Chapter 8 - Nerves of the Lower Limb
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Describe the Nerve Plexuses of the Lower Limb
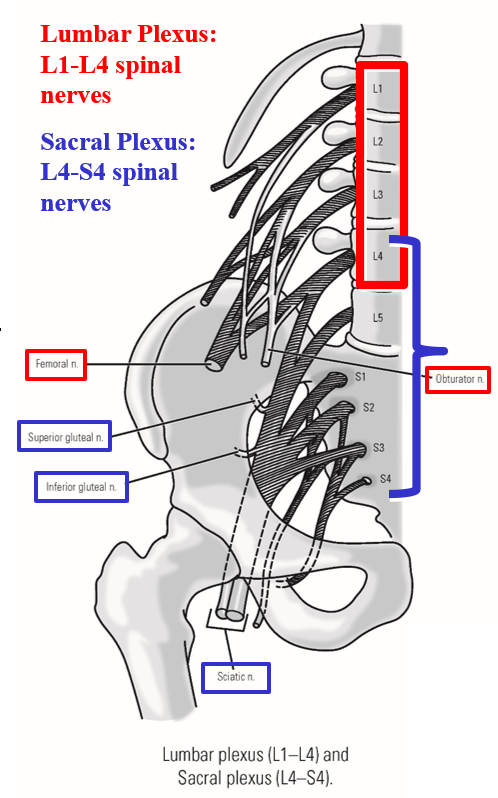
Peripheral nerves of the lower limb arise from:
–Lumbar plexus
Formed by L1-L4 spinal nerves
Primary peripheral nerves: femoral nerve & obturator nerve
–Sacral plexus
Formed by L4-S4 spinal nerves
Primary peripheral nerves: superior gluteal nerve, inferior gluteal nerve, & sciatic nerve (tibial division and common fibular division)
Note: L4 spinal nerve contributes to both lumbar & sacral plexus
*Every nerve in the lower trunk is a derivative of the lumbar-sacral plexus
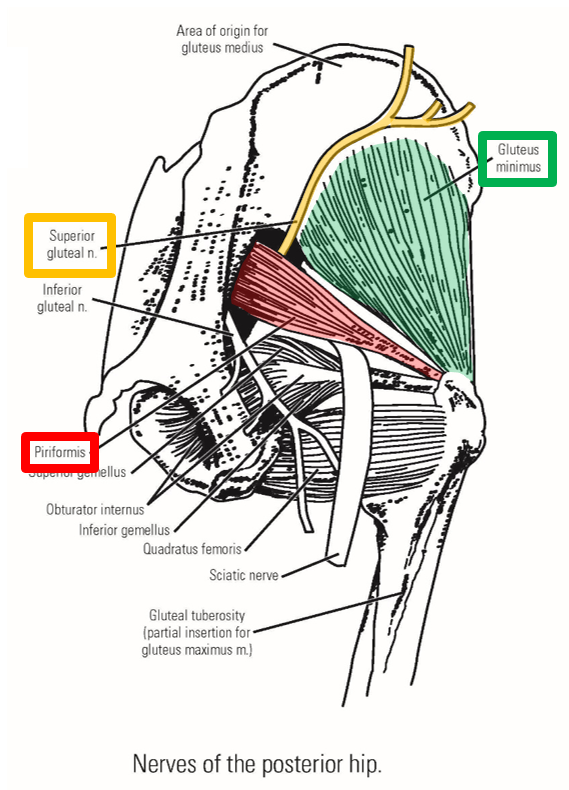
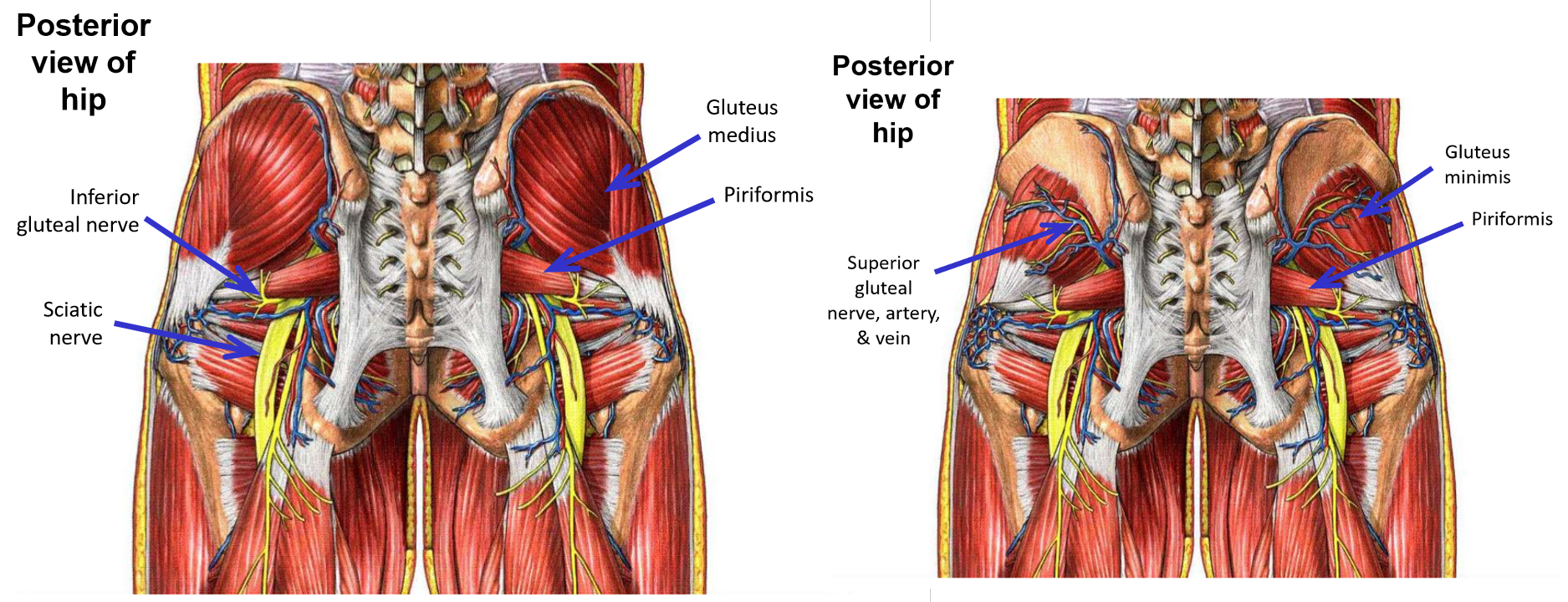
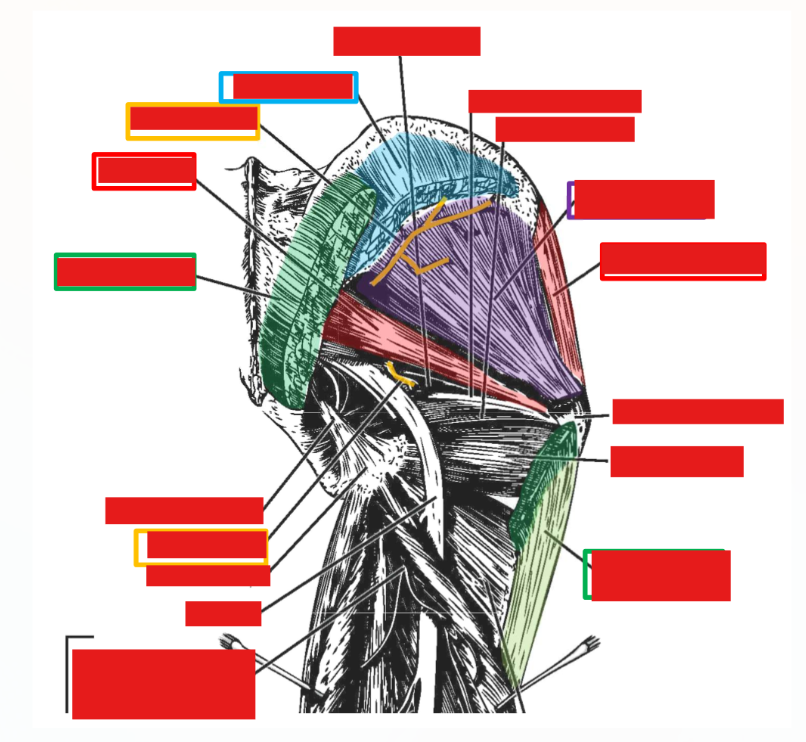
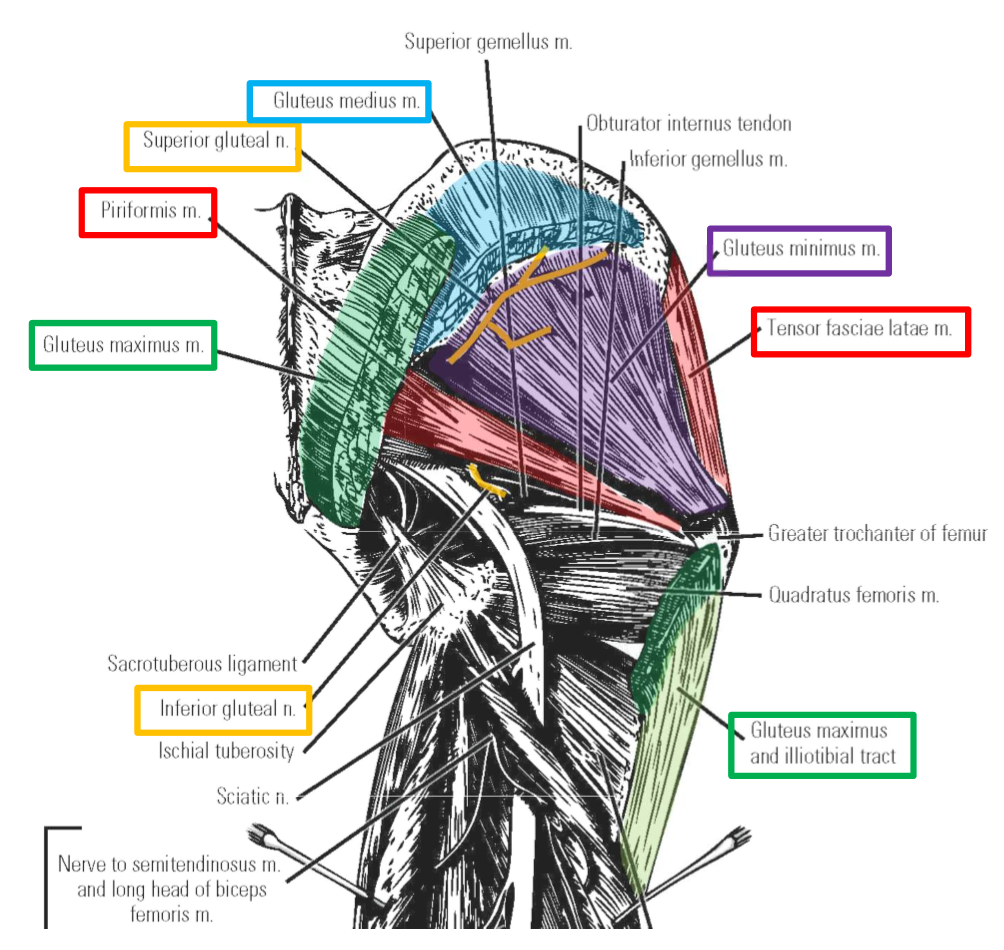
Describe Innervation of Gluteal Muscles. Plexus, nerve, emerges, exits, muscles supplied
Superior gluteal nerve
–From sacral plexus
–Exits pelvis through greater sciatic foramen
Emerges at superior margin of piriformis muscle
–Supplies gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fasciae latae muscles
Runs laterally, passing deep to m. gluteus medius (between gluteus medius and gluteus minimus)
Inferior gluteal nerve
–From sacral plexus
–Exits pelvis through greater sciatic foramen
Emerges at inferior margin of piriformis muscle
–Supplies m. gluteus maximus only
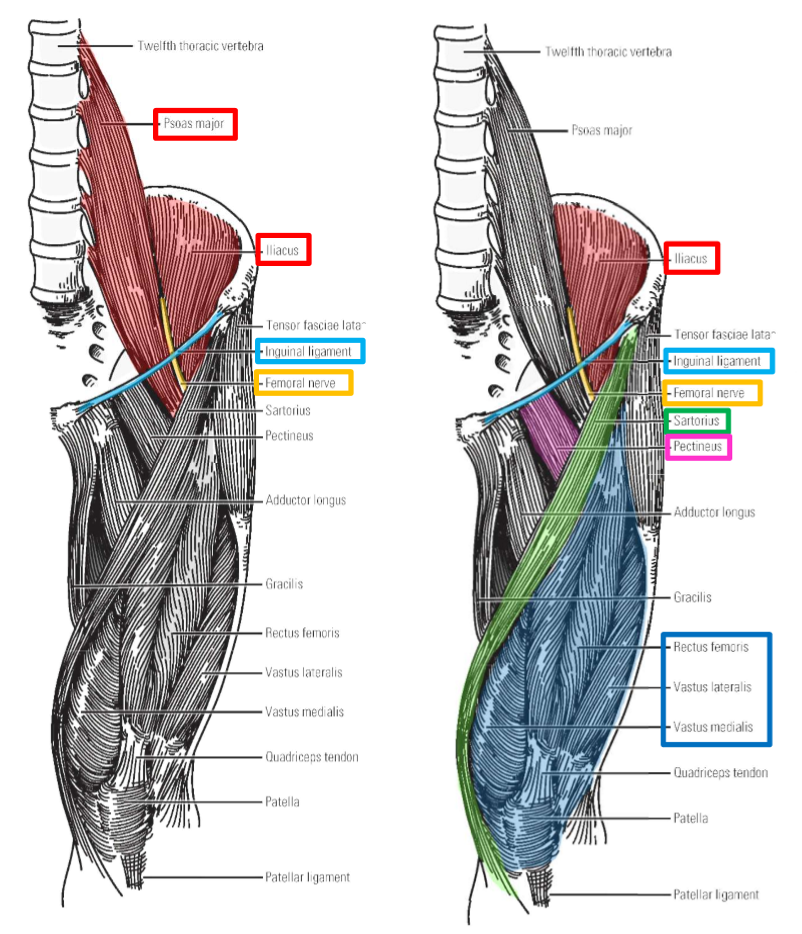
Innervation of Anterior Thigh Muscles. Muscles supplied.
Femoral nerve
–Largest nerve from lumbar plexus
–In pelvic area, runs inferiorly within groove between mm. iliacus and psoas major
Femoral nerve supplies m. iliacus, but not m. psoas major
–Femoral nerve then passes under inguinal ligament to enter femoral triangle region of proximal, anterior thigh
Muscles supplied by femoral nerve
M. Iliacus
M. Sartorius
M. Quadriceps femoris (all four muscle heads)
M. Pectineus (which is classified with muscles of the medial thigh compartment)
–Note that the femoral nerve supplies all muscles of the anterior thigh compartment, plus 2 additional muscles (mm. iliacus and pectineus).
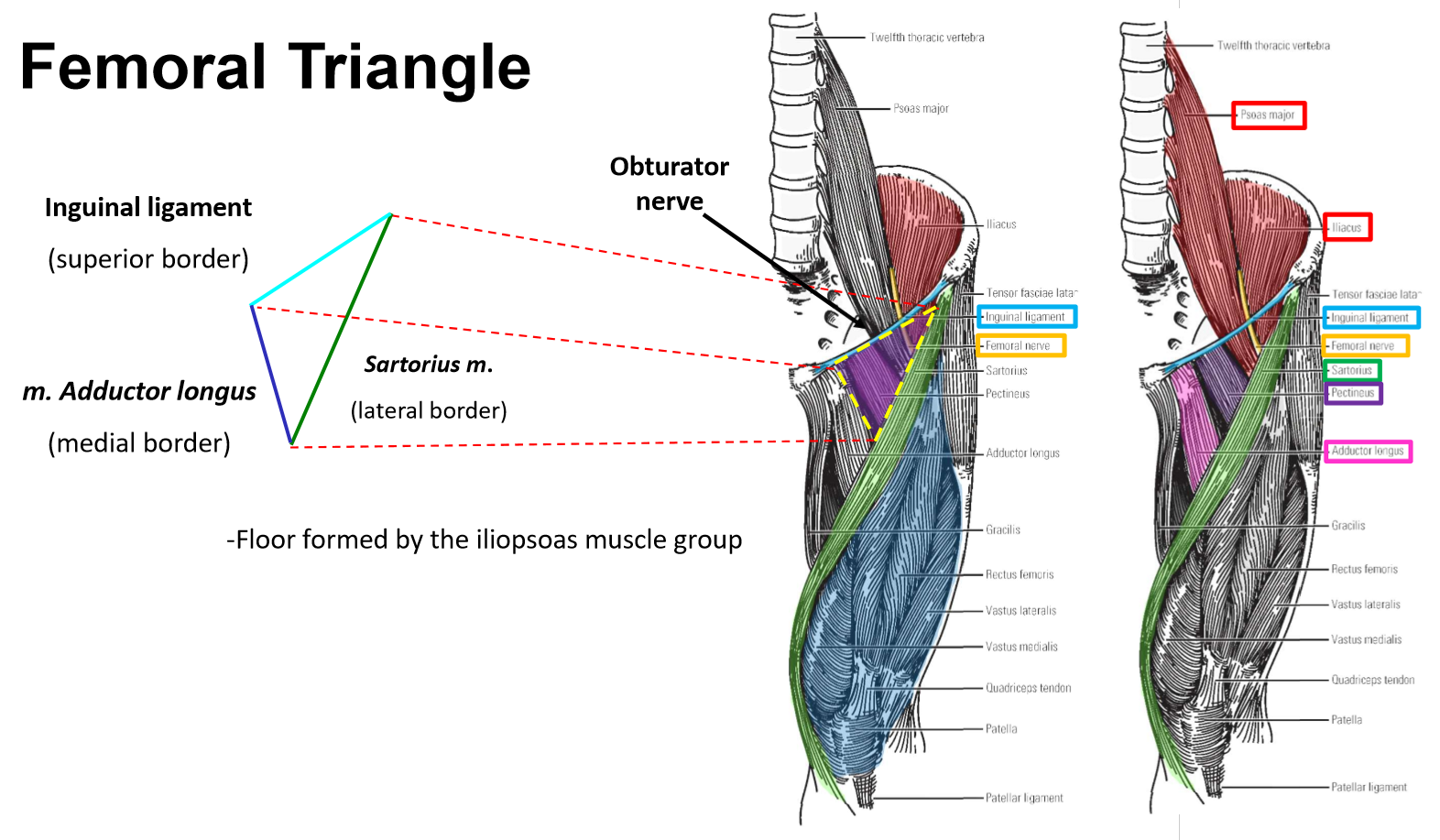
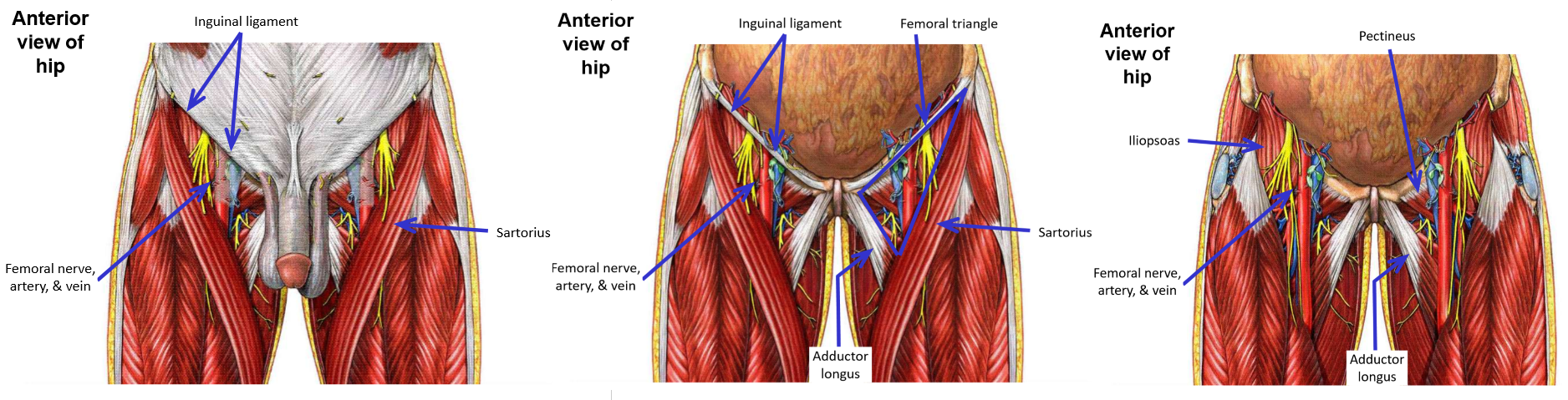
Femoral triangle
–Region in proximal ⅓ of anterior thigh
–Borders:
Inguinal ligament (superior)
M. Adductor longus (medial)
M. Sartorius (lateral)
–Contents: femoral nerve, femoral artery, and femoral vein
M. Iliopsoas located deep to femoral nerve
M. Pectineus located deep to femoral artery & vein
Muscles innervated by Femoral Nerve
Femoral Triangle
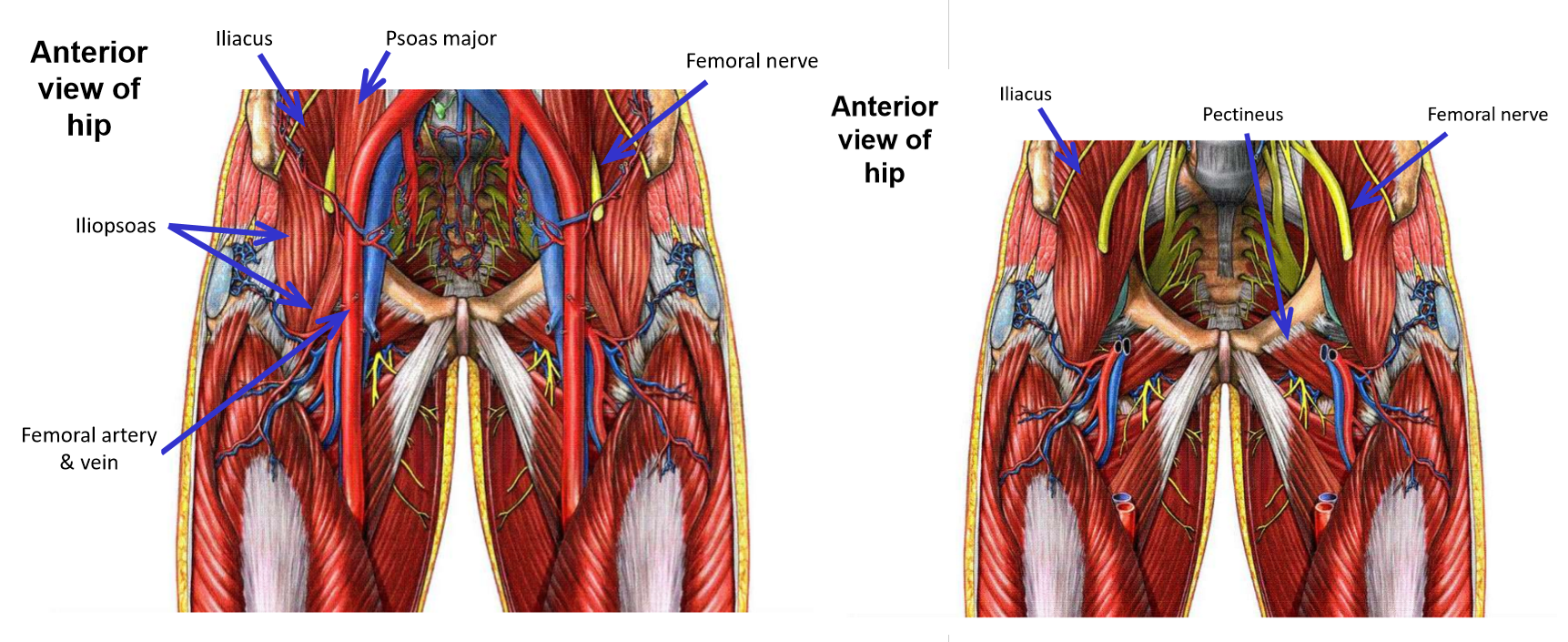
Innervation of Medial Thigh Muscles. Plexus, exit, muscles supplied.
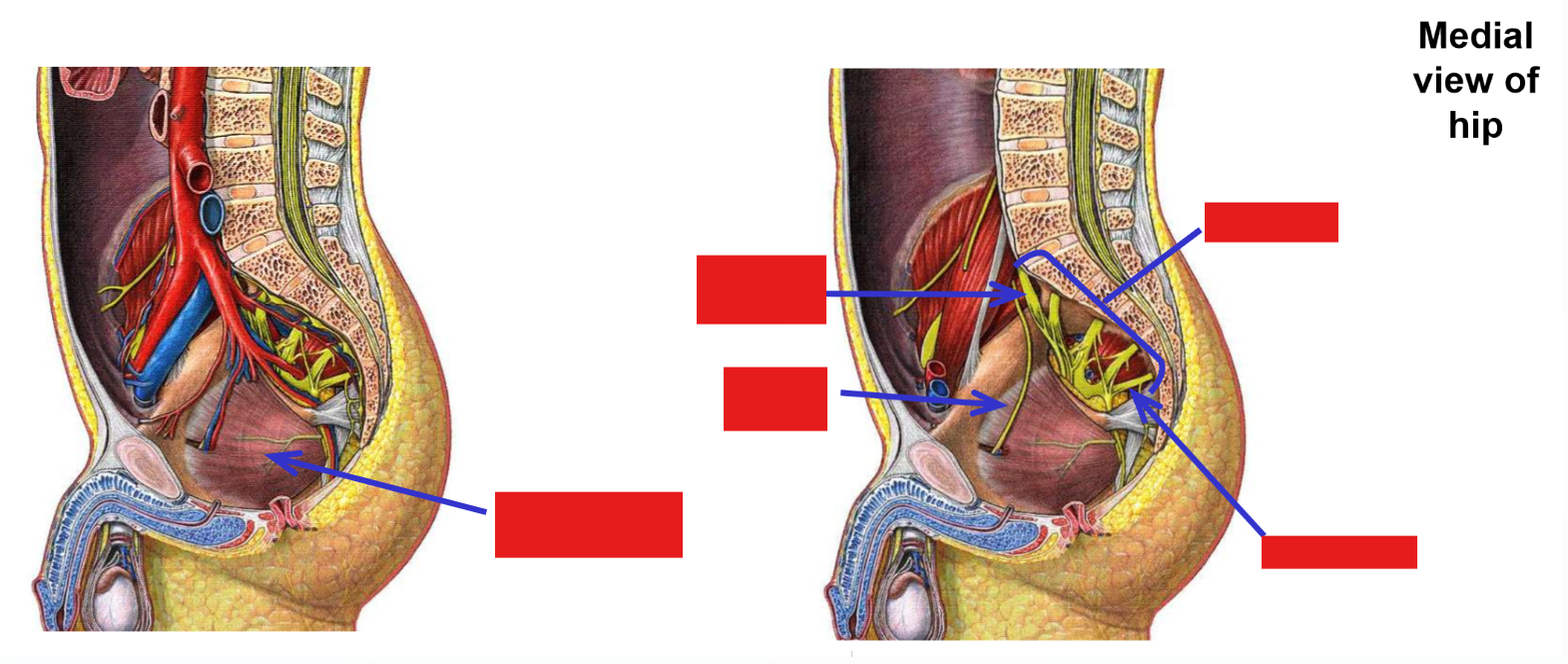
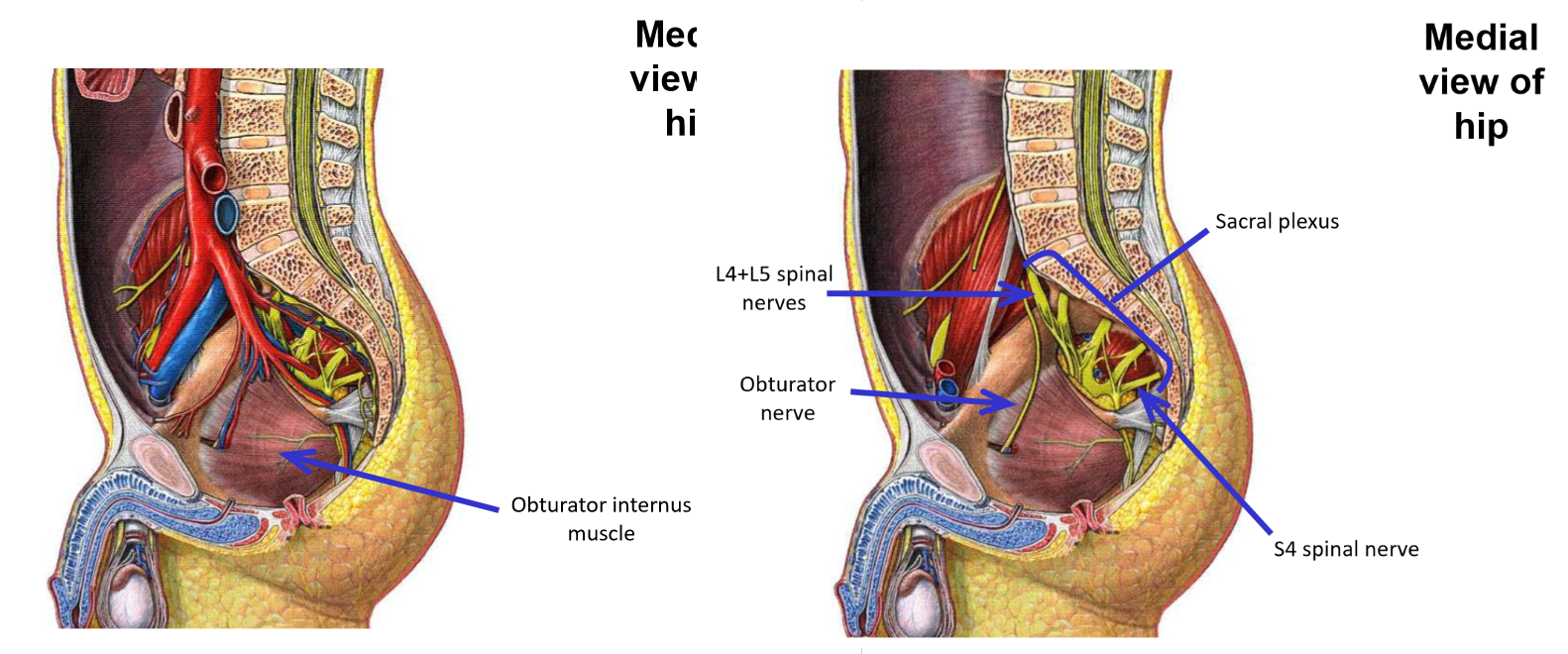
Obturator nerve
–From lumbar plexus
–Exits pelvis via obturator foramen to enter medial thigh
Penetrates through both obturator internus and obturator externus muscles as it exits pelvis
Note: only the obturator nerve, artery, and vein pass through the obturator foramen (no muscle exits pelvis through obturator foramen)
Muscles supplied by the obturator nerve
M. Obturator externus (but not obturator internus)
M. Gracilis
M. Adductor longus
M. Adductor brevis
Adductor part of adductor magnus (but not hamstring part)
Note: obturator nerve supplies all muscles of the medial thigh, except m. pectineus and hamstring part of adductor magnus muscle
Obturator nerve and muscles supplied
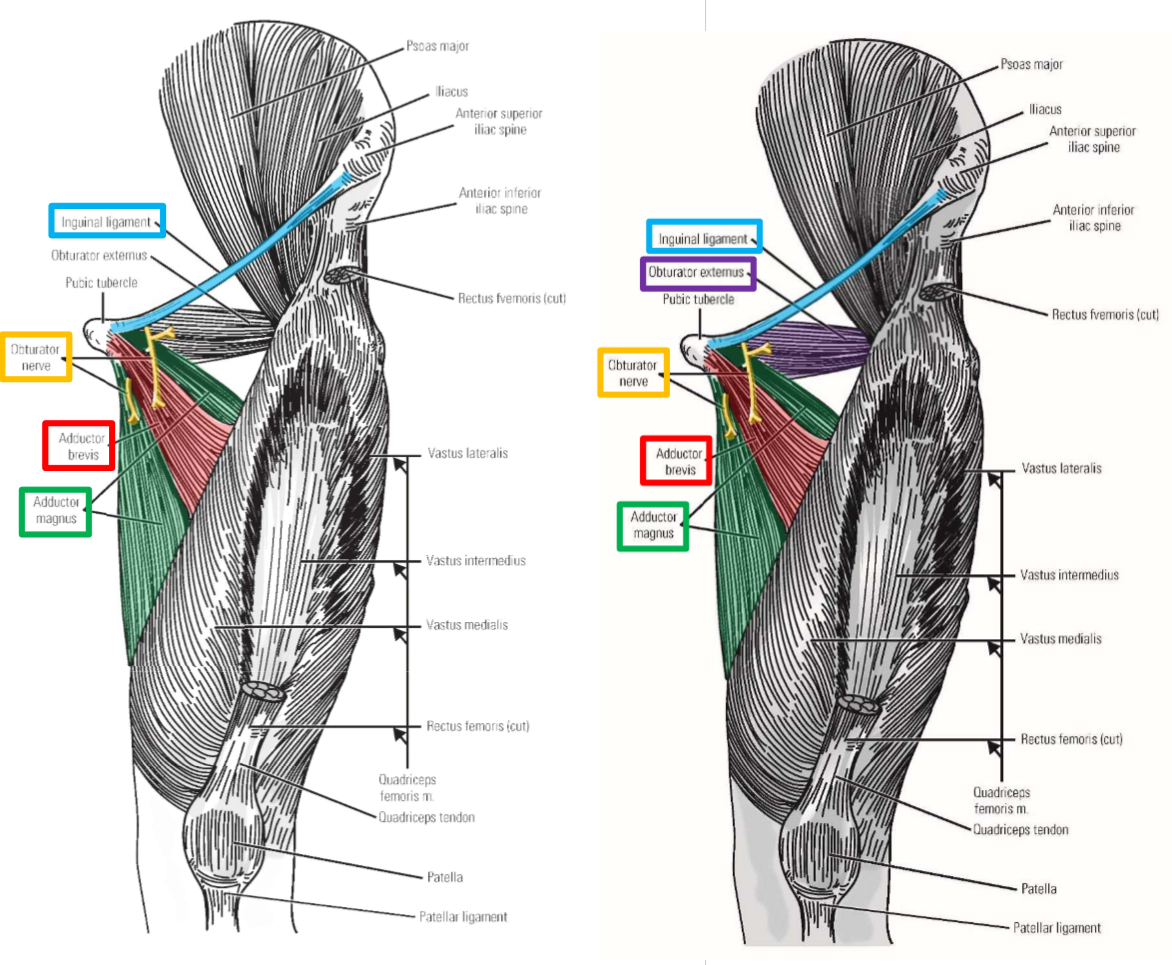
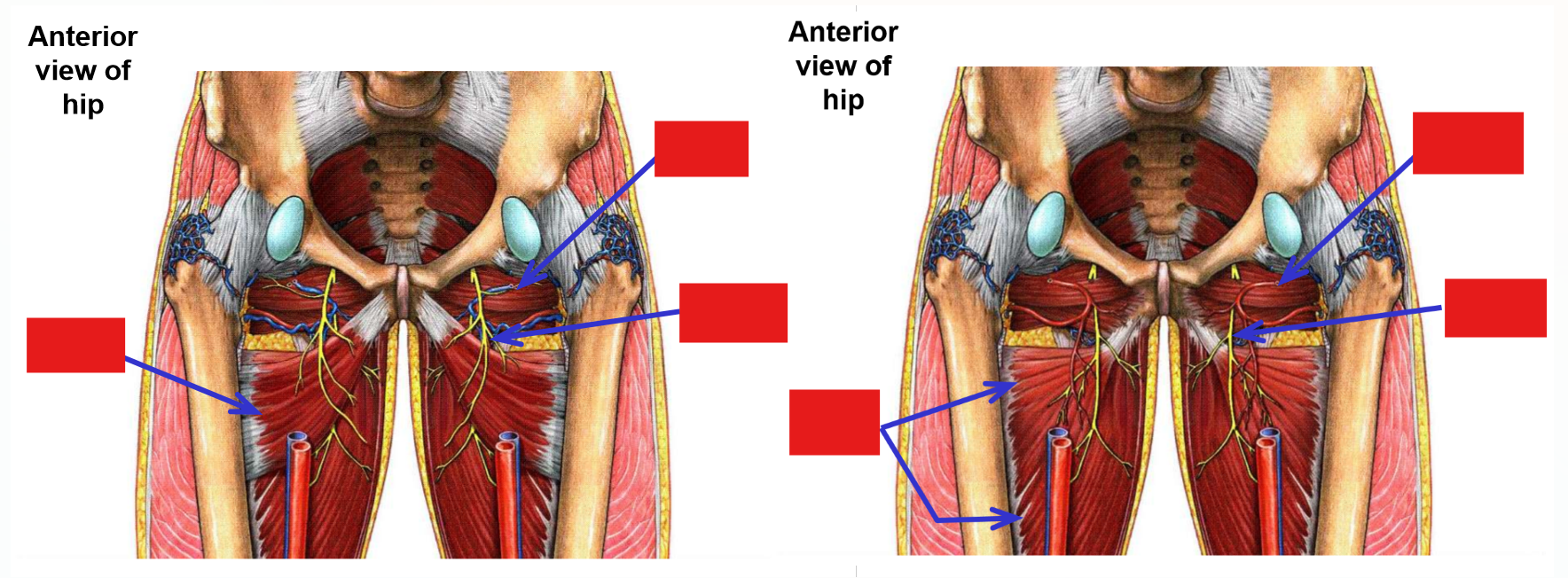
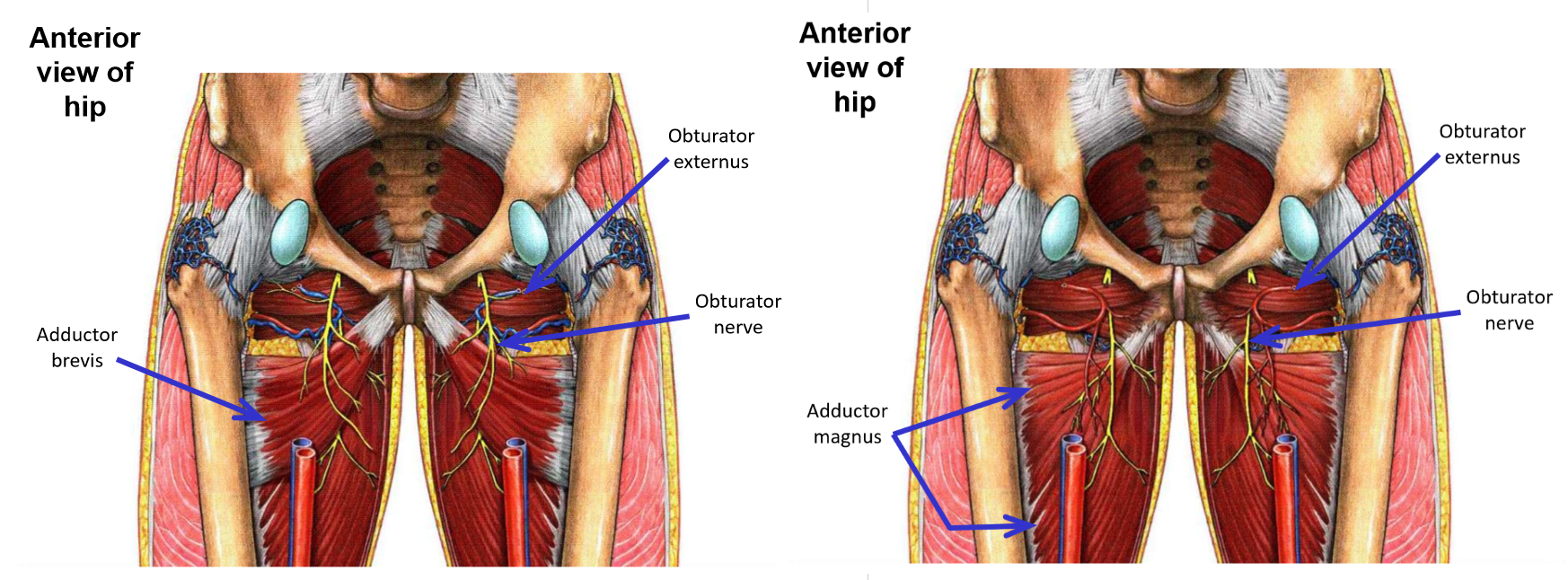
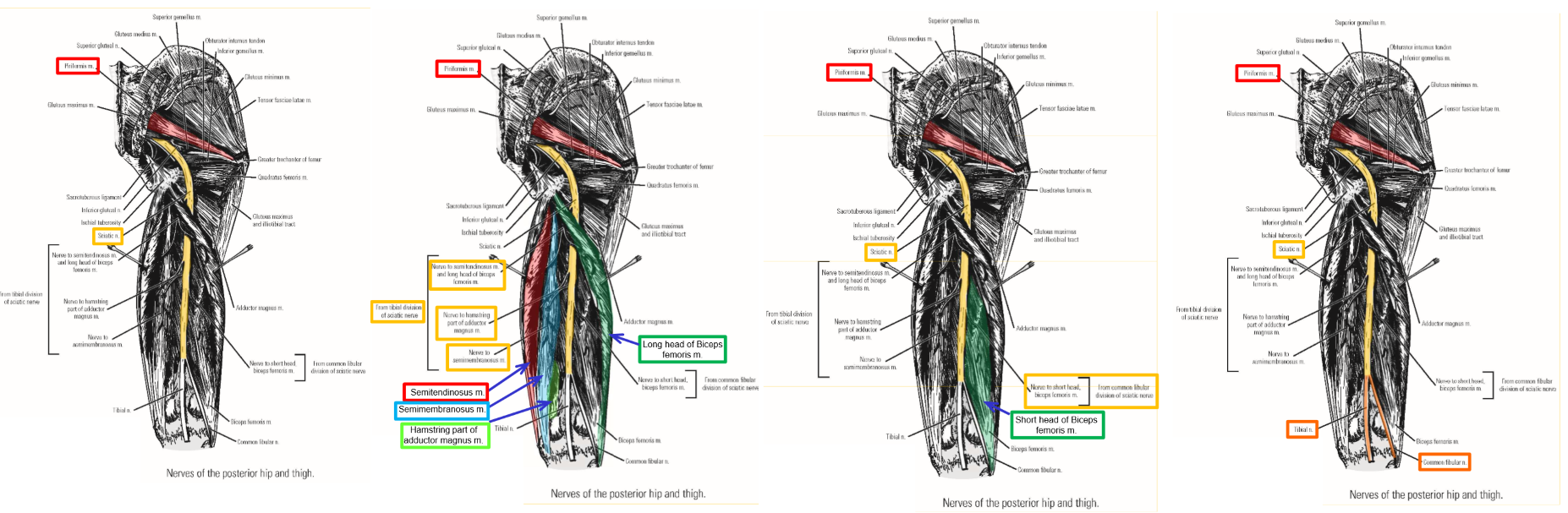
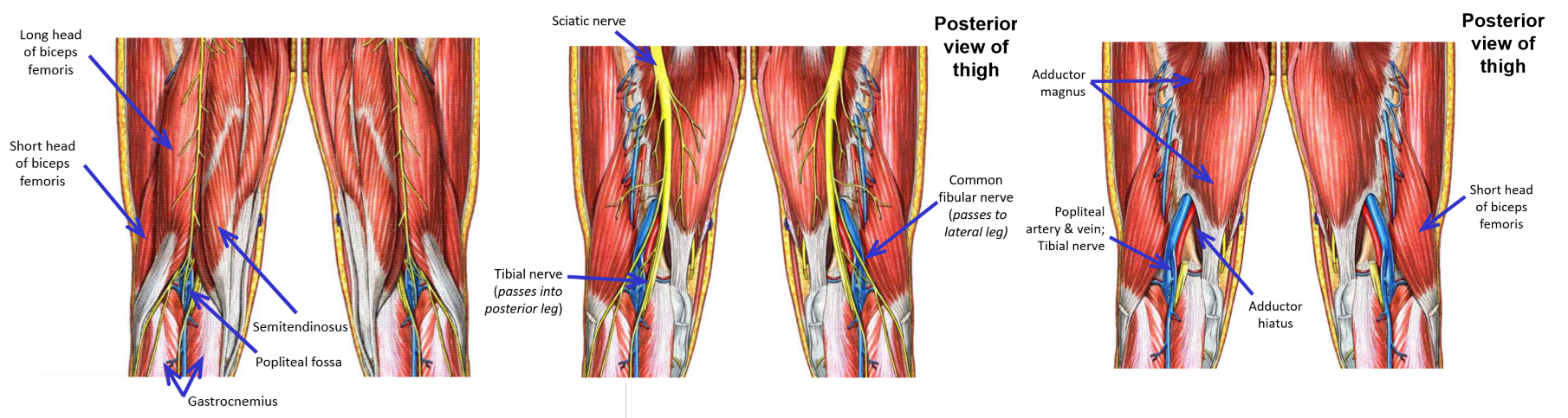
Innervation of Posterior Thigh Muscles. Muscles supplied. Termination?
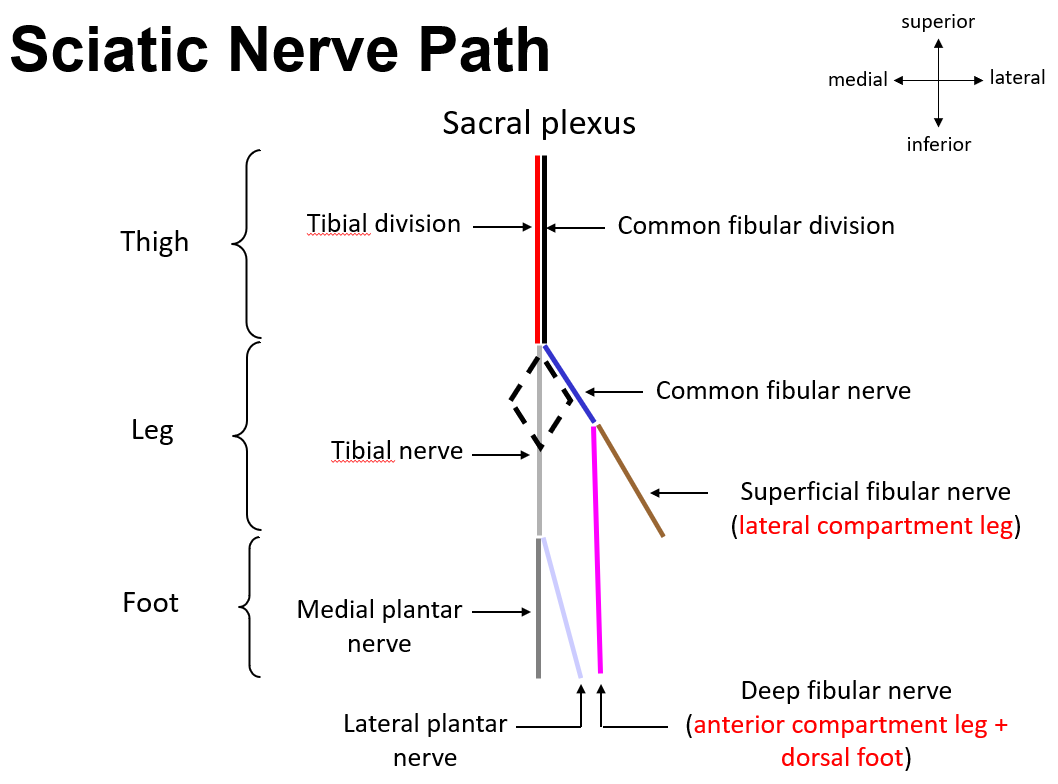
Sciatic nerve (largest nerve of the body)
–From sacral plexus
–Exits pelvis via greater sciatic foramen
Emerges at inferior margin of m. piriformis
–Consists of 2 divisions:
Tibial division of sciatic nerve
Common fibular division of sciatic nerve
Sciatic nerve runs inferiorly within posterior thigh compartment
In posterior thigh, tibial division and common fibular division joined together to form sciatic nerve
Tibial division of sciatic nerve supplies:
M. Semitendinosus
M. Semimembranosus
Long head of m. biceps femoris
Hamstring part of adductor magnus muscle
Note: tibial division of sciatic nerve supplies all muscle components that have their origin from ischial tuberosity
Common fibular division of sciatic nerve supplies only:
Short head of m. biceps femoris (origin from linea aspera of posterior femur)
Sciatic nerve terminates as it enters popliteal fossa
–Nerve physically divides into:
Tibial nerve
Common fibular nerve
Tibial and common fibular nerves then cross the knee to enter the leg
Innervation of Posterior Thigh Muscles
Summary: Thigh Muscle Innervations
The thigh is divided into 3 compartments, but is supplied by 4 nerves
Each compartment has exceptions to its nerve supply
Femoral nerve
–Supplies all anterior thigh muscles + 2 other muscles
Mm. Sartorius and quadriceps femoris
Also supplies mm. iliacus and pectineus
Obturator nerve
–Supplies all medial thigh muscles (with 2 exceptions)
Supplies mm. obturator externus, gracilis, adductor longus, adductor brevis, & adductor part of adductor magnus
Does not supply m. pectineus or hamstring part of adductor magnus muscle
Tibial division of sciatic nerve
–Supplies all posterior thigh muscles and muscle components that take origin from ischial tuberosity
Semitendinosus, semimembranosus, long head of biceps femoris, and hamstring part of adductor magnus
Note: adductor part of adductor magnus muscle has origin from ischiopubic ramus (not ischial tuberosity)
Common fibular division of sciatic nerve
–Supplies short head of m. biceps femoris only
Origin from linea aspera of posterior femur
Only posterior thigh muscle component that does not originate from ischial tuberosity
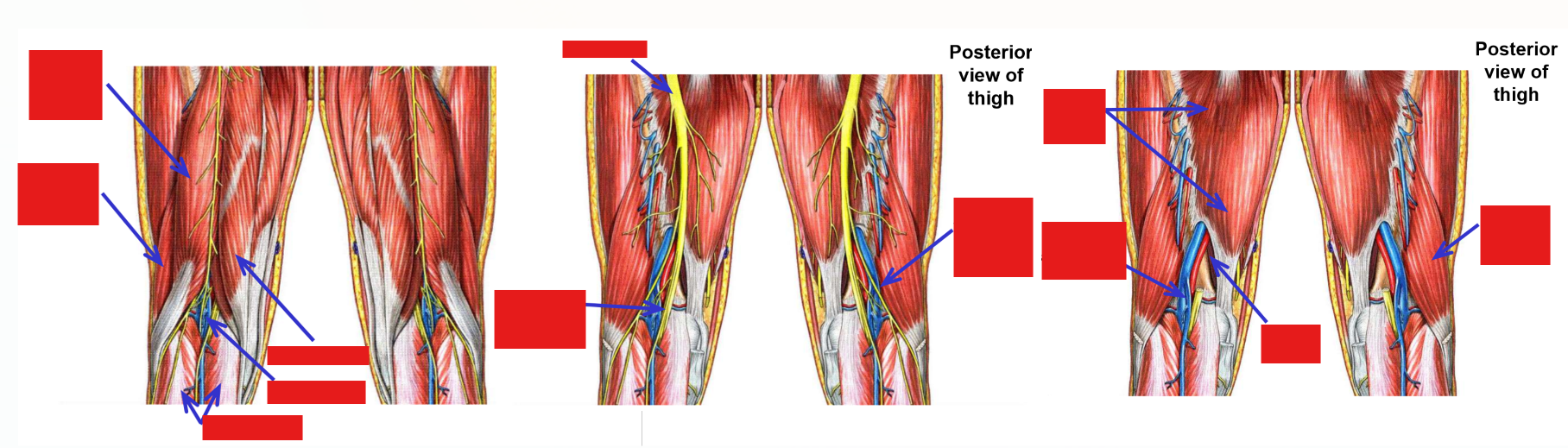
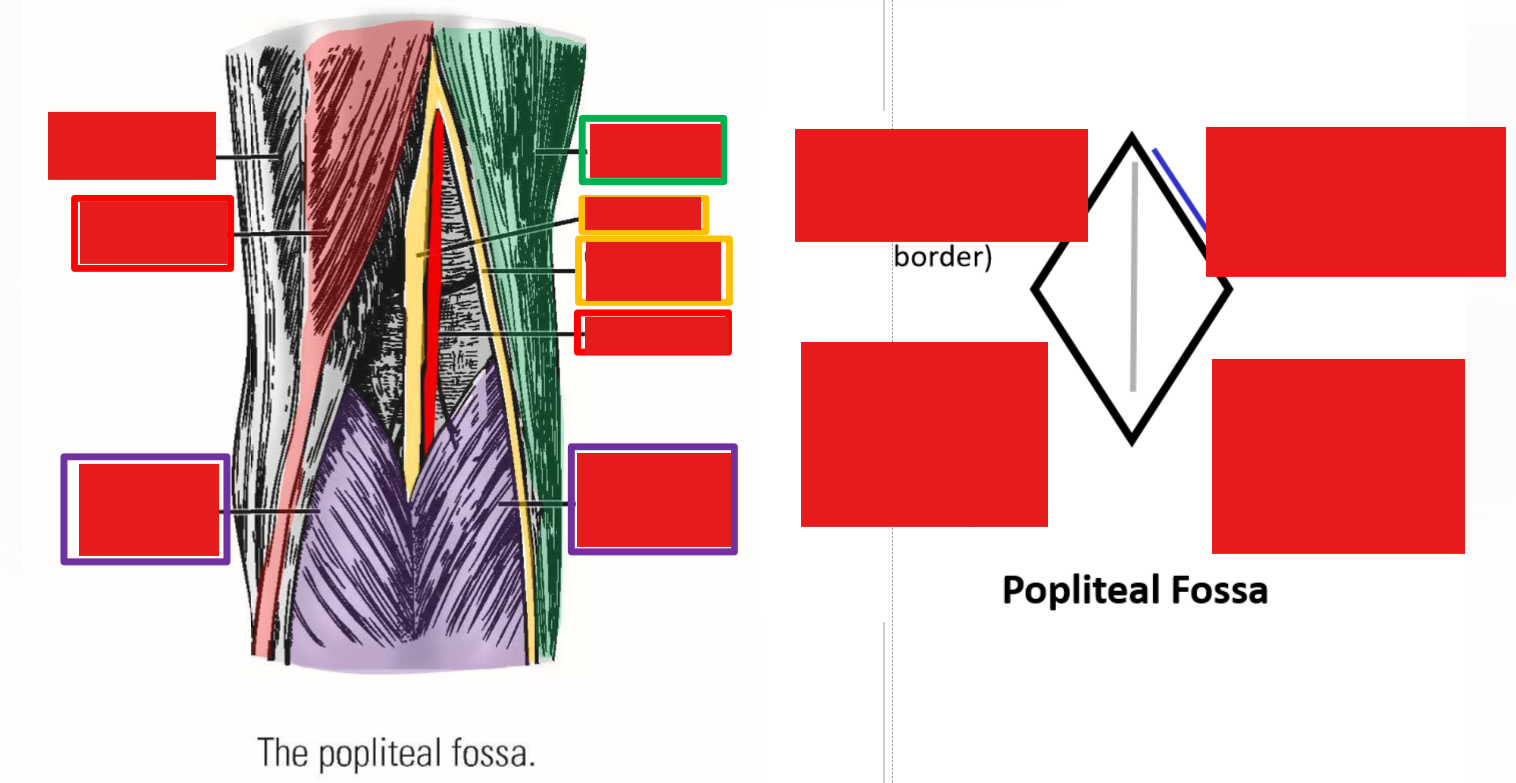
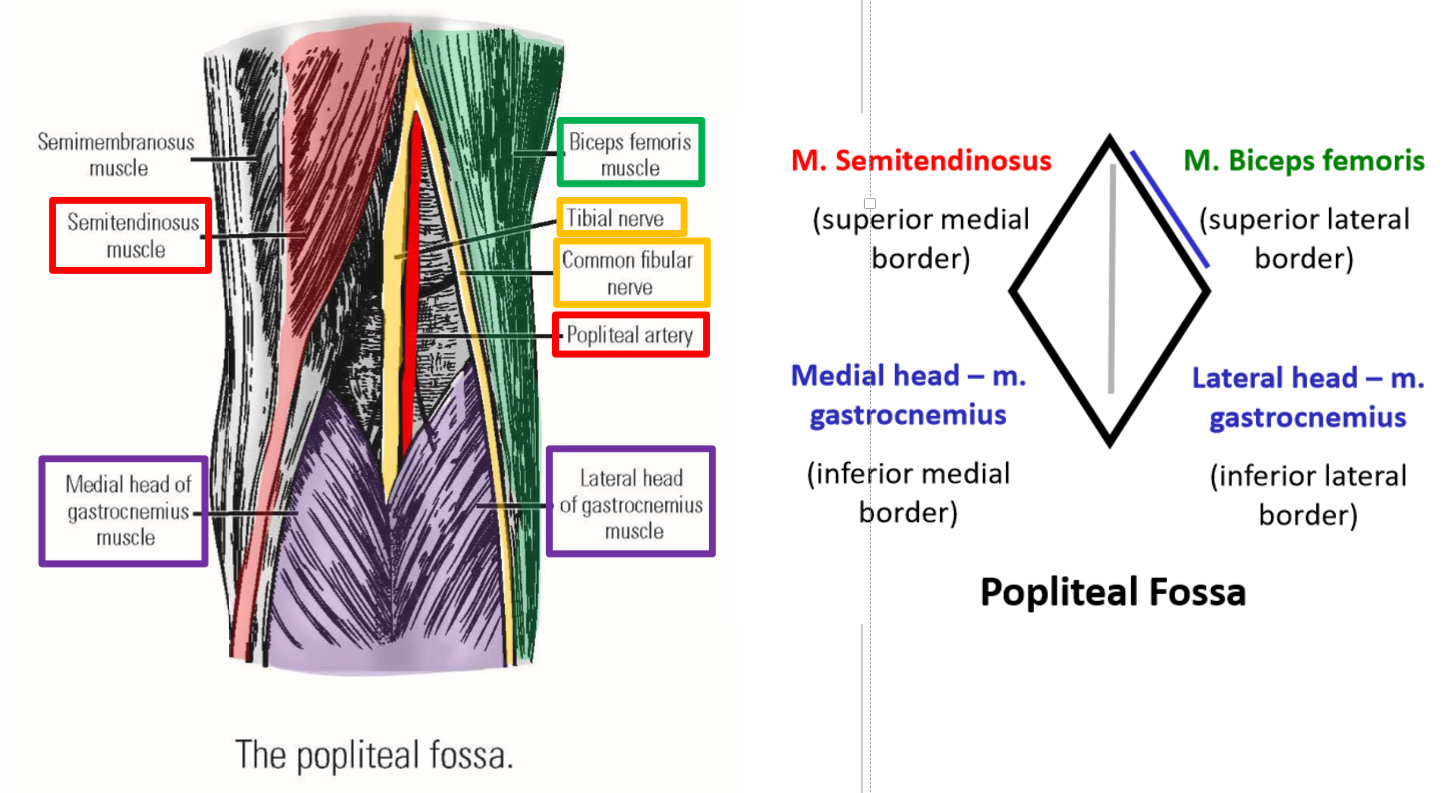
Describe the Popliteal Fossa. Borders. Nerves
The popliteal fossa is the diamond-shaped depression located behind the knee joint
Borders:
–Superior-medial: m. semitendinosus
–Superior-lateral: m. biceps femoris
–Inferior-medial: medial head of m. gastrocnemius
–Inferior-lateral: lateral head of m. gastrocnemius
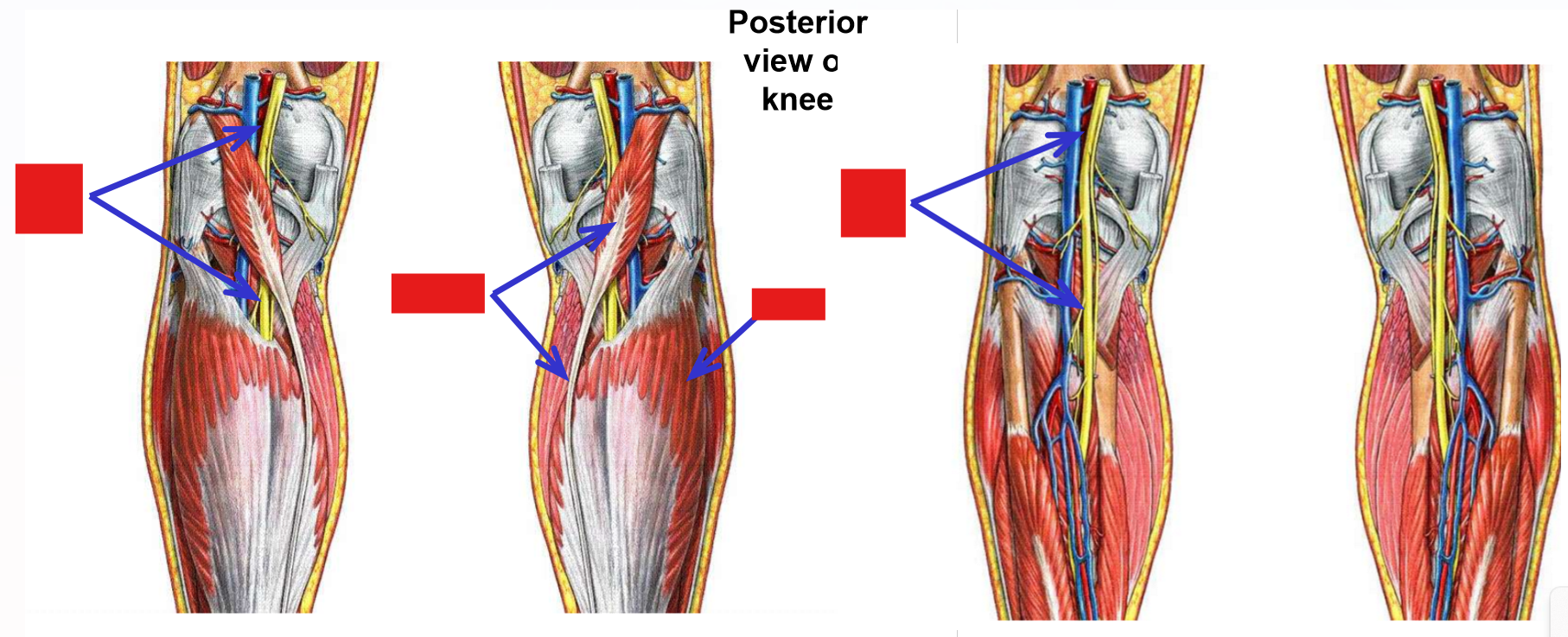
Contents of the popliteal fossa
–Tibial nerve - derived from tibial division of sciatic nerve
Runs inferiorly, down mid-line of popliteal fossa
Passes deep to gastrocnemius muscle to enter posterior leg
–Common fibular nerve - derived from common fibular division of sciatic nerve
Runs inferiorly and laterally, next to m. biceps femoris, to enter lateral leg
–Popliteal artery and popliteal vein
Located deep to tibial nerve
Continue into posterior leg
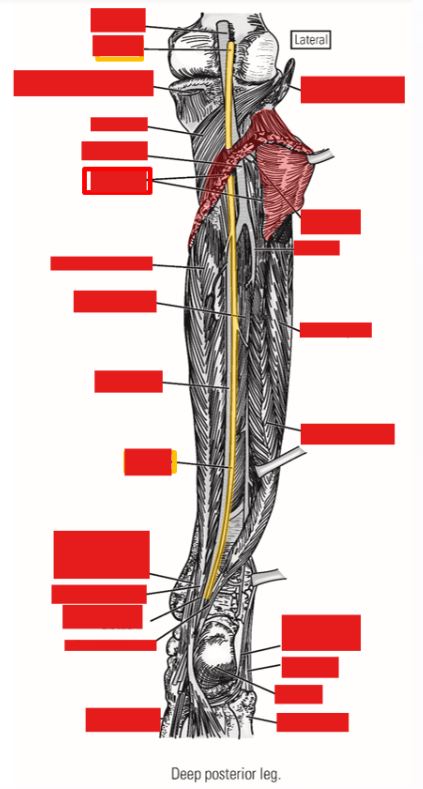
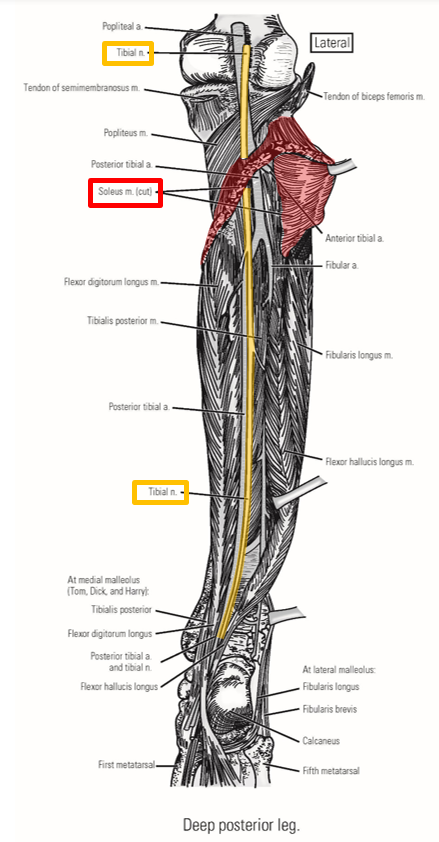
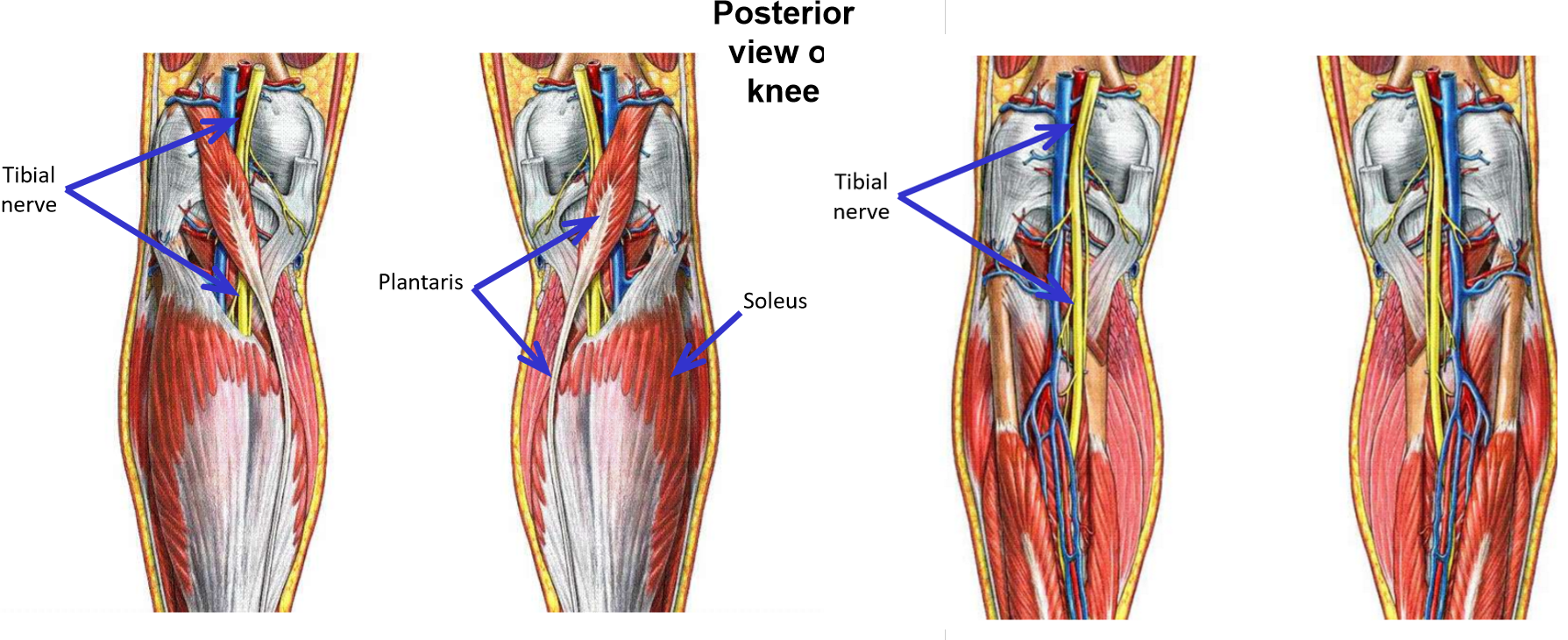
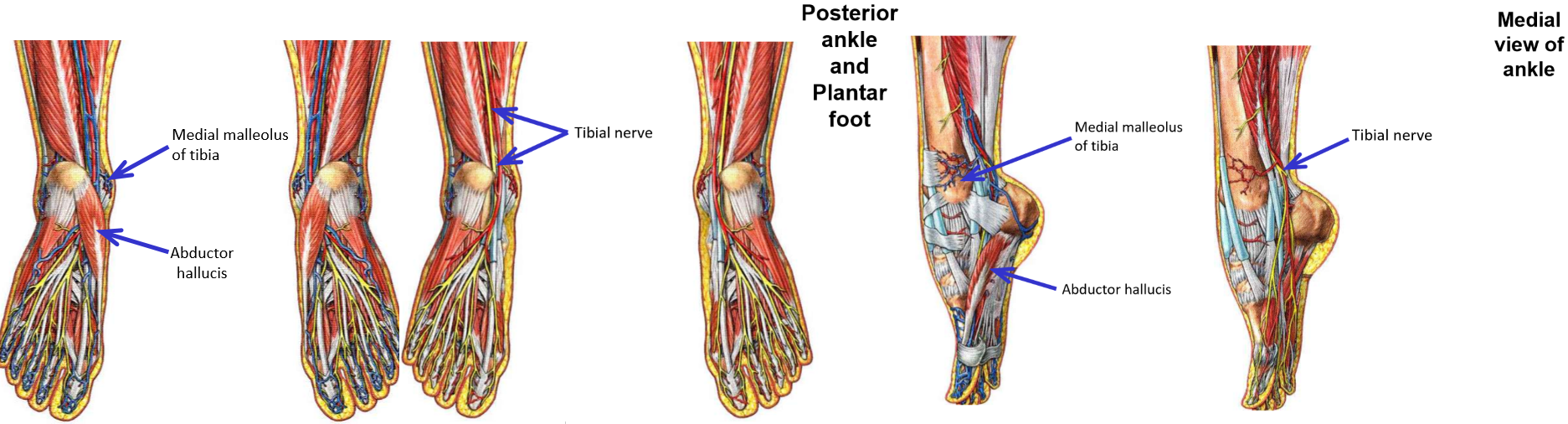
Tibial Nerve
Tibial nerve - a terminal branch of the sciatic nerve
Runs inferiorly down mid-line of popliteal fossa
Enters superficial posterior leg by passing between medial & lateral heads of m. gastrocnemius
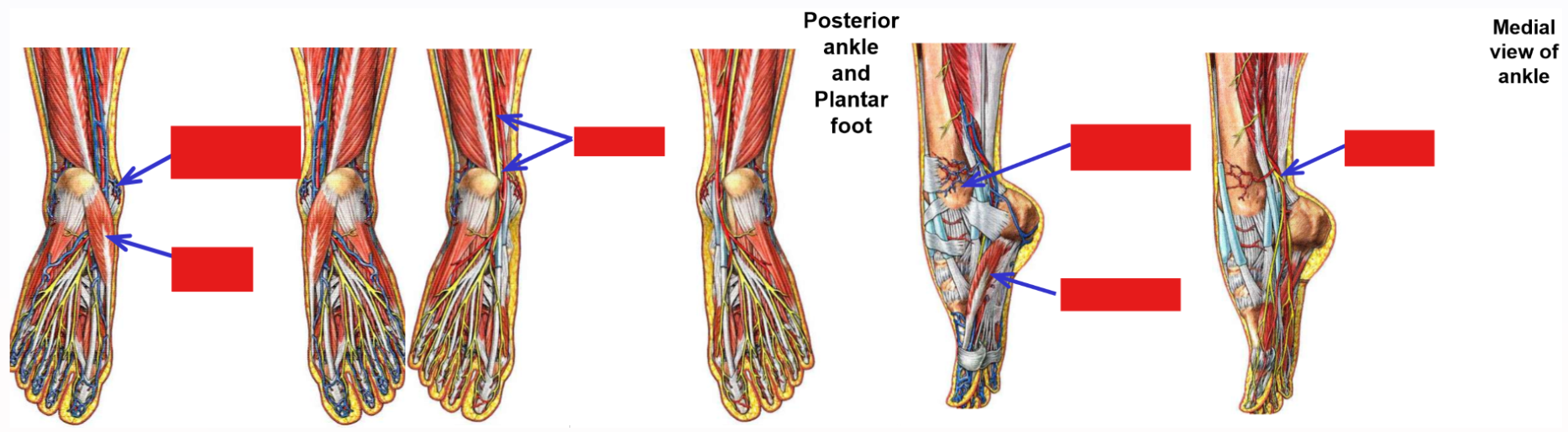
Passes deep to m. soleus to enter deep posterior leg compartment
Passes posterior to medial malleolus to enter plantar foot*
Tibial nerve - supplies all muscles of posterior leg
Superficial posterior leg muscles: mm. gastrocnemius, soleus, & plantaris
Deep posterior leg muscles: mm. popliteus, tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus, & flexor digitorum longus
Tibial nerve enters plantar foot
Supplies all muscles of plantar foot: mm. abductor hallucis, abductor digit minimi, flexor digitorum brevis, & quadratus plantae
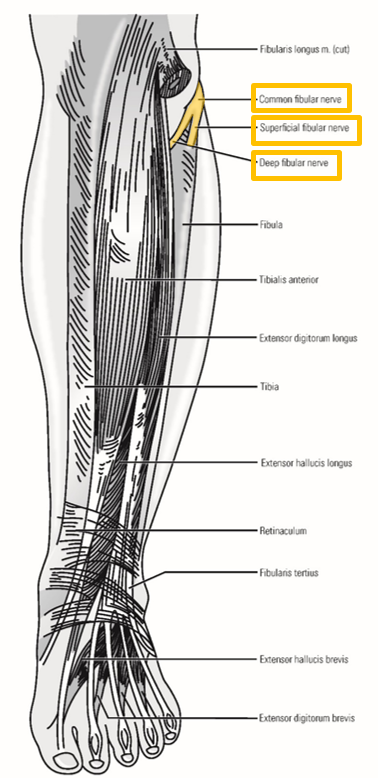
Common Fibular Nerve
Common fibular nerve - second terminal branch of sciatic nerve
–Runs inferiorly along superior-lateral border of popliteal fossa
Follows m. biceps femoris
Crosses posterior side of lateral knee
–Passes superficial to neck of fibula (just inferior to fibula head) - enters lateral leg compartment
–Terminates by dividing into:
Superficial fibular nerve
Deep fibular nerve
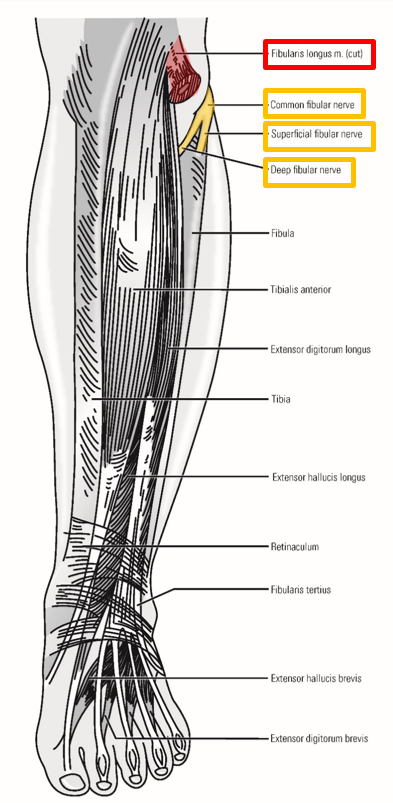
Superficial Fibular Nerve
Superficial fibular nerve
–Runs inferiorly within lateral compartment of leg
Located superficially (just under crural fascia of leg)
–Supplies both muscles of the lateral leg:
Mm. fibularis longus and fibularis brevis
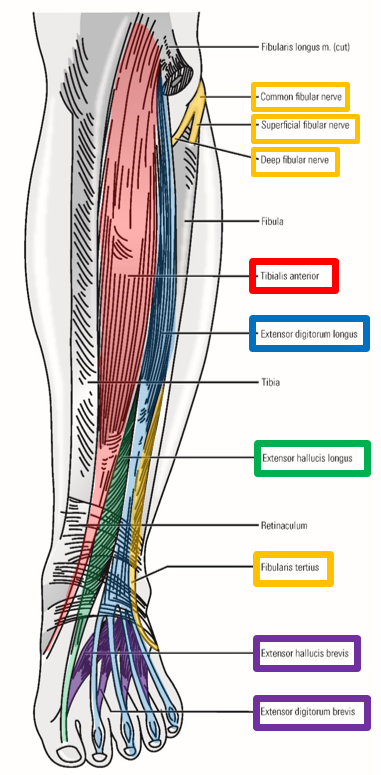
Deep Fibular Nerve
Deep fibular nerve
–Dives deep and continues into anterior compartment of leg
Runs inferiorly within anterior leg compartment
Located deep, next to interosseous membrane
–Supplies all anterior leg muscles:
Mm. tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, & fibularis tertius
–Crosses ankle and passes to dorsal foot - supplies dorsal foot muscles
Mm. extensor hallucis brevis & extensor digitorum brevis
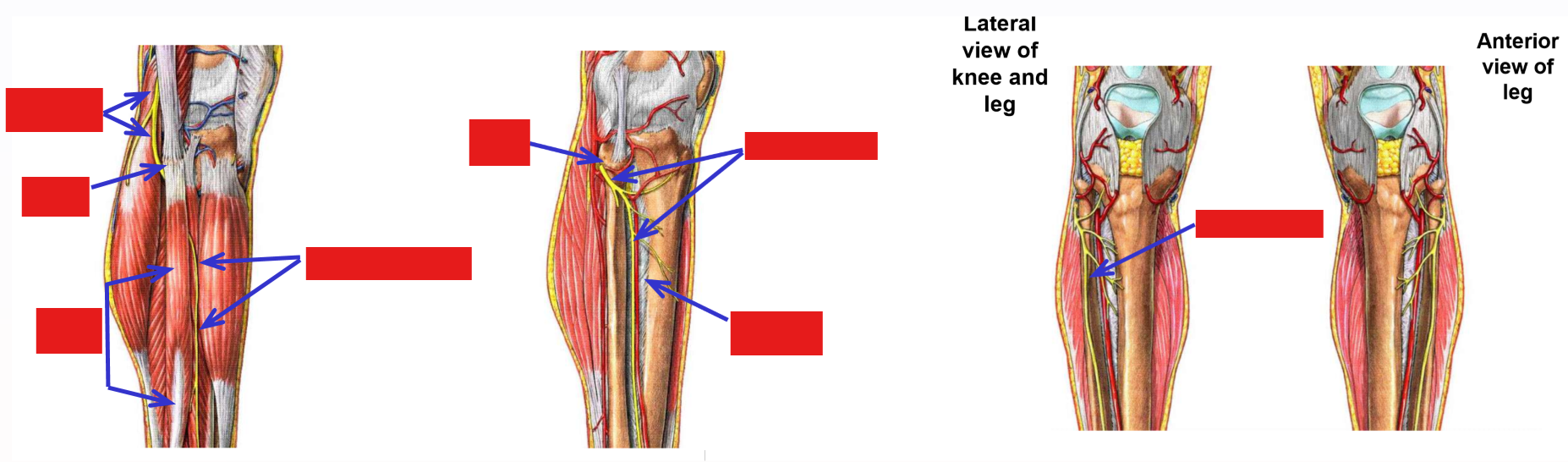
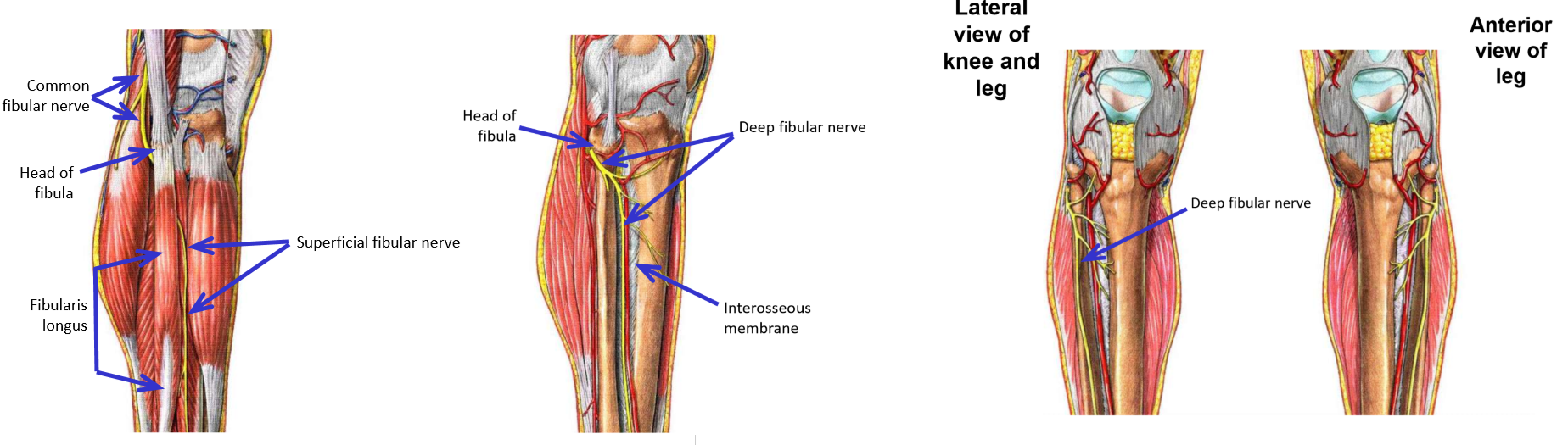
Fibular Nerve Injuries
Most common lower limb nerve injury is to branches of common fibular nerve as they cross superficial to neck of fibula
–Injury to superficial fibular nerve
Foot is inverted (loss of strong evertor muscles - fibularis longus & brevis)
–Injury to deep fibular nerve
Unable to dorsi(*flex*) foot (loss of all anterior leg muscles)
Produces “foot drop” - toes drag as foot is swung forward during walking
Describe the Sciatic Nerve Path