Introduction to Ecology and Population Ecology (5)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Ecology
Study of organism-environment interactions.
Ecosystem
Community of organisms and their physical environment.
Community
Group of populations of different species.
Population
Group of individuals of the same species.
Organismal ecology
How organisms structure, physiology, and behavior meet environmental challenges.
Population ecology
Factors affecting population size over time. (a group of individuals of the same species living in an area)
Community ecology
Interactions of species within a community ( a group of populations of different species in an area).
Ecosystem ecology
Focus on energy flow and chemical cycling.
Landscape ecology
Exchanges of energy, materials, and organisms across ecosystems.
Climate
Long-term prevailing weather conditions.
Major abiotic components of climate
Temperature
Precipitation
Sunlight
Wind
Macroclimate
Patterns on global, regional, and landscape levels.
Microclimate
Fine-scale environmental patterns
Abiotic factors
Nonliving components like temperature and light.
Biotic factors
Living components, including other organisms.
Biomes
Major life zones defined by vegetation or environment.
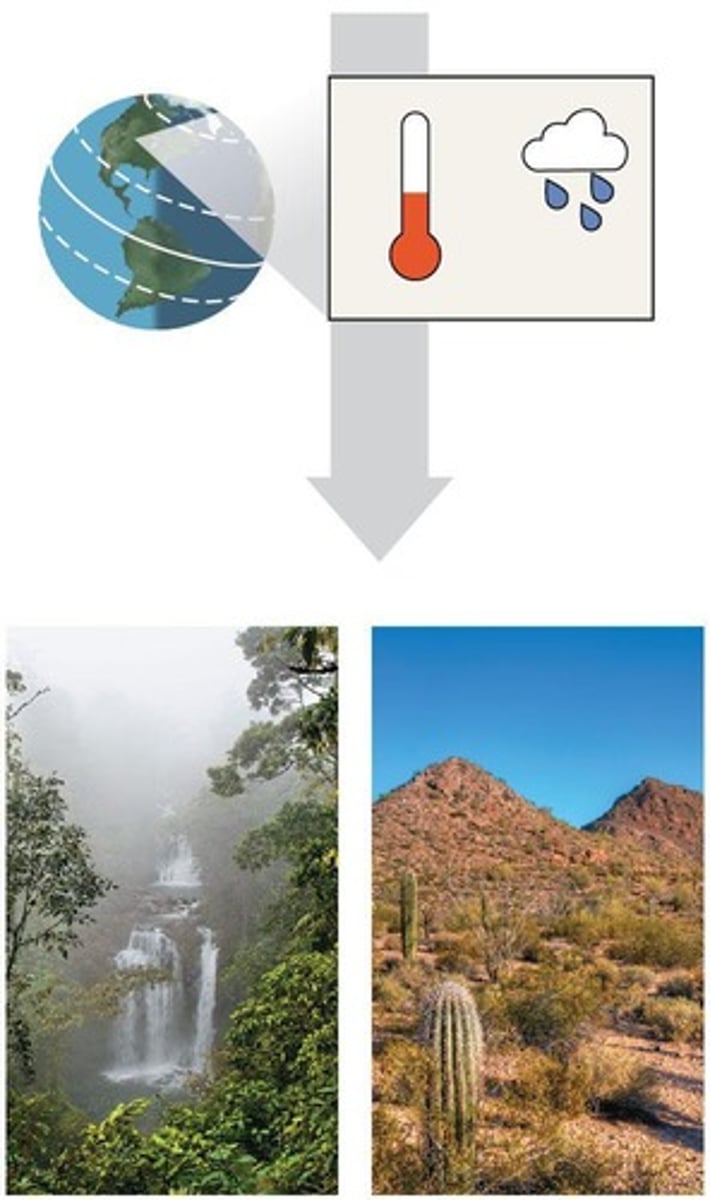
Ecotone
Area of intergradation between biomes.
Layers of aquatic biomes
Photic zone
Aphotic Zone
Benthic zone
(together its the pelagic zone)
Photic zone
Light-penetrated layer in aquatic biomes.
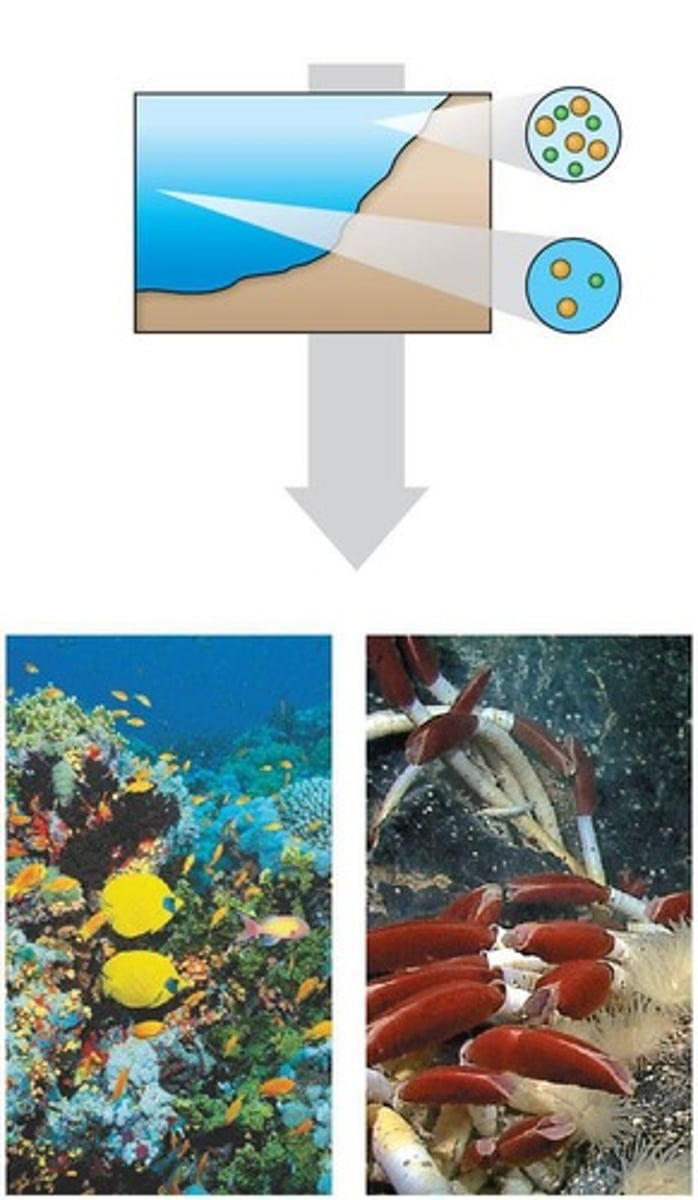
Aphotic zone
Light-deprived layer in aquatic biomes.
Benthic zone
Sediment layer at the bottom of water bodies.
Abyssal zone
Deepest part of the ocean, 2,000-6,000 m.

Hadal zone
Below 6,000m in the ocean
Demography
Study of population statistics and changes.
Life table
an age-specific summary of the survival pattern of a population
Cohort
Group of individuals of the same age.
Survivorship curve
Graphical representation of survival data.
Exponential growth
Population increase under ideal conditions.
Logistic growth
Population growth model with carrying capacity.
Carrying capacity (K)
Maximum sustainable population size.
What influences K (Carrying capacity)
Foodm water, shelter, space, predation, competition, disease, and climate conditions
Density
Number of individuals per unit area.
Dispersion
Pattern of spacing among individuals.
Clumped
Uniform
Random
Clumped dispersion
Individuals grouped due to environmental factors.
Uniform dispersion
Even spacing due to competition.
Random dispersion
Independent positioning of individuals. Occurs in the absence of strong attractions or repulsions