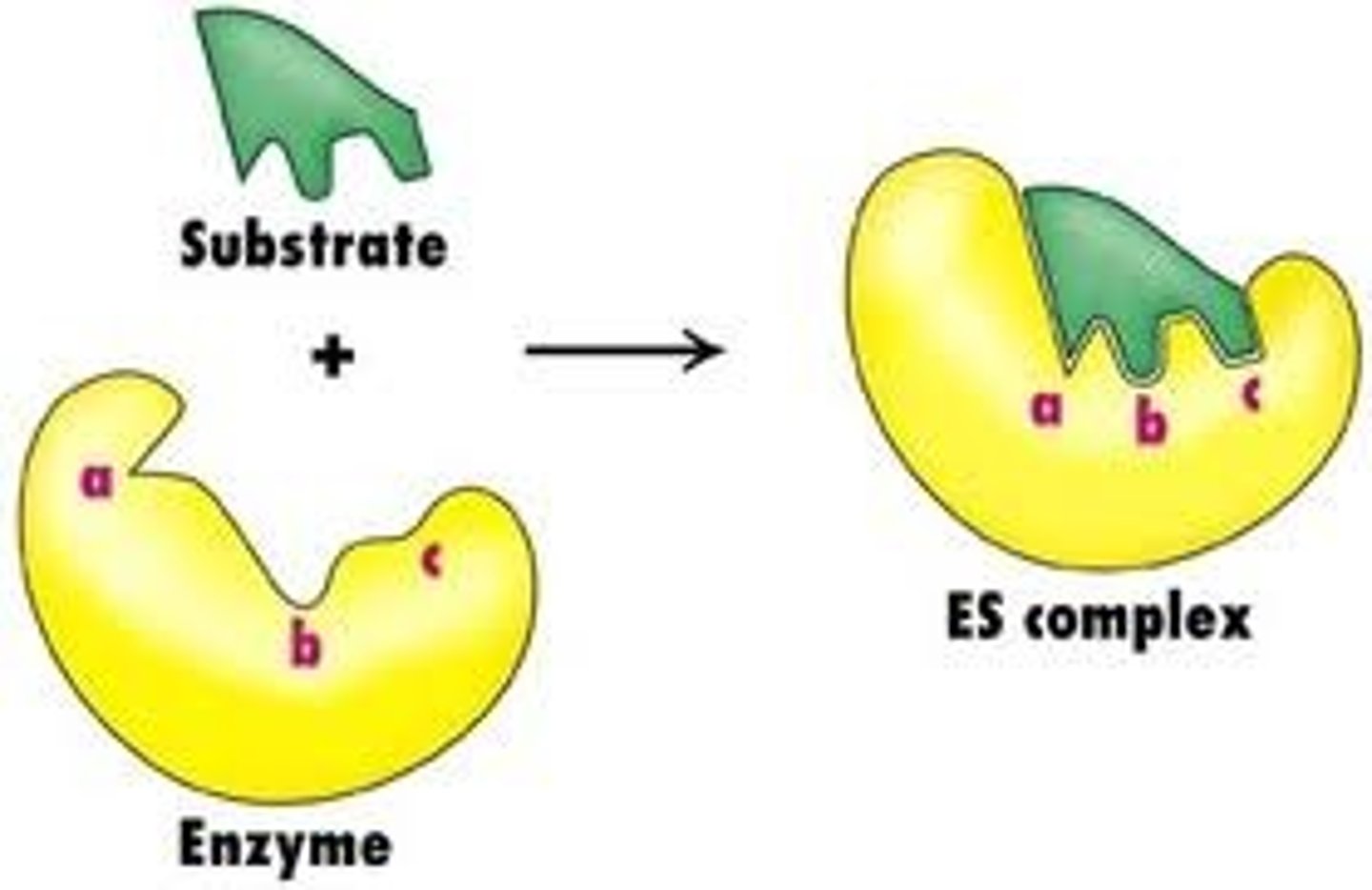
How can the active site bond to the substrate?
The enzyme and so the active site are made up of proteins.
The R-groups that line the active site allow the substrate to bond to it by hydrogen or ionic bonds.
They also still have complimentary shapes.
What are polymers?
Long chains of repeating units (monomers) joined/bonded together.
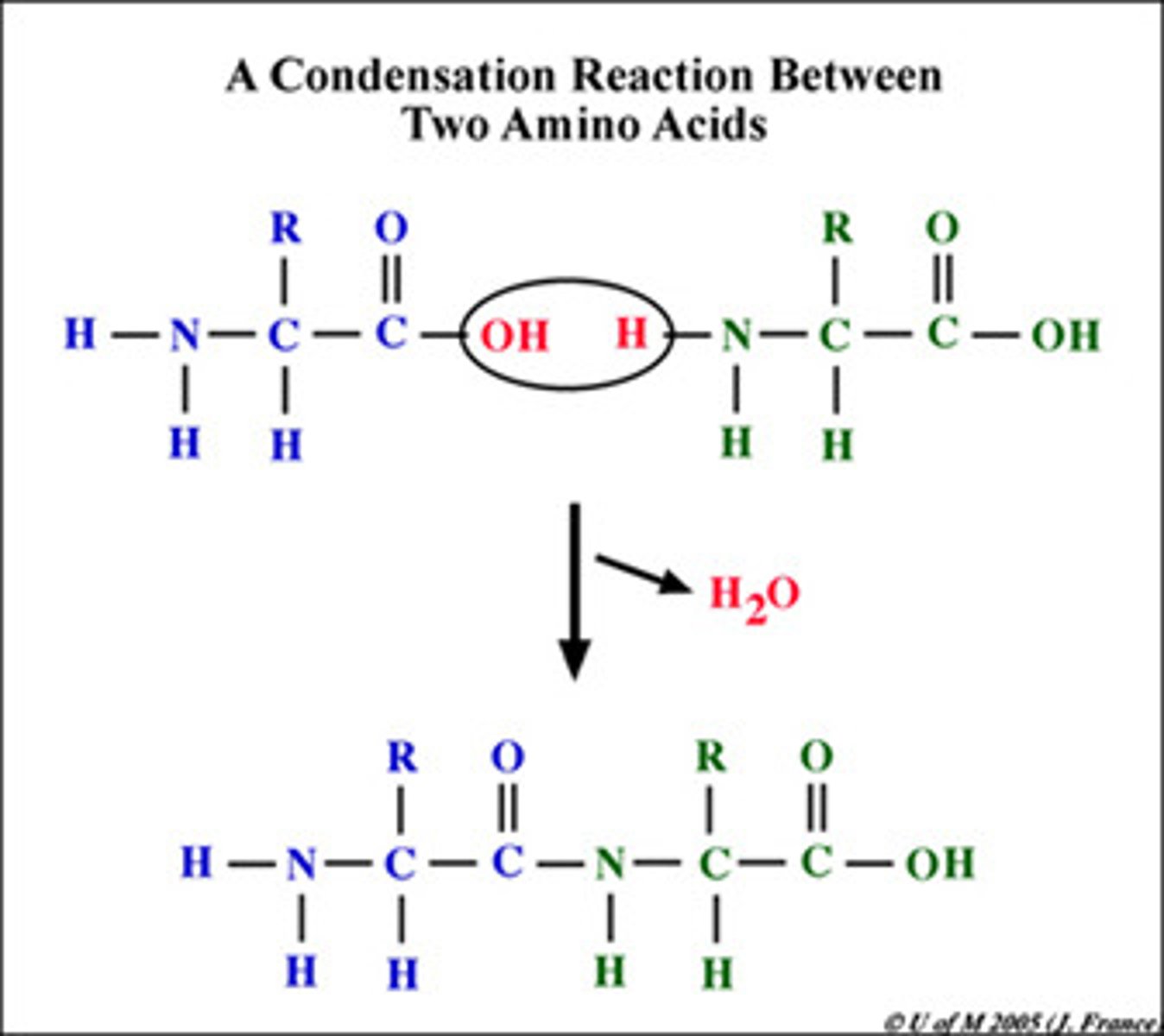
What occurs in a condensation reaction?
The joining of two molecules/monomers which produces/eliminates water (H2O) as a by-product and forms a covalent bond.
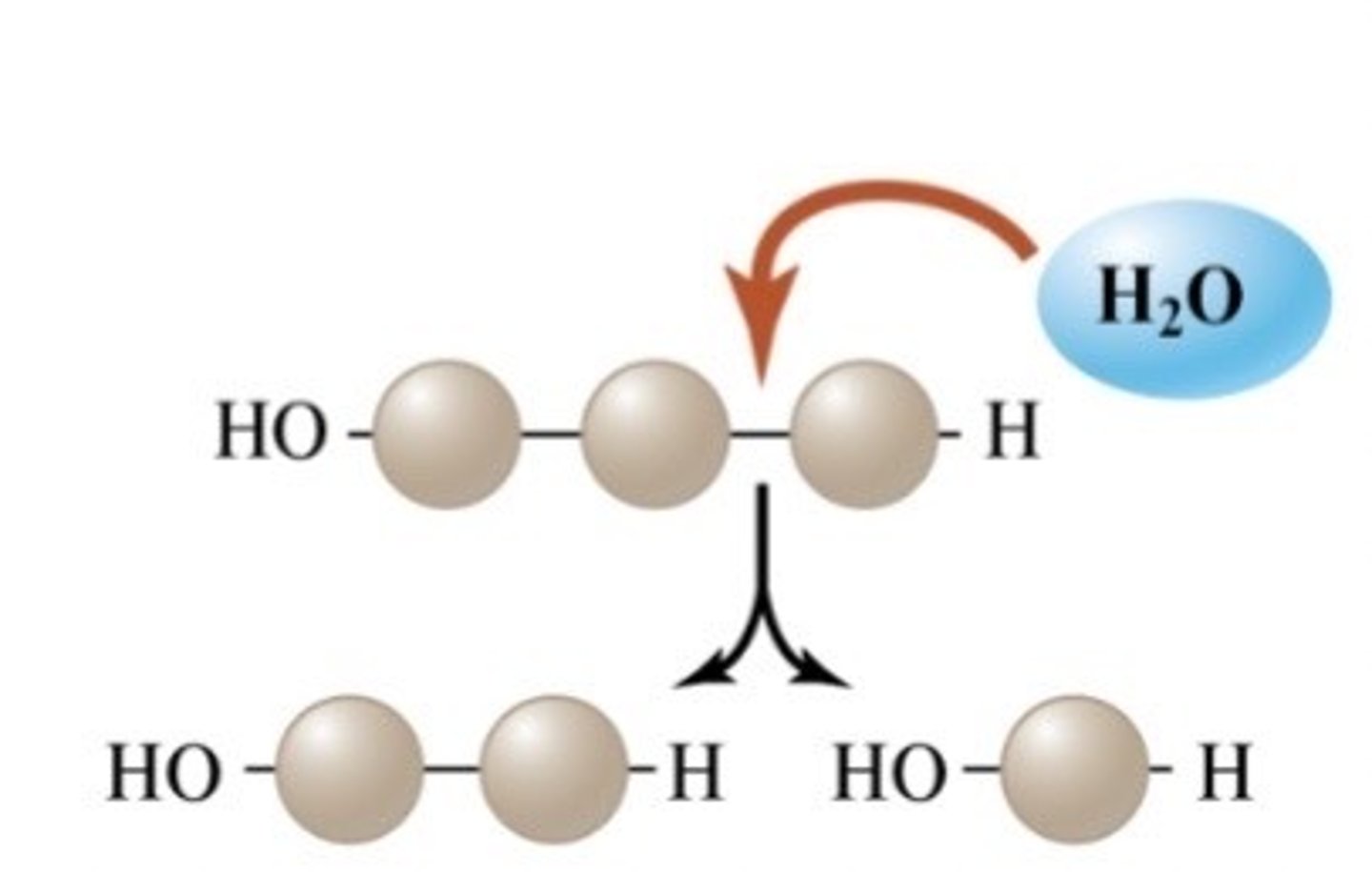
What occurs in hydrolysis?
The breaking down of a covalent bond between two monomers by using water (H2O).
How do you find the percentage uncertainty for the mean from a table of results?
range x 0.5/ mean x 100
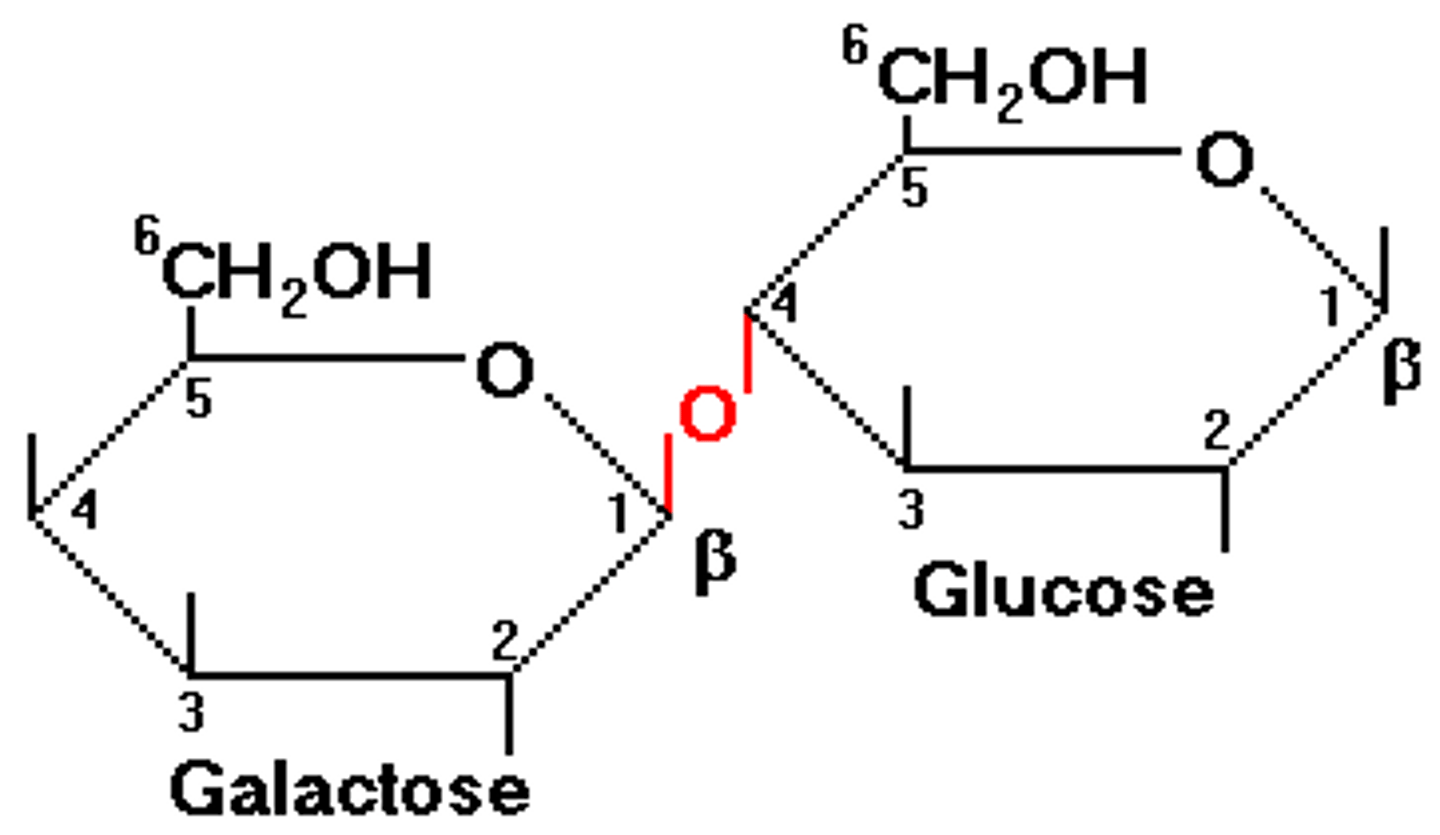
What does the making of lactose look like?
In galactose it is identical to glucose except it has the OH above the H on the left side
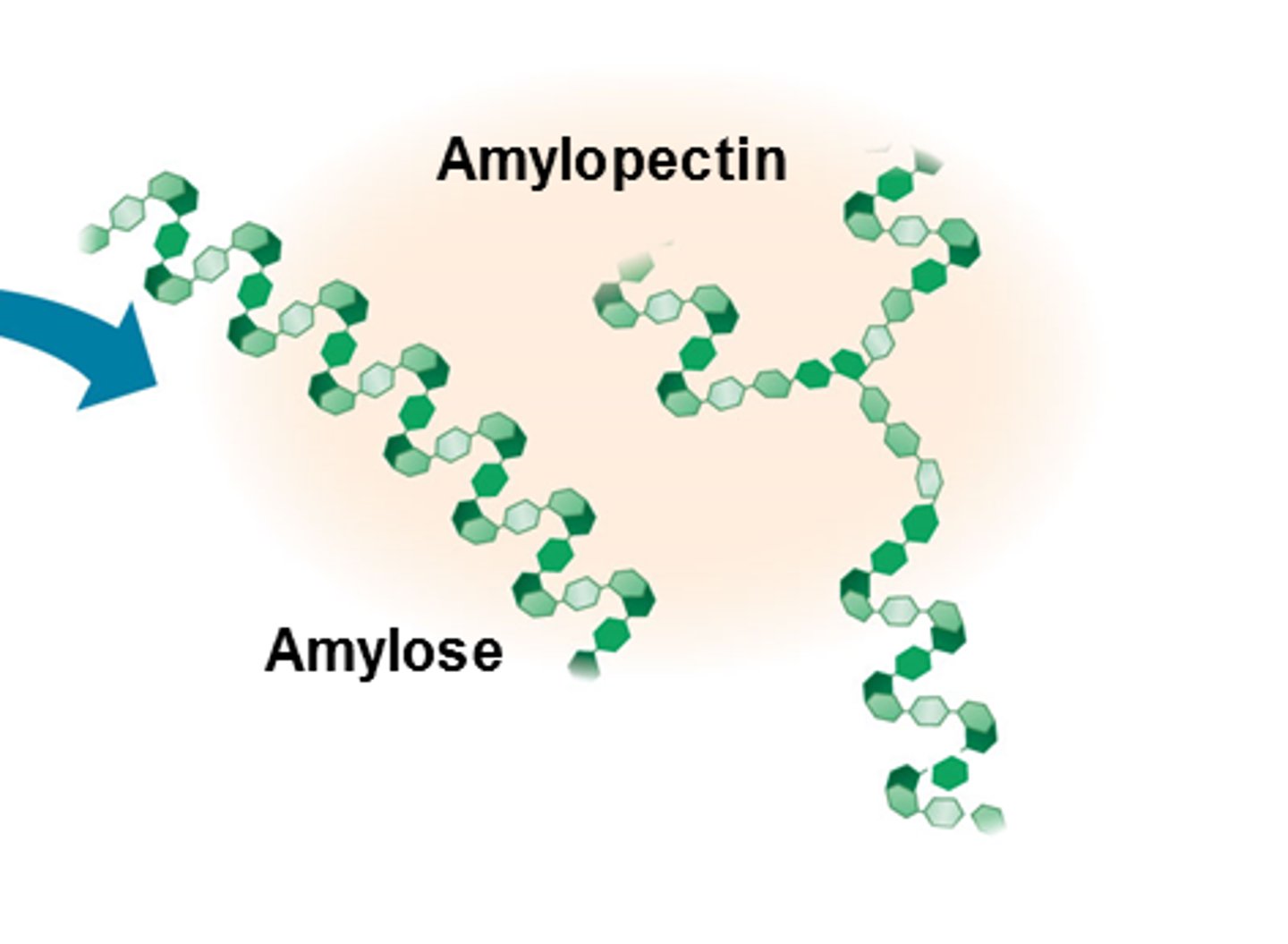
What is starch?
- polymer of alpha glucose
- storage form of glucose in plants
- made up of amylose and amypectin
- insoluble in water and doesn't effect water potential so doesn't cause osmosis to occur = good for storage in cells
What is amylose?
A long unbranched chain of alpha glucose in a coil shape in order to be compact for storage. Formed by condensation reactions between a glucoses.
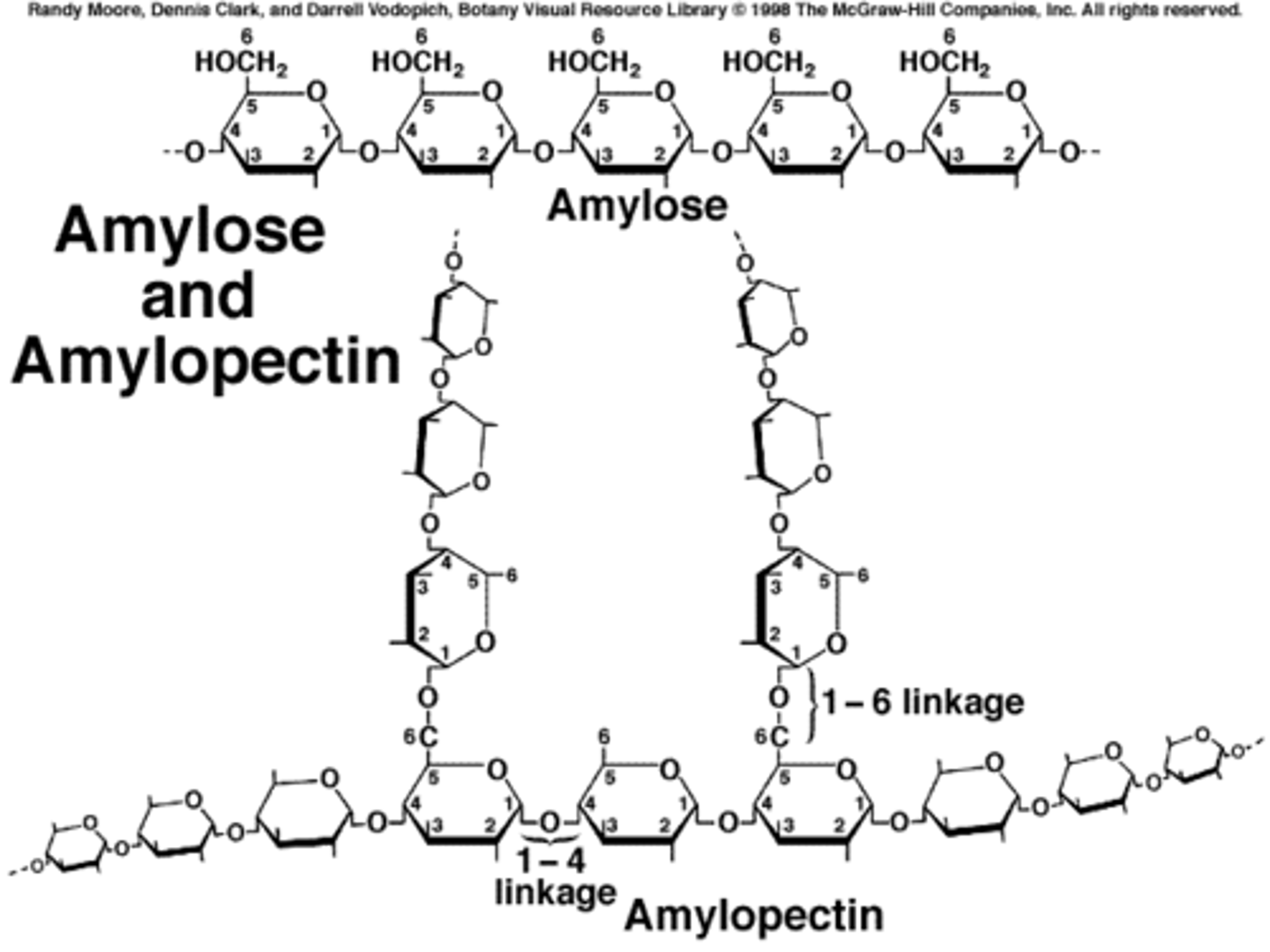
What is amylopectin?
One of the two components of starch
- 1 to 4 carbon links between alpha glucoses formed by condensation reactions - branches of 1- 6 carbon links also exist
- branched coiled spring structure in order to increase the number of binding sites for enzymes so increases the rate of hydrolysis
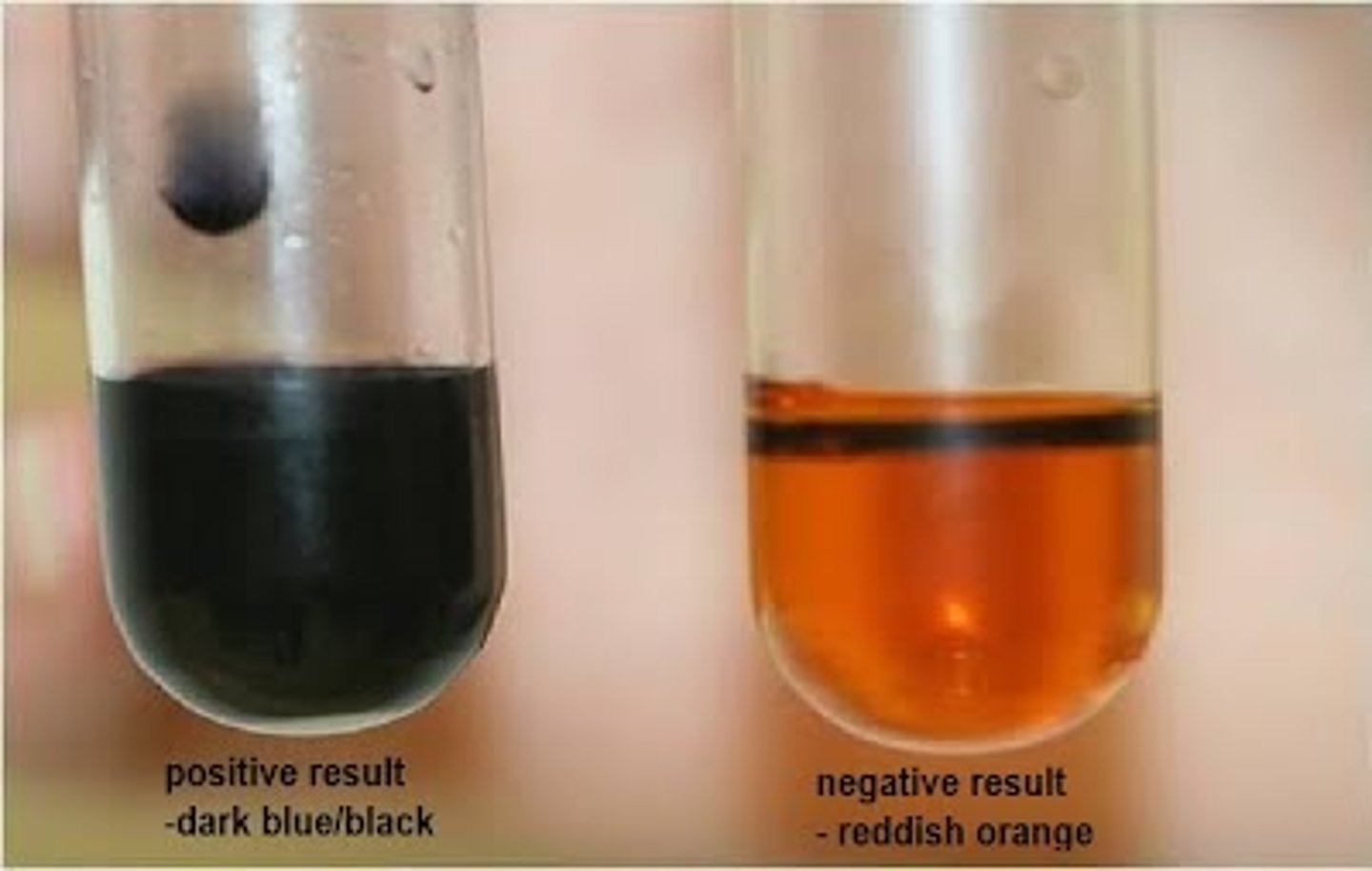
What is the iodine test for starch?
1. Add iodine dissolved in potassium iodide to solution and shake/stir
2. Blue-black colour = starch present

What are the 5 main uses of lipids?
- To provide a source of energy
- To help insulate organisms (e.g. body fat)
- To form membranes
- To act as waterproofing
- To form hormones
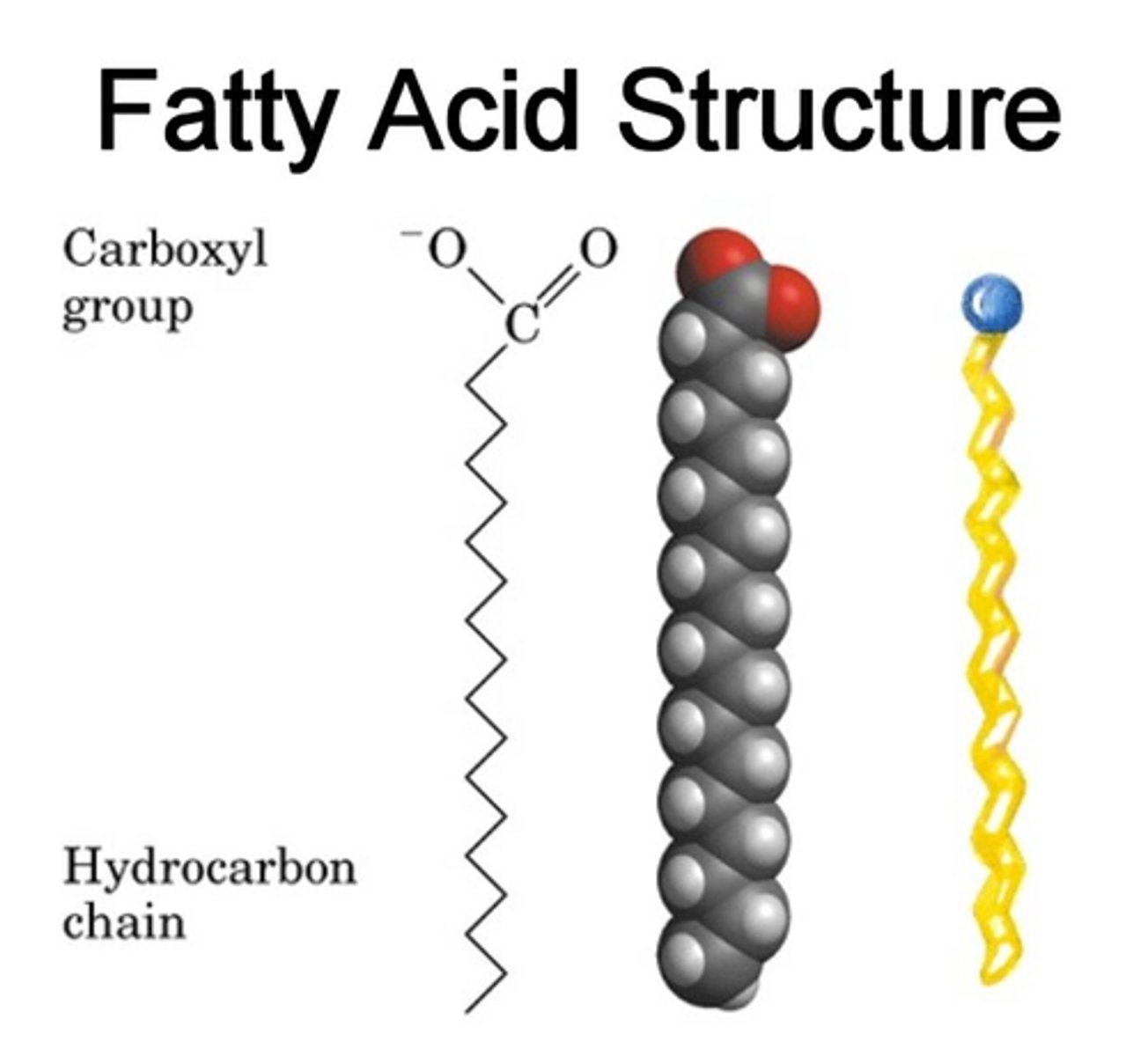
What are fatty acids?
An acid/carboxyl group attached to a hydrocarbon chain.
The hydrocarbon chain is represented as R as it can be a variable group as a hydrocarbon chain can have between 2 to 25 carbons.
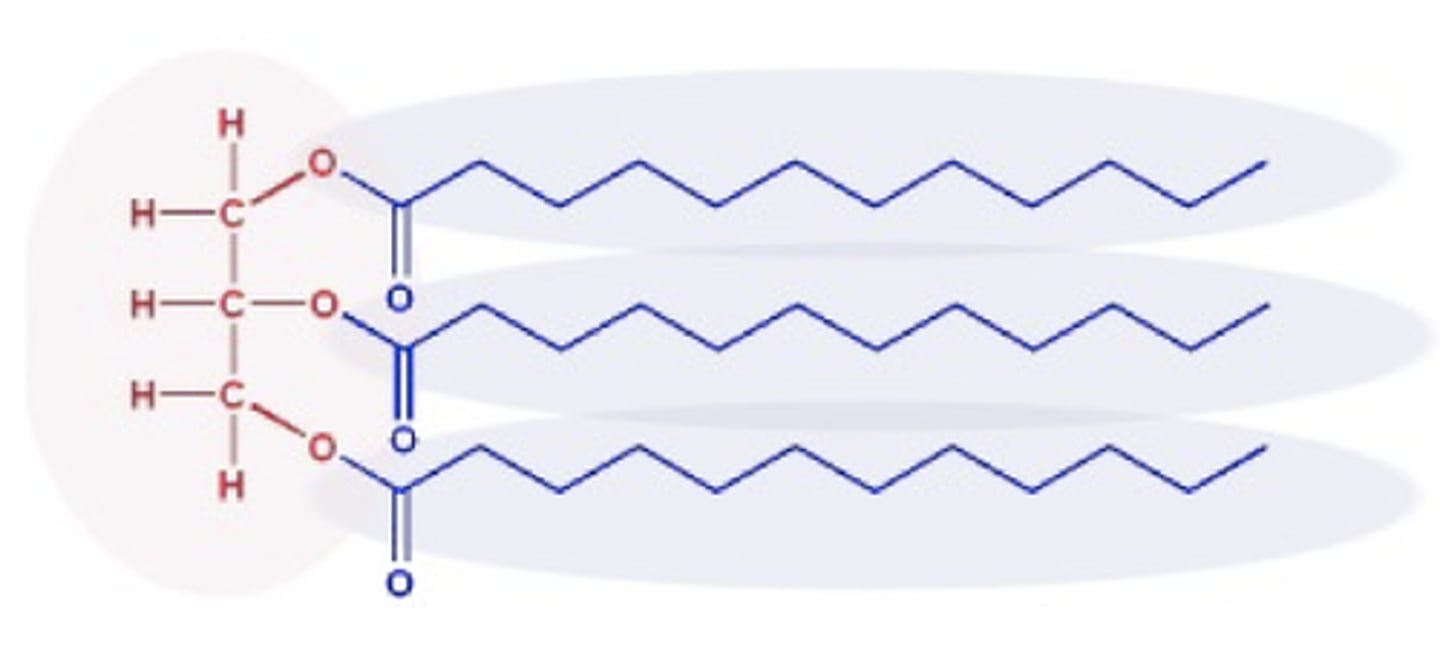
What is a trigylceride?
glycerol + 3 fatty acid chains the tails/fatty acid chains are hydrophobic making lipids insoluble in water.
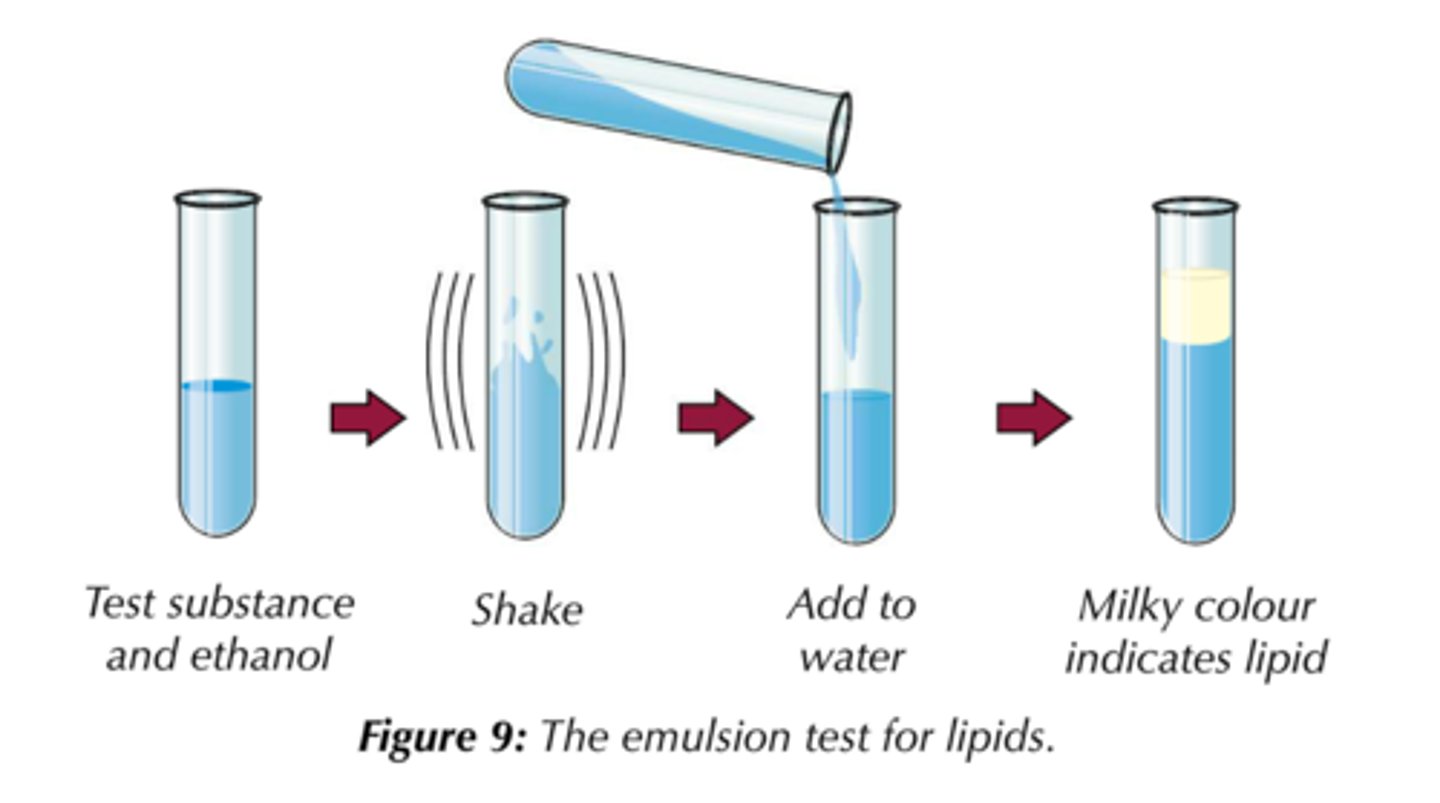
What is the emulsion test for lipids?
-Shake the test substance with ethanol for about a minute, then pour the solution into water.
-If lipid is present, the solution will turn milky.
-The more lipid there is, the more noticeable the milky colour will be
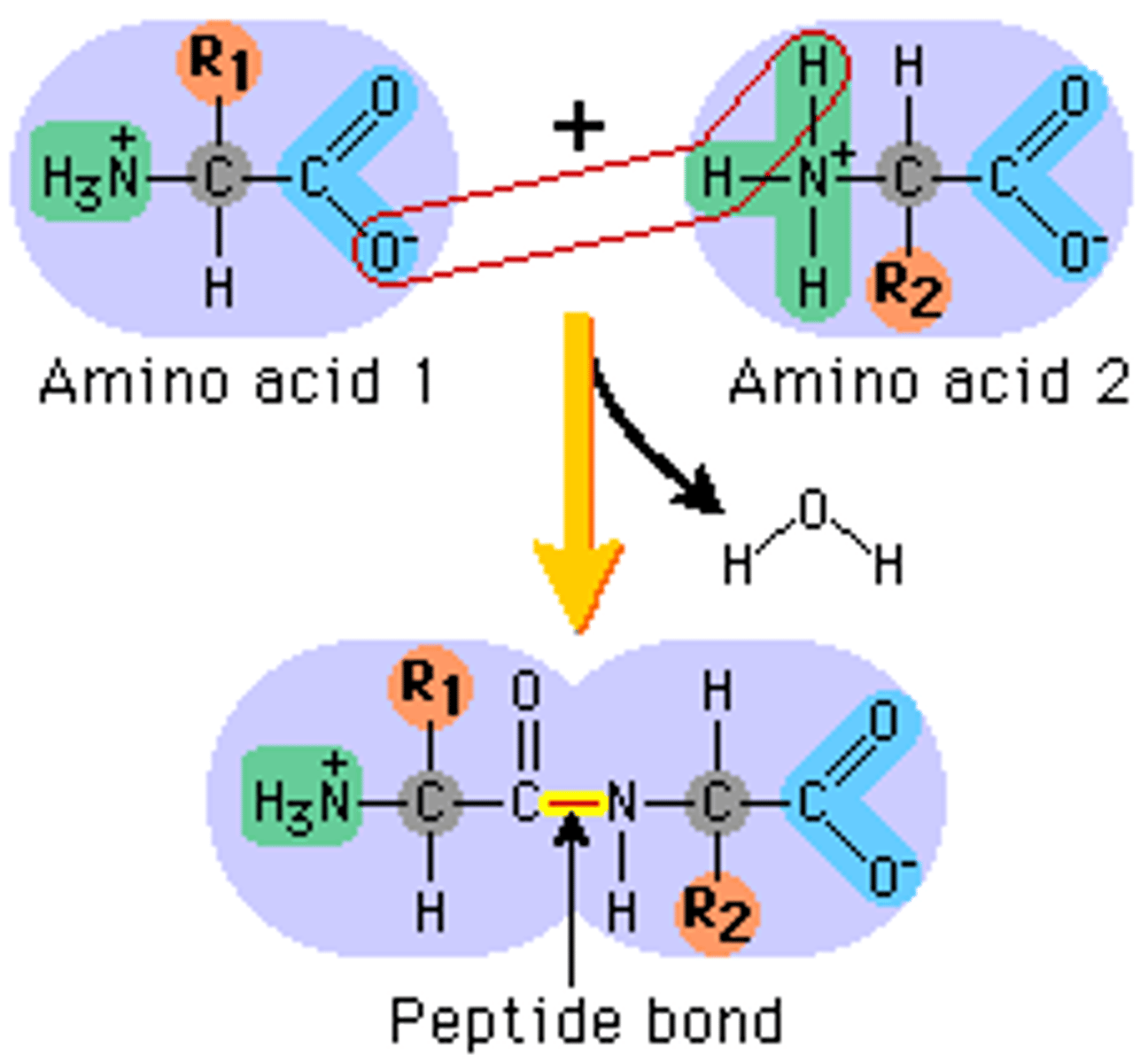
What is a peptide bond?
Bond formed between the OH on one amino acids carboxyl group and anothers hydrogen on its amine group.
This forms a direct covalent bond between carbon and nitrogen.
Formed by a condensation reaction.
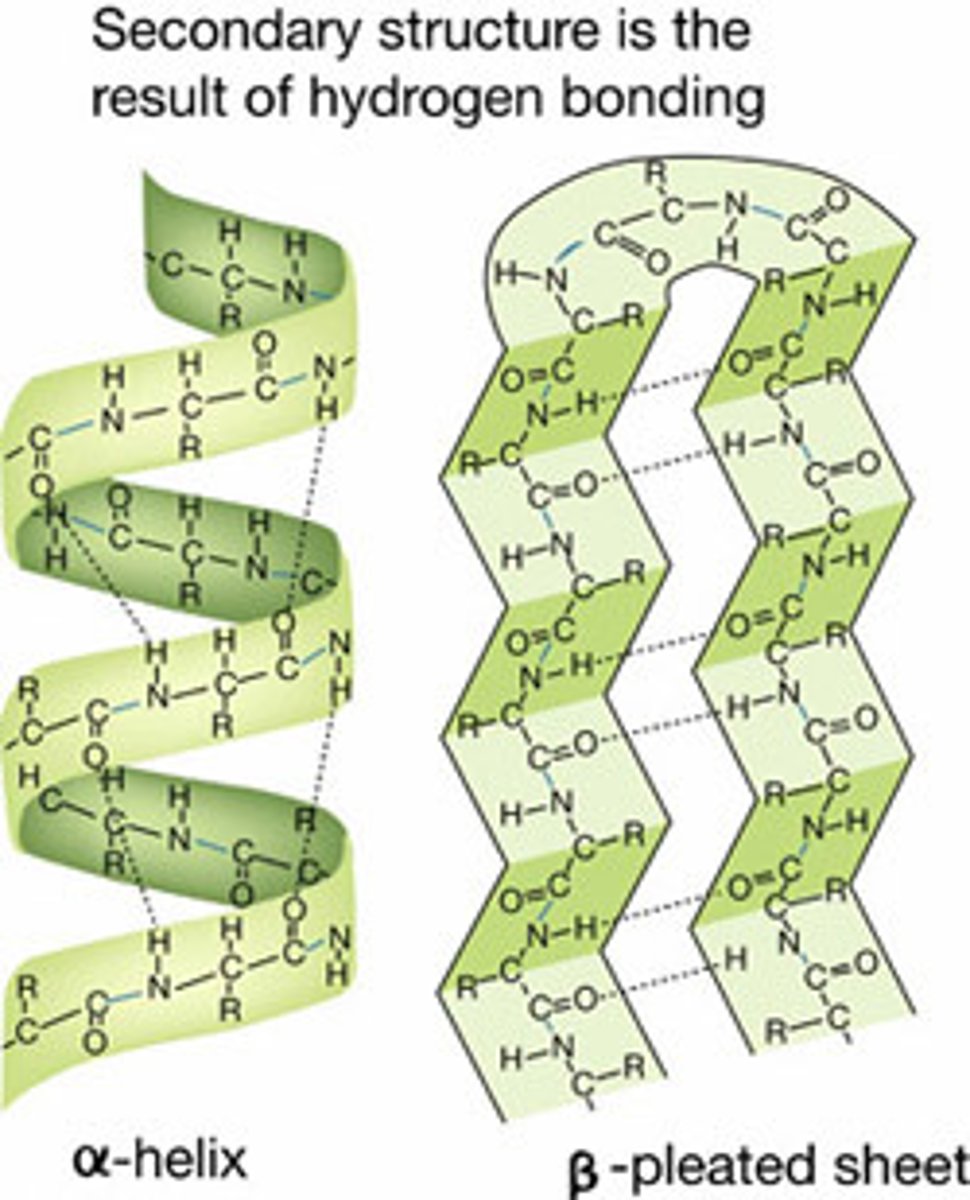
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
The structure created by the hydrogen bonds between the amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Can form either alpha-helixes or beta pleated sheets depending on the hydrogen bonding.
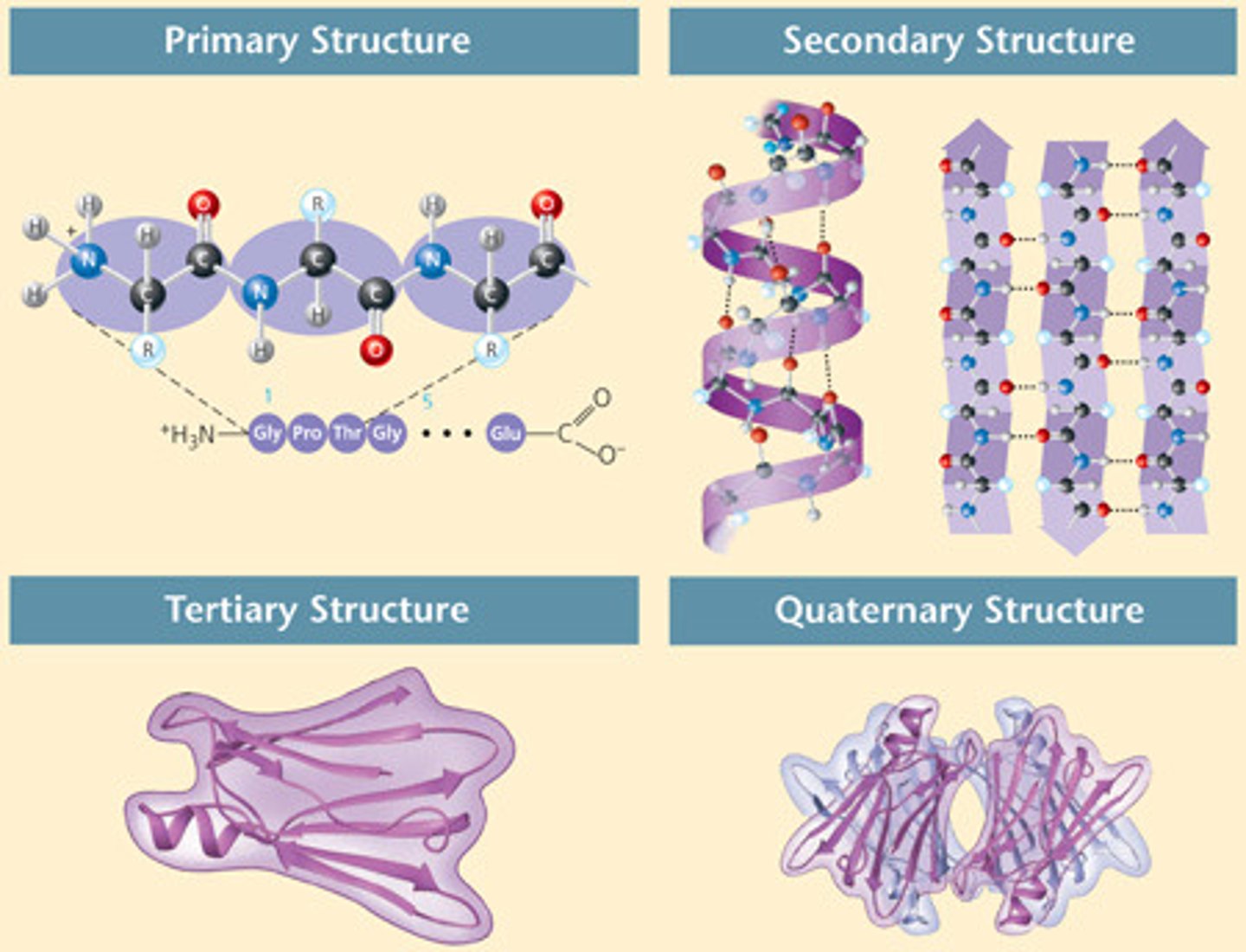
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
folding of a polypeptide chain due to interactions between side chains of amino acids that lie in different regions of the primary sequence which creates a 3D structure
What are ionic bonds ( in a tertiary structure)?
Formed between a negative Oxygen on the acidic carboxyl group (negative due to OH bond being broken up) and a positive Hydrogen on basic amine group.
The bonds are relatively strong but can be split by changing the pH.
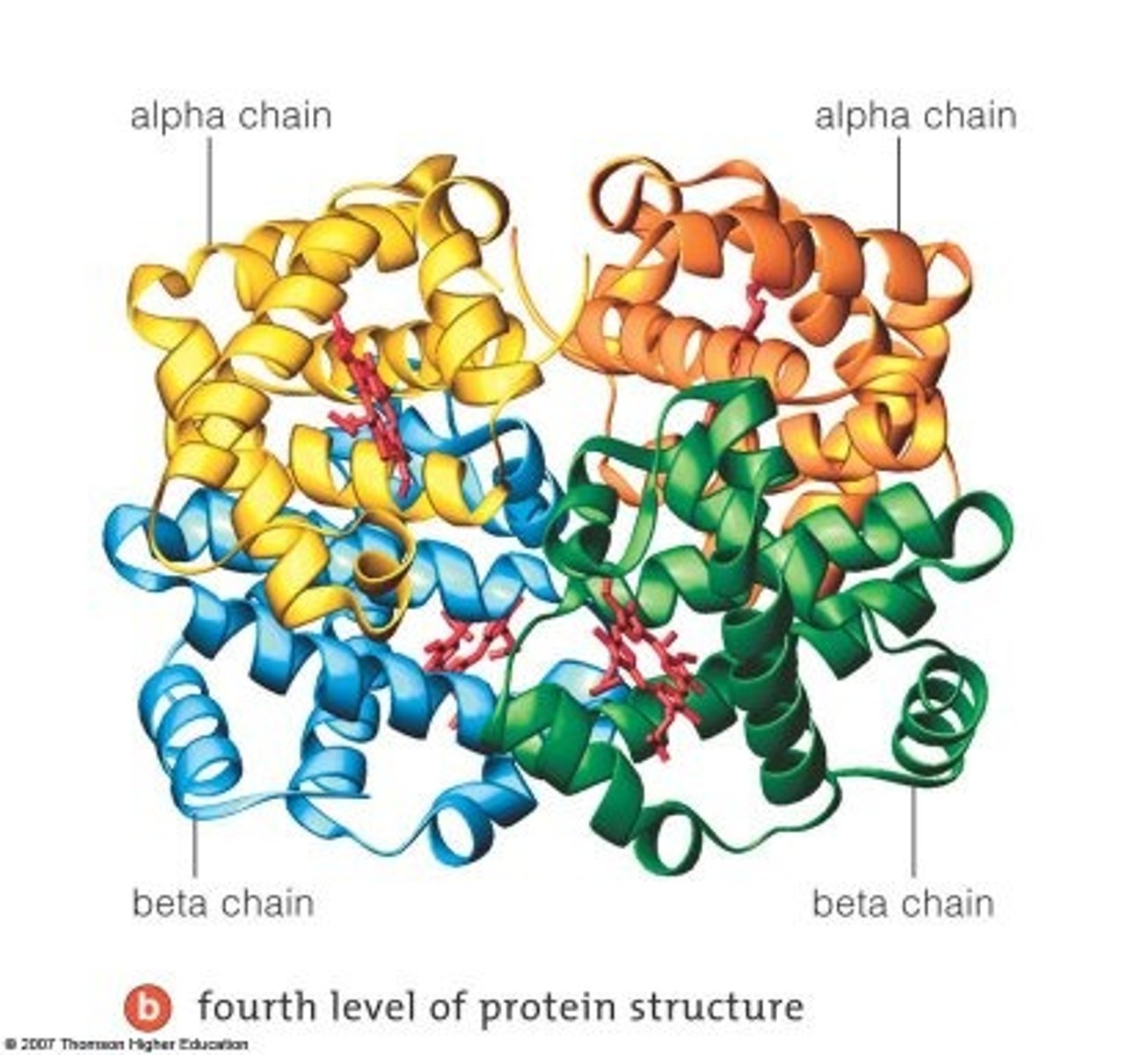
What is the quartenary structure of a protein?
two or more polypeptide chains, each with its own tertiary structure held together in a precise 3D structure
the quarternary structure is formed by the same bonds which form tertiary structures
How does the active site of an enzyme lower the activation energy needed for the substrate's reaction?
The induced fit of the active site causes tension on the bonds in the substrate making it easier for them to be broken therefore the activation energy is lowered.
What are enzyme inhibitors?
Substances that directly or indirectly interfere with the functioning of the active site of an enzyme and so reduce its activity:
- can be competitive or non-competitive
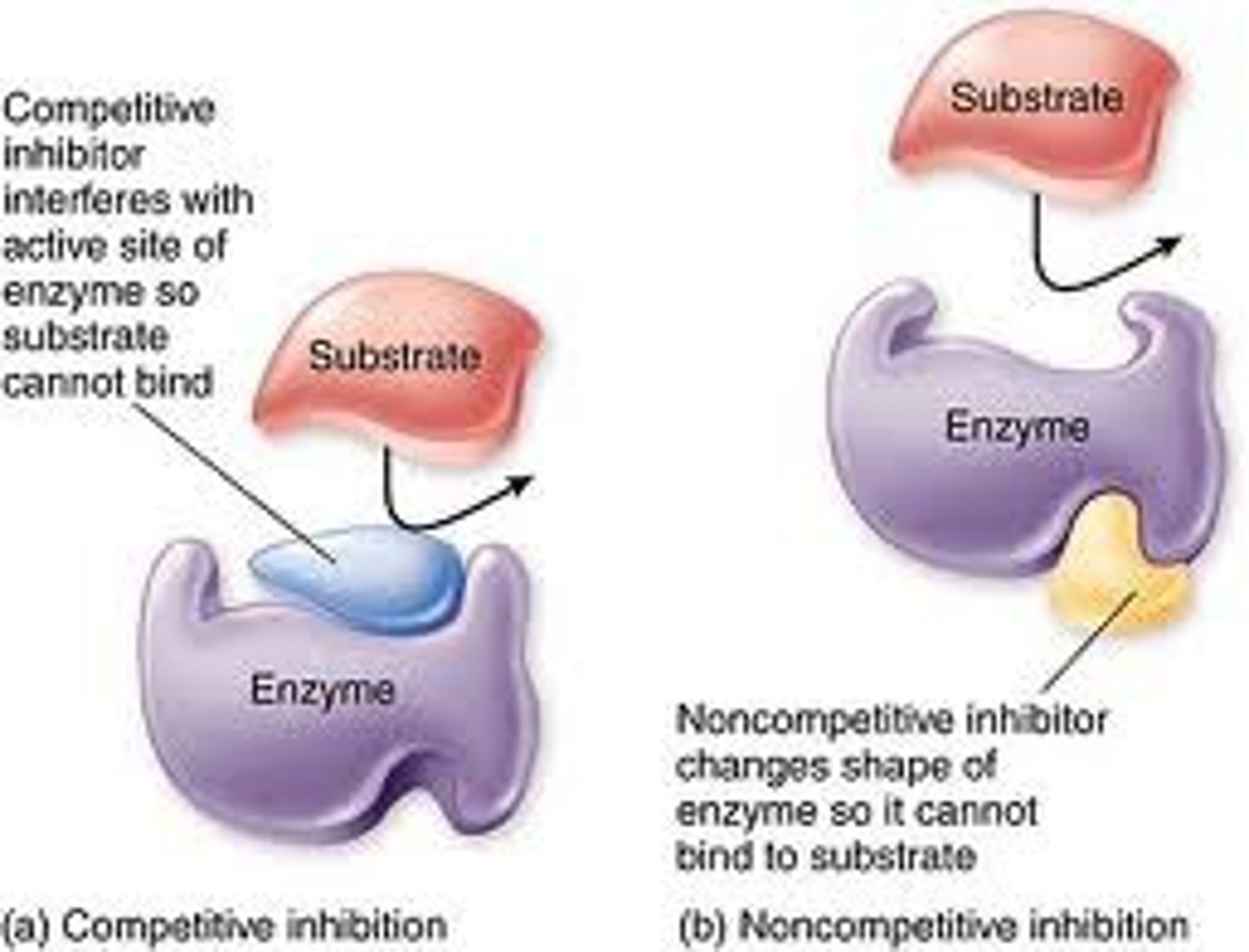
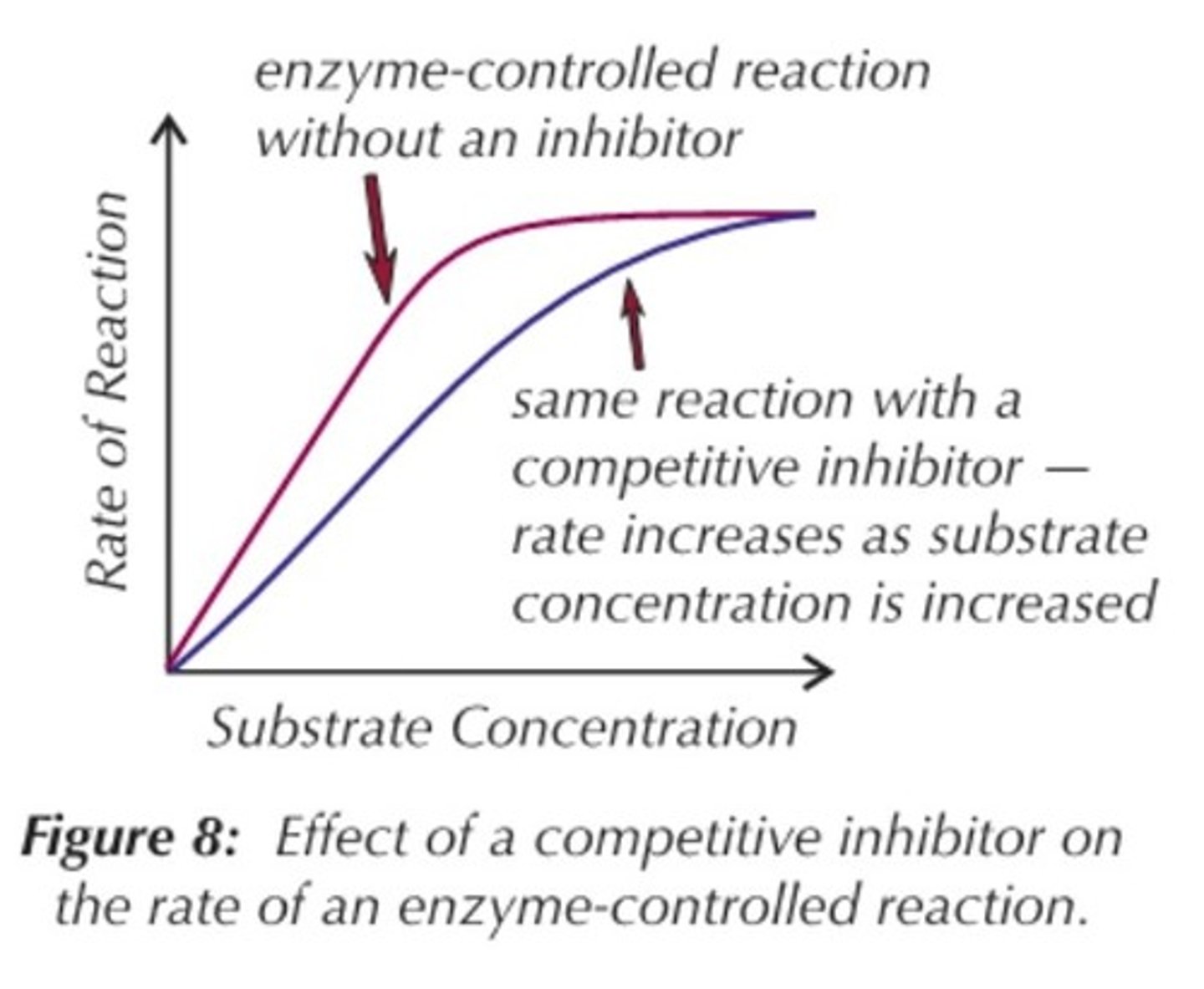
How do competitive inhibitors affect enzyme activity?
The competitive inhibitors cause less E-S complexes to occur but increasing the substrate conc causes it to out-compete the competitive inhibitor.
Overall they will create the same number of E-S complexes but will take longer = lower rate.
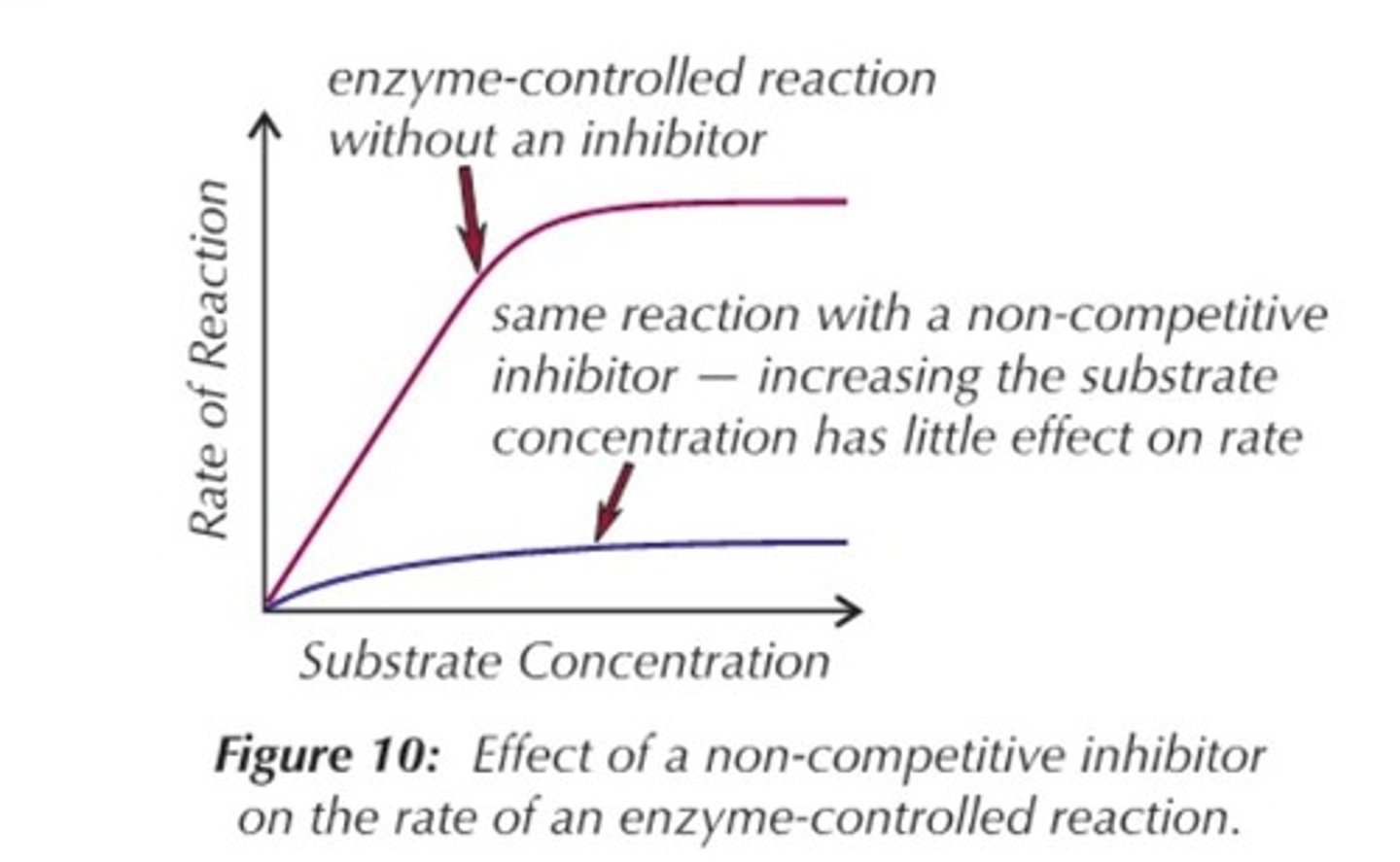
How do non-competitive inhibitors affect enzyme activity?
Non-competitive inhibitors cause the active site shape to change so the enzyme is permanently denatured.
Increasing the substrate conc doesn't increase the rate.
What are monomers?
Single biological units that join up to make polymers
Why are lipids not polymers?
They are not repeating chains - they have different fatty acids attached to the end of the glycerols
What are sugars?
A type of carbohydrate and a general term for monosaccharides and discaccharides
What are monosaccharides?
The simplest sugars :
- Triose - 3 carbons.
- Pentose - 5 carbons
- Hexose - 6 carbons
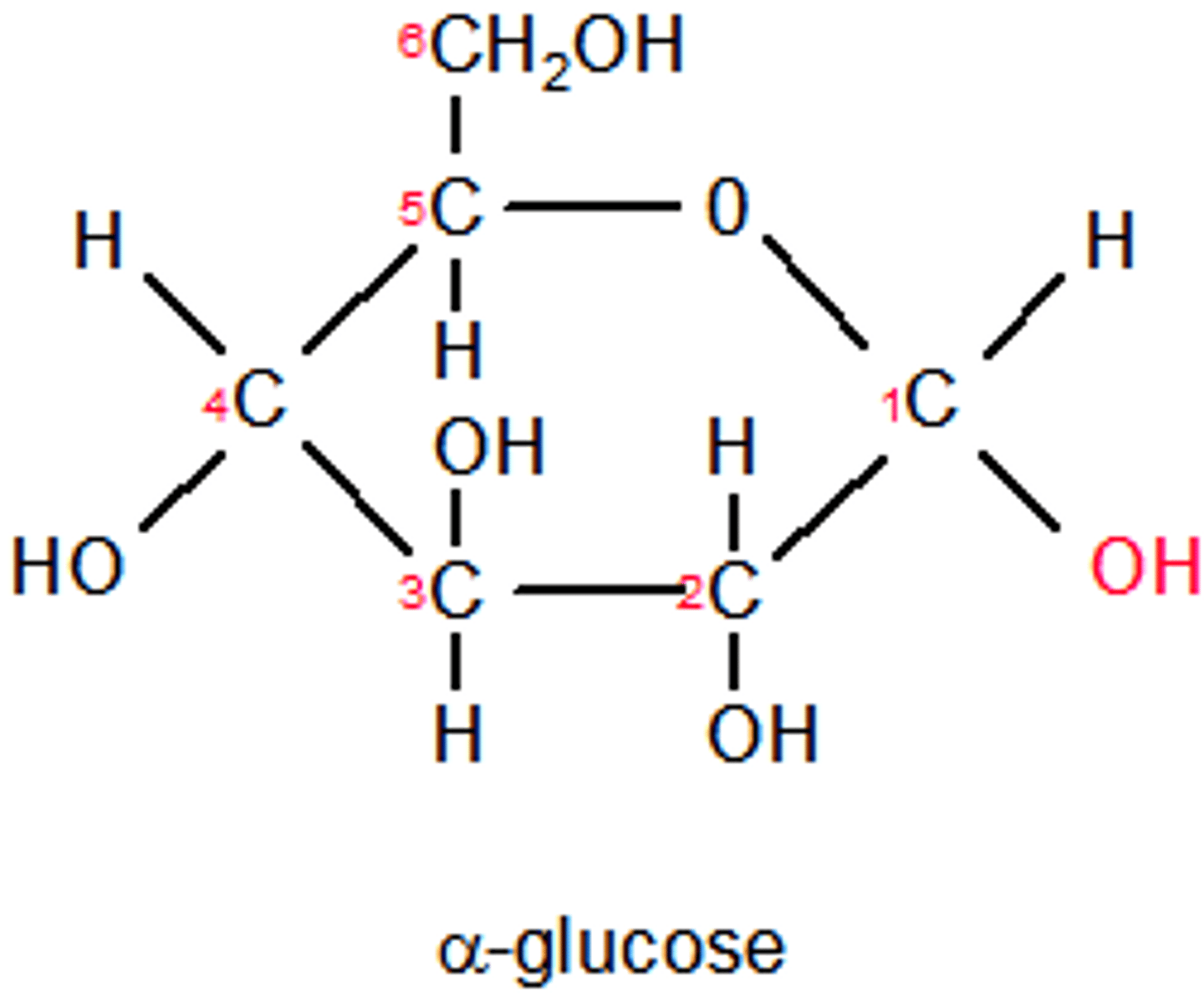
What is alpha (α) glucose?
An isomer of glucose - it has the hydrogen on the first carbon (after the oxygen) αbove the carbon
This is the same for all other carbons except C3 & C6 which have the hydrogen underneath the carbon.
How do you figure out the uncertainty and the margin of error?
To find the uncertainty you : find half of what the measuring device goes up in e.g if its 1cm cubed the uncertainty would be 0.5
To find the margin of error you times the uncertainty by 2
How do you find the uncertainty for a volume measured with two different pieces of equipment?
You add the different uncertainties together.
How do you find the percentage error?
uncertainty/reading x 100
What is beta glucose?
A structural isomer of glucose which as hydrogen below the oxygen on the right side of the molecule.
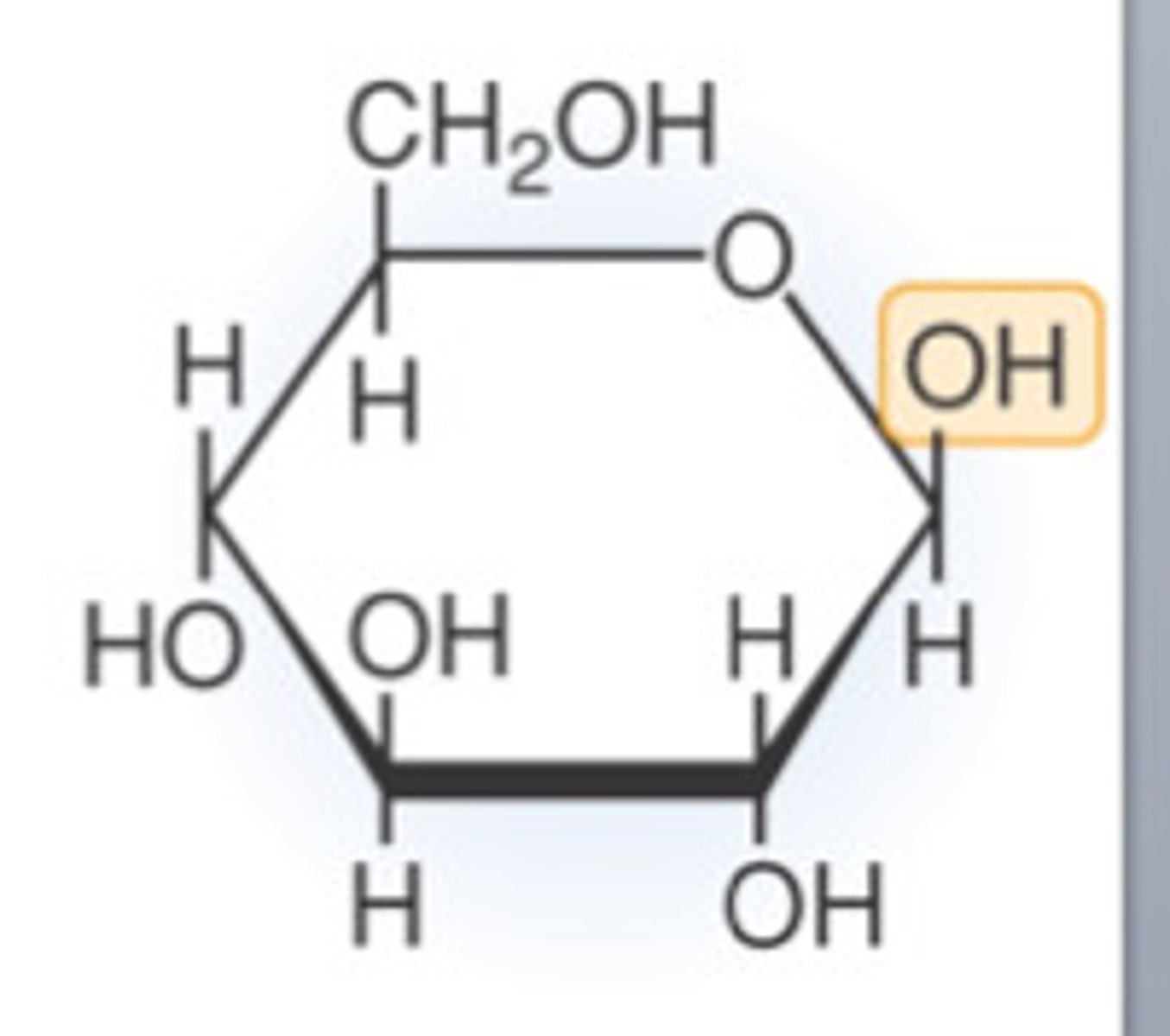
What is a glycosidic bond?
A bond formed when 2 or more monosaccharides join together in a condensation reaction.
Two OHs are needed as the O forms the bond and the rest of the OHs join to make water.
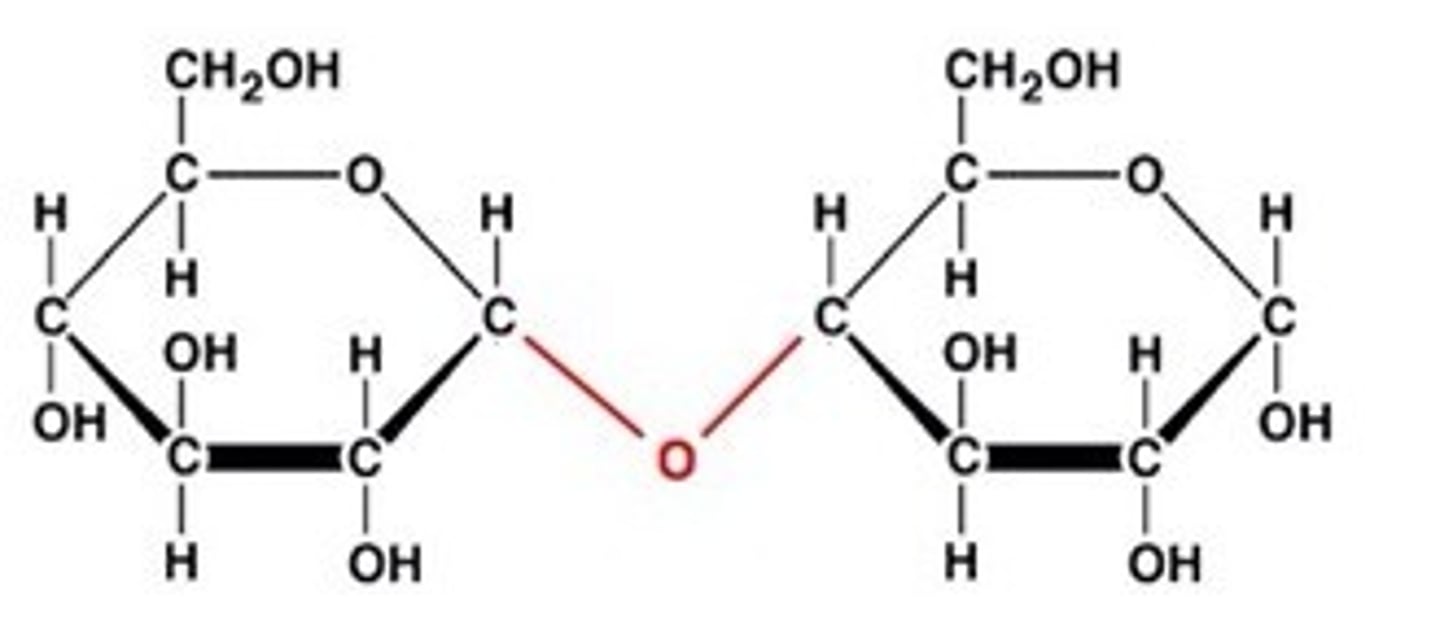
What are the different disaccharides and the monosaccharides that form them?
Maltose = Alpha glucose + alpha glucose
Sucrose = Alpha glucose + fructose
Lactose = Alpha glucose + galactose
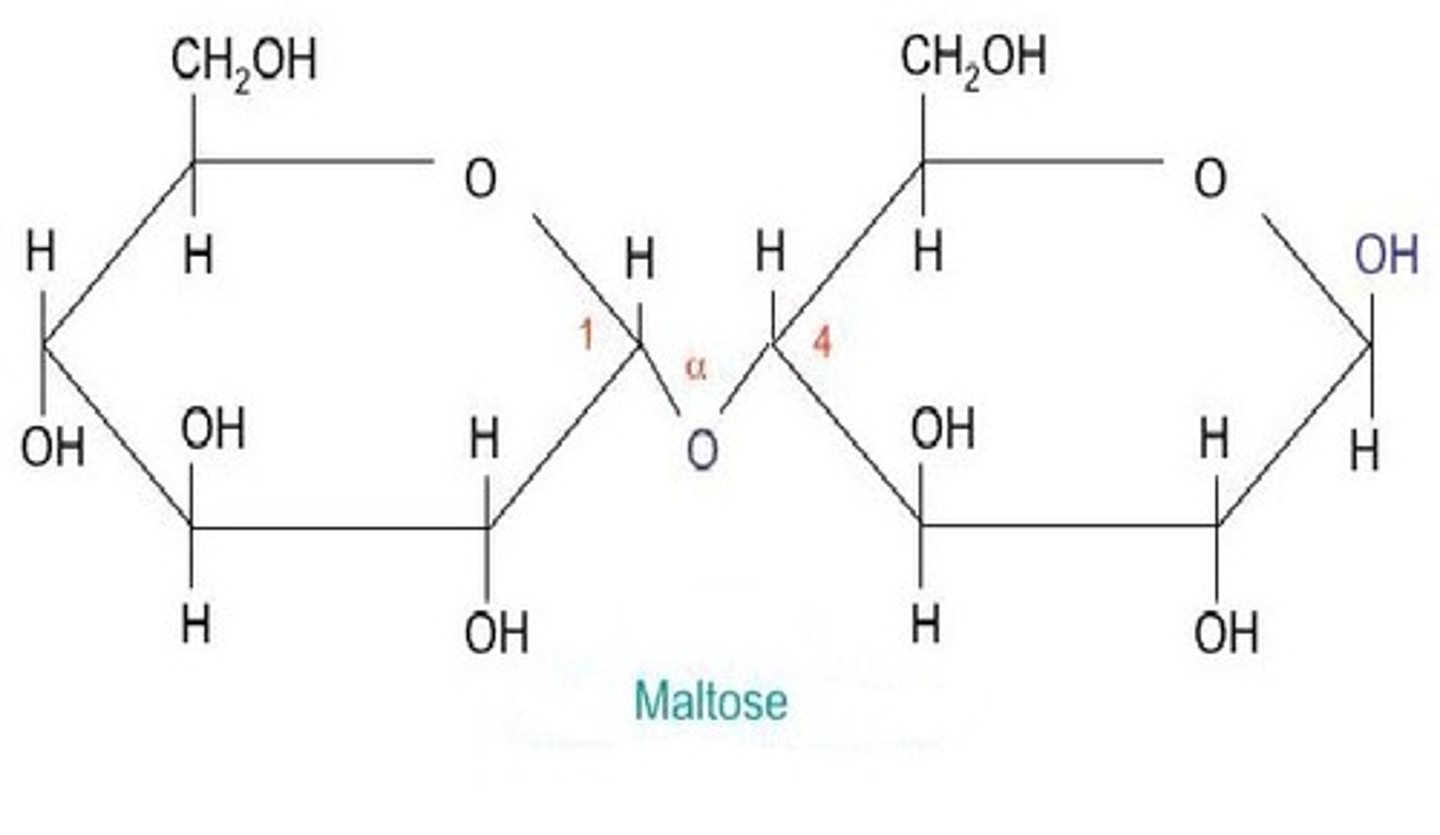
What does the making of maltose look like?
Two alpha glucoses joined together.
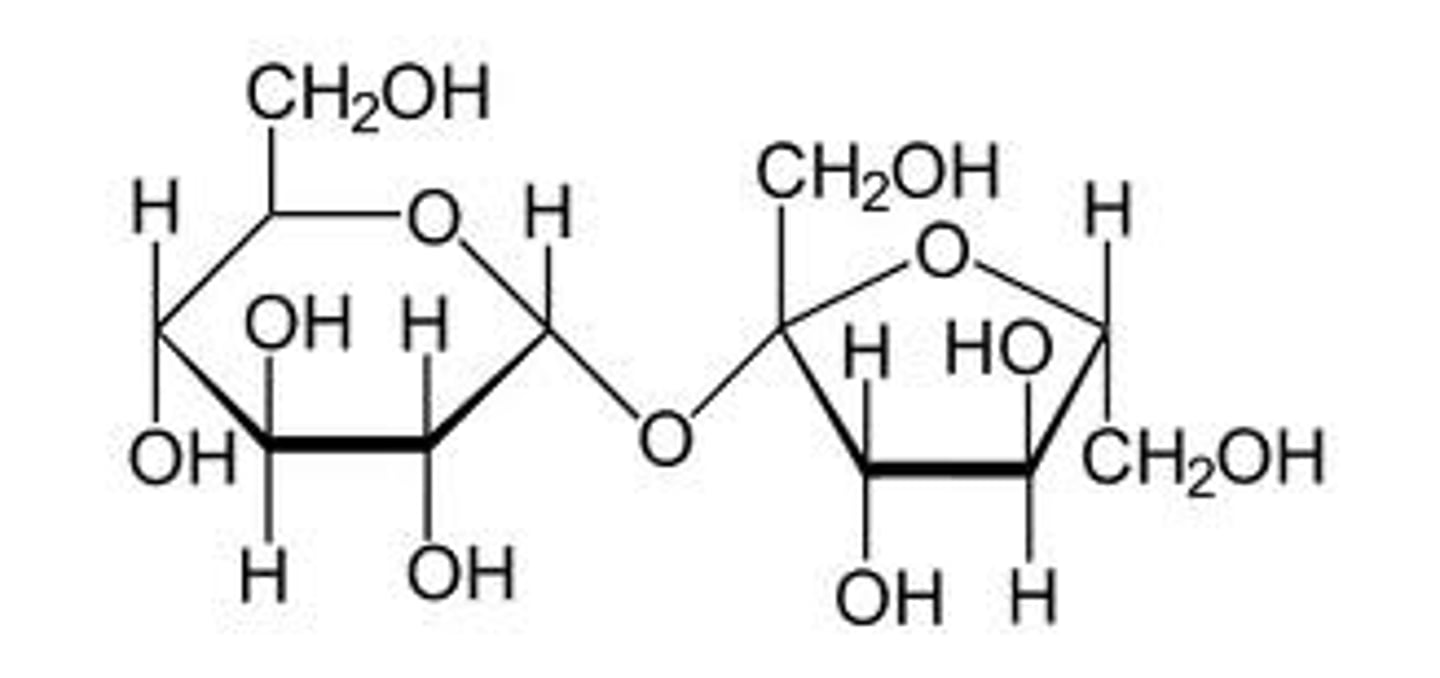
What does the making of sucrose look like?
Fructose is the pentagonal one
What are all the different monosacchirides?
Glucose ( alpha & beta)
Fructose
Galactose
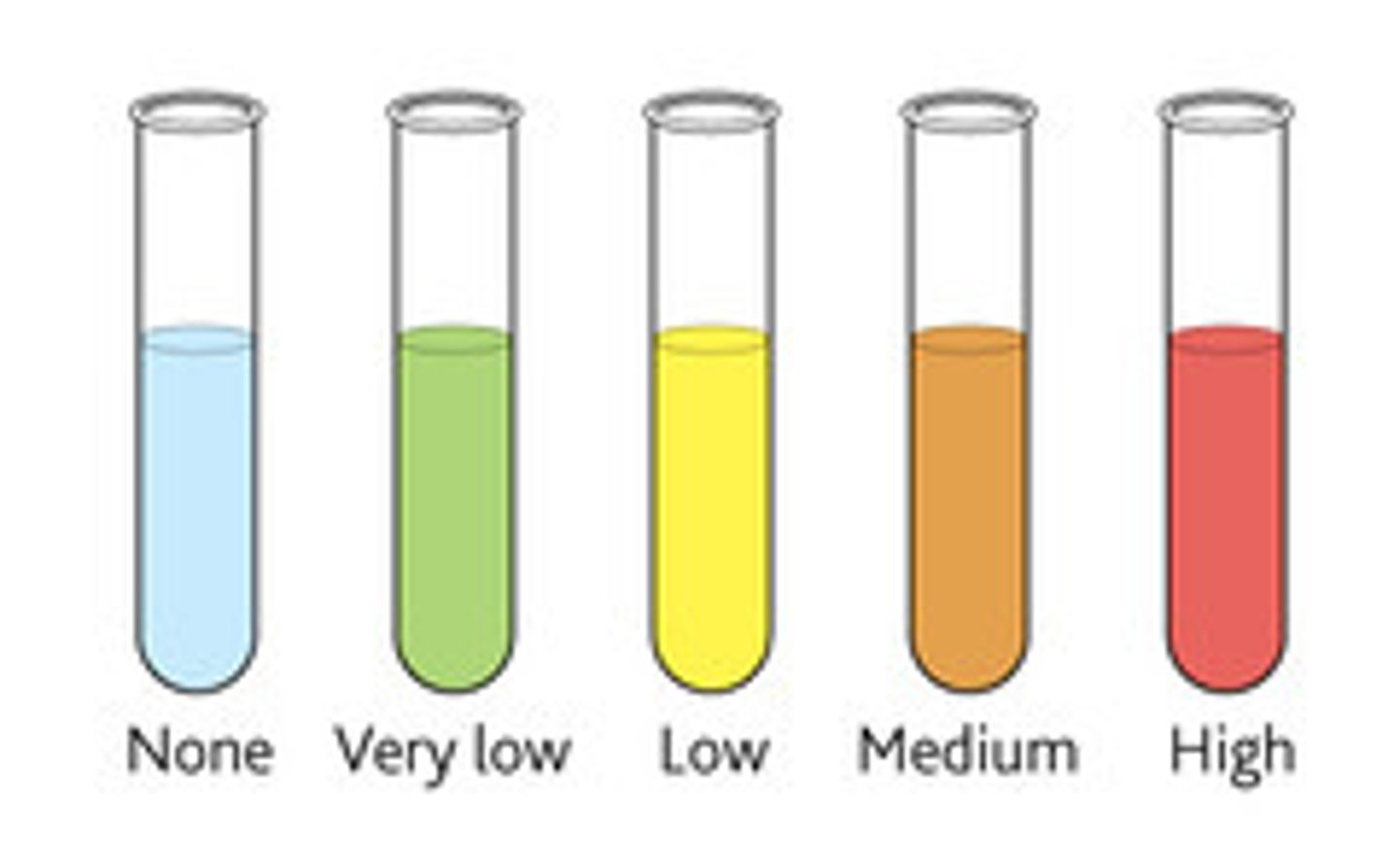
What is the Benedicts test for reducing sugars?
-You add Benedict's reagent (which is blue) to a sample and heat it in a water bath that's been brought to the boil.
-If the test's positive it will form a coloured precipitate.
-The colour of the precipitate changes.
-If the sample forms green, yellow, orange, or brick-red precipitate, there is a reducing sugar present.
-The higher the concentration of the reducing sugar, the further the colour change goes.

How do you do a Benedicts test for non-reducing sugars?
A normal Benedicts test will make the sample stay blue so you need to break down the non-reducing disaccharide into its reducing monosaccsharide.
This is done by heating a sample with dilute HCl and then neutralising the solution with sodium hydrogencarbonate and then testing with Benedicts solution.
If there is still no reaction then there is no reducing or non-reducing sugar present.

Which disaccharide is soluble / a reducing sugar?
Maltose is the only soluble disaccharide.
What are the different polysaccharides?
starch, glycogen, cellulose
What is glycogen?
- storage polysaccharide in animals
- made out of alpha glucoses
- has main chains (1 - 4 links) and branches with many 1-6 carbon bonded side chains
- branches increase the number of binding sites for enzymes as there are more terminal glucoses for them to bind to increasing rate of hydrolysis
What are lipids?
Organic molecules which are not polymers (like carbohydrates and proteins)
What are lipids made out of?
glycerol and fatty acids - all of them contain hydrocarbons
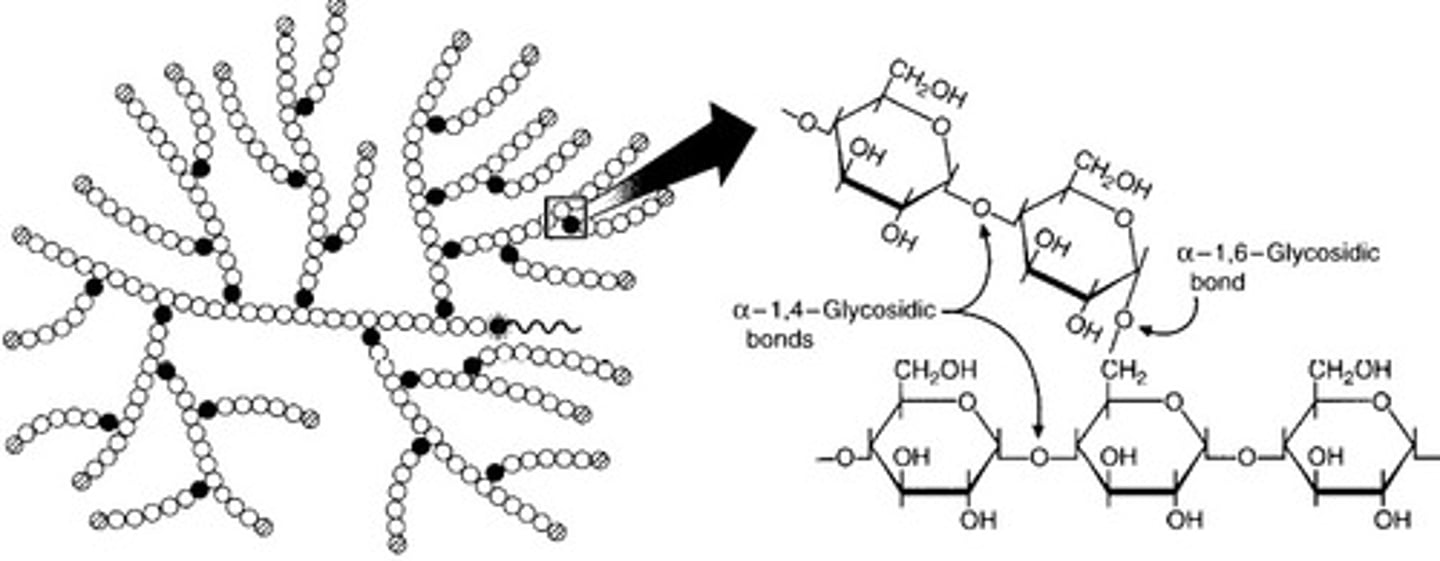
What is glycerol?
a three-carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon - meaning 3 condensation reactions can happen (on each OH) per glycerol
The backbone of a lipid
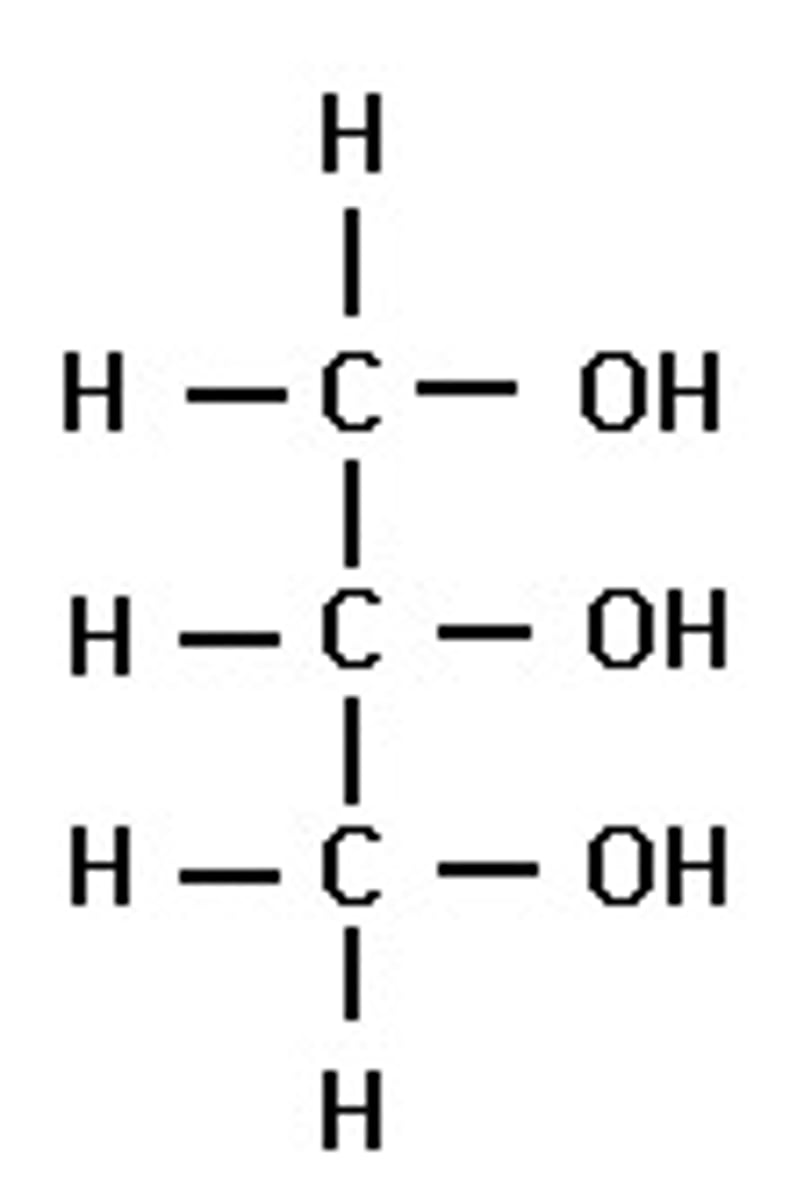
What is the difference between a saturated fatty acid and an unsaturated fatty acid?
A saturated fatty acid only has single carbon bonds so each carbon is bonded to as many hydrogens as possible.
An unsaturated fatty acid has at least one carbon double bond in its structure - double bond "bends" molecule and lowers its melting point
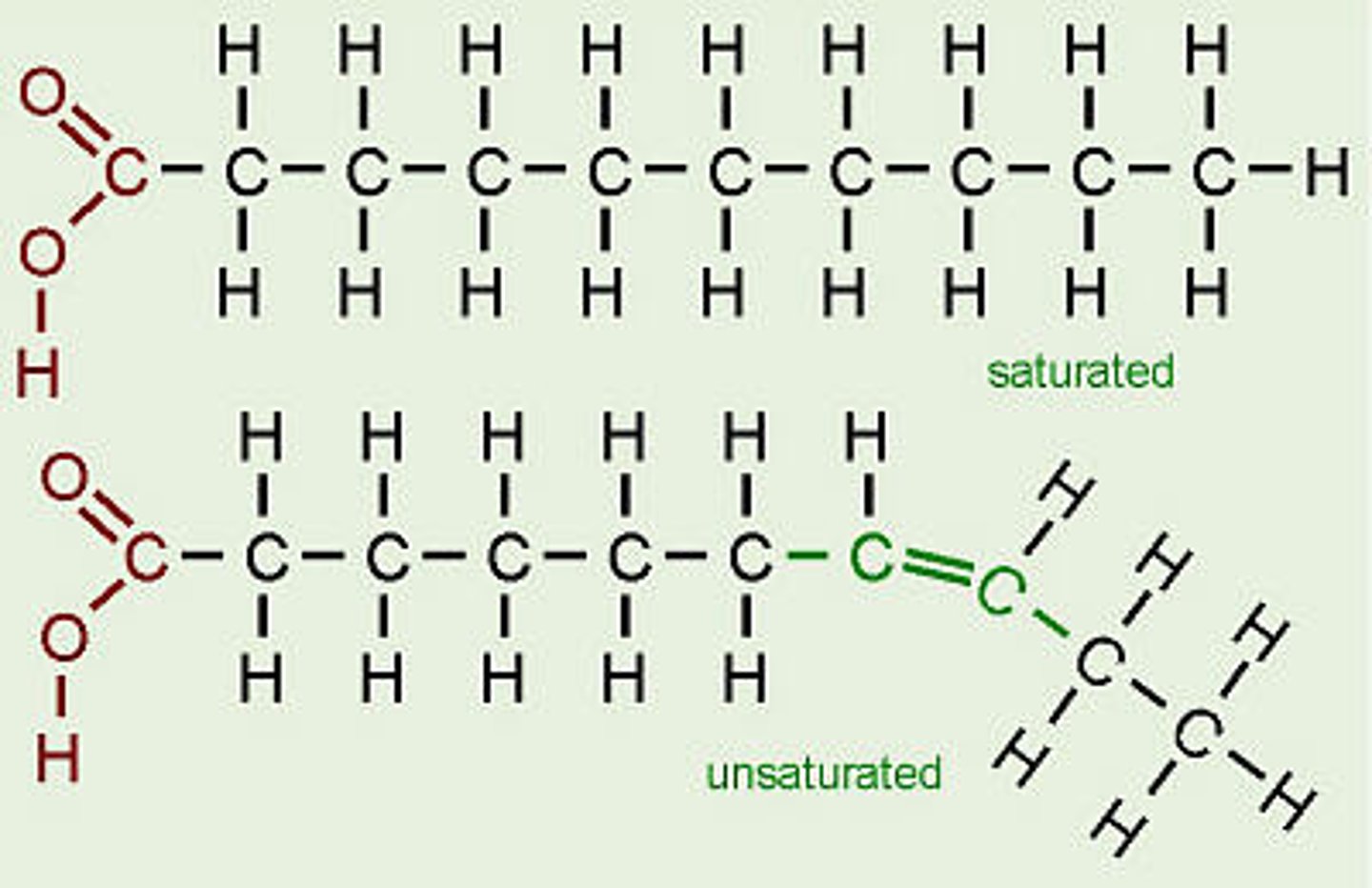
What is the bond between a lipid called?
An ester bond/link.
Formed between the OH groups on the glycerol and fatty acid by a condensation reaction.
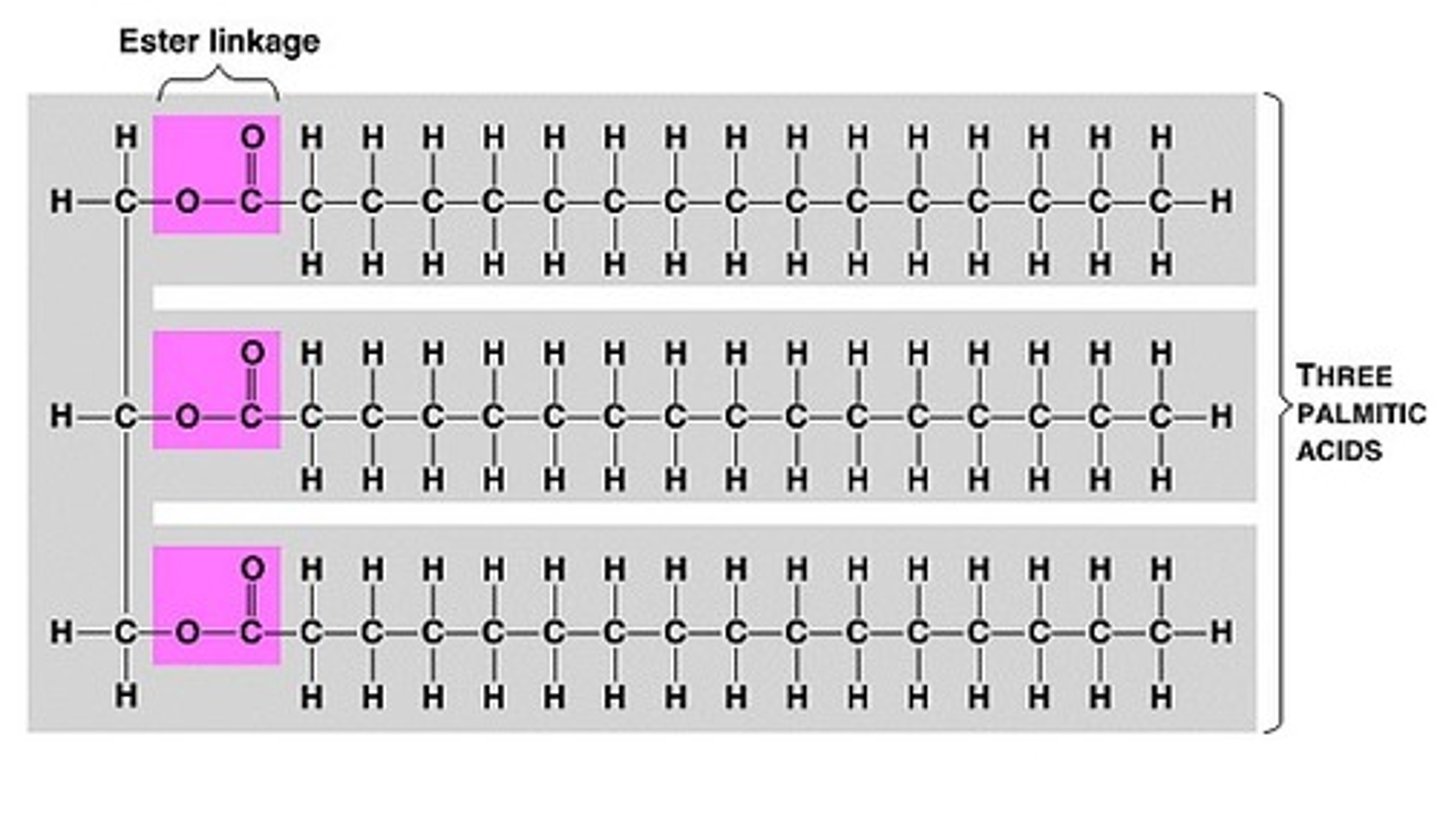
Why are trigylcerides good energy storage molecules?
The long hydrocarbon tails contain lots of chemical energy so when broken down all of this is released.
They are also insoluble in water and they don't effect water potential .
What is a phospholipid?
a lipid that has a phosphate group attached to the glycerol and only two fatty acid chains.
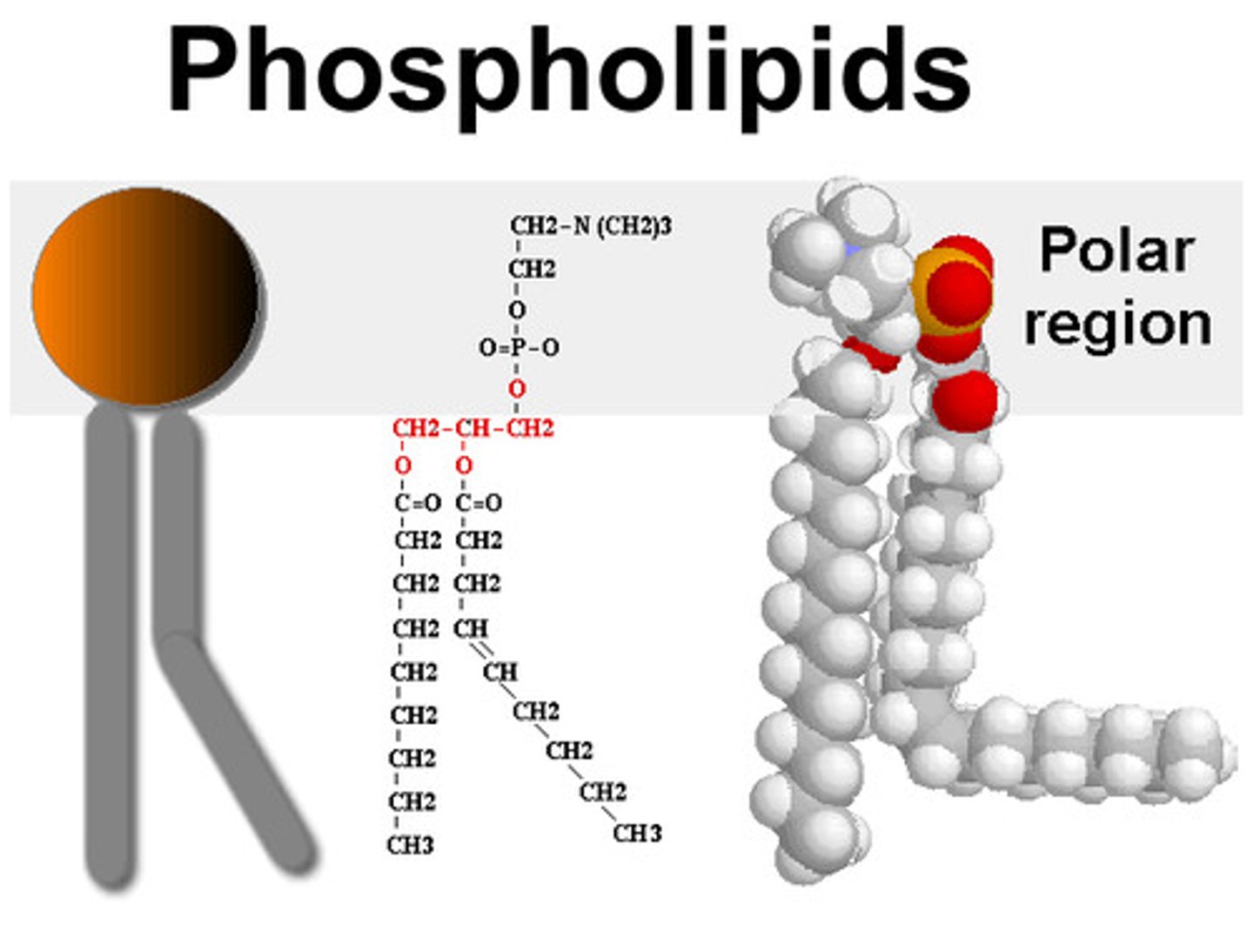
Why are phospholipids hydrophillic and hydrophobic?
The phosphate group is polar giving it a negative charge making it hydrophillic.
The fatty acid chains are hydrophobic so move away from water.
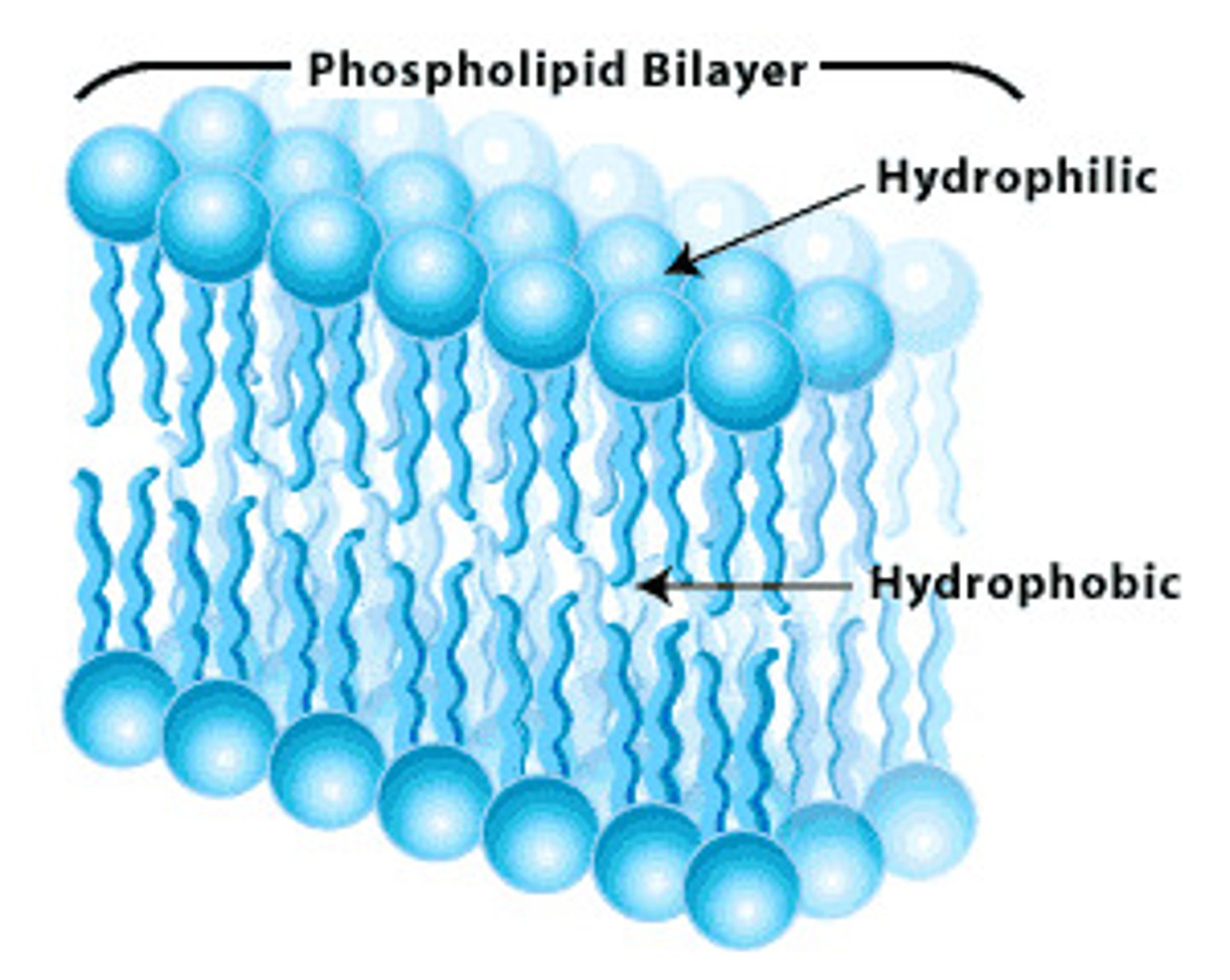
What is the phospholipid bilayer?
thin membrane made of 2 layers of phospholipid molecules formed when phospholipids meet water in order to avoid the hydrophobic tails touching the water.
Found in all membranes cell, mitochondria etc
the centre of the bilayer is hydrophobic so water-soluble substances can't get through = bilayer acts as a barrier.
What are amino acids?
monomers of proteins
What is the structure of amino acids?
One central carbon bonded to an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a variable group (differs between each amino acid)
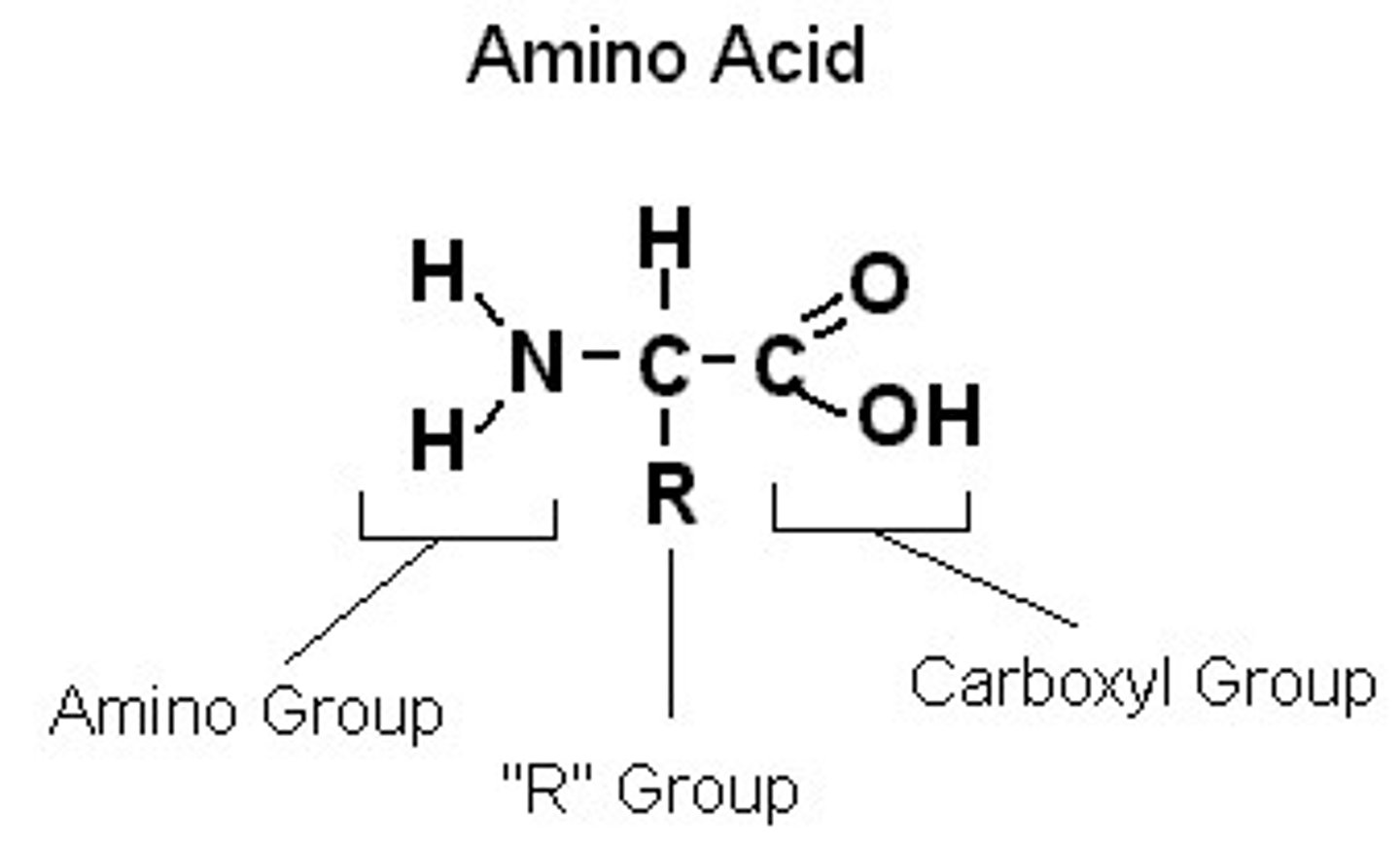
What is the variable region of an amino acid?
R group - where 20 different things could attach which is easier to represent overall as one variable thing
What is the biuret test?
The test for proteins.
1. Test solution must be alkaline - add a few drops of sodium hydroxide solution.
2. Add some copper (II) sulfate solution.
If protein present = solution turns purple.
No protein present = remains blue.
What is the difference between a dipeptide and a polypeptide?
A dipeptide is 2 amino acids bonded together.
A polypeptide is more than 2 amino acids bonded together.
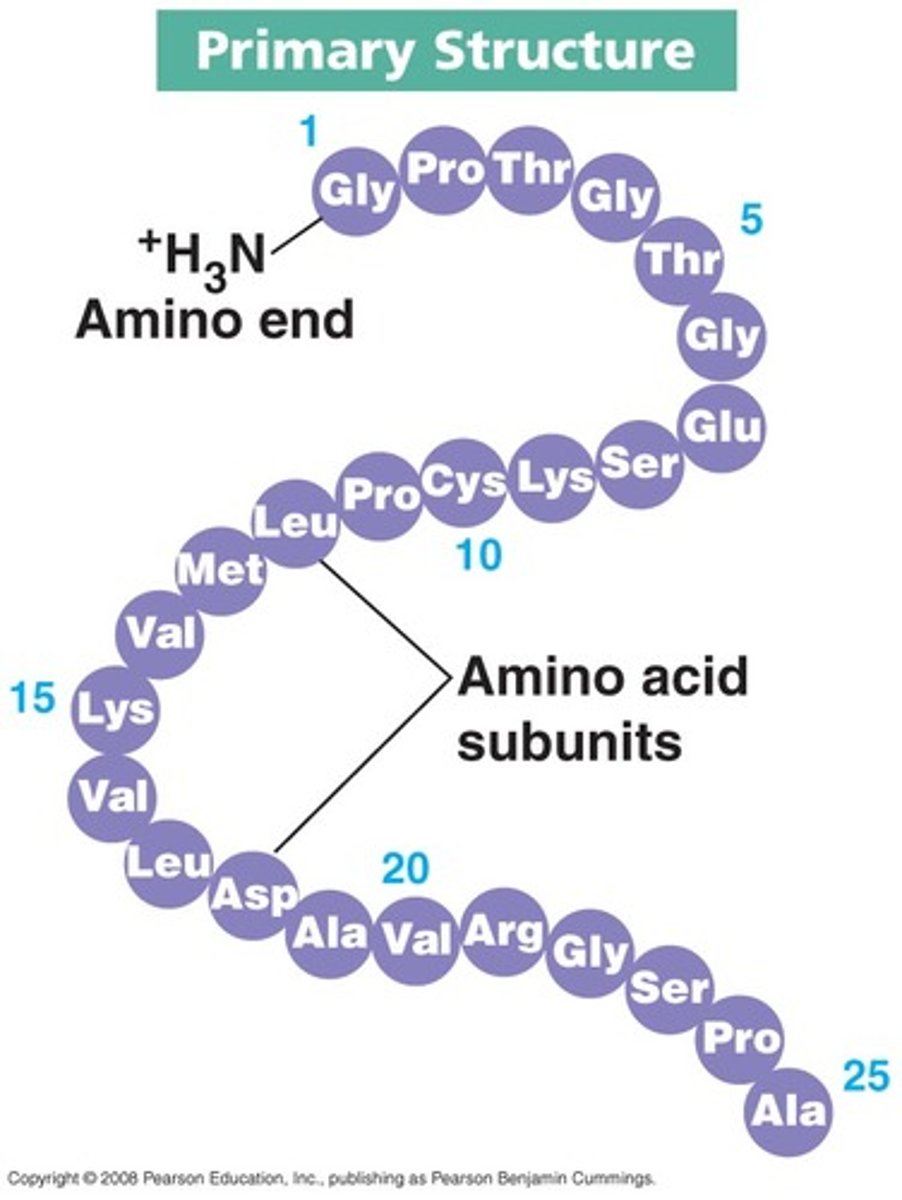
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain which determines its properties and shape
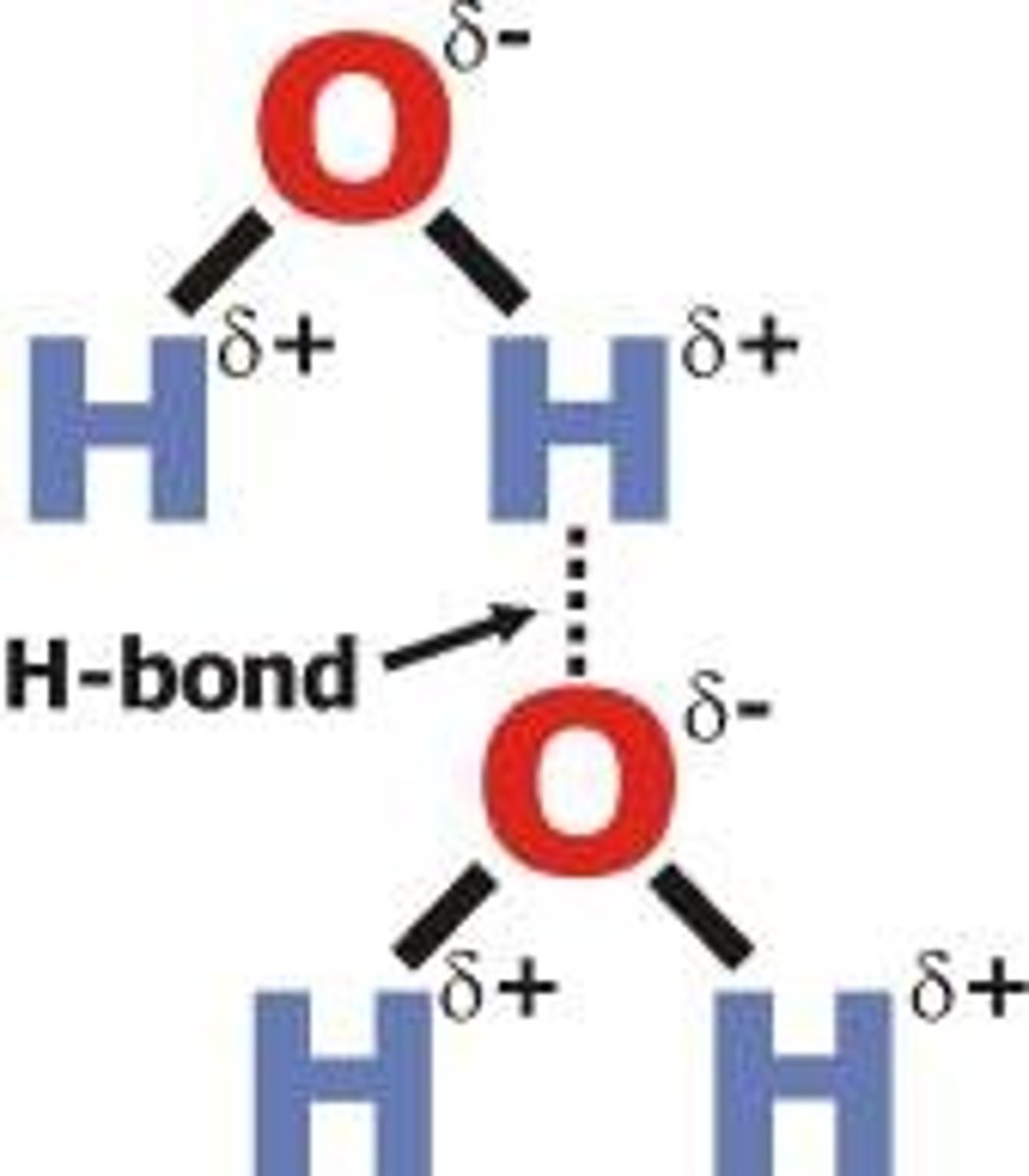
What is a hydrogen bond ( in the tertiary structure)?
A bond between a slightly negative Oxygen on a carboxyl group and a slightly positive Hydrogen on a amine group.
It's a weak bond which can be split easily by high temperatures and altered pH.
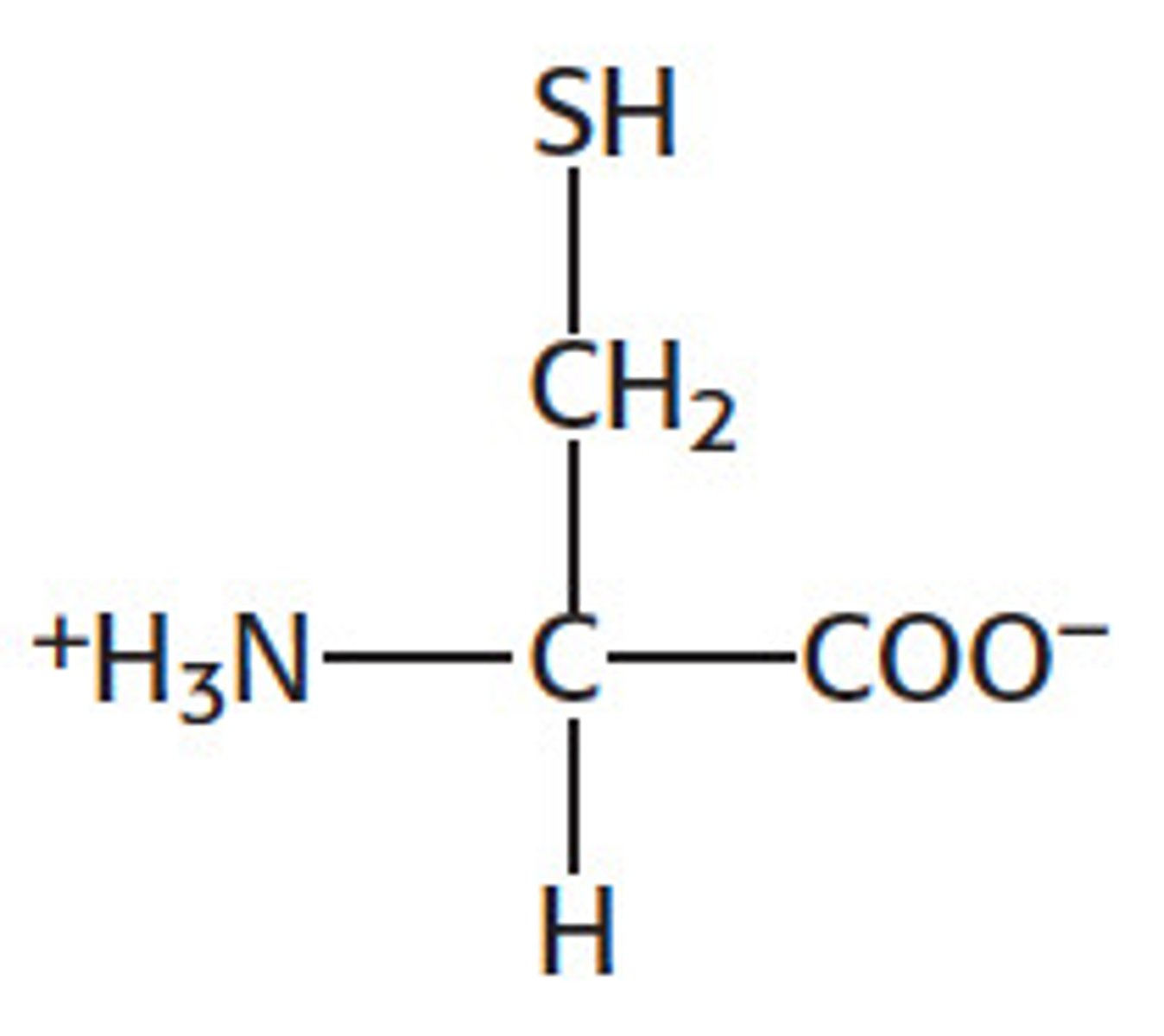
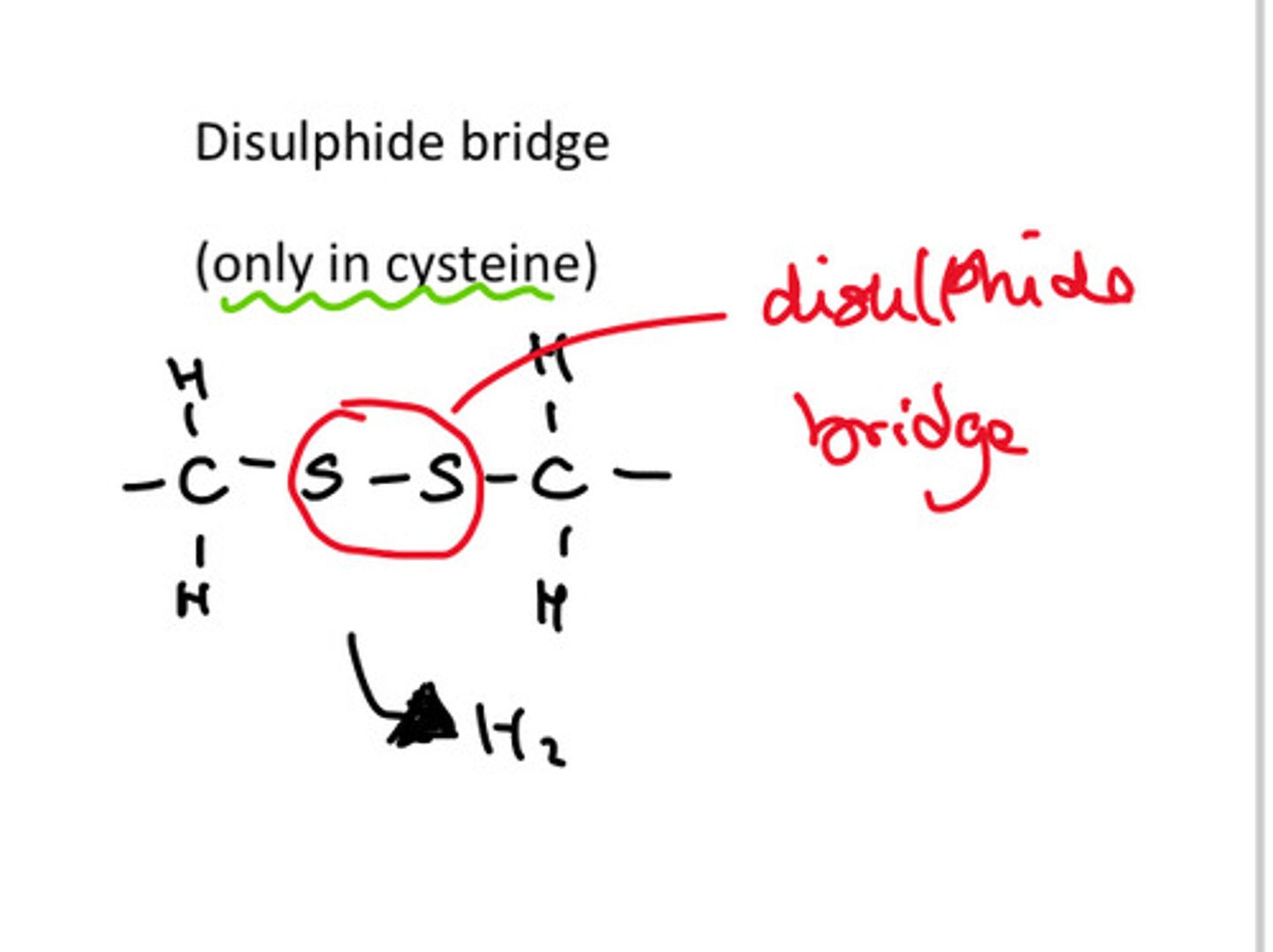
What are disulphide bonds or bridges?
they are covalent bonds that form between sulphur containing amino acids
they are strong and nearly permanent as they can only be broken by reducing agents so they help hold the tertiary structure of protein together.
What are some proteins with a quartenary structure?
Hemoglobin and keratin
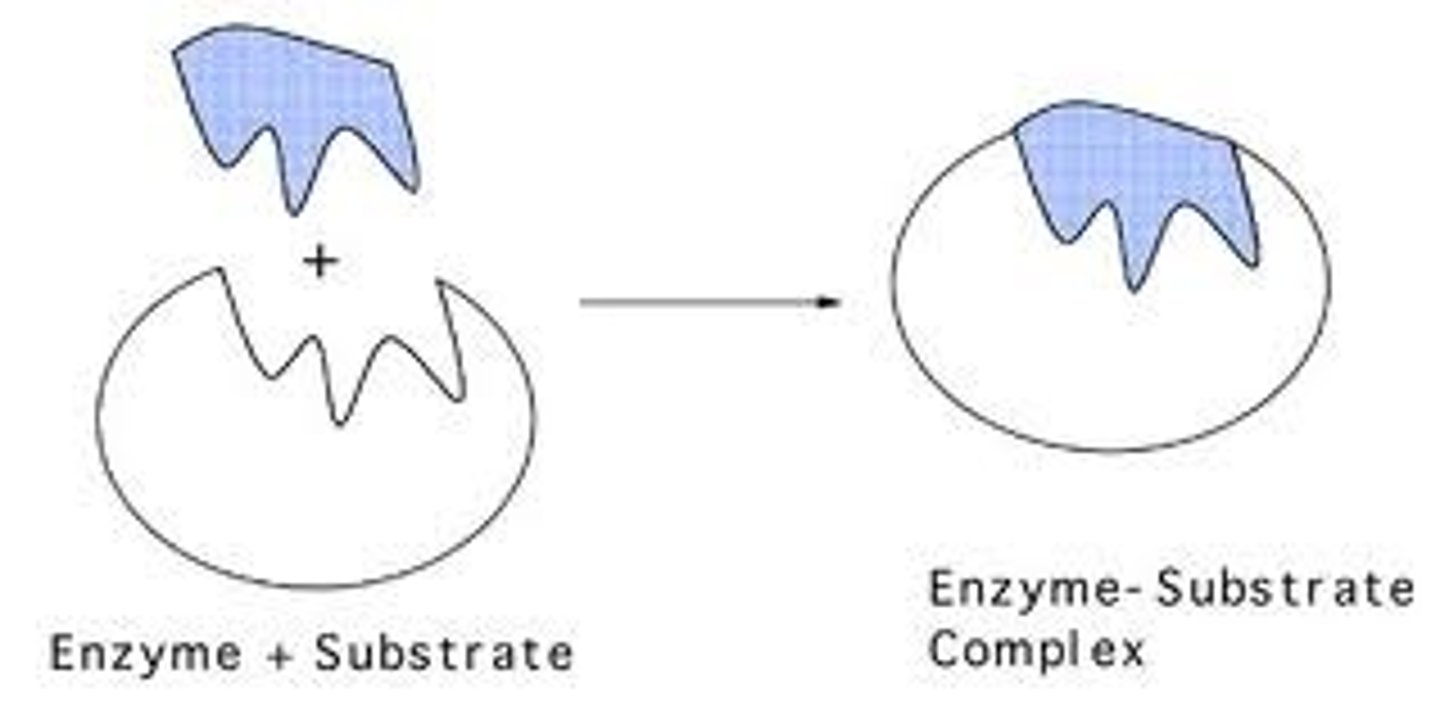
What is the active site?
The active site is the region on the enzyme where the substrate binds.
What is the induced fit model?
The enzyme shape alters slightly to accommodate the substrate as it is slightly flexible.

What is an enzyme-substrate complex?
the binding of a substrate to the active site of an enzyme once its changed shape etc (duh..)
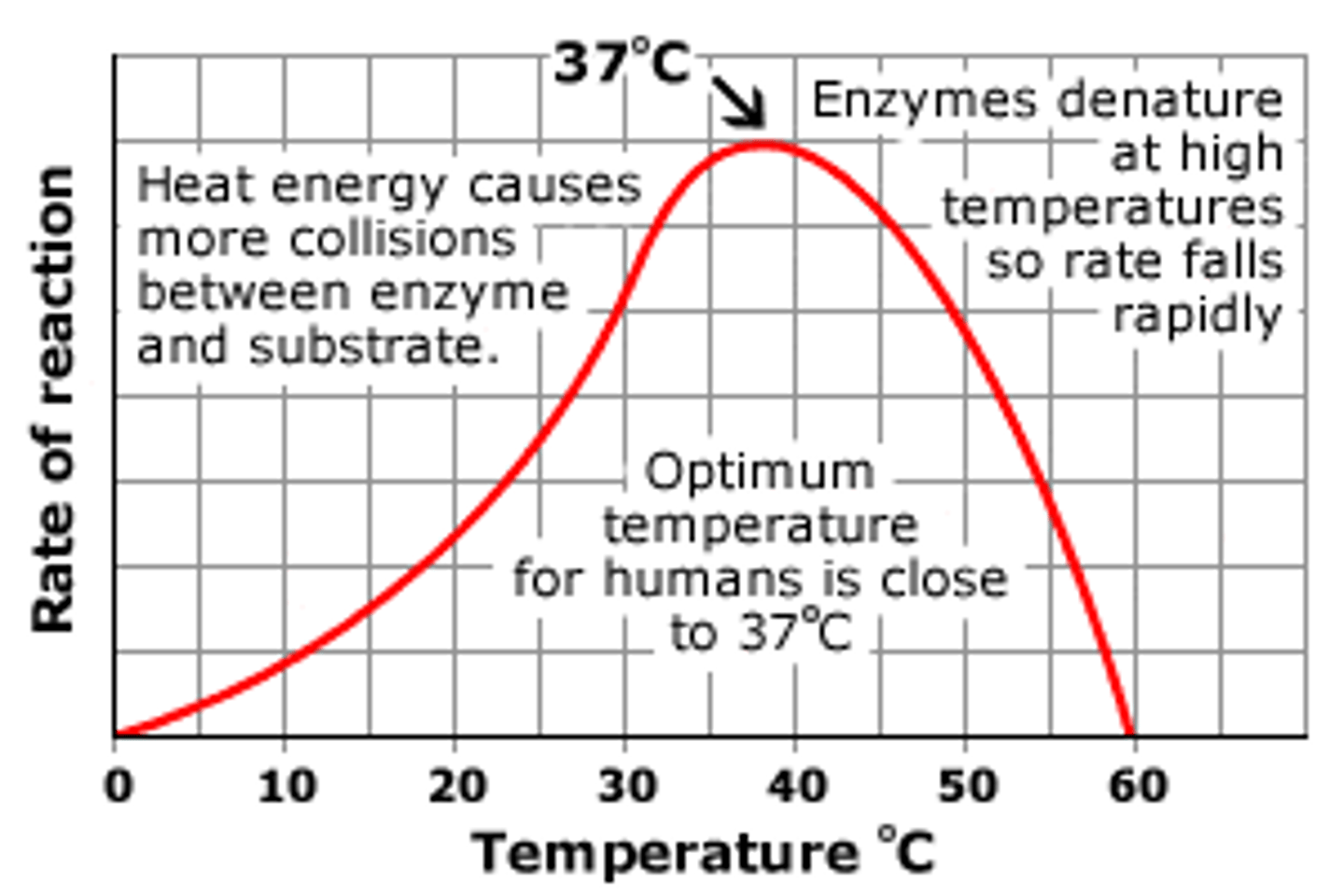
What is the effect of temperature on enzyme activity/ rate of reaction?
A rise in temp causes the activity/rate to increase as there is more kinetic energy so more collisions between particles therefore more enzyme-substrate complexes.
There is an optimum temp - 40 ish.
After the optimum the increase in temp will cause the H & I bonds to break causing the active site the change - the enzyme is denatured.
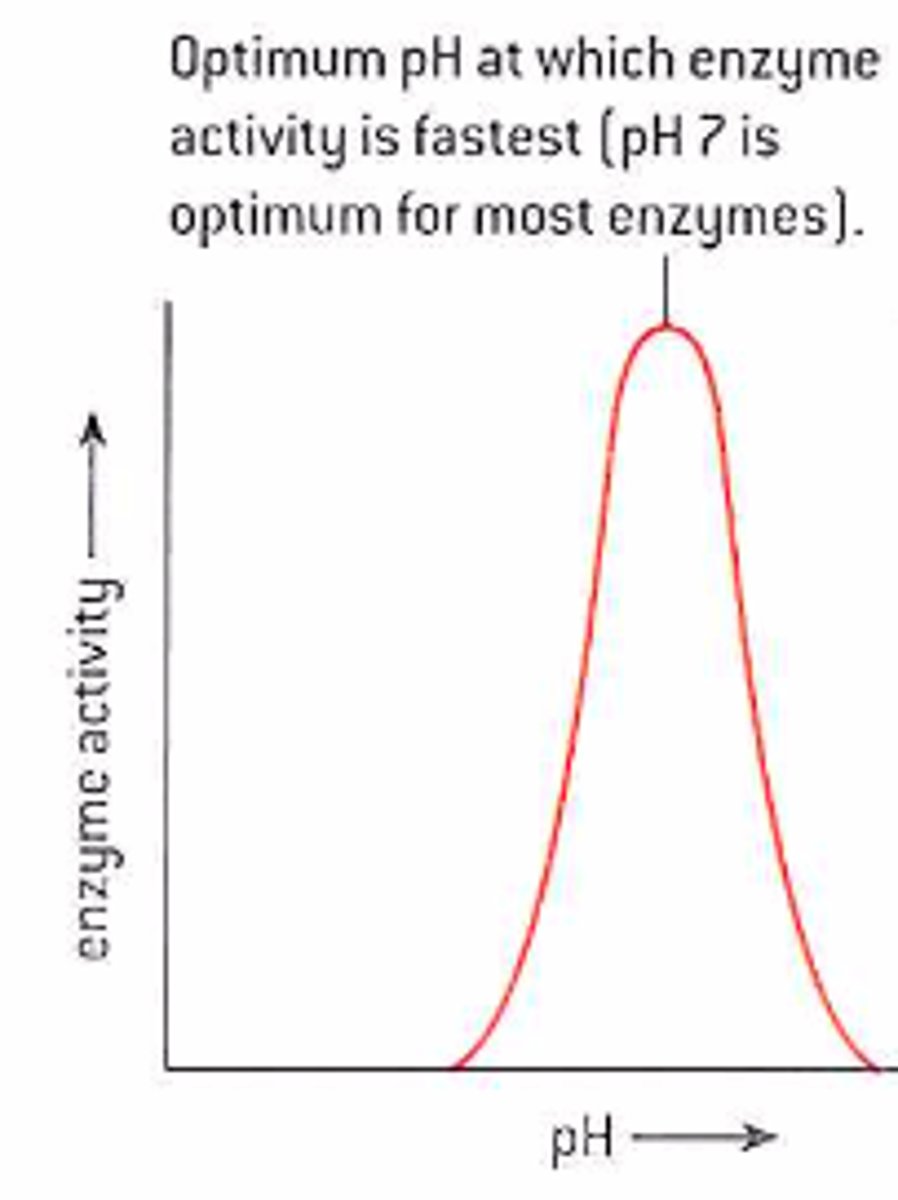
How does pH affect enzyme activity?
Changes in pH affect how many H ions are in the solution :
- too few or too many causes damage to the hydrogen and ionic bonds
- this is why an enzyme can become denatured if the pH is too high or low
There is an optimum which for most enzymes is 7.
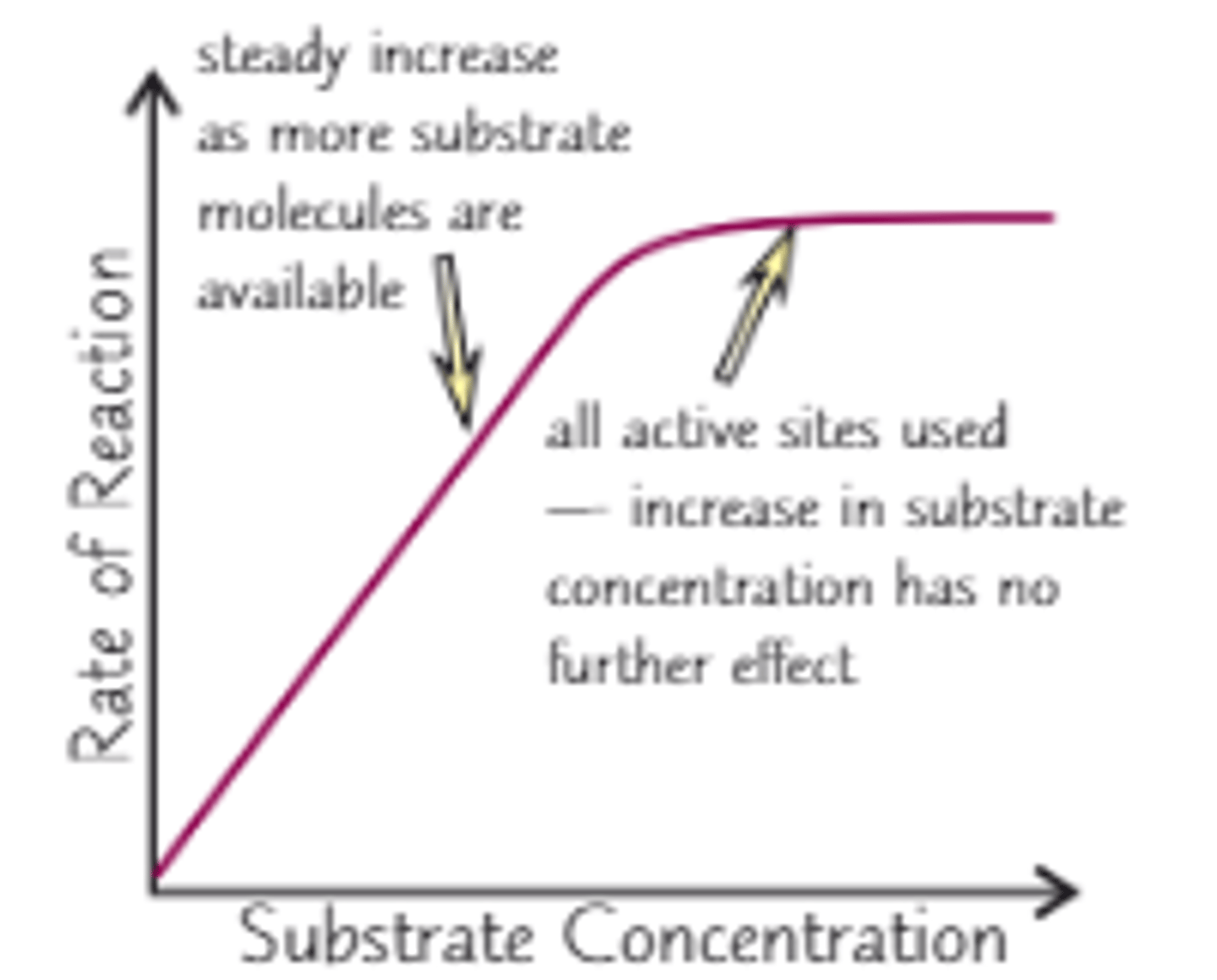
How does substrate concentration affect enzyme activity?
At the start the increase causes more substrate enzyme complexes to be made.
However it will reach a point where all the active sites are saturated so no more E-S complexes can be made therefore the rate stays the same.
How does enzyme concentration affect enzyme activity?
At the start increasing the enzyme conc increases the number of E-S complexes formed.
However at some point it will reach a maximum where the active sites don't have enough substrate so the rate plateaus.

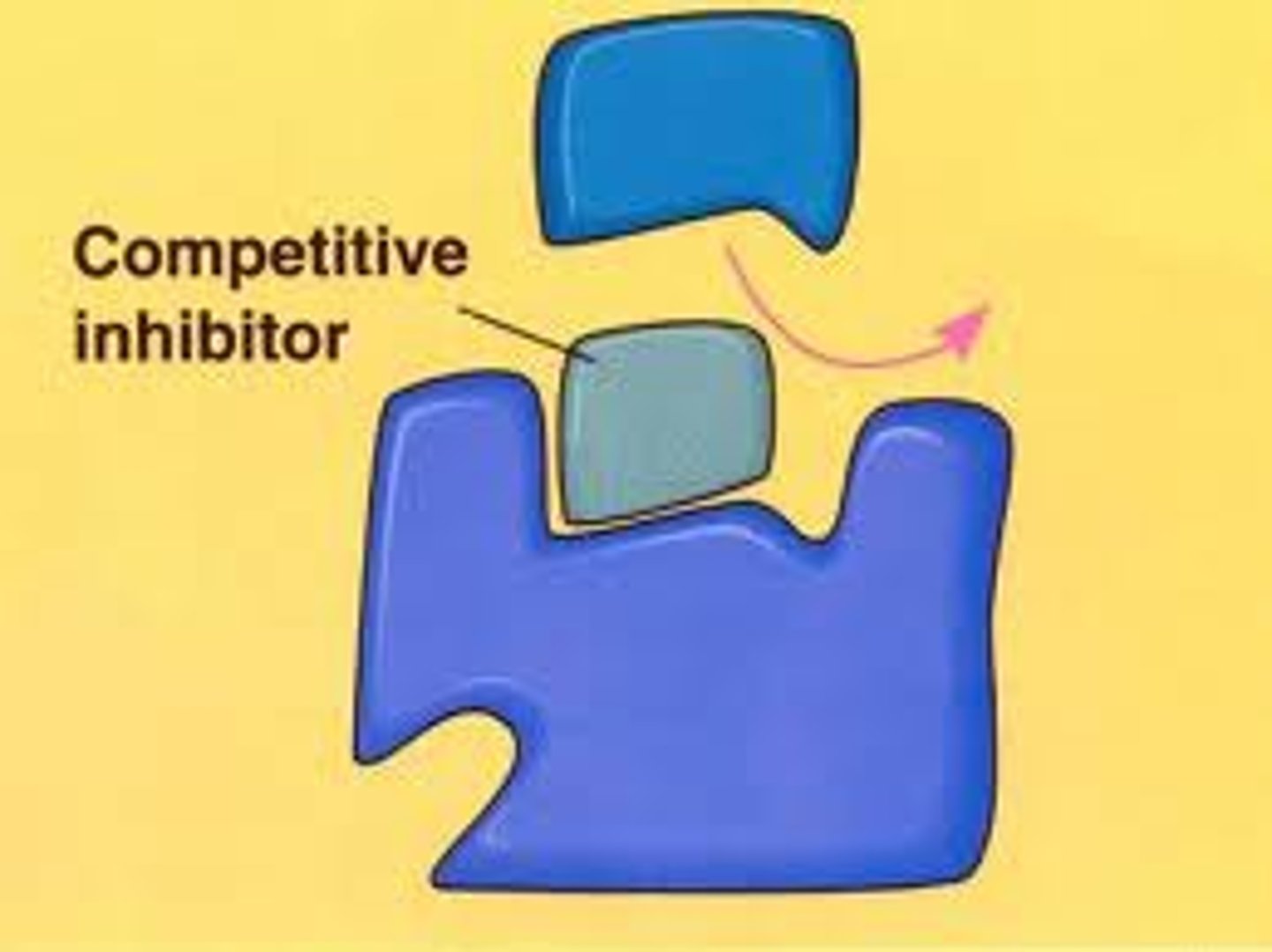
What are competitive inhibitors?
They form enzyme -substrate complexes with the enzymes blocking them and so competing with the substrate.
The bonding isn't permanent so the the all the substrates will be broken down but this will take longer.

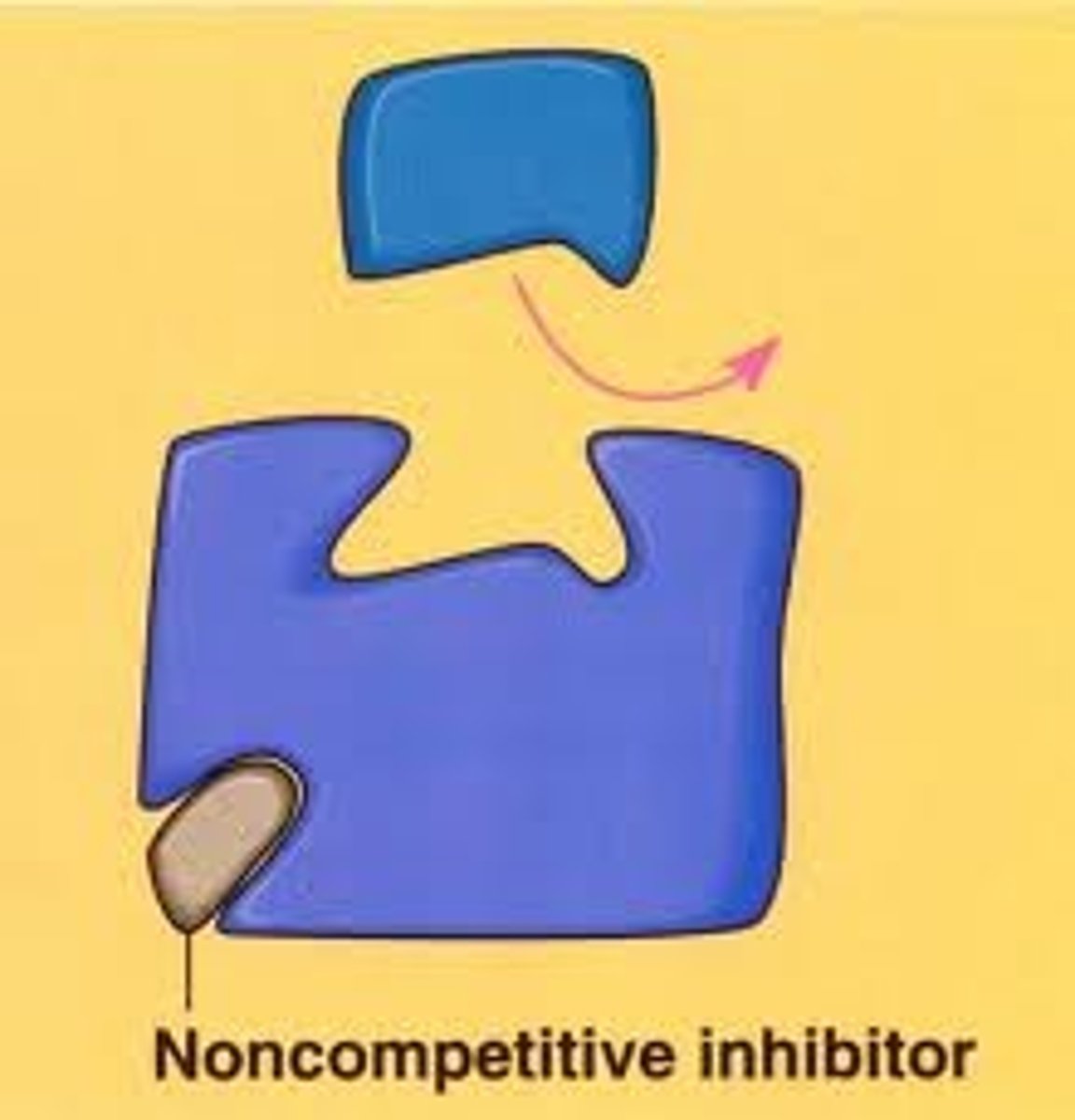
What happens in non-competitive inhibition?
An inhibitor binds to an allosteric site on the enzyme to deactivate it by changing the enzymes shape and therefore the active site but doesn't occupy the active site.
What is DNA?
DNA or deoxyribose acid is a polymer made up of monomer nucleotides forming 2 anti-parallel strands
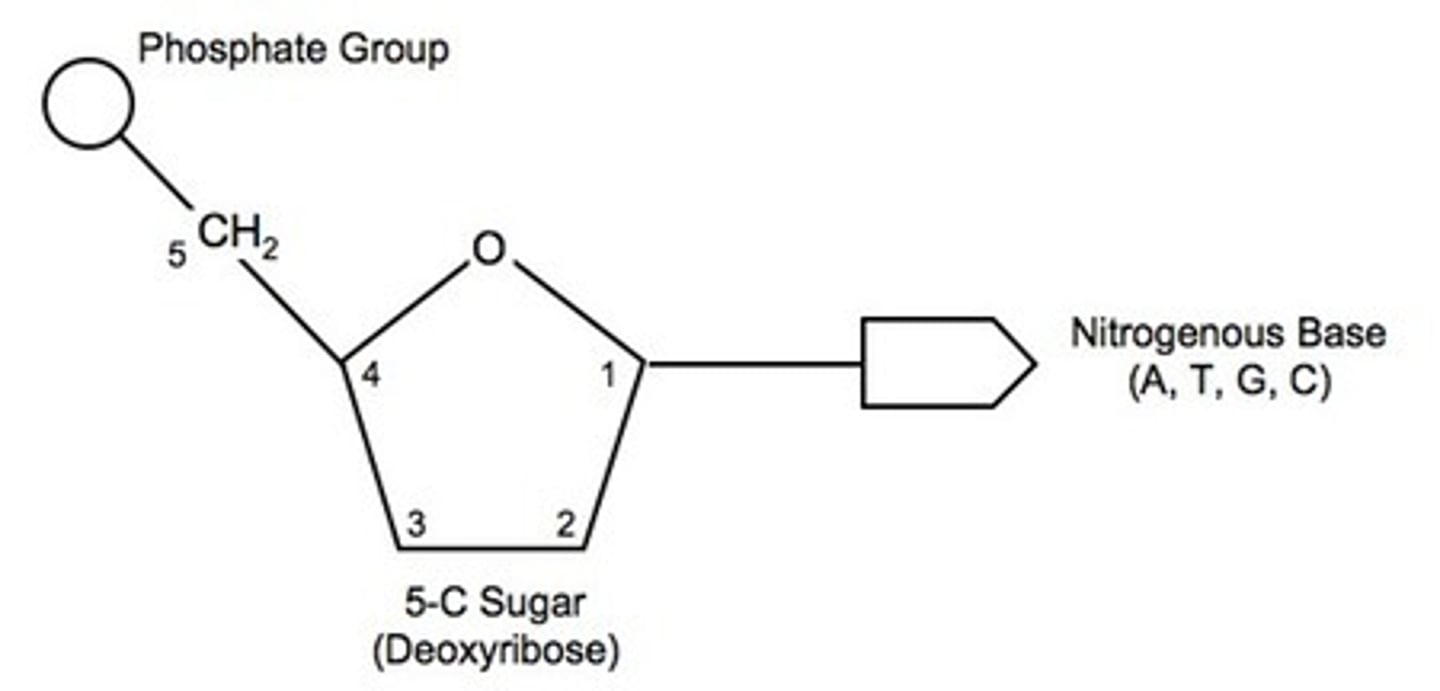
What is the structure of a nucleotide?
phosphate group, deoxyribose (pentose sugar) & a nirogenous base
the chain of sugars & phosphates is a sugar-phosphate backbone
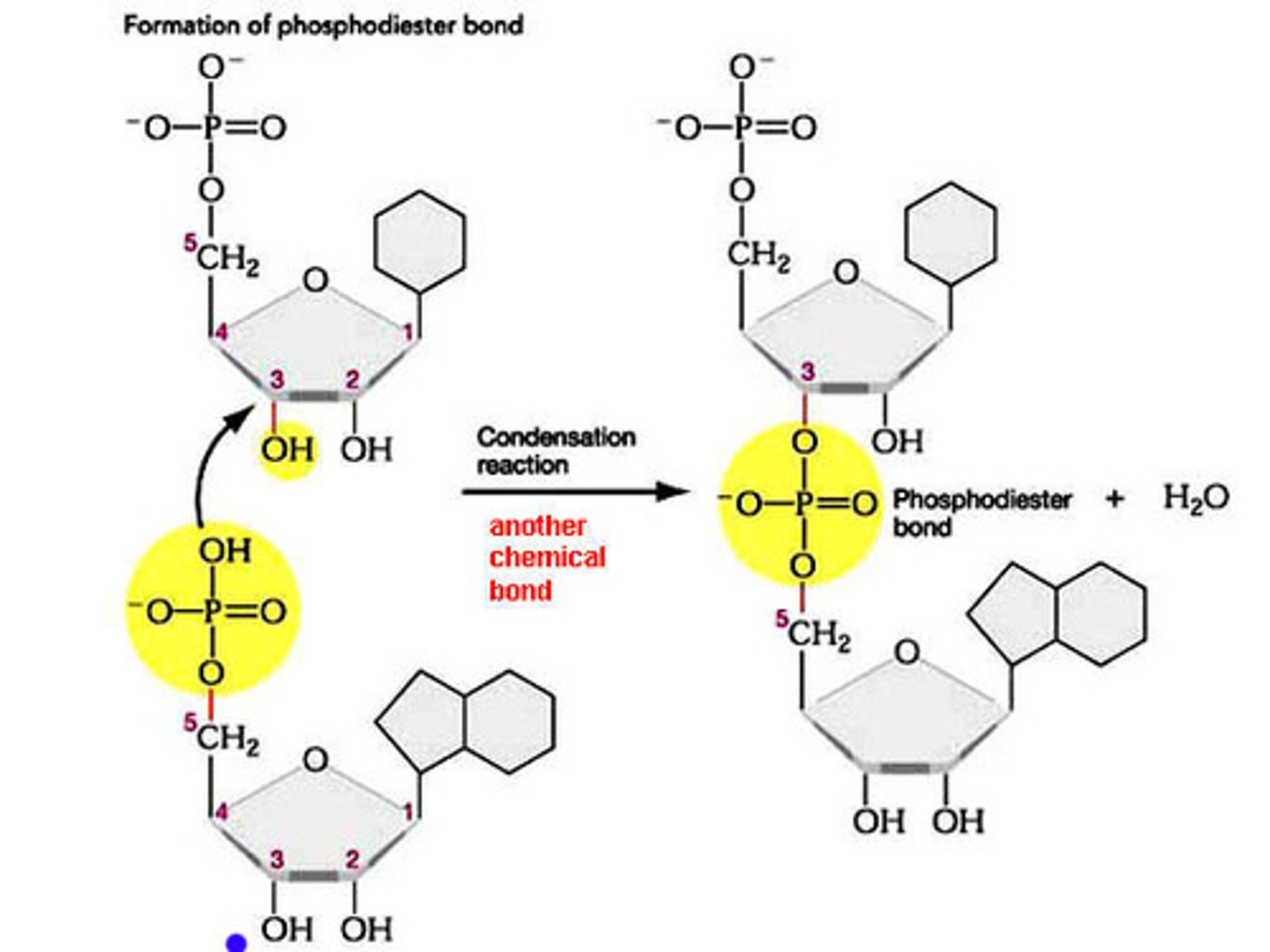
How are nucleotides joined together?
A condensation reaction between 2 forms a phosphodiester bond ( very strong )
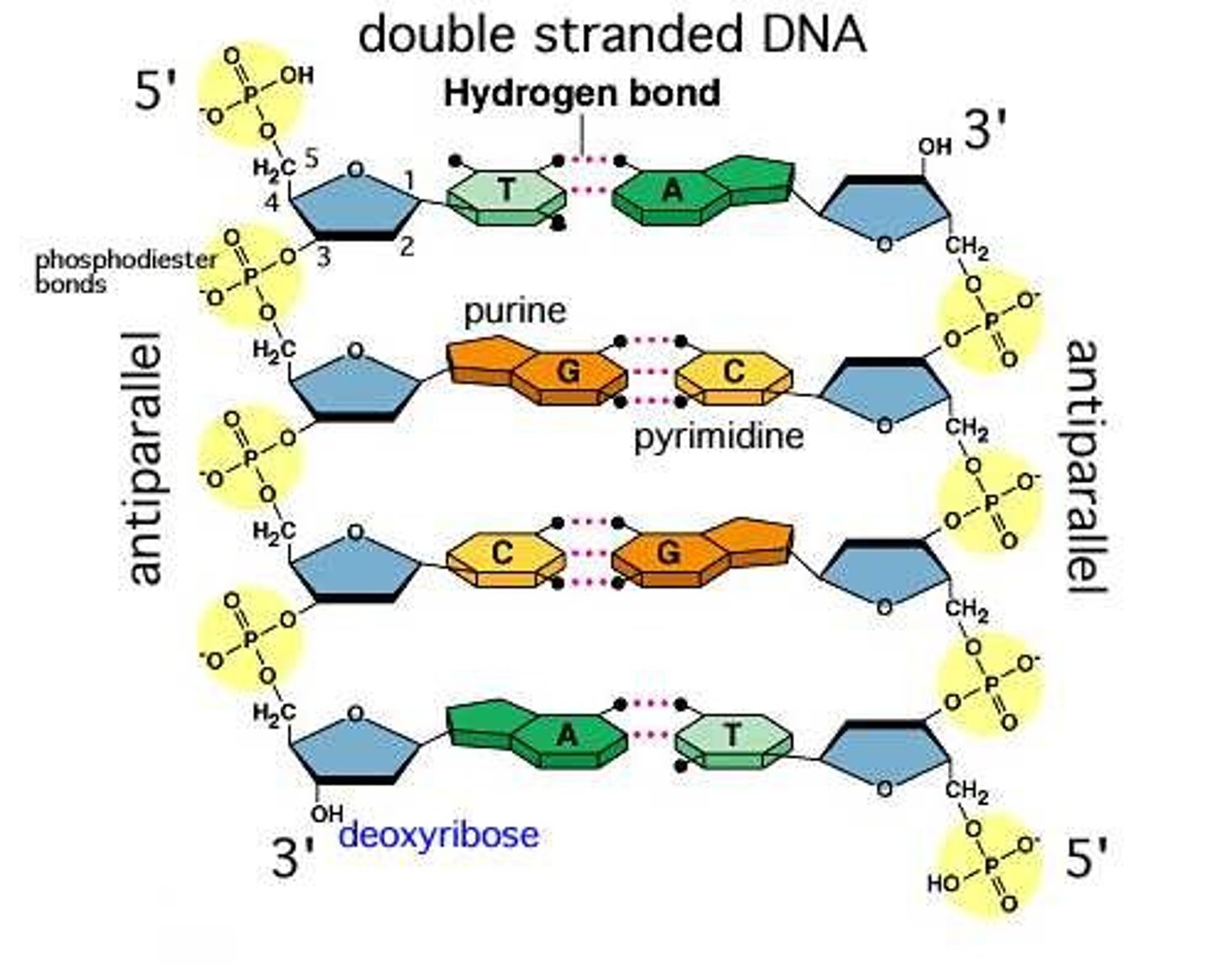
How do the bases pair in DNA?
They form base pairs:
Adeine -- Thymine with 2 hydrogen bonds
Cytosine --- Guanine with 3 hydrogen bonds
The bases only bond in this way because the pairs are complementary to each other.
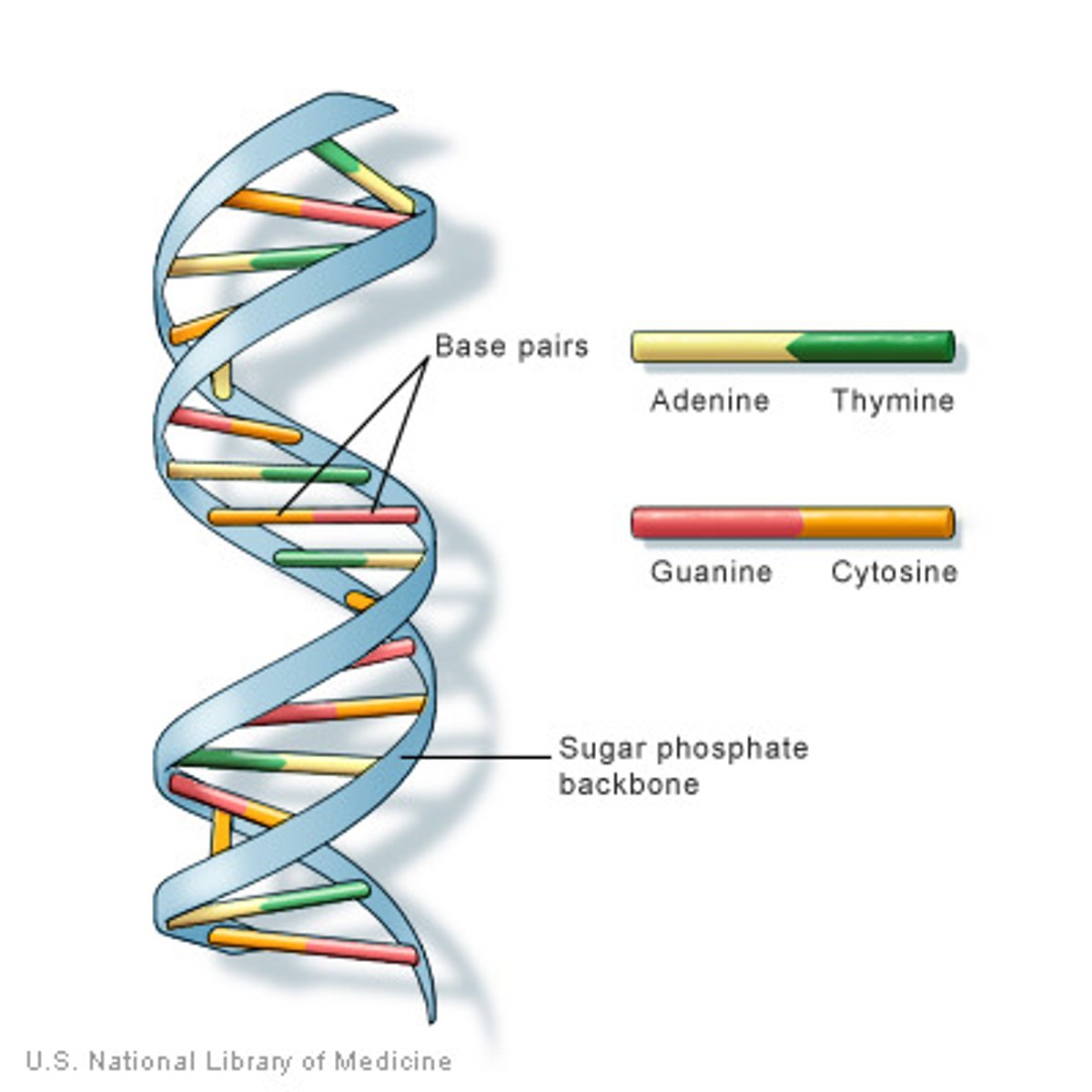
What are the different bonds in DNA?
Phosphodiester between nucleotides - very strong and hold the sequence of bases together therefore dictating the primary structure of a protein
Hydrogen between base pairs - join the 2 strands but can be easily separated by enzymes for protein synthesis or copying the DNA however the large number means it's overall quite strong.
What does the bonding in DNA allow it to do?
The strong regulated structure means DNA can become a giant molecule while other polymers can't meaning it can store lots of information.
The bases in the helix are also partially protected from damage.
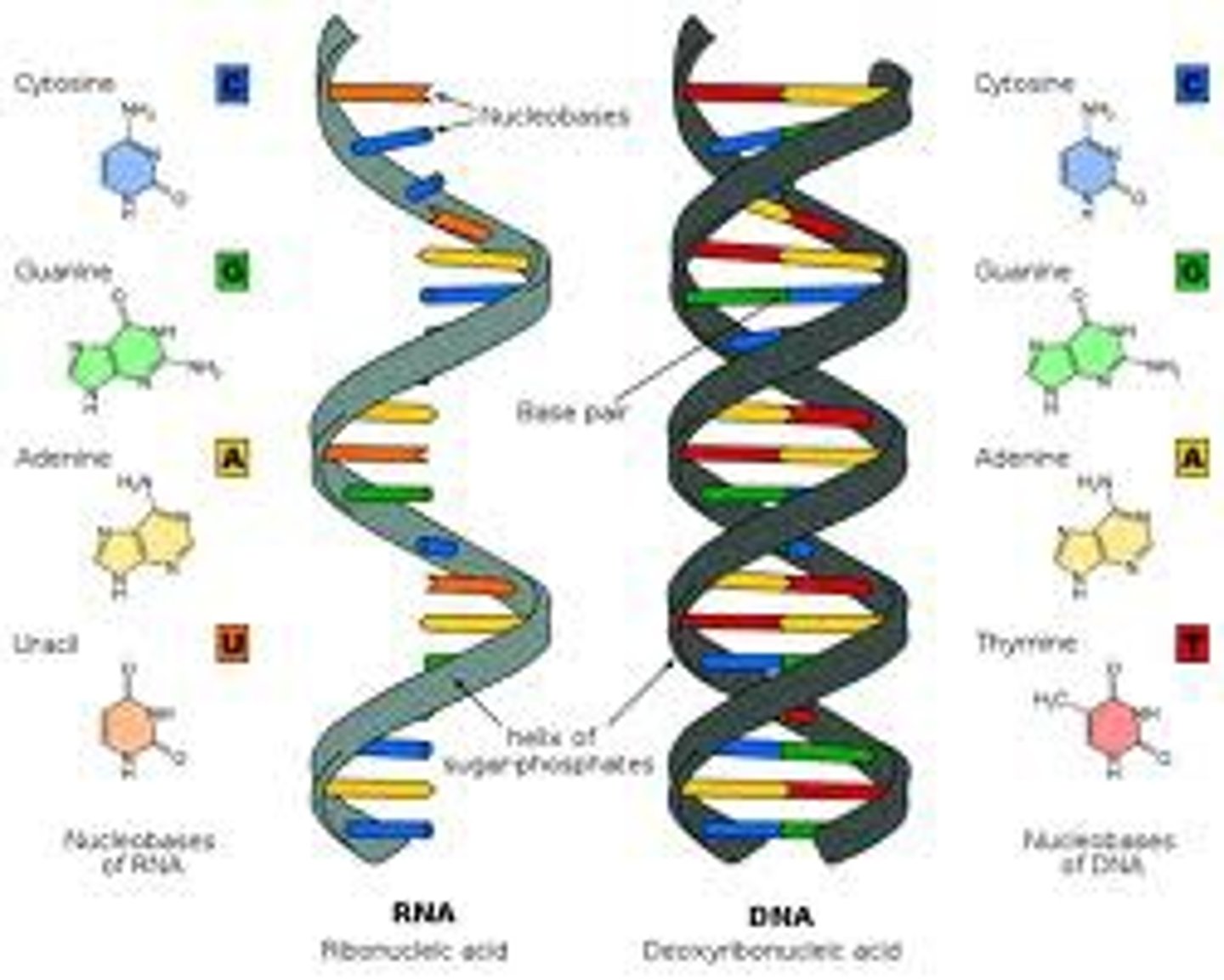
What is the structure of RNA?
RNA has a ribose sugar instead of a deoxyribose sugar like DNA. RNA nucleotides have a uracil base instead of thymine. RNA is also much shorter and denatures faster which is why its used in protein transportation.
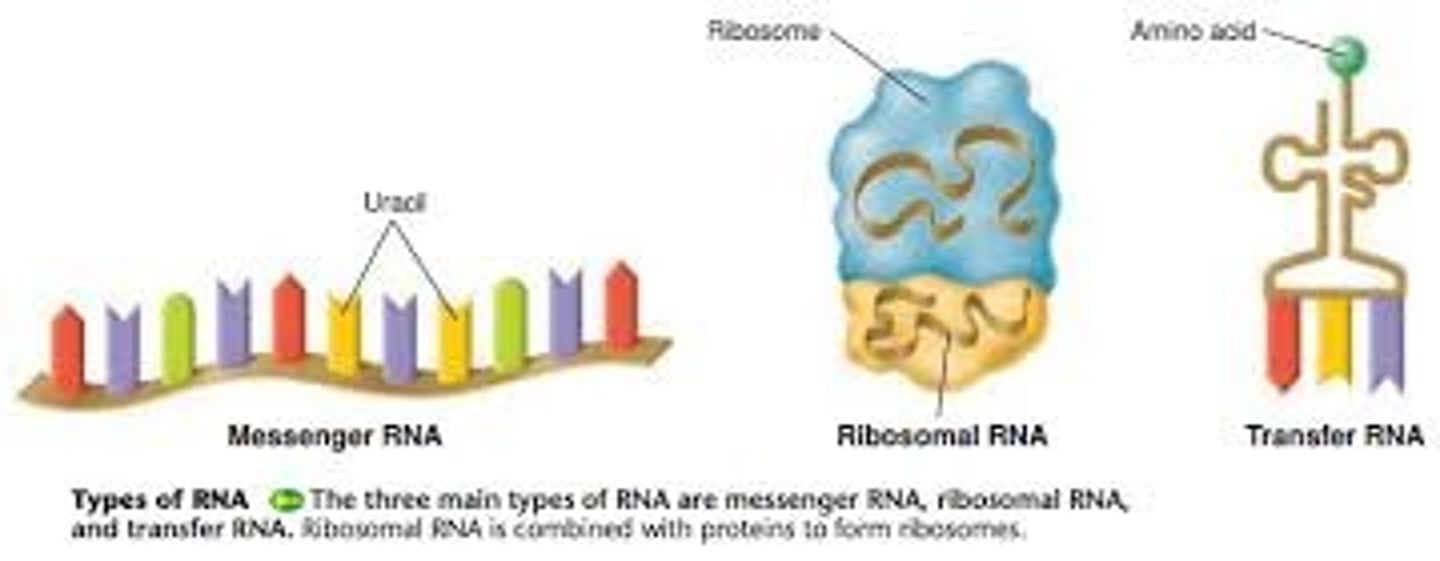
What are the different types of RNA?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) - single stranded - carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosome
Transfer RNA (tRNA) - 4 leaf clover shape - carries amino acids to the ribosome
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - part of the structure of ribosomes
What does it mean for the DNA strands to be anti-parallel?
One strand runs from 5' to 3' and the other runs from 3' to 5'.
Aka the last deoxyribose sugar can be facing so the 3rd carbon is facing up or that the 5th carbon is facing up.
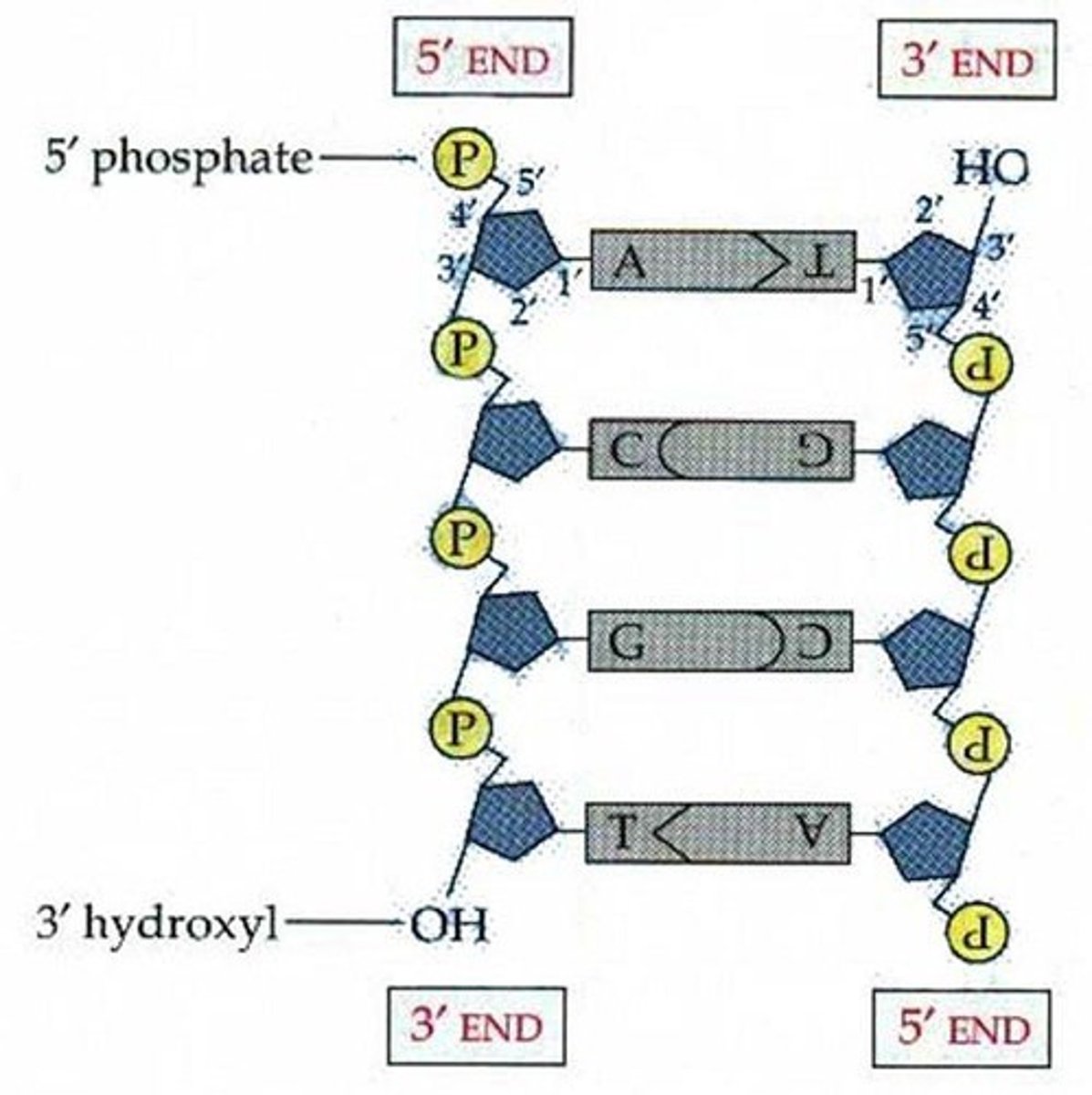
Why is it a problem for DNA replication that DNA strands are anti-parallel?
The enzyme DNA polymerase can only work from 5' to 3' as it has a specific shape so when the enzyme works on the 3' to 5' strand it has to work in segments.
What are the enzymes involved in DNA replication?
Helicase - it unhelixes/unwinds the double helix into a replication fork
DNA polymerase - binds to a strand and actually forms the new strand that binds directly onto the old strand
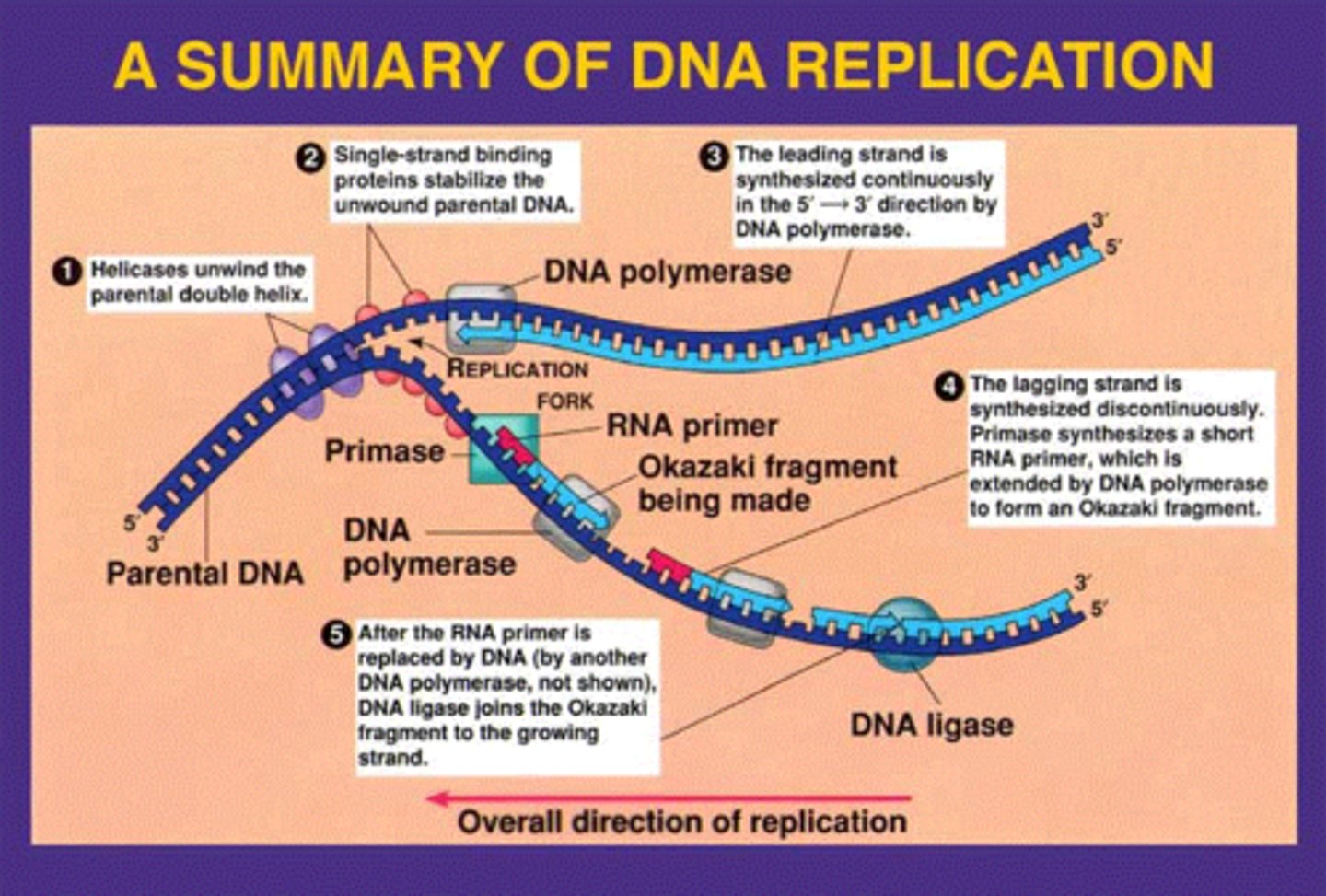
What is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in DNA replication?
The leading strand - runs in the 5' to 3' direction so is synthesized continuously by DNA polymerase
The lagging strand - runs in the 3' to 5' direction so can only be synthesized discontinuously in Okazaki fragments
How are the unpaired bases in single strand of DNA stabilized during DNA replication?
There are "loose" unpaired bases in the nucleoplasm that can bind to the bases on the strand before DNA polymerase actually creates a new strand for it to pair up with.
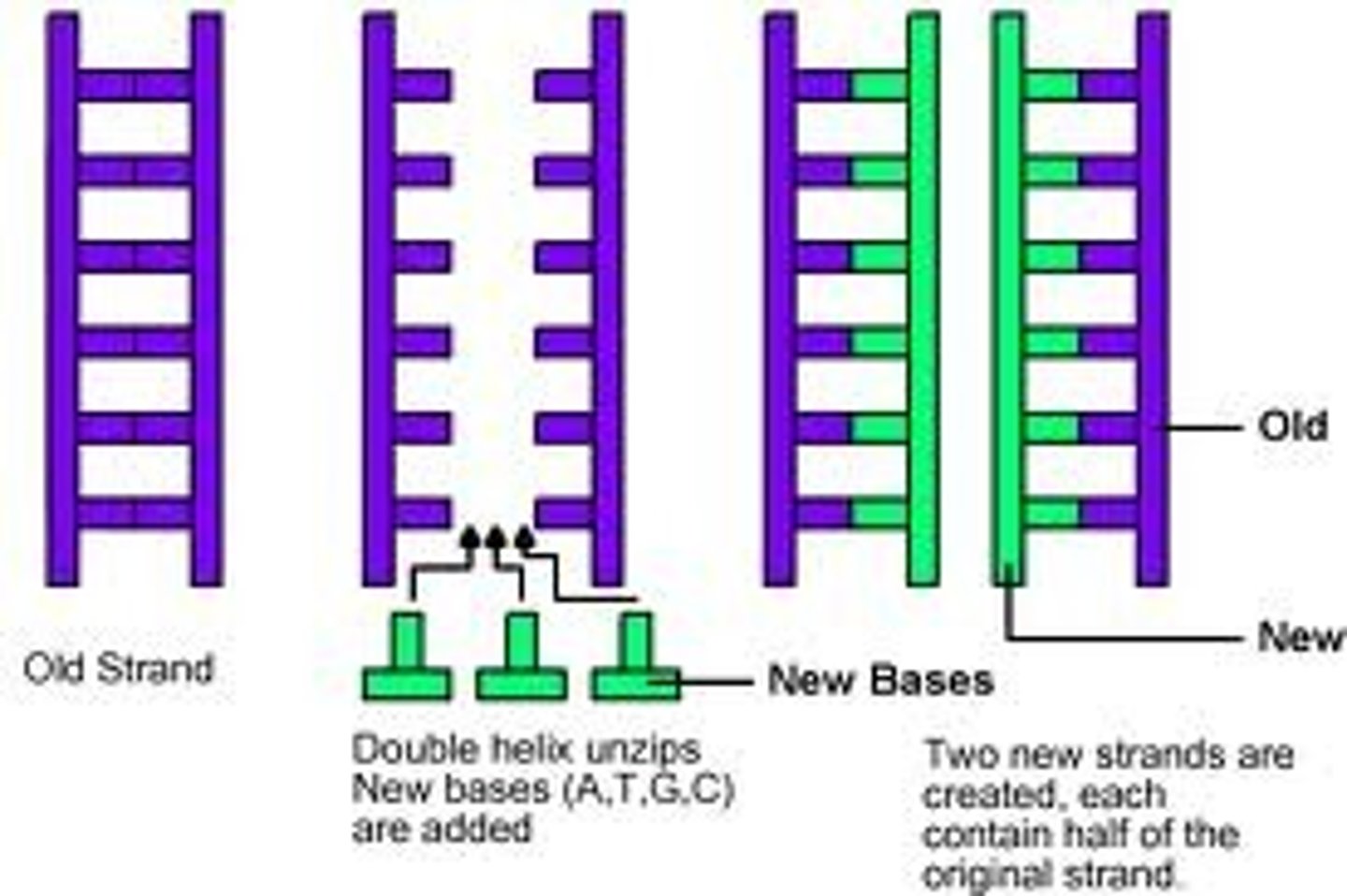
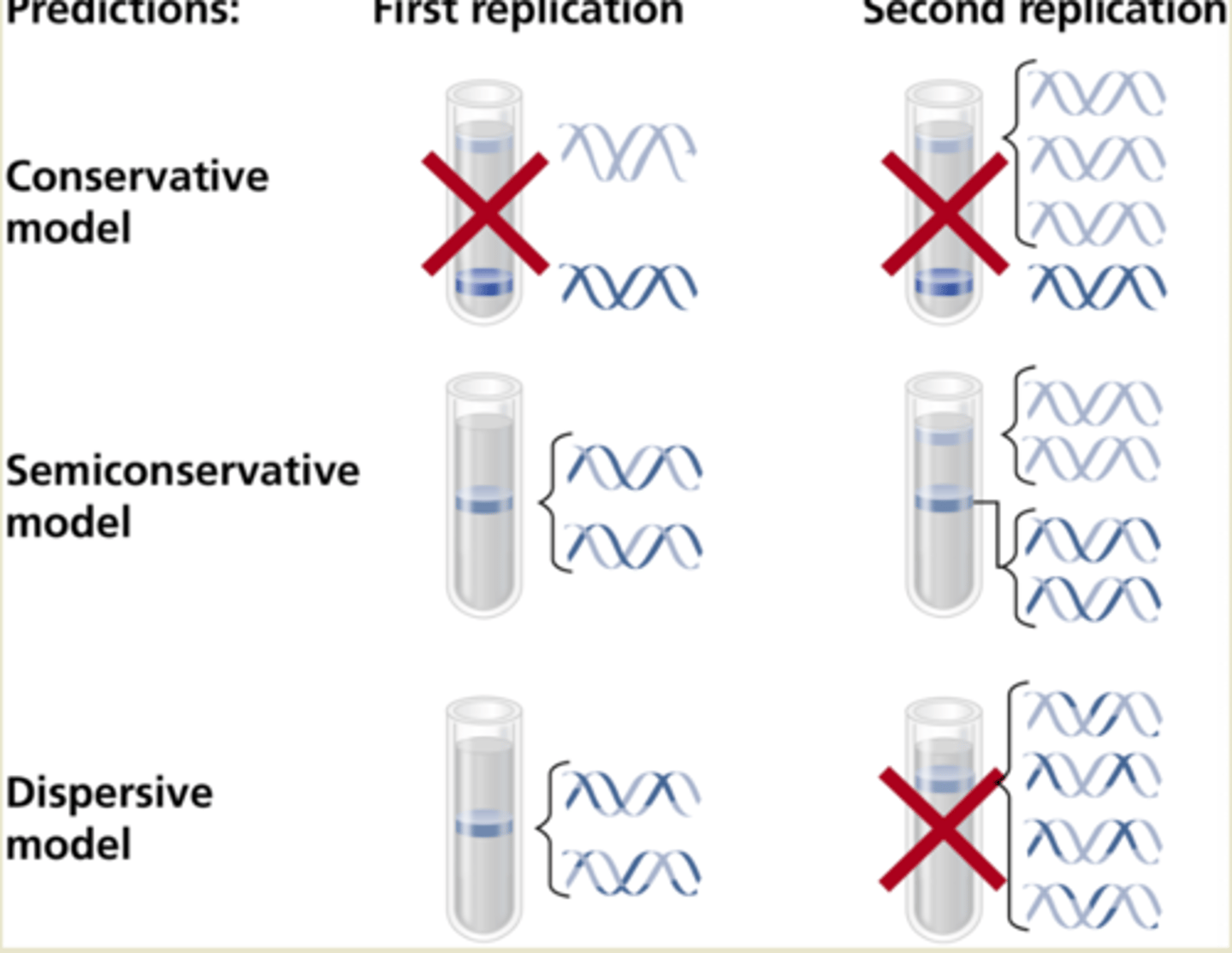
Why is DNA called semi-conservative?
Because when DNA copies itself during replication, the new DNA is made up of 1 old strand and 1 new strand
What was the Meselson-Stahl experiment?
Experiment to test the possible models of DNA replication.
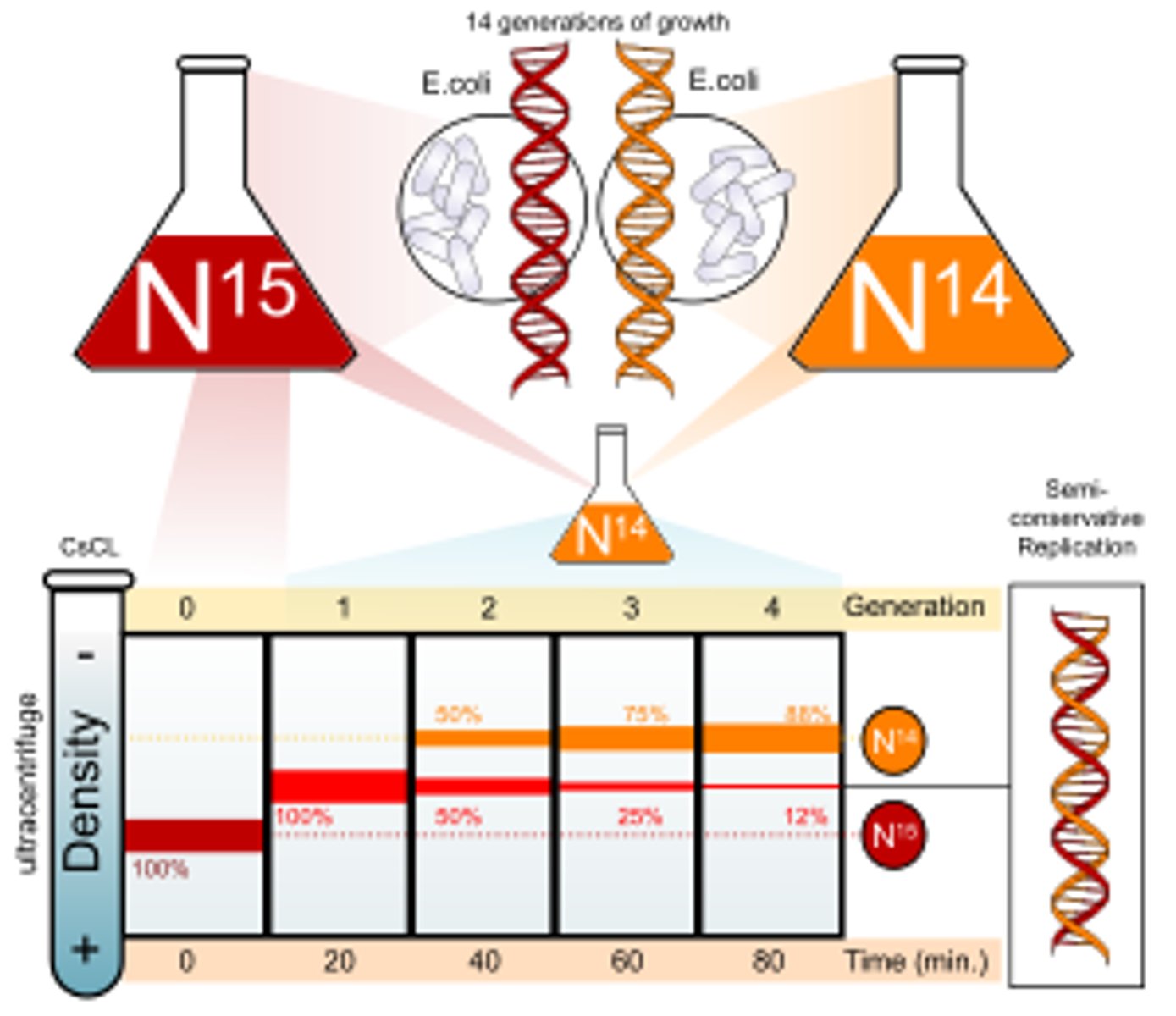
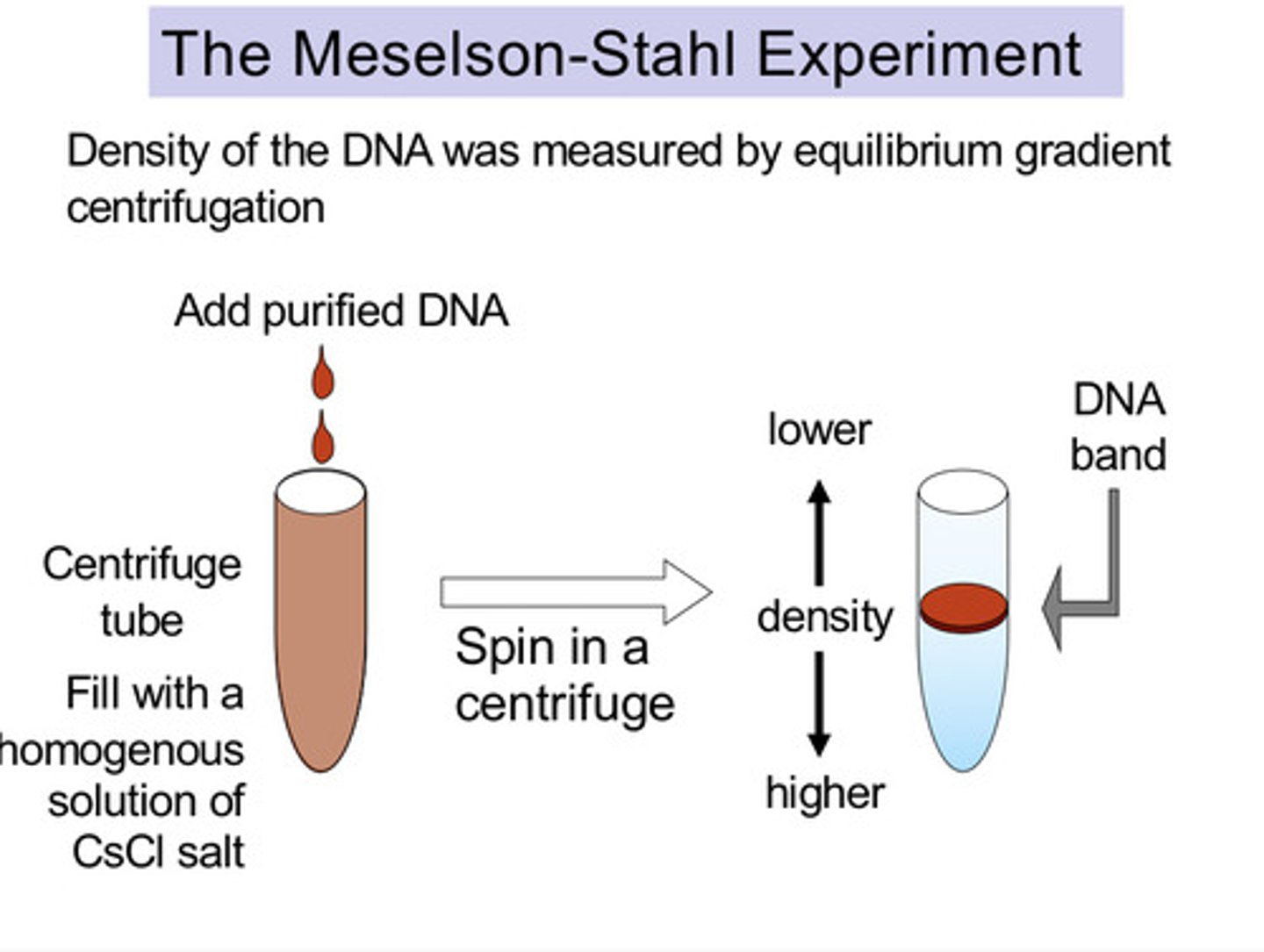
What were the steps in the Meselson & Stahl experiment?
- Bacteria were grown on a medium containing "heavy" nitrogen - 15N so that when the DNA in the bacteria replicated it could contain the heavy nitrogen
- The 1st generation of DNA of the experiment were spun in a centrifuge
- The next generation was then grown in a medium containing 14N and then spun in a centrifuge
- The generation after that was grown in a 14N medium again etc
What were the results of the Meselson & Stahl experiment?
When they were spun in a centrifuge:
- the normal DNA formed a band at the top due it being light
- the heavy DNA/ 15N DNA formed a band at the bottom due to it being heavy
- the 1st gen DNA formed a band in the middle due to it having one "heavy" DNA strand and one "light" DNA strand
- the 2nd gen formed 2 bands one higher than the 1st gen and 1 at the same place due to there being both 14N DNA and the 1st gen DNA ( compositionally)
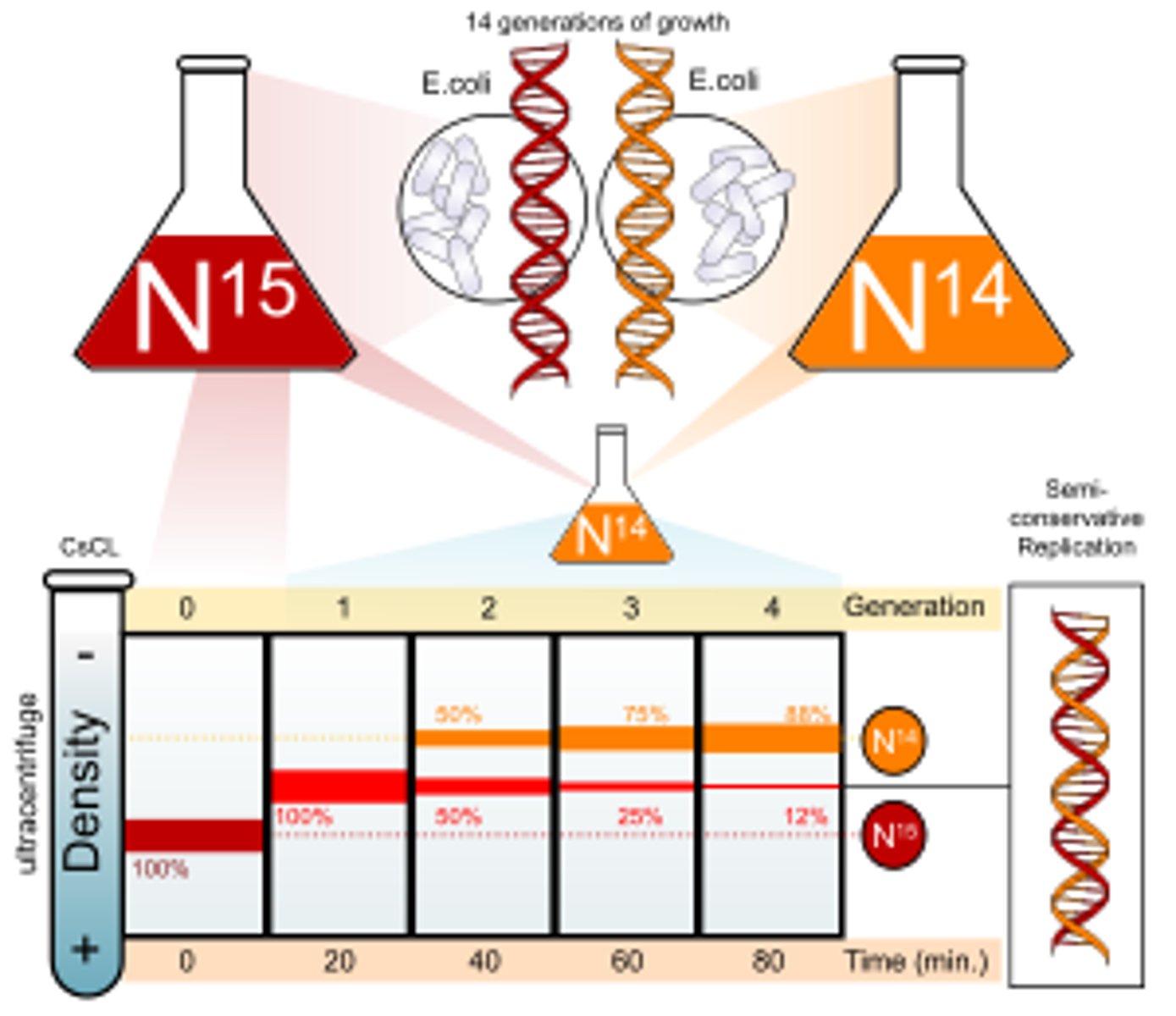
What was the conclusion of the Meselson & Stahl experiment?
That DNA replication was a semi-conservative process as they found that 1 strand of 15N DNA was maintained even when it replicated in a 14N medium.
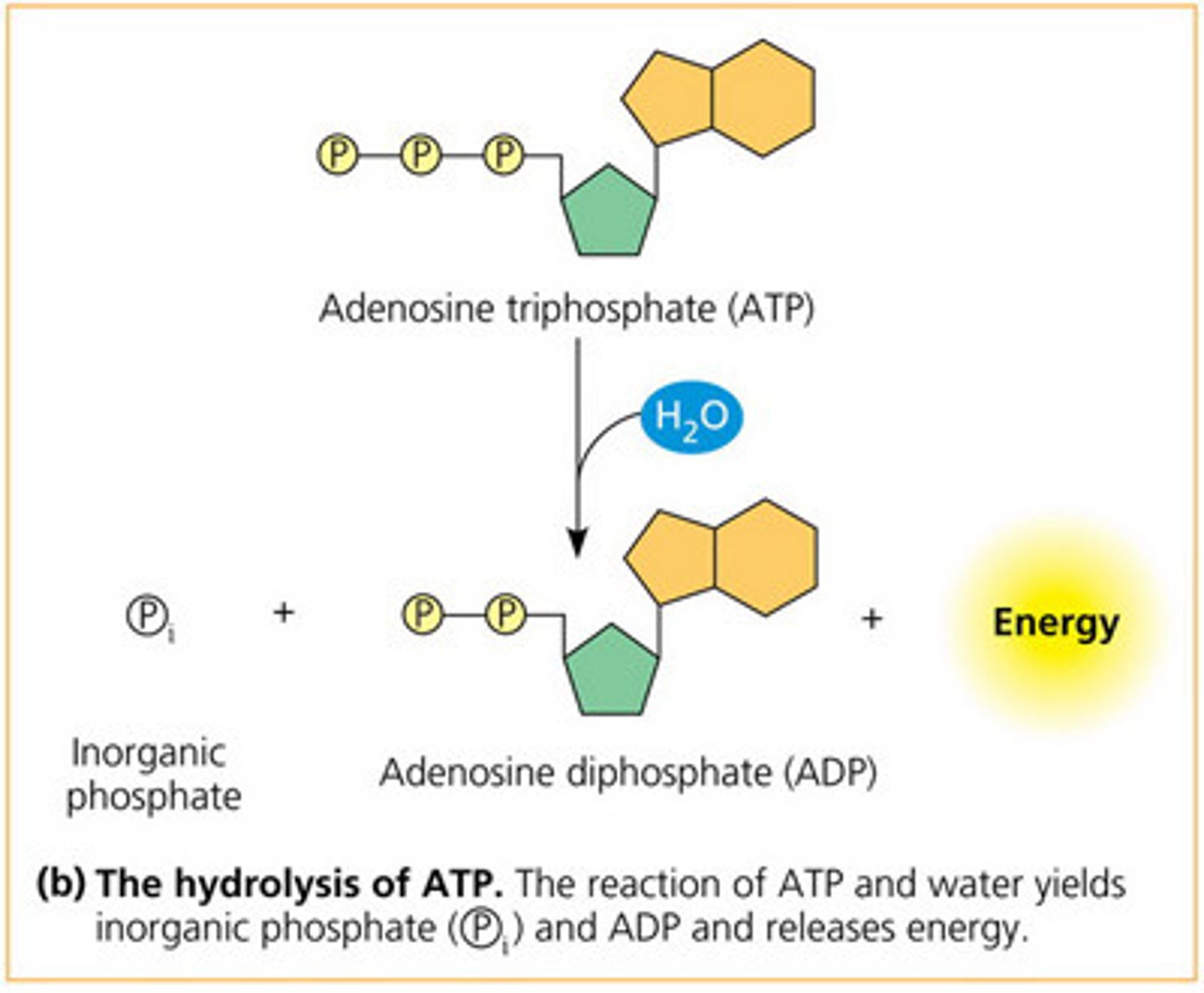
What is ATP?
adenosine triphosphate
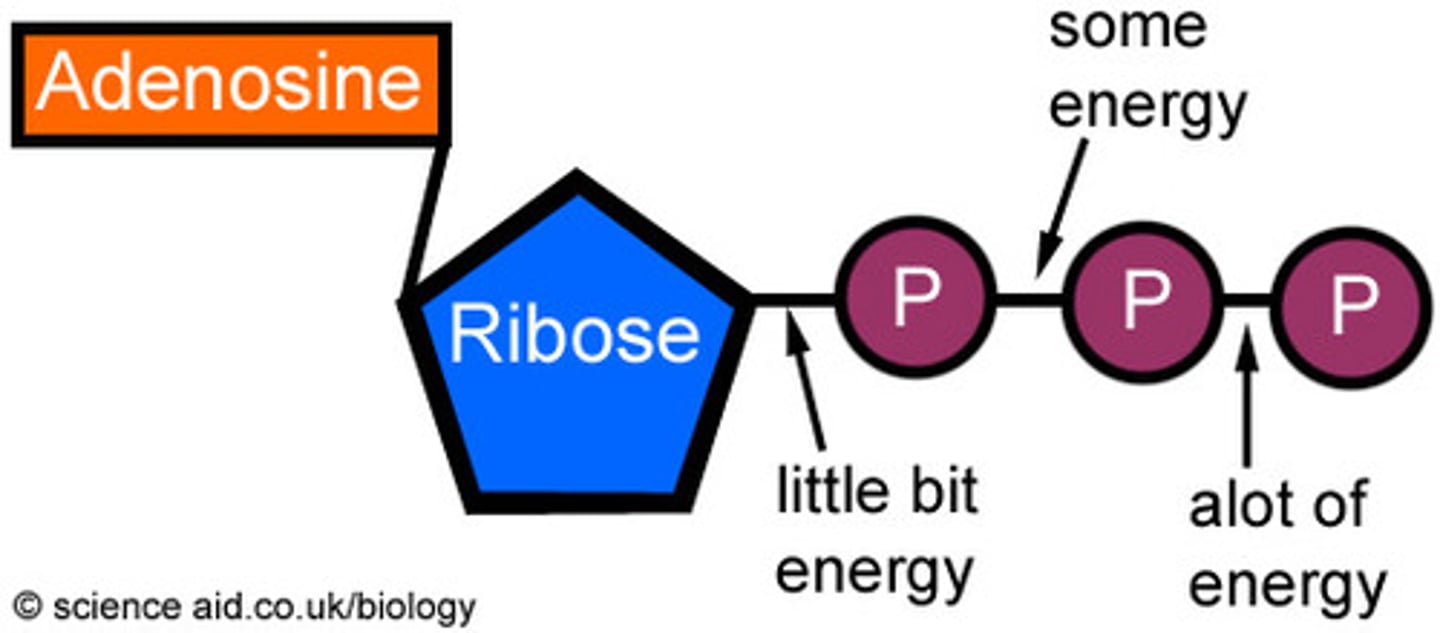
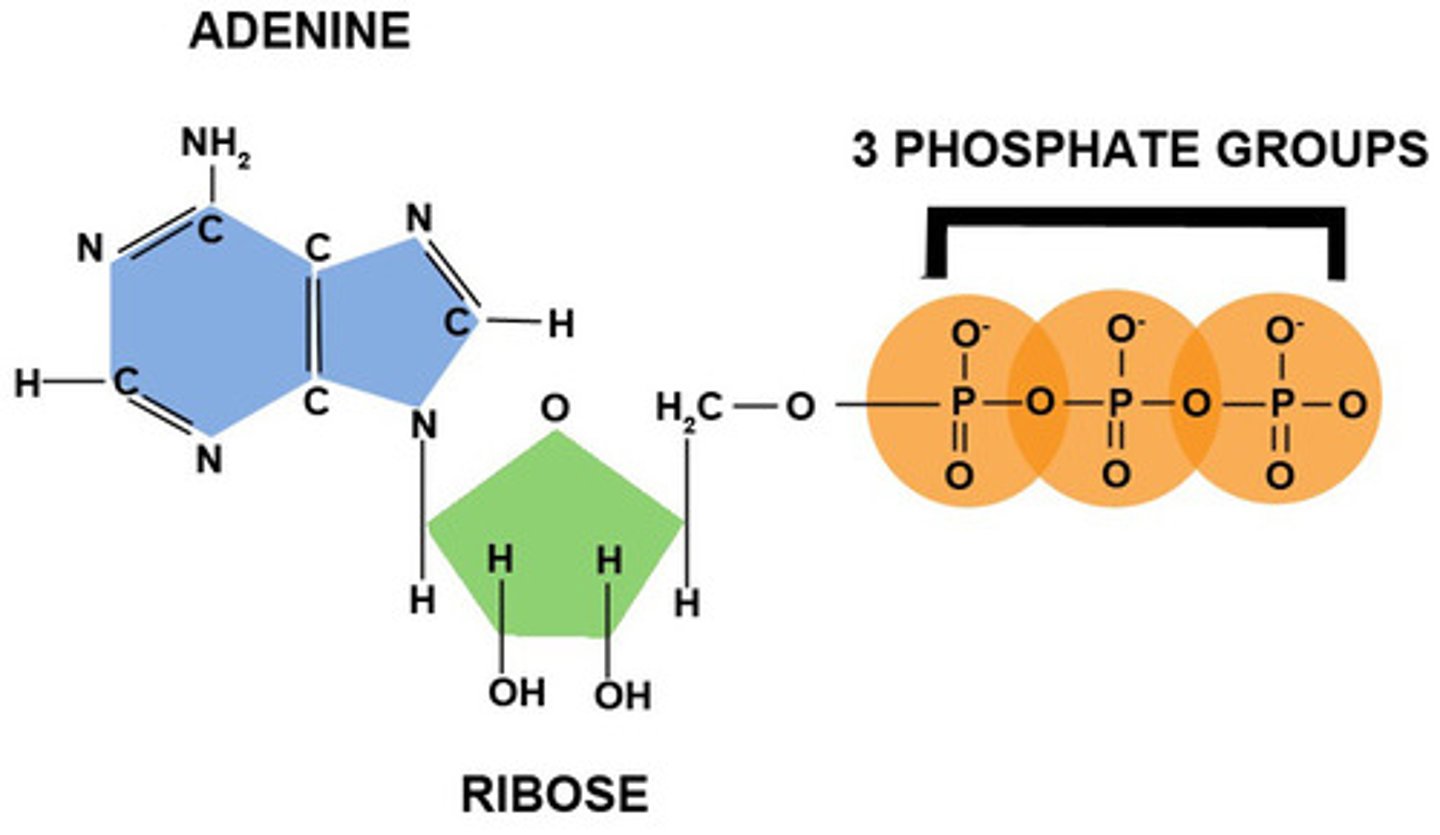
Why is ATP called a nucleotide derivative?
It is a modified form of a nucleotide - it has an adenine base along with a ribose sugar and 3 phosphate groups.
How is energy released from ATP?
ATP is moved to where energy is needed in the cell.
There the molecule is broken down into ADP & P/ adensoine diphosphate & an inorganic phosphate via hydrolysis.
They high energy covalent bond between the phosphate groups releases lots of energy when broken.
How is ATP used along with other chemical reactions?
ATP hydrolysis can be coupled with other chemical reactions so the energy is directly used by the reaction once its released. This means there's no loss of energy as heat.
Phosphorylation can also be done - the inorganic phosphate group is attached to another compound - to make a compound more reactive.
How can ATP be remade?
A condensation reaction occurs between ADP & P to form ATP.
This is how energy is released in photosynthesis & respiration.
What are the enzymes associated with ATP?
ATP hydrolase - the ATP to ADP & P hydrolysis reaction is catalysed by this enzyme
ATP synthase - the ADP & P to ATP condensation reaction is catalysed by this enzyme
Why is water so essential to life?
- it acts as a metabolite in important metabolic reactions e.g. condensation & hydrolysis
- it is a solvent and most metabolic reactions need solutions to take place
- it helps with temperature control
- water molecules stick together which helps it be transported e.g. in plants
What is a metabolite?
A substance involved in a metabolic reaction
Why is water an important metabolite?
many reactions involve a hydrolysis reaction e.g energy from ATP is released through hydrolysis
Why is water a good solvent?
Lots of substances in biological reactions are ionic e.g salt.
Water is polar so its slightly negative oxygen will attract cations and the slightly positive hydrogen will do the same for anions.
This means water molecules surround the ions disrupting their structure - the ionic substance has dissolved.
This allows e.g. mineral ions to be dissolved in the body and then transported.