bio 7.1.2 Protein Synthesis
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Whole presentation done
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
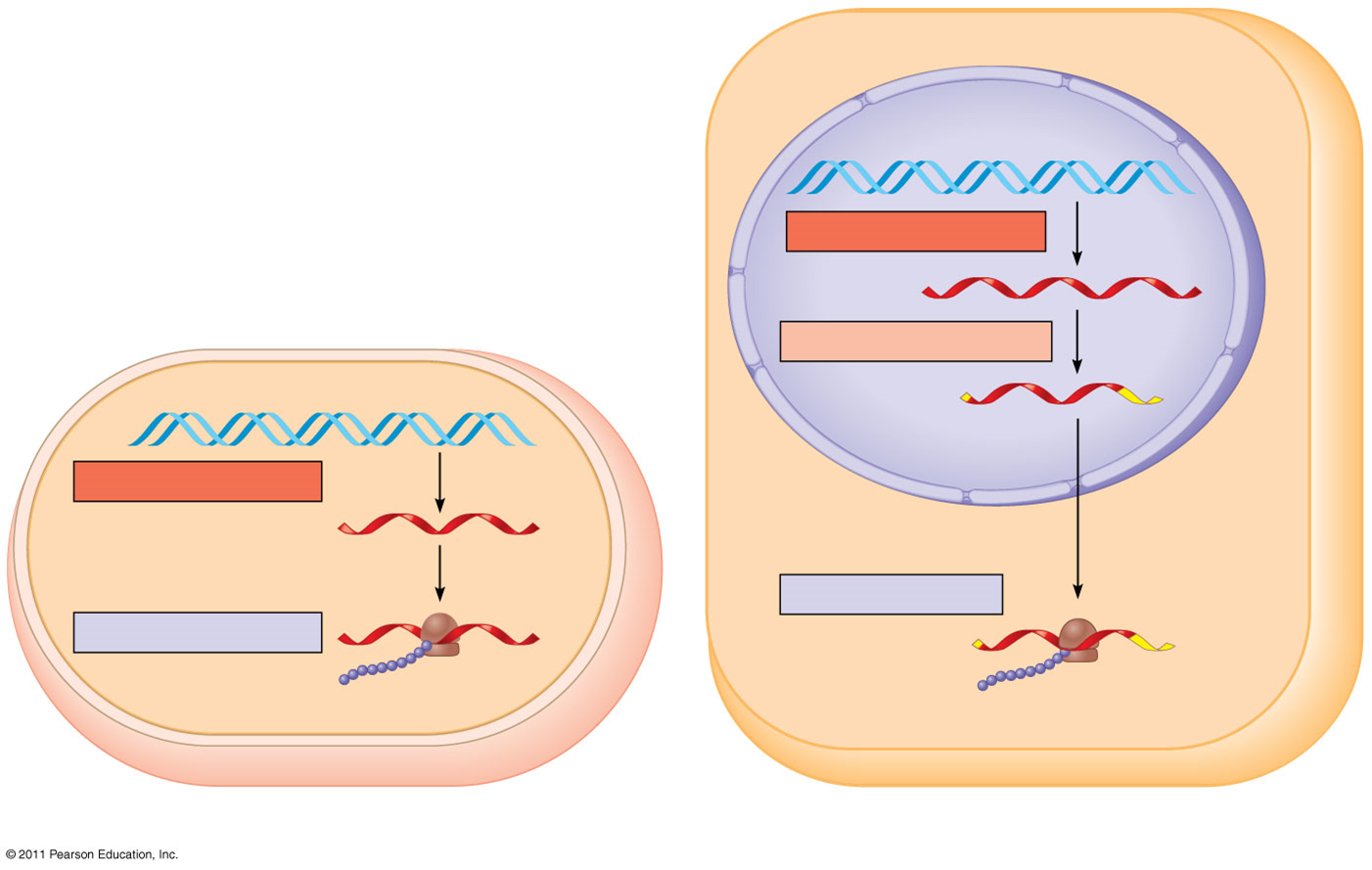
Central dogma of biology
DNA gets transcribed into RNA which is translated into proteins
What direction is the DNA template strand?
3’ to 5’
DNA template strand definition
The strand that RNA will be complementary to
mRNA direction if DNA is 3’ to 5’?
5’ to 3’
codons definition
mRNA base triplets
What is RNA synthesis catalyzed by?
RNA polymerase
what does RNA polymerase do?
It seperates DNA strands and hooks together RNA nucleotides
DNA sequence where RNA polymerase attaches
promoter
sequence signaling the end of RNA transcription
terminator
stretch of DNA that is transcribed
transcription unit
3 steps of transcription (and translation)
initiation, elongation, termination
Initiation (transcription)
After RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, the DNA strands unwind, the polymerase initates RNA synthesis at the start point on the template strand
Elongation (transcription)
The polymerase moves downstream, unwinding the DNA and elongating the RNA transcript 5´ to 3´. After, DNA strands re-form a double helix
Termination (transcription)
the RNA transcript is released and the polymerase detaches from the DNA
noncoding regions
introns
Intron long form
intervening sequences
Expressed regions short
exons
what does RNA splicing do
removes introns and joins exons, creating an mRNA molecule with a continuous coding sequence
What is RNA splicing carried out by sometimes?
spliceosomes
What do spliceosomes consist of?
a variety of proteins and several small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) that recognize the splice sites
Ribozymes definition
catalytic RNA molecules that function as enzymes and can splice RNA
Alternative RNA splicing definition
process that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins
what does tRNA do?
it transfers amino acids to the growing polypeptide in a ribosome
What do ribosomes facilitate?
specific coupling of tRNA anticodons with mRNA codons in protein synthesis
What are the two ribosomal units made out of?
proteins and ribosomal RNA
Are bacterial and eukaryotic ribosomes the same?
no
3 binding sites of a ribosomes
E, P, A
A-site description/function
binding site, holds the tRNA that carries the next amino acid to be added to the chain
P-site description/function
holds the tRNA that carres the growing polypeptide chain
E-site description/function
exit site, where discharged tRNAs leave the ribosome
Initiation (translation) (what does it bring together?)
a mRNA, a tRNA with the first amino acid, and two ribosomal subunits
Initiation (translation) steps
A small ribosomal subunit binds with mRNA and a special initiator tRNA, then the small subunit moves along the mRNA until it reaches the start codon, then initiation factors bring in the large subunit that completes the translation initiation complex
Elongation (translation)
amino acids are added one by one at the C-terminus of the growing chain, involves elongation factors
elongation (translation) steps of each addition
codon recognition, peptide bond formation, and translocation
termination (translation)
when a stop codon in mRNA reaches the A site of the ribosome
termination (translation) steps
A site accepts a release factor, it causes the addition of a water molecule instead of an amino acid, this reaction releases the polypeptide, the translation assembly comes apart
polyribosome
when multiple ribosomes translate a single mRNA simultaneuosly
types of point mutations
substitution, addition, deletion
silent mutation
change in mRNA codon but amino acid coded is the same
missense mutation
codes for a different amino acid
non sense mutation
codes for a stop codon
frame-shift mutation
creates change in number of nucleotides and amino acids produced
how many codons are there?
64
of the 64 triplets how many code for different things?
61 code for amino acids, 3 are stop codons
Genetic code properties (3) + brief description
universality (same for all living organisms), redundancy (more than one codon may specify a particular amino acid), unambiguousness (no codon may specify more than one amino acid)
redundancy genetic code explanation
more than one codon may specify a particular amino acid