patho ch 42 GI disorders
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
4 cardinal signs & symptoms
pain, altered ingestion, altered mobility, bleeding
digestive pathway
food & liquids enter the mouth—>mastication & addition of salivary enzymes—>voluntary transport of food & liquids (positioned at back of throat for esophageal entry)—>involuntary transit to the stomach
common manifestations of esophageal defects
pain, alteration in ingestion, bleeding
dysphagia
difficulty swallowing
causes of dysphagia
neurological deficit, muscular disorder, mechanical obstruction
presentations of dysphagia
pain w/ swallowing, inability to swallow larger pieces of solid material, difficulty swallowing liquids
dysphagia caused by fibrosis
scar tissue causes contraction of esophagus
dysphagia caused by compression
cyst/mass/tumor causes narrowing of the esophagus
diverticulum
fold in the esophagus where food gets accumulated; bad breath is a symptom
esophageal atresia
born w/ walls of esophagus closed
indications of esophageal atresia
baby is always hungry but always throwing up
congenital tracheoesophageal fistula
connection between esophagus & trachea
achalasia
walls of esophagus don’t contract properly, food gets stuck
neurologic causes of dysphagia
damage to cranial nerves that control mastication or swallowing can affect digestion
esophageal web & rings
thin membranes or folds that narrow the esophagus
causes of esophageal web & rings
iron deficiency anemia, autoimmune disease, gastroesophageal reflux
esophageal web & rings treatment
dietary restrictions (soft food), endoscopic dilation therapy
esophageal cancer
primary squamous cell carcinoma (most common distal esophagus), significant dysphagia in later stages, poor prognosis due to late manifestation
esophageal cancer is associated w/ chronic irritation due to
chronic esophagitis, achalasia, hiatal hernia, alcohol abuse & smoking
hernia
a condition where an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the muscle or CT that surround it
hiatal hernia
part of the stomach protrudes into the thoracic cavity
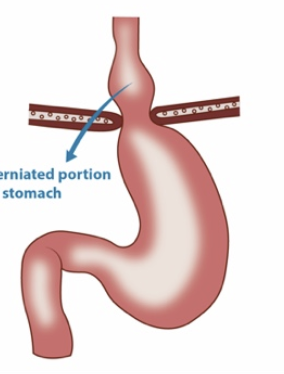
sliding hiatal hernia
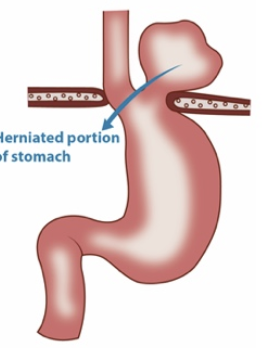
paraesophageal (rolling) hiatal hernia
etiology of hiatal hernia
multifactorial, may involve genetic link
pathogenesis of hiatal hernia
herniation of stomach through esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm, lower esophageal sphincter permits reflux of gastric contents
manifestations of hiatal hernia
may be asymptomatic; frequently involves symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux
type IV paraesophageal hernia
may produce dyspnea, reduced exercise tolerance, syncope, may cause chronic esophagitis
signs of hiatal hernia
heartburn/pyrosis, frequent belching, increased discomfort when laying down, substernal pain that may radiate to the shoulder & jaw
treatment for hiatal hernia
medications for symptomatic gastric reflux, surgery may be indicated
etiology of eosinophilic esophagitis
cause unknown, many associated factors
etiology of radiation esophagitis
treatment of thoracic cancers, exacerbated by chemotherapeutic agents
etiology of corrosive esophagitis
ingestion of strong alkaline or acid substances
etiology of pull esophagitis
Swallowed pill lodges transversely in esophageal lumen and causes inflammation
pathogenesis of esophagitis
irritation to & inflammation of esophageal tissues lead to esophageal damage
treatment of esophagitis
varies based on etiology, thorough history & physical exam is required
most common cause of esophageal diverticula
impaired esophageal mobility
etiology of esophageal diverticula
acquired condition, may be caused by traction on esophagus due to inflammatory disease of mediastinum such as tuberculosis
pathogenesis of esophageal diverticula
increasing pressure on esophageal lumen, esophageal mucosa protrudes through weakened esophageal wall & produces outpouching
manifestations of esophageal diverticula
most often asymptomatic, vary based on location, may produce dysphagia & heartburn
treatment of esophageal diverticula
depends on size & location, surgical intervention may be needed if it is too large
main categories of stomach disorders
disorders of secretion, disorders of mobility
associated cardinal GI symptoms of stomach disorders
pain, altered ingestion, altered digestion, GIT bleeding
peptic ulcer disease
Inflammatory process that damages epithelial lining of stomach and body is not able to replace the injured area—critical injury
stomach perforation
very bad complication; full thickness tear in stomach wall, fluid of stomach leaks to surrounding organs
most common causes of peptic ulcer disease
H. pylori infection and NSAID use
contributing factors of peptic ulcer disease
smoking, excessive alcohol use, drug use, emotional stress, psychosocial components
pathogenesis of peptic ulcer disease
increased gastric acid secretion or a weakened mucosal barrier leads to mucosal erosion or ulceration of GIT
manifestations of peptic ulcer disease
epigastric pain, dyspepsia (upset stomach)
common complications of peptic ulcer disease
bleeding, perforation, obstruction
treatment of peptic ulcer disease caused by H. pylori
triple or quadruple therapy
treatment of peptic ulcer disease caused by NSAID use
H2 receptor antagonist & cease NSAID use
gastritis
inflammation of stomach wall
common etiology of gastritis
infection induced (H. pylori), NSAID use
etiology of acute gastritis
drug induced (NSAIDs, steroids, some chemotherapeutic drugs, alcohol, iron supplements), ulcerohermorrhagic—physiologic stress & ischemic changes caused by shock, hypotension
pathogenesis of acute gastritis
acute imbalance between mucosal injury & repair mechanisms, development of mucosal hyperemia & erosive changes w/ histologic presence of inflammation
etiology of chronic gastritis
chemical & caustic agents (NSAIDs, excessive alcohol ingestion, radiation exposure), autoimmune disease (Crohn, Wegener granulomatosis, sarcoidosis)
pathogenesis of chronic gastritis
begins w/ superficial gastritis—>progresses to atrophic gastritis—>advances to gastric atrophy—>gastric glandular structures are lost and/or metaplasia
what is gastric atrophy a precursor to?
gastric cancer
manifestations of gastritis
most often asymptomatic or report mild dyspepsia; may have abd pain/upset, burning sensation in chest or upper abd, feeling of fullness, bloating, belching, reflux
more severe symptoms of gastritis
nausea, vomiting, GI bleeding, fever, weight loss
common treatments of gastritis
elimination of causative/exacerbating factors, eradication
etiology of gastric outlet obstruction
malignancies of digestive organs, surgical & interventional induced obstructions, metastatic cancer
pathogenesis of gastric outlet obstruction
mechanical obstruction in the pyloric region
manifestations of gastric outlet obstruction
abd pain/distention/bloating, vomiting, dehydration, weight loss, possibly early satiety & nausea
treatment of benign gastric outlet obstruction
nasogastric tube suction, medications to suppress gastric acid production, IV fluid & electrolyte replacement, nutritional supplementation, trial liquid diet, endoscopic balloon dilation or surgery
treatment of malignant gastric outlet obstruction
based on underlying cause; may include stenting, chemotherapy, endoscopic balloon dilation or surgery
treatment of gastric outlet obstruction in advanced cancers
palliative procedures may be preferred
stomach cancer risk factors
H. pylori infection, cigarette smoking, high alcohol ingestion, excessive dietary salt, inadequate fruit & vegetable consumption, pernicious anemia, high nitrate diet
pathogenesis of stomach cancer
tumors or neoplasms in the stomach arise from gastric mucosa
most common stomach cancer
adenocarcinoma (about 85% of case)
what are clinical manifestations of stomach cancer known as
alarm features
most common clinical manifestations of stomach cancer
weight loss & abdominal pain
other clinical manifestations of stomach cancer
dysphagia, nausea, early satiety, occult GI bleeding, palpable abd mass
stomach cancer treatment
depends on staging, endoscopic resection, radiation, chemotherapy, and/or surgical resection
absorption in lower GIT
chyme enters small bowel via duodenum
what is primarily absorbed in the small bowel
nutrients & vitamins, electrolytes, water
what can impaired motility cause?
malabsorption, malnutrition, dehydration
inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
chronic inflammatory disorder involving GIT
two major IBD disorders
ulcerative colitis (UC) & Crohn disease (CD)
ulcerative colitis (UC)
chronic inflammatory condition limited to mucosal layers of colon and characterized by relapsing & remitting episodes of inflammation; develops as a continuous lesion
Crohn disease (CD)
chronic inflammatory condition that may involve any portion of GIT and is characterized by transmural inflammation of the bowel; most commonly affects ileum & proximal colon, lesions are not always continuous (skip lesions)
manifestations of IBD (including UC & CD)
active: fever, loss of appetite, weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
remission: symptoms may decrease & even disappear
etiology of UC & CD
not completely understood; appears to involve environmental factors, microbial imbalance in the gut, genetic susceptibility, & inappropriate immune response
pathogenesis of UC
inflammation of mucosal & submucosal layers of colon, continuous lesion of inflammation may extend into the proximal colon or may affect the whole colon (pancolitis), bowel changes include epithelial damage, inflammation, crypt abscesses, loss of goblet cells
manifestations of UC
bloody and/or mucoid, diarrhea, dehydration, anemia, crampy abd pain, pain w/ defecation, tenesmus; involvement of rectum may lead to constipation
tenesmus
sense of urgency and a feeling of incomplete bowel evacuation
pathogenesis of CD
inflammation & destruction of the bowel
manifestations of CD
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea w/ or w/o blood, abd pain, pain w/ defecation due to anorectal fissures
complications of CD
bowel strictures, obstructions, perforations in the bowel & intra-abd abscesses
treatment guidelines for IBD
optimize quality of life by treating acute processes, induce & maintain remission, decrease use of corticosteroids, wholesome nutrition & healthy lifestyle habits, anti-inflammatory agents, immunosuppressants, anti-tumor necrosis factor agents, antibiotics, probiotics, surgery if indicated
appendicitis etiology
not fully understood, believed to be due to appendiceal obstruction
pathogenesis of appendicitis
obstruction is thought to lead to bacterial overgrowth & luminal distention, increased intraluminal pressure and/or excessive inflammation can inhibit blood flow causing vascular compromise to affected tissue, appendix may become gangrenous & can rupture
manifestations of appendicitis
cramping abd pain, tenderness w/ palpation of the RLQ, nausea or vomiting, increased WBC, low-grade fever
appendicitis treatment
gold standard is laparoscopic surgery
etiology of bowel obstruction
75% due to adhesions; other causes are hernia, adhesion neoplasm/tumor, gallstone ileus, intussusception, volvulus (small intestine twists)
pathogenesis of bowel obstruction
intestinal tract blockage develops due to various etiologies, up to 80% can be small bowel obstructions, obstruction can be partial or complete
complications of bowel obstruction
strangulation & bowel necrosis; may lead to bowel perforation, sepsis, & death
bowel obstruction manifestations
abd pain, nausea, vomiting, abd distention, inability to satisfactorily pass gas or stool, hyperactive high pitched bowel sounds
when will bowel sounds be absent (in bowel obstruction)
if ileus develops
treatment of bowel obstruction
gastric decompression, IV fluids, serial physical & serum tests, surgery if other methods fail