Bio lab exam III
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
1
New cards
Gymnosperms
"Naked" seed, not enclosed in a fruit. Include conifers, which produce cones during sexual reproduction.
2
New cards
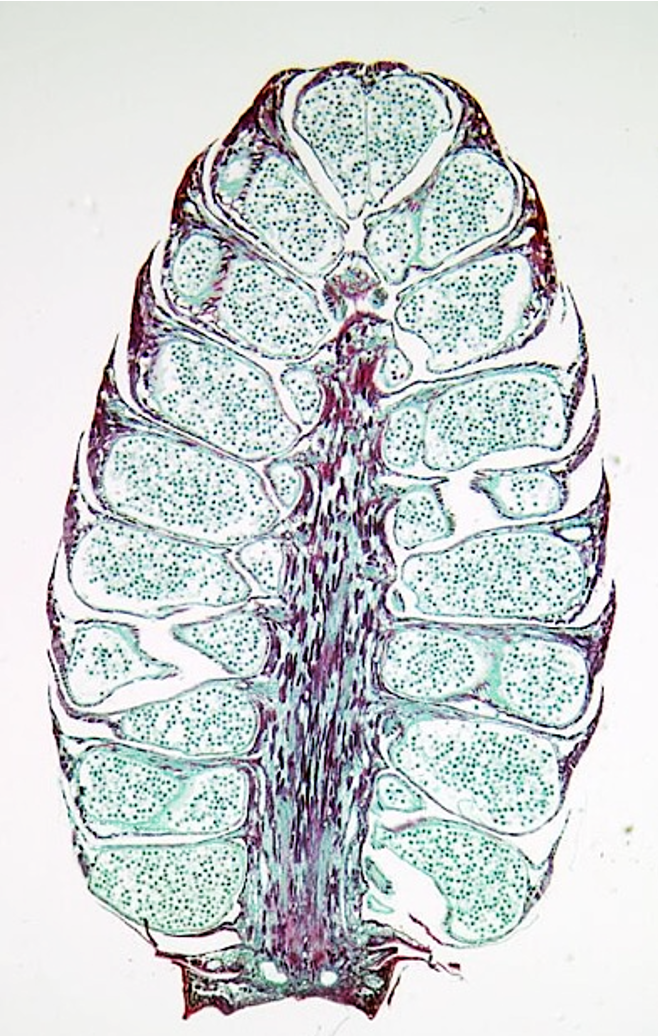
Pollen cone
- Male cone, usually smaller in size than a female cone
- each scale of the cone contains one microsporangium, which undergoes meiosis to create microspores, which undergo mitosis to produce the microgametophyte
- each scale of the cone contains one microsporangium, which undergoes meiosis to create microspores, which undergo mitosis to produce the microgametophyte
3
New cards
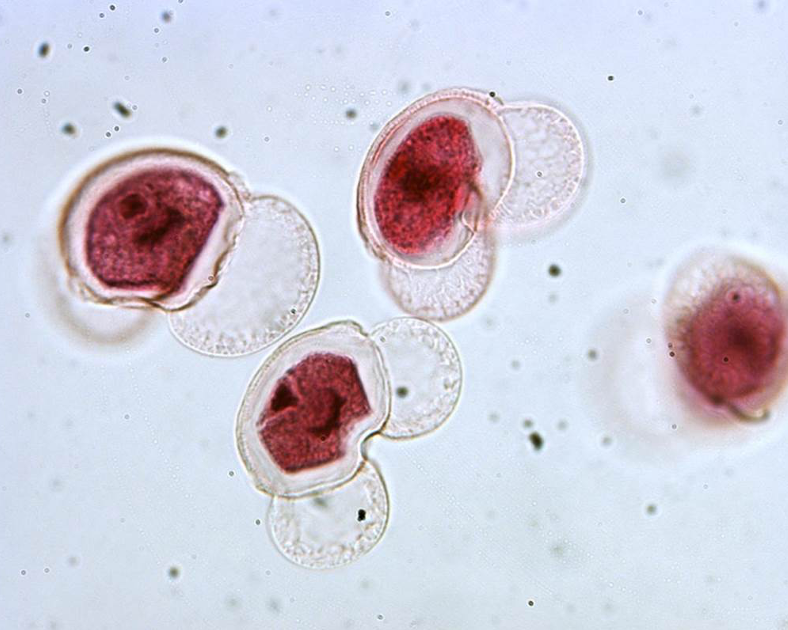
pollen grain
- male gametophyte
- one of these contains 2 living cells (one is sperm nucleus) and 2 dead cells that form "wings" to help it travel through the air
- one of these contains 2 living cells (one is sperm nucleus) and 2 dead cells that form "wings" to help it travel through the air
4
New cards
Life cycle of a seeded plant
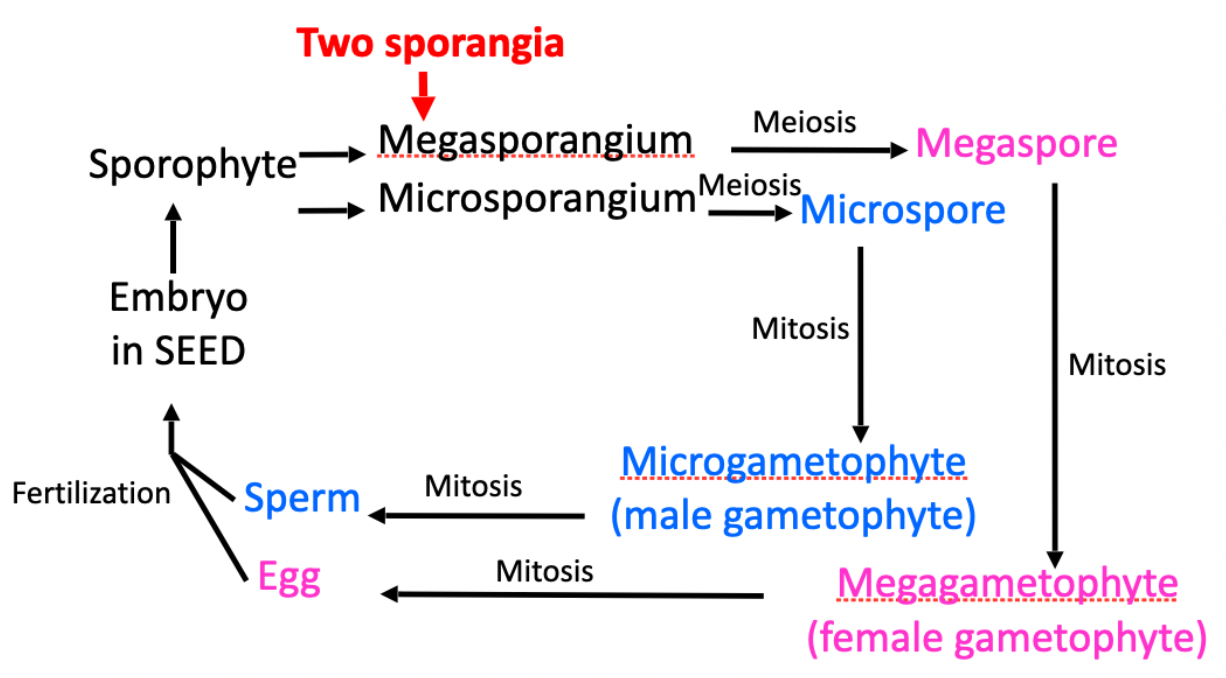
5
New cards
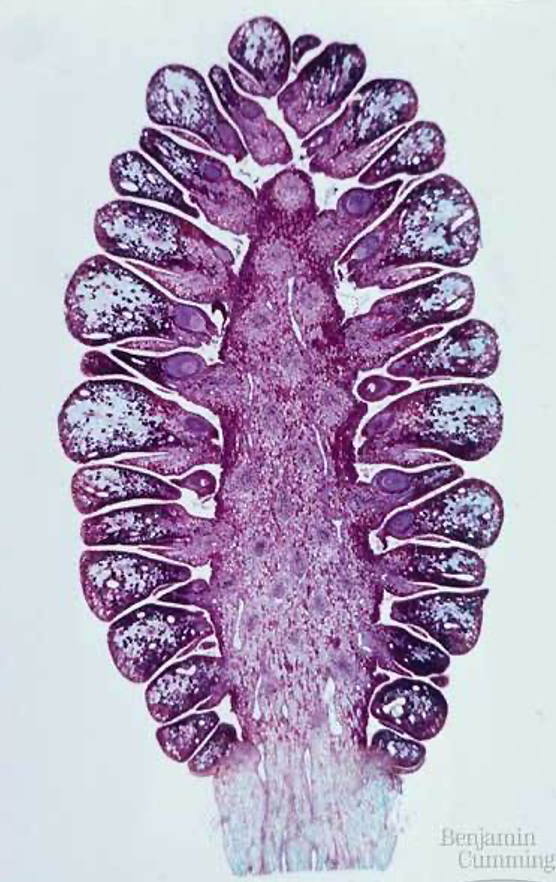
seed cone
- female cone, usually larger in size than a male cone
- each ovule contains one scale, a megasporangium which undergoes meiosis to megaspores, which undergo mitosis to produce the megagametophyte
- each ovule contains one scale, a megasporangium which undergoes meiosis to megaspores, which undergo mitosis to produce the megagametophyte
6
New cards
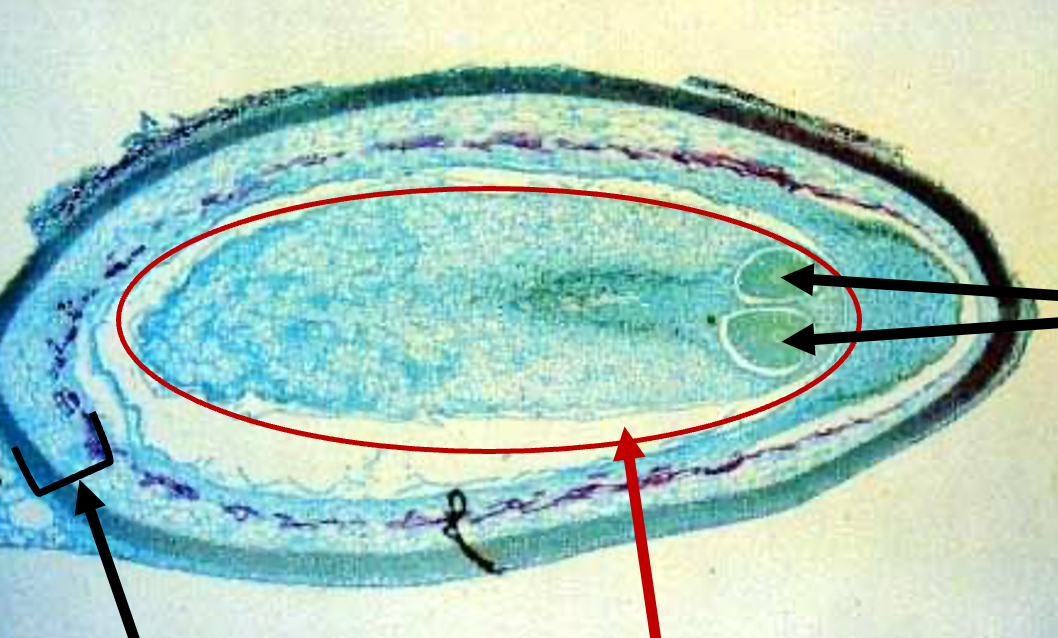
Megasporangium
- black bracket
- undergoes meiosis
- one in each scale of a seed cone
- undergoes meiosis
- one in each scale of a seed cone
7
New cards
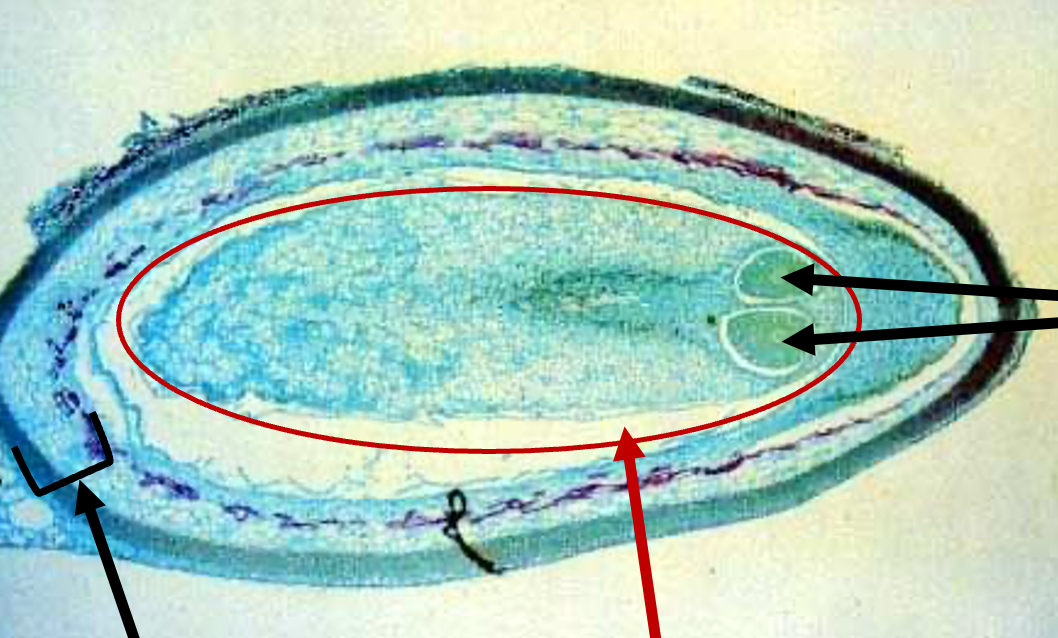
Megagametophyte
- red oval
- undergoes mitosis to produce eggs
- undergoes mitosis to produce eggs
8
New cards
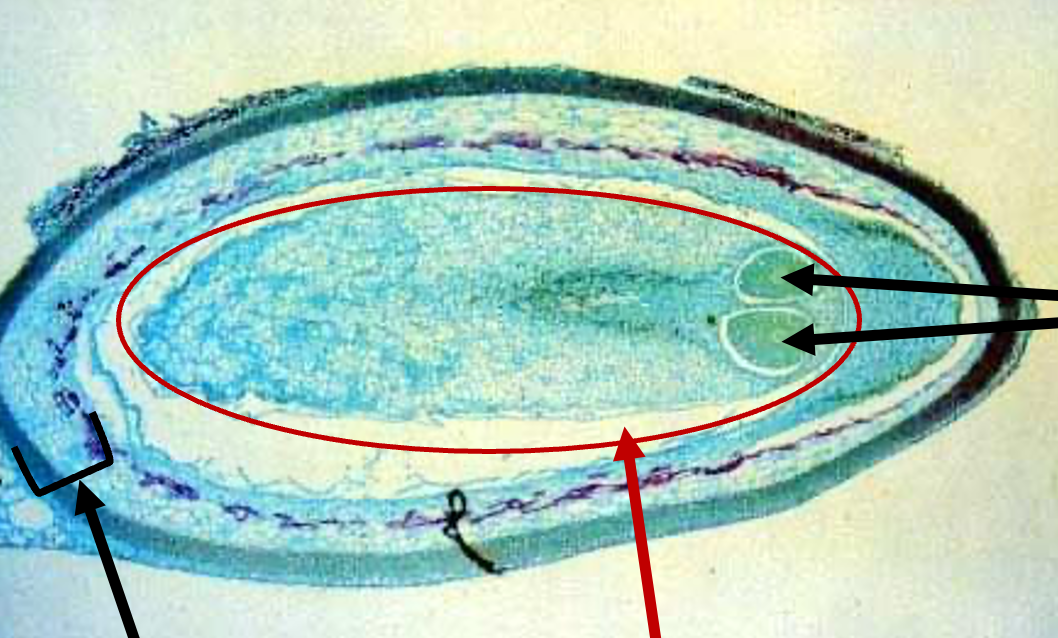
Archegonium
white layer of cells surrounding eggs
9
New cards
Eggs
- 2 black arrows
- undergo fertilization by combining with sperm to form embryo in seed, which grows into sporophyte
- undergo fertilization by combining with sperm to form embryo in seed, which grows into sporophyte
10
New cards
1st spring in seeded plant cycle
- scales on ovulate cone are open to allow pollen in
- scales close and allow pollen inside
- over the next year, the megagametophyte develops and produces eggs while tapped pollen grains wait
- scales close and allow pollen inside
- over the next year, the megagametophyte develops and produces eggs while tapped pollen grains wait
11
New cards
2nd spring in seeded plant cycle
- sperm fuses with egg and grows into embryo in the seed
- seed coat and stored food develop from megasporangium and megagametophyte tissue
- seed coat and stored food develop from megasporangium and megagametophyte tissue
12
New cards
Benefits of seed dormancy
- seeds can dry out completely and still be alive
- seeds can remain dormant for a VERY long time and still germinate when exposed to the proper conditions
- seeds can remain dormant for a VERY long time and still germinate when exposed to the proper conditions
13
New cards
Contents of a seed, function, and ploidy
- seed coat protects embryo (2n)
- food supply provides energy to embryo when seed germinates (n)
- embryo is baby plant (2n)
- food supply provides energy to embryo when seed germinates (n)
- embryo is baby plant (2n)
14
New cards
Angiosperm
Seed is covered by a fruit, includes flowering plants
15
New cards
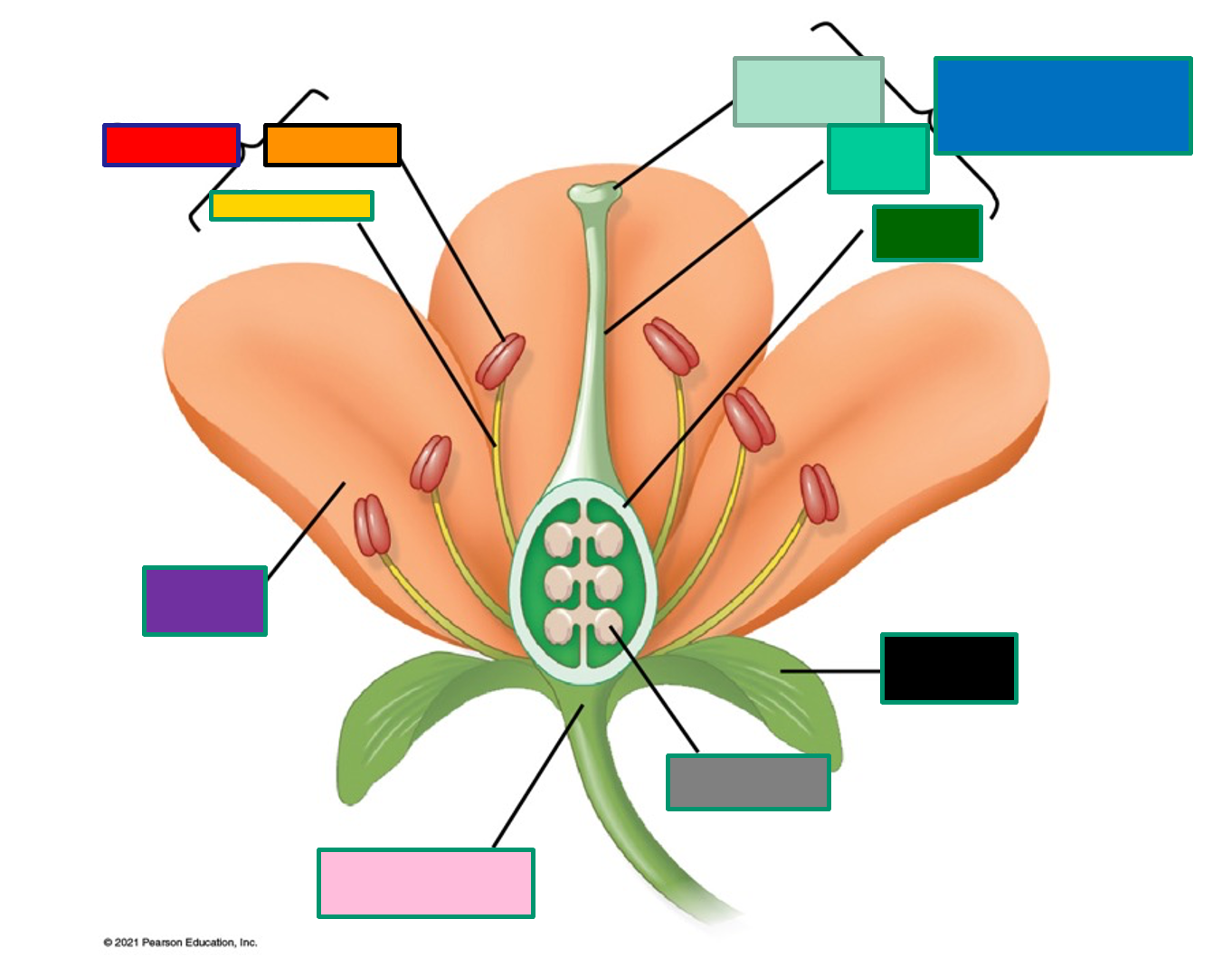
Parts of a flower
- stamen (male) (red)
- anther (orange)
- filament (yellow)
- stigma (light green)
- style (mid green)
- ovary (female) (dark green)
- carpel (blue)
- petals (purple)
- receptacle (pink)
- ovule (grey)
- sepal (black)
- anther (orange)
- filament (yellow)
- stigma (light green)
- style (mid green)
- ovary (female) (dark green)
- carpel (blue)
- petals (purple)
- receptacle (pink)
- ovule (grey)
- sepal (black)
16
New cards
Pollination of flowering plants
Stigma traps pollen from air and it travels through the style to the ovule. Plants with petals rely on pollinators for this, while plants without petals rely on the wind.
17
New cards
Flower is defined as
the presence of stamens and/or carpels, not petals
18
New cards
Double fertilization (flowering plants only)
- megagametophyte is only 7 cells
- large cell in center is made up of 2 polar nuclei
- when this cell is fertilized it is triploid, with 2 sets of eggs and 1 set of sperm chromosomes
- this cell grows to form endosperm which provides food in the seed
- large cell in center is made up of 2 polar nuclei
- when this cell is fertilized it is triploid, with 2 sets of eggs and 1 set of sperm chromosomes
- this cell grows to form endosperm which provides food in the seed
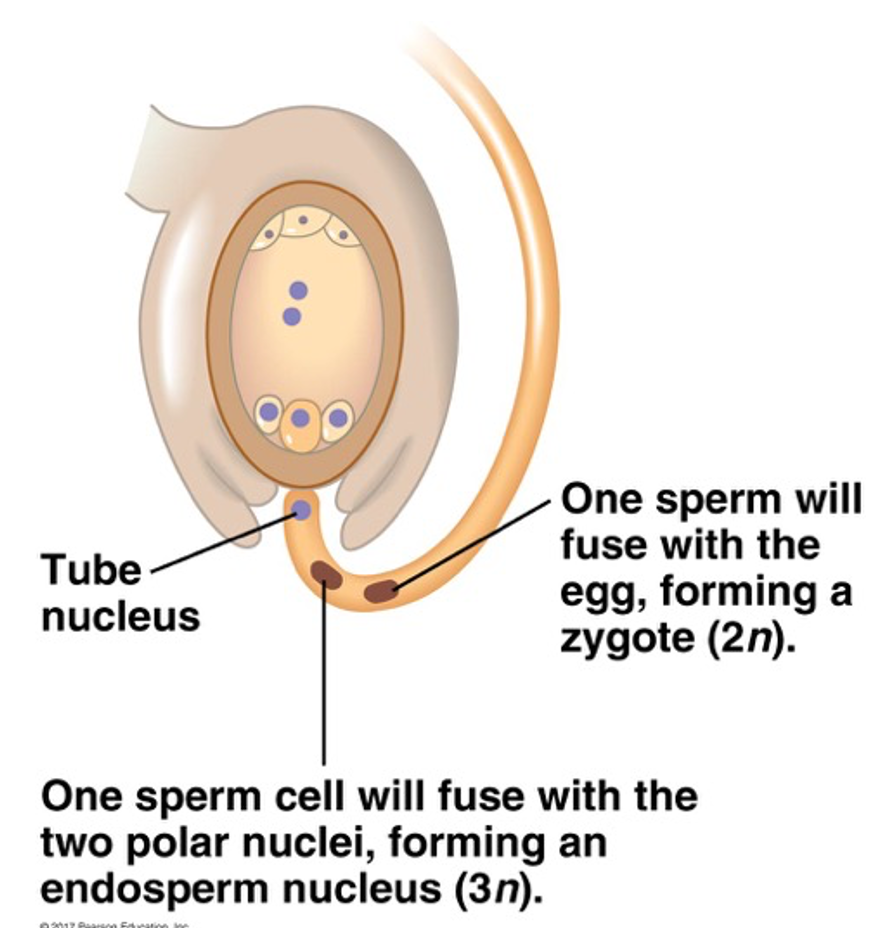
19
New cards
Main function of fruits
To aid in dispersal. Animals eat fruits and poop out seeds, thereby dispersing plant.
20
New cards
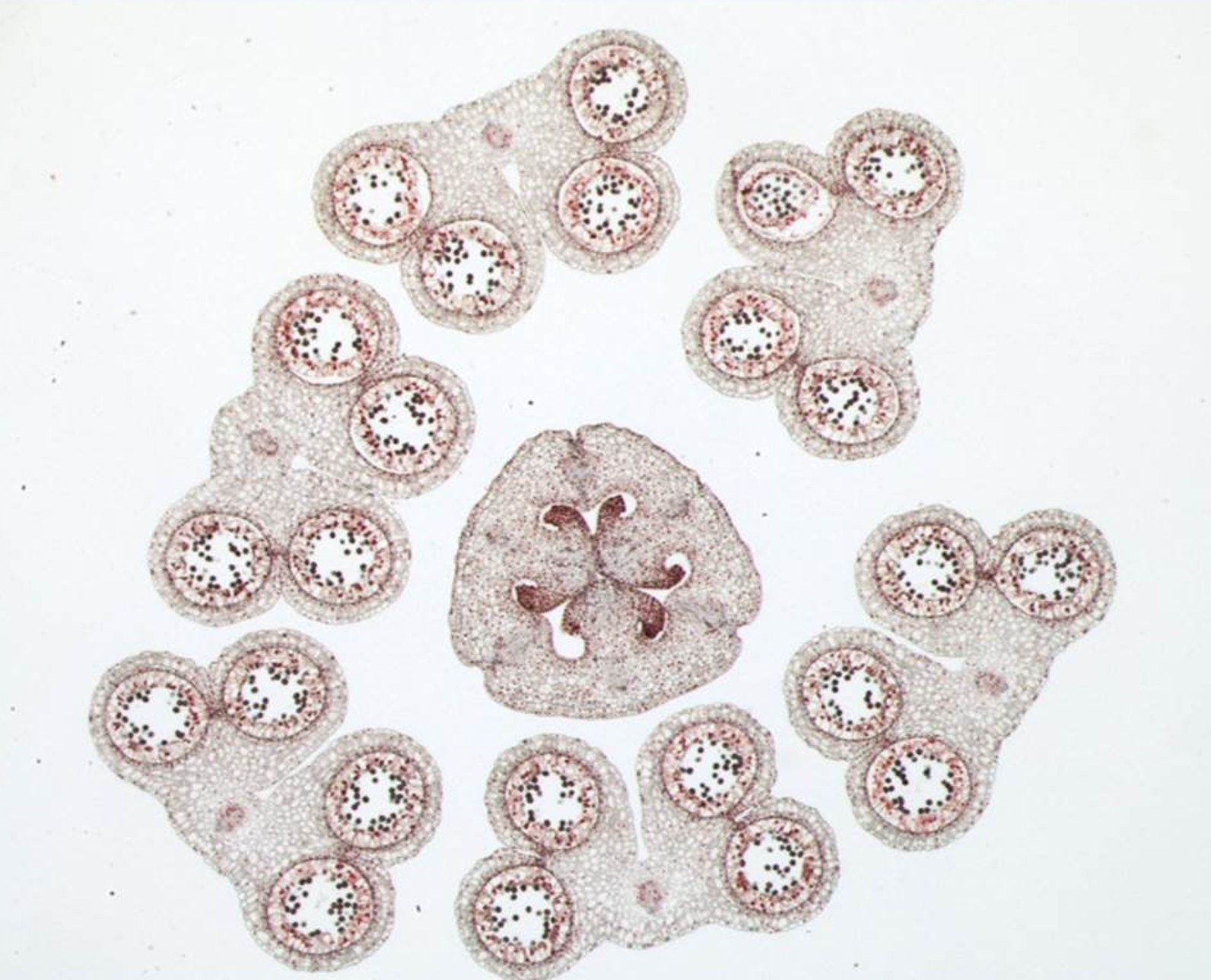
cross section of flowering plant
21
New cards
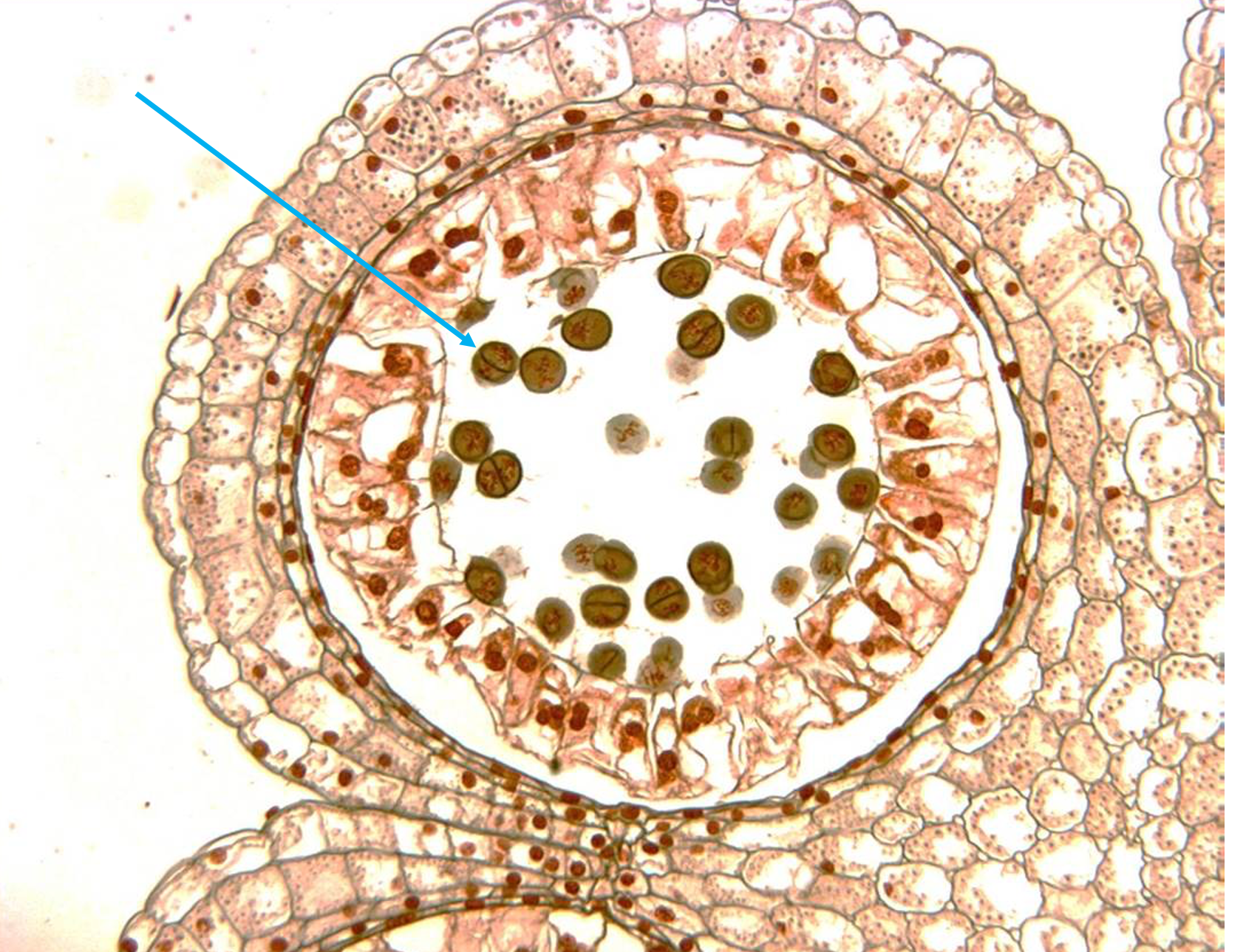
What is arrow pointing to?
Microspores, which grow into microgametophyte (pollen)
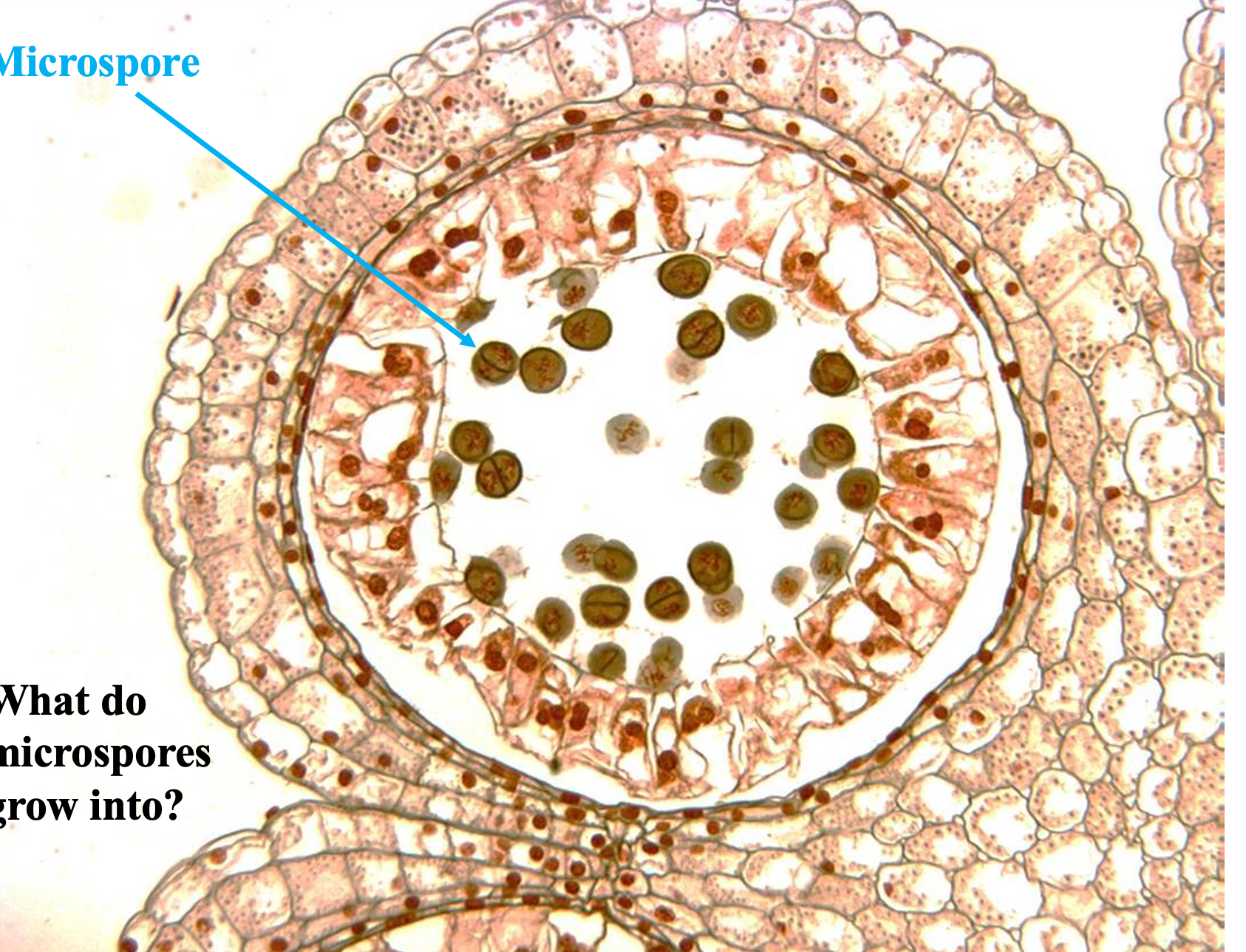
22
New cards
Where can growth only occur in plants? How do cells in those places divide?
Meristems; mitosis
23
New cards
Apical meristems
- growth in length
- know as primary (1 degree) growth
- happens at root tips and shoot tips
- know as primary (1 degree) growth
- happens at root tips and shoot tips
24
New cards
Lateral meristems
- also called cambium
- growth in width
- known as secondary (2 degree) growth
- trees have a lot, grass has none
- growth in width
- known as secondary (2 degree) growth
- trees have a lot, grass has none
25
New cards
Function of root cap
To protect apical meristem
26
New cards
Function of roots hairs on radish seedling
increase surface area for absorption of water/nutrients from soil
27
New cards
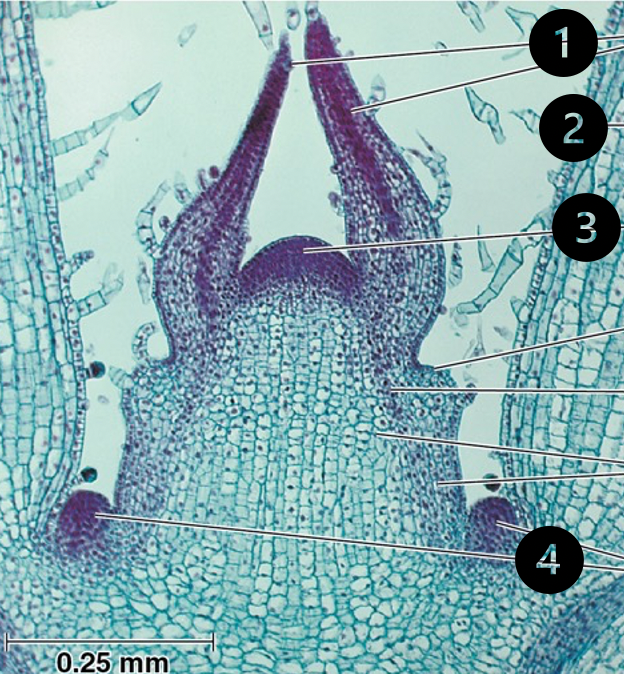
Coleus stem tip
1. leaf primordia
2. young leaf
3. shoot apical meristem
4. bud primordia
2. young leaf
3. shoot apical meristem
4. bud primordia
28
New cards
Parenchyma
- living
- relatively thin cell walls
- function in storage
- may or may not have chloroplasts
- pretty big, found in pretty much everything
- relatively thin cell walls
- function in storage
- may or may not have chloroplasts
- pretty big, found in pretty much everything
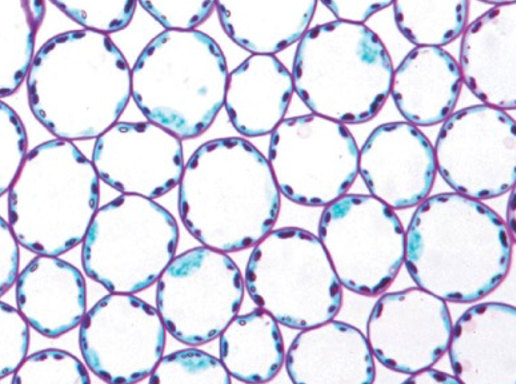
29
New cards
Collenchyma
- found in celery
- living
- thicker cell walls provide flexible support
- smaller cells
- living
- thicker cell walls provide flexible support
- smaller cells
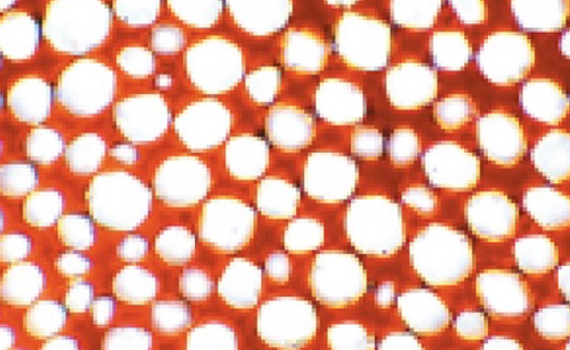
30
New cards
Sclerenchyma
- found in pear skins and gives them their gritty texture
- can be in sclereid (what we saw in lab) and fiber forms
- cells dead at maturity
- very thick cell walls provide rigid support
- can be in sclereid (what we saw in lab) and fiber forms
- cells dead at maturity
- very thick cell walls provide rigid support
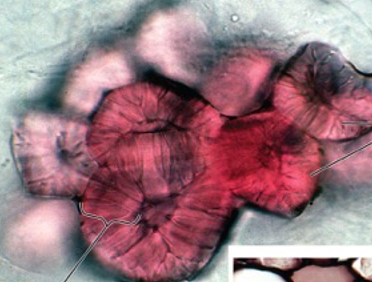
31
New cards
Xylem
- long, vessel-like structures used for water transport
- dead at maturity
- dead at maturity
32
New cards
Phloem
- used for sugar transport
- living cells with nucleated companion cells
- living cells with nucleated companion cells
33
New cards
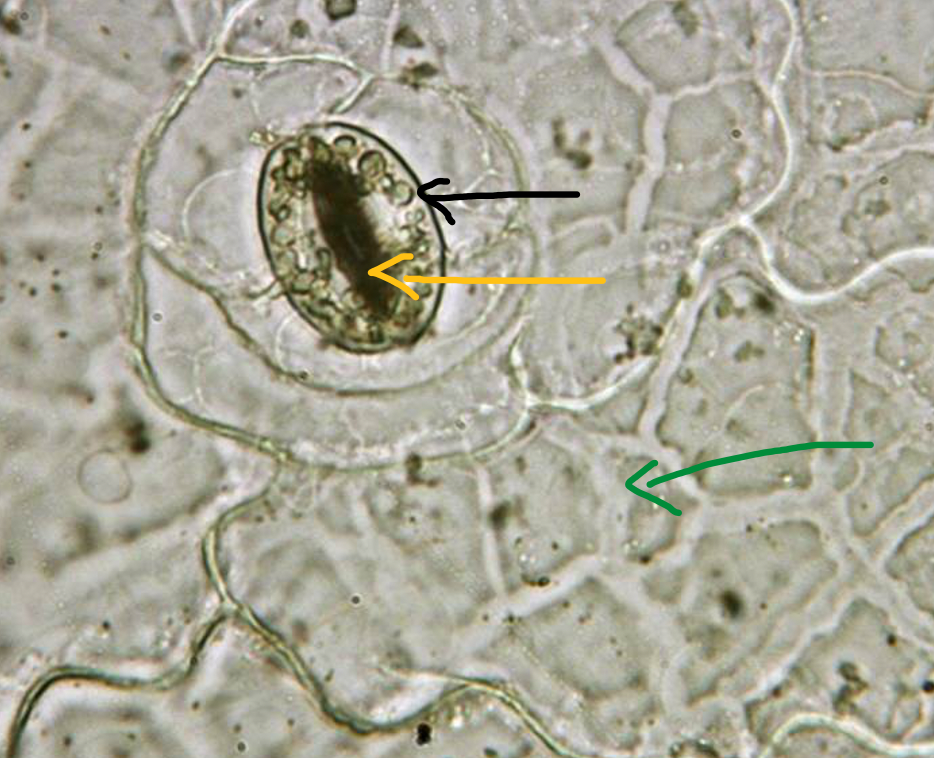
Leaf epidermis
- stoma (yellow arrow)
- guard cells (black arrow)
- parenchyma (green arrow)
- guard cells (black arrow)
- parenchyma (green arrow)
34
New cards
Function of guard cells
Control when stoma open and close, which prevents water loss
35
New cards
Function of stomata
allows for intake of CO2 and excretion of O2
36
New cards
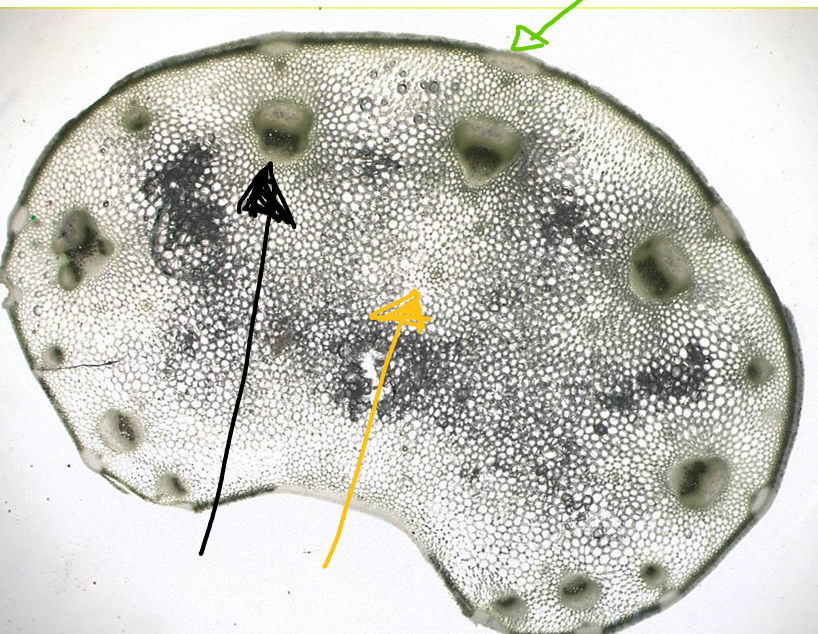
Celery
- vascular bundles (black arrow)
- parenchyma (yellow arrow)
- collenchyma (green arrow)
- parenchyma (yellow arrow)
- collenchyma (green arrow)
37
New cards
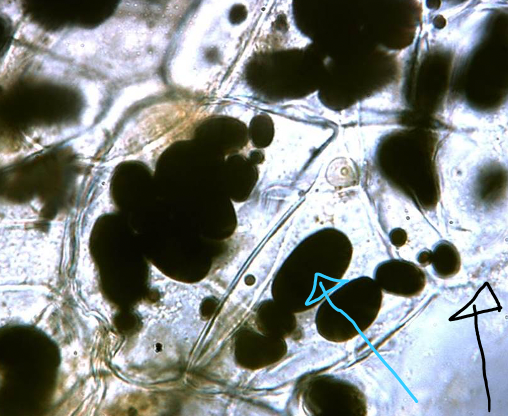
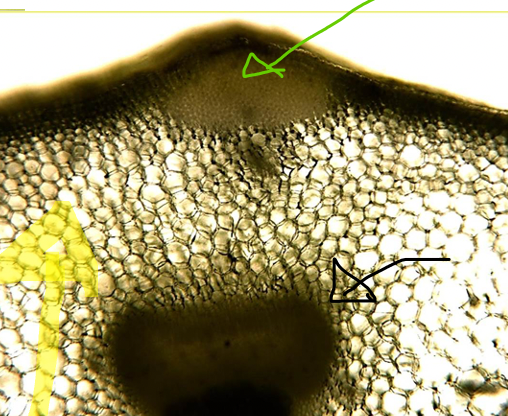
Potato
- leucoplasts (blue arrow)
- cell wall (black arrow)
- cell wall (black arrow)
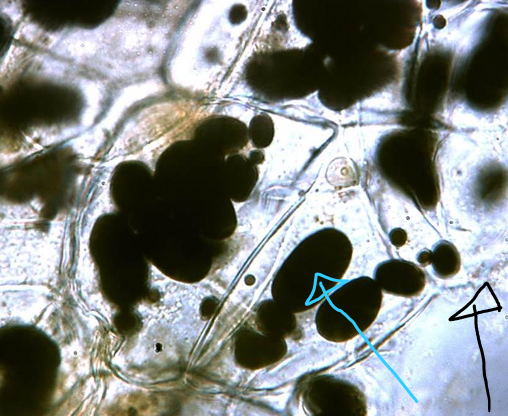
38
New cards
Where leucoplasts are found and their function
Potatoes; starch storage
39
New cards
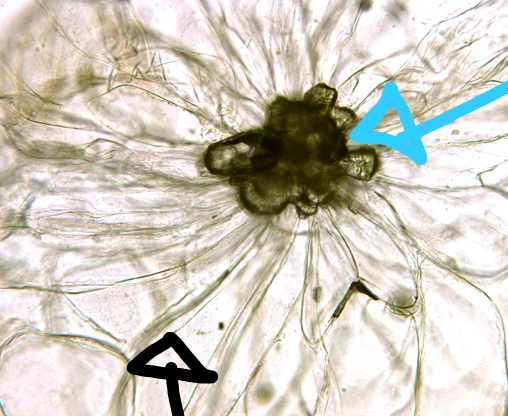
Pear
- slcereid form of sclerenchyma (blue arrow)
- parenchyma (black arrow)
- parenchyma (black arrow)
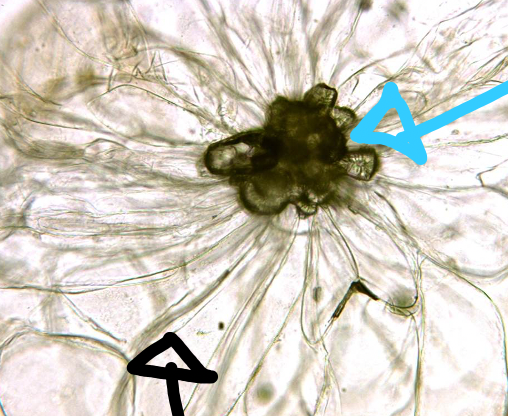
40
New cards
Key differences between monocots and dicots
Monocots:
- one cotyledon
- parallel veins
- scattered vascular tissue
Dicots:
- two cotyledons
- netlike veins
- vascular tissue arranged in ring
- one cotyledon
- parallel veins
- scattered vascular tissue
Dicots:
- two cotyledons
- netlike veins
- vascular tissue arranged in ring
41
New cards
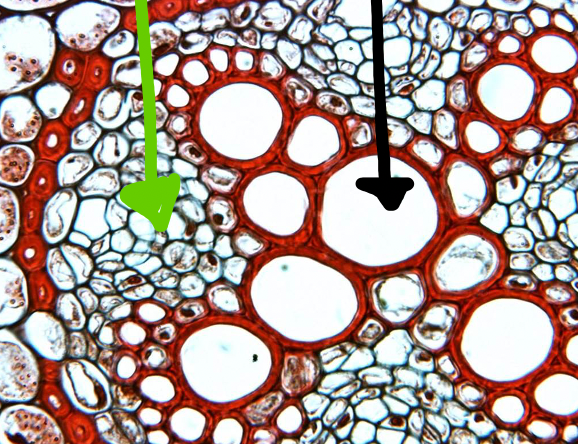
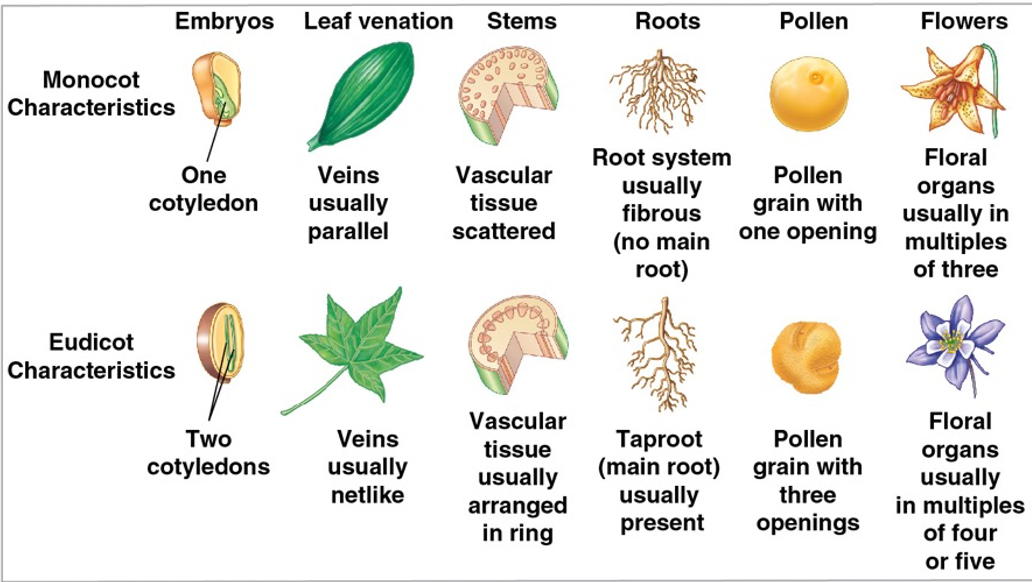
Ranunculus (dicot root) zoomed in
- xylem (black arrow)
- phloem (green arrow)
- phloem (green arrow)
42
New cards
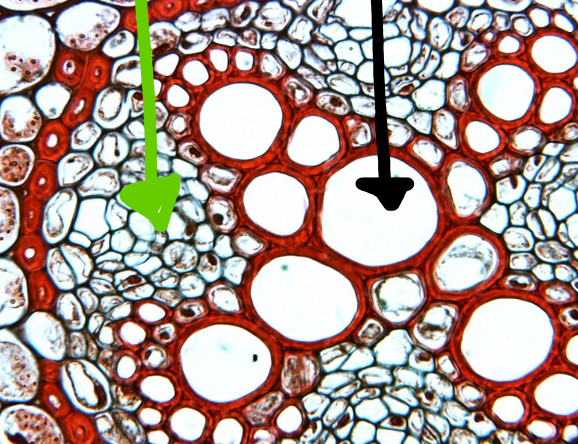
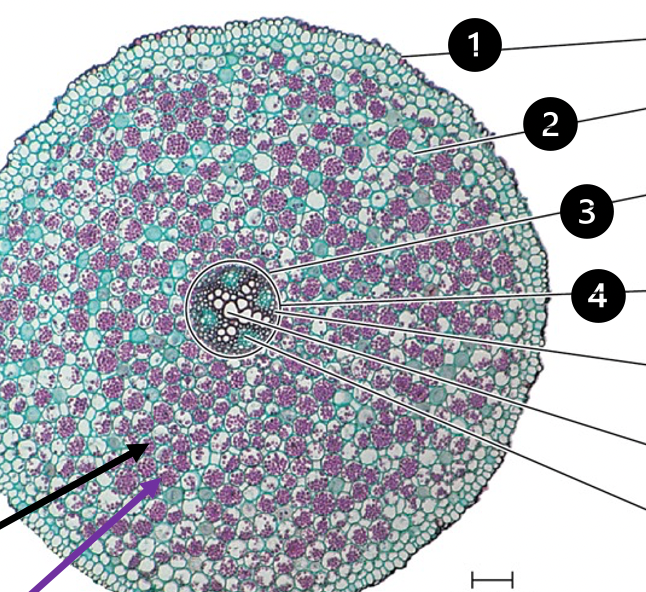
Ranunculus (dicot root) zoomed out
1. epidermis
2. cortex
3. endodermis
4. vascular cylinder
parenchyma (black arrow)
2. cortex
3. endodermis
4. vascular cylinder
parenchyma (black arrow)
43
New cards
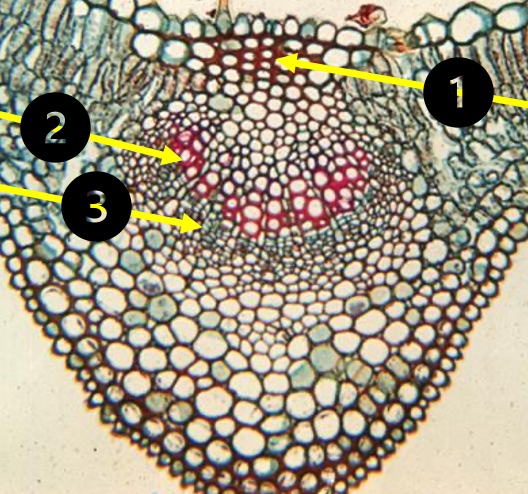
Midrib Vein
1. collenchyma
2. xylem
3. phloem
2. xylem
3. phloem
44
New cards
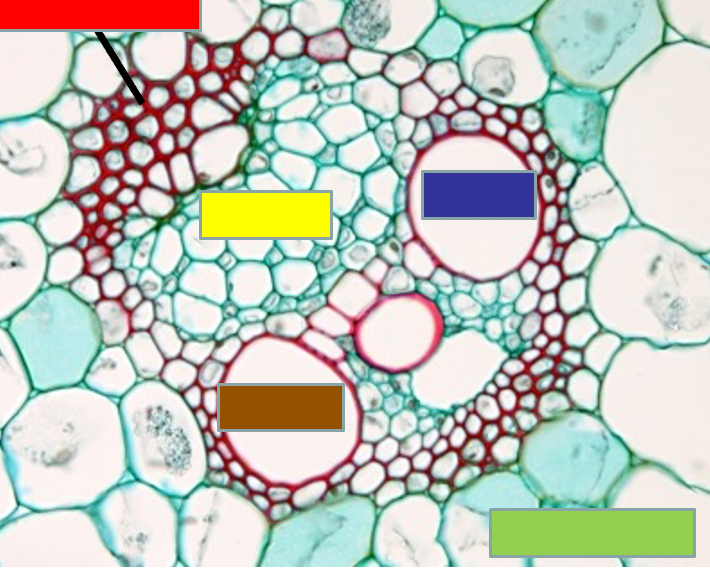
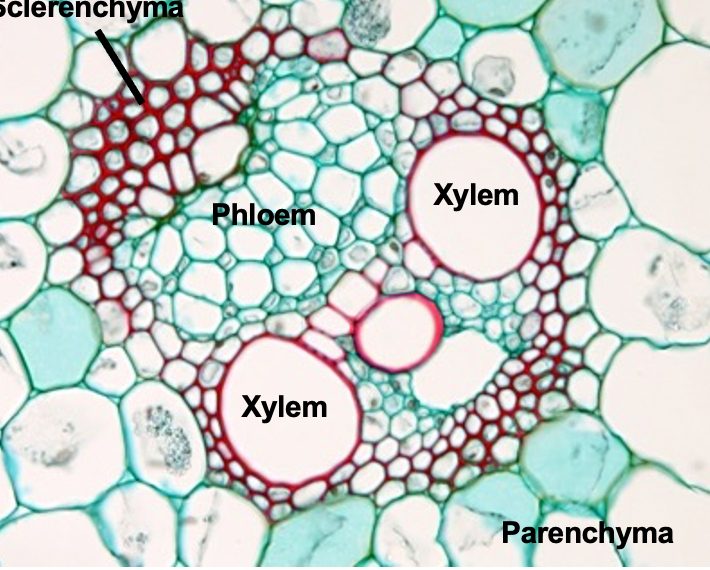
Monocot stem vascular bundles
- xylem (purple and brown)
- phloem (yellow)
- sclerenchyma (red)
- parenchyma (green)
- phloem (yellow)
- sclerenchyma (red)
- parenchyma (green)
45
New cards
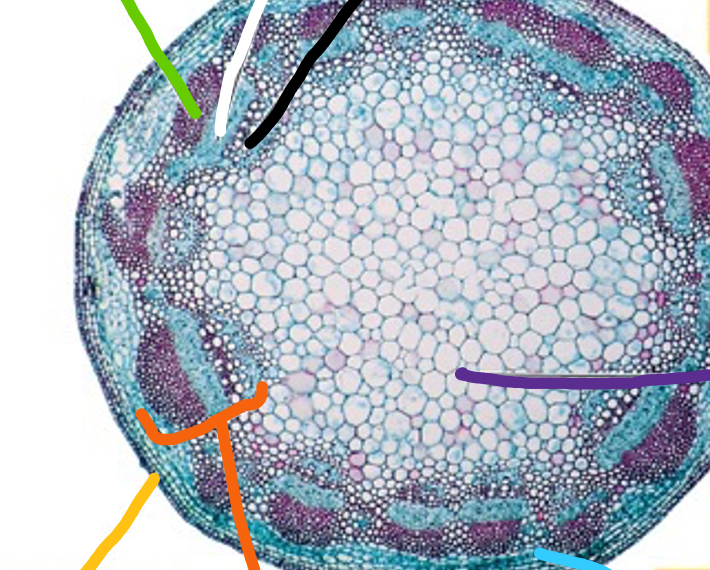
Dicot stem
- sclerenchyma (green)
- phloem (white)
- xylem (black)
- pith (purple)
- cortex (blue)
- orange (vascular bundle)
- epidermis (yellow)
- phloem (white)
- xylem (black)
- pith (purple)
- cortex (blue)
- orange (vascular bundle)
- epidermis (yellow)
46
New cards
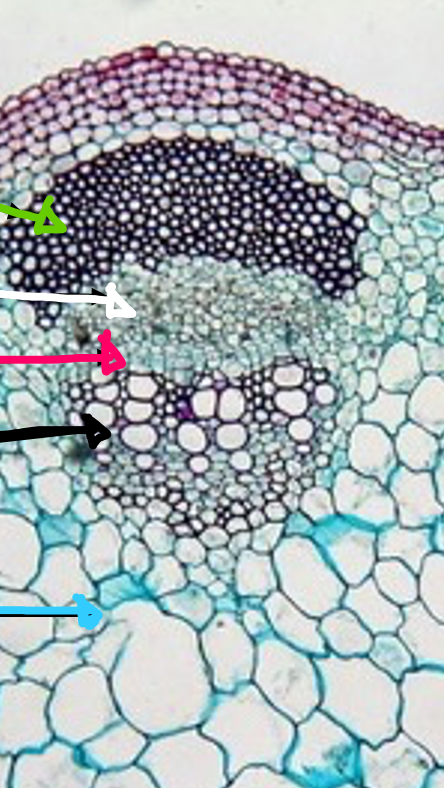
Dicot vascular bundle
- sclerenchyma (green)
- phloem (white)
- vascular cambium (pink)
- xylem (black)
- parenchyma (blue)
- phloem (white)
- vascular cambium (pink)
- xylem (black)
- parenchyma (blue)
47
New cards
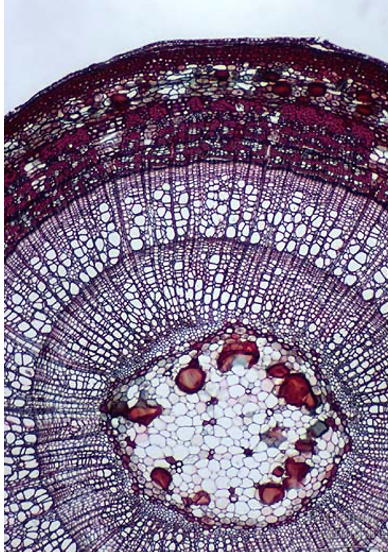
Secondary growth is trees
- xylem accumulates each year and makes up most of "wood" of tree
- new phloem is produced and becomes part of bark, and older phloem collapses
- new phloem is produced and becomes part of bark, and older phloem collapses
48
New cards
Hyphae
Thin filaments that make up fungi
49
New cards
Mycelium
All of the hyphae that make up a single fungus individual
50
New cards
Septate hyphae
Walled hyphae
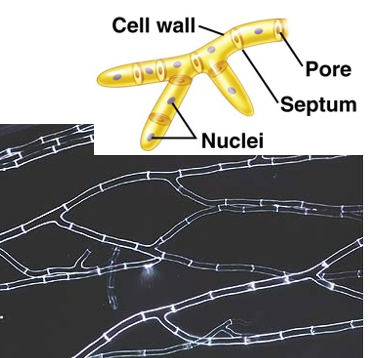
51
New cards
Nonseptate hyphae
Unwalled, coenocytic hyphae
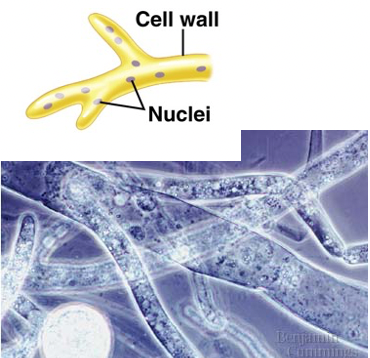
52
New cards
Chitin
Structural polysaccharide that makes up fungal cell walls.
53
New cards
How do fungi digest large food particles?
Cell walls prevent fungi from ingesting large food particles, so fungi must secrete digestive enzymes into its environment that break down the food into smaller particles that the fungi can then absorb.
54
New cards
Saprotroph
most free living fungi are decomposers, AKA
55
New cards
Symbiosis
relationships in which organisms live together (sometimes one inside the other) and are dependent on each other
56
New cards
Mutualism
a relationship between 2 organisms in which both benefit
57
New cards
commensalism
a relationship in which one partner requires and benefits from the relationship but the other is neutral
58
New cards
Parasitism
one partner requires and benefits from the relationship and the other is harmed
59
New cards
ploidy of fungal hyphae
haploid; spores are produced by mitosis
60
New cards
Heterokaryotic
cytoplasm fuses but nuclei do not
61
New cards
Reproductive cycle of fungi
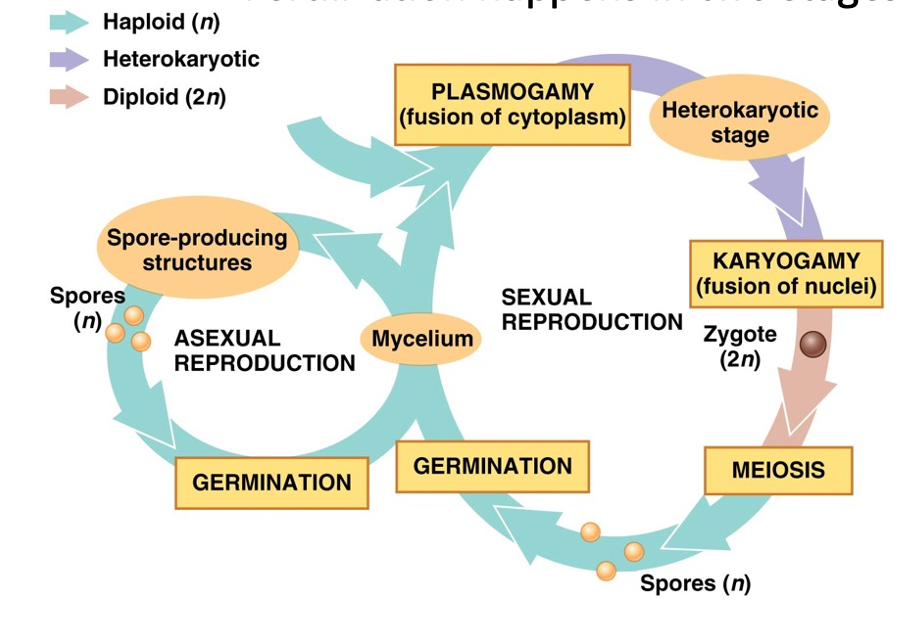
62
New cards
Zygomycota
many molds and mildews; found on strawberries
63
New cards
young zygosporangium of zygomycota
arrows pointing to gametangia
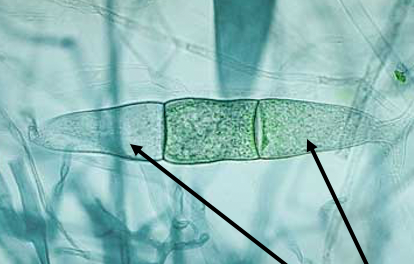
64
New cards
mature zygosporangium of zygomycota
notice diploid nuclei, arrows pointing to gametangia
65
New cards
Ascomycota
produce asexual spores called conidia, which bud off of the tips of hyphae called conidiophores
66
New cards
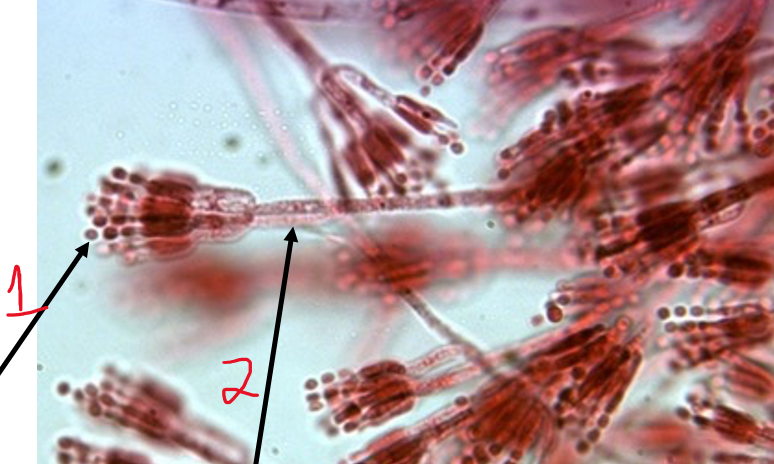
Penicillium
1. conidia
2. conidiophore
2. conidiophore
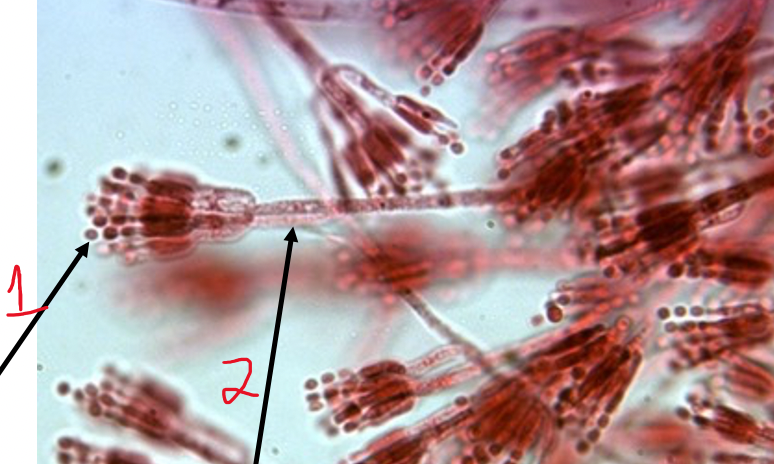
67
New cards
Plasmogamy
dikaryotic hyphae result from a plasmogamy between 2 different mating strains. Eventually, these dikaryotic hyphae grow into a fruiting body, in which a karyogamy occurs.
68
New cards
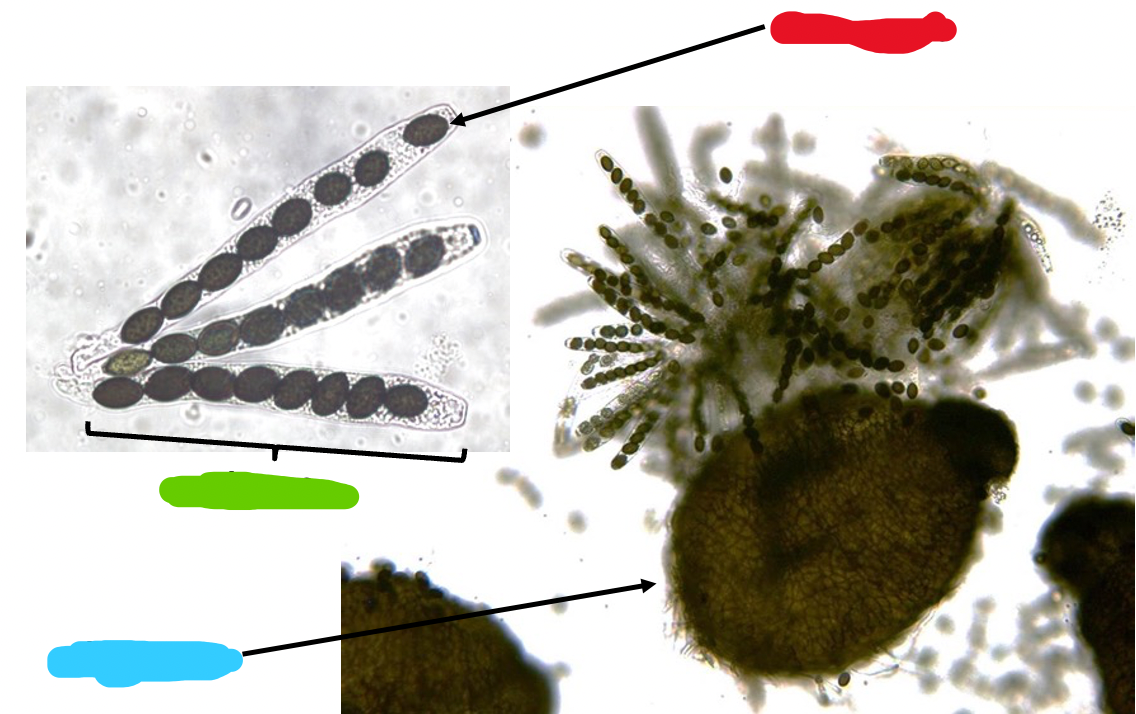

ascocarps
Contain asci (sacs) which contain ascospores
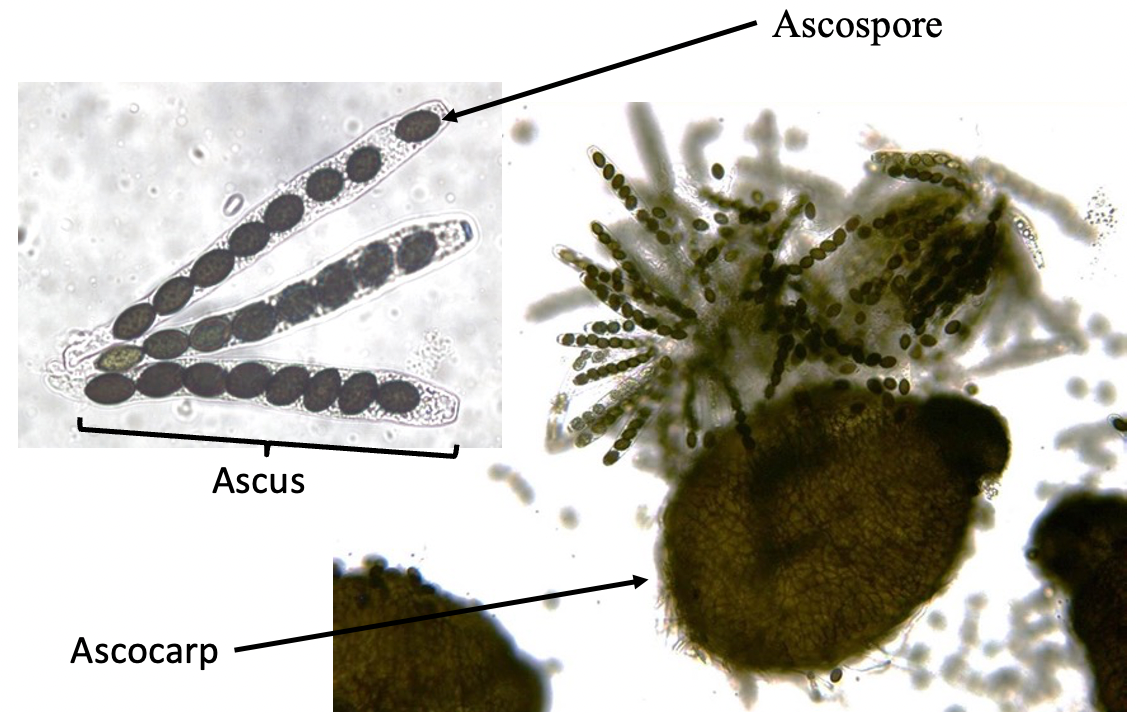
69
New cards
Basidiomycota
plasmogamy results in dikaryotic hyphae (n+n) that develop into basidiocarp in which karyogamy (2n nuclei) and meiosis will eventually occur
70
New cards
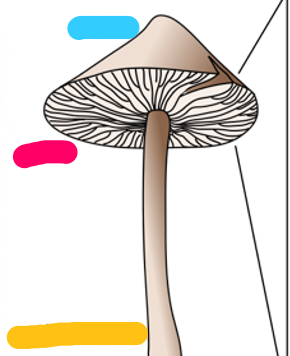
mushroom anatomy
- cap (blue)
- gills, which contain basidia on their surface (pink)
- stalk/stipe (yellow)
- gills, which contain basidia on their surface (pink)
- stalk/stipe (yellow)
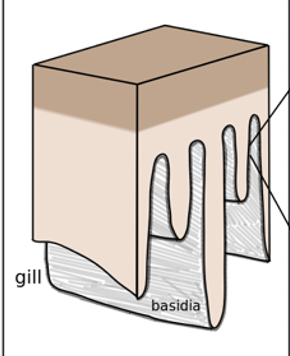
71
New cards
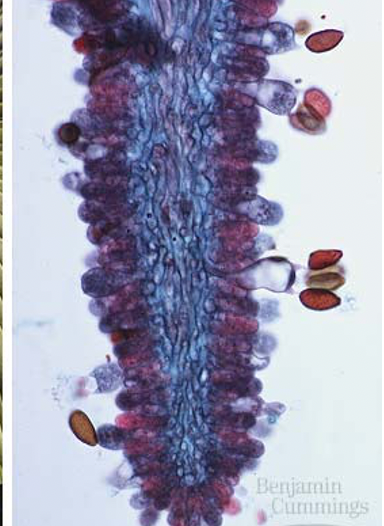
basidia
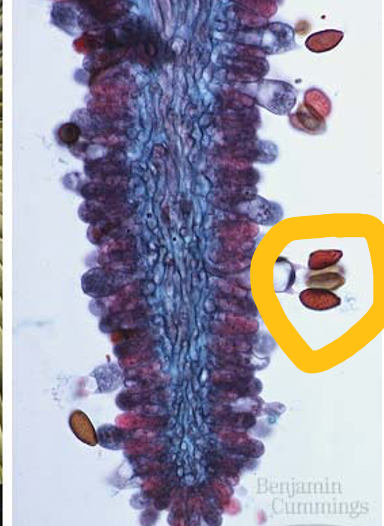
72
New cards
Mycorrhizae
mutualistic relationship between fungi and plant roots-- plants provide food for fungus and fungus provides increased absorption of water and minerals from soil as well as growth factors and antibiotics. Mycorrhizal networks connect plants, allowing them to communicate
73
New cards
lichen
mutualistic relationship between fungi and algae. alga provides food and sometimes nitrogen, and fungus provides support, protection, and acquisition of minerals
74
New cards
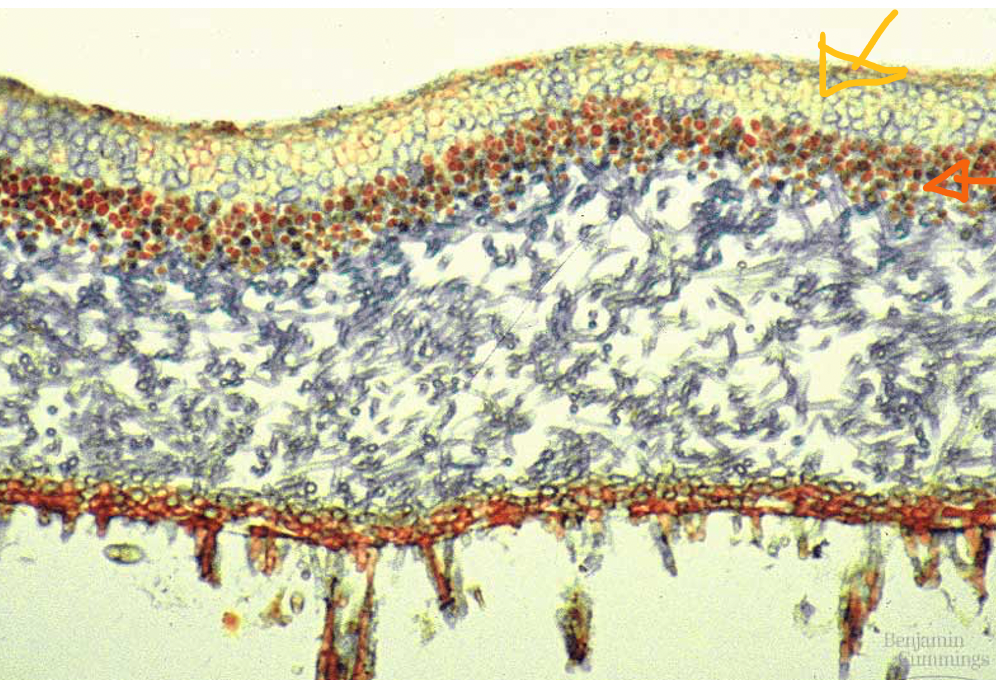
lichen anatomy
- fungal hyphae (yellow arrow)
- algal layer (orange arrow)
- algal layer (orange arrow)
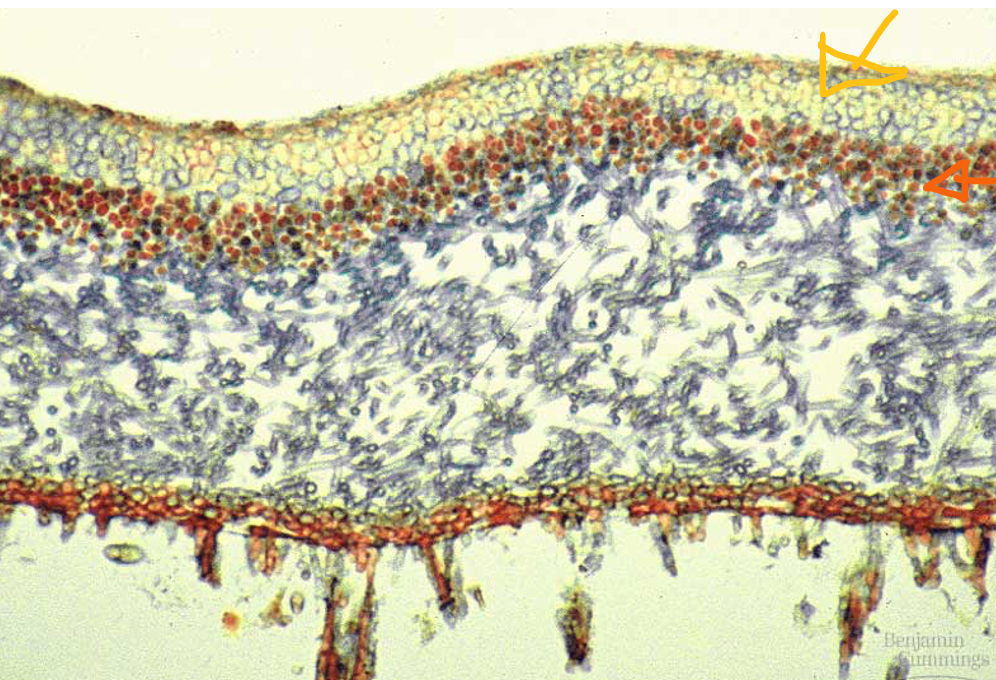
75
New cards
chi-square (X^2)
hypothesis test that compares collected data to predictions made based on hypothesis. it is used to determine if the deviation between your data and your predictions can be explained by random variation alone
76
New cards
chi-square formula

77
New cards
degrees of freedom formula
# of cases - 1
for example, if you have 2 phenotypes, the degree of freedom = 1
for example, if you have 2 phenotypes, the degree of freedom = 1