CompTIA A+ Core 1 (220-1101) Flashcards
1/365
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Prepare for the CompTIA A+ Core 1 (220-1101) exam with over 300 detailed flashcards. These cover key topics and include questions inspired by Professor Messer's and Jason Dion's practice tests.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
366 Terms
Twisted Nematic (TN)
This type of LCD panel uses technology where the panel is black when no electric current is running through the liquid crystal cells because the cells align themselves in a twisted state. When an electric current is applied, the liquid crystal cells untwist, allowing light to pass through, resulting in a white display screen. These displays can be made with high refresh rates of 120 Hz or 144 Hz which makes them popular with gamers.
Inverter
Liquid Crystal Displays that use CCFL backlighting (essentially fluorescent tubes) need a high voltage AC power source. This component takes the laptop DC power and turns it into the AC power that the CCFL tubes need.
Secure Shell (SSH)
The protocol used for remote administration and file copying using TCP port 22.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
A protocol used to transfer files across the internet over ports 20 and 21.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
A protocol used to provide web content to browsers using port 80.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS)
A connection-oriented secure protocol that utilizes TCP to provide web content to browsers using SSL/TLS encryption over port 443.
Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3)
A TCP/IP application protocol providing a means for a client to access email messages stored in a mailbox on a remote server over port 110. The server usually deletes messages once the client has downloaded them.
In-Plane Switching (IPS)
This type of LCD panel uses technology designed to resolve the quality issues inherent in TN panel technology, including strong viewing angle dependence and low-quality color reproduction. Have great color accuracy, but they do not support higher refresh rates.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
The protocol used to only send mail between hosts on the Internet using TCP port 25.
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
This is a form of network security that detects and prevents identified threats. These systems continuously monitor your network, looking for possible malicious incidents, and capturing information about them. It can block malicious network traffic.
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
This system detects identified threats and continuously monitor your network, looking for possible malicious incidents, and capturing information about them.
Proxy server
A server application that acts as an intermediary between a client requesting a resource and the server providing that resource.
System Logging Protocol (Syslog)
A networking protocol that is primarily used for logging system messages and events using UDP port 514.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
This is a connectionless, non-guaranteed method of data communication. It does not provide any sequencing or flow control. Data sent over could be lost and never resent. Streaming videos or making Voice over IP (VoIP) calls are examples of use cases that rely upon this for their transmission.
Toner tap
This is used to create a physical connection to the network that sends a copy of every packet received to a monitoring device for capture and analysis.

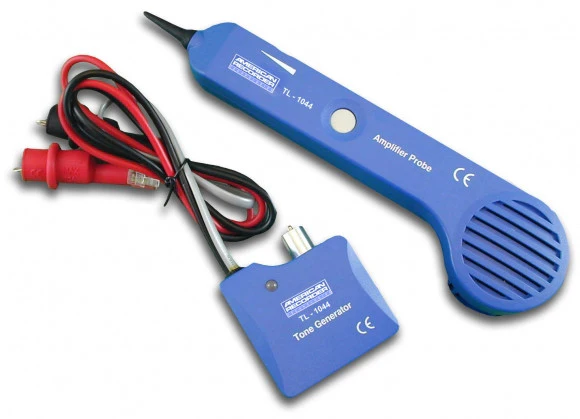
Tone generator
This is connected to a wall jack and sends a repeating signal over the cable. The probe can then be used to detect which cable is attached to the wall jack by detecting the signal being sent by it.

Overlapping
With wireless access points that run 2.4 GHz frequencies, you can only select channels between 1 and 11 in the United States. This includes 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, and 802.11ax networks. You should select channels 1, 6, and 11 to avoid this network issue.
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
This allows a single physical switch to be divided into logical networks. They are only supported on managed switches, but they allow for a different logical subnetwork address to be assigned to various ports on the switch. This requires that communications between these must go through a router, just as if you had multiple switches.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
This extends a private network across a public network and enables users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network.
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
This is a technology that provides high-speed internet access over traditional copper RJ-11 phone lines, allowing for simultaneous use of internet and phone services.
This allows the telecommunications company to connect a user's home to the local switching center using normal telephone lines, then connect that local switching center (using a DSLAM to multiplex the connections) to the central office over a single high-speed cable (such as a fiber connection).
Network Address Translation (NAT)
This is the process of mapping an IP address to another by changing the header of IP packets while in transit via a router. This helps to improve security and decrease the number of IP addresses an organization needs.
Static
This IP address type should be used for servers to ensure they are easy to find, access, and manage on the network. When configuring this, you need to include the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS server's IP address. Additionally, it should be used when the DHCP server is disabled and clients are configured manually to join the network properly.
Dynamic
This IP address type is set automatically by a DHCP server when a new host joins the network.
Automatic Private IP Addressing IP (APIPA)
Otherwise known as link-local, it is a feature of Windows-based operating systems that enables a computer to automatically assign itself an IP address when there is no Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server available to perform that function.
Power over Ethernet (PoE)
These types of switches provide power over ordinary data cabling to devices such as VoIP handsets and wireless access points.
F-type
This connection type is a coaxial connector commonly used for cable television (CATV), satellite TV, and broadband internet connections. It features a screw-on design that provides a secure and reliable connection. The connector is known for its simplicity, durability, and effectiveness in transmitting high-frequency signals with minimal signal loss.

DB-9
This is a older type of electrical connector commonly used for serial communication in computers and other devices. is a connector used to send serial signals to another device. It is used to connect to the management interface of a switch, router, firewall, or another infrastructure device.

0
This RAID type is also called striping, where file blocks are split across multiple physical drives increasing performance. However, this does not include any redundancy features. A single drive failure results in data loss. Minimum 1 drive.
Organic LEDS (OLED)
This display type works without a backlight because it emits its own visible light.
Five Authentication Factors
This is something you know, something you have, something you are, something you do, and somewhere you are.
1
This RAID type is also called mirroring, because file blocks are duplicated between two or more physical drives. Losing a single drive in this array will still allow access to the data on the other mirrored drive, but losing two drives would cause the data to be inaccessible. Minimum 2 drives.
5
This RAID type is striping with parity, where file blocks are striped across multiple storage drives and one storage drive maintains parity data. Data would still be available after a single drive failure, but two failed drives would cause data loss. Minimum 3 drives.
10
This RAID type is nested RAID array configuration that creates a mirrored set of drives. As long as only one drive fails in each RAID 0 mirror, the redundancy will remain valid and the user's data will continue to be available. Minimum 4 drives.
Network Interface Card (NIC)
This is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a computer network.
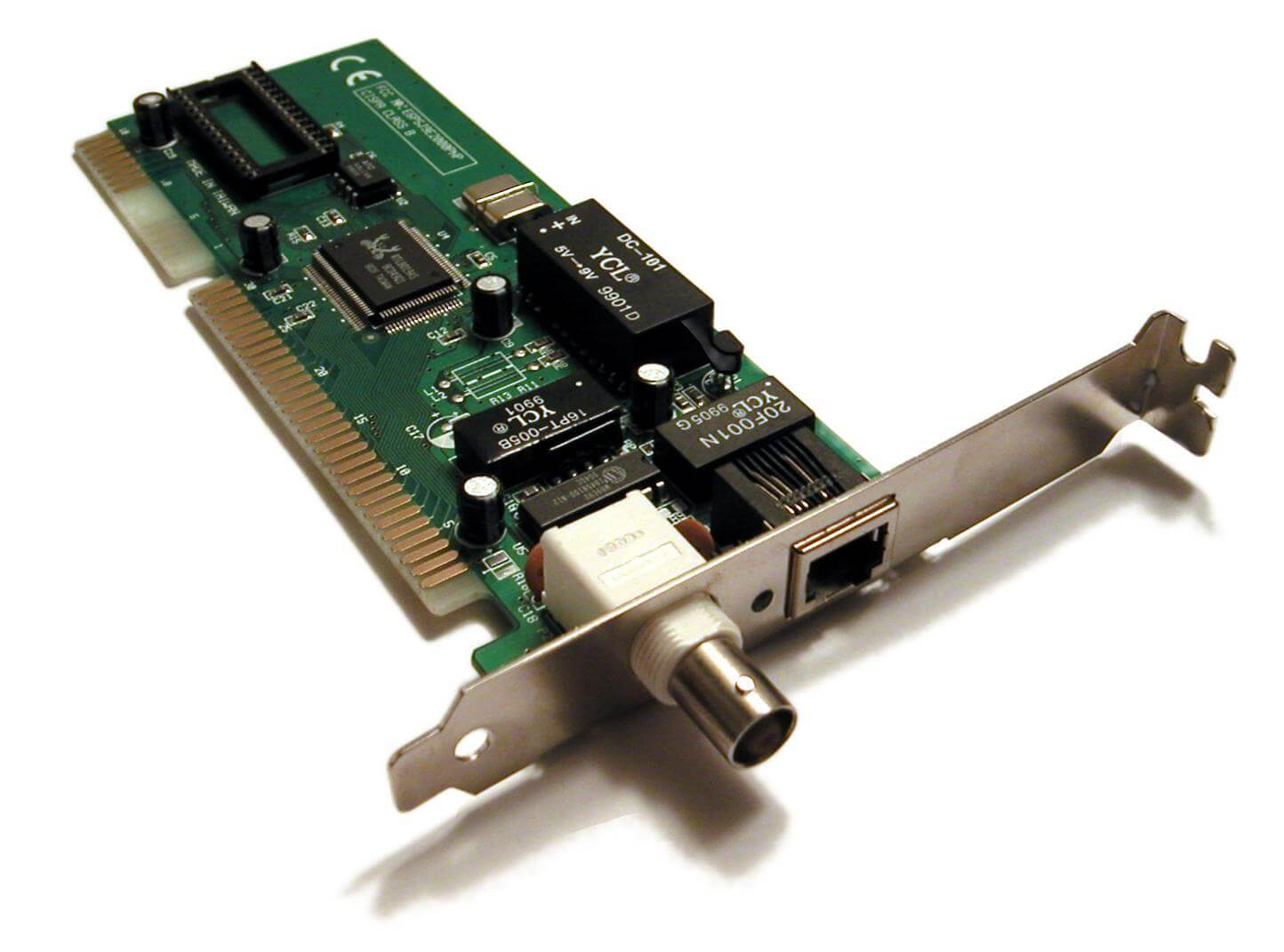
Main Distributed Frame (MDF)
This is the primary hub or demarcation point that interconnects private or public IT and telecommunication lines coming into a building.
Intermediary Distributed Frame (IDF)
This is a distribution frame in a central office or customer premises that connects to the main distribution frame.
110
A type of punch block used to terminate runs of on-premises wiring in a structured cabling system. Provides more spacing between the terminals and is designed for Cat 5e and above networks.
RJ-11
This connection type is used to terminate cables used for phone lines.
66
A class of punch down block used to terminate runs of on-premises wiring in a structured cabling system. Only used with older telephone Cat3 networks.
Printer Command Language (PCL)
This is used to tell printers how to properly layout and print the contents of a document on a page. It is a common printing language that is supported by many different printer manufacturers. Faster than PS.
PostScript (PS)
A page description language used in the electronic publishing and desktop publishing business. Slower than PCL but produces higher quality outputs.
Internet Printing Protocol (IPP)
This is a specialized Internet protocol for communication between client devices and printers (or print servers) using the HTTP protocol for data transport.
Line Printer Daemon (LPD)
This is a protocol is a network printing protocol for submitting print jobs to a remote printer. It is an older protocol than IPP.
Dedicated virtualization
This workstation setup requires maximum RAM and multiple CPU cores.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
This is a instant computing infrastructure, provisioned, and managed over the internet. It is a cloud computing service that enables a consumer to outsource computing equipment purchases and running their own data center. Quickly scales up and down with demand, letting you pay only for what you use. A cloud computing service provider manages the infrastructure while you purchase, install, configure, and manage your software.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
This is a cloud computing service that enables consumers to rent fully configured systems that are set up for specific purposes.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
This is a cloud computing service that enables a service provider to make applications available over the Internet to end-users. This can be a calendar, scheduling, invoicing, word processor, database, or other programs.
Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
This is a cloud computing offering where a service provider delivers virtual desktops to end-users over the Internet, licensed with a per-user subscription. Often combined with Virtual Desktop Infrastructure.
-Identify the problem
-Establish a theory of probable cause
-Test the theory to determine the cause
-Establish a plan of action to resolve the problem and implement the solution
-Verify full system functionality and, if applicable, implement preventive measures
-Document findings, actions, and outcomes.
(IETEVD)
What is the CompTIA troubleshooting process?
Image drum (Double images or ghost printing occurs when an image or text is repeated more than once on a printed page. This often occurs due to an issue with the drum unit. If the drum unit is not being properly charged by the corona wire, ghost prints can become a problem with the unit.)
The laser printer has recently begun creating printouts that contain a double image or ghost image appearance to them. Jason just printed out a test page:
Which of the following components is most likely to cause a ghost image to appear on the printout such as the one above?

Repair GPT/MBR (The "OS not found" error at boot time is an indication that the MBR (Master Boot Record) or GPT (Globally Unique ID Partition Table) is corrupted or faulty. If this occurs, you should reboot into the Windows recovery mode and use the 'bootrec /fixboot' command to fix the GPT.)
You are troubleshooting a workstation for a customer. The workstation will not boot. When it is powered on, an error message of "OS not found" is displayed on the screen. What is the MOST likely solution to fix this error?
This error is an indication that the MBR (Master Boot Record) or GPT (Globally Unique ID Partition Table) is corrupted or faulty. If this occurs, you should reboot into the Windows recovery mode and use the 'bootrec /fixboot' command to do this.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
This is a computer network that interconnects users with computer resources in a geographic region of the size of a metropolitan or city area.
Laser printer voltages
The DCPS (DC Power Supply/Source) converts 115VAC or 220VAC power into +5 VDC and -5 VDC for use by the printer's logic board, and +24 VDC to power the motors that feed the paper through the printing path. What does this describe?
Power supply wattage (If the power supply does not provide enough power, the system may turn on partially (fans spinning) but not fully power the components needed to display output or perform a POST (Power-On Self-Test), therefore no beep codes would be present.)
You are attempting to troubleshoot a computer for a user. When you attempt to turn on the computer by pressing the power button, the computer turns on, and the fan spins normally. There is no output displayed on the screen from the PCIe x16 video card. You turn off the computer, remove the processor and the memory, and attempt to power on the computer again. During the boot-up sequence, you do not hear any POST beep codes, but the fans still spin normally. Which of the following is the MOST likely cause of his issue?
Internal
This type of Virtual Machine can communicate between the host and other VMs.
External
This type of Virtual Machine can access the internet.
Private
This type of Virtual Machine will create a switch that is usable only by the VMs. The VMs cannot use the switch to communicate with the host.
Localhost
This type of Virtual Machine will only communicate with itself.
Digitizer
This is is used to convert touch events to digital signals that can be interpreted as different types of input.
Server Message Block (SMB)
A network protocol for sharing files, printers, and resources over a network, primarily in Windows, using ports TCP 445 (modern) and dual TCP/UDP for ports 137-139 (older).
Network Time Protocol (NTP)
This is a network protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable-latency data networks that uses port 123.
Loopback
This describes an IPv6 address of ::1.
The address is used to send a test signal sent to a network destination to diagnose problems.
Loopback
This describes an IPv4 address of 127.0.0.1.
The address is used to send a test signal sent to a network destination to diagnose problems.
Broadcast
This IP address type describes a network address used to send data to all devices in a particular network segment simultaneously. When a packet is sent to a this address, every device on that network receives it. They are useful for network discovery, announcements, and certain protocols that require all devices to receive specific information.
Multicast
This address type describes a network address used to deliver data only to a specific group of devices that have opted to receive that data. Devices must join this address group to receive traffic, rather than to just a single recipient (unicast) or every device on a network (broadcast). They are crucial in scenarios where the same data needs to be sent to multiple receivers, like live video streaming, online gaming, or conferencing.
Continuous reboots
Susan, a computer technician, received a complaint from a client about an issue with their laptop. Based on the symptoms observed, she believes that there is an issue with the laptop's memory. Which of the following symptoms was MOST likely observed during their troubleshooting?
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
This is a protocol for monitoring and managing network devices over UDP ports 161 and 162.
Burning smell (A burning smell is indicative of a bad power supply.)
A technician is troubleshooting an issue with a workstation. The technician believes that the power supply needs to be replaced based on the symptoms they observed. Which of the following symptoms did the technician likely observe to lead them to this conclusion?
Resource pooling
This refers to the concept that allows a virtual environment to allocate memory and processing capacity for a Virtual Machines use.
Measured Service
This cloud computing concept refers to services where the cloud provider measures or monitors the provision of services for various reasons, including billing, effective use of resources, or overall predictive planning.
Cable modem
This networking device is a type of network bridge that provides bi-directional data communication via radio frequency channels on a hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC), radio frequency over glass (RFoG), and coaxial cable infrastructure. They are primarily used to deliver broadband internet access as cable internet, taking advantage of an Hybrid Fiber Coax and Radio Frequency over Glass network's high bandwidth.
It is most associated with a coaxial cable input using an F-connector. The output commonly uses an RJ45 Ethernet connector.

Community cloud
This is a collaborative effort in which infrastructure is shared between several organizations from a specific community with common concerns, whether managed internally or by a third party and hosted internally or externally.
Hybrid cloud
This is a cloud computing environment that uses a mix of on-premises, private cloud, and third-party public cloud services with orchestration between these platforms. This typically involves a connection from an on-premises data center to a public cloud.
Reset the BIOS using jumpers
A company has acquired computers that were previously part of a third party lease. All of the computers prompt for a password when powering on the system before the operating system will load, but the password was not included with the computers. Which of the following would be the BEST way to resolve this issue?
Refresh rate (This is defined by the vertical scan frequency of a monitor and how many times in one second an image can be redrawn on the screen. LCD monitors have a fixed refresh rate based on the specifications of their panel.)
This describes how many times the image on the monitor changes per second.
Zigbee
This is a open-source wireless communication protocol operating in the 2.4 GHz frequency band and is primarily used for home automation.
Z-Wave
This is a proprietary wireless communications protocol used primarily for home automation. It uses radio frequencies in the 800 MHz and 900 MHz frequency ranges.
Service Location Protocol (SLP)
This is a protocol or method of organizing and locating the resources (such as printers, disk drives, databases, e-mail directories, and schedulers) in a network that uses port 427.
Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
The protocol used for retrieving and managing email from a mail server using TCP port 143.
Server Message Block (SMB)
Ports 137-139 and 445
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
The protocol used for dynamically assigning IP addresses and other network configuration using UDP ports 67 and 68.
Domain Name Service (DNS)
The protocol used for domain name resolution and lookup using UDP and TCP port 53.
802.3af
Which of the following network standards allows a networking device to provide up to 15.4W of power to a connected device?
802.3at
Which of the following network standards allows a networking device to provide up to 25W of power to a connected device?
SODIMM (A small outline dual inline memory module can be purchased in various types and sizes to fit any laptop, router, or other small form factor computing device. For the exam, if you are ever asked about installing memory in a small form factor device or a laptop, the answer will usually be SODIMM.)
You are troubleshooting a memory issue on a customer's laptop and have determined that the memory module needs to be replaced. You walk into the storage room to select a memory module to use as a replacement. Which of the following choices would be the MOST LIKELY choice for you to select for use on the laptop?
Keystone (A keystone effect occurs when the top of a projected image is wider or narrower than the bottom of the image. This creates a trapezoid instead of a rectangular image and leads to distortion. To fix the keystone effect in an image, you need to adjust the keystone setting in the projector.)
The projector in the Dion Training conference room is creating a distorted image when in use. The technician measures the top of the screen at 72” wide and the bottom of the screen at only 66” wide. The technician checks the projector’s resolution and the resolution in the operating system’s display settings. They notice that they are both set correctly to HDTV (1920 x 1080) mode. Which of the following settings on the project should the technician adjust to fix this distortion?
Reset
Which button on a desktop computer begins a reboot of the computer without power being removed from the computer's components?
Code-Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
This is a standard for digital cellular networks used for mobile communication used mostly inside the United States. It uses spread-spectrum techniques to allow multiple users to share the same frequency band simultaneously, improving bandwidth efficiency and security. It assigns a unique code to each user's data, enabling efficient bandwidth utilization and enhanced security.
Software-defined Networking (SDN)
Which of the following types of networking hardware is used to create network infrastructures within the cloud?
Connect Network, Install Applications and Security Updates
Your company uses a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) environment for employees to access their desktop applications. To allow employees access to the VDI environment, the company is installing thin clients in each employee's office. Which THREE of the following tasks must you first complete to install a thin client for a new employee?
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
This is a network protocol used for remote desktop access and control using TCP port 3389.
Bonjour
What is the name of the networking protocol used by macOS to find available printers on the network to use?
Gateway
This in a router refers to a network point that acts as an entrance to another network, typically providing access between a local network and external networks, such as the internet. It routes traffic from devices within the local network to destinations outside the local network, managing data flow and ensuring proper communication between different network segments.
Overheating
Jason presents a "how to pass your certification exams on the first attempt" lesson for his students using an overhead projector. After 24 minutes, the project goes blank. Jason allows the students to take a 15-minute coffee break while he attempts to turn the project back on. The project runs for another 4 minutes and then turns off again. What is MOST likely wrong with the projector and the laptop setup?
Calibrate the monitor and printer (For the best possible color match, it's important to calibrate the monitor and the printer. This calibration process will ensure the colors seen on the screen will match the tone and hue of the final output.)
A user in the marketing department is printing to a color printer, but the colors on the output don't match the colors on the screen. Which of the following would be the BEST next step?
Check for user error
Tom, a salesman, is trying to print a 3-page report to the network printer located in the Sales department’s office space. He walks over to the printer but doesn’t see the pages in the printer’s output tray. He checks the on-screen display of the printer, but he doesn’t see any errors listed. Tom tries a few more times, but he gets the same results. Frustrated, Tom selects the network printer for the Customer Service department and sends his print job there. He walks over to their offices and finds his 3-page report sitting in that printer’s output tray. Tom asks you to help him solve this printing problem. What action should you take FIRST to help solve Tom’s problem?
Signal attenuation (The most likely reason is signal attenuation from the new flag being placed between the signal path which may be obstructing the line-of-sight between the antennas. Based on where the flag is precisely located, it is possible to only block the signal when the wind is blowing in a certain direction. This would lead to the intermittent connectivity experienced by the users caused by the signal attenuation when the flag is blocking the communication path between the antennas.)
Several users at an adjacent office building report intermittent connectivity issues after a new flag pole was installed between the two offices. The network technician has determined the adjacent office building is connected to the main office building via an 802.11ac bridge. The network technician logs into the AP and confirms the SSID, encryption, and channels are all correct. Which of the following is MOST likely the cause of this issue?
Enable virtualization in BIOS
A computer technician tries to determine if a computer with an Intel i7 processor has virtualization enabled to run a second operating system within VirtualBox. Which of the following should be checked to determine if the system can run a virtual machine?
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
This is a simple protocol that provides a basic file transfer function with no user authentication. It uses port 69 to communicate.
Establish a print share on local host
What is the simplest and most cost-efficient way to allow other network users to access a printer if the printer does not have an RJ-45 or WiFi adapter available?